Distract Your Attention: Multi-Head Cross Attention Network for Facial Expression Recognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To maximize class separability, this work proposes a simple yet effective feature clustering strategy in FCN to simultaneously optimize intra-class variations and inter-class margins.
- Our work demonstrates that a single attention module cannot sufficiently capture all the subtle and complex appearance variations across different expressions. To address this issue, MAN and AFN are proposed to capture multiple non-overlapping local attentions and fuse them to encode higher-order interactions among local features.
- The experimental results show that the proposed DAN method achieves an accuracy of 62.09% on AffectNet-8, 65.69% on AffectNet-7, 89.70% on RAF-DB, and 53.18% on SFEW 2.0, respectively, which represent the state of the art in facial expression recognition performance.
2. Related Work
3. Our Approach
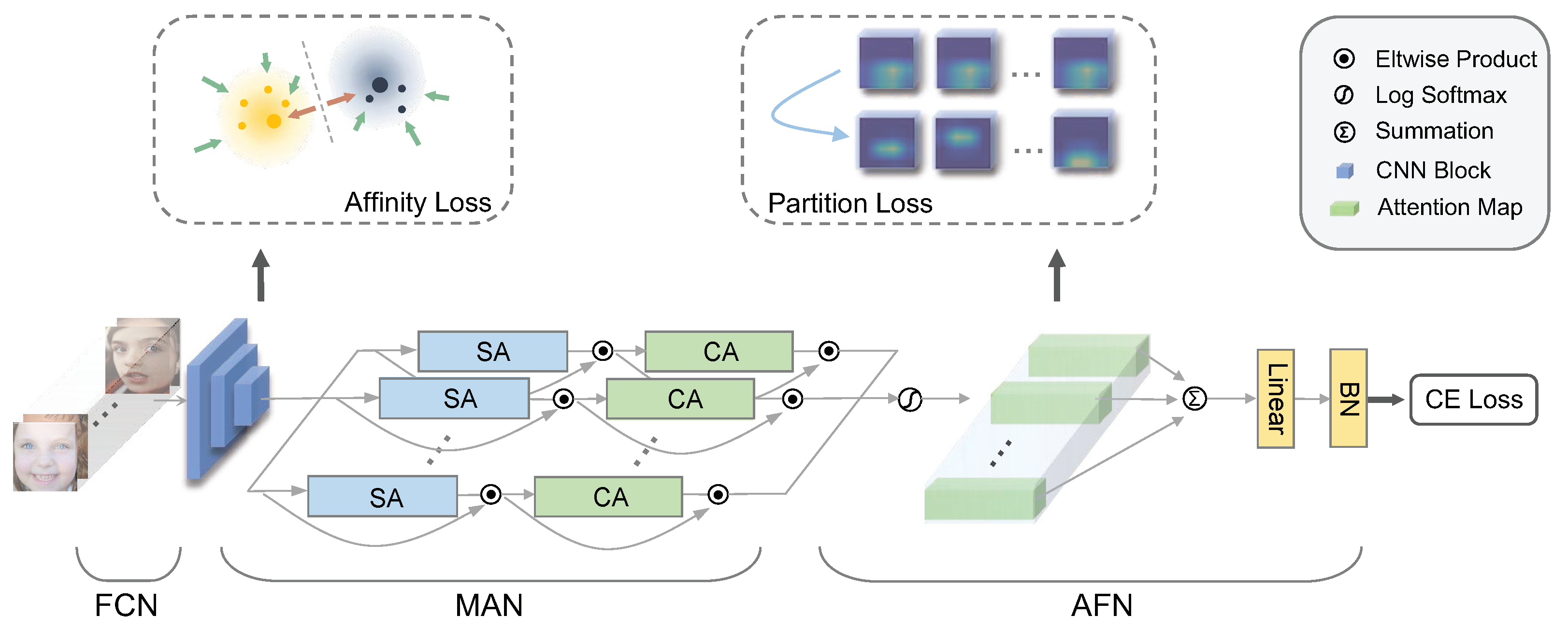
3.1. Feature Clustering Network (FCN)
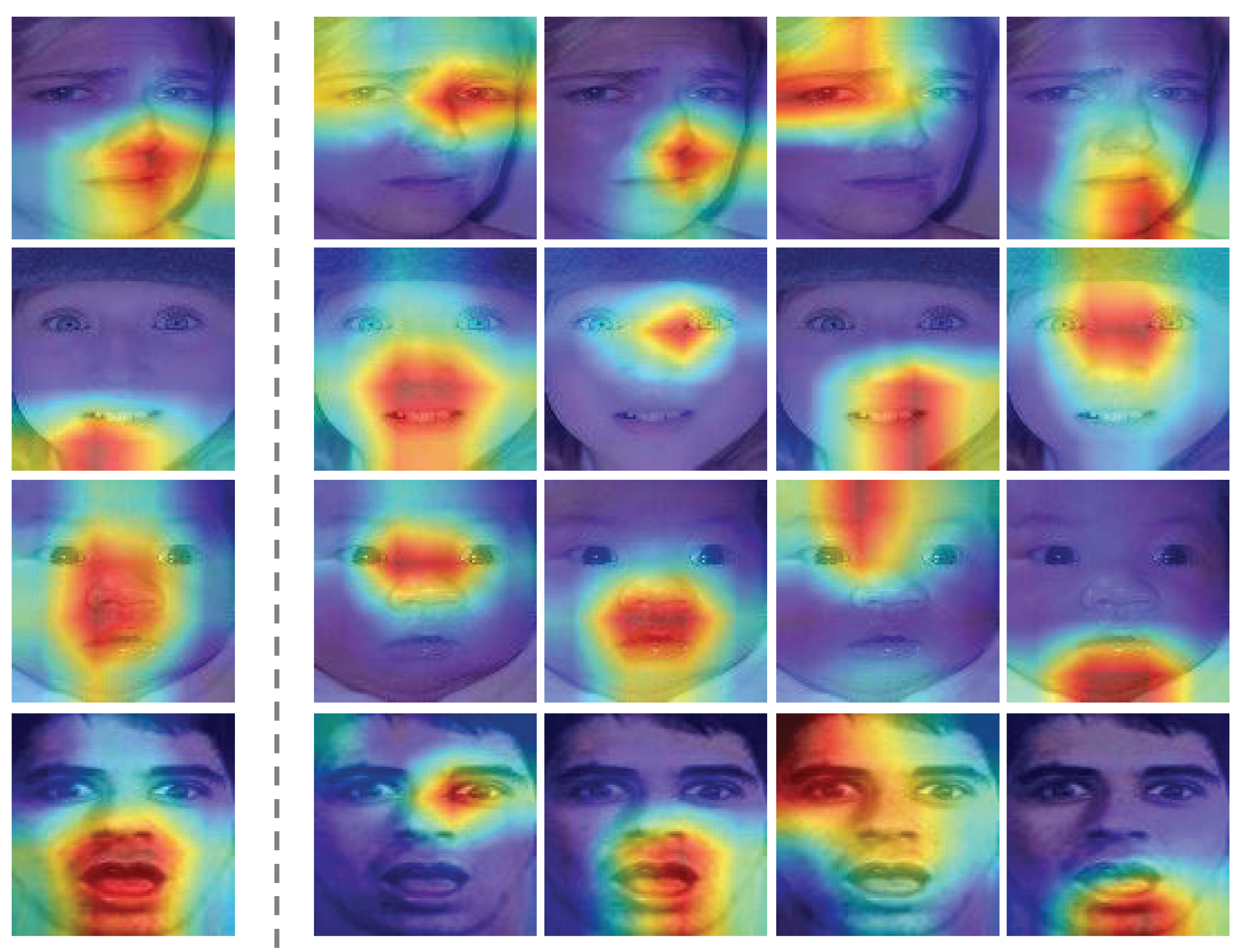
3.2. Multi-Head Attention Network (MAN)
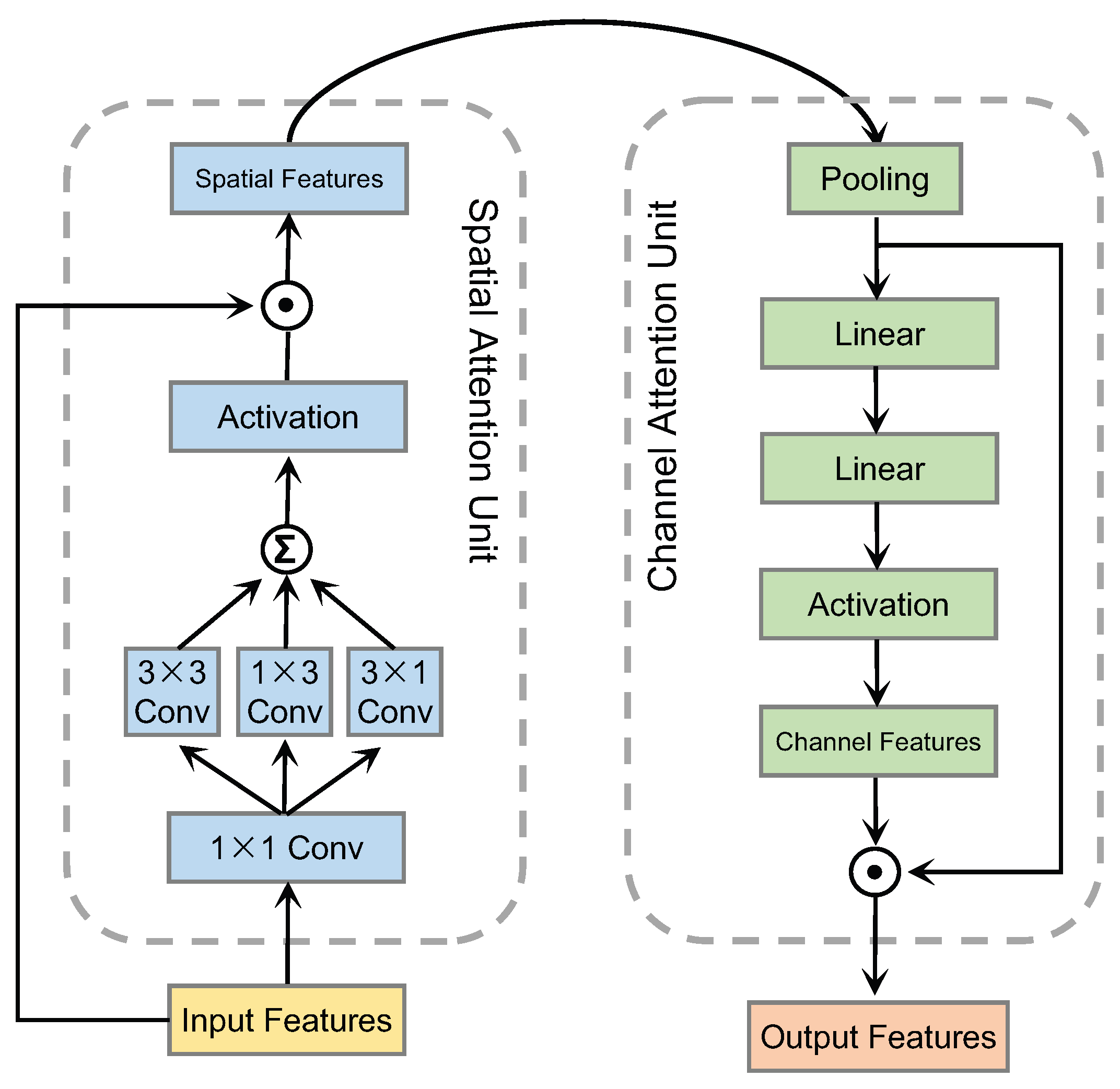
3.3. Attention Fusion Network (AFN)
3.4. Model Learning
4. Experimental Evaluation
4.1. Datasets
4.1.1. AffectNet
4.1.2. RAF-DB
4.1.3. SFEW 2.0
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Quantitative Performance Comparisons
4.4. Ablation Studies and Computational Complexity
4.4.1. Effects of Loss Functions for FCN and AFN
| Methods | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|
| PhaNet [46] | 54.82 |
| ESR-9 [47] | 59.30 |
| RAN [48] | 59.50 |
| SCN [49] | 60.23 |
| PSR [50] | 60.68 |
| EfficientFace [51] | 59.89 |
| EfficientNet-B0 [52] | 61.32 |
| MViT [53] | 61.40 |
| ResNet-18 | 56.84 |
| DAN (ours) | 62.09 |
| Methods | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|
| Separate-Loss [54] | 58.89 |
| FMPN [55] | 61.25 |
| LDL-ALSG [56] | 59.35 |
| VGG-FACE [57] | 60.00 |
| OADN [58] | 61.89 |
| DDA-Loss [40] | 62.34 |
| EfficientFace [51] | 63.70 |
| MViT [53] | 64.57 |
| ResNet-18 | 56.97 |
| DAN (ours) | 65.69 |
| Methods | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|
| Separate-Loss [54] | 86.38 |
| DDA-Loss [40] | 86.9 |
| SCN [49] | 87.03 |
| PSR [50] | 88.98 |
| DACL [7] | 87.78 |
| IF-GAN [59] | 88.33 |
| EfficientFace [51] | 88.36 |
| MViT [53] | 88.62 |
| ResNet-18 | 86.25 |
| DAN (ours) | 89.70 |
| Methods | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|
| IACNN [60] | 50.98 |
| DLP-CNN [43] | 51.05 |
| Island Loss [8] | 52.52 |
| TDTLN [61] | 53.10 |
| RAN [48] | 54.19 |
| LDL-ALSG [56] | 56.50 |
| ViT + SE [62] | 54.29 |
| FaceCaps [63] | 58.50 |
| Baseline (ResNet-18) | 51.29 |
| DAN (ours) | 53.18 |
| Task | Methods | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|
| FCN | - | 88.17 |
| center loss | 88.91 | |
| affinity loss | 89.70 | |
| AFN | - | 88.20 |
| partition loss | 89.70 |
4.4.2. Number of Attention Heads
4.4.3. Computational Complexity
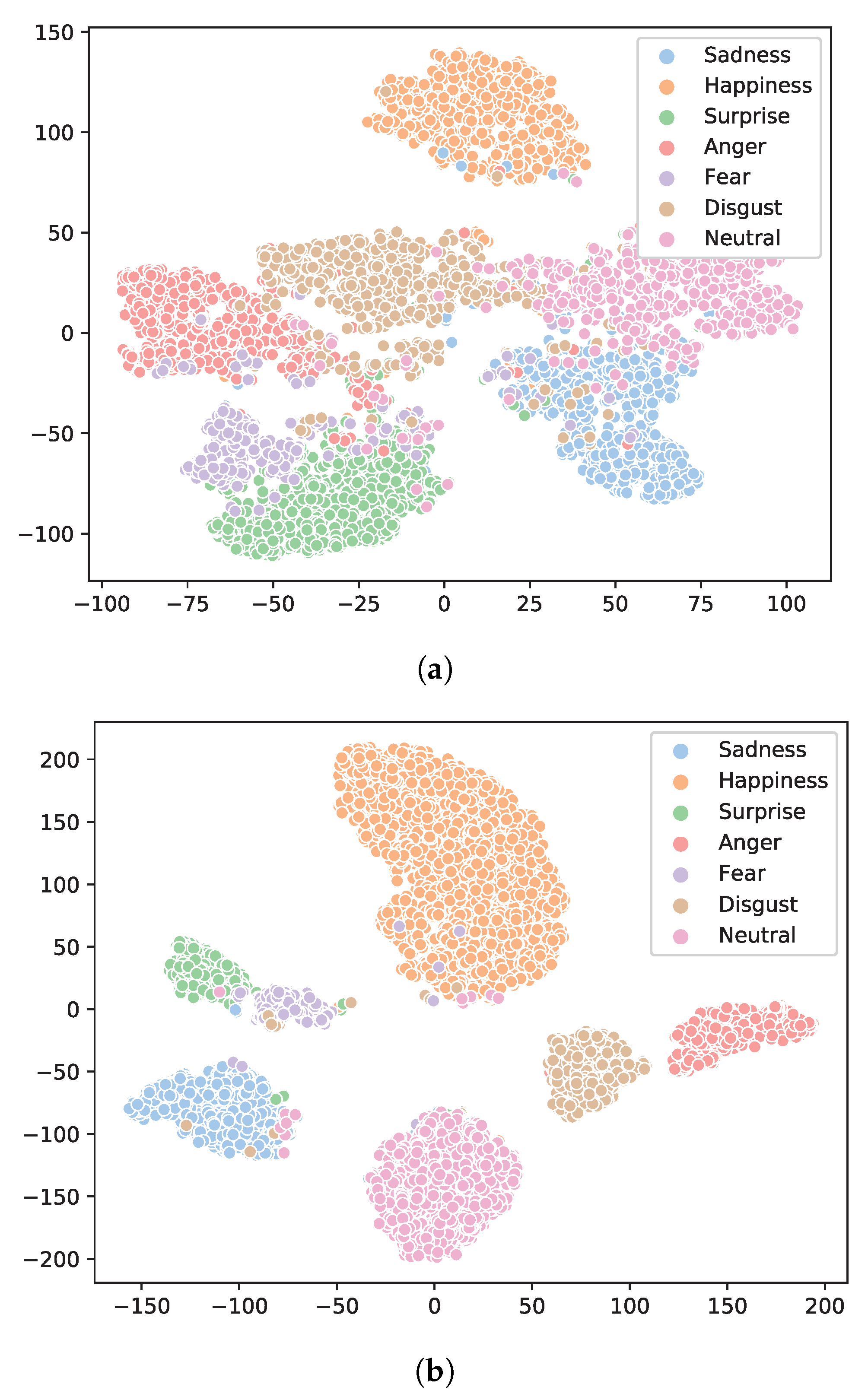
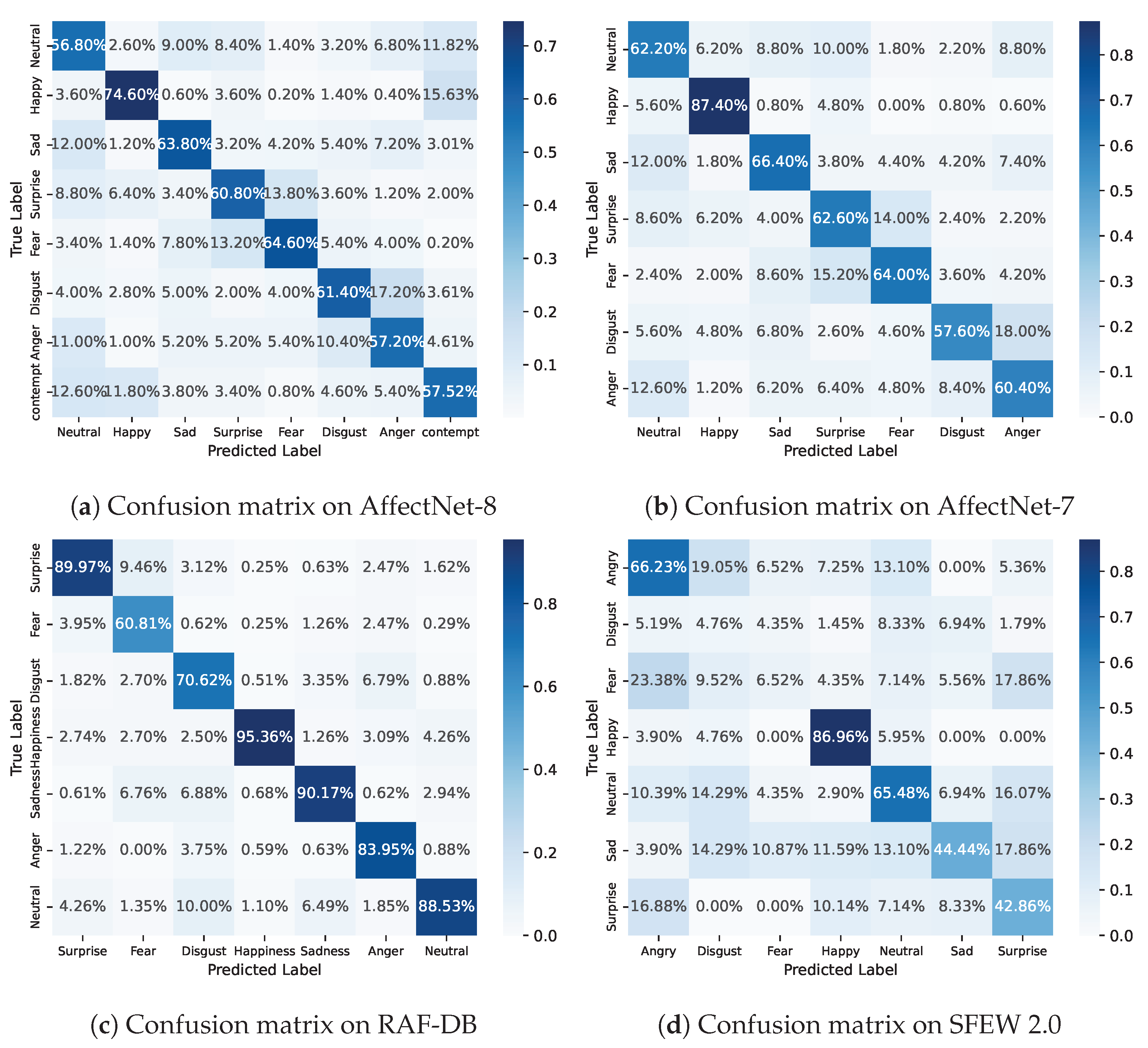
4.5. Confusion Matrix
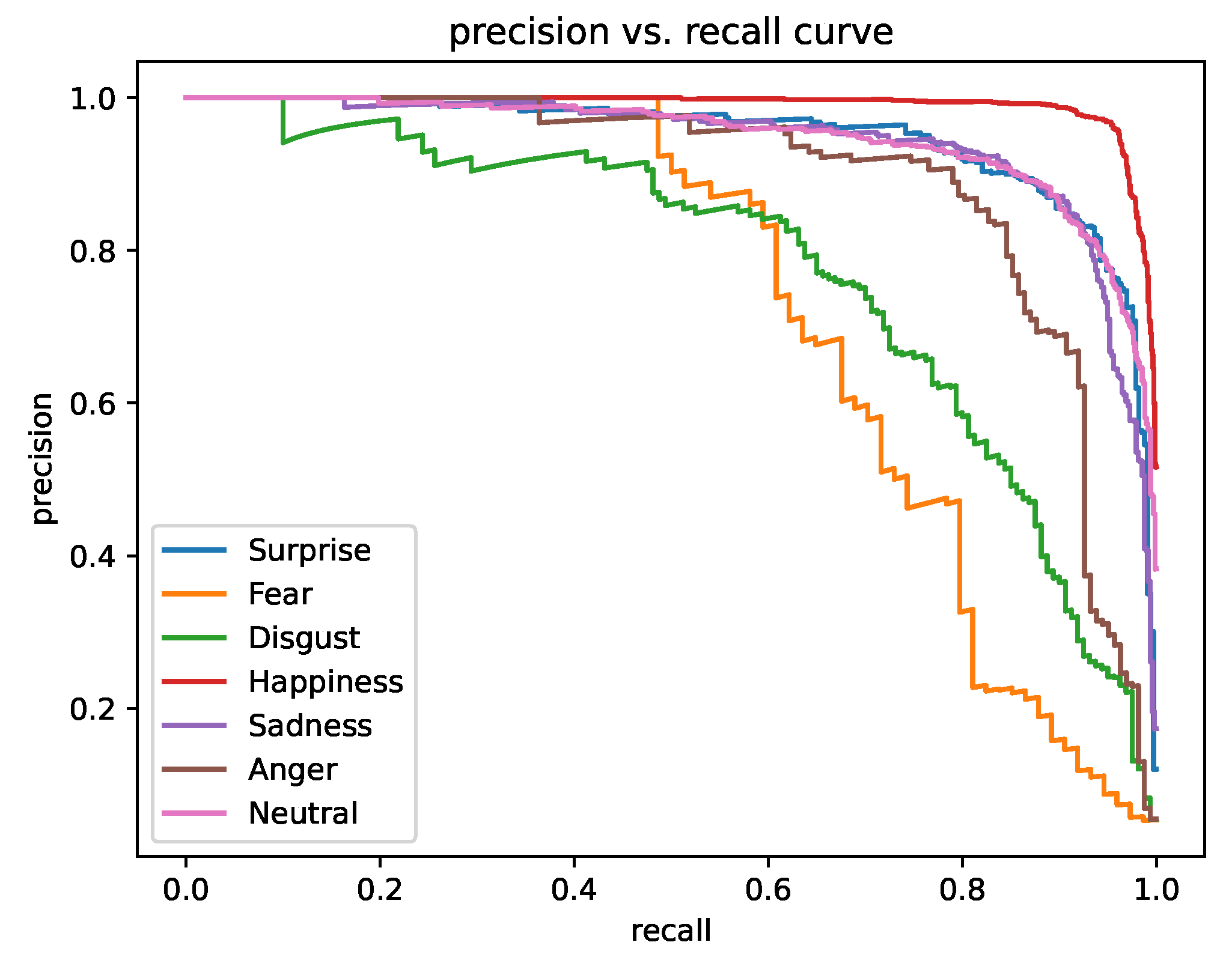
4.6. Precision–Recall Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ekman, P.; Rosenberg, E.L. What the Face Reveals: Basic and Applied Studies of Spontaneous Expression Using the Facial Action Coding System (FACS); Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Darwin, C. The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fasel, B.; Luettin, J. Automatic facial expression analysis: A survey. Pattern Recognit. 2003, 36, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shergill, G.S.; Sarrafzadeh, A.; Diegel, O.; Shekar, A. Computerized Sales Assistants: The Application of Computer Technology to Measure Consumer Interest-A Conceptual Framework; California State University: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ekman, P.; Friesen, W.V. Constants across cultures in the face and emotion. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1971, 17, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Qiao, Y. A discriminative feature learning approach for deep face recognition. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 499–515. [Google Scholar]
- Farzaneh, A.H.; Qi, X. Facial expression recognition in the wild via deep attentive center loss. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2021; pp. 2402–2411. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Meng, Z.; Khan, A.S.; Li, Z.; O’Reilly, J.; Tong, Y. Island loss for learning discriminative features in facial expression recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), Xi’an, China, 15–19 May 2018; pp. 302–309. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wu, S.; Xiao, G. Facial expression recognition by multi-scale cnn with regularized center loss. In Proceedings of the 2018 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Beijing, China, 20–24 August 2018; pp. 3384–3389. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, P.D.M.; Pena, F.A.G.; Ren, T.I.; Cunha, A. Feratt: Facial expression recognition with attention net. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.03284. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Jin, K.; Zhou, D.; Kubota, N.; Ju, Z. Attention mechanism-based CNN for facial expression recognition. Neurocomputing 2020, 411, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mase, K. Recognition of facial expression from optical flow. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 1991, 74, 3474–3483. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Fu, S.; Yang, G. Survey of the facial expression recognition research. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Brain Inspired Cognitive Systems, Shenyang, China, 11–14 July 2012; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 392–402. [Google Scholar]
- Bibbo’, L.; Cotroneo, F.; Vellasco, M. Emotional Health Detection in HAR: New Approach Using Ensemble SNN. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccacci, S.; Generosi, A.; Giraldi, L.; Mengoni, M. Emotional Valence from Facial Expression as an Experience Audit Tool: An Empirical Study in the Context of Opera Performance. Sensors 2023, 23, 2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Ning, X.; Xu, J.; Yu, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, L. A Recognizable Expression Line Portrait Synthesis Method in Portrait Rendering Robot. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rensink, R.A. The dynamic representation of scenes. Vis. Cogn. 2000, 7, 17–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbetta, M.; Shulman, G.L. Control of goal-directed and stimulus-driven attention in the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Zhang, P.; Wu, F.; Li, X. Fcanet: Frequency channel attention networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 783–792. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Hu, X.; Yang, J. Spatial group-wise enhance: Improving semantic feature learning in convolutional networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.09646. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13713–13722. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, D.; Nalamada, T.; Arasanipalai, A.U.; Hou, Q. Rotate to attend: Convolutional triplet attention module. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2021; pp. 3139–3148. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3146–3154. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.14030. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; Qi, X.; Su, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, L. Dab-detr: Dynamic anchor boxes are better queries for detr. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.12329. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, M.; Xiao, B.; Codella, N.; Luo, P.; Wang, J.; Yuan, L. Davit: Dual attention vision transformers. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2022: 17th European Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 74–92. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Tao, D. Vision Transformer with Quadrangle Attention. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.15105. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Hu, H.; Wu, Y. Deep multi-path convolutional neural network joint with salient region attention for facial expression recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 92, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Du, Z.; Li, W.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L. Discriminative attention-based convolutional neural network for 3D facial expression recognition. In Proceedings of the 2019 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2019), Lille, France, 14–18 May 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, X.; Gong, K.; Li, W.; Zhang, L. JWSAA: Joint weak saliency and attention aware for person re-identification. Neurocomputing 2021, 453, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Phonevilay, V.; Gu, K.; Xia, R.; Xie, J.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, K. Image super-resolution reconstruction based on feature map attention mechanism. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 4367–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Mao, Z.; Wang, D.; Lin, H.; Xu, D. DM3Loc: Multi-label mRNA subcellular localization prediction and analysis based on multi-head self-attention mechanism. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadsell, R.; Chopra, S.; LeCun, Y. Dimensionality reduction by learning an invariant mapping. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’06), New York, NY, USA, 17–22 June 2006; Volume 2, pp. 1735–1742. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Wen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Li, M.; Raj, B.; Song, L. Sphereface: Deep hypersphere embedding for face recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 212–220. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, X. Learning deep features via congenerous cosine loss for person recognition. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.06890. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Ji, X.; Gong, D.; Zhou, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, W. Cosface: Large margin cosine loss for deep face recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 5265–5274. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Guo, J.; Xue, N.; Zafeiriou, S. Arcface: Additive angular margin loss for deep face recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 4690–4699. [Google Scholar]
- Farzaneh, A.H.; Qi, X. Discriminant distribution-agnostic loss for facial expression recognition in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 406–407. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Dhall, A.; Goecke, R.; Lucey, S.; Gedeon, T. Collecting large, richly annotated facial-expression databases from movies. IEEE Multimed. 2012, 19, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Deng, W. Reliable crowdsourcing and deep locality-preserving learning for unconstrained facial expression recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 28, 356–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhall, A.; Goecke, R.; Lucey, S.; Gedeon, T. Static facial expression analysis in tough conditions: Data, evaluation protocol and benchmark. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCV Workshops), Barcelona, Spain, 7 November 2011; pp. 2106–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Guo, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, J.; Kotsia, I.; Zafeiriou, S. Retinaface: Single-stage dense face localisation in the wild. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.00641. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Peng, J.; Zeng, J.; Shan, S. Pose-adaptive hierarchical attention network for facial expression recognition. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.10059. [Google Scholar]
- Siqueira, H.; Magg, S.; Wermter, S. Efficient facial feature learning with wide ensemble-based convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 5800–5809. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Peng, X.; Yang, J.; Meng, D.; Qiao, Y. Region attention networks for pose and occlusion robust facial expression recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4057–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Peng, X.; Yang, J.; Lu, S.; Qiao, Y. Suppressing uncertainties for large-scale facial expression recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 6897–6906. [Google Scholar]
- Vo, T.H.; Lee, G.S.; Yang, H.J.; Kim, S.H. Pyramid with super resolution for In-the-Wild facial expression recognition. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 131988–132001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, F. Robust lightweight facial expression recognition network with label distribution training. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 3510–3519. [Google Scholar]
- Savchenko, A.V. Facial expression and attributes recognition based on multi-task learning of lightweight neural networks. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.17107. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Sui, M.; Zhao, F.; Zha, Z.; Wu, F. MViT: Mask Vision Transformer for Facial Expression Recognition in the wild. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.04520. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, G. Separate loss for basic and compound facial expression recognition in the wild. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Machine Learning (PMLR), Nagoya, Japan, 17–19 November 2019; pp. 897–911. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Shi, Z.; Cai, J. Facial motion prior networks for facial expression recognition. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP), Suzhou, China, 13–16 December 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Shi, Z.; Geng, X.; Rui, Y. Label distribution learning on auxiliary label space graphs for facial expression recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 13984–13993. [Google Scholar]
- Kollias, D.; Cheng, S.; Ververas, E.; Kotsia, I.; Zafeiriou, S. Deep neural network augmentation: Generating faces for affect analysis. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2020, 128, 1455–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhou, P.; Chellappa, R. Occlusion-adaptive deep network for robust facial expression recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), Houston, TX, USA, 28 September–1 October 2020; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Meng, Z.; Khan, A.S.; O’Reilly, J.; Li, Z.; Han, S.; Tong, Y. Identity-free facial expression recognition using conditional generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Anchorage, AK, USA, 19–22 September 2021; pp. 1344–1348. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Z.; Liu, P.; Cai, J.; Han, S.; Tong, Y. Identity-aware convolutional neural network for facial expression recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 12th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2017), Washington, DC, USA, 30 May–3 June 2017; pp. 558–565. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, K.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, T.; Zong, Y.; Tang, C.; Lu, C.; Cui, Z. Cross-domain facial expression recognition based on transductive deep transfer learning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 108906–108915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouayeb, M.; Hamidouche, W.; Soladie, C.; Kpalma, K.; Seguier, R. Learning Vision Transformer with Squeeze and Excitation for Facial Expression Recognition. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.03107. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Pang, C.; Zhang, B. FaceCaps for facial expression recognition. Comput. Animat. Virtual Worlds 2021, 32, e2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Methods | Params (M) | FLOPs (G) |
|---|---|---|
| EfficientFace [51] | 1.28 | 0.15 |
| SCN [49] | 11.18 | 1.82 |
| RAN [48] | 11.19 | 14.55 |
| PSR[50] | 20.24 | 10.12 |
| DACL [7] | 103.04 | 1.91 |
| ResNet 18 | 11.69 | 1.82 |
| DAN (ours) | 19.72 | 2.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, Z.; Lin, W.; Wang, T.; Xu, G. Distract Your Attention: Multi-Head Cross Attention Network for Facial Expression Recognition. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8020199
Wen Z, Lin W, Wang T, Xu G. Distract Your Attention: Multi-Head Cross Attention Network for Facial Expression Recognition. Biomimetics. 2023; 8(2):199. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8020199
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Zhengyao, Wenzhong Lin, Tao Wang, and Ge Xu. 2023. "Distract Your Attention: Multi-Head Cross Attention Network for Facial Expression Recognition" Biomimetics 8, no. 2: 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8020199
APA StyleWen, Z., Lin, W., Wang, T., & Xu, G. (2023). Distract Your Attention: Multi-Head Cross Attention Network for Facial Expression Recognition. Biomimetics, 8(2), 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8020199




