Pollen- and Weather-Based Machine Learning Models for Estimating Regional Olive Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
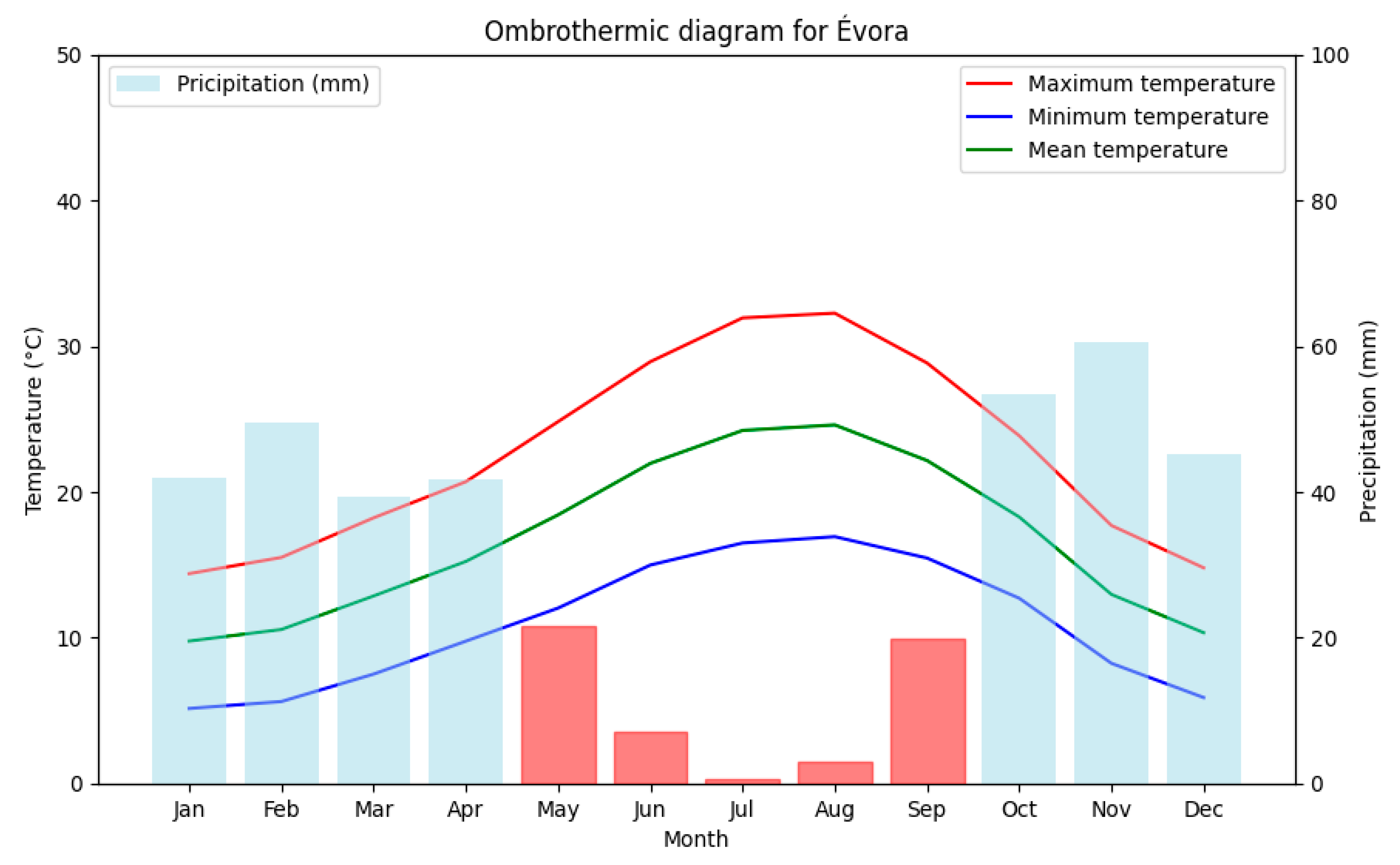
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Aerobiological Data
2.3. Climatic Data
2.4. Machine Learning Models
2.5. Feature Selection and Model Training
3. Results
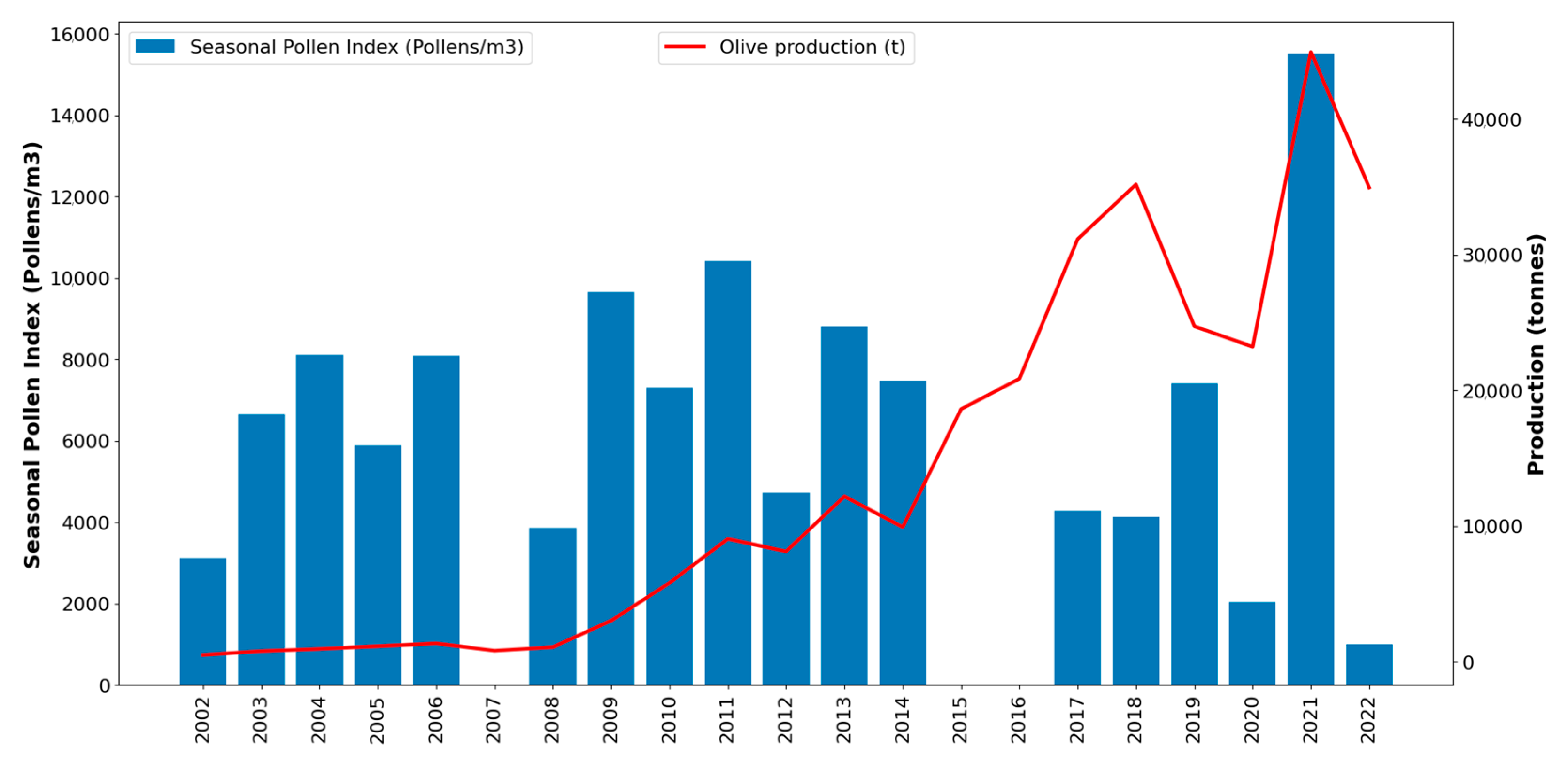
3.1. Characterization of Olea Pollen Season between the Years 2002 and 2022
3.2. Relationship between Pollen/Weather and Olive Production
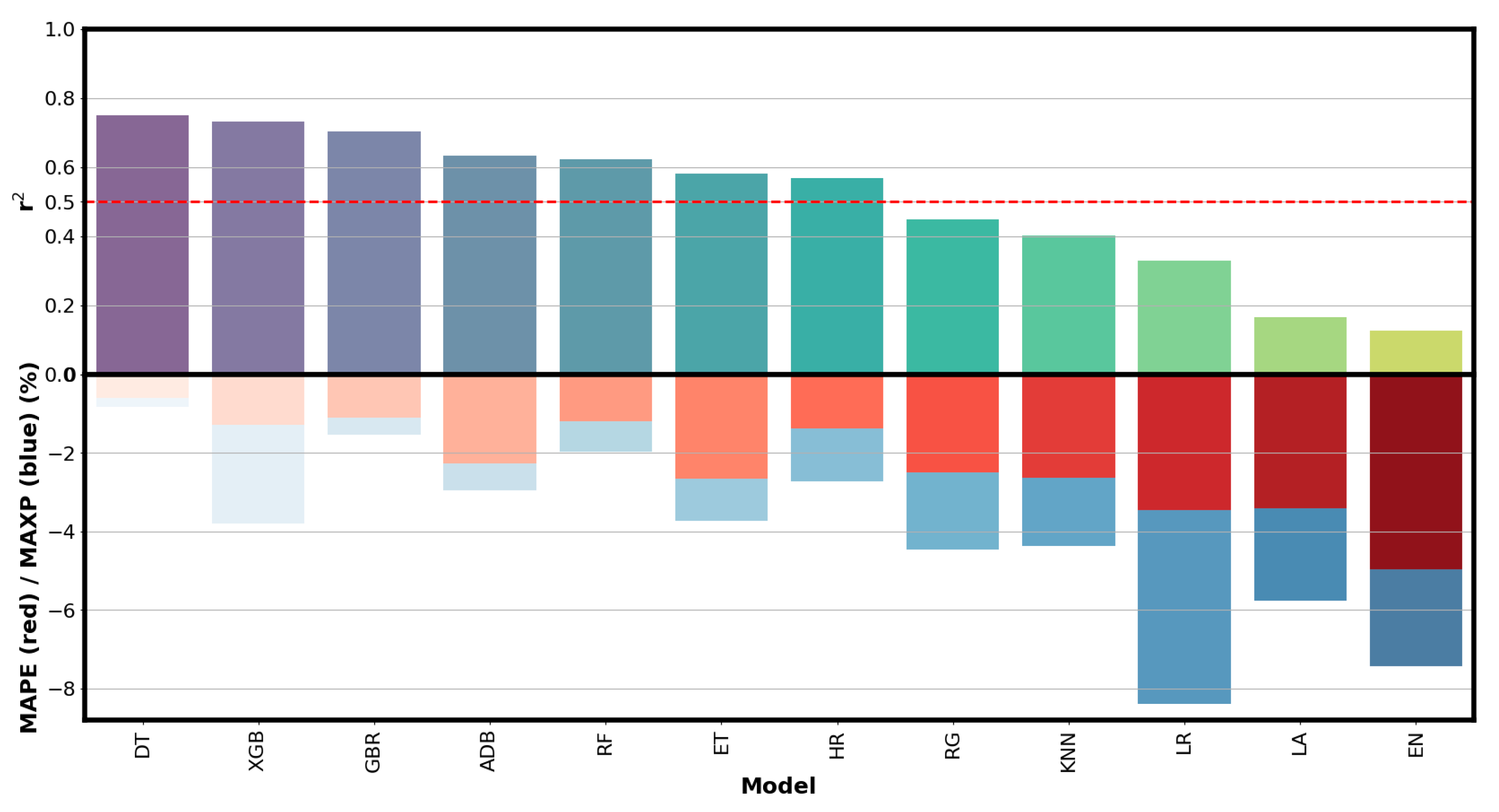
3.3. Model Performance
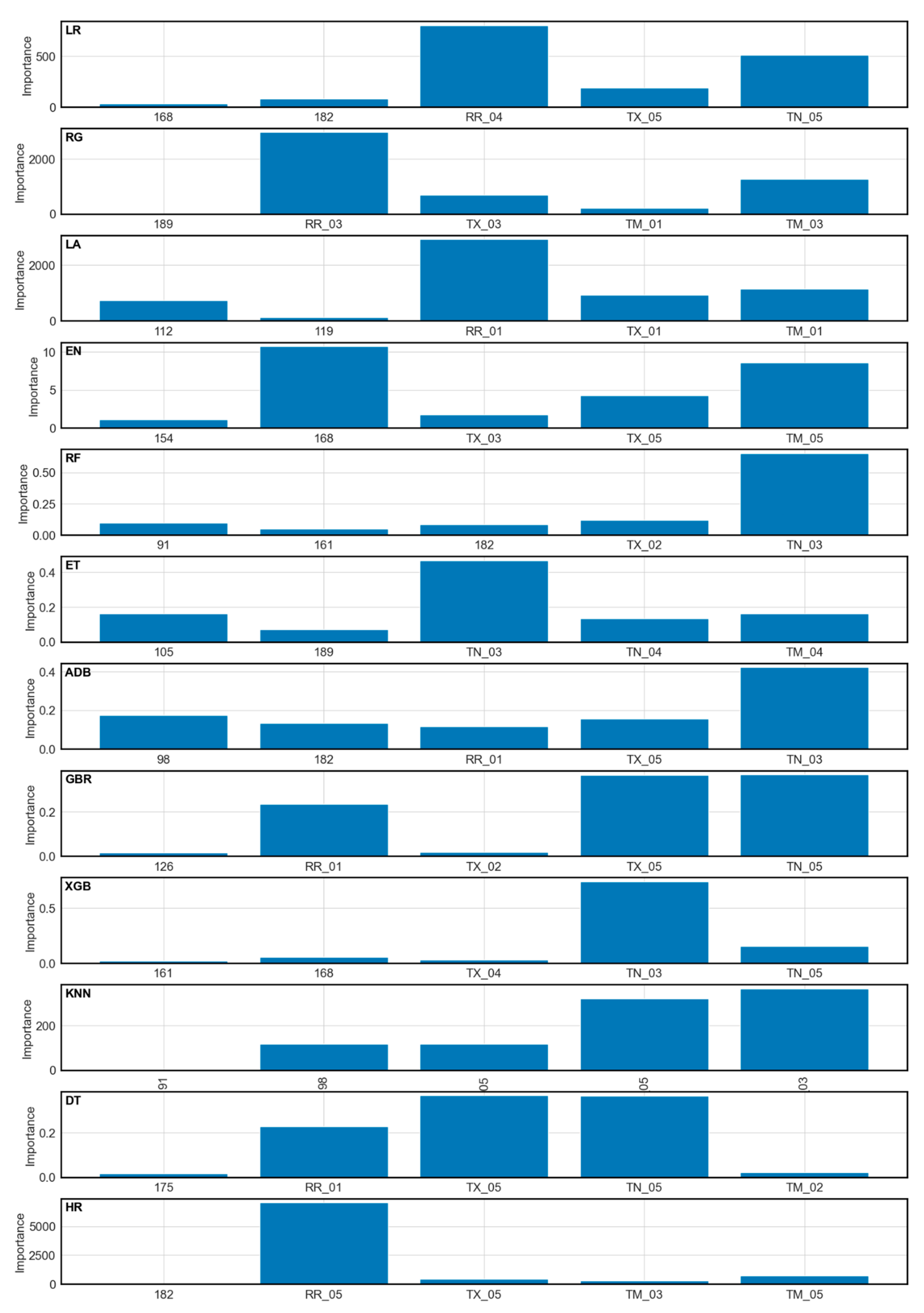
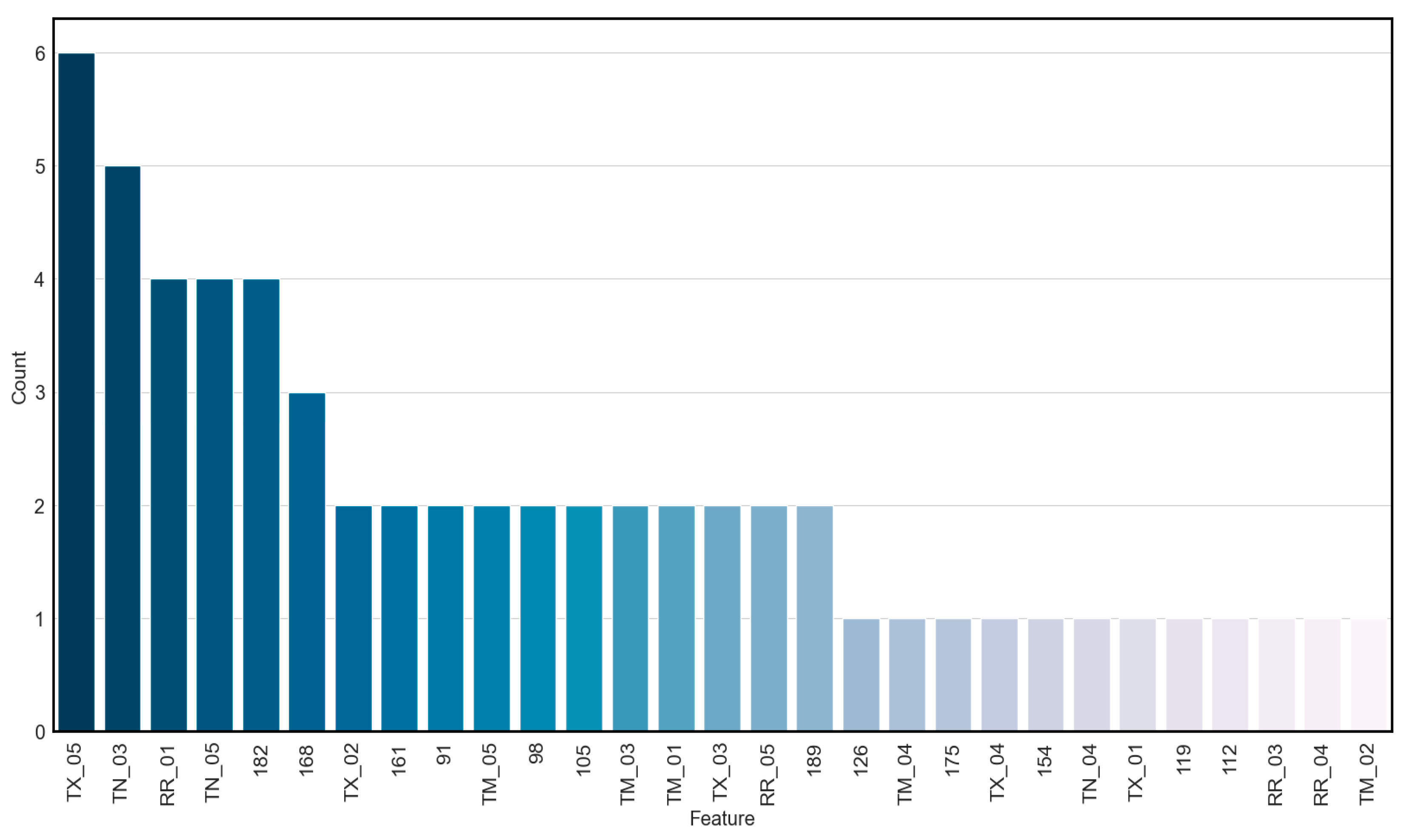
3.4. Feature Importance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diego, B.; Rallo, L. Olive Cultivars in Spain. HortTechnology 2000, 10, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langgut, D.; Cheddadi, R.; Carrión, J.S.; Cavanagh, M.; Colombaroli, D.; Eastwood, W.J.; Greenberg, R.; Litt, T.; Mercuri, A.M.; Miebach, A.; et al. The Origin and Spread of Olive Cultivation in the Mediterranean Basin: The Fossil Pollen Evidence. Holocene 2019, 29, 902–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL/visualize (accessed on 5 February 2024).
- PORDATA—Ambiente de Consulta. Available online: https://www.pordata.pt/db/portugal/ambiente+de+consulta/tabela (accessed on 5 February 2024).
- Portal Do INE. Available online: https://www.ine.pt/xportal/xmain?xpgid=ine_main&xpid=INE (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- EDIA, S.A. Empresa de Desenvolvimento e Infra-estruturas do Alqueva, S.A. Available online: https://www.edia.pt/pt/ (accessed on 9 February 2024).
- Fraga, H.; Pinto, J.G.; Santos, J.A. Olive Tree Irrigation as a Climate Change Adaptation Measure in Alentejo, Portugal. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 237, 106193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ges, A. Sustentabilidade dos Olivais em Portugal: Desafios e Respostas; Princípia Editora: Parede, Portugal, 2022; 174p. [Google Scholar]
- Barros, A.; Cordeiro, A.M.; Inês, C.S.F.; Serra, C.; Sá, C.; Lourenço, E.; Calouro, F.; Pavão, F.A.; Herculano, H. Azeites de Portugal: Guia 2018; Enigma Editores: Lisbon, Portugal, 2018; 96p. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, J.-W. Pollen Allergy in a Changing Planetary Environment. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2022, 14, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łysiak, G.P.; Szot, I. The Use of Temperature Based Indices for Estimation of Fruit Production Conditions and Risks in Temperate Climates. Agriculture 2023, 13, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo, J.; Rapp, A.; Lara, B.; Fernández-González, F.; Pérez-Badia, R. Effect of Land Uses and Wind Direction on the Contribution of Local Sources to Airborne Pollen. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrol, D.P. Pollination Biology: Biodiversity Conservation and Agricultural Production; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; p. 792. [Google Scholar]
- Cruden, R. Pollen Grains: Why so Many? Plant Syst. Evol. 2000, 222, 143–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, J.; Nelson, M.M. Effects of Crop Load, Girdling, and Auxin Application on Alternate Bearing of the Pistachio1. J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 1972, 97, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CuevaS, J.; Rallo, L.; Rapoport, H. Initial Fruit Set at High Temperature in Olive, Olea europaea L. J. Hortic. Sci. 1994, 69, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shdiefat, S.; Qrunfleh, M. Alternate Bearing of the Olive) Olea europaea L.) as Related to Endogenous Hormonal Content. Jordan. J. Agric. Sci. 2008, 4, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Benlloch-González, M.; Sánchez-Lucas, R.; Benlloch, M.; Ricardo, F.-E. An Approach to Global Warming Effects on Flowering and Fruit Set of Olive Trees Growing under Field Conditions. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 240, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelle, R. The Flowering Process and Its Control. Acta Hortic. 1984, 149, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Camba, R.; Sánchez, C.; Vidal, N.; Vielba, J.M. Plant Development and Crop Yield: The Role of Gibberellins. Plants 2022, 11, 2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trigo, M.M.; Jato, V.; Fernández, D.; Galán, C. Atlas Aeropalinológico de España; Secretariado de Publicaciones de la Universidad de Leon: Leon, Spain, 2008; ISBN 978-84-9773-403-5. [Google Scholar]
- del Carmen Fernández, M.; Romero-García, A.T.; Rodríguez-García, M.I. Aperture Structure, Development and Function in Lycopersicum Esculentum Miller (Solanaceae) Pollen Grain. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 1992, 72, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacini, E.; Juniper, B.E. The Ultrastructure of Pollen-Grain Development in the Olive (Olea europaea). 2. Secretion by the Tapetal Cells. New Phytol. 1979, 83, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Vilches, E.; Infante, F.; Galán, C.; Pasadas, F.; Torre, F. Variations in the Concentration of Airborne Olea Pollen and Associated Pollinosis in Cordoba (Spain): A Study of the 10-Year Period 1982–1991. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. Off. Organ Int. Assoc. Asthmology (INTERASMA) Soc. Latinoam. Alerg. Inmunol. 1993, 3, 121–129. [Google Scholar]
- Florido, J.F.; Delgado, P.G.; de San Pedro, B.S.; Quiralte, J.; de Saavedra, J.M.; Peralta, V.; Valenzuela, L.R. High Levels of Olea europaea Pollen and Relation with Clinical Findings. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1999, 119, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlandi, F.; Garcia-Mozo, H.; Ben Dhiab, A.; Galán, C.; Msallem, M.; Fornaciari, M. Olive Tree Phenology and Climate Variations in the Mediterranean Area over the Last Two Decades. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 115, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, F.; Fornaciari, M.; Ruiz-Valenzuela, L.; Galán, C.; Msallem, M.; Dhiab, A.B.; la Guardia, C.D.; Del Mar Trigo, M.; Bonofiglio, T.; Orlandi, F. Phenological Models to Predict the Main Flowering Phases of Olive (Olea europaea L.) along a Latitudinal and Longitudinal Gradient across the Mediterranean Region. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2015, 59, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán, C.; Vázquez, L.; García-Mozo, H.; Domínguez, E. Forecasting Olive (Olea europaea) Crop Yield Based on Pollen Emission. Field Crops Res. 2004, 86, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán, C.; Garcia-Mozo, H.; Vazquez, L.; Valenzuela, L.; Guardia, C.; Dominguez-Vilches, E. Modeling Olive Crop Yield in Andalusia, Spain. Agron. J. 2008, 100, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, H.; Cunha, M.; Calado, L.; Abreu, I. Pollen Morphology and Quality of Twenty Olive (Olea europaea L.) Cultivars Grown in Portugal. Acta Hortic. 2012, 949, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minero, F.J.G.; Candau, P.; Morales, J.; Tomas, C. Forecasting Olive Crop Production Based on Ten Consecutive Years of Monitoring Airborne Pollen in Andalusia (Southern Spain). Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1998, 69, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Ali, S. A New Crop Yield Forecasting Model Based on Satellite Measurements Applied across the Indus Basin, Pakistan. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 94, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cour, P.; Van Campo, M. Previsions de Recoltes a Partir de l’analyse Du Contenu Pollinique de l’atmosphere [Intensite de La Pollinisation]. Comptes Rendus Hebd. Des Seances De L’academie Des Sciences. Ser. D 1980, 290, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilera, F.; Ruiz-Valenzuela, L. Forecasting Olive Crop Yields Based on Long-Term Aerobiological Data Series and Bioclimatic Conditions for the Southern Iberian Peninsula. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2014, 12, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, J.; Teixeira Santos, M.; Carneiro, L.C.; Fevereiro, P.; Eiras-Dias, J.E. Portuguese Traditional Grapevine Cultivars and Wild Vines (Vitis vinifera L.) Share Morphological and Genetic Traits. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2009, 56, 975–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Mozo, H.; Dominguez-Vilches, E.; Galan, C. A Model to Account for Variations in Holm-Oak (Quercus Ilex Subsp. Ballota) Acorn Production in Southern Spain. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2012, 19, 403–408. [Google Scholar]
- Oteros, J.; García-Mozo, H.; Hervás, C.; Galán, C. Biometeorological and Autoregressive Indices for Predicting Olive Pollen Intensity. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2013, 57, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, H.; Guimarães, N.; Freitas, T.R.; Malheiro, A.C.; Santos, J.A. Future Scenarios for Olive Tree and Grapevine Potential Yields in the World Heritage Côa Region, Portugal. Agronomy 2022, 12, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, H.; Pinto, J.G.; Viola, F.; Santos, J.A. Climate Change Projections for Olive Yields in the Mediterranean Basin. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas Gómez, M.D.L.M.; Moral, J.; López-Orozco, R.; Cabello, D.; Oteros, J.; Diego, B.; Galán, C.; Díez, C. Pollen Production in Olive Cultivars and Its Interannual Variability. Ann. Bot. 2023, 132, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oteros, J.; Orlandi, F.; García-Mozo, H.; Aguilera, F.; Dhiab, A.; Bonofiglio, T.; Abichou, M.; Ruiz-Valenzuela, L.; Trigo, M.; Díaz de La Guardia, C.; et al. Better Prediction of Mediterranean Olive Production Using Pollen-Based Models. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, H.; Cunha, M.; Abreu, I. Quantitative Forecasting of Olive Yield in Northern Portugal Using a Bioclimatic Model. Aerobiologia 2008, 24, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirst, J.M. An Automatic Volumetric Spore Trap. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1952, 39, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, H.; Cunha, M.; Abreu, I. Definition of Main Pollen Season Using a Logistic Model. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2007, 14, 259–264. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha, M.; Ribeiro, H.; Costa, P.; Abreu, I. A Comparative Study of Vineyard Phenology and Pollen Metrics Extracted from Airborne Pollen Time Series. Aerobiologia 2015, 31, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornes, R.C.; Van Der Schrier, G.; Van Den Besselaar, E.J.M.; Jones, P.D. An Ensemble Version of the E-OBS Temperature and Precipitation Data Sets. JGR Atmos. 2018, 123, 9391–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstra, N.; Haylock, M.; New, M.; Jones, P.D. Testing E-OBS European High-Resolution Gridded Data Set of Daily Precipitation and Surface Temperature. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction; Springer Series in Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-0-387-21606-5. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, V.P.M.; Edwards, A.L. An Introduction to Linear Regression and Correlation; Books in Psychology; W. H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 1976; ISBN 978-0-7167-0562-8. [Google Scholar]
- Hilt, D.E.; Seegrist, D.W.; United States. Forest Service; Northeastern Forest Experiment Station (Radnor, Pa.). In Ridge, a Computer Program for Calculating Ridge Regression Estimates; Dept. of Agriculture, Forest Service, Northeastern Forest Experiment Station: Upper Darby, PA, USA, 1977; Volume 236. [Google Scholar]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression Shrinkage and Selection via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Society. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Hastie, T. Regularization and Variable Selection Via the Elastic Net. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2005, 67, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, J. Huber Robust Estimation of a Location Parameter. Ann. Math. Stat. 1964, 35, 73–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerome, H. Friedman Greedy Function Approximation: A Gradient Boosting Machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomatine, D.P.; Shrestha, D.L. AdaBoost.RT: A Boosting Algorithm for Regression Problems. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IEEE Cat. No.04CH37541), Budapest, Hungary, 25–29 July 2004; Volume 2, pp. 1163–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, V.; Liu, Z.; Guo, C.; Mita, S.; Kidono, K. Real-Time Lane Estimation Using Deep Features and Extra Trees Regression; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 721–733. [Google Scholar]
- Fix, E.; Hodges, J.L. Discriminatory Analysis: Nonparametric Discrimination: Consistency Properties; USAF School of Aviation Medicine: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Studer, M.; Ritschard, G.; Gabadinho, A.; Nicolas, S. Müller Discrepancy Analysis of State Sequences. Sociol. Methods Res. 2011, 40, 471–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, R.L.; Tadlock, J. Mostly Harmless Statistics; Lulu.com: Morrisville, NC, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-1-71639-891-9. [Google Scholar]
- Fraga, H.; Guimarães, N.; Santos, J. Vintage Port Prediction and Climate Change Scenarios. OENO One 2023, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K. Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; Volume 58. [Google Scholar]
- Cover, T.M.; Thomas, J.A. Elements of Information Theory; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-1-118-58577-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, H.; Abreu, I.; Cunha, M. Olive Crop-Yield Forecasting Based on Airborne Pollen in a Region Where the Olive Groves Acreage and Crop System Changed Drastically. Aerobiologia 2017, 33, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, F.; Romano, B.; Fornaciari, M. Relationship between Pollen Emission and Fruit Production in Olive (Olea europaea L.). Grana 2005, 44, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Dhiab, A.; Ben Mimoun, M.; Oteros, J.; Garcia-Mozo, H.; Domínguez-Vilches, E.; Galán, C.; Abichou, M. Modeling olive-crop forecasting in Tunisia. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 128, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, J.C.; Tíscar, P.A. Climate Change Impacts and Vulnerability of the Southern Populations of Pinus nigra Subsp. Salzmannii. Tree Physiol. 2010, 30, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alba, F.; De La Guardia, C.D.; Comtois, P. The Effect of Meteorological Parameters on Diurnal Patterns of Airborne Olive Pollen Concentration. Grana 2000, 39, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, L.M.; Galán, C.; Domínguez-Vilches, E. Influence of Meteorological Parameters on Olea Pollen Concentrations in Córdoba (South-Western Spain). Int. J. Biometeorol. 2003, 48, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatfield, J.L.; Boote, K.J.; Kimball, B.A.; Ziska, L.H.; Izaurralde, R.C.; Ort, D.; Thomson, A.M.; Wolfe, D. Climate Impacts on Agriculture: Implications for Crop Production. Agron. J. 2011, 103, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Ruiz, M.; Martínez-Guanter, J.; Upadhyaya, S.K. Chapter 15—High-Precision GNSS for Agricultural Operations. In GPS and GNSS Technology in Geosciences; Petropoulos, G.P., Srivastava, P.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 299–335. ISBN 978-0-12-818617-6. [Google Scholar]

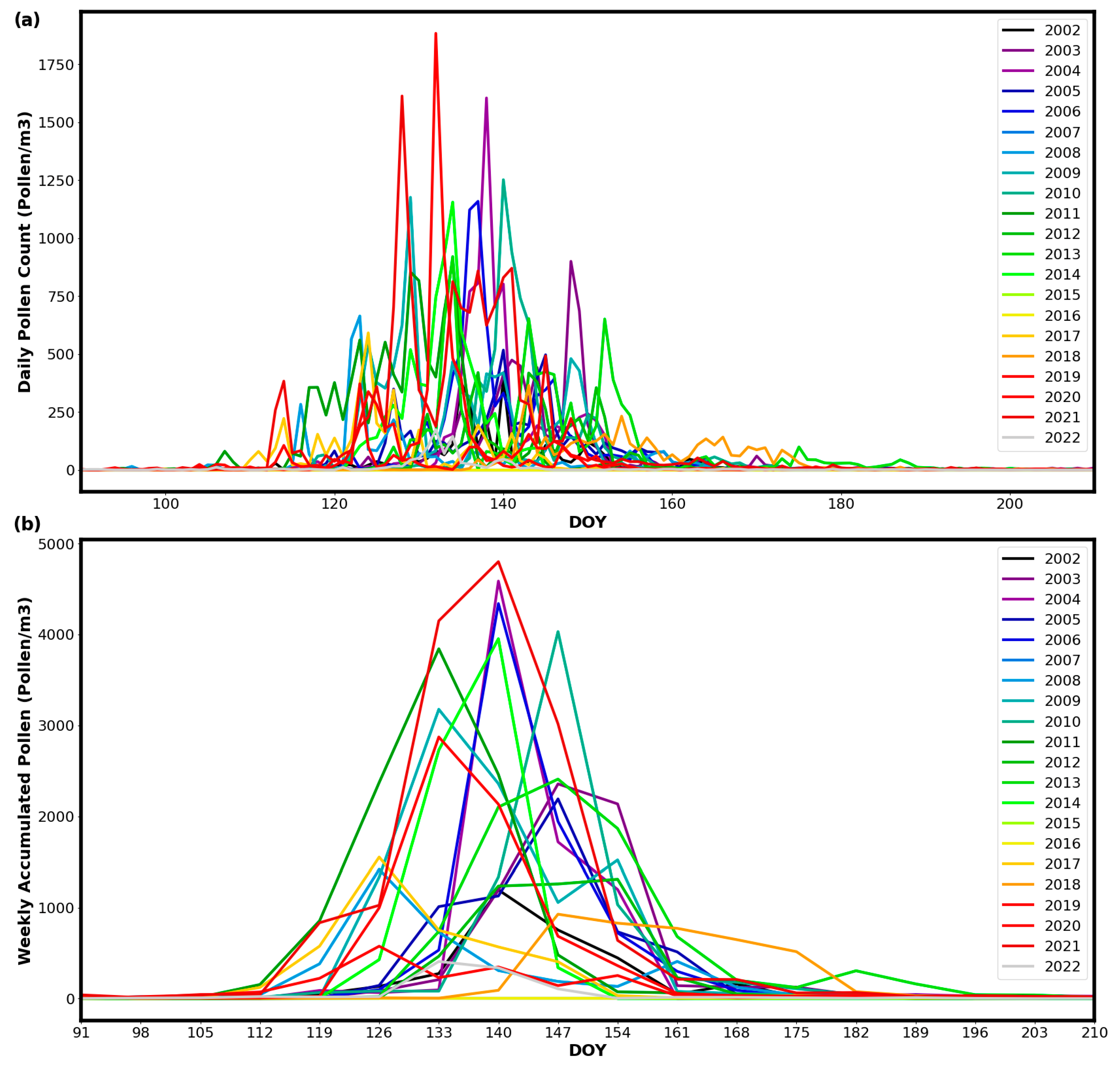

| Year | Start Date | Start DOY | End Date | End DOY | PSD (Days) | Peak Date | Peak DOY | Peak Value (Pollen/m3) | SPIn, (Pollen/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2002 | 02/05 | 123 | 05/06 | 157 | 35 | 20/05 | 141 | 396 | 2789 |
| 2003 | 10/05 | 131 | 06/06 | 158 | 28 | 28/05 | 149 | 900 | 5933 |
| 2004 | 06/05 | 127 | 05/06 | 157 | 31 | 18/05 | 139 | 1605 | 8201 |
| 2005 | 03/05 | 124 | 08/06 | 160 | 37 | 20/05 | 141 | 517 | 5567 |
| 2006 | 07/05 | 128 | 30/05 | 151 | 24 | 17/05 | 138 | 1159 | 7340 |
| 2008 | 14/04 | 105 | 03/06 | 155 | 51 | 03/05 | 124 | 664 | 3246 |
| 2009 | 26/04 | 117 | 01/06 | 153 | 37 | 09/05 | 130 | 1176 | 9435 |
| 2010 | 12/05 | 133 | 31/05 | 152 | 20 | 20/05 | 141 | 1252 | 6255 |
| 2011 | 24/04 | 115 | 22/05 | 143 | 29 | 14/05 | 135 | 906 | 9737 |
| 2012 | 07/05 | 128 | 08/06 | 160 | 33 | 17/05 | 138 | 420 | 4489 |
| 2013 | 02/05 | 123 | 15/06 | 167 | 45 | 14/05 | 135 | 920 | 8009 |
| 2014 | 04/05 | 125 | 24/05 | 145 | 21 | 14/05 | 135 | 1155 | 7483 |
| 2017 | 17/04 | 108 | 25/05 | 146 | 39 | 04/05 | 125 | 591 | 3967 |
| 2018 | 11/05 | 132 | 28/06 | 180 | 49 | 23/05 | 144 | 365 | 3855 |
| 2019 | 01/05 | 122 | 24/05 | 145 | 24 | 12/05 | 133 | 1884 | 6420 |
| 2020 | 11/04 | 102 | 07/06 | 159 | 58 | 03/05 | 124 | 372 | 1896 |
| 2021 | 26/04 | 117 | 01/06 | 153 | 37 | 08/05 | 129 | 1613 | 13,718 |
| 2022 | 01/05 | 122 | 24/05 | 145 | 24 | 12/05 | 133 | 174 | 869 |
| Avg | 30/04 | 121 | 03/06 | 155 | 35 | 14/05 | 135 | 893 | 6067 |
| Group | Algorithms | Acronym |
|---|---|---|
| Linear | Linear Regression | LR |
| Ridge Regression | RG | |
| Lasso Regression | LA | |
| ElasticNet Regression | EN | |
| Huber Regression | HR | |
| Bagging | Random Forest Regression | RF |
| Extra Trees Regression | ET | |
| Boosting | Gradient Boosting Regression | GBR |
| AdaBoost Regression | ADB | |
| XGBoost Regression | XGB | |
| Other | Nearest Neighbors Regression | KNN |
| Decision Tree Regression | DT |
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| 91 | Pollen Accumulation—DOY 91–97 (1st week of April) |
| 98 | Pollen Accumulation—DOY 98–104 (2nd week of April) |
| 105 | Pollen Accumulation—DOY 105–111 (3rd week of April) |
| 112 | Pollen Accumulation—DOY 112–118 (4th week of April) |
| 119 | Pollen Accumulation—DOY 119–125 (1st week of May) |
| 126 | Pollen Accumulation—DOY 126–132 (2nd week of May) |
| 133 | Pollen Accumulation—DOY 133–139 (3rd week of May) |
| 140 | Pollen Accumulation—DOY 140–146 (4th week of May) |
| 147 | Pollen Accumulation—DOY 147–153 (1st week of June) |
| 154 | Pollen Accumulation—DOY 154–160 (2nd week of June) |
| 161 | Pollen Accumulation—DOY 161–167 (3rd week of June) |
| 168 | Pollen Accumulation—DOY 168–174 (4th week of June) |
| 175 | Pollen Accumulation—DOY 175–181 (5th week of June) |
| 182 | Pollen Accumulation—DOY 182–188 (1st week of July) |
| 189 | Pollen Accumulation—DOY 189–195 (2nd week of July) |
| TX_01 | Maximum Temperature—January |
| TN_01 | Minimum Temperature—January |
| TM_01 | Mean Temperature—January |
| RR_01 | Precipitation—January |
| TX_02 | Maximum Temperature—February |
| TN_02 | Minimum Temperature—February |
| TM_02 | Mean Temperature—February |
| RR_02 | Precipitation—February |
| TX_03 | Maximum Temperature—March |
| TN_03 | Minimum Temperature—March |
| TM_03 | Mean Temperature—March |
| RR_03 | Precipitation—March |
| TX_04 | Maximum Temperature—April |
| TN_04 | Minimum Temperature—April |
| TM_04 | Mean Temperature—April |
| RR_04 | Precipitation—April |
| TX_05 | Maximum Temperature—May |
| TN_05 | Minimum Temperature—May |
| TM_05 | Mean Temperature—May |
| RR_05 | Precipitation—May |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galveias, A.; Antunes, C.; Costa, A.R.; Fraga, H. Pollen- and Weather-Based Machine Learning Models for Estimating Regional Olive Production. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10060584
Galveias A, Antunes C, Costa AR, Fraga H. Pollen- and Weather-Based Machine Learning Models for Estimating Regional Olive Production. Horticulturae. 2024; 10(6):584. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10060584
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalveias, Ana, Célia Antunes, Ana Rodrigues Costa, and Helder Fraga. 2024. "Pollen- and Weather-Based Machine Learning Models for Estimating Regional Olive Production" Horticulturae 10, no. 6: 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10060584
APA StyleGalveias, A., Antunes, C., Costa, A. R., & Fraga, H. (2024). Pollen- and Weather-Based Machine Learning Models for Estimating Regional Olive Production. Horticulturae, 10(6), 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10060584









