Emerging Battery Technologies: The Main Aging Mechanisms and Challenges
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To provide an overview of emerging battery technologies, with a focus on advanced LIBs, SSBs, Li-S batteries, and NIBs. Each technology offers distinct advantages for specific applications while posing unique technical challenges, which make them central to current research efforts.
- To analyze the specific aging mechanisms associated with each battery type. For instance, Li–S batteries are affected by sulfur dissolution, NIBs by electrode expansion, and SSBs by interface instability between electrodes and electrolytes. Understanding these mechanisms is key to improving performance and extending battery life.
- To propose avenues for improvement, based on current research. Potential solutions include electrode coatings, innovative electrolyte design, and improved mechanical stress management within cells.
2. Overview of New-Generation Batteries
2.1. Advanced Lithium-Ion Batteries
2.1.1. NMC and NCA
2.1.2. Doped or Nanostructured LFP
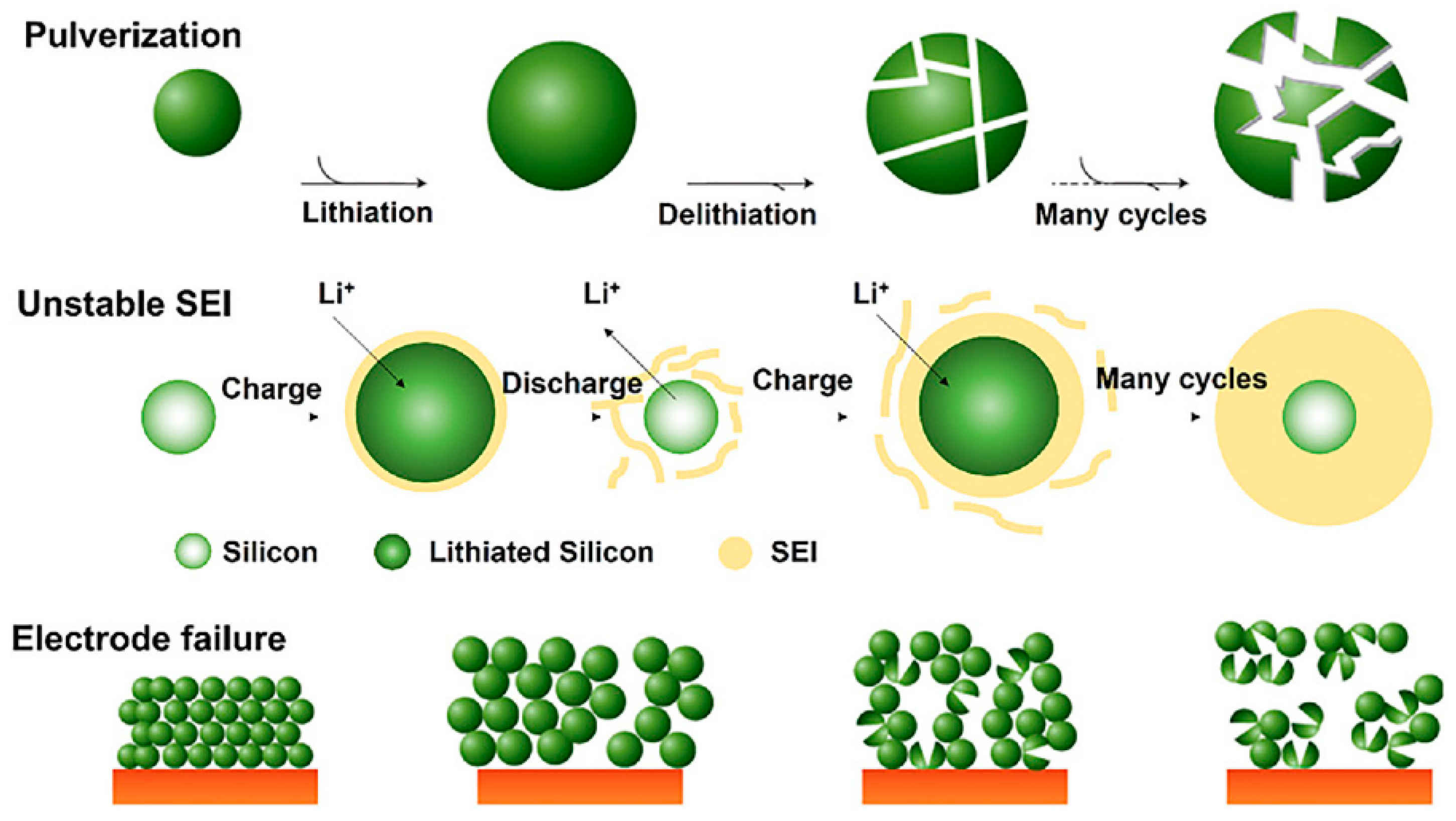
2.1.3. Silicon-Based Negative Electrodes and Si/C Composites
2.1.4. LNMO High-Voltage Spinel Cells
2.1.5. Li-Rich Manganese-Based Positive Electrode Materials
2.2. Solid-State Batteries
2.3. Lithium-Sulfur Batteries
2.4. Sodium-Ion Batteries
2.5. Other Emerging Technologies
2.5.1. Zinc-Air Batteries
2.5.2. Lithium-Air (Li-Air) Batteries
2.5.3. Magnesium-Ion Batteries
2.5.4. Aluminum-Ion (Al-Ion) Batteries
2.5.5. Potassium-Ion (K-Ion) Batteries
2.5.6. Some Promising Cathodes
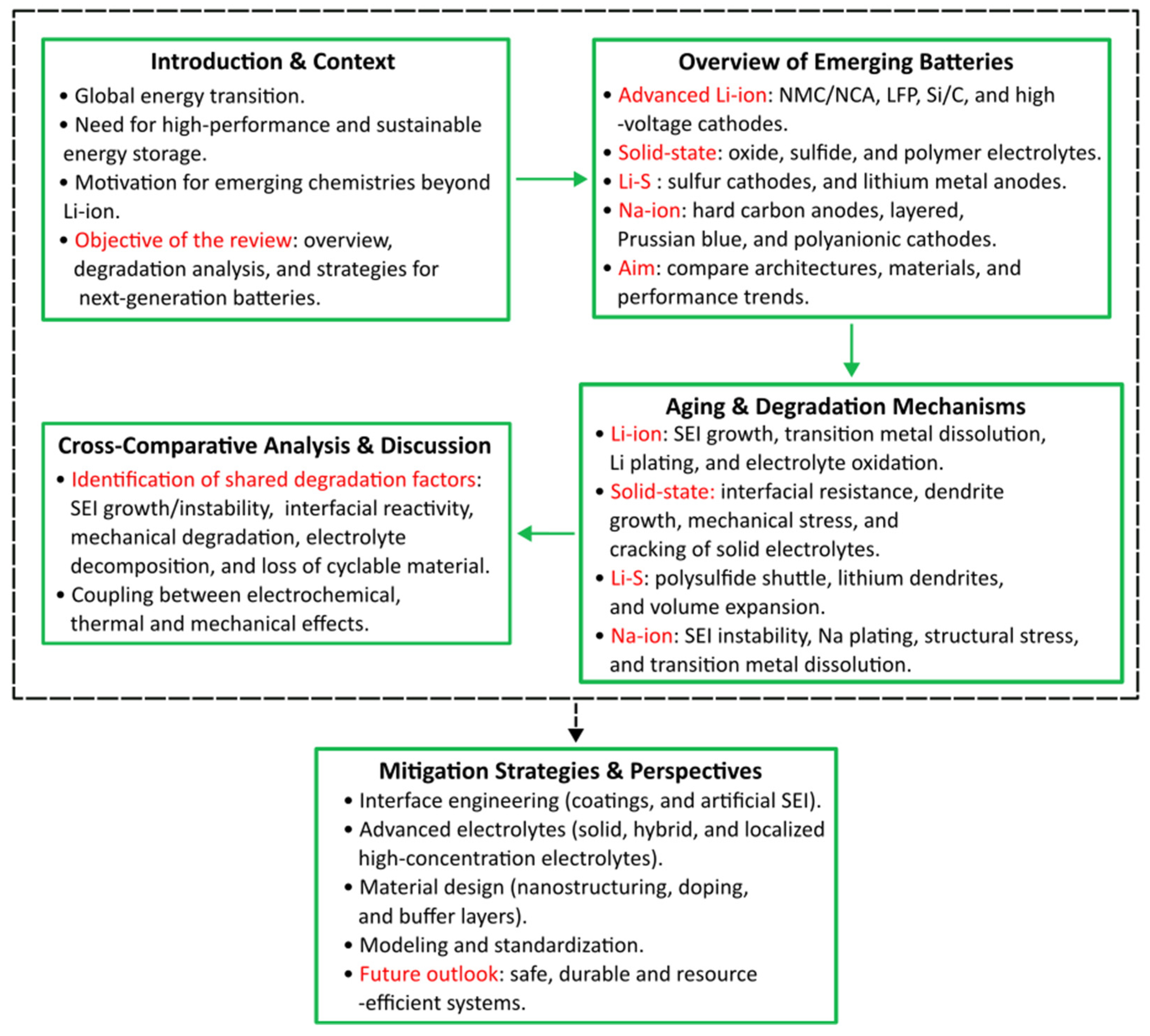
3. Degradation Mechanisms for Each Technology
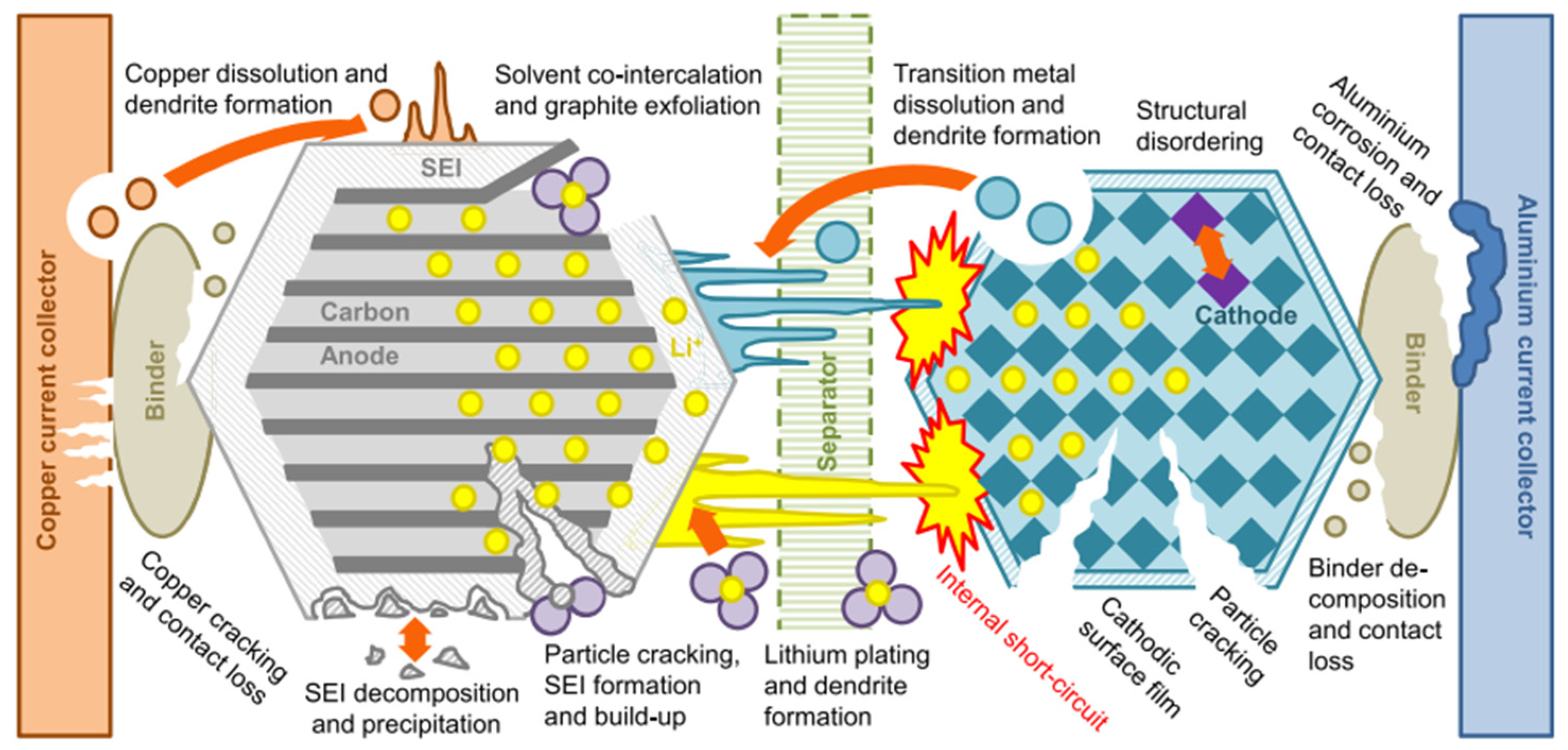
3.1. Degradation of Advanced Lithium-Ion Batteries (NMC, NCA, Enhanced LFP, Si/C, LNMO)
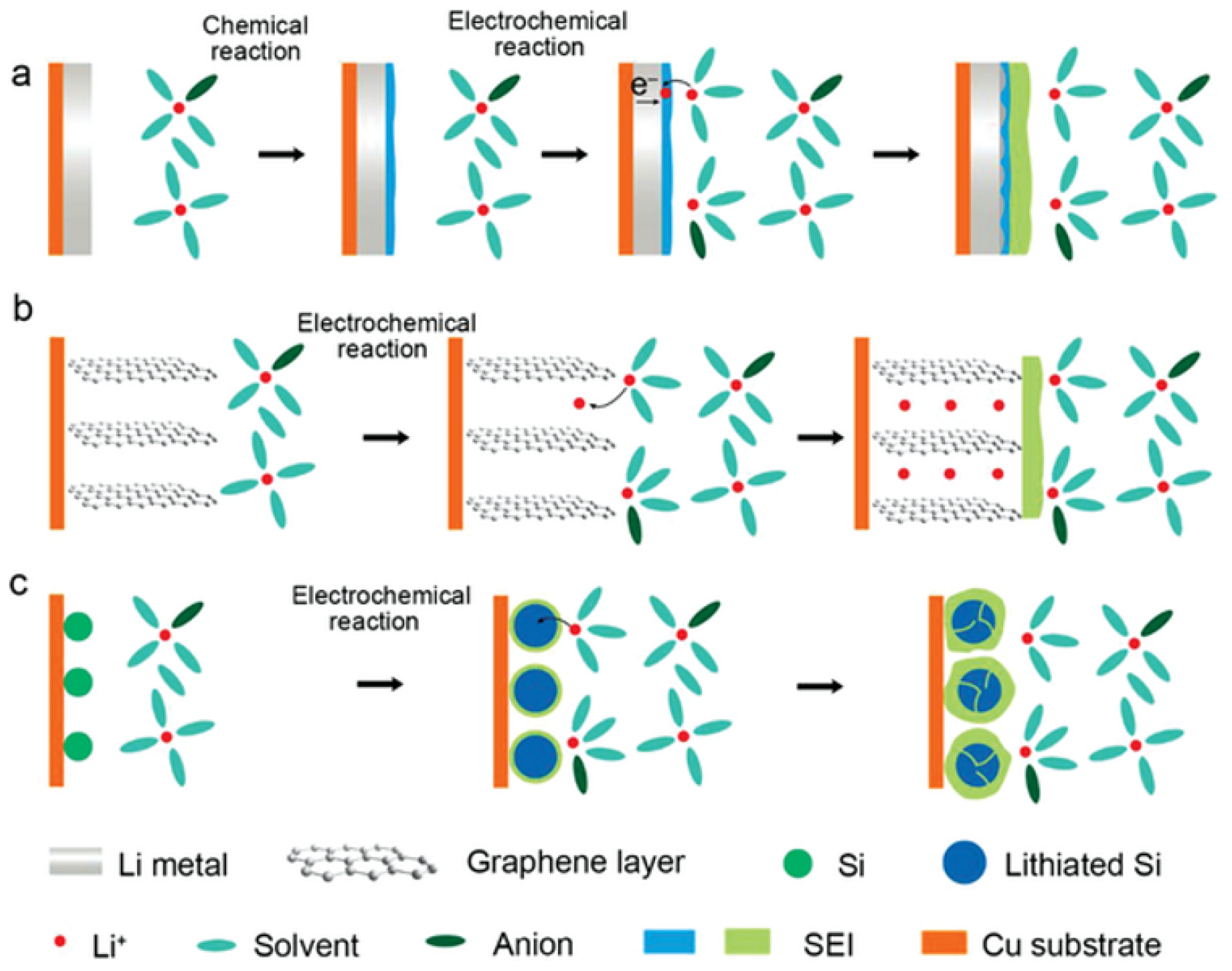
3.1.1. Degradation of the Negative Electrode (Graphite and Si/C)
3.1.2. Degradation of the Positive Electrode (NMC, NCA, LFP, LNMO)
3.1.3. Degradation of the Organic Electrolyte
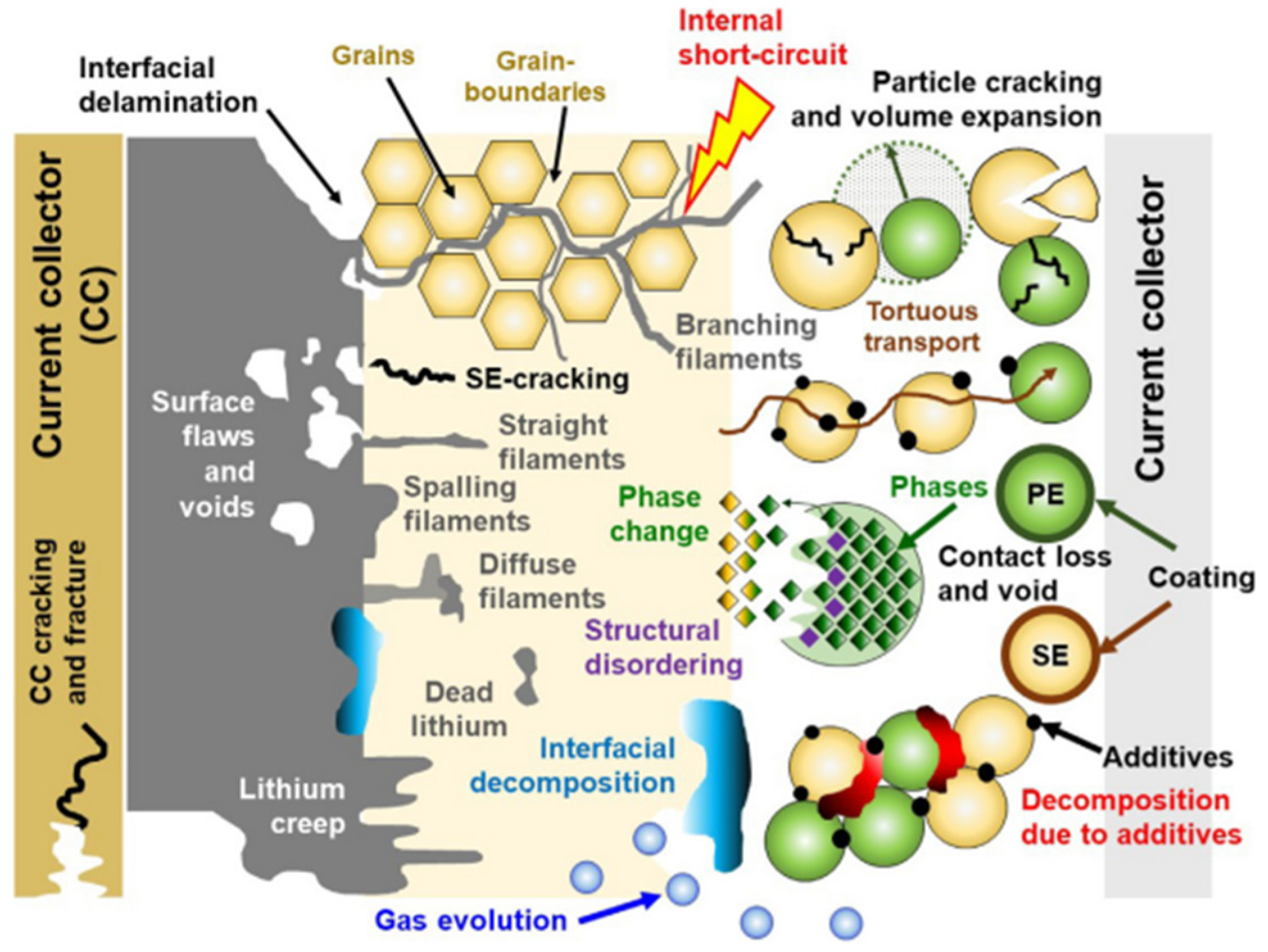
3.2. Degradation of Solid-State Batteries (SSB)
3.2.1. Degradation at Electrode/Solid Electrolyte Interfaces
3.2.2. Degradation of the Negative Electrode
3.2.3. Degradation of the Positive Electrode
3.2.4. Degradation of the Solid Electrolyte
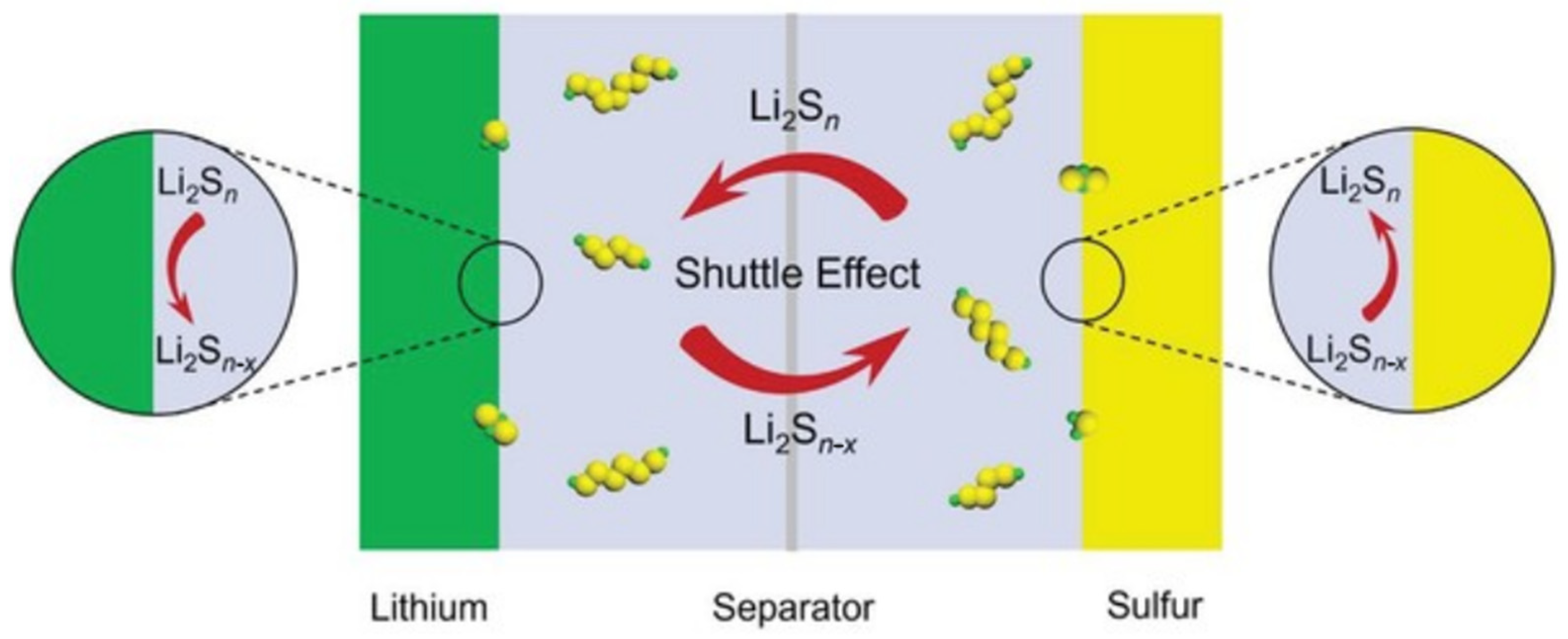
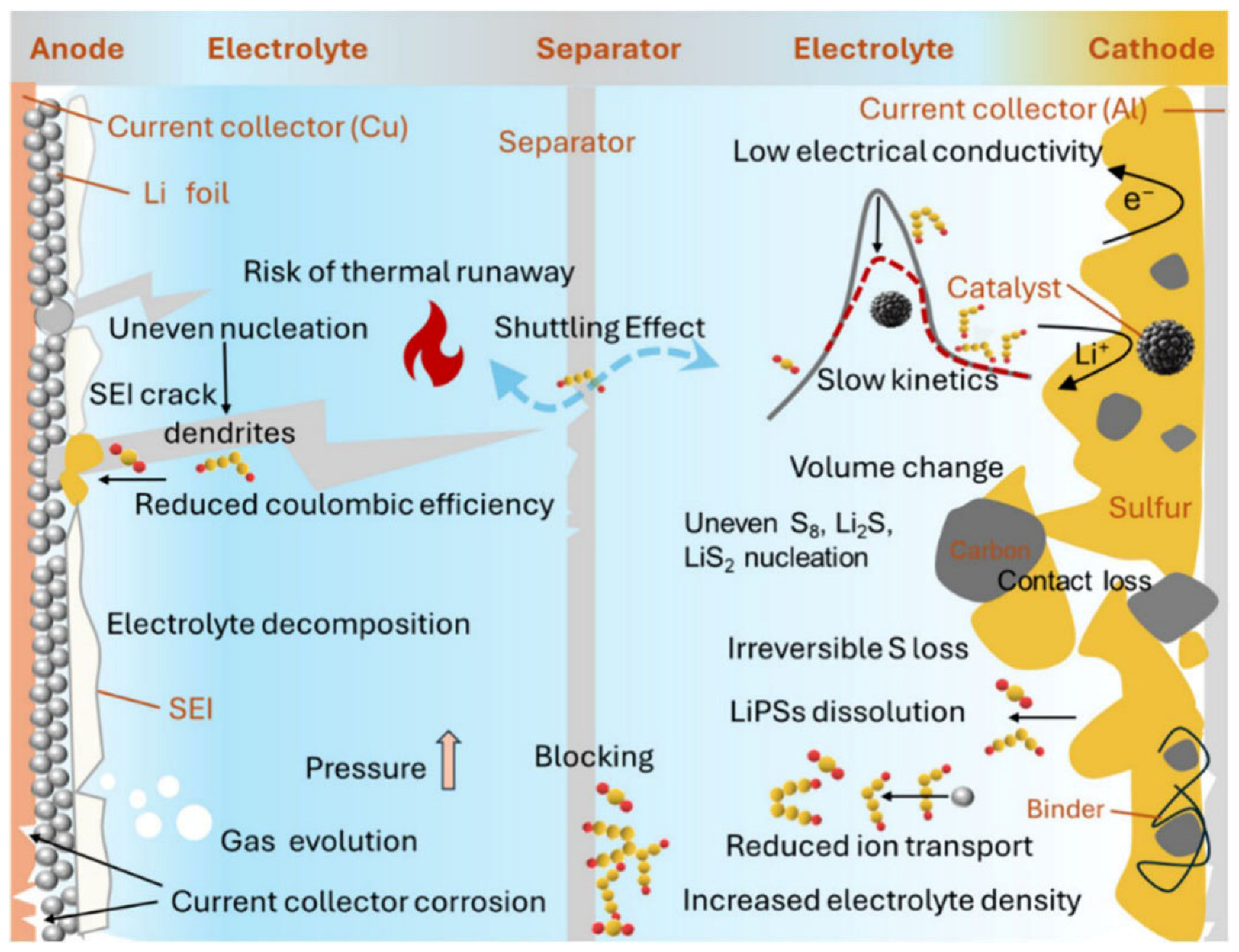
3.3. Degradation of Lithium-Sulfur Batteries
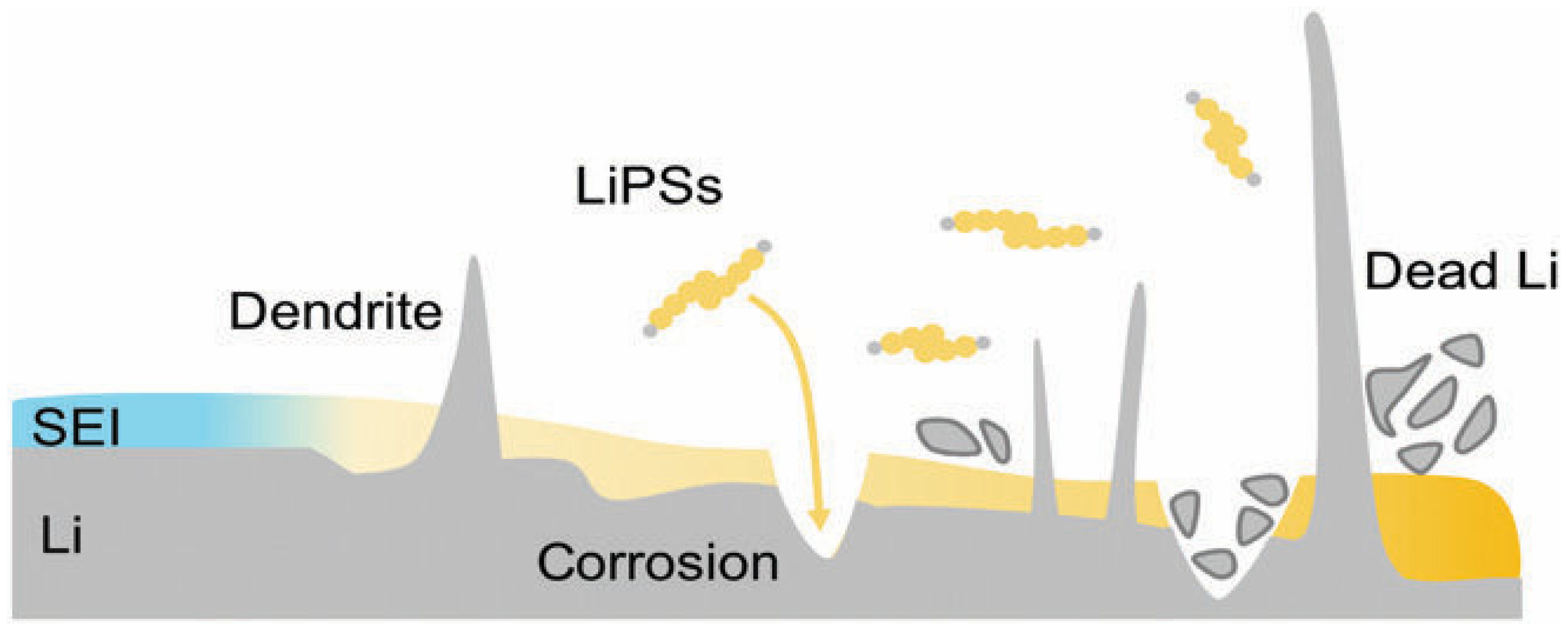
3.3.1. Degradation of the Negative Electrode
3.3.2. Degradation of the Positive Electrode
3.3.3. Degradation of the Electrolyte
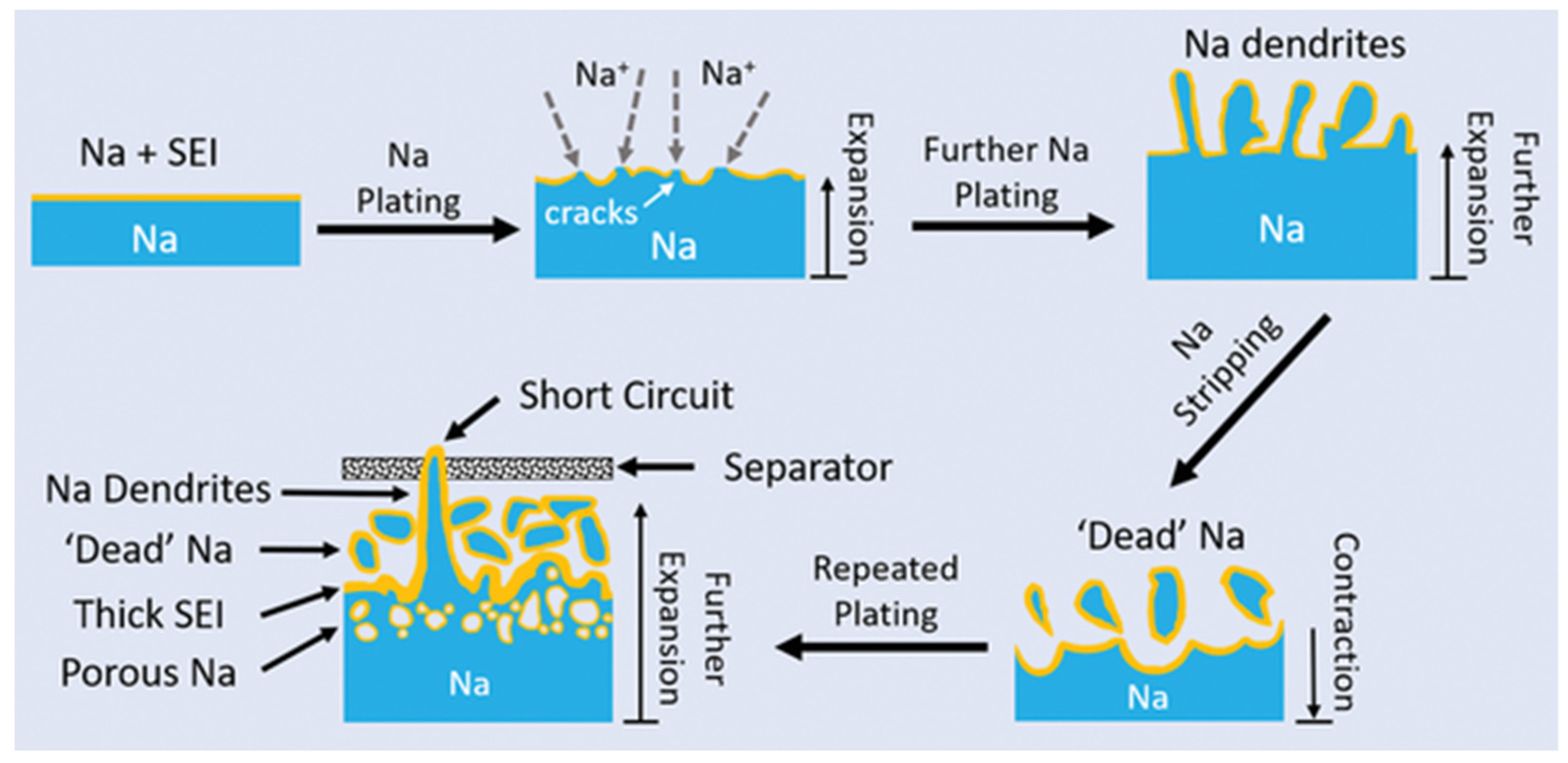
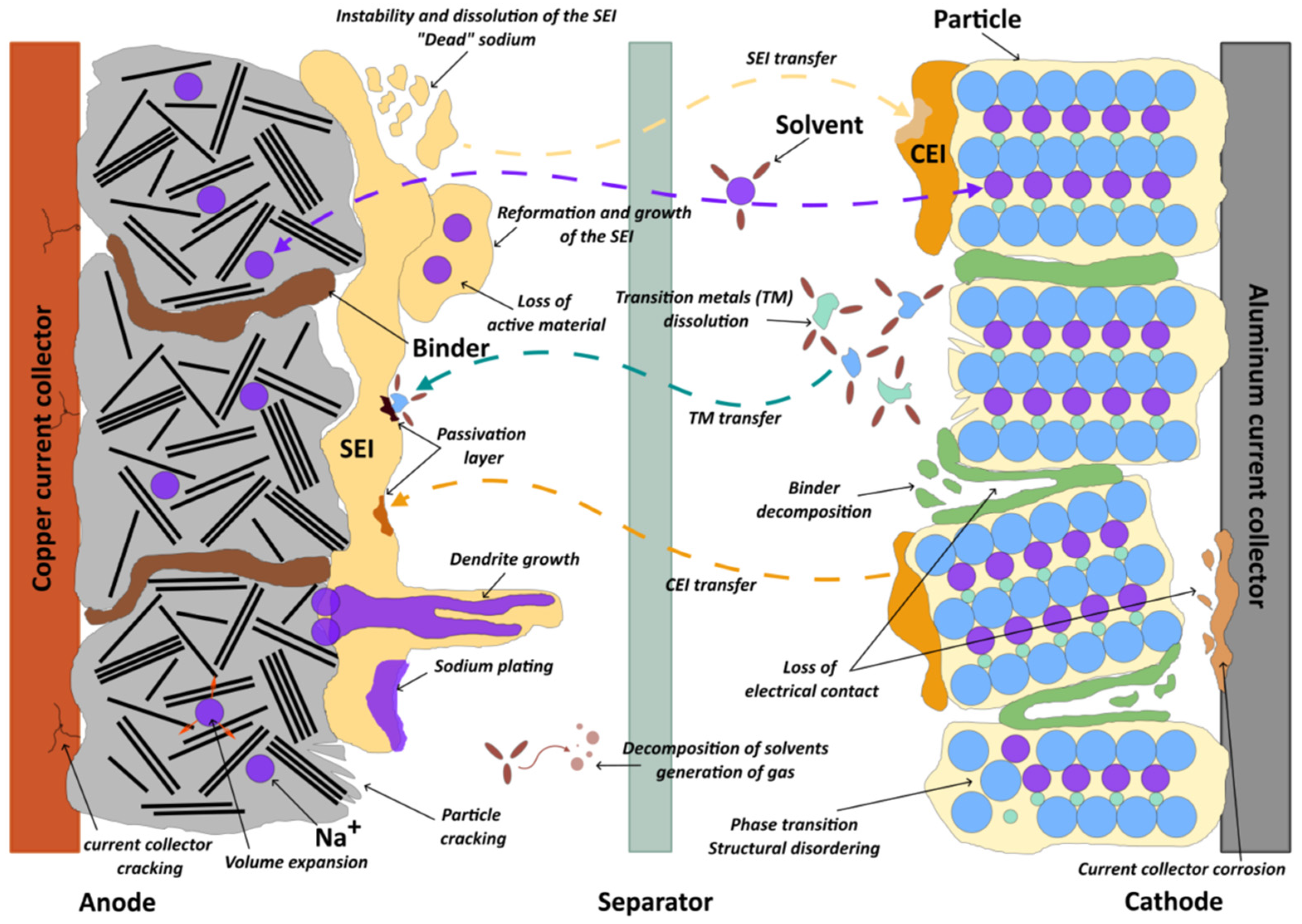
3.4. Degradation of Sodium-Ion Batteries
3.4.1. Degradation at the Negative Electrode/Electrolyte Interface
3.4.2. Degradation of the Negative Electrode
3.4.3. Degradation of the Positive Electrode
3.4.4. Electrolyte Degradation
4. Comparison of Degradation Mechanisms Between Different Technologies
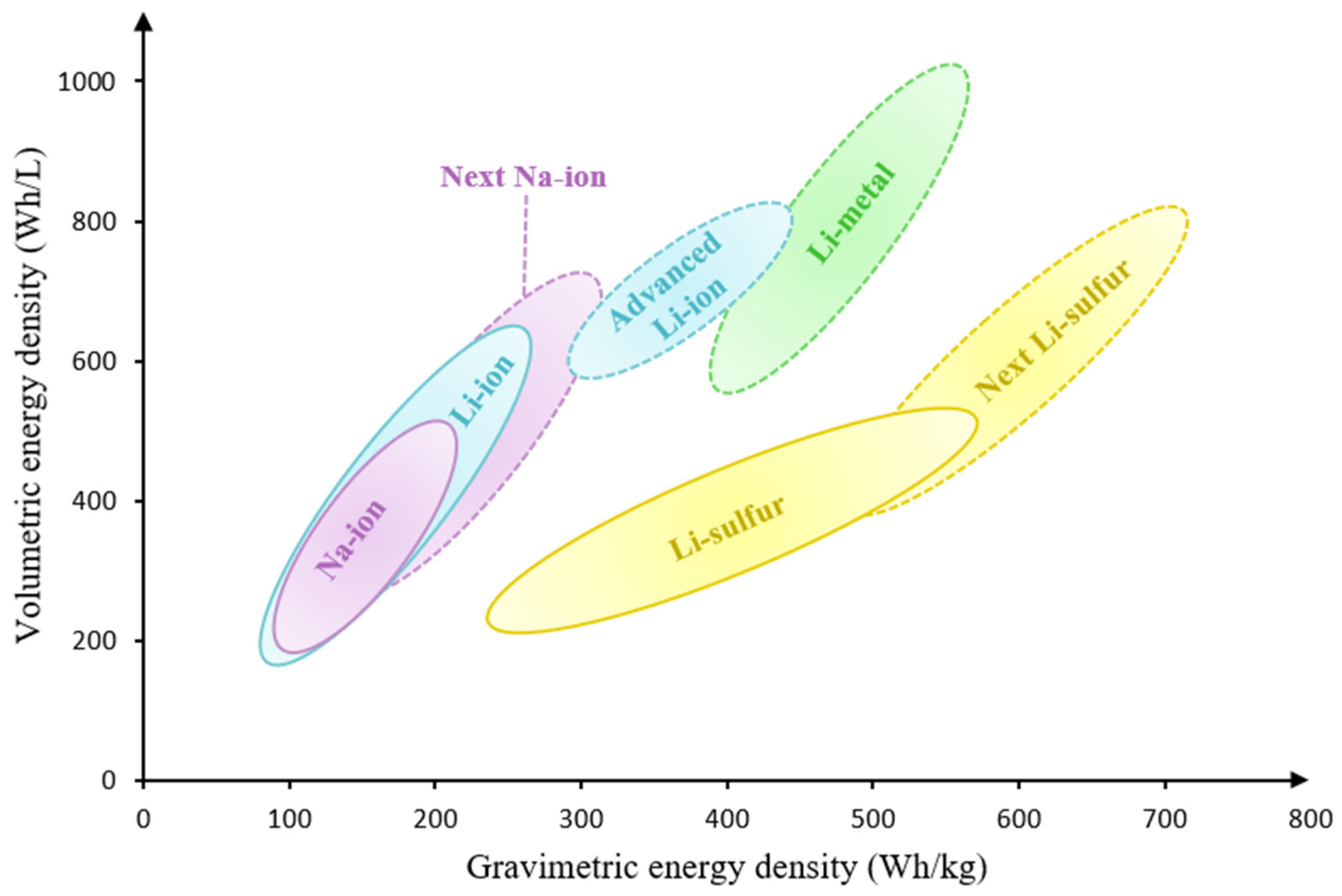
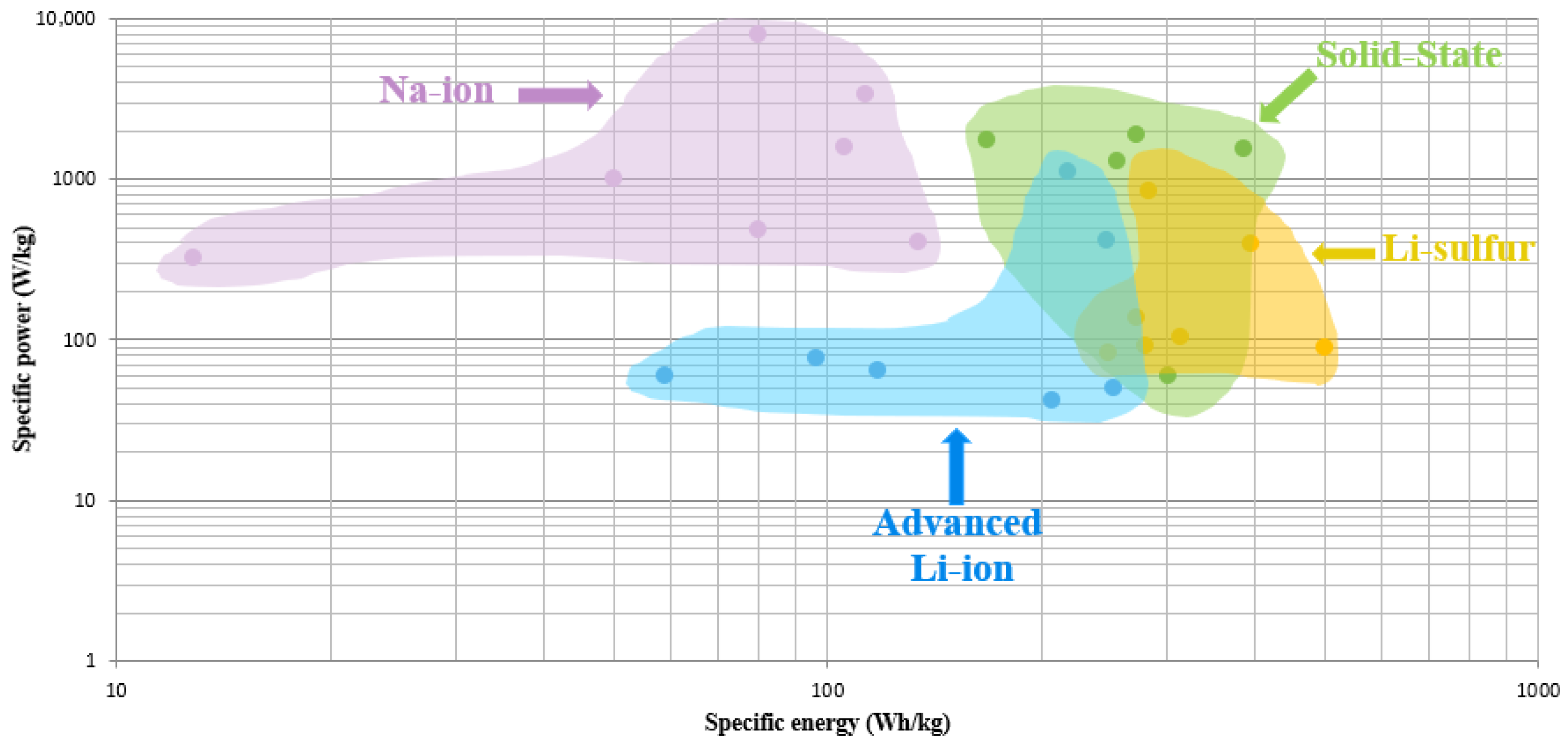
5. Challenges and Prospects
5.1. Current Challenges
5.2. Necessary Innovations
5.2.1. Advanced Lithium-Ion
5.2.2. SSB
5.2.3. Li-S
5.2.4. Na-Ion
5.2.5. Degradation Analysis and Performance in Emerging Batteries
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schleussner, C.-F.; Rogelj, J.; Schaeffer, M.; Lissner, T.; Licker, R.; Fischer, E.M.; Knutti, R.; Levermann, A.; Frieler, K.; Hare, W. Science and Policy Characteristics of the Paris Agreement Temperature Goal. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, A. European Green Deal—Legal and Financial Challenges of the Climate Change. ERA Forum 2021, 21, 681–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Energy-Related CO2 Emissions by Sector—Charts—Data & Statistics. Available online: https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/charts/global-energy-related-co2-emissions-by-sector (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Annual Electricity Demand Growth by Region, Historical and in the Stated Policies Scenario, 2010–2035—Charts—Data & Statistics. Available online: https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/charts/annual-electricity-demand-growth-by-region-historical-and-in-the-stated-policies-scenario-2010-2035 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- World Energy Outlook 2024—Analysis. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-outlook-2024 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario (NZE)—Global Energy and Climate Model—Analysis. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/global-energy-and-climate-model/net-zero-emissions-by-2050-scenario-nze (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Annual Battery Demand by Application and Scenario, 2023 and 2030—Charts—Data & Statistics. Available online: https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/charts/annual-battery-demand-by-application-and-scenario-2023-and-2030 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Installed Storage Capacity in the Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario, 2030 and 2035—Charts—Data & Statistics. Available online: https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/charts/installed-storage-capacity-in-the-net-zero-emissions-by-2050-scenario-2030-and-2035 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Electric LDV Battery Capacity by Chemistry, 2018–2022—Charts—Data & Statistics. Available online: https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/charts/electric-ldv-battery-capacity-by-chemistry-2018-2022 (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- Liu, W.; Placke, T.; Chau, K.T. Overview of Batteries and Battery Management for Electric Vehicles. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 4058–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Critical Minerals Outlook 2024—Analysis. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/global-critical-minerals-outlook-2024 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Chen, Y.; Kang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Liang, Z.; He, X.; Li, X.; Tavajohi, N.; et al. A Review of Lithium-Ion Battery Safety Concerns: The Issues, Strategies, and Testing Standards. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 59, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournir des Métaux Pour le Marché des Batteries. Available online: https://infos.ademe.fr/lettre-recherche-janvier-2022/fournir-des-metaux-pour-le-marche-des-batteries/ (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Itani, K.; De Bernardinis, A. Review on New-Generation Batteries Technologies: Trends and Future Directions. Energies 2023, 16, 7530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomares, V.; Serras, P.; Villaluenga, I.; Hueso, K.B.; Carretero-González, J.; Rojo, T. Na-Ion Batteries, Recent Advances and Present Challenges to Become Low Cost Energy Storage Systems. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 5884–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamenkovic, B.; Meng, Y.S.; Moreau, P.; Gaubicher, J. Communication—Fueling from the Electrochemistry of Halide Solid Electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2024, 171, 050554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Yin, Q.; Chen, H.; Li, M.; Zhou, S.; Wen, S.; Pan, J.; Zheng, Q.; Jiang, B.; Liu, H.; et al. Building Better Solid-State Batteries with Silicon-Based Anodes. Interdiscip. Mater. 2023, 2, 635–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaleddine, H. Fonctionnalisation de Nanotubes pour la Fabrication de Batteries Lithium/Soufre et Lithium/Organique. Ph.D. Dissertation, Université Paris-Saclay, Gif-sur-Yvette, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Y.; Hynan, P.; von Jouanne, A.; Yokochi, A. Current Li-Ion Battery Technologies in Electric Vehicles and Opportunities for Advancements. Energies 2019, 12, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xu, H.; Yang, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Peng, J.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Development of Strategies for High-Energy-Density Lithium Batteries. Energy Storage Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 448–478. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Yu, X.; Li, H. A 700 W·h·kg−1 Rechargeable Pouch Type Lithium Battery. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2023, 40, 048201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-E.; Jeong, J.; Lee, Y.; Lim, H.; Chung, K.Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.-O. Enhancing High-Voltage Structural Stability of Single-Crystalline Ni-Rich LiNi0.9Mn0.05Co0.05O2 Cathode Material by Ultrathin Li-Rich Oxide Layer for Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Power Sources 2024, 601, 234300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.; Burnett, D.; Slater, P.; Kendrick, E. Investigation of Firing Conditions and Boron Fluxes for the Optimized Synthesis of LiNi0.9Mn0.05Co0.05O2 for High Energy Density Li-Ion Batteries. ChemElectroChem 2025, 12, e202400677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Tang, A.; Mu, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, C. Aging Mechanisms of Electrode Materials in Lithium-Ion Batteries for Electric Vehicles. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 104673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preger, Y.; Barkholtz, H.M.; Fresquez, A.; Campbell, D.L.; Juba, B.W.; Romàn-Kustas, J.; Ferreira, S.R.; Chalamala, B. Degradation of Commercial Lithium-Ion Cells as a Function of Chemistry and Cycling Conditions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 120532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, N.; Gadkari, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Bai, J.; Cai, Q. A Comparative Analysis of Lithium-Ion Batteries with Different Cathodes under Overheating and Nail Penetration Conditions. Energy 2023, 278, 128027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, M.; Ye, Z.; Chen, T.; Cao, J.; Yang, H.; Ma, C.; Jia, Z.; Xie, J.; Cui, N.; et al. Lithium Iron Phosphate and Layered Transition Metal Oxide Cathode for Power Batteries: Attenuation Mechanisms and Modification Strategies. Materials 2023, 16, 5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Raj, R.P.; George, L.; Kannangara, G.S.K.; Milev, A.; Varadaraju, U.V.; Selvam, P. Surfactant-Mediated and Morphology-Controlled Nanostructured LiFePO4/Carbon Composite as a Promising Cathode Material for Li-Ion Batteries. ChemistryOpen 2020, 9, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Song, F.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Q. Mn-Doped LiFePO4@C as a High-Performance Cathode Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Particuology 2024, 90, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evro, S.; Ajumobi, A.; Mayon, D.; Tomomewo, O.S. Navigating Battery Choices: A Comparative Study of Lithium Iron Phosphate and Nickel Manganese Cobalt Battery Technologies. Future Batter. 2024, 4, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y. Silicon Based Lithium-Ion Battery Anodes: A Chronicle Perspective Review. Nano Energy 2017, 31, 113–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kana, N. Optimisation D’électrodes de Silicium Pour Batteries Lithium-Ion: Nouveaux Liants Moléculaires et Revêtements de Coordination. Ph.D. Dissertation, Nantes Université, Nantes, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Cui, L.; Zhong, B.; Qu, G. Research Progress on the Structural Design and Optimization of Silicon Anodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries: A Mini-Review. Coatings 2023, 13, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, F.; Nallan, H.C.; Dolocan, A.; Xie, Q.; Li, J.; Coffey, B.M.; Ekerdt, J.G.; Manthiram, A. Long-Life LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4/Graphite Lithium-Ion Cells with an Artificial Graphite-Electrolyte Interface. Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 43, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Peterson, V.K.; See, K.W.; Guo, Z.; Pang, W.K. Developing High-Voltage Spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 Cathodes for High-Energy-Density Lithium-Ion Batteries: Current Achievements and Future Prospects. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 15373–15398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Feng, W.; Xia, Y. Recent Progress of High Voltage Spinel LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4 Cathode Material for Lithium-Ion Battery: Surface Modification, Doping, Electrolyte, and Oxygen Deficiency. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 18688–18708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, W.; Luo, M.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Winter, M.; Fu, R.; Yang, W.; Yang, Y. Li-Rich Cathodes for Rechargeable Li-Based Batteries: Reaction Mechanisms and Advanced Characterization Techniques. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 4450–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, L.; Xue, W.; Fang, Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, K.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; et al. Synergistic Enhancement of Li-Rich Manganese-Based Cathode Materials through Single Crystallization and in-Situ Spinel Coating. Nano Energy 2024, 121, 109241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, R.; Liu, Y.; Lv, F.; Xu, N. Opportunities and Challenges of Layered Lithium-Rich Manganese-Based Cathode Materials for High Energy Density Lithium-Ion Batteries. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 18243–18265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Tang, M.; Zhan, L.; Zhai, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhou, M.; Ji, Y.; Wang, P. A Review of High-Capacity Lithium-Rich Manganese-Based Cathode Materials for a New Generation of Lithium Batteries. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2024, 572, 122239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yan, H.; Ma, J.; Yu, P.; Xia, D.; Huang, W.; Chu, W.; Wu, Z. Manipulating the Electronic Structure of Li-Rich Manganese-Based Oxide Using Polyanions: Towards Better Electrochemical Performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 5112–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Yan, Y.; Zhou, S.; Tang, Y.; Zeng, G.; Wu, X.; Liao, H.-G.; et al. Role of Substitution Elements in Enhancing the Structural Stability of Li-Rich Layered Cathodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 8700–8713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Ning, F.; Zuo, Y.; Li, A.; Wang, H.; Zhang, K.; Yang, T.; Yang, Y.; Gao, C.; Xiao, W.; et al. Entropy Stabilization Strategy for Enhancing the Local Structural Adaptability of Li-Rich Cathode Materials. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2208726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Liao, J.; Zhang, W.; Dai, P.; Yu, C.; Gao, T.; Hou, T.; Cao, G.; Zhao, S. High-Entropy Li-Rich Layered Cathodes with Negligible Voltage Decay through Migration Retardation Effect. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2505189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alloin, F.; Iojoiu, C. L’électrolyte, un Élément Clé des Batteries. Actual. Chim. 2021, 464, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Fu, J.; Zhou, X.; Gui, S.; Wei, L.; Yang, H.; Li, H.; Guo, X. Ionic Conduction in Polymer-Based Solid Electrolytes. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2201718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-M.; Hsu, C.-H.; Yang, J.-S.; Tsai, P.-C. Ab Initio Study on Lithium Anode Interface Instability and Stabilization of Superionic Li3InCl6 and Li6PS5Cl Solid Electrolytes. J. Power Sources 2024, 640, 236719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajith, K.; Christopher Selvin, P.; Abhilash, K.P.; Sivaraj, P.; Nalini, B.; Soundarya, G.G. A Correlative Study on Electrochemical and Optical Properties of LLZO (Li7La3Zr2O12) Garnet Electrolyte. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 50, 2836–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Sun, C. NASICON-Type Na1+xZr2SixP3−xO12 Electrolytes: Progress and Perspectives for Solid-State Sodium Metal Batteries. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2025, 12, 6011–6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Cui, C.; Zhao, J.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, W.; Zhao, C.; Huang, S. Advancing NASICON Solid-State Electrolytes for Lithium Metal Batteries: Interfacial Challenges, Engineering Strategies, and Future Directions. Energy Storage Mater. 2025, 81, 104471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgelall, R. Solid-State Battery Developments: A Cross-Sectional Patent Analysis. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, M.-C.; Yang, K.; Brugge, R.; Zhang, T.; Liu, X.; Pan, F.; Yang, S.; Aguadero, A.; Wu, B.; Marinescu, M.; et al. Interactions Are Important: Linking Multi-Physics Mechanisms to the Performance and Degradation of Solid-State Batteries. Mater. Today 2021, 49, 145–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-T.; Jang, J.; Oh, J.A.S.; Ham, S.-Y.; Yang, H.; Lee, D.-J.; Vicencio, M.; Lee, J.B.; Tan, D.H.S.; Chouchane, M.; et al. Enabling Uniform and Accurate Control of Cycling Pressure for All-Solid-State Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 14, 2304327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jia, P.; Liu, X.; Qiu, P.; Zhang, H.; Huang, J. A Review of the Effect of External Pressure on All-Solid-State Batteries. eTransportation 2023, 15, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzweil, P.; Garche, J. 2—Overview of Batteries for Future Automobiles. In Lead-Acid Batteries for Future Automobiles; Garche, J., Karden, E., Moseley, P.T., Rand, D.A.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 27–96. ISBN 978-0-444-63700-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wolff, D.; Canals Casals, L.; Benveniste, G.; Corchero, C.; Trilla, L. The Effects of Lithium Sulfur Battery Ageing on Second-Life Possibilities and Environmental Life Cycle Assessment Studies. Energies 2019, 12, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-T.; Liu, S.; Li, G.-R.; Yan, T.-Y.; Gao, X.-P. High Volumetric Energy Density Sulfur Cathode with Heavy and Catalytic Metal Oxide Host for Lithium–Sulfur Battery. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1903693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Ticey, J.; Oleshko, V.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, C.; Cumings, J.; Qi, Y. Carbon-Nanotube-Encapsulated-Sulfur Cathodes for Lithium–Sulfur Batteries: Integrated Computational Design and Experimental Validation. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Hu, E.; Gaskell, K.J.; Fan, X.; Gao, T.; Cui, C.; Ghose, S.; Yang, X.-Q.; Wang, C. A Chemically Stabilized Sulfur Cathode for Lean Electrolyte Lithium Sulfur Batteries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 14712–14720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohari, S.; Knap, V.; Yaftian, M.R. Investigation on Cycling and Calendar Aging Processes of 3.4 Ah Lithium-Sulfur Pouch Cells. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kang, J.; Kim, S.-W.; Halim, W.; Frey, M.W.; Joo, Y.L. Effective Suppression of the Polysulfide Shuttle Effect in Lithium–Sulfur Batteries by Implementing rGO–PEDOT:PSS-Coated Separators via Air-Controlled Electrospray. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 16465–16471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Jia, G.; Yang, H.; Wang, M. Recent Advances for SEI of Hard Carbon Anode in Sodium-Ion Batteries: A Mini Review. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 986541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabeer, Y.; Madani, S.S.; Panchal, S.; Mousavi, M.; Fowler, M. Different Metal–Air Batteries as Range Extenders for the Electric Vehicle Market: A Comparative Study. Batteries 2025, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Hao, Y.; Jia, H.; Shen, X.; Qu, B.; Huang, G.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Xu, C.; et al. Challenges and Progress in Rechargeable Magnesium-Ion Batteries: Materials, Interfaces, and Devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2410406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, G.A.; Kravchyk, K.V.; Kovalenko, M.V.; Chacón, J.; Holland, A.; Wills, R.G.A. An Overview and Prospective on Al and Al-Ion Battery Technologies. J. Power Sources 2021, 481, 228870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Fu, H.; Xia, H.; He, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, J.; Fan, L.; Lu, B. Synergistic Kinetics Modulation at Graphite Interface Enables Ultrafast and Durable Potassium-Ion Batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2504576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fu, H.; Gu, M.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J.; Fan, L.; Lu, B. Ether-Based Gel Polymer Electrolyte for High-Voltage Potassium Ion Batteries. Nano Lett. 2024, 24, 11419–11428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Dai, Z.; Fan, L.; Fu, H.; Geng, Y.; Guan, J.; Sun, F.; Rao, A.M.; Zhou, J.; Lu, B. Cosolvent Electrolyte Chemistries for High-Voltage Potassium-Ion Battery. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2024, 11, nwae359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, H.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, H.; Huang, J.; Yang, H.; Guo, D. In-Situ Amorphous Transformation of V2O5 in V2O5/V6O13 for Aqueous Zinc Ion Batteries with High Capacity and Long Cycles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 697, 137999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Wu, T.; Huang, K. Understanding the Dissolution and Phase Transformation Mechanisms in Aqueous Zn/α-V2O5 Batteries. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 4089–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Huang, H.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pan, H.; Yan, M.; Jiang, Y. Interfacial Coupling with Halide Solid Electrolyte Enables High-Energy-Density and Reversible FeCl3 Cathode for All-Solid-State Lithium Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2025, e03269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Leung, C.L.A.; Huang, C. Exploring the Properties of Disordered Rocksalt Battery Cathode Materials by Advanced Characterization. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2308165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Cui, Y. Designing Nanostructured Si Anodes for High Energy Lithium Ion Batteries. Nano Today 2012, 7, 414–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, W.; Bultel, Y.; Venet, P.; Sari, A.; Riviere, E. Postmortem Analysis of 18650 Graphite/LFP Cells in a Long-Term Aging Study for Second-Life Applications. Batteries 2024, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Jia, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.-G.; Xu, W. Recent Progress in Understanding Solid Electrolyte Interphase on Lithium Metal Anodes. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2003092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshetu, G.G.; Figgemeier, E. Confronting the Challenges of Next-Generation Silicon Anode-Based Lithium-Ion Batteries: Role of Designer Electrolyte Additives and Polymeric Binders. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 2515–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertzberg, B.; Alexeev, A.; Yushin, G. Deformations in Si−Li Anodes Upon Electrochemical Alloying in Nano-Confined Space. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 8548–8549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweidler, S.; de Biasi, L.; Schiele, A.; Hartmann, P.; Brezesinski, T.; Janek, J. Volume Changes of Graphite Anodes Revisited: A Combined Operando X-Ray Diffraction and In Situ Pressure Analysis Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 8829–8835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Haran, B.S.; Durairajan, A.; White, R.E.; Podrazhansky, Y.; Popov, B.N. Studies on Capacity Fade of Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Power Sources 2000, 91, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaguemont, J.; Boulon, L.; Venet, P.; Dubé, Y.; Sari, A. Lithium-Ion Battery Aging Experiments at Subzero Temperatures and Model Development for Capacity Fade Estimation. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 4328–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riviere, E. Détermination In-Situ de L’état de Santé de Batteries Lithium-Ion Pour un Véhicule Électrique. Ph.D. Dissertation, Université Grenoble Alpes, Saint-Martin-d’Hères, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Laakso, E.; Efimova, S.; Colalongo, M.; Kauranen, P.; Lahtinen, K.; Napolitano, E.; Ruiz, V.; Moškon, J.; Gaberšček, M.; Park, J.; et al. Aging Mechanisms of NMC811/Si-Graphite Li-Ion Batteries. J. Power Sources 2024, 599, 234159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, T.; Choi, J.W.; Coskun, A. The Emerging Era of Supramolecular Polymeric Binders in Silicon Anodes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2145–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.C.; Choi, J.W.; Han, Y.-K. Anisotropic Volume Expansion of Crystalline Silicon during Electrochemical Lithium Insertion: An Atomic Level Rationale. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5342–5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Weng, J.; Ye, C.; Liu, M.; Wang, C.; Wu, S.; Tong, Q.; Zhu, M.; Gao, F. Strategies for Controlling or Releasing the Influence Due to the Volume Expansion of Silicon inside Si-C Composite Anode for High-Performance Lithium-Ion Batteries. Materials 2022, 15, 4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetter, J.; Novák, P.; Wagner, M.R.; Veit, C.; Möller, K.-C.; Besenhard, J.O.; Winter, M.; Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, M.; Vogler, C.; Hammouche, A. Ageing Mechanisms in Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Power Sources 2005, 147, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, E.R. Étude du Vieillissement des Batteries Lithium-Ion dans les Applications “Véhicule Electrique”: Combinaison des Effets de Vieillissement Calendaire et de Cyclage. Ph.D. Dissertation, Université de Lyon, Lyon, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, S.; Kinoshita, M.; Nakura, K. Capacity Fade of LiNi(1−x−y)CoxAlyO2 Cathode for Lithium-Ion Batteries during Accelerated Calendar and Cycle Life Test. I. Comparison Analysis between LiNi(1−x−y)CoxAlyO2 and LiCoO2 Cathodes in Cylindrical Lithium-Ion Cells during Long Term Storage Test. J. Power Sources 2014, 247, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yuan, X.-Z.; Zhang, L.; Song, D.; Shi, K.; Bock, C. Degradation Mechanisms and Mitigation Strategies of Nickel-Rich NMC-Based Lithium-Ion Batteries. Electrochem. Energy Rev. 2020, 3, 43–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Rao, L.; Yap, J.; Yu, C.-Y.; Kim, J.-H. Stabilizing Cathode-Electrolyte Interphase of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 High-Voltage Spinel by Blending Garnet Solid Electrolyte in Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Power Sources 2023, 561, 232748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieczonka, N.P.W.; Borgel, V.; Ziv, B.; Leifer, N.; Dargel, V.; Aurbach, D.; Kim, J.-H.; Liu, Z.; Huang, X.; Krachkovskiy, S.A.; et al. Lithium Polyacrylate (LiPAA) as an Advanced Binder and a Passivating Agent for High-Voltage Li-Ion Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1501008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.; Lumsden, M.D.; Deshmukh, J.; Zsoldos, E.S.; Black, W.; Azam, S.M.; Dahn, J.R. Comprehensive Study of the Degradation of LiFePO4/Graphite Cells at Elevated Temperatures. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2025, 172, 050502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Geng, M.; Yang, H.; Fan, M.; Sun, Z.; Yu, R.; Wei, B. A Review of Capacity Fade Mechanism and Promotion Strategies for Lithium Iron Phosphate Batteries. Coatings 2024, 14, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qiu, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Cao, G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; He, X. Insights for Understanding Multiscale Degradation of LiFePO4 Cathodes. eScience 2022, 2, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Kim, D.-H.; Shin, J.H.; Jang, J.E.; Ahn, K.H.; Lee, C.; Lee, H. Ionic Conduction and Solution Structure in LiPF6 and LiBF4 Propylene Carbonate Electrolytes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 19438–19446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K. Electrolytes and Interphases in Li-Ion Batteries and Beyond. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11503–11618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, S. A Review on the Optimization of Electrolytes to Enhance Lithium-Ion Batteries’ Safety and Performance under Abuse Conditions. J. Energy Storage 2024, 100, 113439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinkel, B.L.D.; Vivek, J.P.; Garcia-Araez, N.; Grey, C.P. Two Electrolyte Decomposition Pathways at Nickel-Rich Cathode Surfaces in Lithium-Ion Batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 3416–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subaşı, Y.; Afyon, S. High Voltage LiCoO2 Cathodes with High Purity Lithium Bis(Oxalate) Borate (LiBOB) for Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2022, 5, 10098–10107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, L.; Ding, Z.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, H.; Jia, P.; Zhai, J.; Jiao, G. Recent Advances in Semiconductor Gas Sensors for Thermal Runaway Early-Warning Monitoring of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2025, 535, 216624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkl, C.R.; Roberts, M.R.; McTurk, E.; Bruce, P.G.; Howey, D.A. Degradation Diagnostics for Lithium Ion Cells. J. Power Sources 2017, 341, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Shao, B.; Han, F. Interfacial Challenges in All-Solid-State Lithium Batteries. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2022, 33, 100933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony Jose, S.; Gallant, A.; Gomez, P.L.; Jaggers, Z.; Johansson, E.; LaPierre, Z.; Menezes, P.L. Solid-State Lithium Batteries: Advances, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Batteries 2025, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, T.; Park, R.; Sheldon, B.W.; Rettenwander, D.; Porz, L.; Berendts, S.; Uecker, R.; Carter, W.C.; Chiang, Y.-M. Lithium Metal Penetration Induced by Electrodeposition through Solid Electrolytes: Example in Single-Crystal Li6La3ZrTaO12 Garnet. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, A3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhao, S.-X.; Lin, Y.; Nan, C.-W.; Shen, Y. Non-Successive Degradation in Bulk-Type All-Solid-State Lithium Battery with Rigid Interfacial Contact. Electrochem. Commun. 2017, 79, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barai, P.; Higa, K.; Srinivasan, V. Lithium Dendrite Growth Mechanisms in Polymer Electrolytes and Prevention Strategies. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 20493–20505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, T.; Haslam, C.G.; Richter, F.H.; Sakamoto, J.; Janek, J. Evaluating the Use of Critical Current Density Tests of Symmetric Lithium Transference Cells with Solid Electrolytes. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2302383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, D.; Li, G.; Fan, G.; Zhang, X.; Han, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, B.; Chen, S.; Jia, L. Characterization of Cathode Degradation and Development of a Coupled Electrochemical-Aging Model for Sulfide-Based All-Solid-State Batteries. J. Power Sources 2025, 627, 235830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Ma, T.; Chen, L.; Li, H.; Wu, F. Thermal Stability between Sulfide Solid Electrolytes and Oxide Cathode. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 16158–16176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharmann, T.; Özcelikman, C.; Nguyen, D.M.; Heck, C.A.; Wacker, C.; Michalowski, P.; Kwade, A.; Dröder, K. Quantification of Hydrogen Sulfide Development during the Production of All-Solid-State Batteries with Argyrodite Sulfide-Based Separators. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2024, 7, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchasz, C. Développement D’accumulateurs Li/S. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Grenoble Alpes, Grenoble, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Soler, M. All-Solid-State Lithium—Sulfur Batteries with Sulfide Solid Electrolyte. Ph.D. Dissertation, Université Grenoble Alpes, Saint-Martin-d’Hères, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Heim, F.M.; Song, N.; Bartlett, J.L.; Li, X. New Insights into Mossy Li Induced Anode Degradation and Its Formation Mechanism in Li–S Batteries. ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 2696–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.-P.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q.-K.; Li, B.-Q.; Bi, C.-X.; Chen, Z.-X.; Su, L.-L.; Huang, J.-Q.; Wen, R.; et al. Electrolyte Design for Improving Mechanical Stability of Solid Electrolyte Interphase in Lithium-Sulfur Batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2023, 62, e202305466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.-X.; Hou, L.-P.; Li, Z.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Li, B.-Q.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, J.-Q. Protecting Lithium Metal Anodes in Lithium–Sulfur Batteries: A Review. Energy Mater. Adv. 2023, 4, 0010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Danilov, D.L.; Qiao, F.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Eichel, R.-A.; Notten, P.H.L. Sulfur Reduction Reaction in Lithium–Sulfur Batteries: Mechanisms, Catalysts, and Characterization. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2202094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Bertolini, S.; Balbuena, P.B.; Mukherjee, P.P. Li2S Film Formation on Lithium Anode Surface of Li-S Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 4700–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capkova, D.; Knap, V.; Fedorkova, A.S.; Stroe, D.-I. Investigation of the Temperature and DOD Effect on the Performance-Degradation Behavior of Lithium–Sulfur Pouch Cells during Calendar Aging. Appl. Energy 2023, 332, 120543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, D.-J.; Jung, H.-G.; Sun, Y.-K.; Hassoun, J.; Scrosati, B. An Advanced Lithium-Sulfur Battery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 1076–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Xin, S.; Guo, Y.; Wan, L. Lithium–Sulfur Batteries: Electrochemistry, Materials, and Prospects. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 13186–13200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Pinto-Huguet, I.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Vizintin, A.; Velasco-Vélez, J.-J.; Qi, X.; Pan, X.; Oney, G.; et al. Mechanistic Insights and Technical Challenges in Sulfur-Based Batteries: A Comprehensive In Situ/Operando Monitoring Toolbox. ACS Energy Lett. 2024, 9, 6178–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, F.A.; Marzouk, A.; El-Mellouhi, F.; Balbuena, P.B. Understanding Ionic Diffusion through SEI Components for Lithium-Ion and Sodium-Ion Batteries: Insights from First-Principles Calculations. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 3315–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.H.B.; Camacho, P.S.; Fondard, J.; Carlier, D.; Croguennec, L.; Palacin, M.R.; Ponrouch, A.; Courrèges, C.; Dedryvère, R.; Trad, K.; et al. First 18650-Format Na-Ion Cells Aging Investigation: A Degradation Mechanism Study. J. Power Sources 2022, 529, 231253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simone, V. Développement D’accumulateurs Sodium-Ion. Ph.D. Dissertation, Université Grenoble Alpes, Saint-Martin-d’Hères, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, J.-Y.; Myung, S.-T.; Sun, Y.-K. Sodium-Ion Batteries: Present and Future. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3529–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, P.K.; Yang, L.; Brehm, W.; Adelhelm, P. From Lithium-Ion to Sodium-Ion Batteries: Advantages, Challenges, and Surprises. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2018, 57, 102–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Xiong, P.; Maitra, U.; Langsdorf, D.; Yan, K.; Wang, C.; Janek, J.; Schröder, D.; Wang, G. Design Strategies to Enable the Efficient Use of Sodium Metal Anodes in High-Energy Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1903891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, L.F.; Li, Y.; Mundszinger, M.; Geisler, J.; Pfeifer, C.; Mikhailova, D.; Omar, A.; Baran, V.; Biskupek, J.; Kaiser, U.; et al. Origin of Aging of a P2-NaxMn3/4Ni1/4O2 Cathode Active Material for Sodium-Ion Batteries. Chem. Mater. 2023, 35, 8065–8080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garayt, M.D.L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Obialor, M.C.; Deshmukh, J.; Xing, Y.; Yang, C.; Metzger, M.; Dahn, J.R. Practical Alloy-Based Negative Electrodes for Na-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2024, 171, 070523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masse, R.; Uchaker, E.; Cao, G. Beyond Li-Ion: Electrode Materials for Sodium- and Magnesium-Ion Batteries. Sci. China Mater. 2015, 58, 715–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, P. Achieving Na-Ion Battery Advancements Through Decoding Degradation Pathways and Electrolyte Engineering. Ph.D. Dissertation, Sorbonne Université, Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Akcay, T.; Haeringer, M.; Pfeifer, K.; He, Y.; Ma, Y.; Anhalt, J.; Triller, D.; Sarapulova, A.; Dsoke, S.; Binder, J.R.; et al. Degradation Mechanisms of Positive Electrode Materials for Sodium-Ion Batteries. ECS Meet. Abstr. 2023, MA2023-01, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laufen, H.; Klick, S.; Ditler, H.; Quade, K.L.; Mikitisin, A.; Blömeke, A.; Schütte, M.; Wasylowski, D.; Sonnet, M.; Henrich, L.; et al. Multi-Method Characterization of a Commercial 1.2 Ah Sodium-Ion Battery Cell Indicates Drop-in Potential. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2024, 5, 101945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Feng, Y.-H.; Zhu, X.; Liu, M.; Yu, L.; Wei, G.-X.; Fan, X.-Y.; Ji, X.; Wang, P.-F.; Xin, H. Stabilizing Cathode-Electrolyte Interphase by Localized High-Concentration Electrolytes for High-Voltage Sodium-Ion Batteries. Nano Energy 2024, 123, 109389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlasza, C.; Ostertag, P.; Chrenko, D.; Kriesten, R.; Bouquain, D. Review on the Aging Mechanisms in Li-Ion Batteries for Electric Vehicles Based on the FMEA Method. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Dearborn, MI, USA, 15–18 June 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Seok, J.; Lee, W.; Lee, H.; Park, S.; Chung, C.; Hwang, S.; Yoon, W.-S. Aging Mechanisms of Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Sci. Technol. 2024, 15, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkiewicz, J.; Jones, G.M.; Ghanizadeh, S.; Bostanchi, S.; Wasely, T.J.; Yamini, S.A.; Nekouie, V. Large-Scale Manufacturing of Solid-State Electrolytes: Challenges, Progress, and Prospects. Open Ceram. 2023, 16, 100497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xia, L.; Yang, H.; Zhan, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Duan, J. Solid-State Synthesis of Lanthanum-Based Oxides Co-Coated LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 for Advanced Lithium Ion Batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 832, 154959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Wang, D.; Yin, T.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Dai, Z.; Zheng, L. Experimental Study on Thermal-Induced Runaway in High Nickel Ternary Batteries. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 14562–14570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, C.; Hennig, J.; Tegethoff, W.; Schweiger, H.-G.; Koehler, J. Analysis of the Interaction and Variability of Thermal Decomposition Reactions of a Li-Ion Battery Cell. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2023, 170, 060523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boozula, A.R.; Bagheri, K.; Lampuse, R.G.; Shah, S.; Thakkar, J.J. Review of Thermal Runaway Risks in Na-Ion and Li-Ion Batteries: Safety Improvement Suggestions for Na-Ion Batteries. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2025, 72, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innovation in Batteries and Electricity Storage—Analysis. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/innovation-in-batteries-and-electricity-storage (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Kwon, H.; Kim, S.; Hyun, J.; Lee, H.E.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, I.J.; Shin, K.; Kim, S.; Park, C.; et al. Covariance of Interphasic Properties and Fast Chargeability of Energy-Dense Lithium Metal Batteries. Nat. Energy 2025, 10, 1132–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.-Z.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Cheng, X.-B.; Zhang, R.; Xu, R.; Chen, P.-Y.; Peng, H.-J.; Huang, J.-Q.; Zhang, Q. An Anion-Immobilized Composite Electrolyte for Dendrite-Free Lithium Metal Anodes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11069–11074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Lee, S.; Soo Jung, D.; Chul Roh, K.; Seo, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.; Joohyun Kim, P.; Choi, J. Synergistically Enhanced LiF–Rich Protective Layer for Highly Stable Silicon Anodes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 661, 160023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, F.; Han, P.; Xu, M.; Dai, W.; Jiao, J.; Jiang, L.; Gao, Q. LiF-Rich Alloy-Doped SEI Enabling Ultra-Stable and High-Rate Li Metal Anode. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202407315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, W.-J.; Jeong Huh, Y.; Choi, S.; Kulkarni, U.; Shejale, K.P.; Yi, G.-R. Innovations in Non-Flammable and Flame-Retardant Electrolytes for Safer Lithium-Ion Batteries. Chem. Commun. 2025, 61, 12056–12068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Ma, Z.; Kumar, P.; Liang, H.; Cao, Z.; Xie, H.; Cavallo, L.; Li, Q.; Ming, J. Non-Flammable Electrolyte Mediated by Solvation Chemistry toward High-Voltage Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Energy Lett. 2024, 9, 1604–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avvaru, V.S.; Ogunfunmi, T.; Jeong, S.; Diallo, M.S.; Watt, J.; Scott, M.C.; Kim, H. Tin–Carbon Dual Buffer Layer to Suppress Lithium Dendrite Growth in All-Solid-State Batteries. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 17347–17356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Luo, F.; Lai, W.; Ge, M.; Chen, X.; Chen, Q.; Qian, Q.; Zeng, L. Flash Synthesis of Uniform Tin-Modified Carbon Skeleton as Stable Anode for Sodium Metal Batteries. J. Energy Storage 2025, 109, 115206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransom, B.; Ramdas, A.; Lomeli, E.; Fidawi, J.; Sendek, A.; Devereaux, T.; Reed, E.J.; Schindler, P. Electrolyte Coatings for High Adhesion Interfaces in Solid-State Batteries from First Principles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 44394–44403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Gui, C.; Zhang, Y.; Nan, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, L.; Tan, X.; Wang, C.; Yang, F.; et al. An Adhesive Interface between Hydrogel Electrolyte and Electrode for Low-Temperature Solid-State Capacitive Devices. J. Energy Storage 2024, 102, 114061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, W.; Park, S.S.; Yun, J.; Shin, H.R.; Moon, J.; Lee, J.-W. Tailoring Grain Boundary Structures and Chemistry of Li7La3Zr2O12 Solid Electrolytes for Enhanced Air Stability. Energy Storage Mater. 2023, 54, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezabh, H.K.; Abrha, L.H.; Chiu, S.-F.; Nikodimos, Y.; Hagos, T.M.; Tsai, M.-C.; Su, W.-N.; Hwang, B.J. Enhancing Ionic Conductivity and Air Stability of Li7La3Zr2O12 Garnet-Based Electrolyte through Dual-Dopant Strategy. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 177277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, X.; Ju, Z.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Du, Y.; Bai, Z.; Dou, S.; Yu, G. Thickness-Independent Scalable High-Performance Li-S Batteries with High Areal Sulfur Loading via Electron-Enriched Carbon Framework. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzedine, M.; Jardali, F.; Florea, I.; Cojocaru, C.-S. Nanostructured S@VACNTs Cathode with Lithium Sulfate Barrier Layer for Exceptionally Stable Cycling in Lithium-Sulfur Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2024, 171, 050531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, H.; Fu, X.; Awuye, D.E.; Yin, X.; Zhao, Y. Breaking the Barrier: Strategies for Mitigating Shuttle Effect in Lithium–Sulfur Batteries Using Advanced Separators. Polymers 2023, 15, 3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Zhu, X.; Ran, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wei, W. Conductive Polymer-Based Interlayers in Restraining the Polysulfide Shuttle of Lithium–Sulfur Batteries. Molecules 2024, 29, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xiao, Z.; Lai, C.; Zou, S.; Zhang, M.; Liu, K.; Yin, Y.; Liang, T.; Wu, Z. Three-Dimensional Carbon Framework as High-Proportion Sulfur Host for High-Performance Lithium-Sulfur Batteries. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 48, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloch, M.; Shanmukaraj, D.; Bondarchuk, O.; Bekaert, E.; Rojo, T.; Armand, M. Variations on Li3N Protective Coating Using Ex-Situ and in-Situ Techniques for Li° in Sulphur Batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2017, 9, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitch, S.D.S.; Moehl, G.E.; Meddings, N.; Fop, S.; Soulé, S.; Lee, T.-L.; Kazemian, M.; Garcia-Araez, N.; Hector, A.L. Combined Electrochemical, XPS, and STXM Study of Lithium Nitride as a Protective Coating for Lithium Metal and Lithium–Sulfur Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 39198–39210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Yang, M.; Fan, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xu, T.; Li, C.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Sun, Q.; Xia, H. Inorganic-Enriched Solid Electrolyte Interphases: A Key to Enhance Sodium-Ion Battery Cycle Stability? Small 2024, 20, 2407425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Gao, J.; Xu, L.; Li, S.; Zhu, B.; Cheng, Z.; Xing, J.; Wu, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Enhanced Interphase Stability and Longevity of Sodium-Ion Pouch Cells by Compound Additive Engineering. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2025, 8, 11033–11041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Cao, R.; Pu, X.; Zhao, A.; Chen, W.; Song, C.; Fang, Y.; Cao, Y. Access to Advanced Sodium-Ion Batteries by Presodiation: Principles and Applications. J. Energy Chem. 2024, 92, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, X.; Mi, L.; Chen, W. Emerging Presodiation Strategies for Long-Life Sodium-Ion Batteries. Energy Lab 2023, 1, 230008–230017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Liao, S.; Shi, L.; Su, B.; Xu, F.; Guo, Z.; Li, H.; Wei, F. Solid-State Polymer Electrolytes in Lithium Batteries: Latest Progress and Perspective. Polym. Chem. 2024, 15, 473–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzereogu, P.U.; Oyesanya, A.; Ogba, S.N.; Ayanwunmi, S.O.; Sobajo, M.S.; Chimsunum, V.C.; Ayanwunmi, V.O.; Amoo, M.O.; Adefemi, O.T.; Chukwudi, C.C. Solid-State Lithium-Ion Battery Electrolytes: Revolutionizing Energy Density and Safety. Hybrid Adv. 2025, 8, 100339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjendirane, A.C.; Maurya, D.K.; Ren, J.; Hou, H.; Algadi, H.; Xu, B.B.; Guo, Z.; Angaiah, S. Overview of Inorganic Electrolytes for All-Solid-State Sodium Batteries. Langmuir 2024, 40, 16690–16712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Chen, B.; Wang, T.; Liu, C.; Yin, W.; Mao, Q.; Zhou, D.; Hao, Y.; Liu, X. Achieving Stable and High-Rate Quasi-Solid-State Sodium Batteries through Strengthened P-O Covalency and Interface Modification in Na3Zr2Si2PO12. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EC 62660-1:2018; Secondary Lithium-Ion Cells for the Propulsion of Electric Road Vehicles—Part 1: Performance Testing. IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Hassini, M.; Redondo-Iglesias, E.; Venet, P. Lithium-Ion Battery Data: From Production to Prediction. Batteries 2023, 9, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, W.; Venet, P.; Bultel, Y.; Sari, A.; Riviere, E. Aging in First and Second Life of G/LFP 18650 Cells: Diagnosis and Evolution of the State of Health of the Cell and the Negative Electrode under Cycling. Batteries 2024, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBel, F.-A.; Messier, P.; Sari, A.; Trovão, J.P.F. Lithium-Ion Cell Equivalent Circuit Model Identification by Galvanostatic Intermittent Titration Technique. J. Energy Storage 2022, 54, 105303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawaz, W.; Wang, Z.; Ng, K.Y.S. Sulfur Encapsulation into Carbon Nanospheres as an Effective Technique to Limit Sulfide Dissolution and Extend the Cycle Life of Lithium–Sulfur Batteries. Energies 2024, 17, 2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, D.; Min, K.; Lee, B.; Kwon, H.; Baeck, S.-H. Highly Efficient Bifunctional Electrocatalyst for Rechargeable Zinc-Air Batteries: N, S Dual-Doped Carbon Encapsulating Sulfur Vacancy-Rich FeCo/Fe-CoS Nanoparticles. J. Power Sources 2025, 625, 235653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarascon, J.-M.; Armand, M. Issues and Challenges Facing Rechargeable Lithium Batteries. Nature 2001, 414, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Placke, T.; Kloepsch, R.; Dühnen, S.; Winter, M. Lithium Ion, Lithium Metal, and Alternative Rechargeable Battery Technologies: The Odyssey for High Energy Density. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2017, 21, 1939–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebert, F.; Knott, J.; Gorkin, R.; Chou, S.-L.; Dou, S.-X. Polymer Electrolytes for Sodium-Ion Batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 36, 10–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, A.; Benson, S.M.; Chueh, W.C. Critically Assessing Sodium-Ion Technology Roadmaps and Scenarios for Techno-Economic Competitiveness against Lithium-Ion Batteries. Nat. Energy 2025, 10, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Miao, L.; Qie, L.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Li, J. Gravimetric and Volumetric Energy Densities of Lithium-Sulfur Batteries. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2017, 6, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.M.N.U.; Rasul, M.G.; Sayem, A.S.M.; Mandal, N. Maximizing Energy Density of Lithium-Ion Batteries for Electric Vehicles: A Critical Review. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, T.; Li, W.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z. Engineering of Sodium-Ion Batteries: Opportunities and Challenges. Engineering 2023, 24, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Hua, Y.; Li, J.; Yi, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Z.-L. High-Energy Sodium Ion Batteries Enabled by Switching Sodiophobic Graphite into Sodiophilic and High-Capacity Anodes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202410253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, M.; Guan, J.; Sun, J.; Shu, X.; Ding, H.; Chen, L.; Zhou, N.; Xiao, Z. A Cost- and Energy Density-Competitive Lithium-Sulfur Battery. Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 41, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.D.; Cha, E.; Choi, W. Towards the Commercialization of Li-S Battery: From Lab to Industry. Energy Storage Mater. 2024, 72, 103711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QuantumScape Datasheet: A First Look at the QSE-5 B Sample. Available online: https://www.quantumscape.com/blog/a-first-look-at-the-qse-5-b-sample/ (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- BYD Datasheet: BATTERY-BOX PREMIUM HVS/HVM. Available online: https://www.bydbatterybox.com/uploads/downloads/220426%20BYD%20Battery-Box%20Premium%20HVS_HVM%20Datasheet%20V1.6%20FR-626900f5b2621.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Biwatt Datasheet: Digital Green Power Innovator and Sodium-Ion Technology Pioneer. Available online: https://cdn.enfsolar.com/z/pp/2023/12/28a8r7zfqwz90/BIWATT-PowerNest-W1-brochure.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2023).
- Faradion Datasheet: Commercialization of Faradion’s High Energy Density Na-Ion Battery Technology. Available online: https://faradion.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/Faradion-Limited-3rd-International-Meeting-on-Sodium-Batteries.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- HiNa Battery Datasheet: Cylindrical Na-Ion Batteries Specification—NaCR32140-MP10. Available online: https://p.globalsources.com/IMAGES/PDT/SPEC/430/K1214144430.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- GokWh Datasheet: 12V Sodium-Ion Battery. Available online: https://gokwh.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/GoKWh-12V-Sodium-ion-Battery-Storage-Series-User-Manual.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- EEMB Battery Datasheet: Lithium-Ion Battery DATA SHEET—LIR18650 2600mAh. Available online: https://www.ineltro.ch/media/downloads/SAAItem/45/45958/36e3e7f3-2049-4adb-a2a7-79c654d92915.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Palissat, G. Lithium-Sulphur Batteries: Opportunities and Challenges for Space Applications. In Proceedings of the 8th European Conference for Aeronautics and Space Sciences (EUCASS), Madrid, Spain, 1–4 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Natron Energy Datasheet: Natron Energy—BlueTrayTM4000. Available online: https://natron.energy/files/bt4000_data_sheet_061324-1.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Tiamat Datasheet: Sodium-Ion High Power Battery—NVPF18650-B3. Available online: https://www.tiamat-energy.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/2023-09_Datasheet-cylindric.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Lyten. Nasa Performance and Safety Behavior of Lyten’s Li-S Pouch and Cylindrical 18650 Cells. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/05-nasa-workshop-babuganguli.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Dörfler, S.; Walus, S.; Locke, J.; Fotouhi, A.; Auger, D.J.; Shateri, N.; Abendroth, T.; Härtel, P.; Althues, H.; Kaskel, S. Recent Progress and Emerging Application Areas for Lithium–Sulfur Battery Technology. Energy Technol. 2021, 9, 2000694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightning Energy Datasheet: Specification for Rechargeable Sodium-Ion 18650 Cell. Available online: https://lightning-energy.cn/product/seekwatt-18650-1-3ah-sodium-ion-cylindrical-cells/ (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Golden Feather “Sci-Tech Innovation China” National Solid-State Battery Innovation Base. Available online: https://gfenergy.com/cpyjjfa#txt_con_140_34 (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- WeLion Solid-State Lithium Ion Battery—PL10374172-22Ah. Available online: https://www.solidstatelion.com/en/product_page/209.html (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Highstar Datasheet: Specification Approval Sheet—NaCP50160118-50H3. Available online: https://en.highstar.com/cell (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Samsung Datasheet: Specification of Product—INR18650-30Q V6. Available online: https://www.joke-technology.com/media/pdf/c4/9a/9b/datenblatt_inr18650-30q6_cell_specification.pdf?srsltid=AfmBOorj8RmUrHjTkFHOhGhXfwNMf7ghuIAF22qsnq-XX5tuHmj_bEjG (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Samsung Datasheet: Specification of Product—INR21700-50GB V0. Available online: https://www.master-instruments.com.au/file/67273/1/Samsung-INR21700-50G.pdf (accessed on 18 September 2025).
- Panasonic Datasheet: Specifications for NCR18650GA. Available online: https://actec.dk/media/documents/45D7276ABE10.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Tesla Datasheet: Tesla Powerwall. Available online: https://www.tesla.com/sites/default/files/pdfs/powerwall/Powerwall%202_AC_Datasheet_en_AU.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Palissat, G.; ArianeGroup. Ultralight Lithium-Sulphur Cells for Space Applications: Opportunities and Barriers. Available online: https://projects.leitat.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/14.-Ultralight_LiS_Cells_for_Space_Applications_V1.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Xantrex Datasheet: Lithium Ion Battery—884-0100-51. Available online: https://xantrex.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/20220429_100ah51_2v_884-0100-51_LithiumIonBattery_Datasheet.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2025).
| Composition | Ni/Mn/Co Content | Note |
|---|---|---|
| NMC111 | 1/1/1 | First generation LIBs |
| NMC532 | 5/3/2 | Energy density improvement |
| NMC622 | 6/2/2 | A compromise between stability and performance |
| NMC811 | 8/1/1 | High energy density, but a little more unstable |
| NMC90-5-5 | 9/0.5/0.5 | Good energy density but structurally unstable |
| NCA | 80–90% Ni | Tesla batteries, long autonomy |
| Technology | Main Aging Mechanisms | Features/Interest | Limits/Critical Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Li-ion batteries | - SEI instability (cracking on Si/C) - Lithium plating (low temperature, overload, high C-rate) - Volume expansion of Si (nearly 300%) → cracks, loss of contact - Dissolution of metals (Mn, Ni, Co) - Resistive CEI on Ni-rich positive electrodes - Electrolyte decomposition at high voltage/temperature - Electrode cracking/delamination | - Mature, high-performance technology - High energy density - Compatibility with optimized electrolytes - Prospects for improvement with Si and nanomaterials | - Volume expansion of the negative silicon electrode - high-voltage degradation - Unstable CEI (Ni-rich materials) - Cost and criticality of materials (Co, Ni) |
| Solid-Sate batteries | - High interfacial resistance (poor contacts) - Parasitic reactions at interfaces - Cracking of rigid electrolytes - Dendrite growth (LiM) - Delamination under mechanical stress - Chemical degradation (e.g., LLZO with humidity) - Possible gas generation (e.g., H2S) | - Increased safety (no liquid electrolyte) - Potential for lithium metal (high energy density) - Reduced thermal risk | - Unstable solid interfaces - Poor electrode/electrolyte adhesion - Dendrites despite solid electrolyte - Costly and complex to manufacture - Low industrial maturity |
| Li-S batteries | - Shuttle effect of polysulfides - Formation of insulating Li2S/Li2S2 - Lithium dendrites - SEI unstable on LiM - Volumetric expansion of sulfur-positive electrode (>80%) | - Very high theoretical capacity - Inexpensive, abundant and non-toxic sulfur - Possibility of enhancement with conductive hosts (carbon, Metal–Organic Framework (MOF)) | - Loss of active sulfur, self-discharge - Low intrinsic conductivity - High volume variation - Unstable SEI - Limited cyclability |
| Na-ion batteries | - SEI unstable (especially on hard carbon) → loss of active material - Sodium plating (low temperature) → short circuit - Electrolyte decomposition at high voltage - Irreversible electrode damage - Significant volume expansion - Dissolution of sodium in electrolyte | - Abundant and inexpensive sodium - Better environmental sustainability - Good power performance - Compatible with various electrodes - Greater safety at high temperatures | - Energy density still lower than Li-ion - SEI rather unstable - Volume expansion for some negative electrode materials - Risk of plating |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piat, C.; Sari, A.; Viton, C. Emerging Battery Technologies: The Main Aging Mechanisms and Challenges. Batteries 2025, 11, 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11100383
Piat C, Sari A, Viton C. Emerging Battery Technologies: The Main Aging Mechanisms and Challenges. Batteries. 2025; 11(10):383. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11100383
Chicago/Turabian StylePiat, Corentin, Ali Sari, and Christophe Viton. 2025. "Emerging Battery Technologies: The Main Aging Mechanisms and Challenges" Batteries 11, no. 10: 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11100383
APA StylePiat, C., Sari, A., & Viton, C. (2025). Emerging Battery Technologies: The Main Aging Mechanisms and Challenges. Batteries, 11(10), 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11100383







