Effect of Lower- versus Higher-Intensity Isometric Handgrip Training in Adults with Hypertension: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
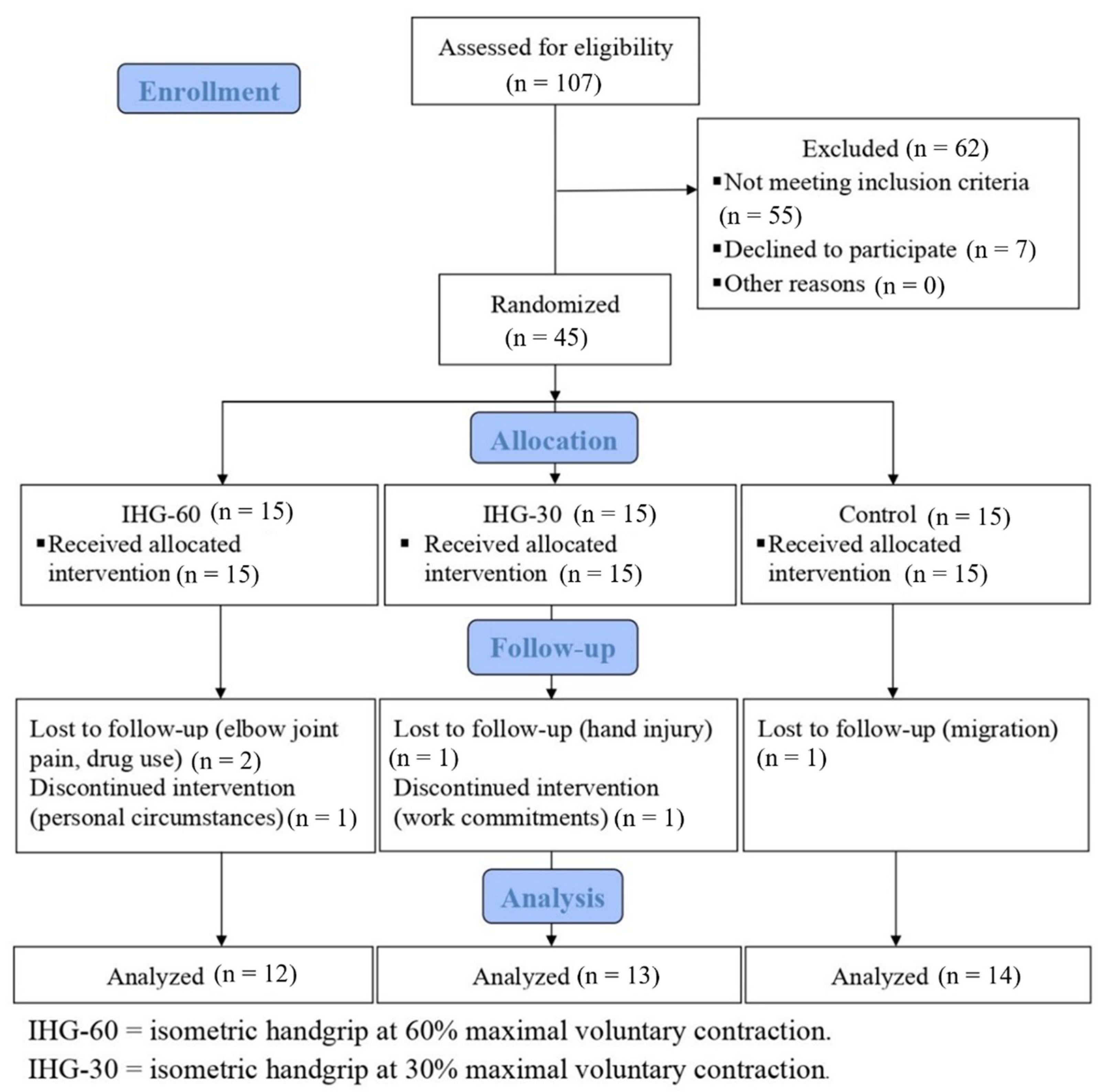
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Intervention
2.3. Pre- and Post-Intervention Assessments
2.4. Blood Pressure Measurement
2.5. Flow-Mediated Dilation Measurement
2.6. Heart Rate Variability Measurement
2.7. Serum Markers of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
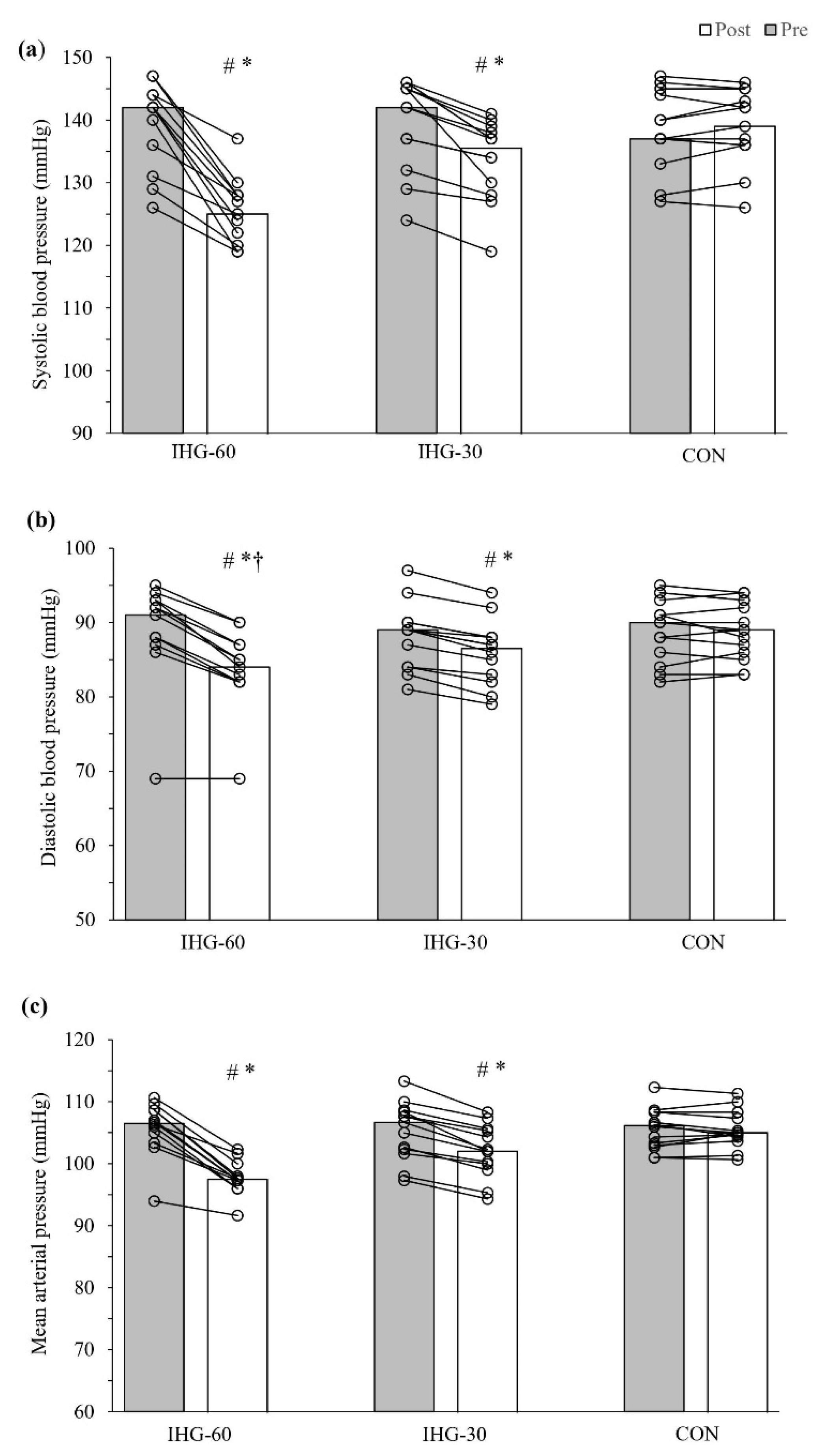
3.1. Blood Pressure
3.2. Flow-Mediated Dilation and Resting Heart Rate
3.3. Heart Rate Variability
3.4. Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joffres, M.; Falaschetti, E.; Gillespie, C.; Robitaille, C.; Loustalot, F.; Poulter, N.; McAlister, F.A.; Johansen, H.; Baclic, O.; Campbell, N. Hypertension prevalence, awareness, treatment and control in national surveys from England, the USA and Canada, and correlation with stroke and ischaemic heart disease mortality: A cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2013, 3, e003423. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Forouzanfar, M.H.; Liu, P.; Roth, G.A.; Ng, M.; Biryukov, S.; Marczak, L.; Alexander, L.; Estep, K.; Hassen Abate, K.; Akinyemiju, T.F.; et al. Global burden of hypertension and systolic blood pressure of at least 110 to 115 mm Hg, 1990–2015. JAMA 2017, 317, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Casey, D.E.; Collins, K.J.; Dennison Himmelfarb, C.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, e127–e248. [Google Scholar]
- Pescatello, L.S.; MacDonald, H.V.; Lamberti, L.; Johnson, B.T. Exercise for Hypertension: A Prescription Update Integrating Existing Recommendations with Emerging Research. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2015, 17, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanssen, H.; Boardman, H.; Deiseroth, A.; Moholdt, T.; Simonenko, M.; Kränkel, N.; Niebauer, J.; Tiberi, M.; Abreu, A.; Solberg, E.E.; et al. Personalized exercise prescription in the prevention and treatment of arterial hypertension: A Consensus Document from the European Association of Preventive Cardiology (EAPC) and the ESC Council on Hypertension. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2022, 29, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, D.J.; Dieberg, G.; Hess, N.C.; Millar, P.J.; Smart, N.A. Isometric exercise training for blood pressure management: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2014, 89, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, V.A.; Smart, N.A. Exercise training for blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2013, 2, e004473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inder, J.D.; Carlson, D.J.; Dieberg, G.; McFarlane, J.R.; Hess, N.C.; Smart, N.A. Isometric exercise training for blood pressure management: A systematic review and meta-analysis to optimize benefit. Hypertens. Res. 2016, 39, 88–94. [Google Scholar]
- Pescatello, L.S.; Buchner, D.M.; Jakicic, J.M.; Powell, K.E.; Kraus, W.E.; Bloodgood, B.; Campbell, W.W.; Dietz, S.; Dipietro, L.; George, S.M.; et al. Physical Activity to Prevent and Treat Hypertension: A Systematic Review. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescatello, L.S.; Buchner, D.M.; Jakicic, J.M.; Powell, K.E.; Kraus, W.E.; Bloodgood Sheppard, B.; Campbell, W.W.; Dietz, S.; Dipietro, L.; George, S.M.; et al. Response. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2020, 52, 1003–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, N.A.; Way, D.; Carlson, D.; Millar, P.; McGowan, C.; Swaine, I.; Baross, A.; Howden, R.; Ritti-Dias, R.; Wiles, J.; et al. Effects of isometric resistance training on resting blood pressure: Individual participant data meta-analysis. J. Hypertens. 2019, 37, 1927–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millar, P.J.; McGowan, C.L.; Cornelissen, V.A.; Araujo, C.G.; Swaine, I.L. Evidence for the Role of Isometric Exercise Training in Reducing Blood Pressure: Potential Mechanisms and Future Directions. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baross, A.W.; Wiles, J.D.; Swaine, I.L. Effects of the intensity of leg isometric training on the vasculature of trained and untrained limbs and resting blood pressure in middle-aged men. Int. J. Vasc. Med. 2012, 964697, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, K.F.; Arthur, S.T.; Swaine, I.; Devereux, G.R.; Huet, Y.M.; Wikstrom, E.; Cordova, M.L.; Howden, R. Intensity-dependent reductions in resting blood pressure following short-term isometric exercise training. J. Sports Sci. 2015, 33, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiles, J.D.; Coleman, D.A.; Swaine, I.L. The effects of performing isometric training at two exercise intensities in healthy young males. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, N.C.; Carlson, D.J.; Inder, J.D.; Jesulola, E.; McFarlane, J.R.; Smart, N.A. Clinically meaningful blood pressure reductions with low intensity isometric handgrip exercise. A randomized trial. Physiol. Res. 2016, 65, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidi, M.; Argani, H.; Ahmadizad, S. Hemodynamic responses to different isometric handgrip protocols in hypertensive men. Sci. Sports 2019, 34, e251–e257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrov, M.B.; Freeman, S.R.; Zokvic, M.A.; Millar, P.J.; McGowan, C.L. Isometric exercise training lowers resting blood pressure and improves local brachial artery flow-mediated dilation equally in men and women. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 116, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, P.J.; Levy, A.S.; McGowan, C.L.; McCartney, N.; MacDonald, M.J. Isometric handgrip training lowers blood pressure and increases heart rate complexity in medicated hypertensive patients. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2013, 23, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, C.L.; Levy, A.S.; Millar, P.J.; Guzman, J.C.; Morillo, C.A.; McCartney, N.; Macdonald, M.J. Acute vascular responses to isometric handgrip exercise and effects of training in persons medicated for hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 291, H1797–H1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, P.G.; Alessio, H.M.; Hagerman, A.E.; Ashton, T.; Nagy, S.; Wiley, R.L. Short-term isometric exercise reduces systolic blood pressure in hypertensive adults: Possible role of reactive oxygen species. Int. J. Cardiol. 2006, 110, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z. Aging, arterial stiffness, and hypertension. Hypertension 2015, 65, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flack, J.M.; Adekola, B. Blood pressure and the new ACC/AHA hypertension guidelines. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 30, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickering, T.G.; Hall, J.E.; Appel, L.J.; Falkner, B.E.; Graves, J.; Hill, M.N.; Jones, D.W.; Kurtz, T.; Sheps, S.G.; Roccella, E.J. Recommendations for Blood Pressure Measurement in Humans and Experimental Animals. Circulation 2005, 111, 697–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicolini, G.; Pizzi, C.; Palma, E.; Bucci, M.; Schioppa, F.; Mezzetti, A.; Manzoli, L. Differences in blood pressure by body position (supine, Fowler’s, and sitting) in hypertensive subjects. Am. J. Hypertens. 2011, 24, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoli, L.; Simonetti, V.; D’Errico, M.M.; De Vito, C.; Flacco, M.E.; Forni, C.; La Torre, G.; Liguori, G.; Messina, G.; Mezzetti, A.; et al. (In)accuracy of blood pressure measurement in 14 Italian hospitals. J. Hypertens. 2012, 30, 1955–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammoud, S.; Karam, R.; Mourad, R.; Saad, I.; Kurdi, M. Stress and Heart Rate Variability during University Final Examination among Lebanese Students. Behav. Sci. 2019, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, F.; McCraty, R.; Zerr, C.L. A healthy heart is not a metronome: An integrative review of the heart’s anatomy and heart rate variability. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loaiza-Betancur, A.F.; Chulvi-Medrano, I. Is Low-Intensity Isometric Handgrip Exercise an Efficient Alternative in Lifestyle Blood Pressure Management? A Systematic Review. Sports Health 2020, 12, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, F.; Müller, P.; Gronwald, T.; Müller, N.G. Dose–Response Matters!—A Perspective on the Exercise Prescription in Exercise–Cognition Research. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osada, T.; Mortensen, S.P.; Rådegran, G. Mechanical compression during repeated sustained isometric muscle contractions and hyperemic recovery in healthy young males. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 2015, 34, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGowan, C.L.; Levy, A.S.; McCartney, N.; MacDonald, M.J. Isometric handgrip training does not improve flow-mediated dilation in subjects with normal blood pressure. Clin. Sci. 2007, 112, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Green, D.J.; Maiorana, A.; O’Driscoll, G.; Taylor, R. Effect of exercise training on endothelium-derived nitric oxide function in humans. J. Physiol. 2004, 561, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badrov, M.B.; Bartol, C.L.; DiBartolomeo, M.A.; Millar, P.J.; McNevin, N.H.; McGowan, C.L. Effects of isometric handgrip training dose on resting blood pressure and resistance vessel endothelial function in normotensive women. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 113, 2091–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeboah, J.; Folsom, A.R.; Burke, G.L.; Johnson, C.; Polak, J.F.; Post, W.; Lima, J.A.; Crouse, J.R.; Herrington, D.M. Predictive value of brachial flow-mediated dilation for incident cardiovascular events in a population-based study: The multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Circulation 2009, 120, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaziri, N.D.; Rodríguez-Iturbe, B. Mechanisms of disease: Oxidative stress and inflammation in the pathogenesis of hypertension. Nat. Clin. Pract. Nephrol. 2006, 2, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.K. Does the Interdependence between Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Explain the Antioxidant Paradox? Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 5698931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiger, R.E.; Miller, J.P.; Bigger, J.T., Jr.; Moss, A.J. Decreased heart rate variability and its association with increased mortality after acute myocardial infarction. Am. J. Cardiol. 1987, 59, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umetani, K.; Singer, D.H.; McCraty, R.; Atkinson, M. Twenty-four hour time domain heart rate variability and heart rate: Relations to age and gender over nine decades. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1998, 31, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, F.; Ginsberg, J.P. An Overview of Heart Rate Variability Metrics and Norms. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.E.; Boushey, C.; Bruemmer, B.; Archer, S.L. Publishing nutrition research: A review of nonparametric methods, part 3. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2008, 108, 1488–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| IHG-60 (n = 12) | IHG-30 (n = 13) | CON (n = 14) | Between-Groups | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Pre | Post | Delta Score | Pre | Post | Delta Score | Pre | Post | Delta Score | p-Value |
| FMD (%) | 5.65 (3.15, 7.35) | 9.18 (5.0, 12.99) | 4.05 (1.65, 5.45), p = 0.002 ** | 5.83 (4.46, 7.07) | 8.15 (6.52, 9.89) | 2.17 (1.69, 2.63), p = 0.001 ** | 6.04 (4.66, 6.83) | 5.54 (4.2, 6.6) | −0.34 (−0.69, 0.05), p = 0.03 * | X2 = 27.29, p < 0.001 ** |
| Resting HR (bpm) | 71.5 (65.5, 78.0) | 67.0 (61.75, 73.75) | −4.0 (−5.0, −4.0), p = 0.002 ** | 74.0 (67.5, 77.5) | 72.0 (65.5, 75.5) | −2.0 (−2.5, −1.0), p = 0.001 ** | 76.0 (67.75, 78.5) | 75.0 (67.25, 80.25) | 1.0 (−1.0, 1.0), p = 0.516 | X2 = 21.70, p < 0.001 ** |
| Heart rate variability | ||||||||||
| SDNN (ms) | 54.0 (39.0, 67.25) | 60.50 (44.75, 67.0) | 5.0 (2.0, 11.5), p = 0.017 ** | 54.0 (40.5, 77.0) | 55.0 (44.0, 78.0) | 4.0 (1.5, 6.5), p = 0.002 ** | 53.0 (48.5, 64.5) | 57.0 (52.5, 64.75) | 4.5 (2.75, 6.25), p = 0.002 ** | X2 = 0.86, p = 0.652 |
| PNN50 (%) | 16.0 (13.25, 19.50) | 18.0 (14.5, 21.75) | 2.0 (1.0, 3.0), p = 0.005 ** | 18.0 (14.0, 24.0) | 18.0 (16.0, 26.5) | 2.0 (0, 3.0), p = 0.019 * | 17.5 (14.75, 20.25) | 20.5 (16.75, 21.5) | 2.0 (1.0, 3.0), p = 0.001 ** | X2 = 0.58, p = 0.750 |
| HF (nu) | 705.50 (403.50, 879.50) | 674.0 (442.5, 927.5) | 72.0 (−60.0, 120.75), p = 0.347 | 812.0 (355.0, 935.0) | 793.0 (407.0, 991.0) | 48.0 (−4.5, 76.0), p = 0.036 * | 678.0 (566.75, 792.0) | 715.5 (648.75, 840.0) | 37.5 (3.0, 69.75), p = 0.109 | X2 = 1.23, p = 0.541 |
| LF (nu) | 1378.0 (996.0, 2104.0) | 1329.5 (893.0, 2002.5) | −89.5 (−104.75, −11.5), p = 0.015 * | 1320.0 (983.5, 2022.0) | 1312.0 (945.5, 2013.0) | −24.0 (−56.5, −6.5), p = 0.087 | 1267.0 (1066.75, 1717.75) | 1260.5 (1028.75, 1648.75) | −46.0 (−74,25, −15.0), p = 0.002 ** | X2 = 3.51, p = 0.173 |
| LF/HF | 2.4 (1.38, 4.58) | 2.0 (1.43, 2.98) | −0.3 (−0.73, 0.13), p = 0.084 | 1.6 (1.1, 4.8) | 1.7 (1.0, 4.1) | −0.2 (−0.6, −0.02), p = 0.007 ** | 1.9 (1.45, 4.33) | 1.85 (1.5, 3.45) | −0.25 (−0.85, 0.2), p = 0.161 | X2 = 0.16, p = 0.922 |
| IHG-60 (n = 12) | IHG-30 (n = 13) | CON (n = 14) | Between-Group | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Pre | Post | Delta Score | Pre | Post | Delta Score | Pre | Post | Delta Score | p-Value |
| TAC (µmol/lit) | 614.5 (541.75, 773.25) | 598.5 (541.25, 780.5) | 6.0 (−23.5, 19.75), p = 0.754 | 583.0 (496.0, 733.5) | 611.0 (511.0, 734.5) | 1.0 (−19.5, 12.0), p = 0.861 | 519.5 (418.75, 820.0) | 532.0 (429.75, 773.5 | −8.0 (−23.25, 10.75), p = 0.167 | X2 = 1.27, p = 0.531 |
| MDA (µmol/lit) | 21.0 (15.0, 26.5) | 19.0 (16.0, 25.25) | −1.0 (−2.75, 1.0), p = 0.102 | 21.0 (12.5, 24.5) | 17.0 (13.0, 23.5) | −1.0 (−2.0, 1.0), p = 0.265 | 17.5 (12.75, 24.5) | 16.5 (13.0, 23.25) | −0.5 (−3.0, 1.25), p = 0.143 | X2 = 0.12, p = 0.940 |
| CP (nmol/mg) | 2.14 (1.32, 2.32) | 2.06 (1.34, 2.24) | −0.08 (−0.12, −0.07), p = 0.004 ** | 2.17 (1.19, 2.34) | 2.17 (1.21, 2.28) | −0.03 (−0.09, 0.08), p = 0.552 | 1.72 (1.1, 2.36) | 1.63 (1.2, 2.16) | −0.01 (−0.25, 0.08), p = 0.315 | X2 = 3.51, p = 0.173 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 1.41 (1.31, 1.55) | 1.49 (1.35, 1.68) | 0.12 (−0.02, 0.16), p = 0.031 * | 1.53 (1.45, 1.72) | 1.36 (1.22, 1.55) | −0.22 (−0.27, −0.01), p = 0.009 ** | 1.34 (1.22, 1.48) | 1.44 (1.26, 1.58) | 0.07 (−0.09, 0.11), p = 0.431 | X2 = 13.96, p = 0.001 ** |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | 4.65 (3.98, 5.68) | 5.2 (4.23, 5.55 | 0.65 (−0.3, 1.05), p = 0.124 | 4.9 (3.5, 6.15) | 4.7 (3.4, 5.75) | −0.3 (−0.55, 0.05), p = 0.022 * | 4.6 (3.65, 8.18) | 6.25 (4.81, 8.31) | 0.9 (−0.24, 1.53), p = 0.035 * | X2 = 8.15, p = 0.017 * |
| ET-1 (pg/mL) | 1.12 (0.9, 2.08) | 1.08 (0.97, 1.84) | −0.09 (−0.16, 0.01), p = 0.041 * | 1.07 (0.96, 1.54) | 1.12 (0.98, 1.28) | −0.01 (−0.07, 0.07), p = 0.674 | 1.22 (1.02, 1.44) | 1.41 (1.15, 1.66) | 0.1 (−0.05, 0.35), p = 0.059 | X2 = 7.66, p = 0.022 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Javidi, M.; Ahmadizad, S.; Argani, H.; Najafi, A.; Ebrahim, K.; Salehi, N.; Javidi, Y.; Pescatello, L.S.; Jowhari, A.; Hackett, D.A. Effect of Lower- versus Higher-Intensity Isometric Handgrip Training in Adults with Hypertension: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2022, 9, 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd9090287
Javidi M, Ahmadizad S, Argani H, Najafi A, Ebrahim K, Salehi N, Javidi Y, Pescatello LS, Jowhari A, Hackett DA. Effect of Lower- versus Higher-Intensity Isometric Handgrip Training in Adults with Hypertension: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2022; 9(9):287. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd9090287
Chicago/Turabian StyleJavidi, Mohsen, Sajad Ahmadizad, Hassan Argani, Abdolrahman Najafi, Khosrow Ebrahim, Narges Salehi, Yasaman Javidi, Linda S. Pescatello, Alireza Jowhari, and Daniel A. Hackett. 2022. "Effect of Lower- versus Higher-Intensity Isometric Handgrip Training in Adults with Hypertension: A Randomized Controlled Trial" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 9, no. 9: 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd9090287
APA StyleJavidi, M., Ahmadizad, S., Argani, H., Najafi, A., Ebrahim, K., Salehi, N., Javidi, Y., Pescatello, L. S., Jowhari, A., & Hackett, D. A. (2022). Effect of Lower- versus Higher-Intensity Isometric Handgrip Training in Adults with Hypertension: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 9(9), 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd9090287






