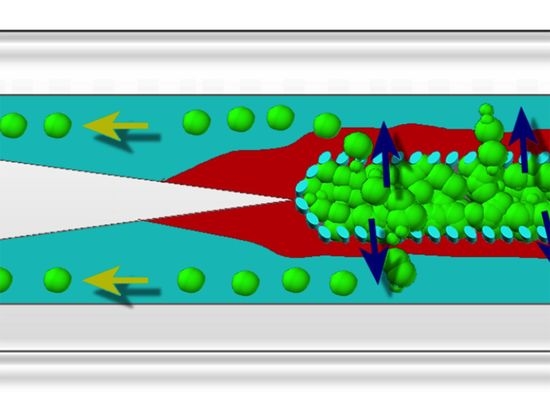
A 3D Microfluidic Model to Recapitulate Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion
Abstract
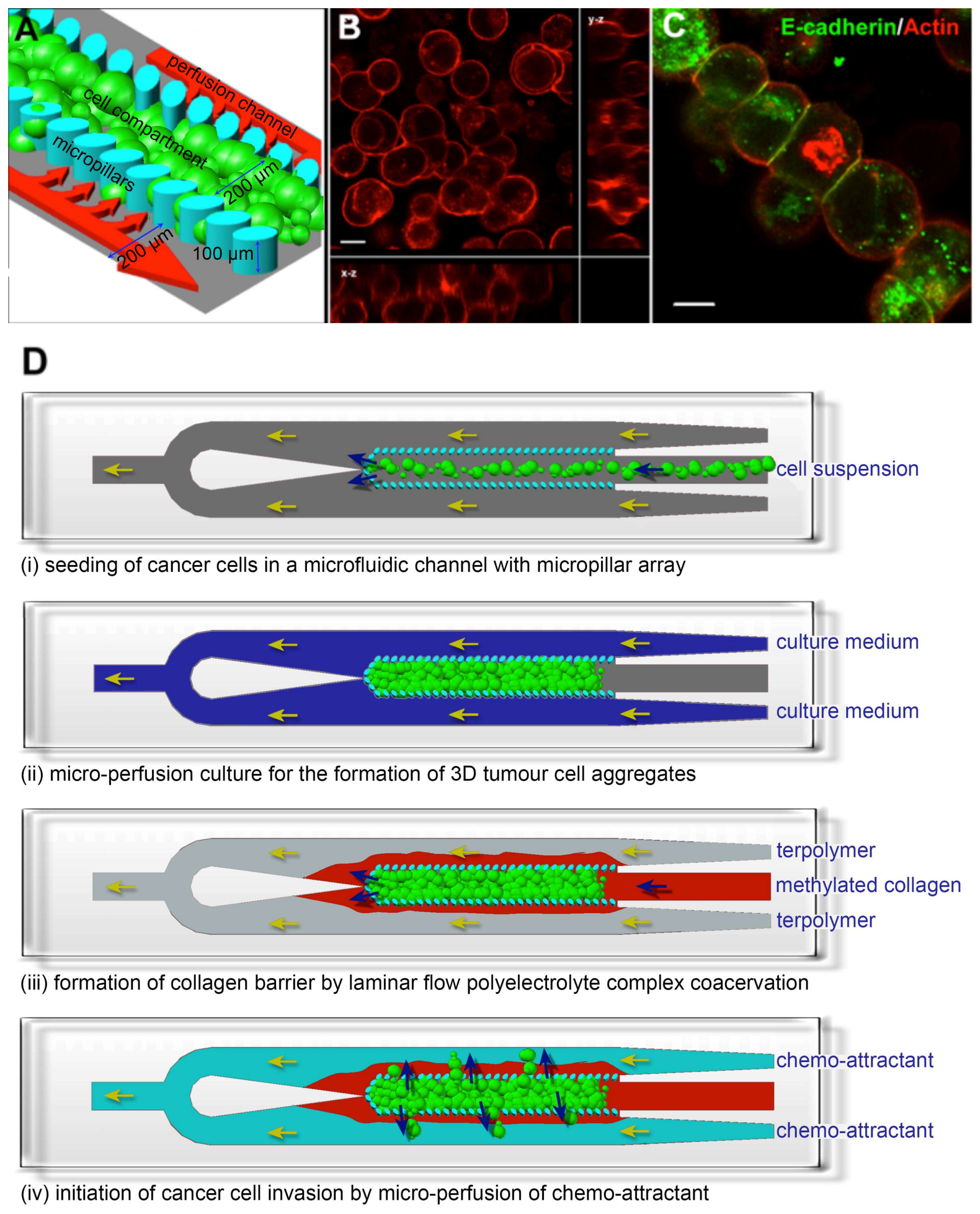
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
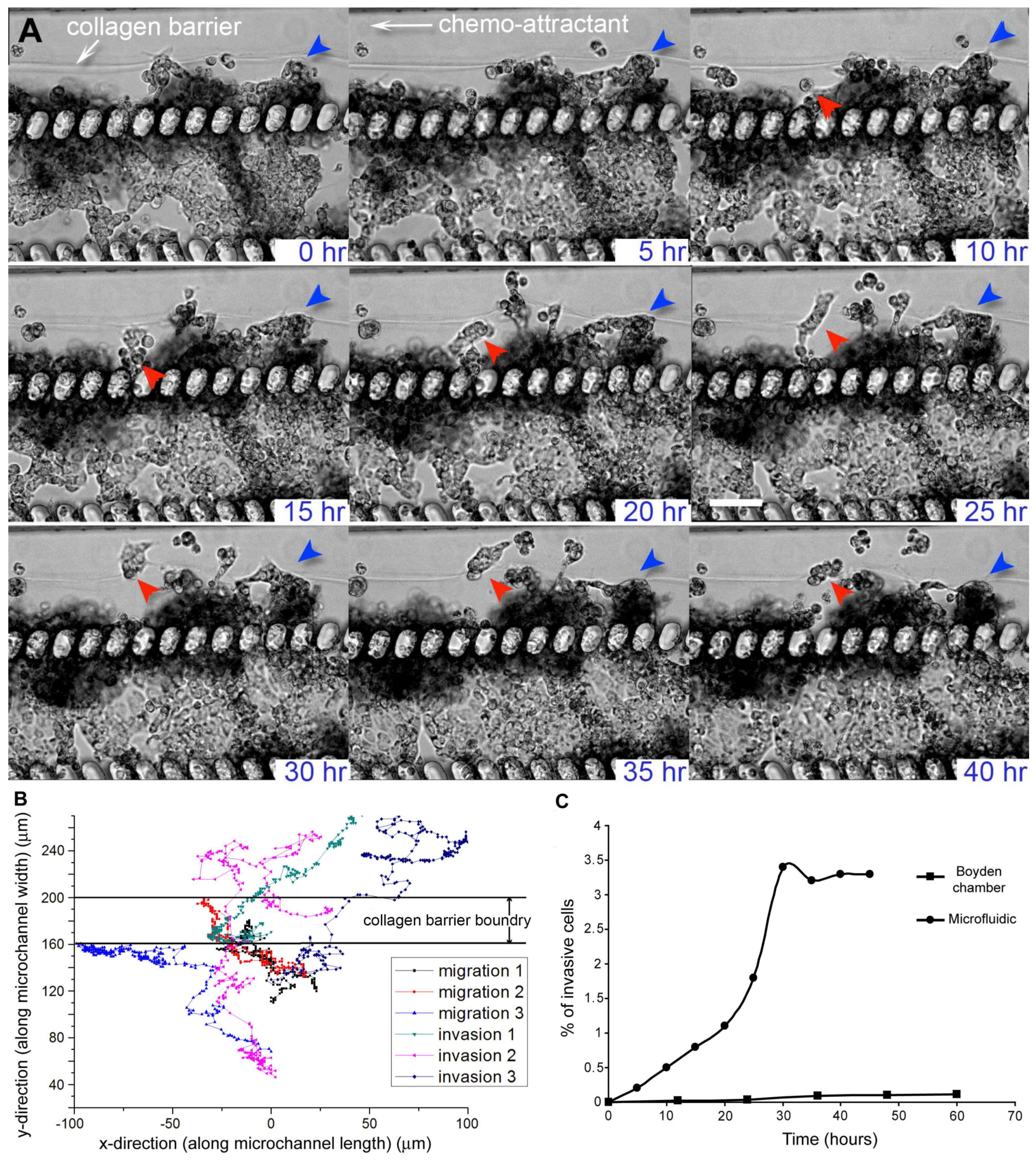
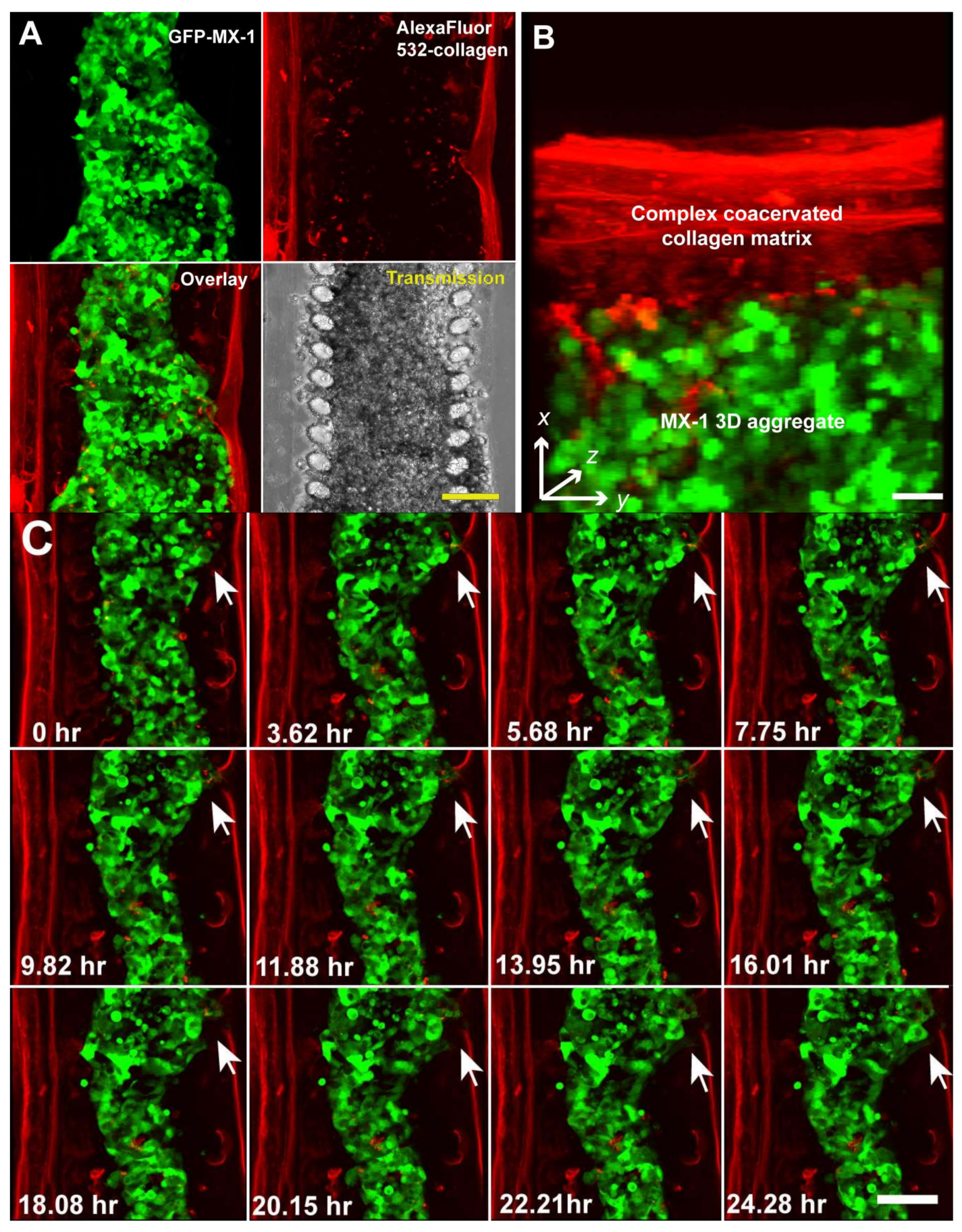
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chaffer, C.L.; Weinberg, R.A. A Perspective on Cancer Cell Metastasis. Science 2011, 331, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, M.J.; McGowan, P.M.; Gallagher, W.M. Cancer invasion and metastasis: Changing views. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zijlstra, A.; Lewis, J.; DeGryse, B.; Stuhlmann, H.; Quigley, J.P. The Inhibition of Tumor Cell Intravasation and Subsequent Metastasis via Regulation of In Vivo Tumor Cell Motility by the Tetraspanin CD151. Cancer Cell 2008, 13, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckhardt, B.L.; Francis, P.A.; Parker, B.S.; Anderson, R.L. Strategies for the discovery and development of therapies for metastatic breast cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 479–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, G.P.; Massagué, J. Cancer metastasis: Building a framework. Cell 2006, 127, 679–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paweletz, C.P.; Charboneau, L.; Liotta, L.A. Overview of Metastasis Assays. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2001, 12, 19.1.1–19.1.9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deryugina, E.; Quigley, J. Chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane model systems to study and visualize human tumor cell metastasis. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 130, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahai, E. Mechanisms of cancer cell invasion. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2005, 15, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenny, H.A.; Krausz, T.; Yamada, S.D.; Lengyel, E. Use of a novel 3D culture model to elucidate the role of mesothelial cells, fibroblasts and extra-cellular matrices on adhesion and invasion of ovarian cancer cells to the omentum. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, W.; O’Kelly, J.; Lu, D.; Leiter, A.; Sohn, J.; Yin, D.; Karlan, B.; Vadgama, J.; Lyons, K.M.; Koeffler, H.P. Expression of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF/CCN2) in breast cancer cells is associated with increased migration and angiogenesis. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 38, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, A.; Yamamura, M.; Katase, N.; Itadani, M.; Okada, N.; Kobiki, K.; Nakamura, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kuribayashi, F. Evaluation of pancreatic cancer cell migration with multiple parameters in vitro by using an optical real-time cell mobility assay device. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarrow, J.C.; Perlman, Z.E.; Westwood, N.J.; Mitchison, T.J. A high-throughput cell migration assay using scratch wound healing, a comparison of image-based readout methods. BMC Biotechnol. 2004, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, M.; Yao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, F.; Mei, H.; Guo, X.; Huang, W. Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR promotes metastasis of renal cell carcinoma by up-regulating histone H3K27 demethylase JMJD3. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 19795–19802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulkower, K.I.; Herber, R.L. Cell Migration and Invasion Assays as Tools for Drug Discovery. Pharmaceutics 2011, 3, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, F.-Q.; Yamada, M.; Kobayashi, J.; Yamato, M.; Kikuchi, A.; Okano, T. On-chip cell migration assay using microfluidic channels. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4017–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadi, W.; Wang, S.-J.; Lin, F.; Jeon, N.L. A parallel-gradient microfluidic chamber for quantitative analysis of breast cancer cell chemotaxis. Biomed. Microdevices 2006, 8, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, N.L.; Baskaran, H.; Dertinger, S.K.W.; Whitesides, G.M.; van der Water, L.; Toner, M. Neutrophil chemotaxis in linear and complex gradients of interleukin-8 formed in a microfabricated device. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaw, K.C.; Manimaran, M.; Tay, E.H.; Swaminathan, S. Multi-step microfluidic device for studying cancer metastasis. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Businaro, L.; de Ninno, A.; Schiavoni, G.; Lucarini, V.; Ciasca, G.; Gerardino, A.; Belardelli, F.; Gabriele, L.; Mattei, F. Cross talk between cancer and immune cells: Exploring complex dynamics in a microfluidic environment. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, S.; Du, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Qian, X.; Zhang, M.; Sun, W. Microfluidic co-culture system for cancer migratory analysis and anti-metastatic drugs screening. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogenrieder, T.; Herlyn, M. Axis of evil: Molecular mechanisms of cancer metastasis. Oncogene 2003, 22, 6524–6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erler, J.T.; Weaver, V.M. Three-dimensional context regulation of metastasis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2009, 26, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.; Sudo, R.; Mack, P.J.; Wan, C.-R.; Vickerman, V.; Kamm, R.D. Cell migration into scaffolds under co-culture conditions in a microfluidic platform. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zervantonakis, I.K.; Hughes-Alford, S.K.; Charest, J.L.; Condeelis, J.S.; Gertler, F.B.; Kamm, R.D. Three-dimensional microfluidic model for tumor cell intravasation and endothelial barrier function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13515–13520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Hyun, E.; Seo, J.; Blundell, C.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, E.; Lee, S.H.; Moon, A.; Moon, W.C.; Huh, D. A microengineered pathophysiological model of early-stage breast cancer. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 3350–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, D.; Liu, H.; Lin, S.; Jiang, Y. Drug cytotoxicity and signaling pathway analysis with three-dimensional tumor spheroids in a microwell-based microfluidic chip for drug screening. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 898, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, Y.C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Khong, Y.M.; Chang, S.; Samper, V.D.; van Noort, D.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Yu, H. A novel 3D mammalian cell perfusion-culture system in microfluidic channels. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kihara, T.; Ito, J.; Miyake, J. Measurement of Biomolecular Diffusion in Extracellular Matrix Condensed by Fibroblasts Using Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, D.; Kurisu, S.; Takenawa, T. Regulation of cancer cell motility through actin reorganization. Cancer Sci. 2005, 96, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croft, D.R.; Olson, M.F. Regulating the conversion between rounded and elongated modes of cancer cell movement. Cancer Cell 2008, 14, 349–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ong, S.M.; Zhang, C.; Toh, Y.-C.; Kim, S.-H.; Foo, H.-L.; Tan, C.-H.; van Noort, D.; Park, S.; Yu, H. A gel-free 3D microfluidic cell culture system. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 3237–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Abdul Rahim, N.A.; van Noort, D.; Yu, H. Towards human on a chip: Culturing multiple cell types on a chip with compartmentalized microenvironments. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 3185–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.T.T.; van Noort, D.; Jeong, I.K.; Park, S. Endocrine systems on chip for a diabetes treatment model. Biofabrication 2017, 9, 015021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaiah, J.F. The organ microenvironment and cancer metastasis. Differentiation 2002, 70, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, B.; Heyder, C.; Gloria-Maercker, E.; Hatzmann, W.; Rötger, A.; Kemming, D.; Zänker, K.S.; Entschladen, F.; Dittmar, T. 3D-extravasation model—Selection of highly motile and metastatic cancer cells. Sem. Cancer Biol. 2005, 15, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyder, C.; Gloria, M.; Gloria-Maercker, E.; Hatzmann, W.; Niggermann, D.; Zänker, K.S.; Dittmar, T. Realtime visualization of tumor cell/endothelial cell interactions during transmigration across the endothelial barrier. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 128, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheridan, C.; Kishimoto, H.; Fuchs, R.; Mehrotra, S.; Bhat-Nakshatri, P.; Turner, C.H.; Goulet, R., Jr.; Badve, S.; Nakshatri, H. CD44+/CD24− breast cancer cells exhibit enhanced invasive properties: An early step necessary for metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. 2006, 8, R59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, N.S.; Bicknell, R. Cell Migration and the Boyden Chamber. In Metastasis Research Protocols; Brooks, S.A., Schumacher, U., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 47–54. ISBN 0-89603-610-3. [Google Scholar]
- Overall, C.M.; Kleifeld, O. Tumour microenvironment—Opinion: Validating matrix metalloproteinases as drug targets and anti-targets for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sliva, D. Signaling Pathways Responsible for Cancer Cell Invasion as Targets for Cancer Therapy. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2004, 4, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toh, Y.-C.; Raja, A.; Yu, H.; Van Noort, D. A 3D Microfluidic Model to Recapitulate Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion. Bioengineering 2018, 5, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering5020029
Toh Y-C, Raja A, Yu H, Van Noort D. A 3D Microfluidic Model to Recapitulate Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion. Bioengineering. 2018; 5(2):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering5020029
Chicago/Turabian StyleToh, Yi-Chin, Anju Raja, Hanry Yu, and Danny Van Noort. 2018. "A 3D Microfluidic Model to Recapitulate Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion" Bioengineering 5, no. 2: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering5020029
APA StyleToh, Y.-C., Raja, A., Yu, H., & Van Noort, D. (2018). A 3D Microfluidic Model to Recapitulate Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion. Bioengineering, 5(2), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering5020029