Biomimetic Directional Liquid Transport on a Planar Surface in a Passive and Energy-Free Way
Abstract
1. Introduction
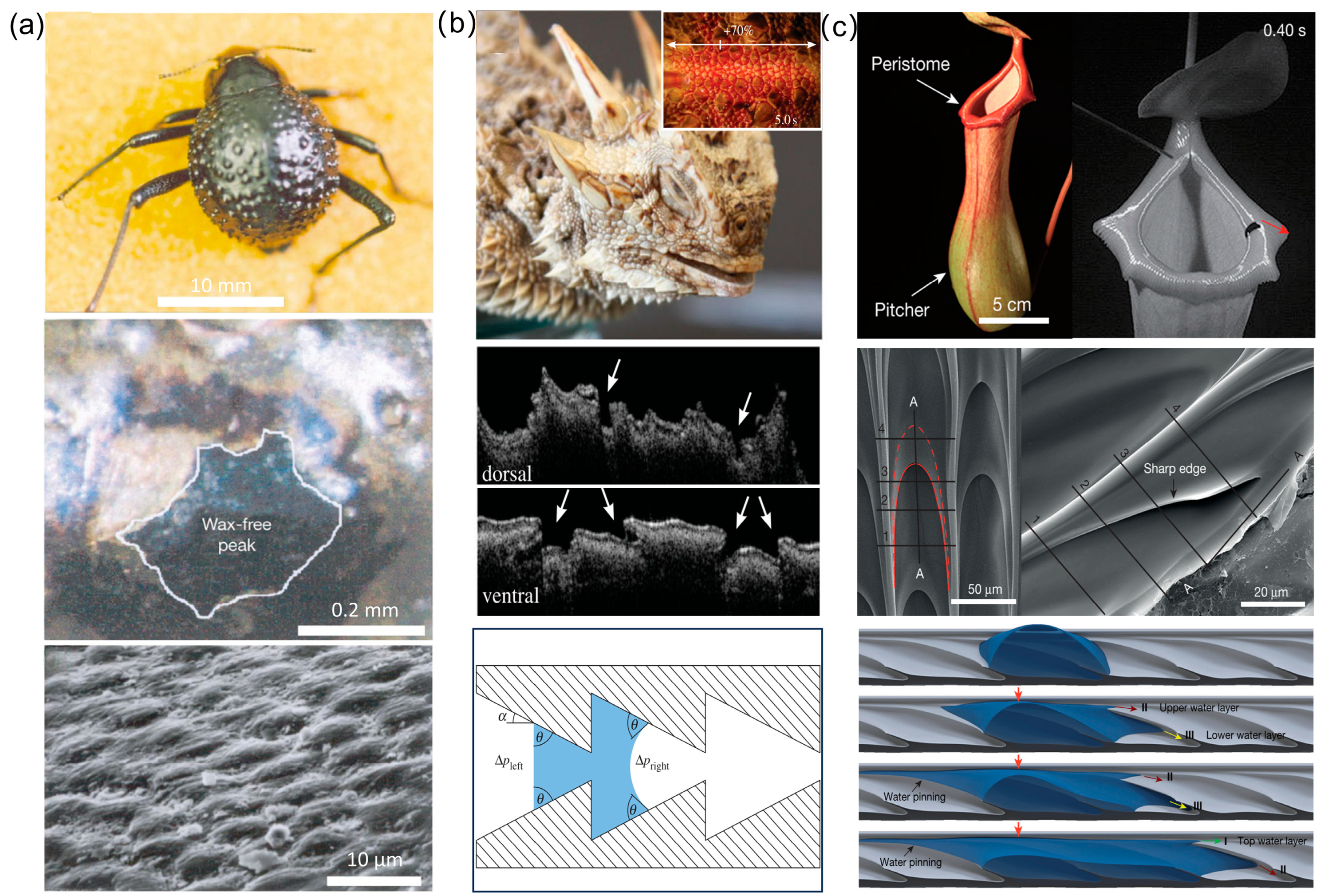
2. Directional Liquid Transport on Natural Planar Systems
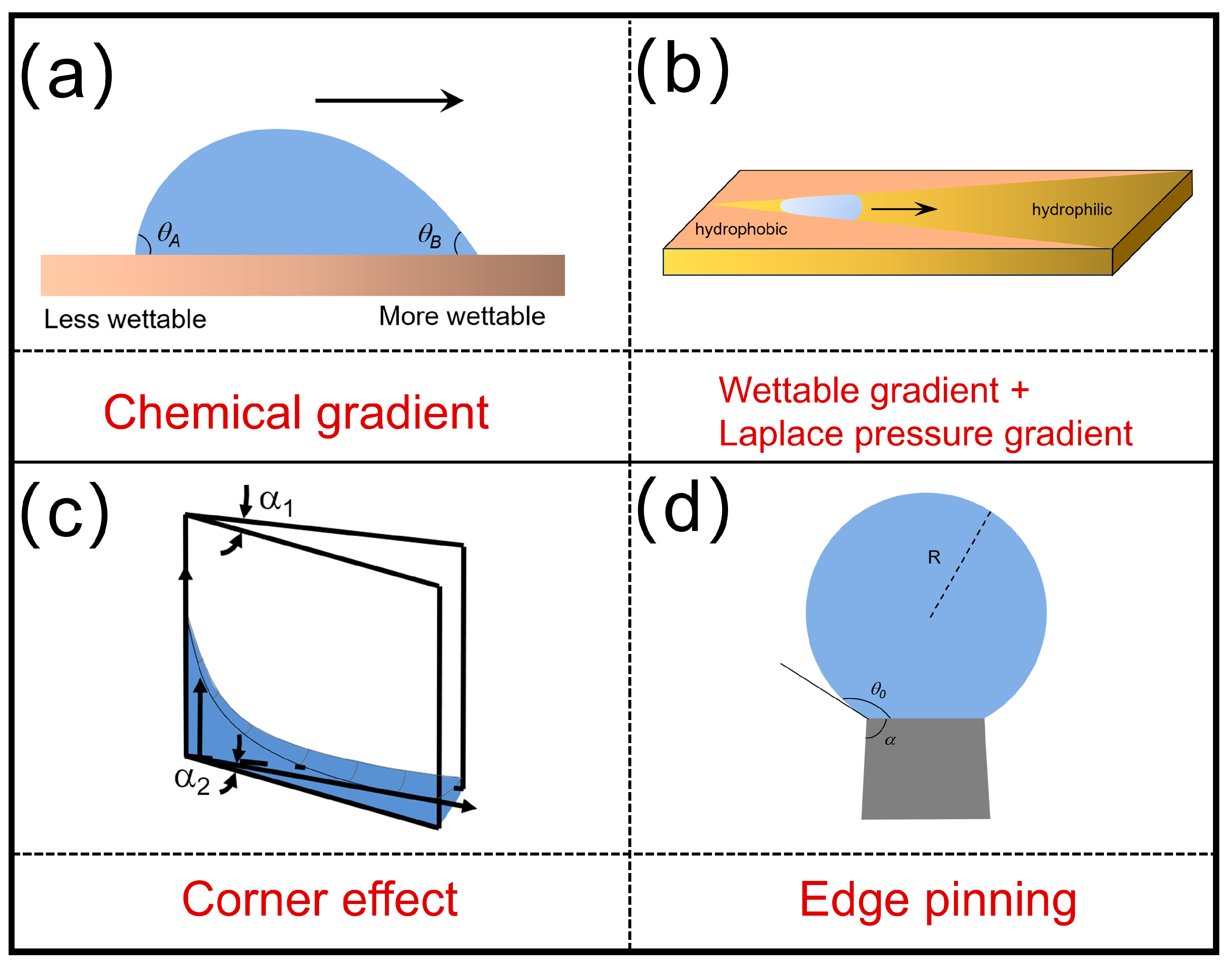
3. Physical Principles and Mechanisms
4. Directional Water Harvesting on Biomimetic Systems

| Preparation Method | Structure | Water Harvesting Efficiency | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Photolithography | star-shaped | 2.11–2.78 g cm−2 h−1 | [36] |
| Inkjet Printing | superhydrophilic-superhydrophobic surfaces | 1316.9 mg cm−2 h−1 | [43] |
| Femtosecond Laser | micro/nanopatterns | 200 mg cm−2 h−1 | [44] |
| Chemical Deposition | wedge-shaped tracks | 467.30 mg cm−2 h−1 | [47] |
| Laser Ablation | superhydrophilic-superhydrophobic surfaces | 97 mg cm−2 h−1 | [54] |
| Laser Ablation | superhydrophilic patterns | 14.9 ± 0.2 mg min−1 cm−2 | [56] |
| Laser Ablation | Superhydrophilic-superhydrophobic surfaces | 110.7 ± 5.7 mg cm−2 h−1 | [57] |
5. Directional Liquid Transport on Biomimetic Systems
| Preparation Method | Structure | Directional Liquid Transport Speed | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stereolithography | microcavity-Arrayed Surface | 50.0 mm/s | [65] |
| UV Lithography | microgrooves | 50.0 mm/s | [66] |
| Lithography | microstructure | 1 mm/s (uphill) | [67] |
| Laser Engraving | capillary channel network | 1 mm/s (average) | [68] |
| Vapor Deposition and Chemical Etching | janus gradient structure | over 400 mm/s | [69] |
| 3D Printing | microgrooves | 50.0 mm/s (average) | [71] |
| Photolithography and UV Exposure | wettability-patterned surfaces | 1 mm/s (uphill) | [72] |
| 3D Printing | topological surface | 50.0 mm/s (average) | [80] |
| 3D Printing | microstructure array | 23 mm/s | [81] |
| Thermal Deposition | wedge-shaped | 47.6 mm/s (average) | [82] |

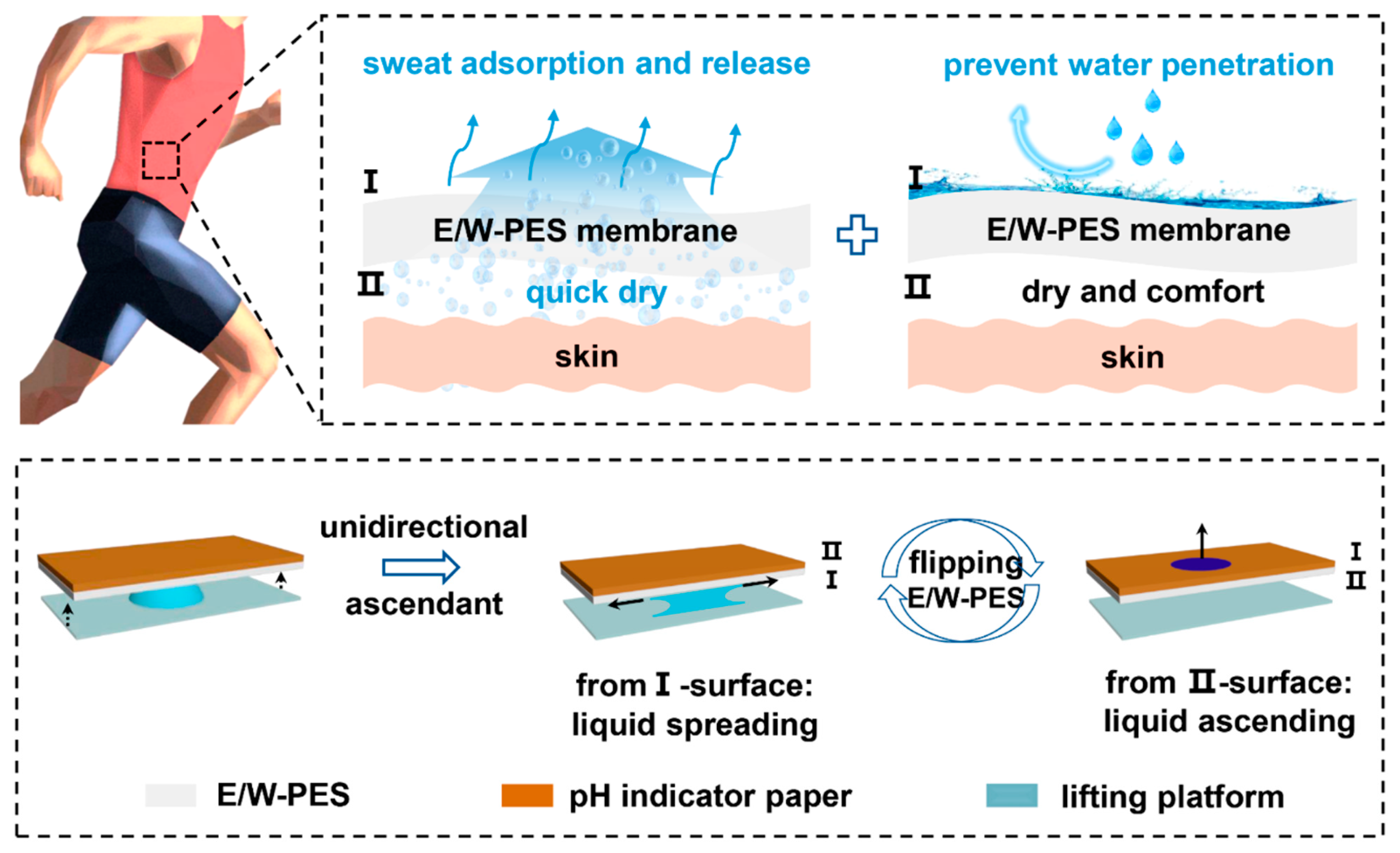
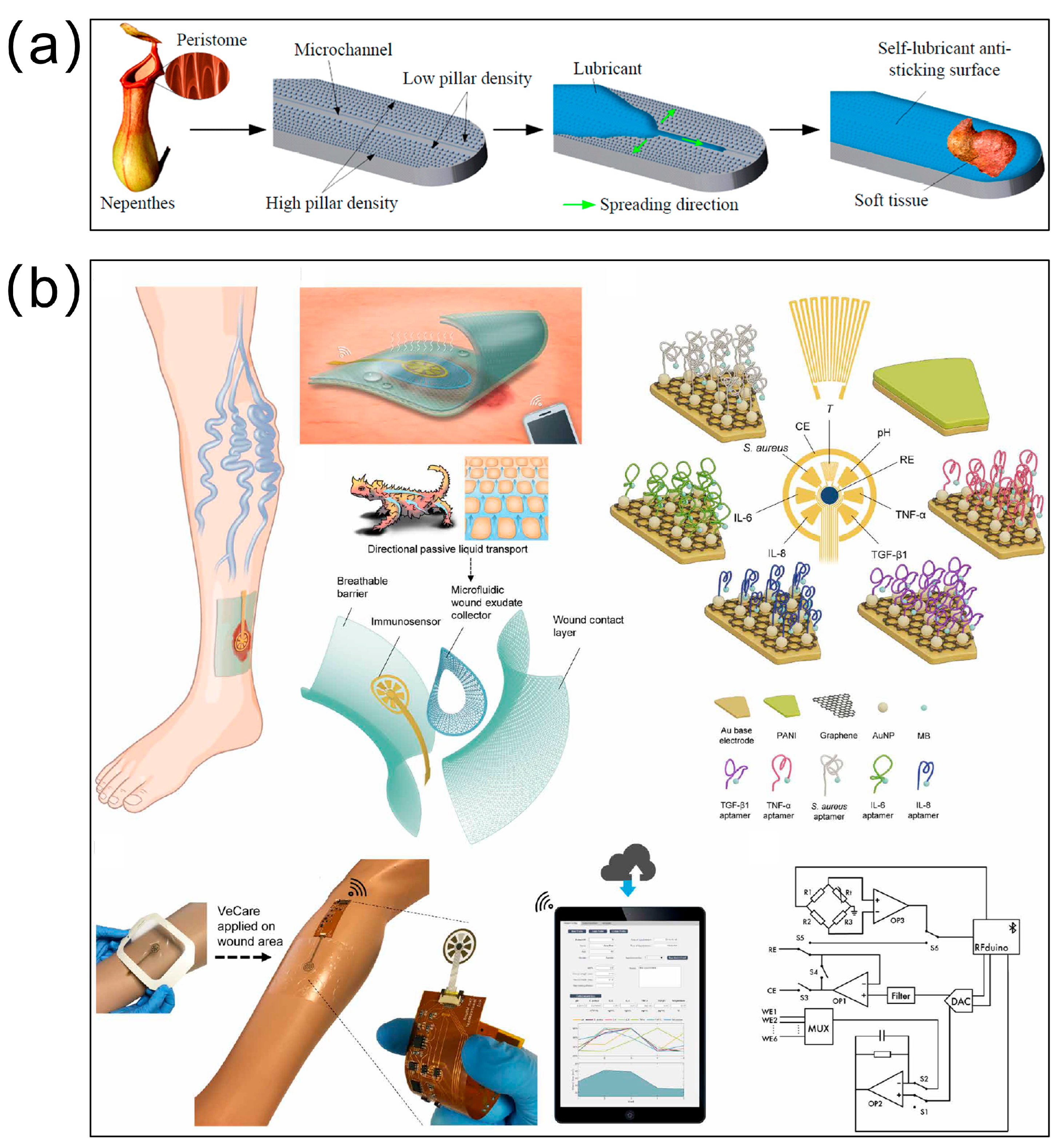
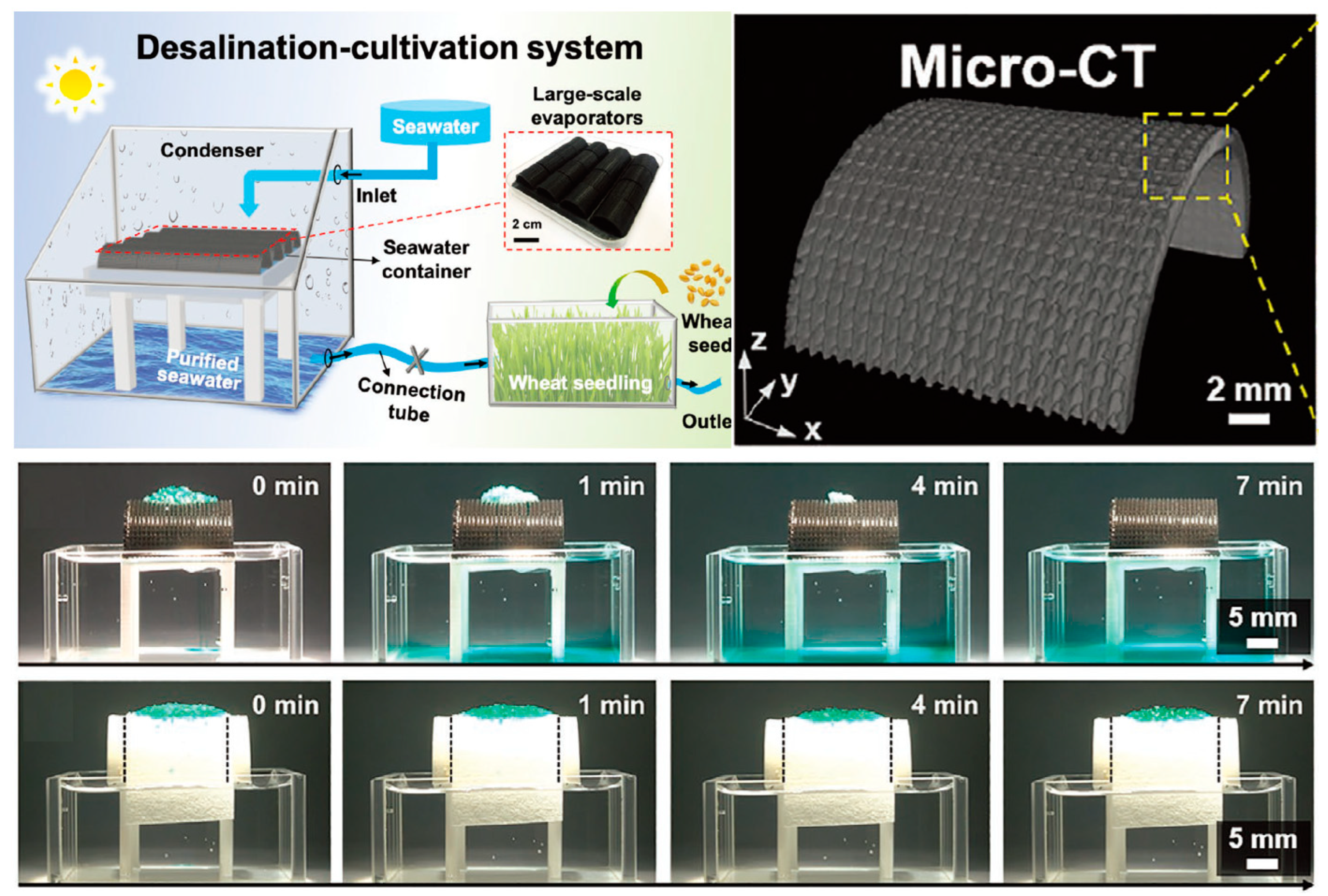
6. Engineering Applications and Innovations
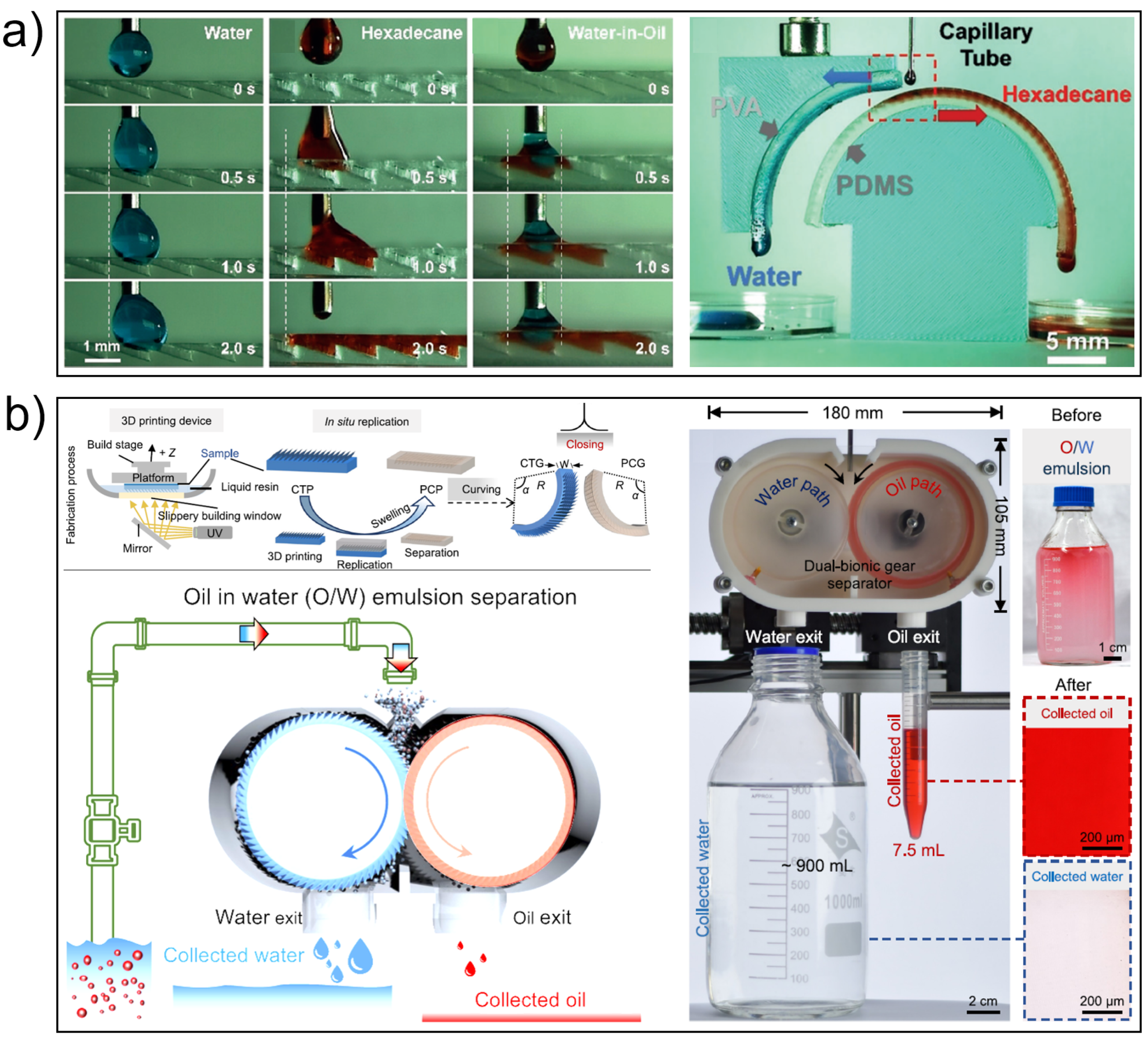
7. Conclusions
8. Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parker, A.R.; Lawrence, C.R. Water Capture by a Desert Beetle. Nature 2001, 414, 33–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Comanns, P.; Buchberger, G.; Buchsbaum, A.; Baumgartner, R.; Kogler, A.; Bauer, S.; Baumgartner, W. Directional, Passive Liquid Transport: The Texas Horned Lizard as a Model for a Biomimetic ‘Liquid Diode’. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 12, 20150415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhai, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. Super-hydrophobic Surfaces: From Natural to Artificial. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1857–1860. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.F.; Jiang, L. Water-Repellent Legs of Water Striders. Nature 2004, 432, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbaum, R.; Zaltzman, L.; Burgert, I.; Fratzl, P. The Role of Wheat Awns in the Seed Dispersal Unit. Science 2007, 316, 884–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Bai, H.; Huang, Z.; Tian, X.; Nie, F.Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhai, J.; Jiang, L. Directional Water Collection on Wetted Spider Silk. Nature 2010, 463, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, J.; Bai, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, T.; Fang, R.; Jiang, L. A Multi-Structural and Multi-Functional Integrated Fog Collection System in Cactus. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yao, X.; Liu, H.; Quere, D.; Jiang, L. Self-Removal of Condensed Water on the Legs of Water Striders. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9247–9252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Han, Z.; Jiang, L. Continuous Directional Water Transport on the Peristome Surface of Nepenthes Alata. Nature 2016, 532, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, W.; Lian, J.; Zhu, H.; Deng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Yin, X.; Wang, L. Selective Directional Liquid Transport on Shoot Surfaces of Crassula Muscosa. Science 2024, 384, 1344–1349. [Google Scholar]
- Butt, H.J.; Liu, J.; Koynov, K.; Straub, B.; Hinduja, C.; Roismann, I.; Berger, R.; Li, X.; Vollmer, D.; Steffen, W.; et al. Contact Angle Hysteresis. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 59, 101574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semprebon, C.; McHale, G.; Kusumaatmaja, H. Apparent Contact Angle and Contact Angle Hysteresis on Liquid Infused Surfaces. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessehaye, M.; Abdul-Wahab, S.A.; Savage, M.J.; Kohler, T.; Gherezghiher, T.; Hurni, H. Fog-Water Collection for Community Use. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 29, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B. Bioinspired Water Collection Methods to Supplement Water Supply. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2019, 377, 20190119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B. Commercial Applications, Projections of Water Collection, and Design of Water Harvesting Towers. Springer Ser. Mater. Sci. 2020, 299, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Machado, C.; Park, K.C.K. From Capture to Transport: A Review of Engineered Surfaces for Fog Collection. Droplet 2023, 2, e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, D.; Guo, Z. Overview of the Design of Bionic Fine Hierarchical Structures for Fog Collection. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 4827–4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Medina, F.J.; Hao, Q. A Dual-Biomimetic Surface with Leaf-Skeleton-Based Hierarchical Structures for Efficient Atmospheric Water Harvesting. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2025, 126, 011603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossey, R. Self-Cleaning Surfaces—Virtual Realities. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Sathasivam, S.; Song, J.; Crick, C.R.; Carmalt, C.J.; Parkin, I.P. Robust Self-Cleaning Surfaces That Function When Exposed to Either Air or Oil. Science 2015, 347, 1132–1135. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, K.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Multifunctional Foam with Self-Cleaning and Oil/Water Separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 2881–2886. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wu, L.; Yu, C.; Dong, Z.; Jiang, L. Peristome-Mimetic Curved Surface for Spontaneous and Directional Separation of Micro Water-in-Oil Drops. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 13623–13628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Ju, J.; Xue, Z.; Ma, J.; Feng, L.; Gao, S.; Jiang, L. Structured Cone Arrays for Continuous and Effective Collection of Micron-Sized Oil Droplets from Water. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, P.; Shang, W.; Song, C.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, F.; Luo, Z.; Yi, N.; Zhang, D.; Deng, T. Bioinspired Engineering of Thermal Materials. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 428–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.J.; Preston, D.J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, E.N. Nanoengineered Materials for Liquid-Vapour Phase-Change Heat Transfer. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 2, 16092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Li, C.; Hu, J.; Zhang, C.; Dong, Z. Bioinspired Superwetting Open Microfluidics: From Concepts, Phenomena to Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2301017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Harake, R.S.; Pan, T. Droplet-Driven Transports on Superhydrophobic-Patterned Surface Microfluidics. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 3642–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, M.; Sprowls, M.; Jackemeyer, D.; Long, M.; Perez, I.D.; Maret, W.; Tao, N.; Forzani, E. Motion in Microfluidic Rachets. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 4477–4481. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Shao, C.; Shang, L.; Zhao, Y. Bio-Inspired Wettability Patterns for Biomedical Applications. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 124–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherbrooke, W.C.; Scardino, A.J.; De Nys, R.; Schwarzkopf, L. Functional Morphology of Scale Hinges Used to Transport Water: Convergent Drinking Adaptations in Desert Lizards (Moloch Horridus and Phrynosoma Cornutum). Zoomorphology 2007, 126, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comanns, P.; Effertz, C.; Hischen, F.; Staudt, K.; Böhme, W.; Baumgartner, W. Moisture Harvesting and Water Transport through Specialized Micro-Structures on the Integument of Lizards. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2011, 2, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhury, M.K.; Whitesides, G.M. How to Make Water Run Uphill. Science 1992, 256, 1539–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazaltarim, A.J.; Bowen, J.J.; Taylor, J.M.; Morin, S.A. Dynamic Manipulation of Droplets Using Mechanically Tunable Microtextured Chemical Gradients. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, J.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired One-Dimensional Materials for Directional Liquid Transport. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2342–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Wang, S.; Gao, L.; Li, G.; Hou, Y.; Zheng, Y. Controlled Directional Water-Droplet Spreading on a High-Adhesion Surface. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014, 53, 6163–6167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.; Wang, L.; Ju, J.; Sun, R.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, L. Efficient Water Collection on Integrative Bioinspired Surfaces with Star-Shaped Wettability Patterns. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5025–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenceau, L.; Qur, D. Drops on a Conical Wire. J. Fluid Mech. 2004, 510, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Ganguly, R.; Schutzius, T.M.; Megaridis, C.M. Wettability Patterning for High-Rate, Pumpless Fluid Transport on Open, Non-Planar Microfluidic Platforms. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 1538–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Shang, W.; Feng, S.; Zhu, S.; Xing, Y.; Li, D.; Hou, Y.; Zheng, Y. Controlled Droplet Transport to Target on a High Adhesion Surface with Multi-Gradients. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, J.F.; Huh, C.; Mason, S.G. Resistance to Spreading of Liquids by Sharp Edges. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1977, 59, 568–581. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, Y.H.; van de Ven, T.G.M.; Mason, S.G. Resistance to Spreading of Liquids by Sharp Edged Microsteps. Colloids Surf. 1982, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Guo, Z. Spontaneous Directional Transportations of Water Droplets on Surfaces Driven by Gradient Structures. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 13814–13831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Yang, F.; Li, J.; Guo, Z. High-Efficiency Water Collection on Biomimetic Material with Superwettable Patterns. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 12415–12417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Du, H.; Dong, X.; Wang, C.; Duan, J.A.; He, J. A Simple Way to Achieve Bioinspired Hybrid Wettability Surface with Micro/Nanopatterns for Efficient Fog Collection. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 14620–14626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Duan, R.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Xia, F. Prewetting Dichloromethane Induced Aqueous Solution Adhered on Cassie Superhydrophobic Substrates to Fabricate Efficient Fog-Harvesting Materials Inspired by Namib Desert Beetles and Mussels. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 13045–13054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.Z.; Chu, D.K.; Qu, S.S.; Yin, K.; Hu, S.S.; Yao, P. Bioinspired Superwetting Surfaces for Fog Harvesting Fabricated by Picosecond Laser Direct Ablation. J. Cent. South Univ. 2022, 29, 3368–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Tan, X.; Shi, T.; Tang, Z.; Liao, G. Leaf Vein-Inspired Hierarchical Wedge-Shaped Tracks on Flexible Substrate for Enhanced Directional Water Collection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 44815–44824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yu, C.; Zhou, S.; Dong, Z.; Jiang, L. Liquid Harvesting and Transport on Multiscaled Curvatures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 23436–23442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, C.; Sun, Z.; Yu, C.; Dong, Z.; Wu, L.; Song, Y. 3D Printing a Biomimetic Bridge-Arch Solar Evaporator for Eliminating Salt Accumulation with Desalination and Agricultural Applications. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2102443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.F.; Ruan, S. Laser Direct Writing of Tree-Shaped Hierarchical Cones on a Superhydrophobic Film for High-E Ffi Ciency Water Collection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 29248–29254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yao, Y.; Li, J.; Peng, Z.; Chen, S. Directional Sliding Behavior of a Water Droplet on a Wedge-Shape Patterned Functional Surface. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 6905–6912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J. Enhanced Water Transportation on a Superhydrophilic Serial Cycloid-Shaped Pattern. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 11473–11481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yong, J.; Hou, X.; Chen, F. Femtosecond Laser Direct Weaving Bioinspired Superhydrophobic/Hydrophilic Micro-Pattern for Fog Harvesting. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 146, 107593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazzam, P.; Tavassoli, H.; Razmjou, A.; Warkiani, M.E.; Asadnia, M. Mist Harvesting Using Bioinspired Polydopamine Coating and Microfabrication Technology. Desalination 2018, 429, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D. Enhancing Water Transportation Capacity by Asymmetrical Patterned Surface with Super-Wettability. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2024, 125, 071601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Cai, S.; Zhou, J.; Li, S.; Wang, D.; Zhu, J.; Wu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, S.; Jin, S.; et al. Integration of Water Collection and Purification on Cactus- and Beetle-Inspired Eco-Friendly Superwettable Materials. Water Res. 2021, 206, 117759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, K.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Chen, X. Tunable Wetting Patterns on Superhydrophilic/Superhydrophobic Hybrid Surfaces for Enhanced Dew-Harvesting Efficacy. Adv. Mater. 2020, 7, 1901683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Peng, Z.; Yao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S. Flexible Functional Surface for Efficient Water Collection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 12256–12263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, X.; Li, K.; Tian, D.; Jiang, L. Curvature Adjustable Liquid Transport on Anisotropic Microstructured Elastic Film. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 6036–6044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Feng, R.; Song, F.; Wu, J.M.; Luo, Y.Q.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, Y.Z. Continuous and Controlled Directional Water Transportation on a Hydrophobic/Superhydrophobic Patterned Surface. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 352, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Bian, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Multibioinspired Slippery Surfaces with Wettable Bump Arrays for Droplets Pumping. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 20863–20868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; Wang, N.; Hou, L.; Cui, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, D.; Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y. A Bioinspired Hybrid Membrane with Wettability and Topology Anisotropy for Highly Efficient Fog Collection. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Feng, R.; Song, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Desert Beetle-Inspired Superhydrophilic/Superhydrophobic Patterned Cellulose Film with E Ffi Cient Water Collection and Antibacterial Performance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 14679–14684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Xia, W.; Mou, X.; Cai, Z. Reusable Hydrophilic–Superhydrophobic Patterned Weft Backed Woven Fabric for High-E Ffi Ciency Water-Harvesting Application. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 7216–7220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, N.; Zhang, X.; Dong, Z.; Chen, H.; Jiang, L. Uni-Directional Transportation on Peristome-Mimetic Surfaces for Completely Wetting Liquids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 14988–14992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, D.; Han, Z.; Jiang, L. A Novel Bioinspired Continuous Unidirectional Liquid Spreading Surface Structure from the Peristome Surface of Nepenthes Alata. Small 2017, 13, 1601676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Tang, L.; Hong, W.; Zhan, Y.; Yang, B.; Liu, J. A Novel Microstructure Inspired from Nepenthes Alata and Lizard Skin and Its Enhanced Uni-Directional Liquid Spreading Property. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 7842–7848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchberger, G.; Baumgartner, R.; Kogler, A.; Fritz, T.; Bauer, S.; Baumgartner, W. Bio-Inspired “Fluidic Diode” for Large-Area Unidirectional Passive Water Transport Even against Gravity. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 283, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Zhang, B.Y.; Wang, G.; Sun, Y.; Wu, C.; Ding, G. High-Performance Directional Water Transport Using a Two-Dimensional Periodic Janus Gradient Structure. Small Methods 2022, 6, 2200812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comanns, P. Laser-Based Biomimetic Functionalization of Surfaces: From Moisture Harvesting Lizards to Specific Fluid Transport Systems. Int. J. Des. Nat. Ecodynamics 2014, 9, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, D. Surfaces Inspired by the Nepenthes Peristome for Unidirectional Liquid Transport. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1702995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Zhou, P.; Xu, Z. Theoretical and Experimental Studies of the Functional Structure Effect on Directional Transport in Biomicrofluidics. Langmuir 2020, 36, 9523–9533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, W.; Song, J. Optimization of Bioinspired Surfaces with Enhanced Water Transportation Capacity. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 134568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Zhao, Z.; Xie, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Wu, F.; Kou, J. Continuous and Spontaneous Directional Droplet Transport on Bioinspired Serial-Wedge-Shaped Groove with Wettability Gradient. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2025, 126, 021601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Open-wedges, S.O.; Meng, Q.; Zhou, J.; Pang, J.; Qiu, W.; Wang, X.; Qin, W. Controlling Directional Liquid Transfer over a Ratchet-Like. Coatings 2024, 14, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Bai, A.; Dong, S.; Hu, Y. Droplet Flow Behavior on a Biomimetic Structure with a Superhydrophobic Gradient Interface Inspired by the Nepenthes Pitcher Plant. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 062012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y. Peristome-Mimetic Surfaces Fabricated by Nanosecond Laser for Unidirectional Liquid Spreading. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2024, 26, 2302240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishina, A.; Filatov, I.; Shchedrina, N.; Prokopiev, V.; Davydova, E.; Suslov, R.; Romanova, G. Laser-Assisted Structures for Efficient Fluid Management on Stainless Steel Surfaces. Langmuir 2024, 40, 5632–5638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhu, K.; Cao, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, B.; Liang, L.; Chai, G.; Liu, A. Smart Design of Wettability-Patterned Gradients on Substrate-Independent Coated Surfaces to Control Unidirectional Spreading of Droplets. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 2995–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, C.; Gao, C.; Dong, Z.; Wu, L.; Jiang, L. Time-Dependent Liquid Transport on a Biomimetic Topological Surface. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5149–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Jiang, K.; Sheng, Y.; Peng, X.; Liu, A.; Wu, H. Continuous Directionalwater Delivery on the 3D-Printed Arrowhead Microstructure Array. Materials 2019, 12, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alheshibri, M.H.; Rogers, N.G.; Sommers, A.D.; Eid, K.F. Spontaneous Movement of Water Droplets on Patterned Cu and Al Surfaces with Wedge-Shaped Gradients. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 174103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, C.; Yu, C.; Li, N.; Gao, C.; Dong, Z.; Jiang, L. Liquids Unidirectional Transport on Dual-Scale Arrays. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 9214–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, J.; Tsang, A.C.H. Smart Directional Liquid Manipulation on Curvature-Ratchet Surfaces. ACS Nano 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Nguyen, D.T.; Yeo, T.; Lim, S.B.; Tan, W.X.; Madden, L.E.; Jin, L.; Yong, J.; Long, K.; Abu, F.; et al. A Flexible Multiplexed Immunosensor for Point-of-Care in Situ Wound Monitoring. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg9614. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, M.; Peng, Y.; Jin, X.; Tian, D.; Liu, K.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Continuous and Spontaneous Antigravity Oil Collection and Transportation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1704220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Dai, S.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Dong, G. Stretch-Controlled Branch Shape Microstructures for Switchable Unidirectional Self-Driven Spreading of Oil Droplets. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 41694–41703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yu, C.; Li, C.; Dong, Z.; Jiang, L. Programmable Unidirectional Liquid Transport on Peristome-Mimetic Surfaces under Liquid Environments. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 18244–18248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Liu, X.; Guo, C.; Ning, Y.; Yang, K.; Yu, C.; Liu, K.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Underwater Superoleophilic Two-Dimensional Surface with Asymmetric Oleophobic Barriers for Unidirectional and Long-Distance Oil Transport. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 22684–22691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, F.; Guo, F.; Guo, Z. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science Stable Janus Superhydrophilic/Hydrophobic Nickel Foam for Directional Water Transport. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 509, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, R.; Yan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tian, D.; Jiang, L. Stretch-Enhanced Anisotropic Wetting on Transparent Elastomer Film for Controlled Liquid Transport. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 19981–19989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, B.; Gu, Z.; Zhou, K. 4D Printing of Butterfly Scale–Inspired Structures for Wide-Angle Directional Liquid Transport. Small 2023, 19, 2207640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, J.; Symes, M.D.; Yang, X.Y. Directional Transport for Efficient Catalysis. Matter 2023, 6, 674–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Wen, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Cao, M. Improved Liquid Collection on a Dual-Asymmetric Superhydrophilic Origami. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2211596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, H.; Niu, H.; Lin, T. Superphobicity/Philicity Janus Fabrics with Switchable, Spontaneous, and Oil Fluids. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tian, D.; Jiang, L. Highly Flexible Monolayered Porous Membrane with Superhydrophilicity-Hydrophilicity for Unidirectional Liquid Penetration. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 7287–7296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Liu, G.H.; Shou, B.B.; Li, T.T.; Ren, H.T.; Lin, J.H.; Lou, C.W.; Xu, Y.M. Design of Nature-Inspired Patterns on Knitted Fabrics for Directional Transportation of Sweat and Study of Their Performances. Text. Res. J. 2024, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Borbora, A.; Chakraborty, P.; Sarma, H.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Bose, A.; Mandal, B.B.; Tenjimbayashi, M.; Manna, U. Controlled Chemical-Patterning of Textile to Accelerate Anti-Gravity Water Flow. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2410955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Mao, J.; Chen, Z. Superwetting Patterned PDMS/PMMA Materials by Facile One-Step Electro-Spraying for Signal Expression and Liquid Transportation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Gu, L.; Zeng, Z.; Xue, Q. Simply Adjusting the Unidirectional Liquid Transport of Scalable Janus Membranes toward Moisture-Wicking Fabric, Rapid Demulsification, and Fast Oil/Water Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 51102–51113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhan, Z.; Shen, T.; Li, N.; Zhang, C. Dual-Bionic Superwetting Gears with Liquid Directional Steering for Oil-Water Separation. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yang, Z.; Dong, Z. Fast-Response, No-Pretreatment, and Robustness Air-Water/Oil Amphibious Superhydrophilic-Superoleophobic Surface for Oil/Water Separation and Oil-Repellent Fabrics. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 132043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Li, F.; Chen, F.; Pan, Y.; Bhushan, B. Dual-Liquid-Diode Janus Mesh with Multisuperwettability for Unidirectional Oil—Water Transportation. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 26086–26096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chen, H. Self-Lubricanting Slippery Surface Withwettability Gradients for Anti-Sticking of Electrosurgical Scalpel. Micromachines 2018, 9, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z. Flexible Topological Liquid Diode Catheter. Mater. Today Phys. 2020, 12, 100170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, D.; Jin, T.; Qi, Y. A Novel Bionic Micro-Textured Tool with the Function of Directional Cutting-Fluid Transport for Cutting Titanium Alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2023, 311, 117816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Dong, Z.; Cai, Z.; Ganapathy, T.; Fang, N.X.; Li, C.; Yu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Y. Highly Efficient Three-Dimensional Solar Evaporator for High Salinity Desalination by Localized Crystallization. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, Q.; Li, Z.; Pang, J.; Yang, K.; Zhou, J. Biomimetic Directional Liquid Transport on a Planar Surface in a Passive and Energy-Free Way. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040223
Meng Q, Li Z, Pang J, Yang K, Zhou J. Biomimetic Directional Liquid Transport on a Planar Surface in a Passive and Energy-Free Way. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(4):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040223
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Qing’an, Zhangcan Li, Jie Pang, Kaicheng Yang, and Junjie Zhou. 2025. "Biomimetic Directional Liquid Transport on a Planar Surface in a Passive and Energy-Free Way" Biomimetics 10, no. 4: 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040223
APA StyleMeng, Q., Li, Z., Pang, J., Yang, K., & Zhou, J. (2025). Biomimetic Directional Liquid Transport on a Planar Surface in a Passive and Energy-Free Way. Biomimetics, 10(4), 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040223





