Timing of Heparin Administration Modulates Arterial Occlusive Thrombotic Response in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Establishment of Vessel Injury Model
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis:
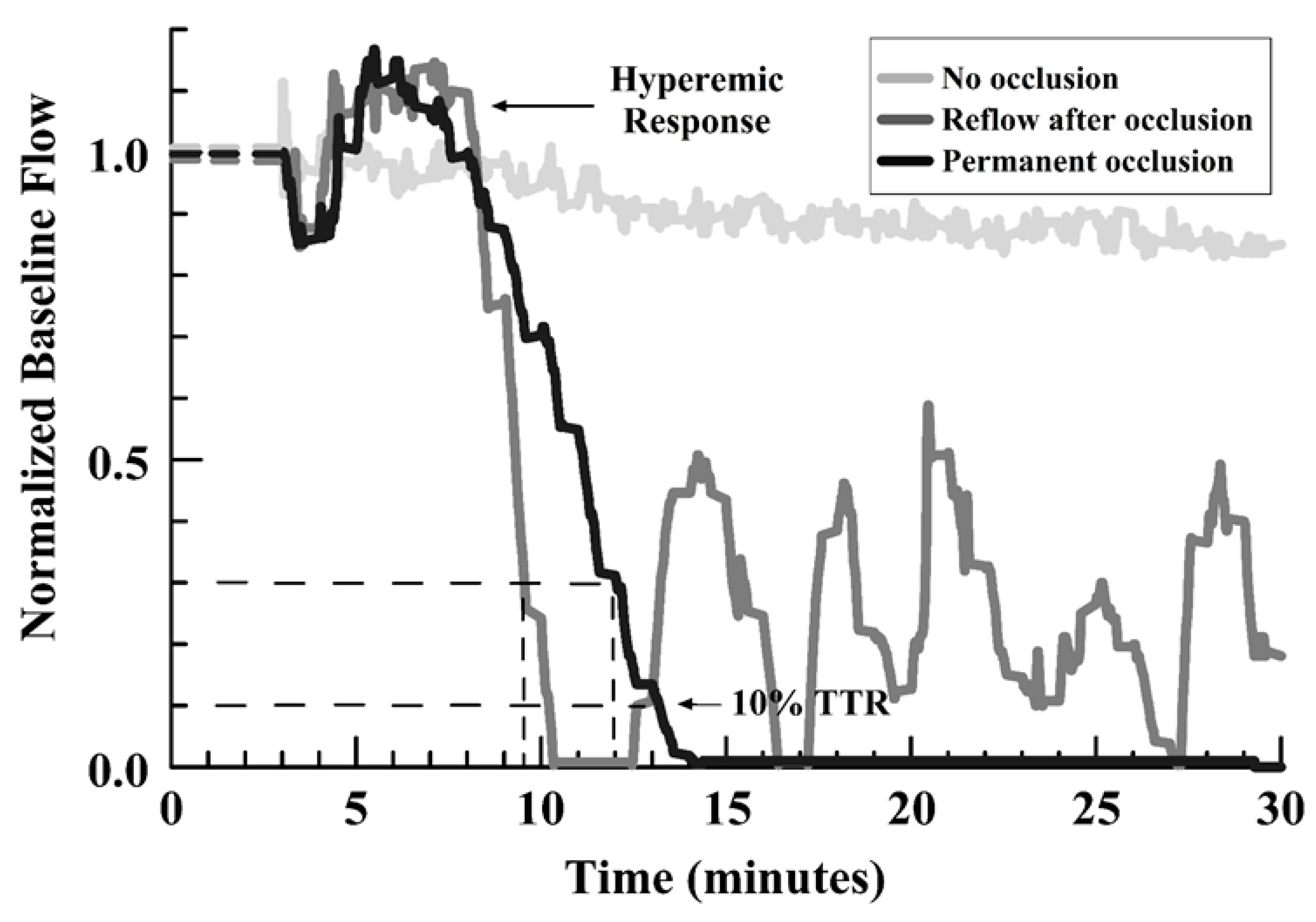
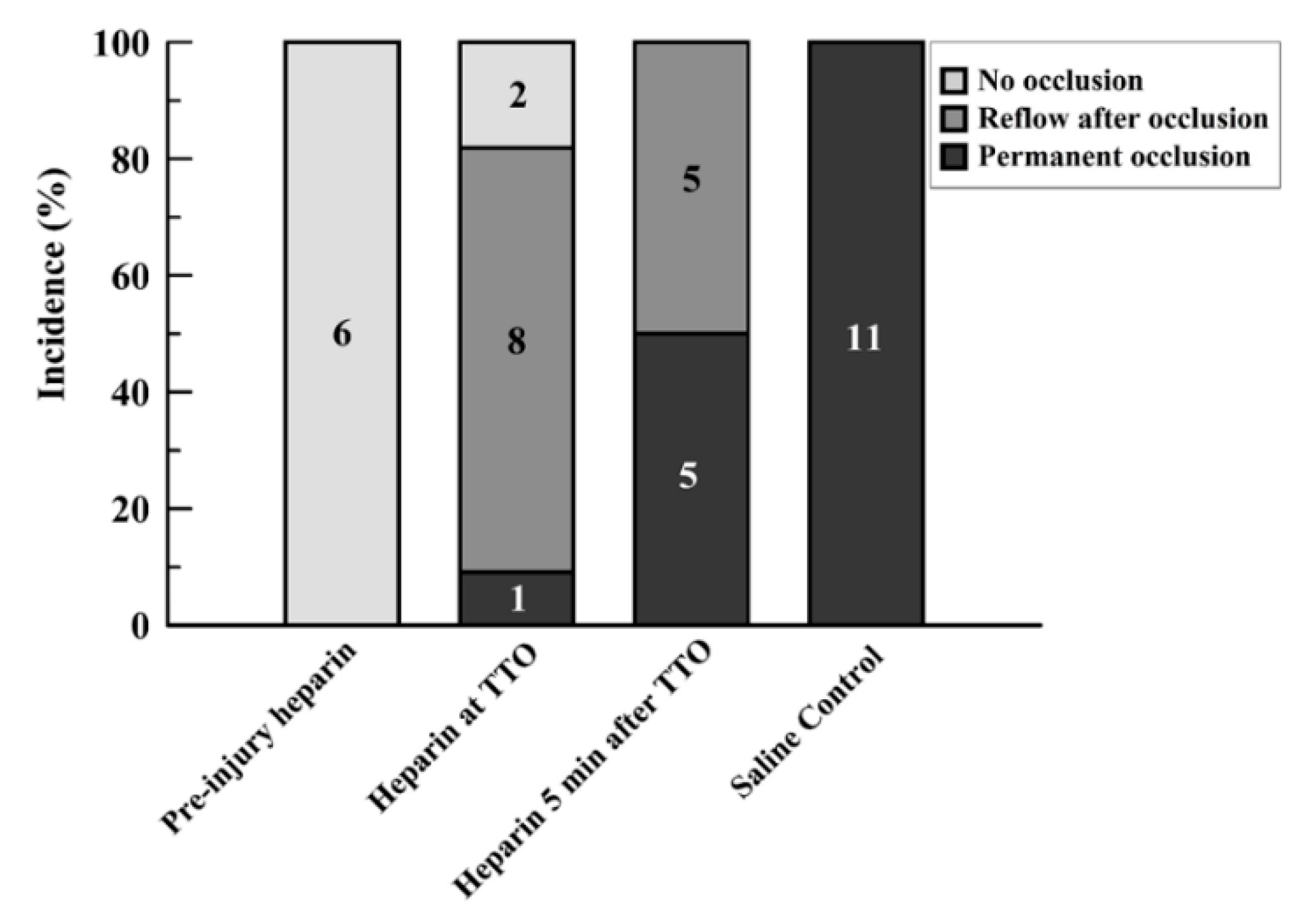
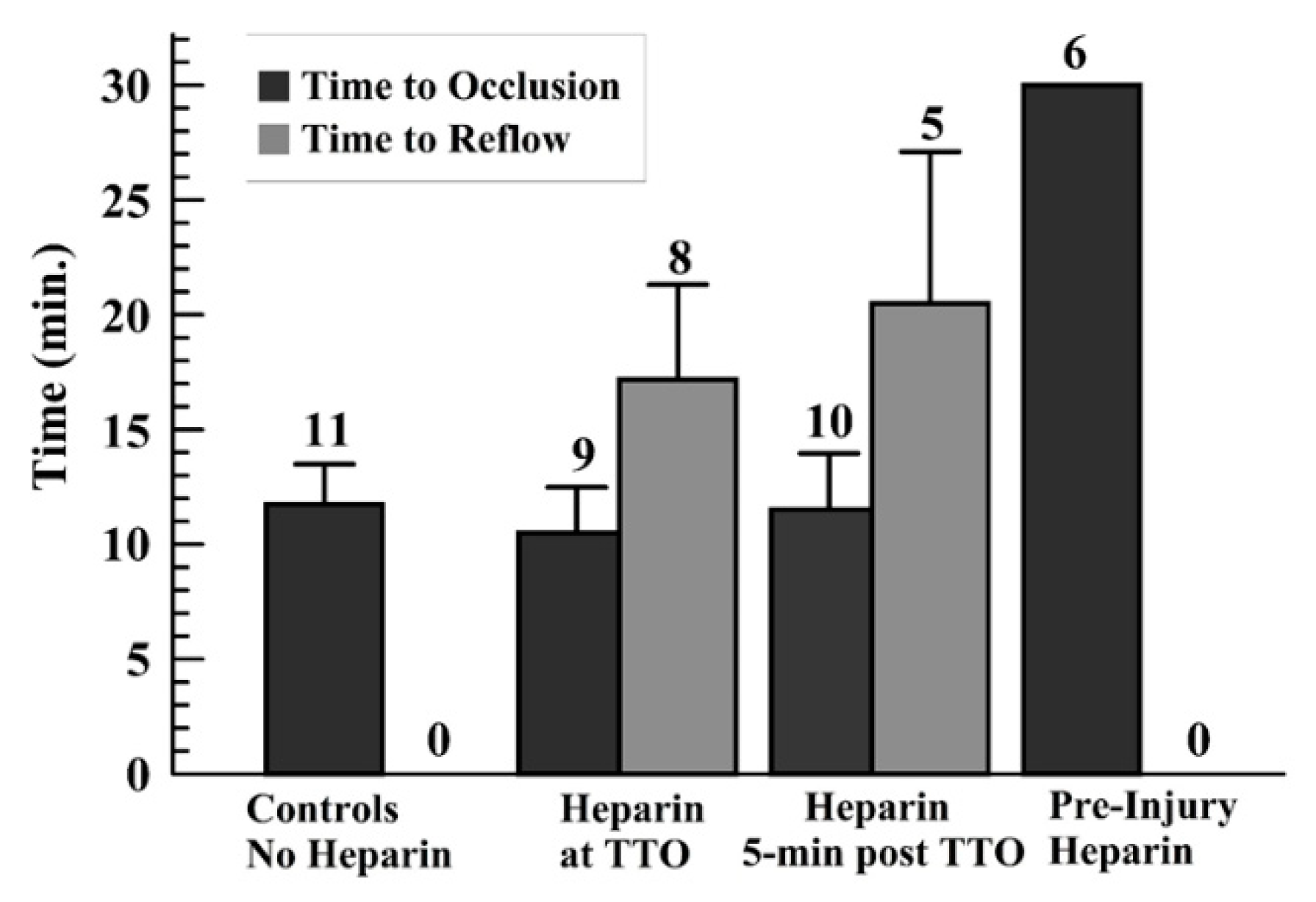
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bucx, J.J.; De Scheerder, I.; Beatt, K.; Brand, M.V.D.; Suryapranata, H.; De Feyter, P.J.; Serruys, P.W. The importance of adequate anticoagulation to prevent early thrombosis after stenting of stenosed venous bypass grafts. Am. Heart J. 1991, 121, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, S.; Andell, P.; Mohammad, M.; Koul, S.; Olivecrona, G.K.; James, S.K.; Fröbert, O.; Erlinge, D. Editor’s Choice- Heparin pre-treatment in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction and the risk of intracoronary thrombus and total vessel occlusion. Insights from the TASTE trial. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2017, 8, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englberger, L.; Streich, M.; Tevaearai, H.; Carrel, T. Different anticoagulation strategies in off-pump coronary artery bypass operations: A European survey. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2008, 7, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hernández, J.M.D.L.T.; Sagredo, M.S.; Arrieta, M.T.; De Carlos, F.G.; Lacuesta, E.S.; Ramírez, J.A.B.; Rocamora, J.P.; Yuste, V.M.; Camarero, T.G.; Larman, M.; et al. Antithrombotic treatment during coronary angioplasty after failed thrombolysis: Strategies and prognostic implications. Results of the RESPIRE registry. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2017, 17, 212. [Google Scholar]
- Frere, C.; Laine, M.; Lemesle, G.; Morange, P.-E.; Paganelli, F.; Dignat-George, F.; Resseguier, N.; Guieu, R.; Camoin-Jau, L.; Bonello, L. Antithrombotic efficacy of bivalirudin compared to unfractionated heparin during percutaneous coronary intervention for acute coronary syndrome. Platelets 2017, 30, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavan, M.V.; Généreux, P.; Kirtane, A.J.; Xu, K.; Witzenbichler, B.; Mehran, R.; Stone, G.W. Is routine post-procedural anticoagulation warranted after primary percutaneous coronary intervention in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction? Insights from the HORIZONS-AMI trial. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2015, 6, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.; Rylance, R.; Karlsson, S.; Koul, S.; Venetsanos, D.; Omerovic, E.; Fröbert, O.; Persson, J.; James, S.; Erlinge, D. Relationship between degree of heparin anticoagulation and clinical outcome in patients receiving potent P2Y12-inhibitors with no planned glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor during percutaneous coronary intervention in acute myocardial infarction: A VALIDATE-SWEDEHEART substudy. Eur. Hear. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2019, 6, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kurz, K.; Main, B.; Sandusky, G. Rat model of arterial thrombosis induced by ferric chloride. Thromb. Res. 1990, 60, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westrick, R.J.; Winn, M.E.; Eitzman, D.T. Murine Models of Vascular Thrombosis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Boil. 2007, 27, 2079–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagadeeswaran, P.; Cooley, B.C.; Gross, P.L.; Mackman, N. Animal Models of Thrombosis From Zebrafish to Nonhuman Primates. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1363–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, J.D.; Chauhan, A.K.; Schaeffer, G.V.; Hansen, J.K.; Motto, D.G. Red blood cells mediate the onset of thrombosis in the ferric chloride murine model. Blood 2013, 121, 3733–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooley, B.C. Murine Arterial Thrombus Induction Mechanism Influences Subsequent Thrombodynamics. Thromb. Res. 2015, 135, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, S.; Ikeda, H.; Haramaki, N.; Yasukawa, H.; Murohara, T.; Imaizumi, T. Platelet P-selectin plays an important role in arterial thrombogenesis by forming large stable platelet-leukocyte aggregates. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 45, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinides, S.; Ware, J.; Marchese, P.; Almus-Jacobs, F.; Loskutoff, D.J.; Ruggeri, Z.M. Distinct antithrombotic consequences of platelet glycoprotein Ibα and VI deficiency in a mouse model of arterial thrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 2014–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresen, D.M.; O’Shaughnessy, M.; Acland, R.D.; Anderson, G.L.; Schuscke, D.; Banis, J.; Barker, J.H. Direct visualization and measurement of microsurgically induced thromboembolism. Microsurgery 1994, 15, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, B.C.; Hansen, F.C. Microvascular repair following local crush and avulsion vascular injury. Microsurgery 1985, 6, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, B.C.; Ruas, E.J.; Wilgis, E.F.S. Scanning electron microscopy of crush/avulsion arterial trauma: Effect of heparin and aspirin administration. Microsurgery 1987, 8, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, B.C.; Li, X.; Dzwierzynski, W.; Gruel, S.M.; Hall, R.L.; Wright, R.R.; O’Brien, E.M.; Fagan, D.; Hanel, D.P.; Gould, J.S. The de-endothelialized rat carotid arterial graft: A versatile experimental model for the investigation of arterial thrombosis. Thromb. Res. 1992, 67, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.S.; Lee, H.W.; Ryuk, J.A.; Ko, B.S. Effects of an Aqueous Extract of Dangguijagyagsan on Serum Lipid Levels and Blood Flow Improvement in Ovariectomized Rats. Evidence-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Abdurahman, A.; Umar, A.; Iskander, G.; Abdusalam, E.; Berke, B.; Begaud, B.; Moore, N. Effects of Cydonia oblonga Miller extracts on blood hemostasis, coagulation and fibrinolysis in mice, and experimental thrombosis in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 154, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiebert, L.M.; Ping, T.; Wice, S.M. Repeated Doses of Oral and Subcutaneous Heparins Have Similar Antithrombotic Effects in a Rat Carotid Arterial Model of Thrombosis. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 17, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.-Y.; Kim, T.-S.; Cai, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Shin, K.; Kim, K.S.; Park, S.K.; Lee, S.-P.; Choi, E.-K.; et al. Nattokinase improves blood flow by inhibiting platelet aggregation and thrombus formation. Lab. Anim. Res. 2013, 29, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.-Y.; Kim, T.-S.; Cai, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Shin, K.; Kim, K.-S.; Lee, S.-P.; Kang, M.-H.; Choi, E.-K.; et al. Perilla oil improves blood flow through inhibition of platelet aggregation and thrombus formation. Lab. Anim. Res. 2014, 30, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heran, C.; Morgan, S.; Kasiewski, C.; Bostwick, J.; Bentley, R.; Klein, S.; Chu, V.; Brown, K.; Colussi, D.; Czekaj, M.; et al. Antithrombotic efficacy of RPR208566, a novel factor Xa inhibitor, in a rat model of carotid artery thrombosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 389, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennan, J.K.; Morgan, G.A.; Swillo, R.E.; Antrilli, T.M.; Mugford, C.; Vlasuk, G.P.; Gardell, S.J.; Crandall, D.L. Effect of tiplaxtinin (PAI-039), an orally bioavailable PAI-1 antagonist in a rat model of thrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 1558–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-J.; Kim, T.; Cho, W.-K.; Ma, J.Y. Antithrombotic and antiplatelet activities of Soshiho-tang extract. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-W.; Yun, J.-W.; Bae, I.-H.; Park, Y.-H.; Jeong, Y.S.; Park, J.W.; Chung, J.-H.; Park, Y.-H.; Lim, K.-M. Evaluation of anti-platelet and anti-thrombotic effects of cilostazol with PFA-100® and Multiplate® whole blood aggregometer in vitro, ex vivo and FeCl3-induced thrombosis models in vivo. Thromb. Res. 2011, 127, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, W.; Yang, H.; Fang, W.; Xi, T.; Li, Y.; Xiong, J. Stimulation of nitric oxide production contributes to the antiplatelet and antithrombotic effect of new peptide pENW (pGlu-Asn-Trp). Thromb. Res. 2015, 136, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinel, C.; Wice, S.M.; Hiebert, L.M. Orally administered heparins prevent arterial thrombosis in a rat model. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 91, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.; Welsh, D.C.; Bickel, D.J.; Lynch, J.J.; Lyle, E. Differential effects of sodium nitroprusside and hydralazine in a rat model of topical FeCl3-induced carotid artery thrombosis. Thromb. Res. 2003, 111, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, P.; Misra, A.; Surin, W.R.; Jain, M.; Bhatta, R.S.; Pal, R.; Raj, K.; Barthwal, M.K.; Dikshit, M. Anti-platelet effects of Curcuma oil in experimental models of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion and thrombosis. Thromb. Res. 2011, 127, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, S.; Ikeda, H.; Haramaki, N.; Yasukawa, H.; Katoh, A.; Imaizumi, T. HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitor Protects Against In Vivo Arterial Thrombosis by Augmenting Platelet-Derived Nitric Oxide Release in Rats. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2005, 45, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tien, A.-J.; Chueh, T.-H.; Chien, C.-T.; Hsia, C.-P. Monascus Adlay and Monacolin K Attenuates Arterial Thrombosis in Rats through the Inhibition of ICAM-1 and Oxidative Stress. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2016, 41, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckly, A.; Hechler, B.; Mangin, P.H.; Freund, M.; Zerr, M.; Cazenave, J.-P.; Lanza, F.; Gachet, C. Mechanisms underlying FeCl3-induced arterial thrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esclamado, R.M.; Carroll, W.R. The pathogenesis of vascular thrombosis and its impact in microvascular surgery. Head Neck 1999, 21, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Meister, D.; Daley, R.A.; Cooley, B.C. Thrombodynamics of Microvascular Repairs: Effects of Antithrombotic Therapy on Platelets and Fibrin. J. Hand Surg. 2013, 38, 1784–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matrai, A.B.; Kastetter, B.; Cooley, B.C. Timing of Heparin Administration Modulates Arterial Occlusive Thrombotic Response in Rats. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2020, 7, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd7010010
Matrai AB, Kastetter B, Cooley BC. Timing of Heparin Administration Modulates Arterial Occlusive Thrombotic Response in Rats. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2020; 7(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd7010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatrai, Amanda B., Bryn Kastetter, and Brian C. Cooley. 2020. "Timing of Heparin Administration Modulates Arterial Occlusive Thrombotic Response in Rats" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 7, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd7010010
APA StyleMatrai, A. B., Kastetter, B., & Cooley, B. C. (2020). Timing of Heparin Administration Modulates Arterial Occlusive Thrombotic Response in Rats. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 7(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd7010010



