SlSPS, a Sucrose Phosphate Synthase Gene, Mediates Plant Growth and Thermotolerance in Tomato
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Condition
2.2. Heat Stress Treatment
2.3. Vector Construction and Genetic Transformation
2.4. Expression Analysis
2.5. DAB Staining
2.6. Determination of Physiological Indexes
3. Results
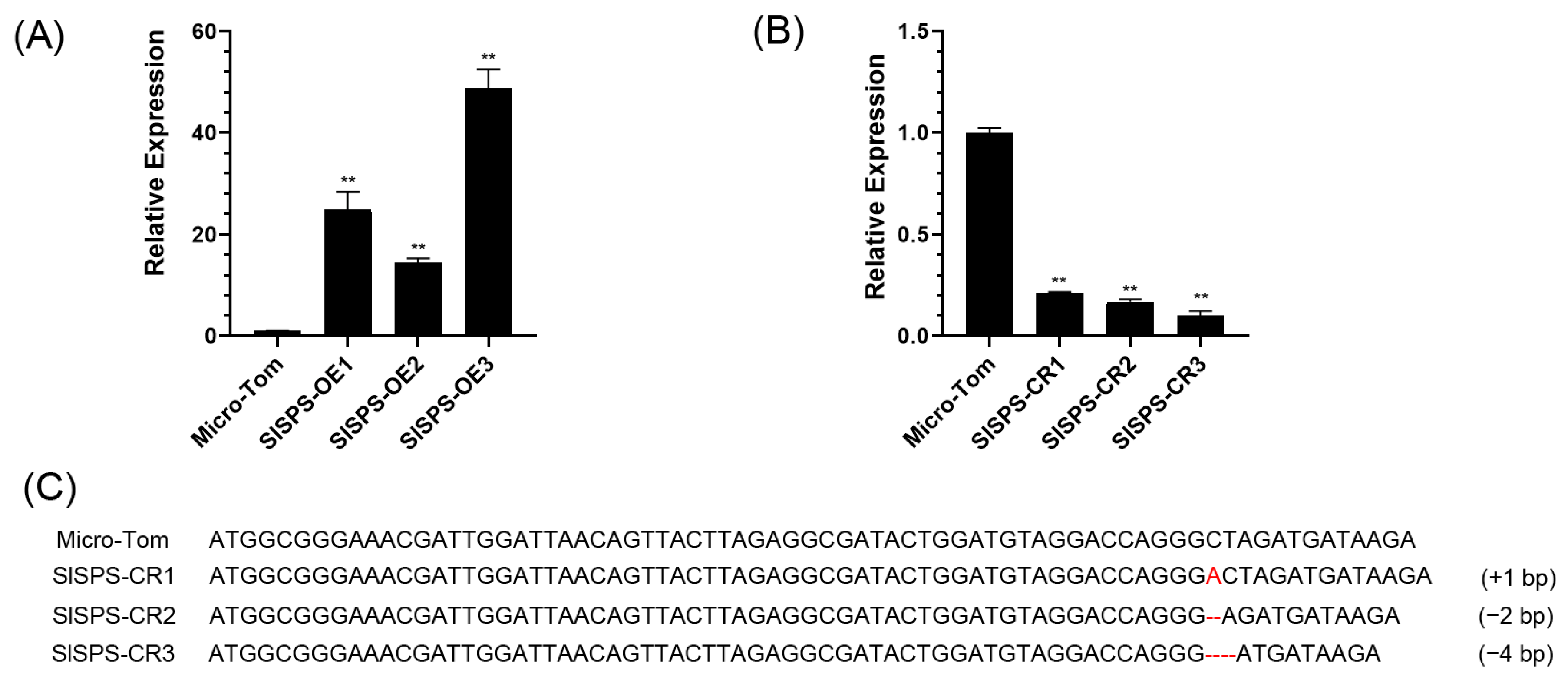
3.1. Generation of Over-Expression and Knock-Out of SlSPS Gene Transgenic Plants
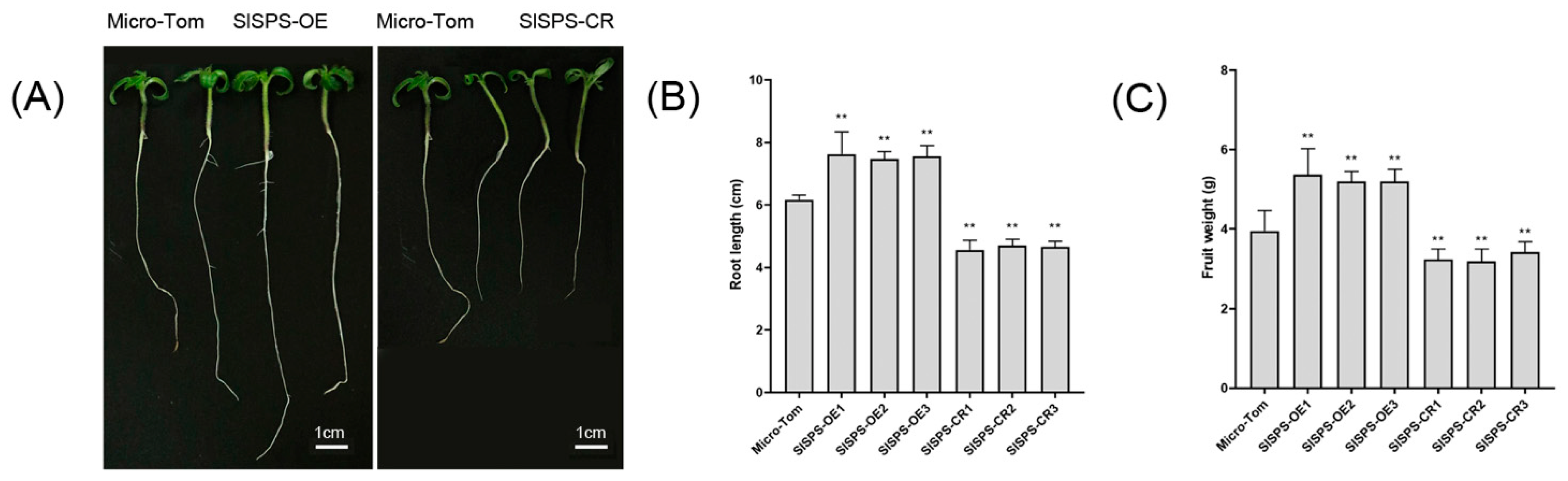
3.2. Effects of Over-Expression and Knock-Out of SlSPS Gene on Plant Phenotypes
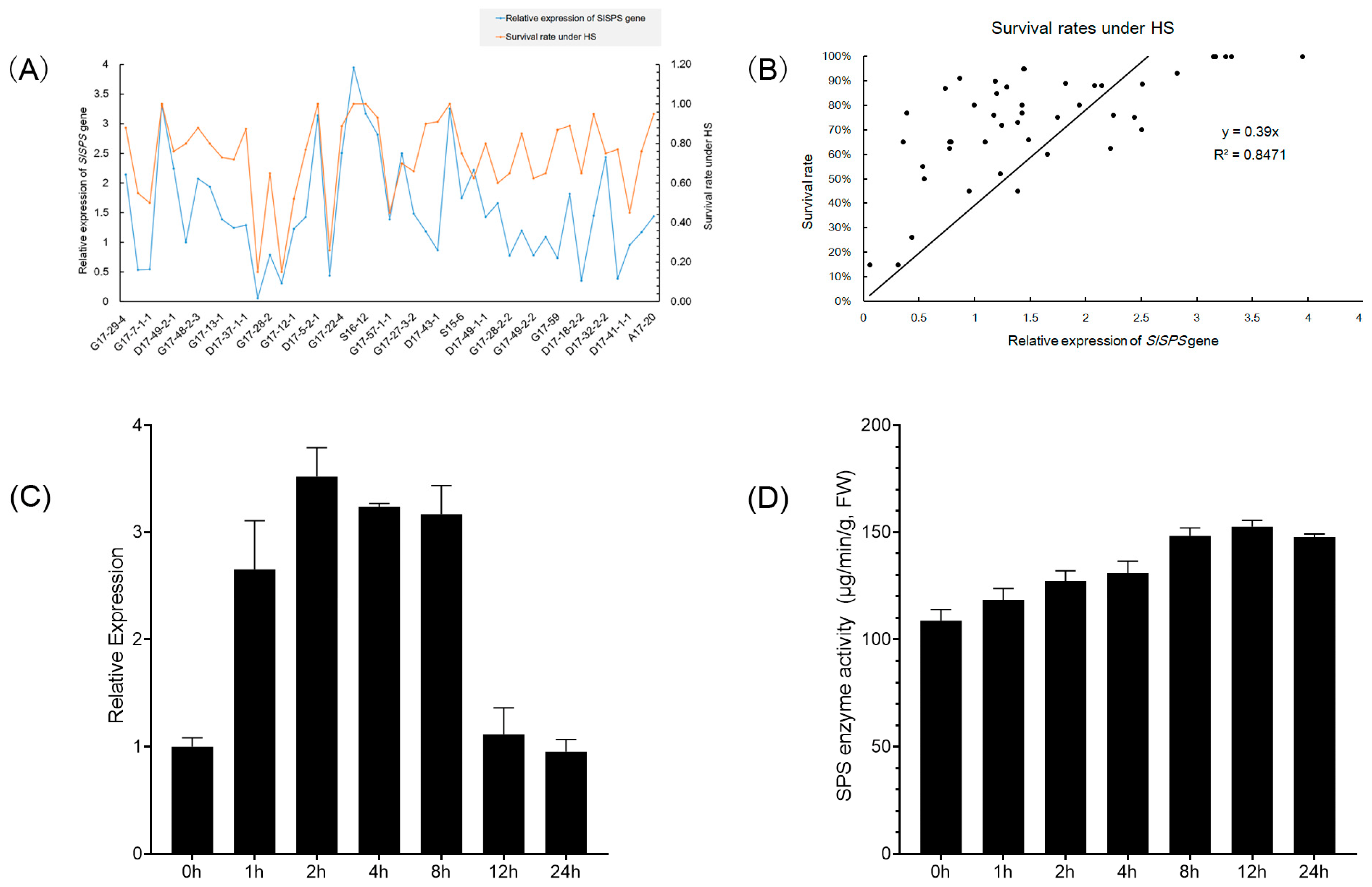
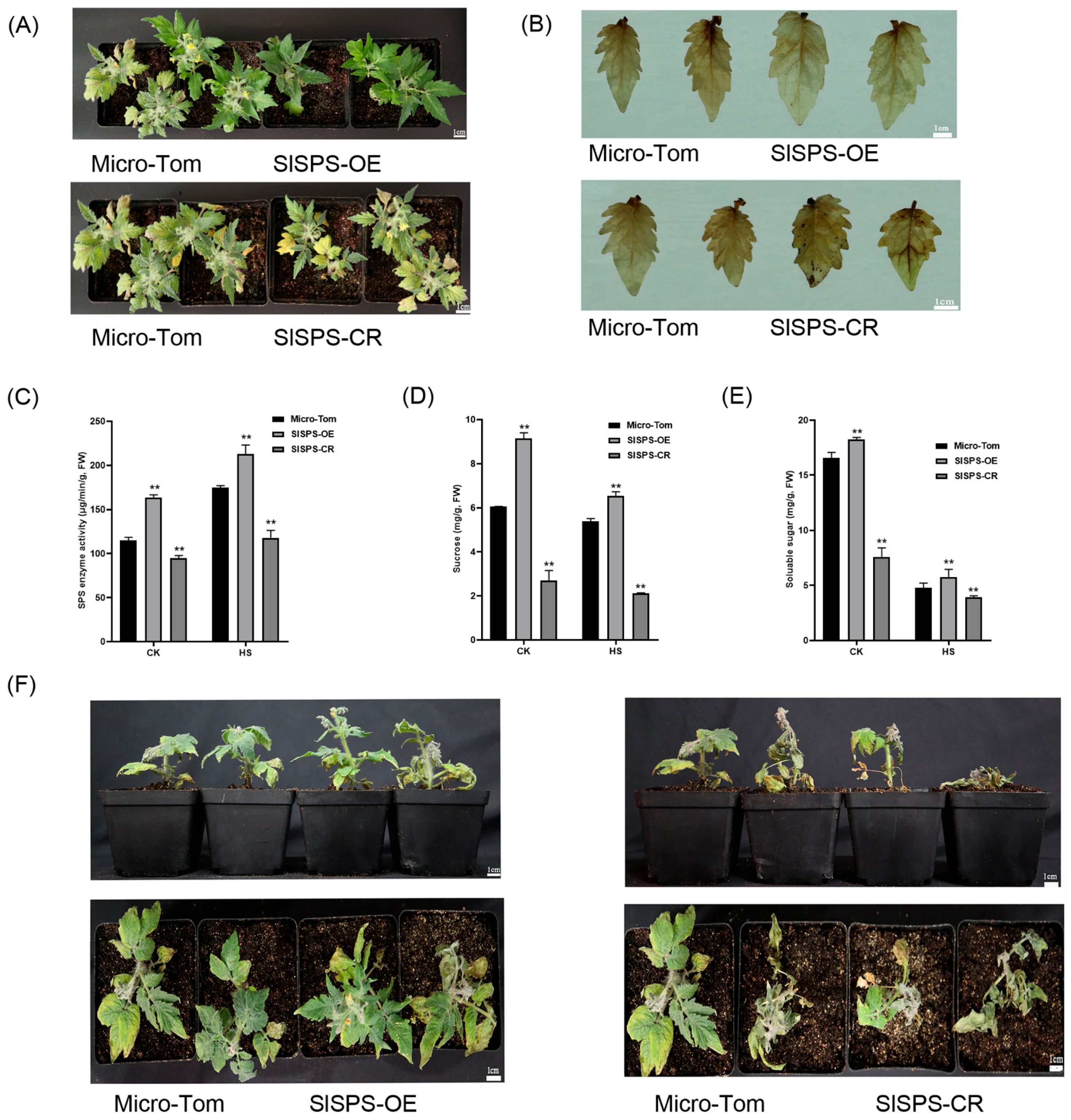
3.3. Effects of Heat Stress on Expression of SlSPS Gene, SPS Enzyme Activity, and Sucrose and Soluble Sugar Contents
3.4. Effects of the Expression of SlSPS Gene on Thermotolerance
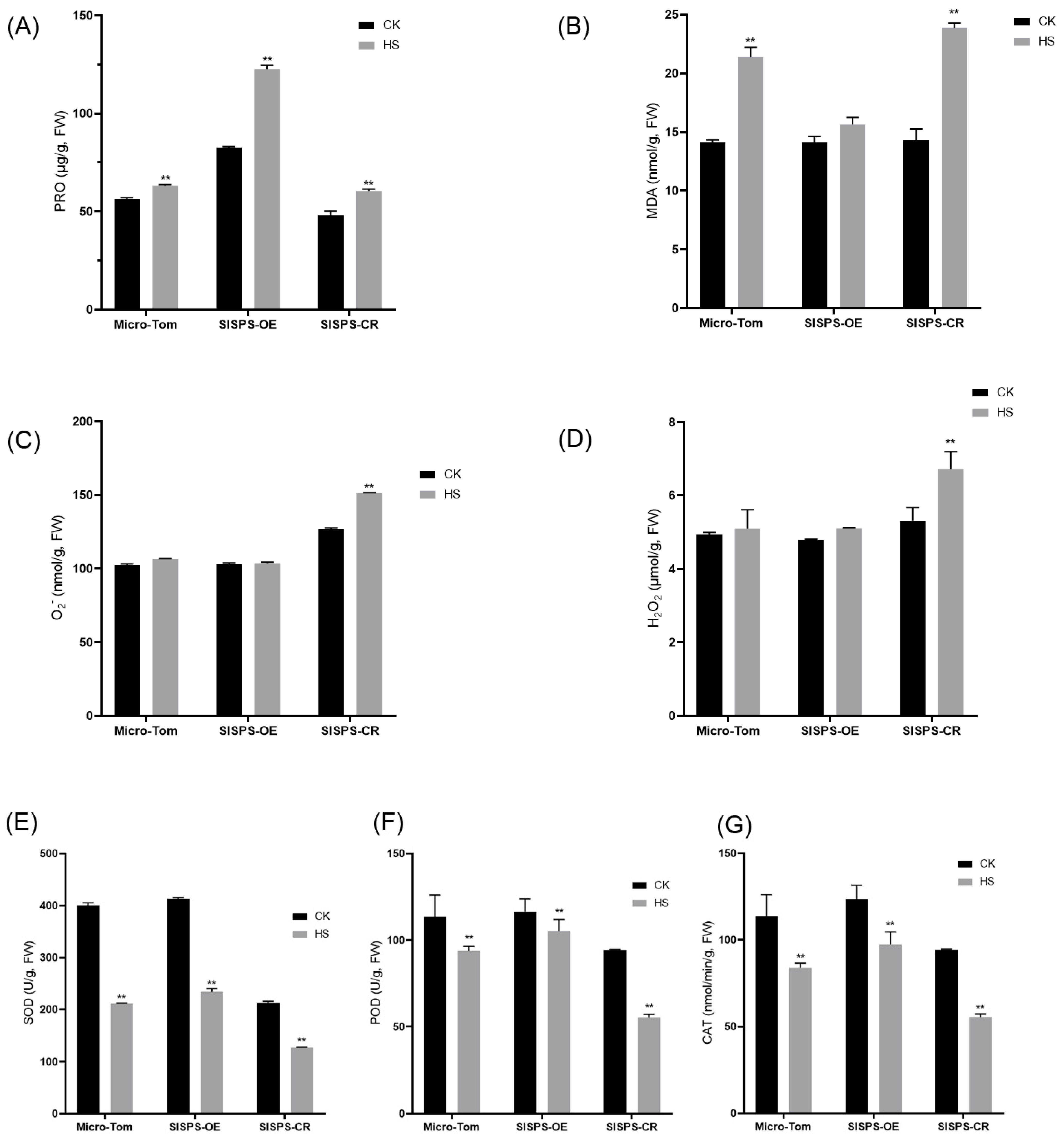
3.5. Effects of the Expression SlSPS Gene on Oxidative Stress Parameters and Antioxidtant Enzymes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lesk, C.; Rowhani, P.; Ramankutty, N. Influence of extreme weather disasters on global crop production. Nature 2016, 529, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobell, D.B.; Schlenker, W.; Costa-Roberts, J. Climate trends and global crop production since 1980. Science 2011, 333, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, B.; Piao, S.; Wang, X.; Lobell, D.B.; Huang, Y.; Huang, M.; Yao, Y.; Bassu, S.; Ciais, P.; et al. Temperature increase reduces global yields of major crops in four independent estimates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 9326–9331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Nahar, K.; Alam, M.M.; Roychowdhury, R.; Fujita, M. Physiological, Biochemical, and Molecular Mechanisms of Heat Stress Tolerance in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 9643–9684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Shahwar, D. Role of Heat Shock Proteins (HSPs) and Heat Stress Tolerance in Crop Plants. In Sustainable Agriculture in the Era of Climate Change; Roychowdhury, R., Choudhury, S., Hasanuzzaman, M., Srivastava, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 211–234. [Google Scholar]
- Das, K.; Roychoudhury, A. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and response of antioxidants as ROS-scavengers during environmental stress in plants. Front. Environ. Sci. 2014, 2, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, H.; Xu, L.; Singh, A.; Wang, H.; Du, L.; Poovaiah, B.W. Involvement of calmodulin and calmodulin-like proteins in plant responses to abiotic stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Euring, D.; Cha, J.Y.; Lin, Z.; Lu, M.; Huang, L.-J.; Kim, W.Y. Plant Hormone-Mediated Regulation of Heat Tolerance in Response to Global Climate Change. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 11, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liang, Z.; Lu, C. Genetic engineering of the biosynthesis of glycinebetaine enhances photosynthesis against high temperature stress in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 2299–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Zhao, X.; Bürger, M.; Wang, Y.; Chory, J. Two interacting ethylene response factors regulate heat stress response. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 338–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, G.; Mo, S.; Chen, Q.; Xu, X.; Wu, X.; Ge, C. In-depth proteome analysis reveals multiple pathways involved in tomato SlMPK1-mediated high-temperature responses. Protoplasma 2019, 257, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; He, J.; Wu, Y.; Wu, X.; Ge, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, S.; Peiter, E.; Liang, J.; Xu, W. The Tomato Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase SlMPK1 Is as a Negative Regulator of the High-Temperature Stress Response. Plant Physiol. 2018, 177, 633–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, W.; Wang, L.; Zhao, R.; Sheng, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Shen, L. Knockout of SlMAPK3 enhances tolerance to heat stress involving ROS homeostasis in tomato plants. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Cai, G.; Xu, N.; Zhang, L.; Sun, X.; Guan, J.; Meng, Q. Novel DnaJ Protein Facilitates Thermotolerance of Transgenic Tomatoes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, H.; Zhong, X.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Y.; Yan, B.; Li, Q.; Chen, G.; Mao, B.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Overexpression of receptor-like kinase ERECTA improves thermotolerance in rice and tomato. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Li, C.; Wei, D.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, T.H.H.; Yang, X. Comparative effects of glycinebetaine on the thermotolerance in codA- and BADH-transgenic tomato plants under high temperature stress. Plant Cell Rep. 2020, 39, 1525–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine, R. Sucrose transporters in plants: Update on function and structure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1465, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keunen, E.; Peshev, D.; Vangronsveld, J.; Van Den Ende, W.I.M.; Cuypers, A.N.N. Plant sugars are crucial players in the oxidative challenge during abiotic stress: Extending the traditional concept. Plant Cell Environ. 2013, 36, 1242–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, S.C.; Huber, J.L. Role and regulation of sucrose-phosphate synthase in higher plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1996, 47, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Ma, L.; Zhao, C.; Hao, H.; Gong, B.; Yu, X.; Wang, X. Antisense repression of sucrose phosphate synthase in transgenic muskmelon alters plant growth and fruit development. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 393, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haigler, C.H.; Singh, B.; Zhang, D.; Hwang, S.; Wu, C.; Cai, W.X.; Hozain, M.; Kang, W.; Kiedaisch, B.; Strauss, R.E.; et al. Transgenic cotton over-producing spinach sucrose phosphate synthase showed enhanced leaf sucrose synthesis and improved fiber quality under controlled environmental conditions. Plant Mol. Biol. 2007, 63, 815–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, K.; Hirotsu, N.; Kashiwagi, T.; Madoka, Y.; Nagasuga, K.; Ono, K.; Ohsugi, R. Overexpression of a Maize SPS Gene Improves Yield Characters of Potato under Field Conditions. Plant Prod. Sci. 2008, 11, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, A.; Martinelli, T.; Farrant, J.M.; Bochicchio, A.; Vazzana, C. Sucrose phosphate synthase activity and the co-ordination of carbon partitioning during sucrose and amino acid accumulation in desiccation-tolerant leaf material of the C4 resurrection plant Sporobolus stapfianus during dehydration. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 3775–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilska-Kos, A.; Mytych, J.; Suski, S.; Magoń, J.; Ochodzki, P.; Zebrowski, J. Sucrose phosphate synthase (SPS), sucrose synthase (SUS) and their products in the leaves of Miscanthus × giganteus and Zea mays at low temperature. Planta 2020, 252, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Gu, X.; Ding, M.; Lu, W.; Lu, D. Heat stress during grain filling affects activities of enzymes involved in grain protein and starch synthesis in waxy maize. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaushal, N.; Awasthi, R.; Gupta, K.; Gaur, P.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Nayyar, H. Heat-stress-induced reproductive failures in chickpea (Cicer arietinum) are associated with impaired sucrose metabolism in leaves and anthers. Funct. Plant Biol. FPB 2013, 40, 1334–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrotta, L.; Aloisi, I.; Faleri, C.; Romi, M.; Del Duca, S.; Cai, G. Chronic heat stress affects the photosynthetic apparatus of Solanum lycopersicum L. cv Micro-Tom. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 154, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, S. Transformation of tomato with Agrobacterium tumefacines. In Plant Tissue Culture Manual: Supplement 7; Lindsey, K., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 311–319. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, Y. Cloning and expression analysis of tomato SlSPS1 gene. Mol. Plant Breed. 2021, 19, 3896–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokesha, A.N.; Shivashankara, K.S.; Laxman, R.H.; Geetha, G.A.; Shankar, A.G. Effect of High Temperature on Fruit Quality Parameters of Contrasting Tomato Genotypes. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2019, 8, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murchie, E.H.; Sarrobert, C.; Contard, P.; Betsche, T.; Foyer, C.H.; Galtier, N. Overexpression of sucrose-phosphate synthase in tomato plants grown with CO2 enrichment leads to decreased foliar carbohydrate accumulation relative to untransformed controls. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 1999, 37, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.L.; Ort, D.R. Circadian Regulation of Sucrose Phosphate Synthase Activity in Tomato by Protein Phosphatase Activity. Plant Physiol. 1997, 113, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bahaji, A.; Baroja-Fernández, E.; Ricarte-Bermejo, A.; Sánchez-López, Á.M.; Muñoz, F.J.; Romero, J.M.; Ruiz, M.T.; Baslam, M.; Almagro, G.; Sesma, M.T.; et al. Characterization of multiple SPS knockout mutants reveals redundant functions of the four Arabidopsis sucrose phosphate synthase isoforms in plant viability, and strongly indicates that enhanced respiration and accelerated starch turnover can alleviate the blockage of sucrose biosynthesis. Plant Sci. Int. J. Exp. Plant Biol. 2015, 238, 135–147. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Yang, X.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y. Ectopic expression of SlSPS gene (Sucrose Phosphate Synthase) promotes plant type in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Hebei Agric. Univ. 2021, 44, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Solís-Guzmán, M.G.; Argüello-Astorga, G.; López-Bucio, J.; Ruiz-Herrera, L.F.; López-Meza, J.E.; Sánchez-Calderón, L.; Carreón-Abud, Y.; Martínez-Trujillo, M. Arabidopsis thaliana sucrose phosphate synthase (sps) genes are expressed differentially in organs and tissues, and their transcription is regulated by osmotic stress. Gene Expr. Patterns GEP 2017, 25–26, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almadanim, M.C.; Alexandre, B.M.; Rosa, M.T.G.; Sapeta, H.; Leitão, A.E.; Ramalho, J.C.; Lam, T.T.; Negrão, S.; Abreu, I.A.; Oliveira, M.M. Rice calcium-dependent protein kinase OsCPK17 targets plasma membrane intrinsic protein and sucrose-phosphate synthase and is required for a proper cold stress response. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 1197–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagemann, M.; Marin, K. Salt-induced Sucrose Accumulation is Mediated by Sucrose-phosphate-synthase in Cyanobacteria. J. Plant Physiol. 1999, 155, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, F.; Ghanati, F.; Ahmadi Gavlighi, H.; Sharifi, M. Comparison of sucrose metabolism in wheat seedlings during drought stress and subsequent recovery. Biol. Plant. 2018, 62, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langenkämper, G.; McHale, R.; Gardner, R.C.; MacRae, E. Sucrose-phosphate synthase steady-state mRNA increases in ripening kiwifruit. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998, 36, 857–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Huang, Z.; Mi, L.; Xu, K.; Wu, J.; Fan, Y.; Ma, S.; Jiang, D. Effects of Low Temperature at Booting Stage on Sucrose Metabolism and Endogenous Hormone Contents in Winter Wheat Spikelet. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, X.; Geng, X.; Wang, F.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, X.; Ni, Z.; Yao, Y.; Xin, M.; et al. Overexpression of wheat ferritin gene TaFER-5B enhances tolerance to heat stress and other abiotic stresses associated with the ROS scavenging. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haider, M.S.; Jaskani, M.J.; Fang, J. 14-Overproduction of ROS: Underlying molecular mechanism of scavenging and redox signaling. In Biocontrol Agents and Secondary Metabolites; Jogaiah, S., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: New Delhi, India, 2021; pp. 347–382. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, M.P.; Nakazato, R.K.; Pedroso, A.N.V.; Lima, M.E.L.; Figueiredo, M.A.; Diniz, A.P.; Kozovits, A.R.; Domingos, M. Oxidant-antioxidant balance and tolerance against oxidative stress in pioneer and non-pioneer tree species from the remaining Atlantic Forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutar, O.; Marin-Guirao, L.; Ruiz, J.M.; Procaccini, G. Antioxidant response to heat stress in seagrasses. A gene expression study. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 132, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zeng, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, W. SlSPS, a Sucrose Phosphate Synthase Gene, Mediates Plant Growth and Thermotolerance in Tomato. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8060491
Zhang Y, Zeng D, Liu Y, Zhu W. SlSPS, a Sucrose Phosphate Synthase Gene, Mediates Plant Growth and Thermotolerance in Tomato. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(6):491. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8060491
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yingying, Dewen Zeng, Yahui Liu, and Weimin Zhu. 2022. "SlSPS, a Sucrose Phosphate Synthase Gene, Mediates Plant Growth and Thermotolerance in Tomato" Horticulturae 8, no. 6: 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8060491
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zeng, D., Liu, Y., & Zhu, W. (2022). SlSPS, a Sucrose Phosphate Synthase Gene, Mediates Plant Growth and Thermotolerance in Tomato. Horticulturae, 8(6), 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8060491







