Magnetic Elastomers with Smart Variable Elasticity Mimetic to Sea Cucumber
Abstract
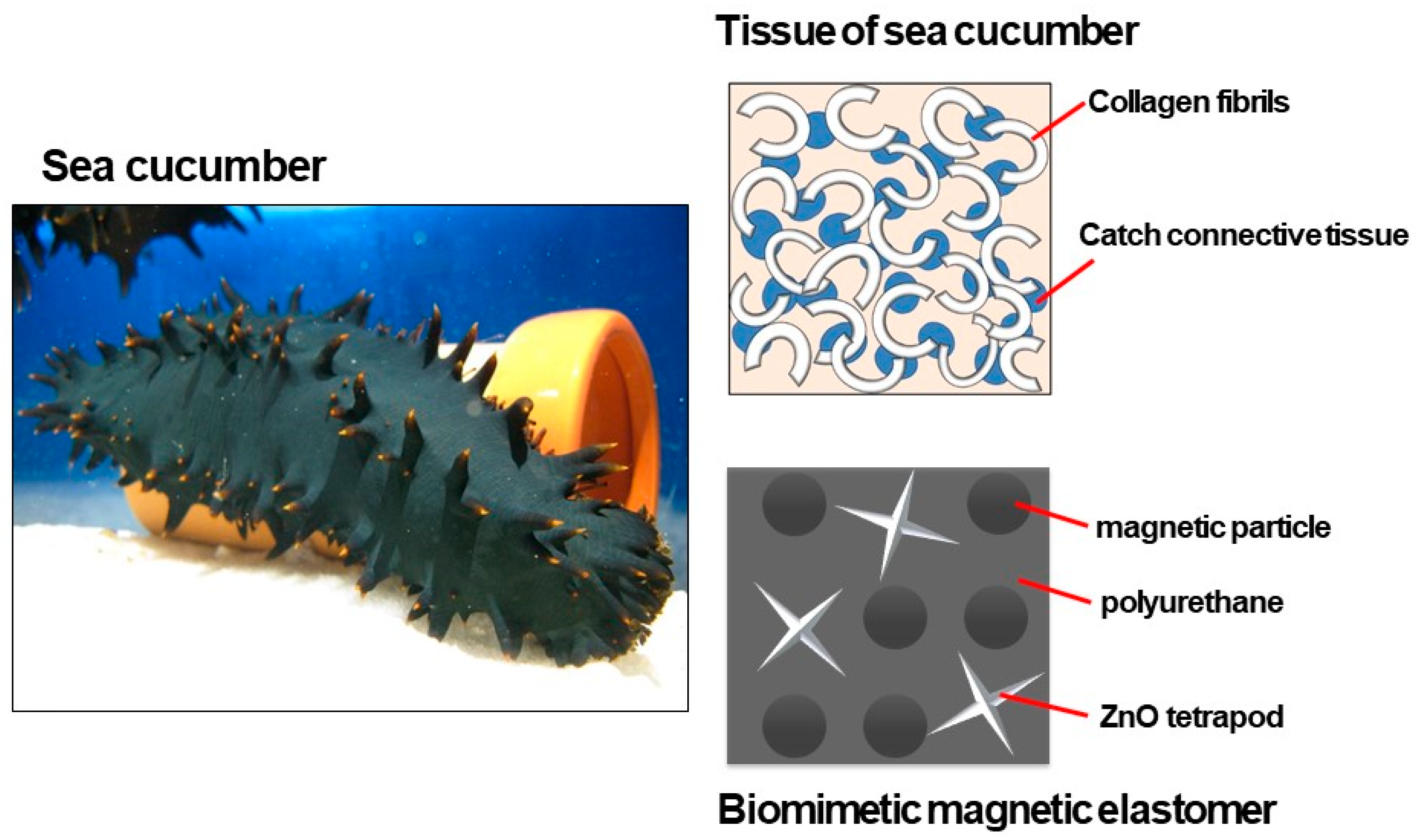
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Bimodal Magnetic Elastomer
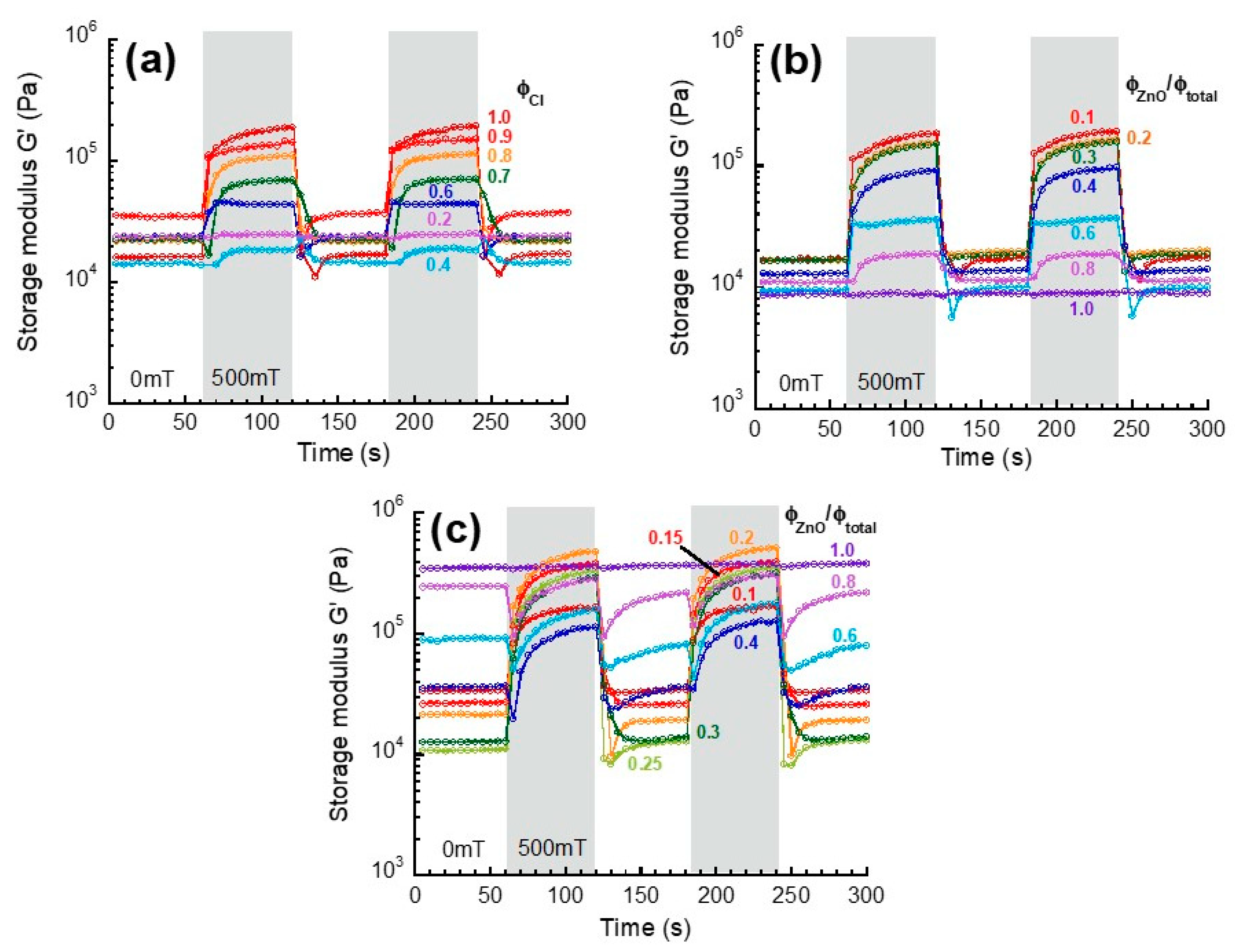
2.2. Rheological Measurements
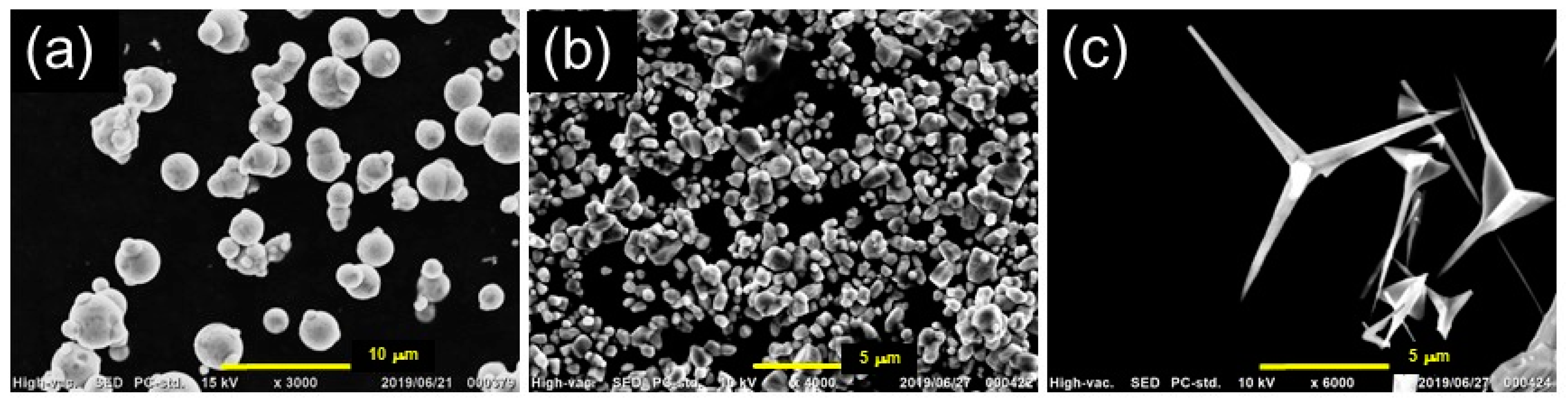
2.3. SEM Observations
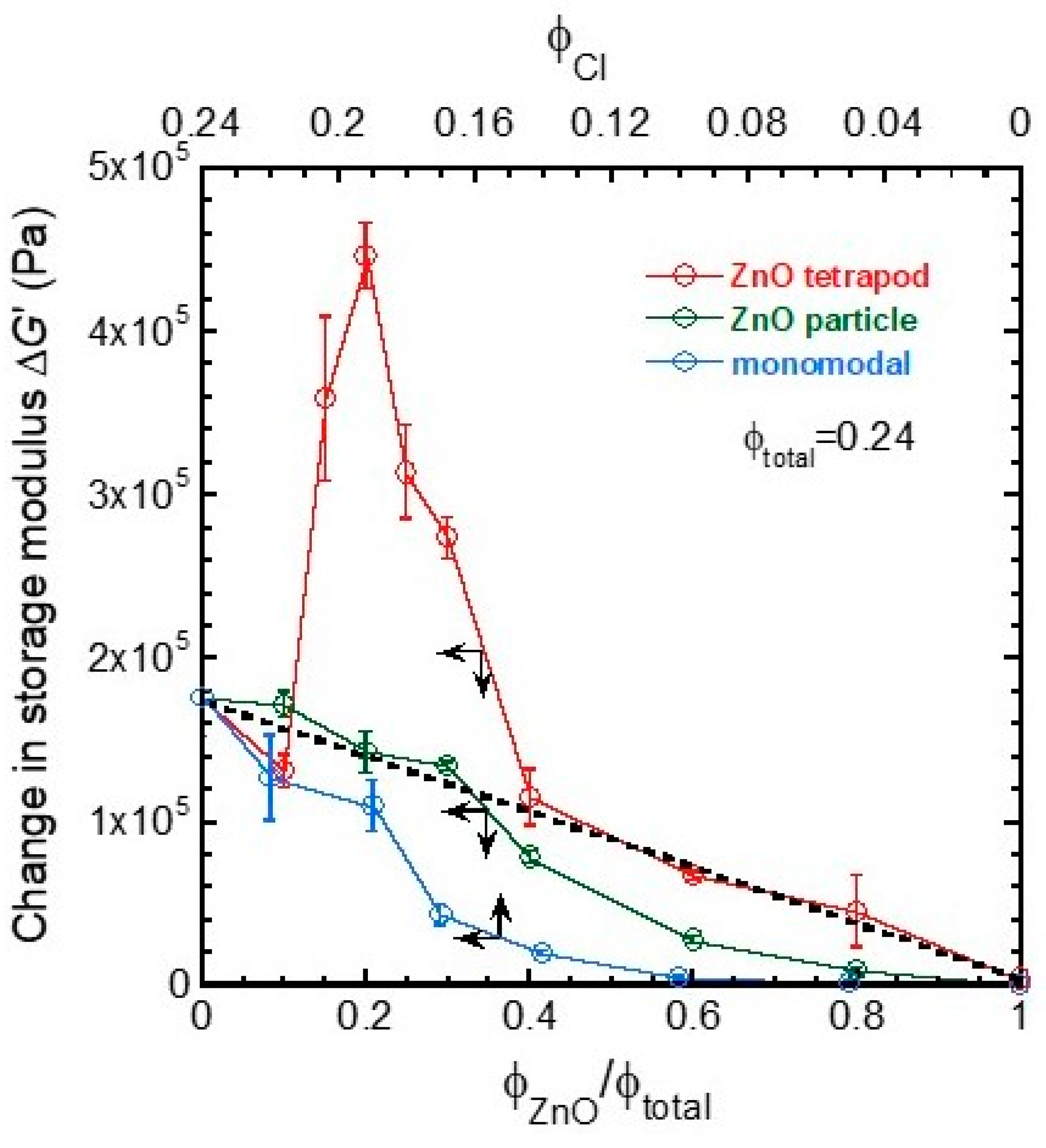
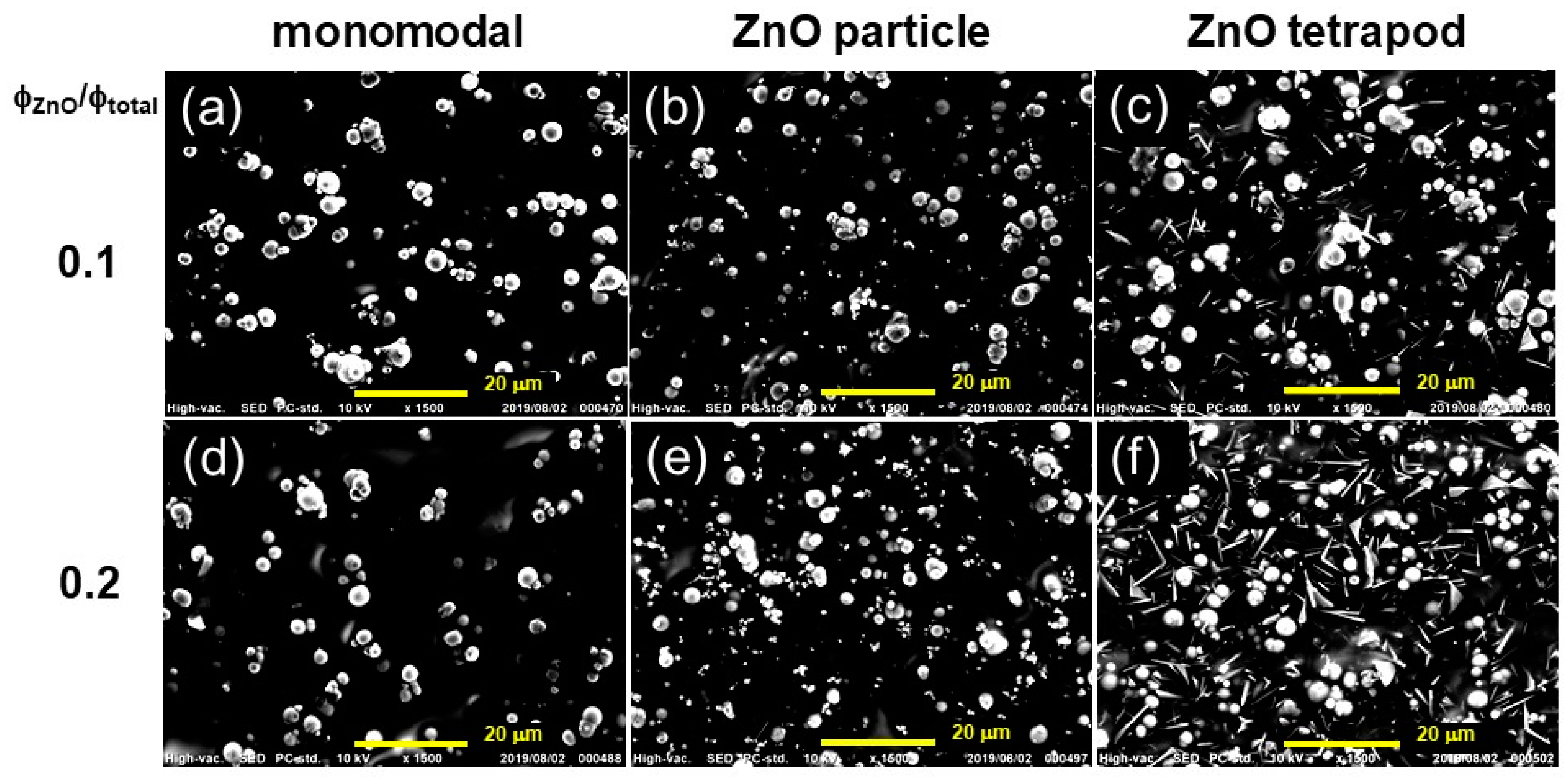
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Espinosa, L.M.; Meesorn, W.; Moatsou, W.; Moatsou, D.; Weder, C. Bioinspired polymer systems with Stimuli-responsive mechanical properties. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 12851–12892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olga, S.; Spec, T. An Overview of Bioinspired and Biomimetic Self-Repairing Materials. Biomimetics 2019, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, R. Design of Self-Oscillating Gels and Application to Biomimetic Actuators. Sensors 2010, 10, 1810–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamada, A.; Tamori, M.; Iketani, T.; Oiwa, K.; Motokawa, T. A novel factor inducing the stiffest state of holo thurian catch connective. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 3416–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuno, A.; Motokawa, T. Evidece for calcium Translocation in catch connective tissue of the sea cucumber Stichopus chlorotus. Cell Tissue Res. 1992, 267, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamori, M.; Nishida, A.; Nishida, N.; Motobayashi, Y.; Oiwa, K.; Motokawa, T. Tensillin-lile stiffening protein from Holothuria leucospilota does not inspired the stiffest state of catch connective tissue. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamori, M.; Ishida, K.; Matsuura, E.; Ogasawara, K.; Hanasaka, T.; Takehana, Y.; Motokawa, T.; Osawa, T. Ultrastructural changes associated with reversible stiffening in catch connective tissue of sea cucumber. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulgit, G.K.; Shadwick, R.E. Dynamic mechanical characterization of a mutable collagenous tissue: response of sea cucuber dermis to cell lysis and dermal extract. J. Exp. Biol. 2000, 203, 1539–1550. [Google Scholar]
- Trotter, J.A.; Koob, T.J. Evidence that calcium-dependent cellular processes are involved in the stiffening response of holothurian dermis and that dermal cells contain an organic stiffening factor. J. Exp. Biol. 1995, 198, 1951–1961. [Google Scholar]
- Koob, T.J.; Koob-emunds, M.M.; Trotter, J.A. Cell-derived stiffening and plasticizing factors in sea cucumber (cucumaria frondosa) dermis. J. Exp. Biol. 1999, 202, 2291–2301. [Google Scholar]
- Thurmond, F.A.; Trotter, J.A. Morphology and bimomechanics of the microfibrillar network of sea cucumber dermis. J. Exp. Biol. 1996, 199, 1817–1828. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Capadona, J.R.; Shanmuganathan, K.; Tyler, D.J.; Rowan, S.J.; Weder, C. Stimuli-Responsive Polymer Nanocomposites Inspired by the Sea Cucumber Dermis. Science 2008, 319, 1370–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, C.; Asoh, T.; Uyama, H. Sea cucumber mimicking bacterial cellulose composite hydrogel with ionic sterength-sensitive. Chem Commun. 2018, 54, 11320–11323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, B.; Cao, Z.; Liu, W. Sea Cucumber-Inspired Autolytic Hydrogels Exhibiting Tunable High Mechanical Performances, Repairability, and Reusability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8956–8966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studart, A.R.; Erb, R.M. Bioinspired materials that self-shape through programmed microstructures. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmuganathan, K.; Capadona, J.R.; Rowan, S.J.; Weder, C. Biomimetic mechanically adaptive nanocomposites. Progr. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, D.; Delpierre, S.; Ke, K.; Raquez, J.; Dubois, P.; Manas-Zloczower, I. Biomimetic water-responsive self-healing epoxy with tunable properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 17853–17862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsumata, T.; Ohori, S. Magnetic polyurethane elastomers with wide range modulation of elasticity. Polym. Chem. 2011, 2, 1063–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsumata, T.; Abe, N. Magnetic-field sensitive gels with wide modulation of dynamic modulus. Chem Lett. 2009, 38, 922–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsumata, T.; Ohori, S.; Chiba, N.; Kawai, M. Enhancement of magnetoelastic behavior of bimodal magnetic elastomers by stress transfer via nonmagnetic particles. Soft Matter. 2013, 9, 10108–10116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, K.; Kanauchi, S.; Kawai, M.; Mitsumata, T.; Tamesue, S.; Yamauchi, T. Nonmagnetic particles enhance magnetoelastic response of magnetic elastomers. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118, 024903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanpo, J.; Kawai, M.; Mitsumata, T. Magnetic-field sensitivity for magnetic elastomers with various elasticities. Chem Lett. 2016, 45, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, K.; Kawai, M.; Mitsumata, T. Amphoteric of loss factor for bimodal magnetic elastomers by magnetic fields. Chem Lett. 2016, 45, 1033–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanpo, J.; Nagashima, K.; Umehara, Y.; Kawai, M.; Mitsumata, T. Magnetic-Field Sensitivity of Storage Modulus for Bimodal Magnetic Elastomers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 12993–13000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, K.; Nanpo, J.; Kawai, M.; Mitsumata, T. Transition from Linear to Nonlinear Viscoelasticity for Bimodal Magnetic Elastomers under a Magnetic Field. Chem. Lett. 2017, 46, 366–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, H.; Kato, S.; Watanabe, M.; Kikuchi, T.; Kawai, M.; Mitsumata, T. Magnetically tunable vibration transmissibility for polyurethane magnetic elastomer. Polymers 2018, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsumata, T.; Honda, A.; Kanazawa, H.; Kawai, M. Magnetically tunable elasticity for magnetic hydrogels consisting for carrageenan and carbonyl iron particles. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2012, 116, 12341–12348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.A.; Merino, J.M.; Fernández Pinel, E.; Quesada, A.; de la Venta, J.; Ruíz González, M.L.; Castro, G.R.; Crespo, P.; Llopis, J.; González-Calbet, J.M.; et al. Magnetic Properties of ZnO Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 1489–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitsumata, T.; Ohori, S.; Honda, A.; Kawai, M. Magnetism and Viscoelasticity for Magnetic Elastomers with Wide Range Modulation of Dynamic Modulus. Soft Matter. 2013, 9, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Ikeda, J.; Takeda, Y.; Kawai, M.; Mitsumata, T. Effect of Sonication Time on Magnetorheological Effect for Monomodal Magnetic Elastomers. Gels 2018, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Takeda, Y.; Maruyama, T.; Ikeda, J.; Kawai, M.; Mitsumata, T. Chain Structure in a Cross-Linked Polyurethane Magnetic Elastomer Under a Magnetic Field. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takehara, Y.; Yamada, A.; Tamori, M.; Motokawa, T. Soften, a novel protein that softens the connective tissue of sea cucumber through inhibiting interaction between collagen fibrils. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85644. [Google Scholar]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kobayashi, Y.; Akama, S.; Ohori, S.; Kawai, M.; Mitsumata, T. Magnetic Elastomers with Smart Variable Elasticity Mimetic to Sea Cucumber. Biomimetics 2019, 4, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics4040068
Kobayashi Y, Akama S, Ohori S, Kawai M, Mitsumata T. Magnetic Elastomers with Smart Variable Elasticity Mimetic to Sea Cucumber. Biomimetics. 2019; 4(4):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics4040068
Chicago/Turabian StyleKobayashi, Yusuke, Shota Akama, Suguru Ohori, Mika Kawai, and Tetsu Mitsumata. 2019. "Magnetic Elastomers with Smart Variable Elasticity Mimetic to Sea Cucumber" Biomimetics 4, no. 4: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics4040068
APA StyleKobayashi, Y., Akama, S., Ohori, S., Kawai, M., & Mitsumata, T. (2019). Magnetic Elastomers with Smart Variable Elasticity Mimetic to Sea Cucumber. Biomimetics, 4(4), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics4040068





