Beat-to-Beat Blood Pressure Monitoring and Orthostatic Hypotension-Related Falls in Two Cohorts of Older Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Orthostatic BP Response Assessments
2.3. Falls Outcome
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
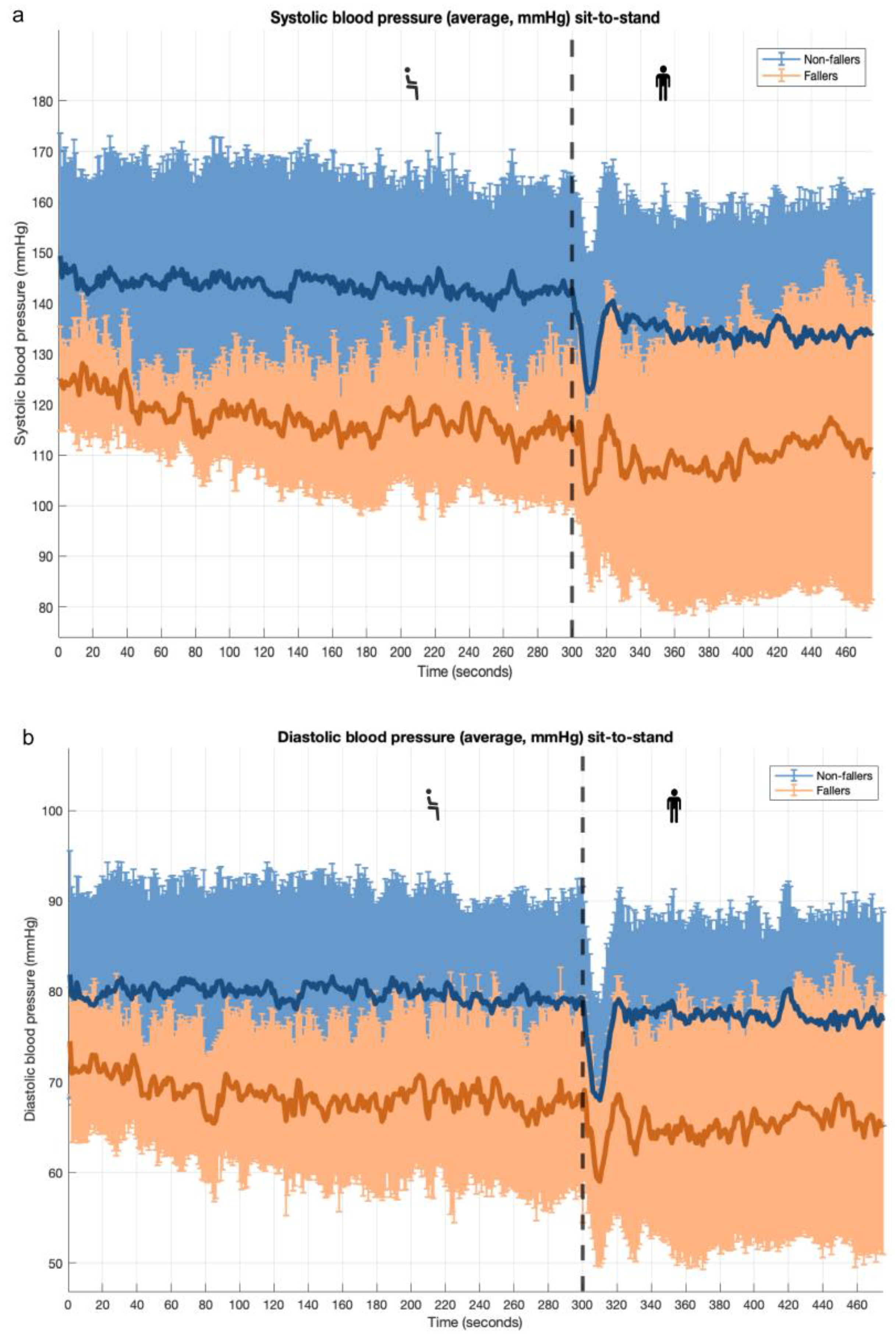
3.1. Sit-to-Stand Maneuver: PROHEALTH Population
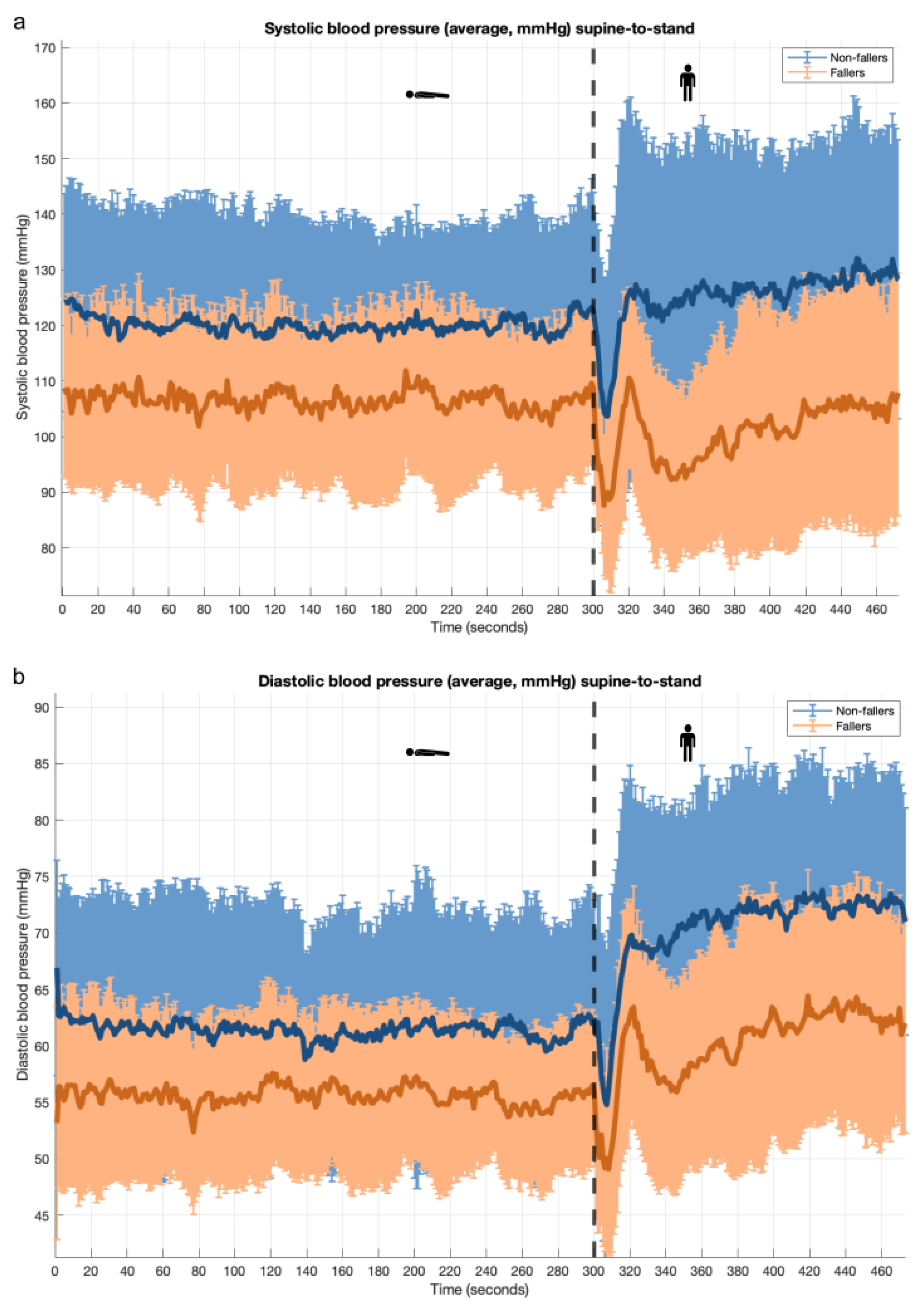
3.2. Supine-to-Stand Maneuver: PROHEALTH Population
3.3. Sit-to-Stand Maneuver: NILVAD-CBF Population
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Petriceks, A.H.; Appel, L.J.; Miller, E.R., 3rd; Mitchell, C.M.; Schrack, J.A.; Mukamal, K.J.; Lipsitz, L.A.; Wanigatunga, A.A.; Plante, T.B.; Michos, E.D.; et al. Timing of orthostatic hypotension and its relationship with falls in older adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2023, 71, 3711–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieling, W.; Krediet, C.T.; van Dijk, N.; Linzer, M.; Tschakovsky, M.E. Initial orthostatic hypotension: Review of a forgotten condition. Clin. Sci. 2007, 112, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, M.P.M.; Finucane, C.; Perez-Denia, L.; Juraschek, S.P.; van Wijnen, V.K.; Lipsitz, L.A.; van Lieshout, J.J.; Wieling, W. Systemic and cerebral circulatory adjustment within the first 60 s after active standing: An integrative physiological view. Auton. Neurosci. 2021, 231, 102756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dani, M.; Dirksen, A.; Taraborrelli, P.; Panagopolous, D.; Torocastro, M.; Sutton, R.; Lim, P.B. Orthostatic hypotension in older people: Considerations, diagnosis and management. Clin. Med. 2021, 21, e275–e282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, M.C.; Shibao, C.A. Morbidity and mortality in orthostatic hypotension. Auton. Neurosci. 2020, 229, 102717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juraschek, S.P.; Cortez, M.M.; Flack, J.M.; Ghazi, L.; Kenny, R.A.; Rahman, M.; Spikes, T.; Shibao, C.A.; Biaggioni, I.; American Heart Association Council on Hypertension. Orthostatic Hypotension in Adults with Hypertension: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Hypertension 2024, 81, e16–e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, S.; Bhangu, J.; de Rooij, S.; Daams, J.; Kenny, R.A.; van der Velde, N. The Association of Cardiovascular Disorders and Falls: A Systematic Review. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2016, 17, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, B.H.; Claydon, V.E. The relationship between orthostatic hypotension and falling in older adults. Clin. Auton. Res. 2014, 24, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Velde, N.; van den Meiracker, A.H.; Stricker, B.H.; van der Cammen, T.J. Measuring orthostatic hypotension with the Finometer device: Is a blood pressure drop of one heartbeat clinically relevant? Blood Press. Monit. 2007, 12, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mol, A.; Bui Hoang, P.T.S.; Sharmin, S.; Reijnierse, E.M.; van Wezel, R.J.A.; Meskers, C.G.M.; Maier, A.B. Orthostatic Hypotension and Falls in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2019, 20, 589–597.e585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Knight, P.; Connolly, E.; Duggan, E.; Romero-Ortuno, R. Functional Clustering of Continuous Cardiovascular and Brain Oxygenation Signals During an Active Stand Test in The Irish Longitudinal Study on Ageing (TILDA). In Proceedings of the 2023 31st European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Helsinki, Finland, 4–8 September 2023; pp. 1080–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buongiorno, L.; Mele, F.; Solarino, B.; Ferorelli, D.; Zotti, F.; Dell’Erba, A.; Carabellese, F.F.; Catanesi, R.; Ferracuti, S.; Mandarelli, G. Falls in the hospital: An Italian clinical risk management perspective. J. Patient Saf. Risk Manag. 2024, 29, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, F.; De Caterina, R.; Fedorowski, A. Orthostatic Hypotension: Epidemiology, Prognosis, and Treatment. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 848–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, R.; Wieling, W.; Axelrod, F.B.; Benditt, D.G.; Benarroch, E.; Biaggioni, I.; Cheshire, W.P.; Chelimsky, T.; Cortelli, P.; Gibbons, C.H.; et al. Consensus statement on the definition of orthostatic hypotension, neurally mediated syncope and the postural tachycardia syndrome. Clin. Auton. Res. 2011, 21, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Odasso, M.; van der Velde, N.; Martin, F.C.; Petrovic, M.; Tan, M.P.; Ryg, J.; Aguilar-Navarro, S.; Alexander, N.B.; Becker, C.; Blain, H.; et al. World guidelines for falls prevention and management for older adults: A global initiative. Age Ageing 2022, 51, afac205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brignole, M.; Moya, A.; de Lange, F.J.; Deharo, J.C.; Elliott, P.M.; Fanciulli, A.; Fedorowski, A.; Furlan, R.; Kenny, R.A.; Martin, A.; et al. 2018 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of syncope. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 1883–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finucane, C.; van Wijnen, V.K.; Fan, C.W.; Soraghan, C.; Byrne, L.; Westerhof, B.E.; Freeman, R.; Fedorowski, A.; Harms, M.P.M.; Wieling, W.; et al. A practical guide to active stand testing and analysis using continuous beat-to-beat non-invasive blood pressure monitoring. Clin. Auton. Res. 2019, 29, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoghue, O.A.; O’Connell, M.D.L.; Bourke, R.; Kenny, R.A. Is orthostatic hypotension and co-existing supine and seated hypertension associated with future falls in community-dwelling older adults? Results from The Irish Longitudinal Study on Ageing (TILDA). PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourke, R.; Doody, P.; Perez, S.; Moloney, D.; Lipsitz, L.; Kenny, R.A. Cardiovascular Disorders and Falls Among Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2023, 79, glad221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, J.; Hillebrand, S.L.; Meskers, C.G.M.; Iseli, R.K.; Maier, A.B. Prevalence of initial orthostatic hypotension in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing 2021, 50, 1520–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juraschek, S.P.; Appel, L.J.; Mitchell, C.M.; Mukamal, K.J.; Lipsitz, L.A.; Blackford, A.L.; Cai, Y.; Guralnik, J.M.; Kalyani, R.R.; Michos, E.D.; et al. Comparison of supine and seated orthostatic hypotension assessments and their association with falls and orthostatic symptoms. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2022, 70, 2310–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klop, M.; de Heus, R.A.A.; Maier, A.B.; van Alphen, A.; Floor-Westerdijk, M.J.; Bronkhorst, M.; Melis, R.J.F.; Meskers, C.G.M.; Claassen, J.; van Wezel, R.J.A. Capturing postural blood pressure dynamics with near-infrared spectroscopy-measured cerebral oxygenation. Geroscience 2023, 45, 2643–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meulenbroek, O.; O’Dwyer, S.; de Jong, D.; van Spijker, G.; Kennelly, S.; Cregg, F.; Olde Rikkert, M.; Abdullah, L.; Wallin, A.; Walsh, C.; et al. European multicentre double-blind placebo-controlled trial of Nilvadipine in mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease-the substudy protocols: NILVAD frailty; NILVAD blood and genetic biomarkers; NILVAD cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers; NILVAD cerebral blood flow. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e011584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imholz, B.P.; Wieling, W.; van Montfrans, G.A.; Wesseling, K.H. Fifteen years experience with finger arterial pressure monitoring: Assessment of the technology. Cardiovasc. Res. 1998, 38, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Heus, R.A.A.; de Jong, D.L.K.; Rijpma, A.; Lawlor, B.A.; Olde Rikkert, M.G.M.; Claassen, J. Orthostatic Blood Pressure Recovery Is Associated With the Rate of Cognitive Decline and Mortality in Clinical Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2020, 75, 2169–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finucane, C.; O’Connell, M.D.; Fan, C.W.; Savva, G.M.; Soraghan, C.J.; Nolan, H.; Cronin, H.; Kenny, R.A. Age-related normative changes in phasic orthostatic blood pressure in a large population study: Findings from The Irish Longitudinal Study on Ageing (TILDA). Circulation 2014, 130, 1780–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgarejo, J.D.; Yang, W.Y.; Thijs, L.; Li, Y.; Asayama, K.; Hansen, T.W.; Wei, F.F.; Kikuya, M.; Ohkubo, T.; Dolan, E.; et al. Association of Fatal and Nonfatal Cardiovascular Outcomes With 24-Hour Mean Arterial Pressure. Hypertension 2021, 77, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finucane, C.; O’Connell, M.D.; Donoghue, O.; Richardson, K.; Savva, G.M.; Kenny, R.A. Impaired Orthostatic Blood Pressure Recovery Is Associated with Unexplained and Injurious Falls. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2017, 65, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truijen, J.; van Lieshout, J.J.; Wesselink, W.A.; Westerhof, B.E. Noninvasive continuous hemodynamic monitoring. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2012, 26, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wijnen, V.K.; Finucane, C.; Harms, M.P.M.; Nolan, H.; Freeman, R.L.; Westerhof, B.E.; Kenny, R.A.; Ter Maaten, J.C.; Wieling, W. Noninvasive beat-to-beat finger arterial pressure monitoring during orthostasis: A comprehensive review of normal and abnormal responses at different ages. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 282, 468–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloney, D.; O’Connor, J.; Newman, L.; Scarlett, S.; Hernandez, B.; Kenny, R.A.; Romero-Ortuno, R. Clinical clustering of eight orthostatic haemodynamic patterns in The Irish Longitudinal Study on Ageing (TILDA). Age Ageing 2020, 50, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feeney, J.; Dooley, C.; Finucane, C.; Kenny, R.A. Stressful life events and orthostatic blood pressure recovery in older adults. Health Psychol. 2015, 34, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagro, J.; Schoon, Y.; Heerts, I.; Meel-van den Abeelen, A.S.; Schalk, B.; Wieling, W.; Olde Rikkert, M.G.; Claassen, J.A. Impaired systolic blood pressure recovery directly after standing predicts mortality in older falls clinic patients. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, R.; Carey, D.; Kennelly, S.P.; Kenny, R.A. Longitudinal Association Between Orthostatic Hypotension at 30 Seconds Post-Standing and Late-Life Depression. Hypertension 2018, 71, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, K.; Lavan, A.; Kenny, R.A.; Briggs, R. Delayed Blood Pressure Recovery After Standing Independently Predicts Fracture in Community-Dwelling Older People. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2021, 22, 1235–1241.e1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, M.D.; Savva, G.M.; Fan, C.W.; Kenny, R.A. Orthostatic hypotension, orthostatic intolerance and frailty: The Irish Longitudinal Study on Aging-TILDA. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2015, 60, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, C.; Pearce, M.; Kerr, S.R.; Newton, J. A prospective study of the association between orthostatic hypotension and falls: Definition matters. Age Ageing 2017, 46, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mol, A.; Slangen, L.R.N.; Trappenburg, M.C.; Reijnierse, E.M.; van Wezel, R.J.A.; Meskers, C.G.M.; Maier, A.B. Blood Pressure Drop Rate after Standing Up is Associated with Frailty and Number of Falls in Geriatric Outpatients. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e014688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mol, A.; Slangen, L.R.N.; van Wezel, R.J.A.; Maier, A.B.; Meskers, C.G.M. Orthostatic blood pressure recovery associates with physical performance, frailty and number of falls in geriatric outpatients. J. Hypertens. 2021, 39, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Heus, R.A.A.; de Jong, D.L.K.; Sanders, M.L.; van Spijker, G.J.; Oudegeest-Sander, M.H.; Hopman, M.T.; Lawlor, B.A.; Olde Rikkert, M.G.M.; Claassen, J. Dynamic Regulation of Cerebral Blood Flow in Patients With Alzheimer Disease. Hypertension 2018, 72, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillebrand, S.L.; Reijnierse, E.M.; Meskers, C.G.M.; Maier, A.B. Orthostatic hypotension assessed by active standing is associated with worse cognition in geriatric rehabilitation inpatients, RESORT. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2021, 96, 104482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgibbon-Collins, L.K.; Heckman, G.A.; Bains, I.; Noguchi, M.; McIlroy, W.E.; Hughson, R.L. Older Adults’ Drop in Cerebral Oxygenation on Standing Correlates With Postural Instability and May Improve With Sitting Prior to Standing. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 1124–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothlisberger, D.; Jungo, K.T.; Butikofer, L.; Poortvliet, R.K.E.; Gussekloo, J.; Streit, S. Association of low blood pressure and falls: An analysis of data from the Leiden 85-plus Study. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0295976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welmer, A.K.; Wang, R.; Rizzuto, D.; Ek, S.; Vetrano, D.L.; Qiu, C. Associations of blood pressure with risk of injurious falls in old age vary by functional status: A cohort study. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 140, 111038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorowski, A.; Ricci, F.; Hamrefors, V.; Sandau, K.E.; Hwan Chung, T.; Muldowney, J.A.S.; Gopinathannair, R.; Olshansky, B. Orthostatic Hypotension: Management of a Complex, But Common, Medical Problem. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2022, 15, e010573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, B.H.; Loughin, T.M.; Robinovitch, S.N.; Claydon, V.E. Cardiovascular responses to orthostasis and their association with falls in older adults. BMC Geriatr. 2015, 15, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, B.H.; Garland, E.M.; Black, B.K.; Paranjape, S.Y.; Shibao, C.A.; Okamoto, L.E.; Gamboa, A.; Diedrich, A.; Plummer, W.D.; Dupont, W.D.; et al. Optimal diagnostic thresholds for diagnosis of orthostatic hypotension with a ‘sit-to-stand test’. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, S.E.; Jorstad-Stein, E.C.; Hauer, K.; Becker, C.; Prevention of Falls Network Europe and Outcomes Consensus Group. Development of a common outcome data set for fall injury prevention trials: The Prevention of Falls Network Europe consensus. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 1618–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauer, K.; Lamb, S.E.; Jorstad, E.C.; Todd, C.; Becker, C.; PROFANE-Group. Systematic review of definitions and methods of measuring falls in randomised controlled fall prevention trials. Age Ageing 2006, 35, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Heus, R.A.A.; Donders, R.; Santoso, A.M.M.; Rikkert, M.G.M.O.; Lawlor, B.A.; Claassen, J.A.H.R.; Segurado, R.; Howard, R.; Pasquier, F.; Börjesson-Hanson, A.; et al. Blood Pressure Lowering With Nilvadipine in Patients With Mild-to-Moderate Alzheimer Disease Does Not Increase the Prevalence of Orthostatic Hypotension. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e011938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivasi, G.; Rafanelli, M.; Mossello, E.; Brignole, M.; Ungar, A. Drug-Related Orthostatic Hypotension: Beyond Anti-Hypertensive Medications. Drugs Aging 2020, 37, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, J. Nilvadipine: Profile of a new calcium antagonist. An overview. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1994, 24 (Suppl. 2), S92–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Velde, N.; Seppala, L.J.; Herrero, A.C.; Annweiler, C.; Jonsdottir, A.B.; Blain, H.; Dionyssiotis, Y.; Duque, S.; Frith, J.; Francis, B.N.; et al. Falls prevention in community-dwelling older adults and implementation of world falls guidelines: A call for action across Europe by the European Geriatric Medicine Society Special Interest Group on Falls and Fractures. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2025. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, A.; Scheipl, F.; Küchenhoff, H.; Gabriel, A.-A. An introduction to semiparametric function-on-scalar regression. Stat. Model. 2018, 18, 346–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Baseline (resting) supine/sitting SBP | Mean SBP value of 30 s–60 s before standing, as baseline [26]; mmHg |
| Baseline (resting) supine/sitting DBP | Mean DBP value of 30 s–60 s before standing, as baseline [26]; mmHg |
| Baseline (resting) supine/sitting MAP | Mean MAP value of 30 s–60 s before standing, as baseline; MAP = DBP + 1/3 × (SBP–DBP) [27] (which is the same as ‘mean SBP’ + 1/3 × (‘mean SBP’–‘mean DBP’); mmHg |
| Orthostatic BP responses, variants, and symptoms | |
| SBP nadir | Minimum SBP value during standing; mmHg |
| DBP nadir | Minimum DBP value during standing; mmHg |
| MAP nadir | Minimum MAP value during standing; mmHg |
| Time to SBP nadir | Related time to SBP nadir during standing; seconds |
| Time to DBP nadir | Related time to DBP nadir during standing; seconds |
| Time to MAP nadir | Related time to MAP nadir during standing; seconds |
| Change in SBP from baseline | SBP(t) on standing–baseline (resting) supine/sitting SBP; ΔSBP(t); mmHg |
| Change in DBP from baseline | DBP(t) on standing–baseline (resting) supine/sitting DBP; ΔDBP(t); mmHg |
| Change in MAP from baseline | MAP(t) on standing–baseline (resting) supine/sitting MAP; ΔMAP(t); mmHg |
| Largest drop in SBP | Maximum change in SBP from baseline, SBP nadir–baseline (resting) supine/sitting SBP; ΔSBPmax; mmHg [22] |
| Largest drop in DBP | Maximum change in DBP from baseline, DBP nadir–baseline (resting) supine/sitting DBP; ΔDBPmax; mmHg [22] |
| Largest drop in MAP | Maximum change in MAP from baseline, MAP nadir–baseline (resting) supine/sitting MAP; ΔMAPmax; mmHg |
| Initial OH (15 s) | A transient BP decrease that exceeds thresholds (a drop in SBP of ≥40 mmHg and/or DBP of ≥20 mmHg) within 15 s of standing [16,26] |
| Sustained OH (10 s interval: 60–110 s) | A sustained SBP drop of ≥20 mmHg or a DBP drop of ≥10 mmHg upon standing, defined as exceeding the thresholds at all following time points: 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, and 110 s [26,28] |
| Sustained OH (1 min interval: 1–3 mins) | A sustained SBP drop of ≥20 mmHg or a DBP drop of ≥10 mmHg upon standing, defined as exceeding the thresholds at least 2 of the following time points: 1, 2, and 3 min. A sustained decline in SBP of ≥20 mmHg occurring 60–180 s after standing [15,16,19,29,30] |
| Classical OH (3 mins) | A sustained SBP drop of ≥20 mmHg and/or a DBP drop of ≥10 mmHg upon standing, defined as exceeding these thresholds at all following time points: 1, 2, and 3 min [10,31] |
| Delayed OH (after 3 mins) | A drop that exceeded the thresholds (an SBP drop of ≥20 mmHg or a DBP drop of ≥10 mmHg upon standing) at the following time points: 4 or 5 min [10,15,31] |
| Orthostatic BP recovery | Full recovery: >95% recovery of SBP/DBP at 60 s relative to baseline; Partial recovery: 80–95% recovery of SBP/DBP at 60 s relative to baseline; No recovery: <80% recovery of SBP/DBP at 60 s relative to baseline [32,33] |
| Delayed orthostatic BP recovery | An SBP drop of >20 mmHg and/or a DBP drop of ≥10 mmHg at 30–40 s, 60 s, and 90 s after standing, without meeting the criteria of classical OH [17,26,30,34,35] |
| Orthostatic intolerance | Symptoms of OH or complaints of participants (e.g., feeling dizzy, lightheadedness, or feeling unstable) during OH measurements [36] |
| PROHEALTH | NILVAD-CBF | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of participants (n) | 30 | 58 | 88 |
| Age (years; mean ±SD) | 74 ± 7 | 73 ± 6 | 74 ± 6 |
| Female sex (n; %) | 11 (37) | 34 (59) | 45 (51) |
| BMI (kg/m2; mean ±SD) | 24 ± 3 | 25 ± 4 | 24 ± 3 |
| Currently smoking (n; %) | 1 (3) | - | 1 (3) |
| MMSE score (median, IQR) | - | 21 (12–26) | 21 (12–26) |
| MoCA score (median, IQR) | 26 (24–28) | - | 26 (24–28) |
| DAD score (median, IQR) | - | 34 (30–38) | 34 (30–38) |
| Cardiovascular disease (n; %) | 4 (13) | 9 (16) | 13 (15) |
| Diabetes mellitus (n; %) | 3 (10) | 3 (5) | 6 (7) |
| Depression (n; %) | 3 (10) | - | 3 (10) |
| Antihypertensive drug use (n; %) | 7 (23) | 17 (29) | 24 (27) |
| Antidepressant use (n; %) | 2 (7) | 8 (14) | 10 (11) |
| Cholinesterase inhibitor use (n; %) | - | 46 (79) | 46 (52) |
| Statin use (n; %) | 3 (10) | 10 (17) | 13 (15) |
| Falls (n; %) | 7 (23) | 14 (24) | 21(24) |
| Variable | All | Fall Previous Year | No Falls Previous Year | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of participants | 30 | 7 | 23 | |
| Baseline (resting) sitting SBP (mmHg; mean ± SD) | 136 (22) | 115 (13) | 142 (21) | 0.004 * |
| Baseline (resting) sitting DBP (mmHg; mean ± SD) | 77 (12) | 68 (10) | 79 (11) | 0.018 * |
| Baseline (resting) sitting MAP (mmHg; mean ± SD) | 96 (14) | 84 (11) | 100 (13) | 0.004 * |
| SBP nadir (mmHg; mean ± SD) | 107 (26) | 90 (22) | 112 (25) | 0.043 * |
| DBP nadir (mmHg; mean ± SD) | 60 (11) | 53 (10) | 62 (11) | 0.059 |
| MAP nadir (mmHg; mean ± SD) | 72 (17) | 65 (14) | 74 (18) | 0.234 |
| Time to SBP nadir (seconds; median, IQR) | 10 (8–86) | 9 (8–34) | 10 (8–88) | 0.573 |
| Time to DBP nadir (seconds; median, IQR) | 8 (6–31) | 8 (6–8) | 9 (6–38) | 0.364 |
| Time to MAP nadir (seconds; median, IQR) | 22 (8–54) | 8 (7–16) | 26 (8–54) | 0.239 |
| Largest drop in SBP (mmHg; mean ± SD) | −29 (14) | −26 (13) | −30 (14) | 0.435 |
| Largest drop in DBP (mmHg; mean ± SD) | −16 (6) | −15 (3) | −17 (6) | 0.332 |
| Largest drop in MAP (mmHg; mean ± SD) | −21 (8) | −18 (6) | −21 (8) | 0.340 |
| Initial OH (at 15 s), n (%) | 1 (3) | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 1.000 |
| Sustained OH (60–110 s), n (%) | 2 (7) | 1 (14) | 1 (4) | 0.418 |
| Sustained OH (1–3 min), n (%) | 5 (17) | 2 (29) | 3 (13) | 0.565 |
| Classical OH (3 min), n (%) | 2 (7) | 1 (14) | 1 (4) | 0.418 |
| Orthostatic BP full recovery at 60 s, n (%) | 19 (63) | 4 (57) | 15 (65) | 0.182 |
| Orthostatic BP partial recovery at 60 s, n (%) | 10 (33) | 2 (29) | 8 (35) | |
| Orthostatic BP no recovery at 60 s, n (%) | 1 (3) | 1 (14) | 0 (0) | |
| Delayed orthostatic BP recovery, n (%) | 12 (40) | 3 (43) | 9 (39) | 0.894 |
| Orthostatic intolerance during stand, n (%) | 1 (3) | 1 (14) | 0 (0) | 0.233 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; van Poelgeest, E.P.; Klop, M.; Claassen, J.A.H.R.; Hoekstra, A.G.; van der Velde, N. Beat-to-Beat Blood Pressure Monitoring and Orthostatic Hypotension-Related Falls in Two Cohorts of Older Adults. Geriatrics 2025, 10, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10040102
Wang L, van Poelgeest EP, Klop M, Claassen JAHR, Hoekstra AG, van der Velde N. Beat-to-Beat Blood Pressure Monitoring and Orthostatic Hypotension-Related Falls in Two Cohorts of Older Adults. Geriatrics. 2025; 10(4):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10040102
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Liping, Eveline P. van Poelgeest, Marjolein Klop, Jurgen A. H. R. Claassen, Alfons G. Hoekstra, and Nathalie van der Velde. 2025. "Beat-to-Beat Blood Pressure Monitoring and Orthostatic Hypotension-Related Falls in Two Cohorts of Older Adults" Geriatrics 10, no. 4: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10040102
APA StyleWang, L., van Poelgeest, E. P., Klop, M., Claassen, J. A. H. R., Hoekstra, A. G., & van der Velde, N. (2025). Beat-to-Beat Blood Pressure Monitoring and Orthostatic Hypotension-Related Falls in Two Cohorts of Older Adults. Geriatrics, 10(4), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10040102





