Searching for Intrinsic Causality between Colonic Dysbiosis and Non-Ischemic Cardiomyopathy: A Mendelian Randomization-Based Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. GWAS Data
2.2. Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization (TSMR) Design
2.3. Instrument Variables (IVs)
2.4. MR Analysis
2.5. Analysis Result Standard
2.6. Sensitivity Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Selection and Validation of the IVs
3.2. MR Analysis
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Braunwald, E. Cardiomyopathies: An Overview. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekulic, M.; Zacharias, M.; Medalion, B. Ischemic Cardiomyopathy and Heart Failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2019, 12, e006006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.W.; Wang, D.Z. Non-coding RNA in Ischemic and Non-ischemic Cardiomyopathy. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2018, 20, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroni, F.; Gertz, Z.; Azzalini, L. Relief of Ischemia in Ischemic Cardiomyopathy. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2021, 23, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, M.A.; Cook, S.A.; Seidman, J.G.; Seidman, C.E. Clinical and Mechanistic Insights into the Genetics of Cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 2871–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariton, E.; Locascio, J.J. Randomised controlled trials—The gold standard for effectiveness research: Study design: Randomised controlled trials. BJOG 2018, 125, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.W.; Barn, P.K.; Lanphear, B.P. Randomized controlled trials in environmental health research: Unethical or underutilized. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emdin, C.A.; Khera, A.V.; Kathiresan, S. Mendelian Randomization. JAMA 2017, 318, 1925–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Xie, S.-Y.; Liu, K.-Q.; Xu, L.; Zhao, P.-P.; Gai, S.-R.; Guan, P.-L.; Zhao, J.-Q.; Zhu, Y.-P.; Tsoi, L.C.; et al. Systemic evaluation of the relationship between psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and osteoporosis: Observational and Mendelian randomisation study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1460–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekula, P.; Del Greco, M.F.; Pattaro, C.; Köttgen, A. Mendelian Randomization as an Approach to Assess Causality Using Observational Data. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 3253–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandek, A.; Bauditz, J.; Swidsinski, A.; Buhner, S.; Weber-Eibel, J.; von Haehling, S.; Schroedl, W.; Karhausen, T.; Doehner, W.; Rauchhaus, M.; et al. Altered intestinal function in patients with chronic heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 50, 1561–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arutyunov, G.P.; Kostyukevich, O.I.; Serov, R.A.; Rylova, N.V.; Bylova, N.A. Collagen accumulation and dysfunctional mucosal barrier of the small intestine in patients with chronic heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2008, 125, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Zou, J.; Fan, H.; Hu, H.; You, Z. Causal effects of gut microbiota on diabetic retinopathy: A Mendelian randomization study. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 930318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamic, P.; Chaikijurajai, T.; Tang, W. Gut microbiome—A potential mediator of pathogenesis in heart failure and its comorbidities: State-of-the-art review. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2021, 152, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurilshikov, A.; Medina-Gomez, C.; Bacigalupe, R.; Radjabzadeh, D.; Wang, J.; Demirkan, A.; Le Roy, C.I.; Garay, J.A.R.; Finnicum, C.T.; Liu, X.; et al. Large-scale association analyses identify host factors influencing human gut microbiome composition. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Shi, Y.Z.; Liang, J.T.; Lu, L.L.; Chen, M. Modifiable factors for migraine prophylaxis: A mendelian randomization analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1010996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemani, G.; Zheng, J.; Elsworth, B.; Wade, K.H.; Haberland, V.; Baird, D.; Laurin, C.; Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Langdon, R.; et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. Elife 2018, 7, e34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, M.S.; Andrews, S.J.; Elsworth, B.; Gaunt, T.R.; Hemani, G.; Marcora, E. The variant call format provides efficient and robust storage of GWAS summary statistics. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, D.A. Commentary: Two-sample Mendelian randomization: Opportunities and challenges. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 45, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Holmes, M.V. Meta-analysis and Mendelian randomization: A review. Res. Synth. Methods 2019, 10, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.D.; Handsaker, R.E.; Pulit, S.L.; Nizzari, M.M.; O’Donnell, C.J.; de Bakker, P.I. SNAP: A web-based tool for identification and annotation of proxy SNPs using HapMap. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2938–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, T.M.; A Lawlor, D.; Harbord, R.M.; A Sheehan, N.; Tobias, J.H.; Timpson, N.J.; Smith, G.D.; Sterne, J.A. Using multiple genetic variants as instrumental variables for modifiable risk factors. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2012, 21, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawlor, D.A.; Harbord, R.M.; Sterne, J.A.; Timpson, N.; Davey Smith, G. Mendelian randomization: Using genes as instruments for making causal inferences in epidemiology. Stat. Med. 2008, 27, 1133–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Butterworth, A.; Thompson, S.G. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data. Genet. Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: Effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, F.P.; Davey Smith, G.; Bowden, J. Robust inference in summary data Mendelian randomization via the zero modal pleiotropy assumption. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Simone, G.; Devereux, R.B.; Camargo, M.J.; Wallerson, D.C.; Laragh, J.H. Influence of sodium intake on in vivo left ventricular anatomy in experimental renovascular hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. 1993, 264 Pt 2, H2103–H2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbanck, M.; Chen, C.Y.; Neale, B.; Do, R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D.; Phillips, A.N. Meta-analysis: Principles and procedures. BMJ 1997, 315, 1533–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokry, L.E.; Ross, S.; Timpson, N.J.; Sawcer, S.; Davey Smith, G.; Richards, J.B. Obesity and Multiple Sclerosis: A Mendelian Randomization Study. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1002053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vojinovic, D.; Radjabzadeh, D.; Kurilshikov, A.; Amin, N.; Wijmenga, C.; Franke, L.; Ikram, M.A.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Zhernakova, A.; Fu, J.; et al. Relationship between gut microbiota and circulating metabolites in population-based cohorts. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandek, A.; Swidsinski, A.; Schroedl, W.; Watson, A.; Valentova, M.; Herrmann, R.; Scherbakov, N.; Cramer, L.; Rauchhaus, M.; Grosse-Herrenthey, A.; et al. Intestinal blood flow in patients with chronic heart failure: A link with bacterial growth, gastrointestinal symptoms, and cachexia. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 64, 1092–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niebauer, J.; Volk, H.D.; Kemp, M.; Dominguez, M.; Schumann, R.R.; Rauchhaus, M.; Poole-Wilson, P.A.; Coats, A.J.; Anker, S.D. Endotoxin and immune activation in chronic heart failure: A prospective cohort study. Lancet 1999, 353, 1838–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogler, G.; Rosano, G. The heart and the gut. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupu, V.V.; Adam Raileanu, A.; Mihai, C.M.; Morariu, I.D.; Lupu, A.; Starcea, I.M.; Frasinariu, O.E.; Mocanu, A.; Dragan, F.; Fotea, S. The Implication of the Gut Microbiome in Heart Failure. Cells 2023, 12, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Lin, S.L.; Kwok, M.K.; Leung, G.M.; Schooling, C.M. The Roles of 27 Genera of Human Gut Microbiota in Ischemic Heart Disease, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, and Their Risk Factors: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 187, 1916–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.J.; Tsai, W.C.; Hung, W.C.; Hung, W.W.; Chang, C.C.; Dai, C.Y.; Tsai, Y.C. Gut Microbiota and Subclinical Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.V.; Hao, L.; Offermanns, S.; Medzhitov, R. The microbial metabolite butyrate regulates intestinal macrophage function via histone deacetylase inhibition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2247–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hou, L.; Kwak, D.; Fassett, J.; Xu, X.; Chen, A.; Chen, W.; Blazar, B.R.; Xu, Y.; Hall, J.L.; et al. Increasing Regulatory T Cells with Interleukin-2 and Interleukin-2 Antibody Complexes Attenuates Lung Inflammation and Heart Failure Progression. Hypertension 2016, 68, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lu, G.; Li, Z.; Wu, B.; Luo, E.; Qiu, X.; Guo, J.; Xia, Z.; Zheng, C.; Su, Q.; et al. Altered Actinobacteria and Firmicutes Phylum Associated Epitopes in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 632482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.-J.; Xu, Q.; Yan, S.-S.; Han, B.-X.; Zhang, H.; Wei, X.-T.; Feng, G.-J.; Zhao, M.; Pei, Y.-F.; Zhang, L. Gut Microbiota and Psychiatric Disorders: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 737197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraeuter, A.K.; Phillips, R.; Sarnyai, Z. The Gut Microbiome in Psychosis from Mice to Men: A Systematic Review of Preclinical and Clinical Studies. Front. Psychiatry. 2020, 11, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isolauri, E.; Kirjavainen, P.V.; Salminen, S. Probiotics: A role in the treatment of intestinal infection and inflammation. Gut 2002, 50 (Suppl. 3), III54–III59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Hu, Y.; Chen, X.; Luo, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, H. Effects of Gut Microbiota and Metabolites on Heart Failure and Its Risk Factors: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 899746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| ID_Exposure | ID_Outcome | Outcome | Exposure | Egger_Intercept | se | Pval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| class.Actinobacteria.id.419 | I9_CARDMYO | Cardiomyopathy | Actinobacteria | 0.00173501 | 0.01841205 | 0.92647976 |
| genus.Coprobacter.id.949 | I9_CARDMYO | Cardiomyopathy | Coprobacter | 0.03430607 | 0.03066712 | 0.29225305 |
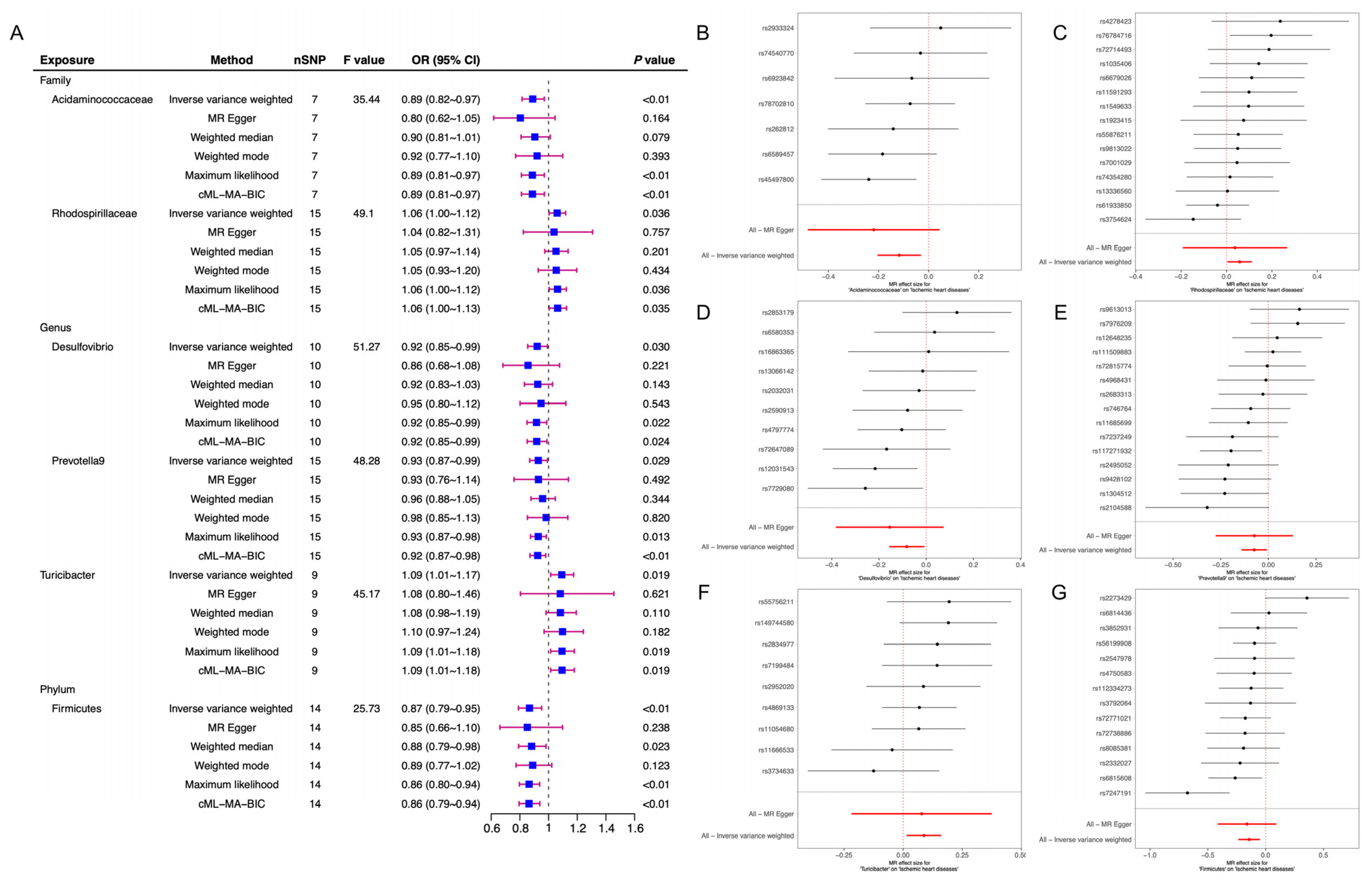
| family.Acidaminococcaceae.id.2166 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Acidaminococcaceae | 0.01072952 | 0.01334403 | 0.45786561 |
| family.Rhodospirillaceae.id.2717 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Rhodospirillaceae | 0.00213828 | 0.01164505 | 0.85714376 |
| genus.Desulfovibrio.id.3173 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Desulfovibrio | 0.00751697 | 0.01143537 | 0.5294142 |
| genus.Prevotella9.id.11183 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Prevotella9 | −0.0001174 | 0.01014531 | 0.9909418 |
| genus.Turicibacter.id.2162 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Turicibacter | 0.00101386 | 0.01577514 | 0.95055273 |
| phylum.Firmicutes.id.1672 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Firmicutes | 0.00143736 | 0.00954687 | 0.88282534 |
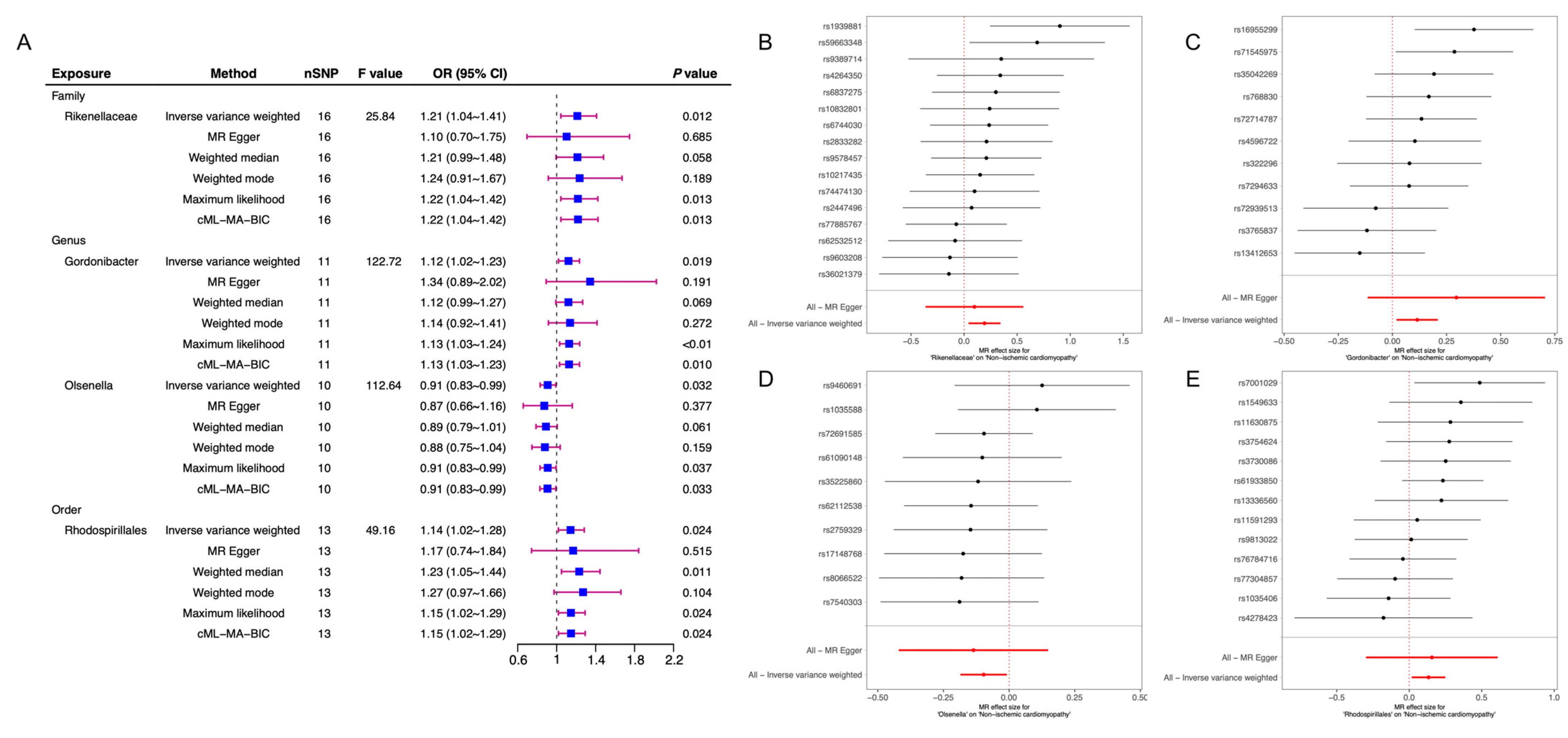
| family.Rikenellaceae.id.967 | I9_NONISCHCARDMYOP | Non-ischemic cardiomyopathy | Rikenellaceae | 0.00710825 | 0.01662915 | 0.67554786 |
| genus.Gordonibacter.id.821 | I9_NONISCHCARDMYOP | Non-ischemic cardiomyopathy | Gordonibacter | −0.0278034 | 0.03120958 | 0.39619398 |
| genus.Olsenella.id.822 | I9_NONISCHCARDMYOP | Non-ischemic cardiomyopathy | Olsenella | 0.00555202 | 0.01966471 | 0.78485406 |
| order.Rhodospirillales.id.2667 | I9_NONISCHCARDMYOP | Non-ischemic cardiomyopathy | Rhodospirillales | −0.0023447 | 0.0228512 | 0.9201207 |
| ID_Exposure | ID_Outcome | Outcome | Exposure | Method | Q | Q_df | Q_pval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| family.Acidaminococcaceae.id.2166 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Acidaminococcaceae | MR Egger | 3.356 | 5.000 | 0.645 |
| family.Acidaminococcaceae.id.2166 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Acidaminococcaceae | IVW | 4.002 | 6.000 | 0.676 |
| family.Rhodospirillaceae.id.2717 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Rhodospirillaceae | MR Egger | 11.409 | 13.000 | 0.577 |
| family.Rhodospirillaceae.id.2717 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Rhodospirillaceae | IVW | 11.442 | 14.000 | 0.651 |
| genus.Desulfovibrio.id.3173 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Desulfovibrio | MR Egger | 8.939 | 8.000 | 0.347 |
| genus.Desulfovibrio.id.3173 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Desulfovibrio | IVW | 9.422 | 9.000 | 0.399 |
| genus.Prevotella9.id.11183 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Prevotella9 | MR Egger | 19.574 | 13.000 | 0.106 |
| genus.Prevotella9.id.11183 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Prevotella9 | IVW | 19.574 | 14.000 | 0.144 |
| genus.Turicibacter.id.2162 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Turicibacter | MR Egger | 5.463 | 7.000 | 0.604 |
| genus.Turicibacter.id.2162 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Turicibacter | IVW | 5.467 | 8.000 | 0.707 |
| phylum.Firmicutes.id.1672 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Firmicutes | MR Egger | 18.581 | 12.000 | 0.099 |
| phylum.Firmicutes.id.1672 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Firmicutes | IVW | 18.616 | 13.000 | 0.135 |
| family.Acidaminococcaceae.id.2166 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Acidaminococcaceae | MR Egger | 3.356 | 5.000 | 0.645 |
| family.Acidaminococcaceae.id.2166 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Acidaminococcaceae | IVW | 4.002 | 6.000 | 0.676 |
| family.Rhodospirillaceae.id.2717 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Rhodospirillaceae | MR Egger | 11.409 | 13.000 | 0.577 |
| family.Rhodospirillaceae.id.2717 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Rhodospirillaceae | IVW | 11.442 | 14.000 | 0.651 |
| genus.Desulfovibrio.id.3173 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Desulfovibrio | MR Egger | 8.939 | 8.000 | 0.347 |
| genus.Desulfovibrio.id.3173 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Desulfovibrio | IVW | 9.422 | 9.000 | 0.399 |
| genus.Prevotella9.id.11183 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Prevotella9 | MR Egger | 19.574 | 13.000 | 0.106 |
| genus.Prevotella9.id.11183 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Prevotella9 | IVW | 19.574 | 14.000 | 0.144 |
| genus.Turicibacter.id.2162 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Turicibacter | MR Egger | 5.463 | 7.000 | 0.604 |
| genus.Turicibacter.id.2162 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Turicibacter | IVW | 5.467 | 8.000 | 0.707 |
| phylum.Firmicutes.id.1672 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Firmicutes | MR Egger | 18.581 | 12.000 | 0.099 |
| phylum.Firmicutes.id.1672 | finngen_R7_I9_ISCHHEART | Ischemic heart diseases | Firmicutes | IVW | 18.616 | 13.000 | 0.135 |
| family.Rikenellaceae.id.967 | I9_NONISCHCARDMYOP | NICM | Rikenellaceae | MR Egger | 11.345 | 14.000 | 0.659 |
| family.Rikenellaceae.id.967 | I9_NONISCHCARDMYOP | NICM | Rikenellaceae | IVW | 11.528 | 15.000 | 0.714 |
| genus.Gordonibacter.id.821 | I9_NONISCHCARDMYOP | NICM | Gordonibacter | MR Egger | 10.943 | 9.000 | 0.280 |
| genus.Gordonibacter.id.821 | I9_NONISCHCARDMYOP | NICM | Gordonibacter | IVW | 11.908 | 10.000 | 0.291 |
| genus.Olsenella.id.822 | I9_NONISCHCARDMYOP | NICM | Olsenella | MR Egger | 4.531 | 8.000 | 0.806 |
| genus.Olsenella.id.822 | I9_NONISCHCARDMYOP | NICM | Olsenella | IVW | 4.611 | 9.000 | 0.867 |
| order.Rhodospirillales.id.2667 | I9_NONISCHCARDMYOP | NICM | Rhodospirillales | MR Egger | 10.019 | 11.000 | 0.529 |
| order.Rhodospirillales.id.2667 | I9_NONISCHCARDMYOP | NICM | Rhodospirillales | IVW | 10.029 | 12.000 | 0.613 |
| Exposure | b | se | T-Stat | Pval |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| class.Actinobacteria.id.419 | −0.208 | 0.063 | −3.311 | 0.006 |
| genus.Coprobacter.id.949 | −0.158 | 0.074 | −2.139 | 0.058 |
| family.Acidaminococcaceae.id.2166 | −0.117 | 0.036 | −3.228 | 0.018 |
| family.Rhodospirillaceae.id.2717 | 0.058 | 0.025 | 2.318 | 0.036 |
| genus.Desulfovibrio.id.3173 | −0.083 | 0.038 | −2.165 | 0.059 |
| genus.Prevotella9.id.11183 | −0.074 | 0.034 | −2.180 | 0.047 |
| genus.Turicibacter.id.2162 | 0.088 | 0.031 | 2.847 | 0.022 |
| phylum.Firmicutes.id.1672 | −0.143 | 0.048 | −3.000 | 0.010 |
| family.Rikenellaceae.id.967 | 0.193 | 0.067 | 2.857 | 0.012 |
| genus.Gordonibacter.id.821 | 0.114 | 0.049 | 2.347 | 0.041 |
| genus.Olsenella.id.822 | −0.097 | 0.032 | −2.993 | 0.015 |
| order.Rhodospirillales.id.2667 | 0.133 | 0.054 | 2.461 | 0.030 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, B.; Yang, Z.-J.; Huang, N.; Zheng, W.-B.; Gui, C. Searching for Intrinsic Causality between Colonic Dysbiosis and Non-Ischemic Cardiomyopathy: A Mendelian Randomization-Based Analysis. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10100420
Qi B, Yang Z-J, Huang N, Zheng W-B, Gui C. Searching for Intrinsic Causality between Colonic Dysbiosis and Non-Ischemic Cardiomyopathy: A Mendelian Randomization-Based Analysis. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2023; 10(10):420. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10100420
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Bin, Zhi-Jie Yang, Nan Huang, Wen-Bo Zheng, and Chun Gui. 2023. "Searching for Intrinsic Causality between Colonic Dysbiosis and Non-Ischemic Cardiomyopathy: A Mendelian Randomization-Based Analysis" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 10, no. 10: 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10100420
APA StyleQi, B., Yang, Z.-J., Huang, N., Zheng, W.-B., & Gui, C. (2023). Searching for Intrinsic Causality between Colonic Dysbiosis and Non-Ischemic Cardiomyopathy: A Mendelian Randomization-Based Analysis. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 10(10), 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10100420





