Taste Perception and Water Swallow Screen Results in Old-Old Women
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Summary of Water Swallow Screen Results
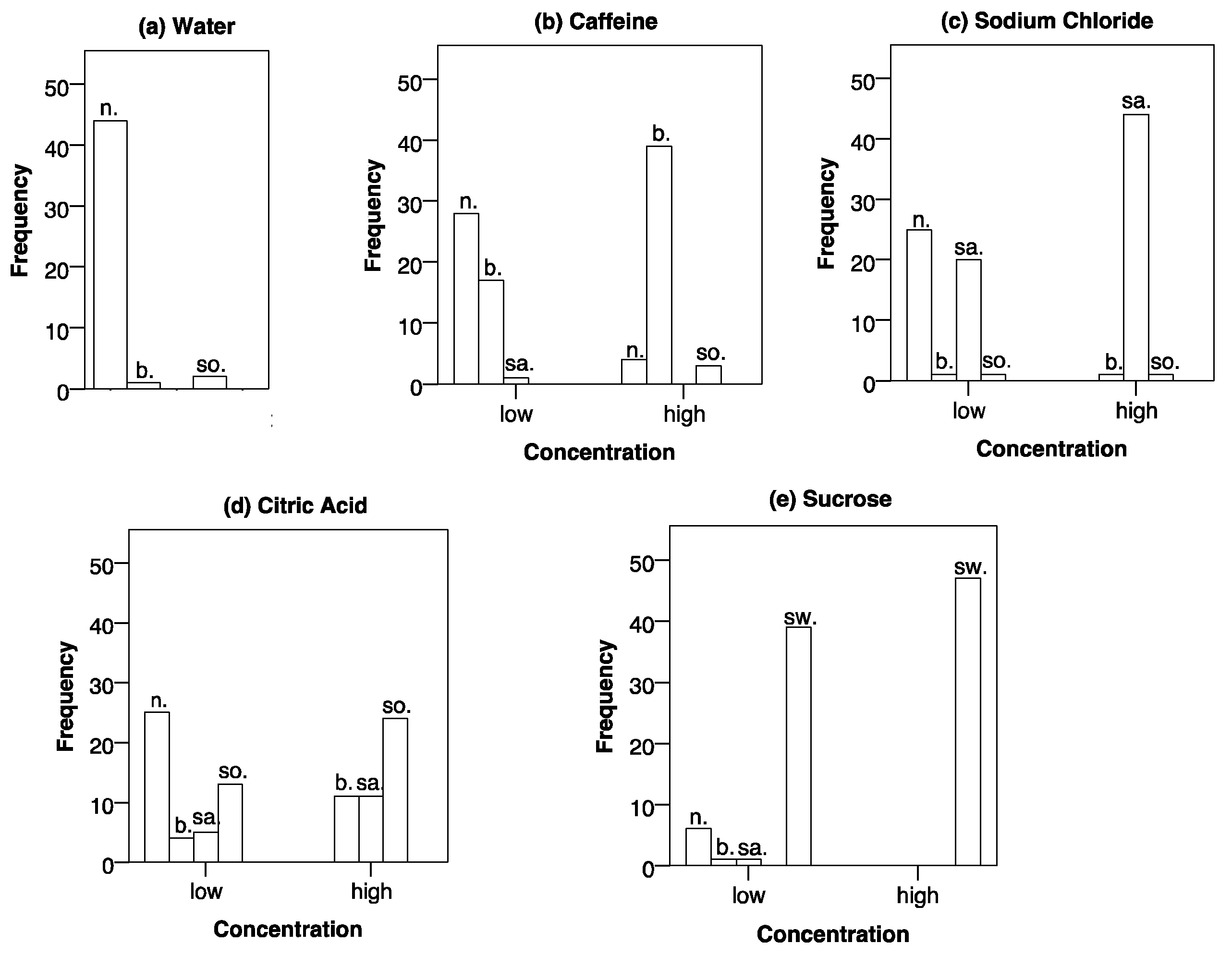
3.2. Taste Perception Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ekberg, O.; Feinberg, M.J. Altered swallowing function in elderly patients without dysphagia: Radiologic findings in 56 cases. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1991, 156, 1181–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, J.; Hamilton, J.W.; Lof, G.L.; Kempster, G.B. Oropharyngeal swallowing in normal adults of different ages. Gastroenterology 1992, 103, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Yoshida, M.; Nagasaki, T.; Tanimoto, K.; Tsuga, K.; Akagawa, Y.; Komatsu, T. Aspects of swallowing in healthy dentate elderly persons older than 80 years. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2005, 60, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, C.M.; Van Lieshout, P. Tongue movements during water swallowing in healthy young and older adults. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2009, 52, 1255–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omari, T.I.; Kritas, S.; Cock, C.; Besanko, L.; Burgstad, C.; Thompson, A.; Rommel, N.; Heddle, R.; Fraser, R. Swallowing dysfunction in healthy older people using pharyngeal pressure-flow analysis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulheren, R.W.; Azola, A.M.; Kwiatkowski, S.; Karagiorgos, E.; Humbert, I.; Palmer, J.B.; González-Fernández, M. Swallowing changes in community-dwelling older adults. Dysphagia 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, K.; Akagi, J. Sarcopenia is an independent risk factor of dysphagia in hospitalized older people. Geriat. Gerontol. Int. 2016, 16, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, B.J.; Bodner, L. Aging and oral motor function: Evidence for altered performance among older persons. J. Dent. Res. 1983, 62, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.H.; Diamond, B.; Aviv, J.E.; Jones, M.E.; Keen, M.S.; Wee, T.A.; Blitzer, A. Age-related changes in pharyngeal and supraglottic sensation. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1994, 103, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landt, H.; Fransson, B.O. Oral ability to recognize forms and oral muscular coordination ability in dentulous young and elderly adults. J. Oral Rehabil. 1975, 2, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra-Prat, M.; Palomera, M.; Gomez, C.; Sar-Shalom, D.; Saiz, A.; Montoya, J.G.; Navajas, M.; Palomera, E.; Clavé, P. Oropharyngeal dysphagia as a risk factor for malnutrition and lower respiratory tract infection in independently living older persons: A population-based prospective study. Age Age. 2012, 41, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rofes, L.; Arreola, V.; Romea, M.; Palomera, E.; Almirall, J.; Cabré, M.; Serra-Prat, M.; Clavé, P. Pathophysiology of oropharyngeal dysphagia in the frail elderly. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Maarel-Wierink, C.D.; Vanobbergen, J.N.; Bronkhorst, E.M.; Schols, J.M.; de Baat, C. Oral health care and aspiration pneumonia in frail older people: A systematic literature review. Gerodontology 2013, 30, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solemdal, K.; Sandvik, L.; Willumsen, T.; Mowe, M.; Hummel, T. The impact of oral health on taste ability in acutely hospitalized elderly. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, H.J.; Ishii, E.K.; Macturk, R.H. Age-related changes in the prevalence of smell/taste problems among the United States adult population: Results of the 1994 Disability Supplement to the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS). Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 855, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojet, J.; Christ-Hazelhof, E.; Heidema, J. Taste perception with age: Generic or specific losses in threshold sensitivity to the five basic tastes? Chem. Sens. 2001, 26, 845–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, A.; Uematsu, H.; Sugimoto, K. Influences of aging on taste perception and oral somatic sensation. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2005, 60, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, R.J.; Feller, R.P. Age and sex effects on taste of sucrose, NaCl, citric acid and caffeine. Neurobiol. Aging 1981, 2, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowart, B.J. Relationships between taste and smell across the adult life span a. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1989, 561, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoshuk, L.M. Taste: Robust across the age span? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1989, 561, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulheren, R.W.; Kamarunas, E.; Ludlow, C.L. Sour taste increases swallowing and prolongs hemodynamic responses in the cortical swallowing network. J. Neurophysiol. 2016, 116, 2033–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nederkoorn, C.; Smulders, F.; Jansen, A. Recording of swallowing events using electromyography as a non-invasive measurement of salivation. Appetite 1999, 33, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdy, S.; Jilani, S.; Price, V.; Parker, C.; Hall, N.; Power, M. Modulation of human swallowing behaviour by thermal and chemical stimulation in health and after brain injury. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2003, 15, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chee, C.; Arshad, S.; Singh, S.; Mistry, S.; Hamdy, S. The influence of chemical gustatory stimuli and oral anaesthesia on healthy human pharyngeal swallowing. Chem. Sens. 2005, 30, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelletier, C.A.; Steele, C.M. Influence of the perceived taste intensity of chemesthetic stimuli on swallowing parameters given age and genetic taste differences in healthy adult women. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2014, 57, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, C.A.; Dhanaraj, G.E. The effect of taste and palatability on lingual swallowing pressure. Dysphagia 2006, 21, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahab, N.A.; Jones, R.D.; Huckabee, M. Effects of olfactory and gustatory stimuli on neural excitability for swallowing. Physiol. Behav. 2010, 101, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leow, L.P.; Huckabee, M.L.; Sharma, S.; Tooley, T.P. The influence of taste on swallowing apnea, oral preparation time, and duration and amplitude of submental muscle contraction. Chem. Senses 2006, 32, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelletier, C.A.; Lawless, H.T. Effect of citric acid and citric acid–sucrose mixtures on swallowing in neurogenic oropharyngeal dysphagia. Dysphagia 2003, 18, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breslin, P.A.; Huang, L. Human taste: Peripheral anatomy, taste transduction, and coding. Adv. Otorhinolaryngol. 2006, 63, 152–190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lewis, D.; Dandy, W.E. The course of the nerve fibers transmitting sensation of taste. Arch. Surg. 1930, 21, 249–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, I.A.; Joel, S. Tactile, gustatory, and visual biofeedback stimuli modulate neural substrates of deglutition. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 1485–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouderoux, P.; Logemann, J.A.; Kahrilas, P.J. Pharyngeal swallowing elicited by fluid infusion: Role of volition and vallecular containment. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 1996, 270, G347–G354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, J.T.; Butler, S.G.; Plonk, D.P.; Grace-Martin, K.; Pelletier, C.A. Main taste effects on swallowing apnea duration in healthy adults. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 147, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, J.T.; Butler, S.G.; Plonk, D.P.; Grace-Martin, K.; Pelletier, C.A. Effects of chemesthetic stimuli mixtures with barium on swallowing apnea duration. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 2248–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humbert, I.A.; Lokhande, A.; Christopherson, H.; German, R.; Stone, A. Adaptation of swallowing hyo-laryngeal kinematics is distinct in oral vs. pharyngeal sensory processing. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 112, 1698–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, R.; Logemann, J.A.; Larson, C.R.; Rademaker, A.W. The effects of taste and consistency on swallow physiology in younger and older healthy individuals: A surface electromyographic study. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2003, 46, 977–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suiter, D.M.; Leder, S.B. Clinical utility of the 3-ounce water swallow test. Dysphagia 2008, 23, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suiter, D.M.; Sloggy, J.; Leder, S.B. Validation of the Yale Swallow Protocol: A prospective double-blinded videofluoroscopic study. Dysphagia 2014, 29, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DePippo, K.L.; Holas, M.A.; Reding, M.J. Validation of the 3-oz water swallow test for aspiration following stroke. Arch. Neurol. 1992, 49, 1259–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrión, S.; Cabré, M.; Monteis, R.; Roca, M.; Palomera, E.; Serra-Prat, M.; Rofes, L.; Clavé, P. Oropharyngeal dysphagia is a prevalent risk factor for malnutrition in a cohort of older patients admitted with an acute disease to a general hospital. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabre, M.; Serra-Prat, M.; Palomera, E.; Almirall, J.; Pallares, R.; Clavé, P. Prevalence and prognostic implications of dysphagia in elderly patients with pneumonia. Age Age. 2009, 39, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Fernández, M.; Humbert, I.; Winegrad, H.; Cappola, A.R.; Fried, L.P. Dysphagia in old-old women: Prevalence as determined according to self-report and the 3-ounce water swallowing test. J. Am. Geriat. Soc. 2014, 62, 716–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, L.P.; Bandeen-Roche, K.; Chaves, P.H.; Johnson, B.A. Preclinical mobility disability predicts incident mobility disability in older women. J. Gerontol. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2000, 55, M43–M52. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy, A.; Steele, C.M.; Pelletier, C.A. Differences in swallowing between high and low concentration taste stimuli. BioMed Res. Int. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoshuk, L.M.; Duffy, V.B.; Green, B.G.; Hoffman, H.J.; Ko, C.; Lucchina, L.A.; Marks, L.E.; Snyder, D.J.; Weiffenbach, J.M. Valid across-group comparisons with labeled scales: The gLMS versus magnitude matching. Physiol. Behav. 2004, 82, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, L.P.; Tangen, C.M.; Walston, J.; Newman, A.B.; Hirsch, C.; Gottdiener, J.; Seeman, T.; Tracy, R.; Kop, W.J.; Burke, G. Frailty in older adults: Evidence for a phenotype. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2001, 56, M146–M156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandeen-Roche, K.; Xue, Q.; Ferrucci, L.; Walston, J.; Guralnik, J.M.; Chaves, P.; Zeger, S.L.; Fried, L.P. Phenotype of frailty: Characterization in the women’s health and aging studies. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2006, 61, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bursac, Z.; Gauss, C.H.; Williams, D.K.; Hosmer, D.W. Purposeful selection of variables in logistic regression. Source Code Biol. Med. 2008, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grill, H.J.; Norgren, R. Neurological tests and behavioral deficits in chronic thalamic and chronic decerebrate rats. Brain Res. 1978, 143, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, J.E. The gustofacial response: observation on normal and anencephalic newborn infants. Symp. Oral Sens. Percept. 1973, 254–278. [Google Scholar]
- Breslin, P.A. An evolutionary perspective on food and human taste. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, R409–R418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrashekar, J.; Mueller, K.L.; Hoon, M.A.; Adler, E.; Feng, L.; Guo, W.; Zuker, C.S.; Ryba, N.J. T2Rs function as bitter taste receptors. Cell 2000, 100, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y. Adaptive diversification of bitter taste receptor genes in mammalian evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, J.E.; Glaser, D.; Hawilo, M.E.; Berridge, K.C. Comparative expression of hedonic impact: affective reactions to taste by human infants and other primates. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2001, 25, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, B.G.; Gelhard, B. Salt as an oral irritant. Chem. Sens. 1989, 14, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, M.M.; Green, B.G. Sensory irritation and taste produced by NaCl and citric acid: Effects of capsaicin desensitization. Chem. Sens. 1993, 18, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, C.M.; Van Lieshout, P.H.; Pelletier, C.A. The influence of stimulus taste and chemesthesis on tongue movement timing in swallowing. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2012, 55, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Eslinger, P.J.; Smith, M.B.; Yang, Q.X. Functional magnetic resonance imaging study of human olfaction and normal aging. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2005, 60, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebihara, T.; Ebihara, S.; Maruyama, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Itou, A.; Arai, H.; Sasaki, H. A randomized trial of olfactory stimulation using black pepper oil in older people with swallowing dysfunction. J. Am. Geriat. Soc. 2006, 54, 1401–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lof, G.L.; Robbins, J. Test-retest variability in normal swallowing. Dysphagia 1990, 4, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, J.C.; Cruz, L.A.; Hoffman, J.M.; Patterson, M.Q. Taste sensitivity and aging: High incidence of decline revealed by repeated threshold measures. Chem. Sens. 1995, 20, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejaeger, E.; Pelemans, W.; Bibau, G.; Ponette, E. Manofluorographic analysis of swallowing in the elderly. Dysphagia 1994, 9, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoshuk, L.M.; Duffy, V.B.; Miller, I.J. PTC/PROP tasting: Anatomy, psychophysics, and sex effects. Physiol. Behav. 1994, 56, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayler, A.H.; Perlmuter, L.C.; Cardello, A.V.; Jones, J.A.; Chauncey, H.H. Effects of age and removable artificial dentition on taste. Spec. Care Dent. 1990, 10, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoshuk, L.M.; Rifkin, B.; Marks, L.E.; Bars, P. Taste and aging. J. Gerontol. 1986, 41, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapur, K.K.; Collister, T.; Fischer, E.E. Masticatory and gustatory salivary reflex secretion rates and taste thresholds of denture wearers. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1967, 18, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoschus, B.; Allescher, H. Drug-induced dysphagia. Dysphagia 1993, 8, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doty, R.L.; Bromley, S.M. Effects of drugs on olfaction and taste. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 37, 1229–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, T.; Uota, M.; Ikebe, K.; Arai, Y.; Kamide, K.; Gondo, Y.; Masui, Y.; Ishizaki, T.; Inomata, C.; Takeshita, H. Longitudinal study of factors affecting taste sense decline in old-old individuals. J. Oral Rehabil. 2017, 44, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Caffeine | Sodium Chloride | Citric Acid | Sucrose | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | 0.36 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.31 |
| Range | 0–2 | 0–0.88 | 0–0.67 | 0–3.75 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mulheren, R.W.; Humbert, I.A.; Cappola, A.R.; Fried, L.P.; González-Fernández, M. Taste Perception and Water Swallow Screen Results in Old-Old Women. Geriatrics 2018, 3, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics3040083
Mulheren RW, Humbert IA, Cappola AR, Fried LP, González-Fernández M. Taste Perception and Water Swallow Screen Results in Old-Old Women. Geriatrics. 2018; 3(4):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics3040083
Chicago/Turabian StyleMulheren, Rachel W., Ianessa A. Humbert, Anne R. Cappola, Linda P. Fried, and Marlís González-Fernández. 2018. "Taste Perception and Water Swallow Screen Results in Old-Old Women" Geriatrics 3, no. 4: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics3040083
APA StyleMulheren, R. W., Humbert, I. A., Cappola, A. R., Fried, L. P., & González-Fernández, M. (2018). Taste Perception and Water Swallow Screen Results in Old-Old Women. Geriatrics, 3(4), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics3040083





