Assessment of Delirium Using the Confusion Assessment Method in Older Adult Inpatients in Malaysia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cognitive Screening Test
2.2. Confusion Assessment Method
2.3. Statistical Analysis
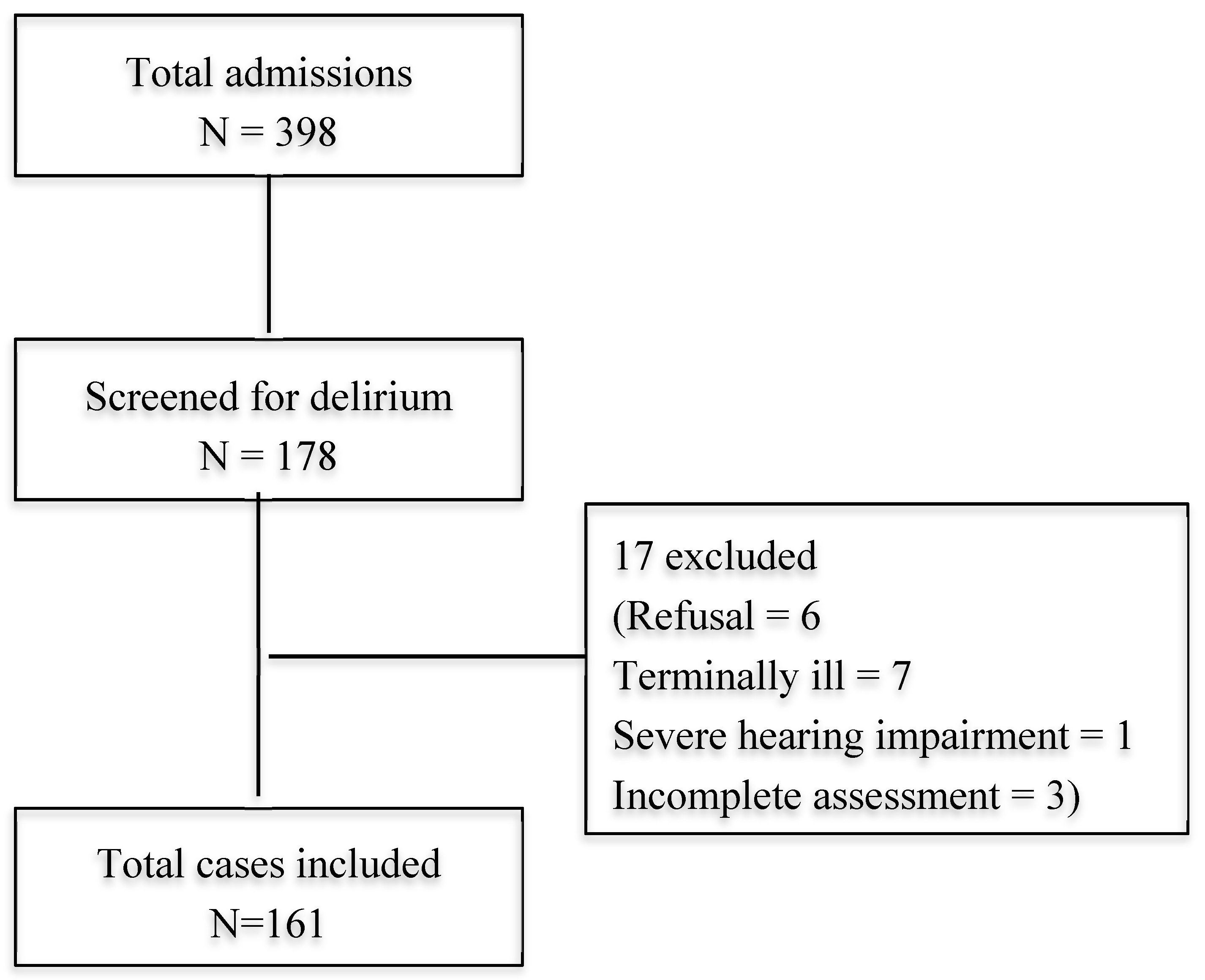
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence of Delirium
3.2. Association between MMSE and CAM
3.3. Risk Factors for Delirium
3.4. Hospitalization Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Variable | Total (n = 398) | Assessed (n = 178) | Not assessed (n = 220) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD) | 75.56 (7.51) | 76.1 (7.62) | 75.15 (7.41) | 0.21 |
| Gender | ||||
| Male, n (%) | 240 (57.8) | 98 (55.1) | 142 (59.9) | 0.19 |
| Female, n (%) | 175 (42.2) | 80 (44.9) | 95 (40.1) |
References
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013.
- Inouye, S.K.; van Dyck, C.H.; Alessi, C.A.; Balkin, S.; Siegal, A.P.; Horwitz, R.I. Clarifying confusion: The confusion assessment method. A new method for detection of delirium. Ann. Intern. Med. 1990, 113, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inouye, S.K.; Westendorp, R.G.; Saczynski, J.S. Delirium in elderly people. Lancet 2014, 383, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, M.; Enander, R.A.; Tadiri, S.P.; Wolfe, R.E.; Shapiro, N.I.; Marcantonio, E.R. Delirium risk prediction, healthcare use and mortality of elderly adults in the emergency department. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2014, 62, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqi, N.; House, A.O.; Holmes, J.D. Occurrence and outcome of delirium in medical in-patients: A systematic literature review. Age Ageing 2006, 35, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gual, N.; Morandi, A.; Perez, L.M.; Britez, L.; Burbano, P.; Man, F.; Inzitari, M. Risk Factors and Outcomes of Delirium in Older Patients Admitted to Postacute Care with and without Dementia. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2018, 45, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, D.L.; Marcantonio, E.R.; Zhang, Y.; Leo-Summers, L.; Inouye, S.K. One-year health care costs associated with delirium in the elderly population. Arch. Intern. Med. 2008, 168, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, M.; Schurch, R.; Boettger, S.; Garcia Nunez, D.; Schwarz, U.; Bettex, D.; Jenewein, J.; Bogdanovic, J.; Staehli, M.L.; Spirig, R.; et al. A hospital-wide evaluation of delirium prevalence and outcomes in acute care patients - a cohort study. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2018, 18, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clegg, A.; Westby, M.; Young, J.B. Under-reporting of delirium in the NHS. Age Ageing 2011, 40, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Zimmerman, E.E.; Cutler, N.; Schnelle, J.; Morandi, A.; Dittus, R.S.; Storrow, A.B.; Ely, E.W. Delirium in older emergency department patients: Recognition, risk factors, and psychomotor subtypes. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2009, 16, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, Y.; Margulin, T.; Grinshpun, Y.; Kagan, E.; Snir, Y.; Berzak, A.; Clarfield, A.M. The diagnosis of delirium among elderly patients presenting to the emergency department of an acute hospital. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2009, 48, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, S.; Fernandes, L. Delirium in elderly people: A review. Front. Neurol. 2012, 3, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magny, E.; Le Petitcorps, H.; Pociumban, M.; Bouksani-Kacher, Z.; Pautas, E.; Belmin, J.; Bastuji-Garin, S.; Lafuente-Lafuente, C. Predisposing and precipitating factors for delirium in community-dwelling older adults admitted to hospital with this condition: A prospective case series. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisani, M.A.; Murphy, T.E.; Van Ness, P.H.; Araujo, K.L.; Inouye, S.K. Characteristics associated with delirium in older patients in a medical intensive care unit. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 1629–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, S.; Lawley, D. Delirium in the elderly: A clinical review. Postgrad. Med. J. 2009, 85, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, J.; Wand, A.P. Delirium Screening: A Systematic Review of Delirium Screening Tools in Hospitalized Patients. Gerontologist 2015, 55, 1079–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayhurst, C.J.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Hughes, C.G. Intensive Care Unit Delirium: A Review of Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment. Anesthesiology 2016, 125, 1229–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voyer, P.; Champoux, N.; Desrosiers, J.; Landreville, P.; McCusker, J.; Monette, J.; Savoie, M.; Richard, S.; Carmichael, P.H. Recognizing acute delirium as part of your routine [RADAR]: A validation study. BMC Nurs. 2015, 14, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Mokhtar, M.A.; Pin, T.M.; Zakaria, M.I.; Hairi, N.N.; Kamaruzzaman, S.B.; Vyrn, C.A.; Hua, P.P. Utilization of the emergency department by older residents in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2015, 15, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Leurent, B.; Sampson, E.L. Risk factors for incident delirium among older people in acute hospital medical units: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing 2014, 43, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, M.J.; Bauer, J.M.; Ramsch, C.; Uter, W.; Guigoz, Y.; Cederholm, T.; Thomas, D.R.; Anthony, P.; Charlton, K.E.; Maggio, M.; et al. Validation of the Mini Nutritional Assessment short-form (MNA-SF): A practical tool for identification of nutritional status. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2009, 13, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inouye, S.K.; Kosar, C.M.; Tommet, D.; Schmitt, E.M.; Puelle, M.R.; Saczynski, J.S.; Marcantonio, E.R.; Jones, R.N. The CAM-S: Development and validation of a new scoring system for delirium severity in 2 cohorts. Ann. Intern. Med. 2014, 160, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, Y.C.; Koh, G.C.; Tay, Y.K.; Tan, C.H.; Merchant, R.A. Underdiagnosis of delirium on admission and prediction of patients who will develop delirium during their inpatient stay: A pilot study. Singapore Med. J. 2016, 57, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, V.; Gambhir, I.S.; Kishore, D. Evaluation of delirium in elderly: A hospital-based study. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2011, 11, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praditsuwan, R.; Sirisuwat, A.; Assanasen, J.; Eiamjinnasuwat, W.; Pakdeewongse, S.; Limmathuroskul, D.; Srinonprasert, V. Short-term clinical outcomes in delirious older patients: A study at general medical wards in a university hospital in Thailand. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2013, 13, 972–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendry, K.; Quinn, T.J.; Evans, J.; Scortichini, V.; Miller, H.; Burns, J.; Cunnington, A.; Stott, D.J. Evaluation of delirium screening tools in geriatric medical inpatients: A diagnostic test accuracy study. Age Ageing 2016, 45, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellelli, G.; Mazzone, A.; Morandi, A.; Latronico, N.; Perego, S.; Zazzetta, S.; Mazzola, P.; Annoni, G. The Effect of an Impaired Arousal on Short- and Long-Term Mortality of Elderly Patients Admitted to an Acute Geriatric Unit. J. Am. Med. Dir Assoc 2016, 17, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, A.; Blackley, S.; Burton, J.K.; Stott, D.J.; Ely, E.W.; Tieges, Z.; MacLullich, A.M.J.; Shenkin, S.D. Reduced level of arousal and increased mortality in adult acute medical admissions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2017, 17, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Delirium, A.; American Delirium, S. The DSM-5 criteria, level of arousal and delirium diagnosis: Inclusiveness is safer. BMC Med. 2014, 12, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, N.; Blanchard, M.R.; Tookman, A.; Sampson, E.L. Detection of delirium in the acute hospital. Age Ageing 2010, 39, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traynor, V.; Cordato, N.; Burns, P.; Xu, Y.; Britten, N.; Duncan, K.; DeVries, L.; McKinnon, C. Is delirium being detected in emergency? Australas. J. Ageing 2016, 35, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Statistics Malaysia. Population Projection (Revised), Malaysia; 2010–2040. Available online: http://www.dosm.gov.my (accessed on 12 November 2018).
- Adamis, D.; Treloar, A.; Martin, F.C.; Macdonald, A.J. Recovery and outcome of delirium in elderly medical inpatients. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2006, 43, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.G.; McCusker, J.; Bailey, R.; Bonnycastle, M.; Fung, S.; Ciampi, A.; Belzile, E. Partial and no recovery from delirium after hospital discharge predict increased adverse events. Age Ageing 2017, 46, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrew, M.K.; Freter, S.H.; Rockwood, K. Incomplete functional recovery after delirium in elderly people: A prospective cohort study. BMC Geriatr 2005, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witlox, J.; Eurelings, L.S.; de Jonghe, J.F.; Kalisvaart, K.J.; Eikelenboom, P.; van Gool, W.A. Delirium in elderly patients and the risk of postdischarge mortality, institutionalization, and dementia: A meta-analysis. JAMA 2010, 304, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levkoff, S.E.; Liptzin, B.; Cleary, P.D.; Wetle, T.; Evans, D.A.; Rowe, J.W.; Lipsitz, L.A. Subsyndromal Delirium. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 1996, 4, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcantonio, E.R.; Kiely, D.K.; Simon, S.E.; John Orav, E.; Jones, R.N.; Murphy, K.M.; Bergmann, M.A. Outcomes of older people admitted to postacute facilities with delirium. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuliani, G.; Bonetti, F.; Magon, S.; Prandini, S.; Sioulis, F.; D’Amato, M.; Zampi, E.; Gasperini, B.; Cherubini, A. Subsyndromal delirium and its determinants in elderly patients hospitalized for acute medical illness. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2013, 68, 1296–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brummel, N.E.; Boehm, L.M.; Girard, T.D.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Jackson, J.C.; Hughes, C.G.; Patel, M.B.; Han, J.H.; Vasilevskis, E.E.; Thompson, J.L.; et al. Subsyndromal Delirium and Institutionalization Among Patients With Critical Illness. Am. J. Crit. Care 2017, 26, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.; McCusker, J.; Dendukuri, N.; Han, L. The prognostic significance of subsyndromal delirium in elderly medical inpatients. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2003, 51, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCusker, J.; Cole, M.G.; Voyer, P.; Monette, J.; Champoux, N.; Ciampi, A.; Vu, M.; Belzile, E. Six-month outcomes of co-occurring delirium, depression, and dementia in long-term care. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2014, 62, 2296–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.; DePalma, G.; Sands, L.P.; Leung, J.M. Prognostic Significance of Postoperative Subsyndromal Delirium. Psychosomatics 2015, 56, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.G.; Ciampi, A.; Belzile, E.; Dubuc-Sarrasin, M. Subsyndromal delirium in older people: A systematic review of frequency, risk factors, course and outcomes. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2013, 28, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynish, E.L.; Hapca, S.M.; De Souza, N.; Cvoro, V.; Donnan, P.T.; Guthrie, B. Epidemiology and outcomes of people with dementia, delirium, and unspecified cognitive impairment in the general hospital: Prospective cohort study of 10,014 admissions. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chester, J.G.; Beth Harrington, M.; Rudolph, J.L.; Group, V.A.D.W. Serial administration of a modified Richmond Agitation and Sedation Scale for delirium screening. J. Hosp. Med. 2012, 7, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Wilber, S.T. Altered mental status in older patients in the emergency department. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2013, 29, 101–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salluh, J.I.; Soares, M.; Teles, J.M.; Ceraso, D.; Raimondi, N.; Nava, V.S.; Blasquez, P.; Ugarte, S.; Ibanez-Guzman, C.; Centeno, J.V.; et al. Delirium Epidemiology in Critical Care Study, G. Delirium epidemiology in critical care (DECCA): An international study. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, C.; Stanley, N.; Cerejeira, J.M.; Jay, R.; Mukaetova-Ladinska, E.B. Screening instruments for delirium in older people with an acute medical illness. Age Ageing 2009, 38, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslaner, M.A.; Boz, M.; Celik, A.; Ahmedali, A.; Eroglu, S.; Metin Aksu, N.; Eroglu, S.E. Etiologies and delirium rates of elderly ED patients with acutely altered mental status: A multicenter prospective study. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2017, 35, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellelli, G.; Morandi, A.; Davis, D.H.; Mazzola, P.; Turco, R.; Gentile, S.; Ryan, T.; Cash, H.; Guerini, F.; Torpilliesi, T.; et al. Validation of the 4AT, a new instrument for rapid delirium screening: A study in 234 hospitalised older people. Age Ageing 2014, 43, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLullich, A.M.; Shenkin, S.D.; Goodacre, S.; Godfrey, M.; Hanley, J.; Stiobhairt, A.; Lavender, E.; Boyd, J.; Stephen, J.; Weir, C.; et al. The 4 ‘A’s test for detecting delirium in acute medical patients: A diagnostic accuracy study. Health Technol. Assess. 2019, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenkin, S.D.; Fox, C.; Godfrey, M.; Siddiqi, N.; Goodacre, S.; Young, J.; Anand, A.; Gray, A.; Hanley, J.; MacRaild, A.; et al. Delirium detection in older acute medical inpatients: A multicentre prospective comparative diagnostic test accuracy study of the 4AT and the confusion assessment method. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Total (n = 161) | Delirium (n = 43) | No Delirium (n = 118) | Unadjusted OR (95% CI) | Adjusted OR † (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (mean, SD) | 76.5 (7.77) | 81.53 (8.62) | 74.66 (6.57) | ||
| Male Gender n (%) | 83 (51.6) | 22 (51.2) | 61 (51.7) | 0.98 (0.49–1.97) | 1.23 (0.57–2.66) |
| Ethnicity | |||||
| Chinese | 82 (50.9) | 26 (60.5) | 56 (47.5) | 0.63 (0.24–1.64) | 0.78 (0.28–2.22) |
| Malay | 42 (26.1) | 9 (20.9) | 33 (28) | 0.59 (0.25–1.40) | 0.84 (0.33–2.18) |
| Indian | 31 (19.3) | 7 (16.3) | 24 (20.3) | 0.43 (0.05–3.88) | 0.14 (0.01–1.81) |
| Nursing Home | 10 (6.2) | 5 (11.6) | 5 (4.2) | 2.97 (0.82–10.83) | 1.50 (0.35–6.38) |
| <6 years Education | 103 (64) | 25 (59.5) | 78(66.1) | 0.75 (0.37–1.56) | 0.99 (0.45–2.20) |
| Comorbidities | |||||
| CCF | 13 (8.1) | 5 (11.6) | 8 (6.8) | 1.81 (0.56–5.87) | 1.93 (0.54–6.88) |
| CKD | 36 (22.5) | 10 (23.3) | 26 (22.2) | 1.06 (0.46–2.44) | 1.23 (0.48–3.12) |
| Dementia | 16 (9.9) | 7 (16.3) | 9 (7.6) | 2.36 (0.82–6.78) | 1.57 (0.49–4.98) |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 74 (46.3) | 20 (46.5) | 54 (46.2) | 1.01 (0.50–2.05) | 1.17 (0.54–2.51) |
| IHD | 46 (28.6) | 9 (20.9) | 37 (31.4) | 0.58 (0.25–1.33) | 0.61 (0.25–1.50) |
| Hypertension | 110 (68.8) | 28 (65.1) | 82 (70.1) | 0.80 (0.38–1.67) | 0.77 (0.34–1.72) |
| COPD | 20 (12.5) | 1 (2.3) | 19 (16.2) | 0.12 (0.02–0.95) | 0.11 (0.01–0.87) |
| Osteoarthritis | 15 (9.3) | 1 (2.3) | 14 (11.9) | 0.18 (0.02–1.39) | 0.16 (0.02–1.28) |
| Stroke | 33 (20.5) | 12 (27.9) | 21 (17.8) | 1.79 (0.79–4.05) | 1.95 (0.8–4.74) |
| Risk Factors | |||||
| Cognitive impairment | 45 (28) | 26 (60.5) | 19 (16.1) | 7.97 (3.64–17.45) | 5.78 (2.53–13.22) |
| Dehydration | 72 (44.7) | 26 (60.5) | 46 (39) | 2.39 (1.17–4.89) | 1.69 (0.77–3.68) |
| Hypoxia | 67 (41.6) | 22 (51.2) | 45 (38.1) | 1.70 (0.84–3.44) | 1.57 (0.73–3.38) |
| Infection | 89 (55.3) | 29 (67.4) | 60 (50.8) | 2.00 (0.96–4.17) | 1.42 (0.64–3.14) |
| Immobility | 84 (52.2) | 34 (79.1) | 50 (42.4) | 5.14 (2.26–11.67) | 3.66 (1.54–8.65) |
| Malnutrition (MNA < 8) | 83 (51.9) | 36 (85.7) | 47 (39.8) | 9.06 (3.54–23.19) | 5.53 (2.05–14.93) |
| Pain | 73 (45.3) | 18 (41.9) | 55 (46.6) | 0.82 (0.41–1.67) | 1.09 (0.51–2.35) |
| Sensory impairment | 27 (16.8) | 9 (20.9) | 18 (15.3) | 1.47 (0.60–3.58) | 1.02 (0.38–2.74) |
| Sleep disturbance | 69 (42.9) | 19 (44.2) | 50 (42.4) | 1.08 (0.53–2.18) | 1.31 (0.61–2.82) |
| CAM | Severity Score n (%) | Unable to Assess n (%) ‡ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | ||
| Item 1 | ||||
| Acute onset and fluctuating course | 109 (67.7) | 52 (32.3) | n/a | 0 |
| Item 2 | ||||
| Inattention | 101 (62.7) | 39 (24.2) | 21 (13) | 13 (8.1) |
| Item 3 | ||||
| Disorganised thinking | 118 (73.3) | 17 (10.6) | 26 (16.1) | 13 (8.1) |
| Item 4 | ||||
| Altered level of consciousness | 110 (68.3) | 38 (23.6) | 13 (8.1) | 0 |
| Item 5 | ||||
| Disorientation | 97 (60.2) | 33 (20.5) | 31 (19.3) | 13 (8.1) |
| Item 6 | ||||
| Memory impairment | 84 (52.2) | 43 (26.7) | 33 (20.5) | 13 (8.1) |
| Item 7 | ||||
| Perceptual Disturbances | 142 (88.2) | 12 (7.5) | 7 (4.3) | 2 (1.2) |
| Item 8 | ||||
| Psychomotor agitation | 135 (83.9) | 22 (13.7) | 4 (2.5) | 0 |
| Item 9 | ||||
| Psychomotor retardation | 137 (85.1) | 13 (8.1) | 11 (6.8) | 0 |
| Item 10 | ||||
| Altered sleep-wake cycle | 112 (69.6) | 30 (18.6) | 19 (11.8) | 0 |
| Assessment Tools | Delirium Unlikely | Possible Delirium | Probable Delirium | Spearman’s Rho | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAM-S Short | |||||
| Total, n (%) | 83 (51.6) | 30 (18.6) | 48 (29.8) | −0.77 | <0.01 |
| MMSE (mean, SD) | 23.19 (6.32) | 14.27 (8.83) | 3.65 (5.12) | ||
| CAM-S Long | |||||
| Total, n (%) | 53 (33.9) | 53 (32.9) | 55 (34.2) | −0.80 | <0.01 |
| MMSE (mean, SD) | 25.32 (5.10) | 17.98 (7.50) | 4.24 (5.74) | ||
| Characteristics | B coefficient | SD | OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.07 | 0.03 | 1.07 (1.01–1.14) |
| Immobility | 1.15 | 0.50 | 3.16 (1.18–8.50) |
| Malnutrition | 1.22 | 0.55 | 3.37 (1.15–9.85) |
| Cognitive impairment | 1.62 | 0.45 | 5.04 (2.07–12.24) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khor, H.M.; Ong, H.C.; Tan, B.K.; Low, C.M.; Saedon, N.; Tan, K.M.; Chin, A.V.; Kamaruzzaman, S.B.; Tan, M.P. Assessment of Delirium Using the Confusion Assessment Method in Older Adult Inpatients in Malaysia. Geriatrics 2019, 4, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics4030052
Khor HM, Ong HC, Tan BK, Low CM, Saedon N, Tan KM, Chin AV, Kamaruzzaman SB, Tan MP. Assessment of Delirium Using the Confusion Assessment Method in Older Adult Inpatients in Malaysia. Geriatrics. 2019; 4(3):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics4030052
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhor, Hui Min, Hwee Chin Ong, Bee Kuan Tan, Chung Min Low, Nor’Izzati Saedon, Kit Mun Tan, Ai Vyrn Chin, Shahrul B. Kamaruzzaman, and Maw Pin Tan. 2019. "Assessment of Delirium Using the Confusion Assessment Method in Older Adult Inpatients in Malaysia" Geriatrics 4, no. 3: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics4030052
APA StyleKhor, H. M., Ong, H. C., Tan, B. K., Low, C. M., Saedon, N., Tan, K. M., Chin, A. V., Kamaruzzaman, S. B., & Tan, M. P. (2019). Assessment of Delirium Using the Confusion Assessment Method in Older Adult Inpatients in Malaysia. Geriatrics, 4(3), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics4030052





