Adaptive Graph Learning with Multimodal Fusion for Emotion Recognition in Conversation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- GASMER framework: We present a multimodal emotion-recognition model that simultaneously exploits contextual history and speaker-to-speaker dependencies through an adaptively learned graph;
- Self-supervised graph module: We design a lightweight objective that infers dialog structure on-the-fly, eliminating the brittleness of preset graphs;
- Layer-wise multimodal fusion: The proposed MFA integrates audio-visual signals inside the Transformer, yielding richer, more discriminative representations;
- Outstanding results: GASMER achieves state-of-the-art performance among graph-based methods, and shows competitive results on the IEMOCAP and MOSEI benchmarks for multimodal emotion recognition.
2. Related Work
2.1. Multimodal Emotion Recognition
2.2. Graph Structure Learning
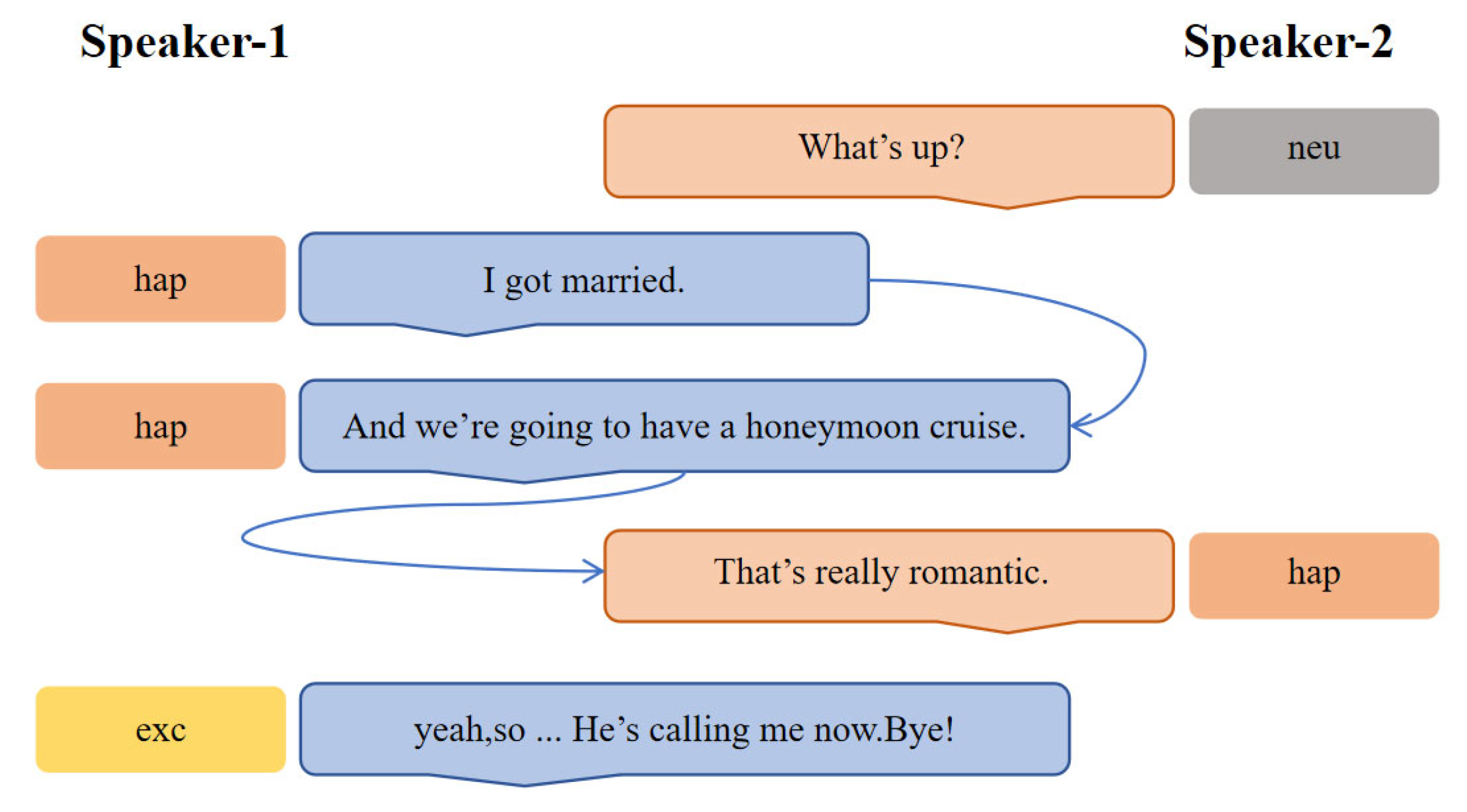
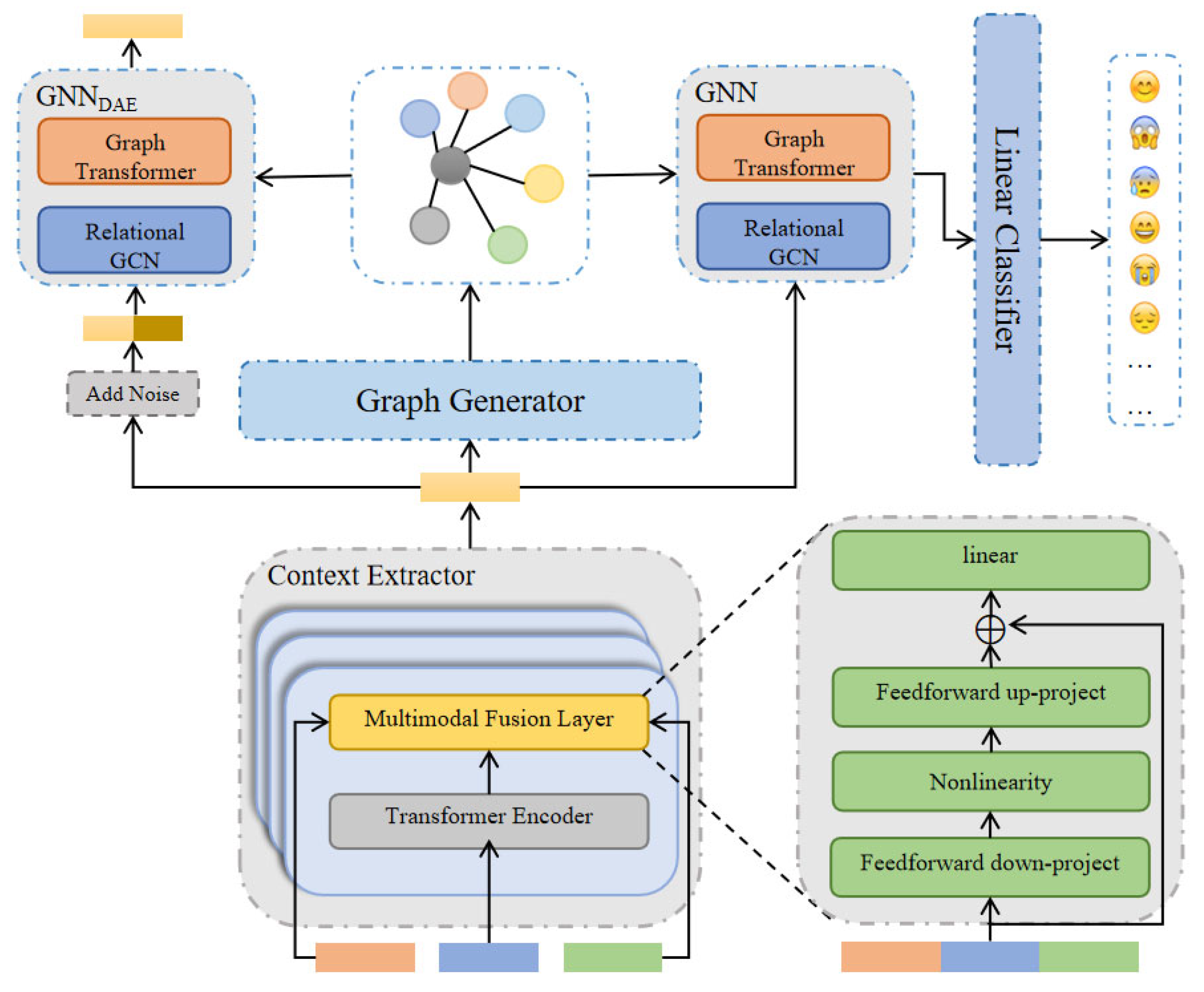
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Overall Architecture
3.2. Context Extractor
3.3. Graph Generator
3.4. Graph Neural Network Components
3.5. Emotion Classifier
3.6. Self-Supervision Task
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Data Preprocessing
4.3. Evaluating Indicator
4.4. Baselines
4.5. Experimental Settings
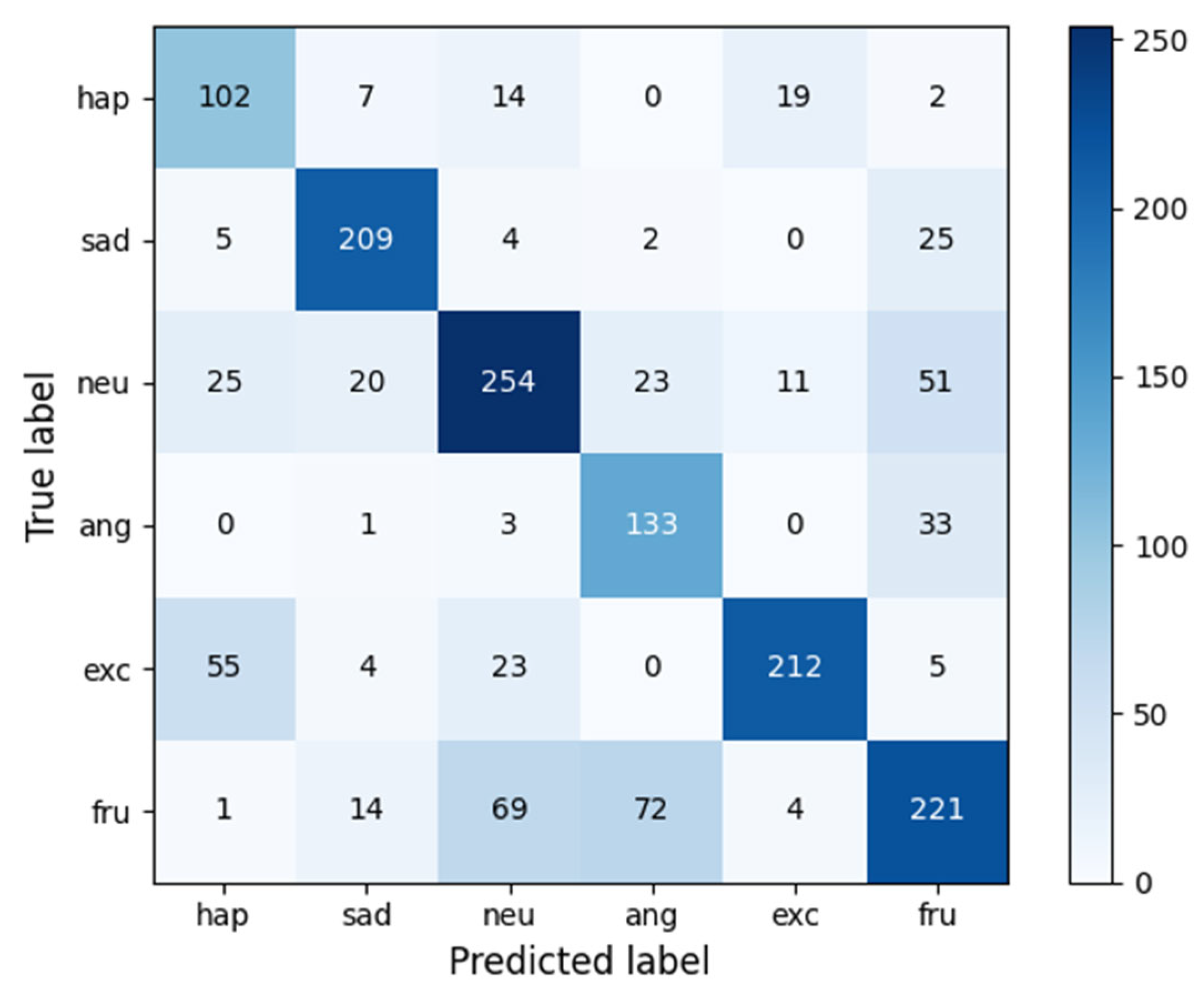
4.6. Results
4.7. Analysis
4.8. Ablation Study
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Node | Intra-Speaker Relationship | Inter-Speaker Relationship |
|---|---|---|
| Relationship Type | Temporal Relationship | Relationship |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Past | |
| 2 | Past | |
| 3 | Past | |
| 4 | Past | |
| 5 | Future | |
| 6 | Future | |
| 7 | Future | |
| 8 | Future |
References
- Pereira, P.; Moniz, H.; Carvalho, J.P. Deep emotion recognition in textual conversations: A survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2025, 58, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhussein, G.; Alkhodari, M.; Khandoker, A.H.; Hadjileontiadis, L.J. Novel speech-based emotion climate recognition in peers’ conversations incorporating affect dynamics and temporal convolutional neural networks. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 16752–16769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Mao, R. PGIF: A Personality-Guided Iterative Feedback Graph Network for Multimodal Conversational Emotion Recognition. In IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Van, C.T.; Tran, T.V.; Nguyen, V.; Hy, T.S. Effective Context Modeling Framework for Emotion Recognition in Conversations. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2025—2025 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Hyderabad, India, 6–11 April 2025; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Gao, J.; Li, D.; Shum, H.-Y. The design and implementation of xiaoice, an empathetic social chatbot. Comput. Linguist. 2020, 46, 53–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, A.B.; Liang, P.P.; Poria, S.; Cambria, E.; Morency, L.-P. Multimodal language analysis in the wild: Cmu-mosei dataset and interpretable dynamic fusion graph. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Melbourne, Australia, 15–20 July 2018; pp. 2236–2246. [Google Scholar]
- Busso, C.; Bulut, M.; Lee, C.-C.; Kazemzadeh, A.; Mower, E.; Kim, S.; Chang, J.N.; Lee, S.; Narayanan, S.S. IEMOCAP: Interactive emotional dyadic motion capture database. Lang. Resour. Eval. 2008, 42, 335–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, P. Facial expression and emotion. Am. Psychol. 1993, 48, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebe, N.; Cohen, I.; Gevers, T.; Huang, T.S. Multimodal approaches for emotion recognition: A survey. In Internet Imaging VI; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005; pp. 56–67. [Google Scholar]
- Datcu, D.; Rothkrantz, L.J. Semantic audiovisual data fusion for automatic emotion recognition. In Emotion Recognition: A Pattern Analysis Approach; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 411–435. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, A.; Bhat, A.; Jain, A.; Singh, A.V.; Modi, A. COGMEN: COntextualized GNN based Multimodal Emotion recognitioN. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.02455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, A.; Chen, M.; Poria, S.; Cambria, E.; Morency, L.P. Tensor Fusion Network for Multimodal Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Copenhagen, Denmark, 9–11 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wöllmer, M.; Metallinou, A.; Eyben, F.; Schuller, B.; Narayanan, S. Context-Sensitive Multimodal Emotion Recognition from Speech and Facial Expression Using Bidirectional Lstm Modeling: Proceedings of the Interspeech 2010, Chiba, Japan, 26–30 September 2010; International Speech Communication Association (ISCA): Baixas, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Yu, N.; Fu, G. A discourse-aware graph neural network for emotion recognition in multi-party conversation. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2021, Punta Cana, Dominican Republic, 16–20 November 2021; pp. 2949–2958. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Lin, Z.; Fu, P.; Wang, W. Past, present, and future: Conversational emotion recognition through structural modeling of psychological knowledge. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2021, Punta Cana, Dominican Republic, 16–20 November 2021; pp. 1204–1214. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.; Sun, Q.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Shen, J. DialogueTRM: Exploring the Intra- and Inter-Modal Emotional Behaviors in the Conversation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.07637. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Tao, J.; Liu, B.; Lian, Z.; Niu, M. Multimodal transformer fusion for continuous emotion recognition. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 3507–3511. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Fu, Y.; Guo, L.; Dang, J. Multimodal emotion recognition with capsule graph convolutional based representation fusion. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 6339–6343. [Google Scholar]
- Siriwardhana, S.; Kaluarachchi, T.; Billinghurst, M.; Nanayakkara, S. Multimodal emotion recognition with transformer-based self supervised feature fusion. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 176274–176285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Duan, F.; Solé-Casals, J.; Caiafa, C.F. A multimodal emotion recognition method based on facial expressions and electroencephalography. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 70, 103029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandeya, Y.R.; Lee, J. Deep learning-based late fusion of multimodal information for emotion classification of music video. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 2887–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, J.; Li, Z. Image–text sentiment analysis via deep multimodal attentive fusion. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2019, 167, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Liu, B.; Tao, J. CTNet: Conversational transformer network for emotion recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2021, 29, 985–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Liu, Y.; Neves, L.; Woodford, O.; Jiang, M.; Shah, N. Data augmentation for graph neural networks. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2–9 February 2021; pp. 11015–11023. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.; Um, D.; Chang, H.J.; Jo, D.U.; Choi, J.Y. Class-attentive diffusion network for semi-supervised classification. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2–9 February 2021; pp. 8601–8609. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Cao, M.; Cheng, H.; Yu, H.; Xie, J.; Wang, C. A unified structure learning framework for graph attention networks. Neurocomputing 2022, 495, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidaris, S.; Komodakis, N. Generating classification weights with gnn denoising autoencoders for few-shot learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sarma, S.E.; Bronstein, M.M.; Solomon, J.M. Dynamic graph cnn for learning on point clouds. ACM Trans. Graph. (Tog) 2019, 38, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halcrow, J.; Mosoi, A.; Ruth, S.; Perozzi, B. Grale: Designing networks for graph learning. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, San Diego, CA, USA, 23–27 August 2020; pp. 2523–2532. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Sun, L.; Xia, C. Only attention is needed for learning graph representations. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.05140 v2. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Wang, S.; Zhu, F.; Huang, J. Adaptive graph convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Franceschi, L.; Niepert, M.; Pontil, M.; He, X. Learning discrete structures for graph neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–15 June 2019; pp. 1972–1982. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Kang, Z.; Cao, X.; Jin, D.; Yang, B.; Guo, Y. Topology Optimization based Graph Convolutional Network. In Proceedings of the IJCAI, Macao, China, 10–16 August 2019; pp. 4054–4061. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, L.; Zaki, M.J. Deep Iterative and Adaptive Learning for Graph Neural Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.07832. [Google Scholar]
- Qasim, S.R.; Kieseler, J.; Iiyama, Y.; Pierini, M. Learning representations of irregular particle-detector geometry with distance-weighted graph networks. Eur. Phys. J. C 2019, 79, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazi, A.; Cosmo, L.; Ahmadi, S.-A.; Navab, N.; Bronstein, M.M. Differentiable graph module (dgm) for graph convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 1606–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, B.; El Asri, L.; Kazemi, S.M. SLAPS: Self-supervision improves structure learning for graph neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 22667–22681. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems: Proceedings of the 30th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2017), San Diego CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosal, D.; Majumder, N.; Poria, S.; Chhaya, N.; Gelbukh, A. Dialoguegcn: A graph convolutional neural network for emotion recognition in conversation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.11540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlichtkrull, M.; Kipf, T.N.; Bloem, P.; Van Den Berg, R.; Titov, I.; Welling, M. Modeling relational data with graph convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the Semantic Web: 15th International Conference, ESWC 2018, Heraklion, Greece, 3–7 June 2018; pp. 593–607. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Huang, Z.; Feng, S.; Zhong, H.; Wang, W.; Sun, Y. Masked label prediction: Unified message passing model for semi-supervised classification. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.03509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houlsby, N.; Giurgiu, A.; Jastrzebski, S.; Morrone, B.; De Laroussilhe, Q.; Gesmundo, A.; Attariyan, M.; Gelly, S. Parameter-efficient transfer learning for NLP. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–15 June 2019; pp. 2790–2799. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Zhu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, A.; Chen, C.; Li, M. Aim: Adapting image models for efficient video action recognition. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.03024. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.; Lin, J.; Mao, R.; Cambria, E. Fusing pairwise modalities for emotion recognition in conversations. Inf. Fusion 2024, 106, 102306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyben, F.; Wöllmer, M.; Schuller, B. Opensmile: The munich versatile and fast open-source audio feature extractor. In Proceedings of the 18th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Firenze, Italy, 25–29 October 2010; pp. 1459–1462. [Google Scholar]
- Baltrušaitis, T.; Robinson, P.; Morency, L.-P. Openface: An open source facial behavior analysis toolkit. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Placid, NY, USA, 7–10 March 2016; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Reimers, N.; Gurevych, I. Sentence-bert: Sentence embeddings using siamese bert-networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.10084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbrouck, J.-B.; Tits, N.; Brousmiche, M.; Dupont, S. A transformer-based joint-encoding for emotion recognition and sentiment analysis. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.15955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFee, B.; Raffel, C.; Liang, D.; Ellis, D.P.; McVicar, M.; Battenberg, E.; Nieto, O. Librosa: Audio and music signal analysis in python. SciPy 2015, 2015, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Jin, Q. MMGCN: Multimodal fusion via deep graph convolution network for emotion recognition in conversation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.06779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, A.; Liang, P.P.; Mazumder, N.; Poria, S.; Cambria, E.; Morency, L.-P. Memory fusion network for multi-view sequential learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Majumder, N.; Poria, S.; Hazarika, D.; Mihalcea, R.; Gelbukh, A.; Cambria, E. Dialoguernn: An attentive rnn for emotion detection in conversations. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HA, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; pp. 6818–6825. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, D.; Hou, X.; Wei, L.; Jiang, L.; Mo, Y. MM-DFN: Multimodal dynamic fusion network for emotion recognition in conversations. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 7–13 May 2022; pp. 7037–7041. [Google Scholar]
- Hazarika, D.; Poria, S.; Mihalcea, R.; Cambria, E.; Zimmermann, R. Icon: Interactive conversational memory network for multimodal emotion detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018; pp. 2594–2604. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, Y.-H.H.; Liang, P.P.; Zadeh, A.; Morency, L.-P.; Salakhutdinov, R. Learning factorized multimodal representations. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.06176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shen, Y.; Lakshminarasimhan, V.B.; Liang, P.P.; Zadeh, A.; Morency, L.-P. Efficient low-rank multimodal fusion with modality-specific factors. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.00064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Sarma, P.; Sethares, W.; Liang, Y. Learning relationships between text, audio, and video via deep canonical correlation for multimodal language analysis. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 8992–8999. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Xu, H.; Yuan, Z.; Wu, J. Learning modality-specific representations with self-supervised multi-task learning for multimodal sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2–9 February 2021; pp. 10790–10797. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.; Chen, H.; Poria, S. Improving multimodal fusion with hierarchical mutual information maximization for multimodal sentiment analysis. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.00412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszke, A. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.01703. [Google Scholar]
- Fey, M.; Lenssen, J.E. Fast graph representation learning with PyTorch Geometric. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.02428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryumina, E.; Ryumin, D.; Axyonov, A.; Ivanko, D.; Karpov, A. Multi-corpus emotion recognition method based on cross-modal gated attention fusion. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2025, 190, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becht, E.; McInnes, L.; Healy, J.; Dutertre, C.-A.; Kwok, I.W.; Ng, L.G.; Ginhoux, F.; Newell, E.W. Dimensionality reduction for visualizing single-cell data using UMAP. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Dataset | Train | Valid | Test | All |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IEMOCAP | 5146 | 664 | 1623 | 7433 |
| MOSEI | 16,327 | 1871 | 4662 | 22,860 |
| Model | IEMOCAP | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Happy | Sad | Neutral | Angry | Excited | Frustrated | Avg | ||
| F1 ↑ | F1 ↑ | F1 ↑ | F1 ↑ | F1 ↑ | F1 ↑ | ACC ↑ | WF1 ↑ | |
| TFN | 33.7 | 68.6 | 55.1 | 64.2 | 62.4 | 61.2 | 58.8 | 58.5 |
| MMGCN | 42.3 | 78.6 | 61.7 | 69.0 | 74.3 | 62.3 | - | 66.2 |
| MFN | 34.1 | 70.5 | 52.1 | 66.8 | 62.1 | 62.5 | 60.1 | 59.9 |
| DialogueRNN | 32.8 | 78.0 | 59.1 | 63.3 | 73.6 | 59.4 | 63.3 | 62.8 |
| DialogueGCN | 42.7 | 87.5 | 63.5 | 64.1 | 63.1 | 66.9 | 65.2 | 64.2 |
| ICON | 32.8 | 74.4 | 60.6 | 68.2 | 68.4 | 66.2 | 64.0 | 63.5 |
| COGMEN | 51.9 | 81.7 | 68.6 | 66.0 | 75.3 | 58.2 | 68.2 | 67.6 |
| MM-DFN | 42.2 | 78.9 | 66.4 | 69.7 | 75.5 | 66.3 | 68.2 | 68.1 |
| GASMER | 64.2 | 85.4 | 67.9 | 66.5 | 80.3 | 62.7 | 70.9 | 71.2 |
| MOSEI | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TFN | COGMEN | MFM | LMF | ICCN | Self-MM | MMIM | GASMER | |
| ACC-7 ↑ | 50.2 | 43.9 | 51.3 | 48.0 | 51.6 | - | 54.2 | 54.3 |
| ACC-2 ↑ | 82.5 | 84.3 | 84.4 | 82.0 | 84.2 | 85.1 | 85.9 | 87.1 |
| Recall | UAR | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Happy | Sad | Neutral | Angry | Excited | Frustrated | |
| 70.83% | 85.31% | 66.15% | 78.24% | 70.90% | 58.01% | 71.57% |
| Modalities | T | A + T | T + V | A + T + V | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IEMOCAP 6-way | Actual | 65.6 | 68.4 | 64.7 | 71.2 |
| w/o MFA | 63.6 | 64.7 | 63.2 | 64.8 | |
| w/o GL | 63.9 | 67.2 | 64.9 | 68.2 | |
| IEMOCAP 4-way | Actual | 81.4 | 83.2 | 79.9 | 85.2 |
| w/o MFA | 80.0 | 81.3 | 81.2 | 83.4 | |
| w/o GL | 80.7 | 83.3 | 80.6 | 83.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Li, J.; Dong, J.; Mo, Z.; Liu, N.; Li, Q.; Yuan, Y. Adaptive Graph Learning with Multimodal Fusion for Emotion Recognition in Conversation. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10070414
Liu J, Li J, Dong J, Mo Z, Liu N, Li Q, Yuan Y. Adaptive Graph Learning with Multimodal Fusion for Emotion Recognition in Conversation. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(7):414. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10070414
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jian, Jian Li, Jiawei Dong, Zifan Mo, Na Liu, Qingdu Li, and Ye Yuan. 2025. "Adaptive Graph Learning with Multimodal Fusion for Emotion Recognition in Conversation" Biomimetics 10, no. 7: 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10070414
APA StyleLiu, J., Li, J., Dong, J., Mo, Z., Liu, N., Li, Q., & Yuan, Y. (2025). Adaptive Graph Learning with Multimodal Fusion for Emotion Recognition in Conversation. Biomimetics, 10(7), 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10070414






