Exploring the Discharge Performance of Li-ion Batteries Using Ohmic Drop Compensation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- –
- A part that does not depend on the current, frequently called open circuit voltage OCV;
- –
- A part that strongly depends on the level of current flowing through the cell and which is mainly located at the positive and negative interfaces, usually called overpotentials or polarizations:
2. Materials and Methods
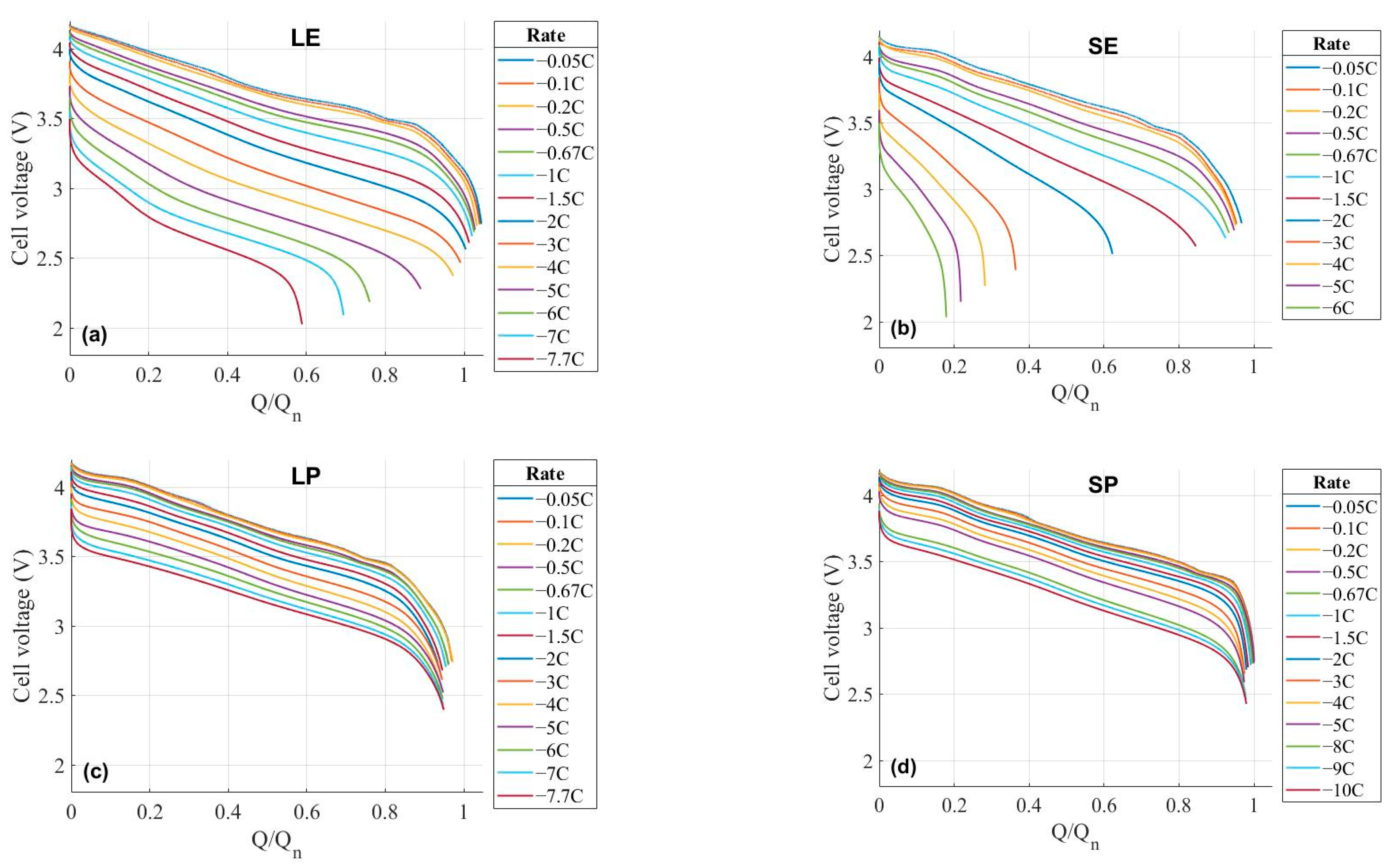
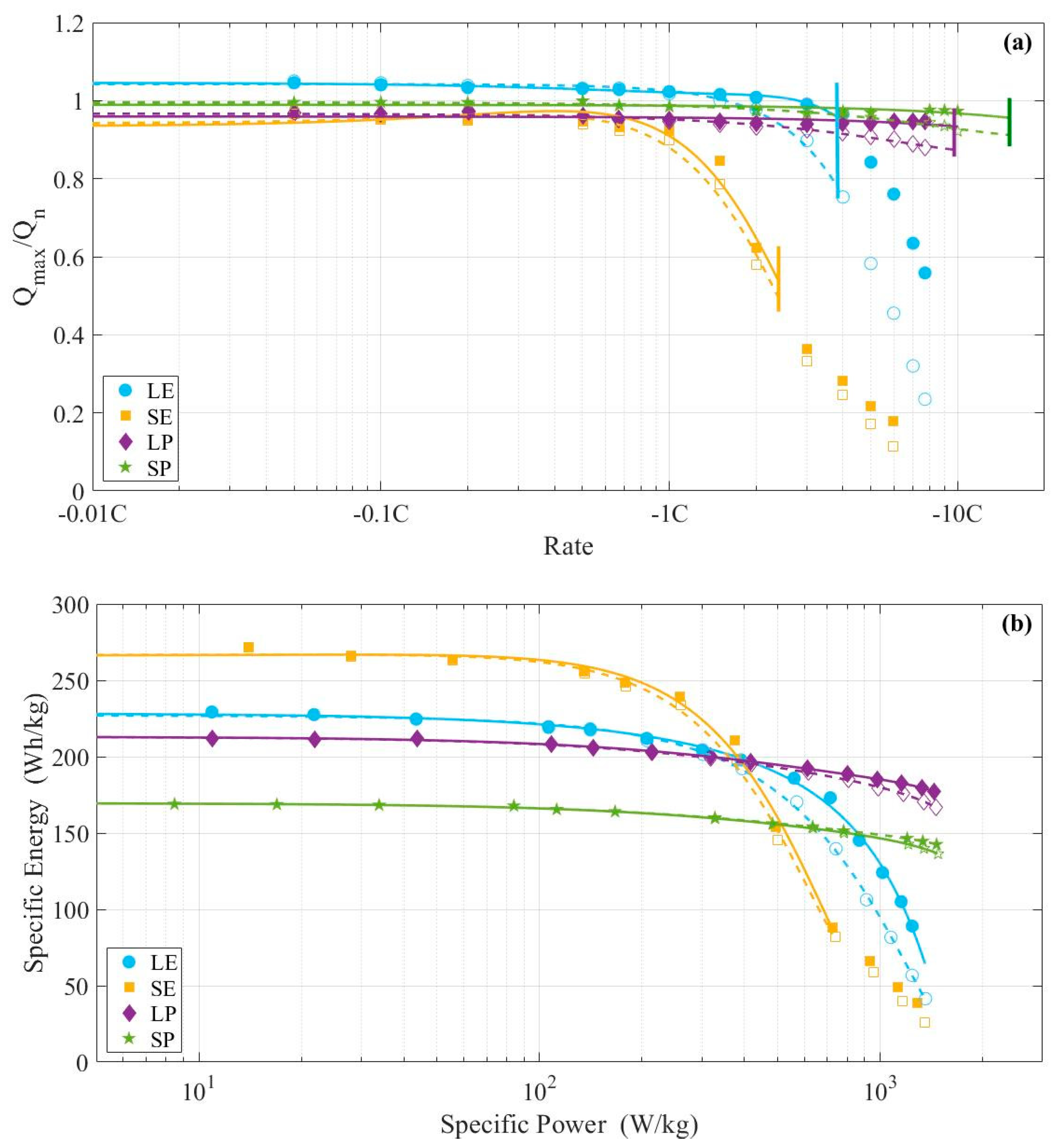
3. Results
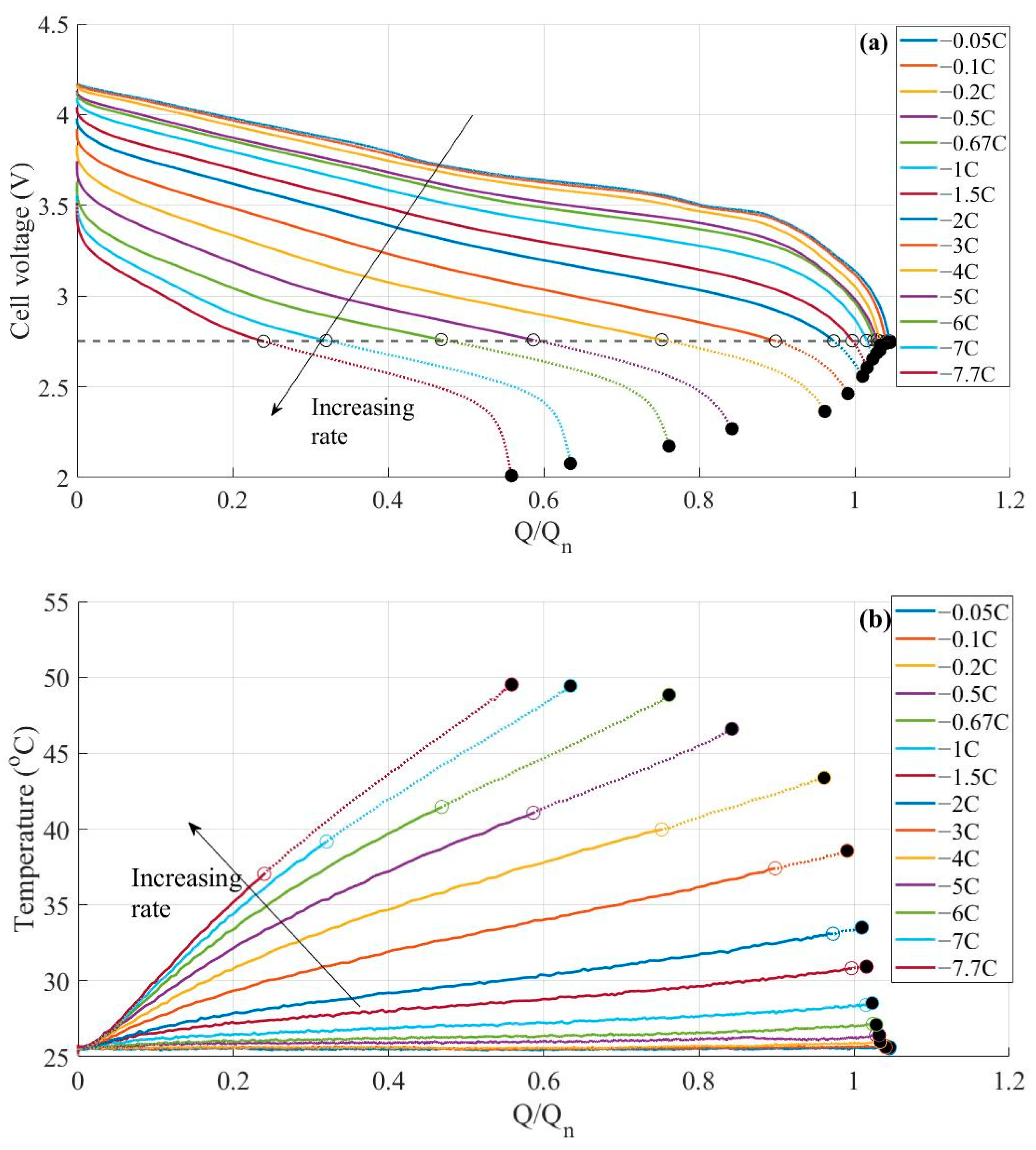
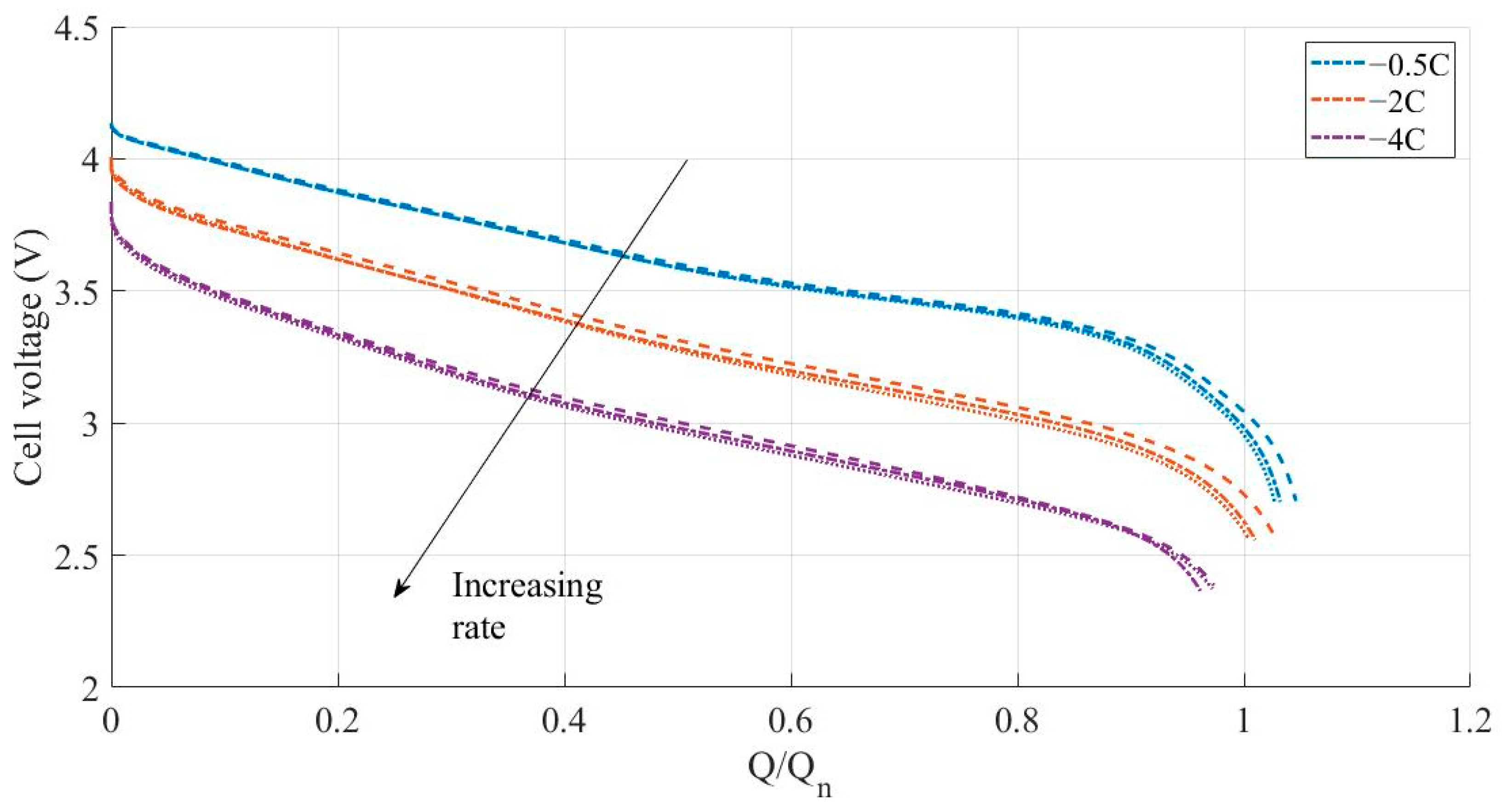
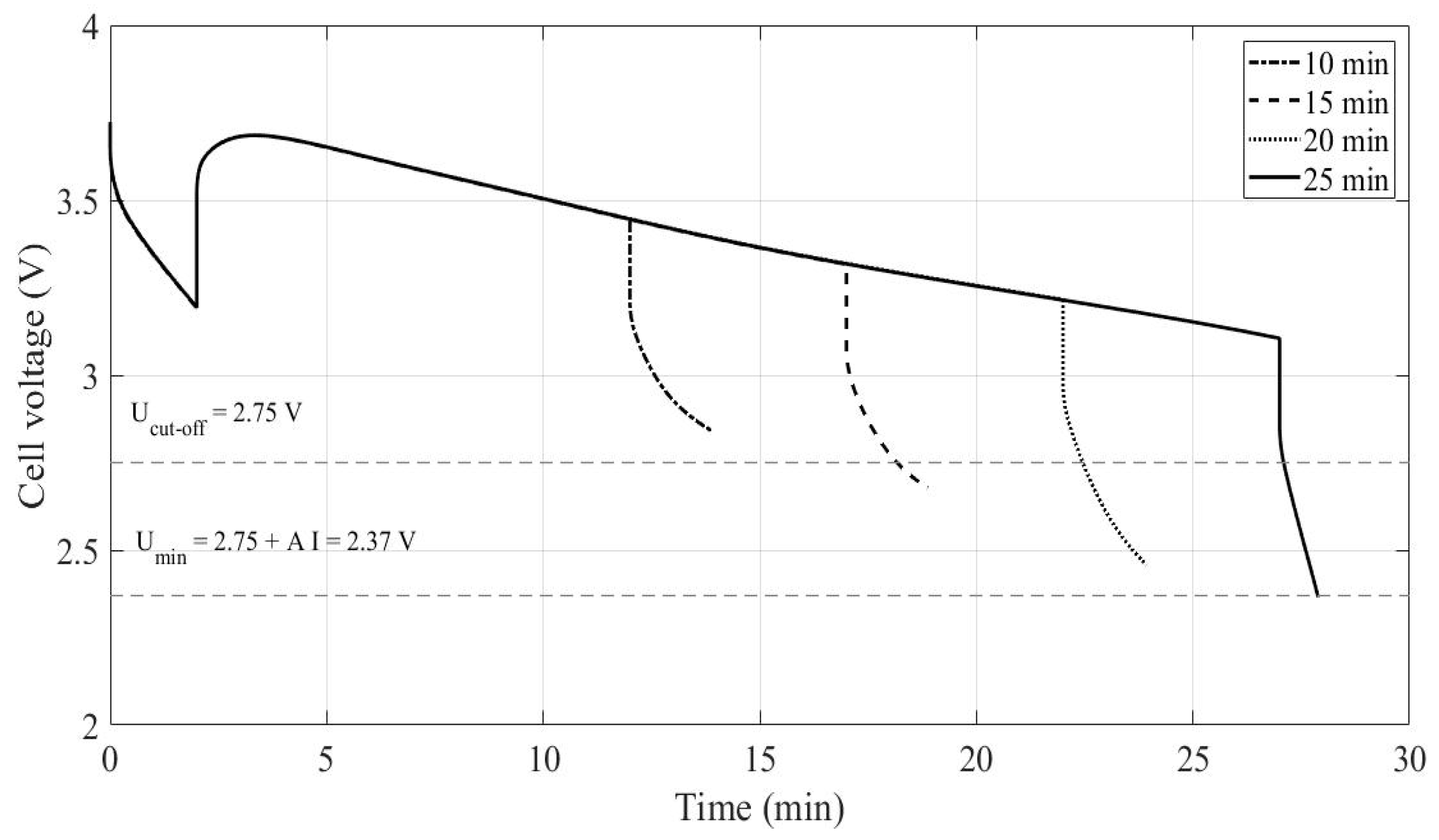
3.1. Constant Current Discharges Using Ohmic Drop Compensation
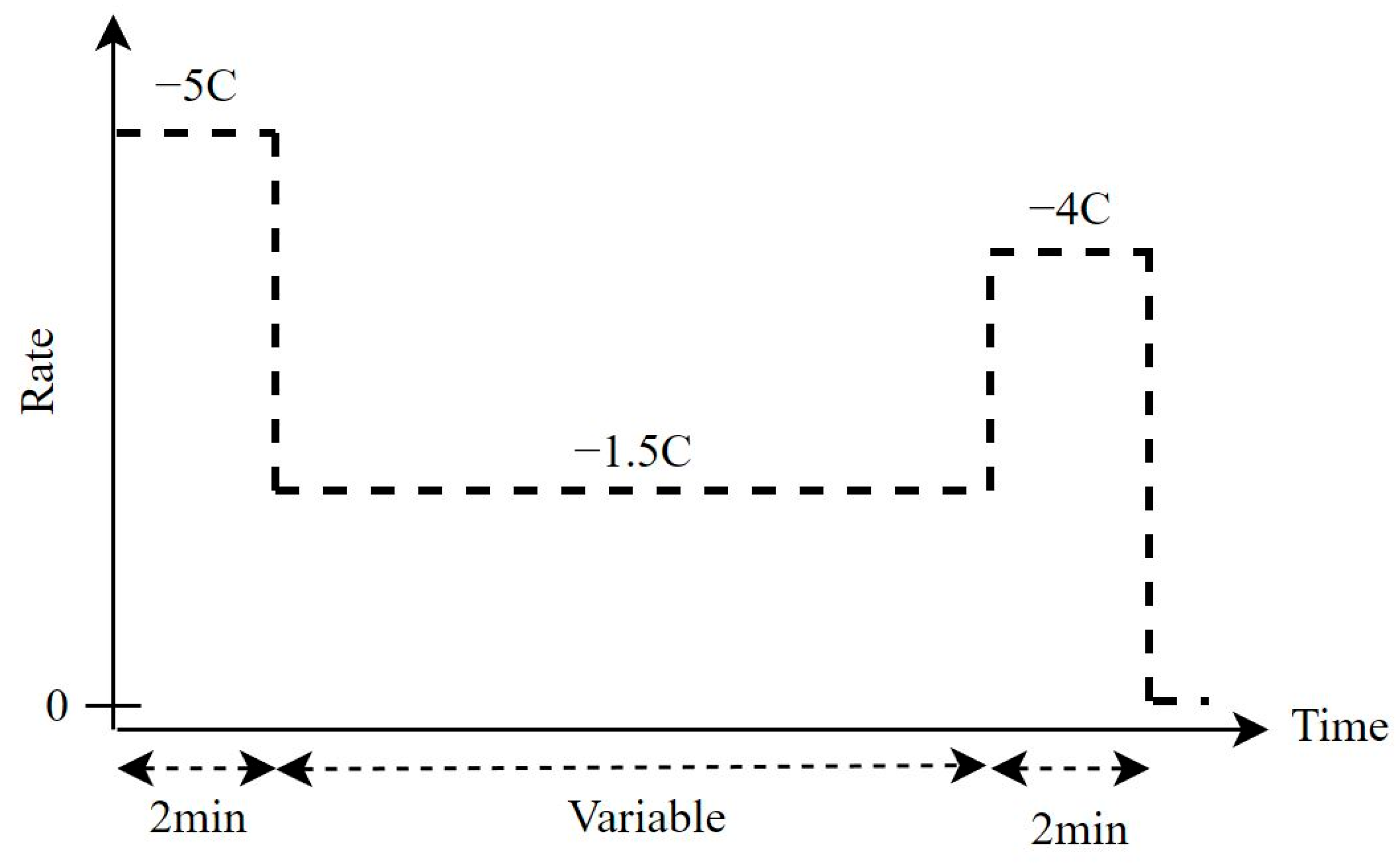
3.2. Extending the Flight Time of a Drone with Ohmic Drop Compensation
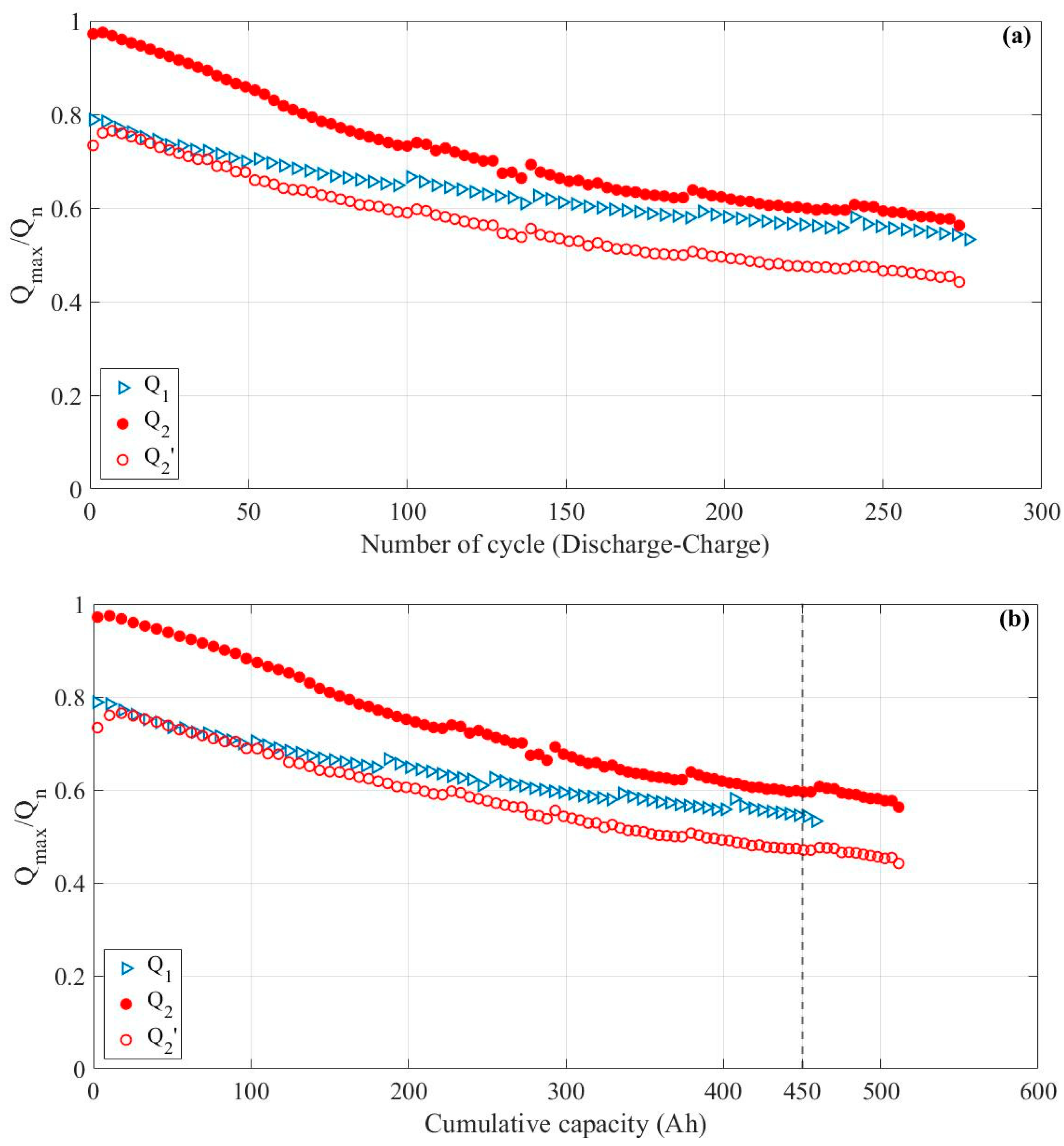
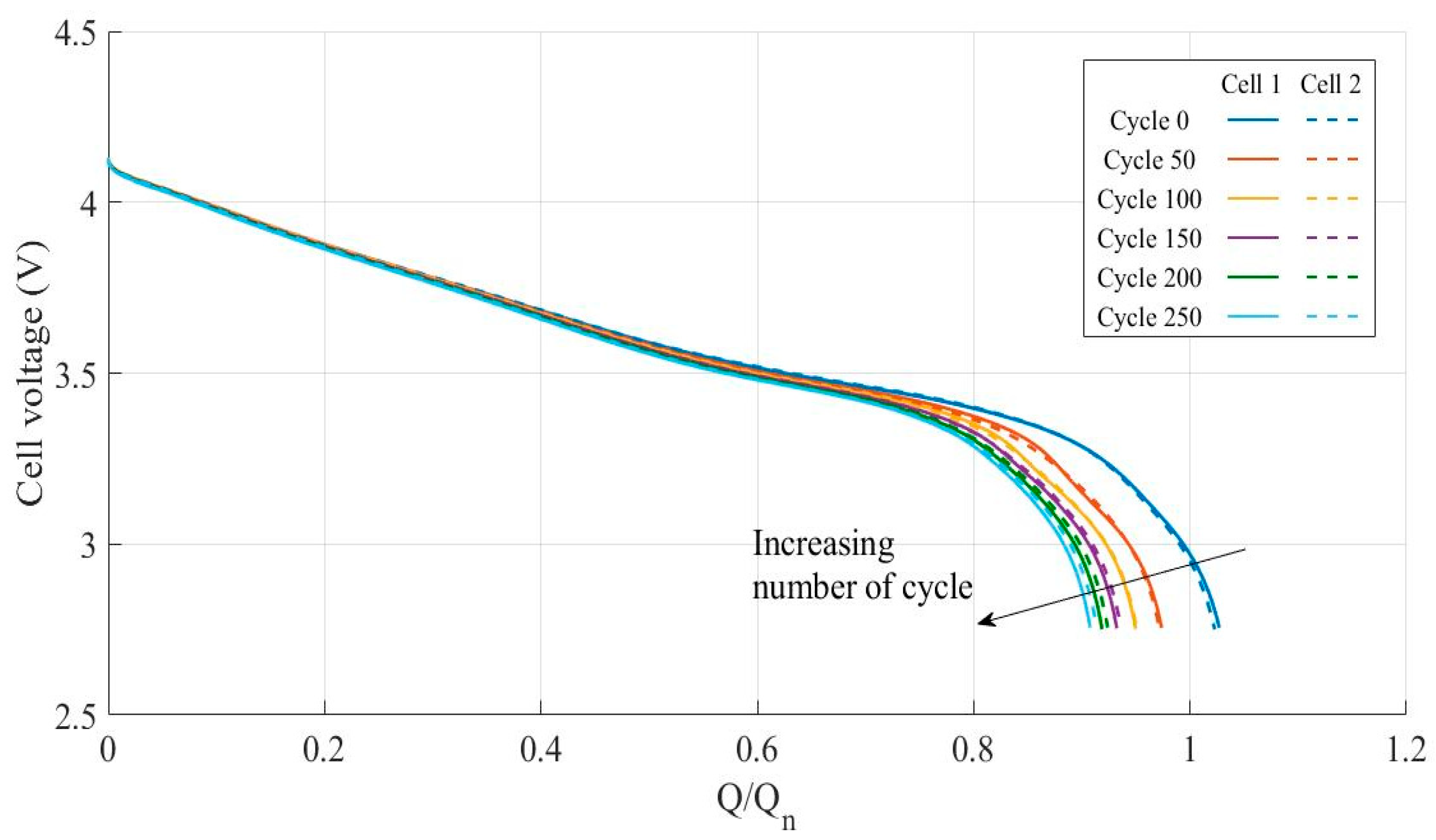
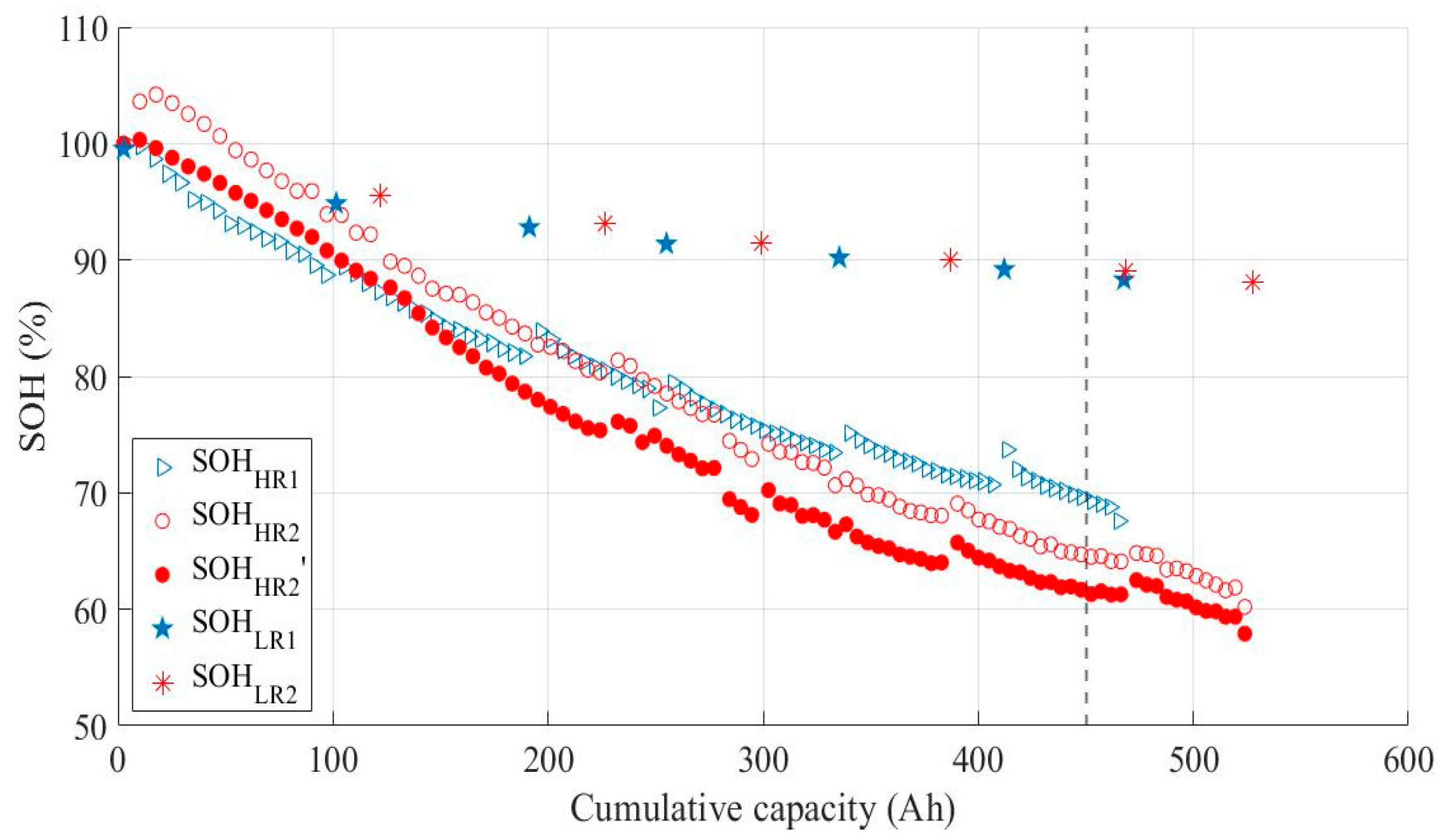
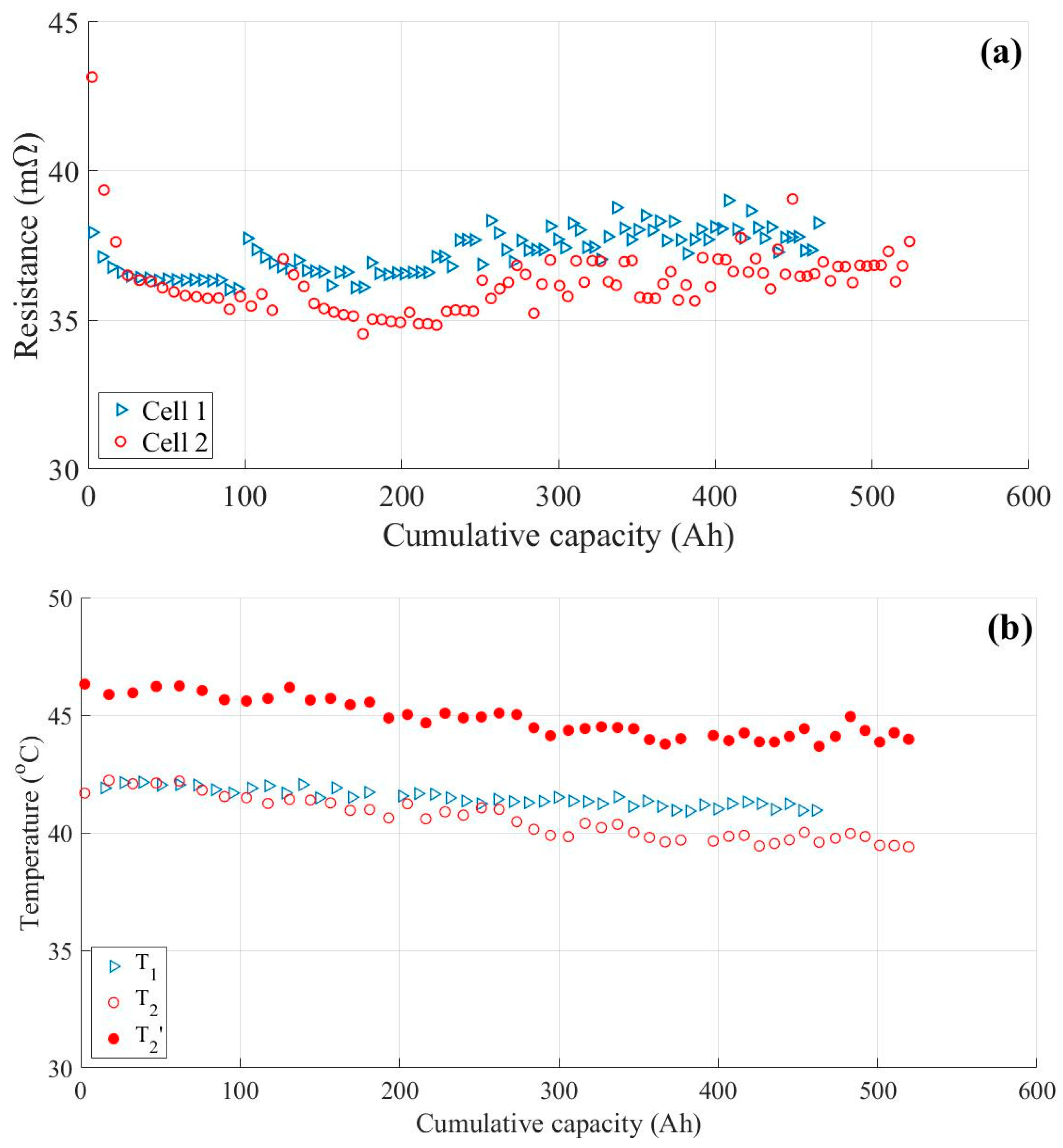
3.3. Impact of Ohmic Drop Compensation on Aging
- For the LE cell aged without ohmic drop compensation (indexed 1, in blue), the capacity is measured when the voltage reaches Ucut-off = 2.75 V (Q1);
- For the LE cell aged with ohmic drop compensation (indexed 2, in red), the capacity is measured when the voltage reaches 2.75 V (Q2) or Umin = 2.37 V (Q2′).
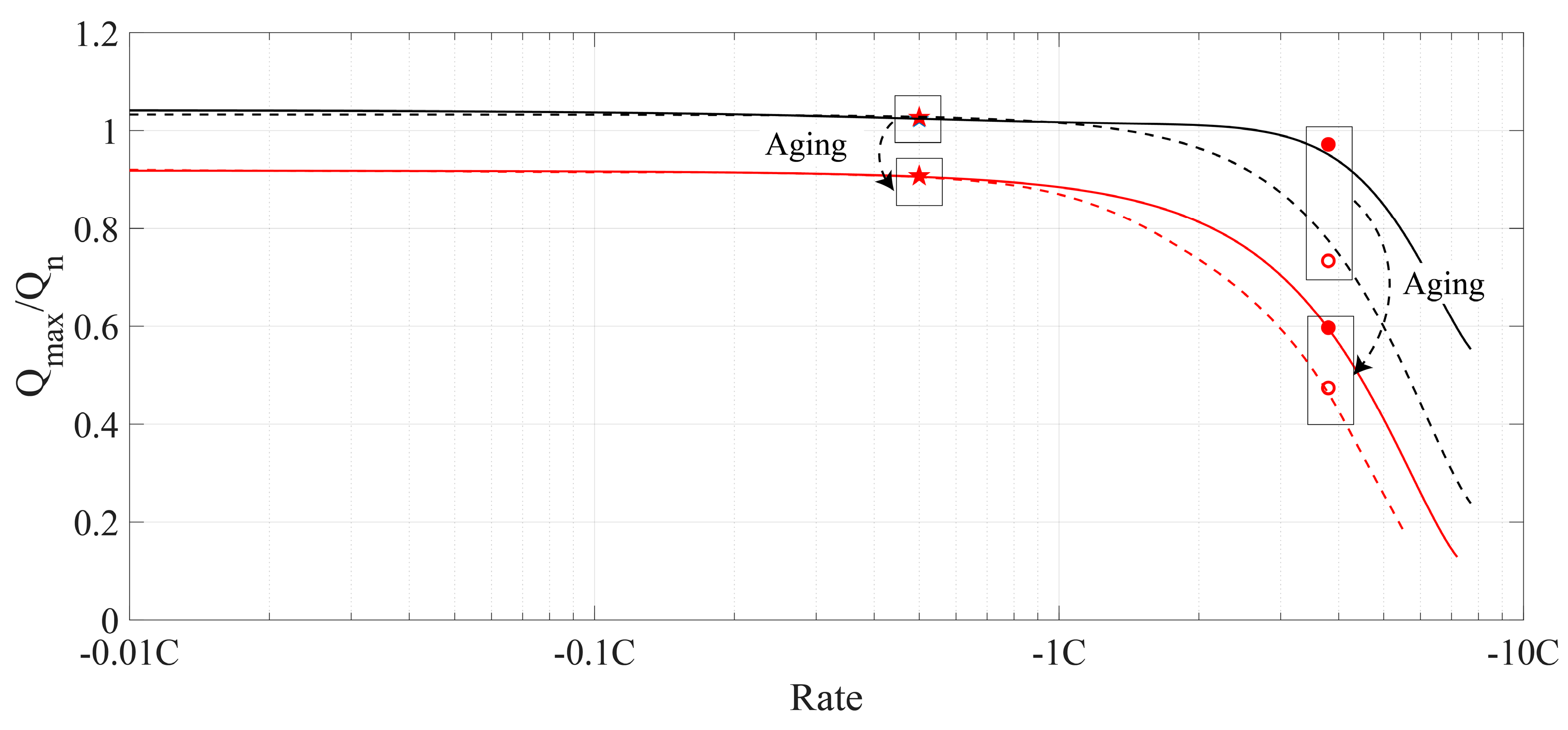
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Luo, X.; Wang, J.; Dooner, M.; Clarke, J. Overview of current development in electrical energy storage technologies and the application potential in power system operation. Appl. Energy 2015, 137, 511–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshio, M.; Brodd, R.J.; Kozawa, A. Lithium-Ion Batteries; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Olabi, A.G.; Abbas, Q.; Shinde, P.A.; Abdelkareem, M.A. Rechargeable batteries: Technological advancement; challenge, current and emerging applications. Energy 2023, 266, 126408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Han, X.; Li, J.; Hua, J.; Ouyang, M. A review on the key issues for lithium-ion battery management in electric vehicles. J. Power Sources 2013, 226, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, O.; Hawkes, A.; Gambhir, A.; Staffell, I. The future cost of electrical energy storage based on experience rates. Nat. Energy 2017, 2, 17110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thackeray, M.; Wolverton, C.; Isaacs, E.D. Electrical energy storage for transportation—Approaching the limits of, and going beyond, lithium-ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 7854–7863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldaña, G.; Martín, J.I.S.; Zamora, I.; Asensio, F.J.; Oñederra, O. Analysis of the current electric battery models for electric vehicle simulation. Energies 2019, 12, 2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.F.; Baumann, M.; Zimmermann, B.; Braun, J.; Weil, M. The environmental impact of Li-Ion batteries and the role of key parameters—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 491–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catenaro, E.; Rizzo, D.M.; Onori, S. Experimental analysis and analytical modeling of Enhanced-Ragone plot. Appl. Energy 2021, 291, 116473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catenaro, E.; Rizzo, D.M.; Onori, S. Framework for energy storage selection to design the next generation of electrified military vehicles. Energy 2021, 231, 120695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragone, D. Review of Battery Systems for Electrically Powered Vehicles. SAE Tech. Pap. 1968, 680453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Shi, S.-Q.; Li, H. Brief overview of electrochemical potential in lithium ion batteries. Chin. Phys. B 2016, 25, 018210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefrou, C.; Fabry, P.; Poignet, J.-C. Electrochemistry: The Basics, With Examples; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 208–209. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, L.; Newman, J. Heat-generation rate and general energy balance for insertion battery systems. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1997, 144, 2697–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Perez, H.E.; Mohan, S.; Siegel, J.B.; Stefanopoulou, A.G.; Ding, Y.; Castanier, M.P. A lumped-parameter electro-thermal model for cylindrical batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 257, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BioLogic. Ohmic Drop Part I: Effect on Measurements (Ohmic Drop Effect on Measurements). 2021. Available online: https://www.biologic.net/documents/ohmic-drop-effect-on-measurements-electrochemistry-battery-corrosion-application (accessed on 7 July 2021).
- BioLogic. Ohmic Drop Part II: Intro. To Ohmic Drop Measurement Techniques (Ohmic Drop Measurement). 2021. Available online: https://www.biologic.net/documents/ohmic-drop-measurement-techniques-electrochemistry-battery-application-note-28/ (accessed on 7 July 2021).
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.-C.; Peng, R.-H.; Tsai, T.-W.; Chen, K.-H.; Wey, C.-L. Fast charging and high efficiency switching-based charger with continuous built-in resistance detection and automatic energy deliver control for portable electronics. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2014, 49, 1580–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-H.; Chen, C.-L.; Lee, Y.-H.; Wang, S.-J.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Huang, H.-W.; Chen, K.-H. Fast Charging Technique for Li-Ion Battery Charger. In Proceedings of the 15th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (2008), Saint Julian’s, Malta, 31 August–3 September 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-H.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Chen, K.-H. A li-ion battery charger with smooth control circuit and built-in resistance compensator for achieving stable and fast charging. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2009, 57, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, M.H.; Thivel, P.-X.; Lefrou, C.; Bultel, Y. Fast-charging of lithium iron phosphate battery with ohmic-drop compensation method. J. Energy Storage 2016, 8, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, R.-H.; Tsai, T.-W.; Chen, K.-H.; Tai, Z.H.; Cheng, Y.H.; Tsai, C.C.; Luo, H.-Y.; Wang, S.-M.; Chen, L.-D.; Yang, C.-C.; et al. Switching-Based Charger with Continuously Built-in Resistor Detector and Analog Multiplication Division Unit for Fast Charging in Li-Ion Battery. In Proceedings of the ESSCIRC (ESSCIRC) (2013), Bucharest, Romania, 16–20 September 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Pierre, R. A Dynamic Voltage-Compensation Technique for Reducing Charge Time in Lithium-Ion Batteries. In Proceedings of the Fifteenth Annual Battery Conference on Applications and Advances (Cat. No. 00TH8490) (2000), Long Beach, CA, USA, 11–14 January 2000; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleury, X.; Noh, M.H.; Genies, S.; Thivel, P.-X.; Lefrou, C.; Bultel, Y. Fast-charging of lithium iron phosphate battery with ohmic drop compensation method: Ageing study. J. Energy Storage 2018, 16, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lain, M.J.; Brandon, J.; Kendrick, E. Design Strategies for High Power vs. High Energy Lithium Ion Cells. Batteries 2019, 5, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-K. Factors Affecting Capacity Design of Lithium-Ion Stationary Batteries. Batteries 2019, 5, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Manufacturer | Samsung | LG | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial name | 20S | 36G | H26 | M26 |
| Internal code 1 | SP | SE | LP | LE |
| Nominal voltage (V) | 3.6 | 3.6 | 3.7 | 3.65 |
| Nominal capacity, Qn (Ah) | 2.0 | 3.35 | 2.6 | 2.6 |
| Maximal discharge current (A) | 30 | 8 | 25 | 10 |
| Internal Code | Available Capacity at –C/2 (Ah) | Compensation Factor A (mΩ) |
|---|---|---|
| LE | 2.65/2.64/2.68 | 36.9/36.2/34.9 |
| SE | 3.14/3.13/3.15 | 35.7/34.5/35.5 |
| LP | 2.49/2.50/2.49 | 18.2/17.4/18.1 |
| SP | 1.99/2.01/2.00 | 16.1/15.8/15.7 |
| Hover Time (min) | Capacity Needed for a Complete Flight Ah) | Capacity Allowed with Conventional BMS (Ah) | Capacity Allowed with BMS Using Ohmic Drop Compensation (Ah) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 1.43 | 1.43 | 1.43 |
| 15 | 1.76 | 1.61 | 1.76 |
| 20 | 2.08 | 1.81 | 2.08 |
| 25 | 2.41 | 2.08 | 2.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Magne-Tang, N.; Decaux, C.; Thivel, P.-X.; Lefrou, C. Exploring the Discharge Performance of Li-ion Batteries Using Ohmic Drop Compensation. Batteries 2023, 9, 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9090451
Magne-Tang N, Decaux C, Thivel P-X, Lefrou C. Exploring the Discharge Performance of Li-ion Batteries Using Ohmic Drop Compensation. Batteries. 2023; 9(9):451. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9090451
Chicago/Turabian StyleMagne-Tang, Nicolas, Céline Decaux, Pierre-Xavier Thivel, and Christine Lefrou. 2023. "Exploring the Discharge Performance of Li-ion Batteries Using Ohmic Drop Compensation" Batteries 9, no. 9: 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9090451
APA StyleMagne-Tang, N., Decaux, C., Thivel, P.-X., & Lefrou, C. (2023). Exploring the Discharge Performance of Li-ion Batteries Using Ohmic Drop Compensation. Batteries, 9(9), 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9090451







