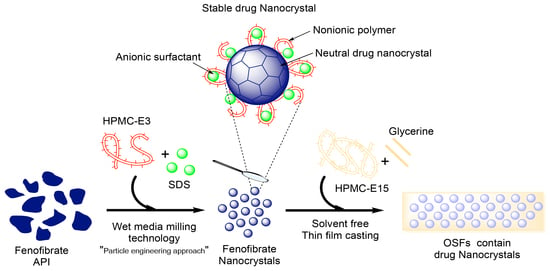
Fenofibrate Nanocrystals Embedded in Oral Strip-Films for Bioavailability Enhancement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Coarse Drug Suspensions
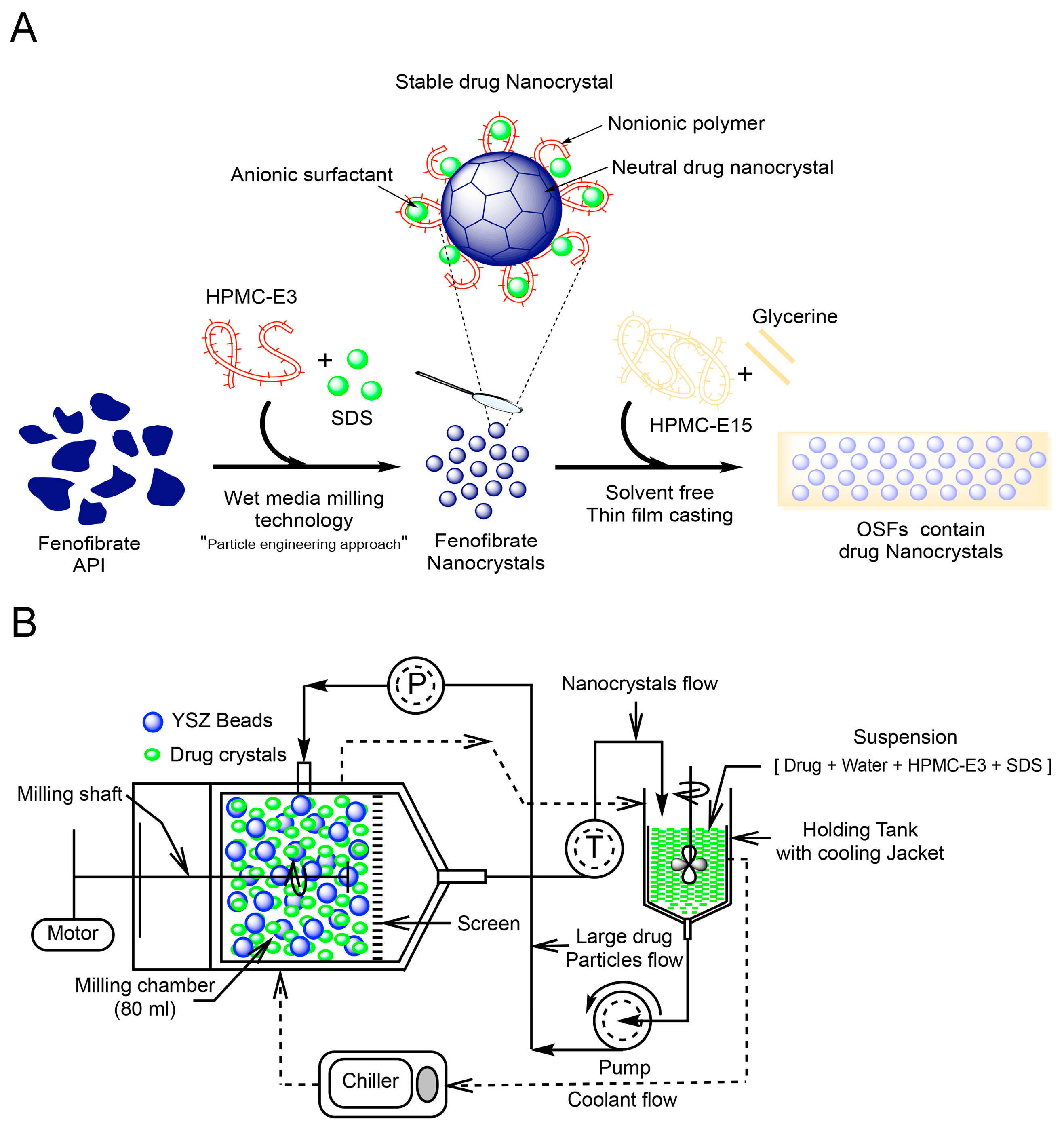
2.3. Preparation of Drug Nanocrystals by Wet Stirred Media Milling (WSMM)
2.4. Preparation of OSFs Containing NCs
2.5. Particle Size and Zeta Potential Analysis
2.6. Analytical Characterization
2.7. Properties of OSFs
2.7.1. OSF Thickness Measurement
2.7.2. Tensile Properties
2.7.3. Determination of Drug Content
2.8. In Vitro Flow-Through Cell Drug Dissolution System
2.9. UV Imaging Release Experiments
2.9.1. Surface Dissolution Imager Setup
2.9.2. In Situ Real Time UV Image Monitoring
2.10. Pharmacokinetic Study
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Particle Size and Zeta Potential Effect on Stability of NCs
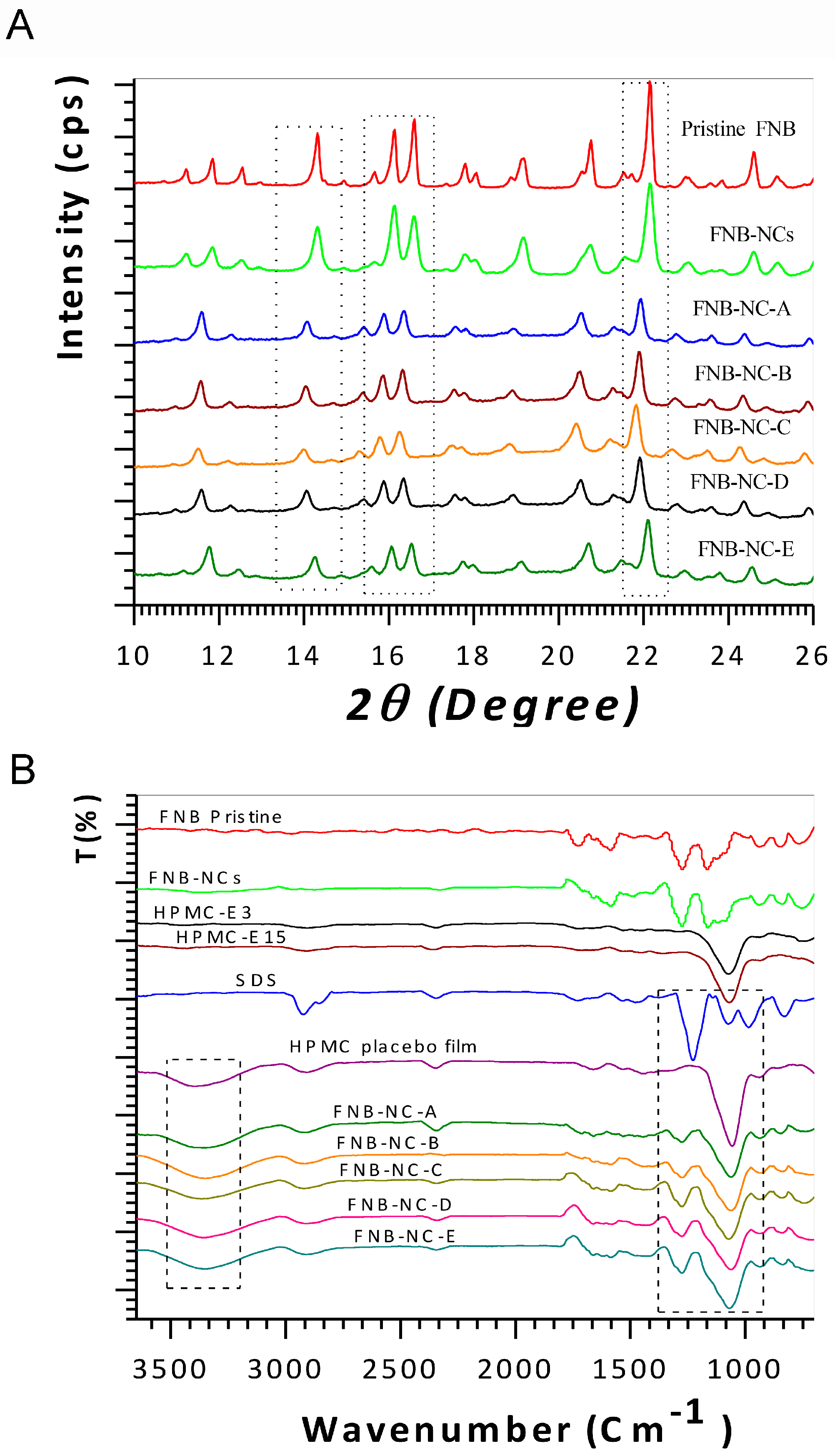
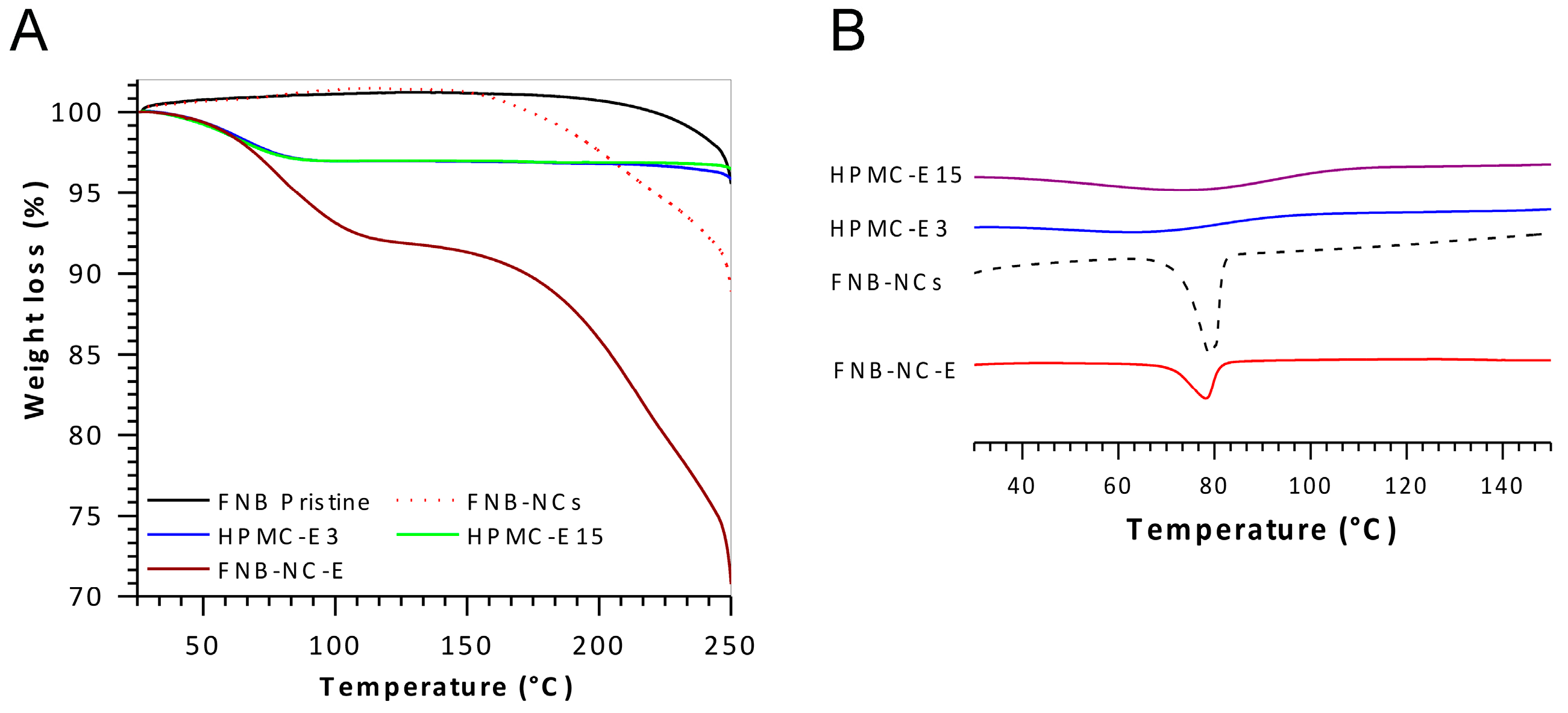
3.2. Solid-State Characterization
3.2.1. X-ray Diffractograms
3.2.2. ATR-FTIR and FT-Raman Spectroscopy Analysis
3.2.3. Thermal Analysis
3.3. Morphological Characterization
3.4. Properties of OSFs
3.4.1. Drug Content and Thickness
3.4.2. Mechanical Properties of OSFs
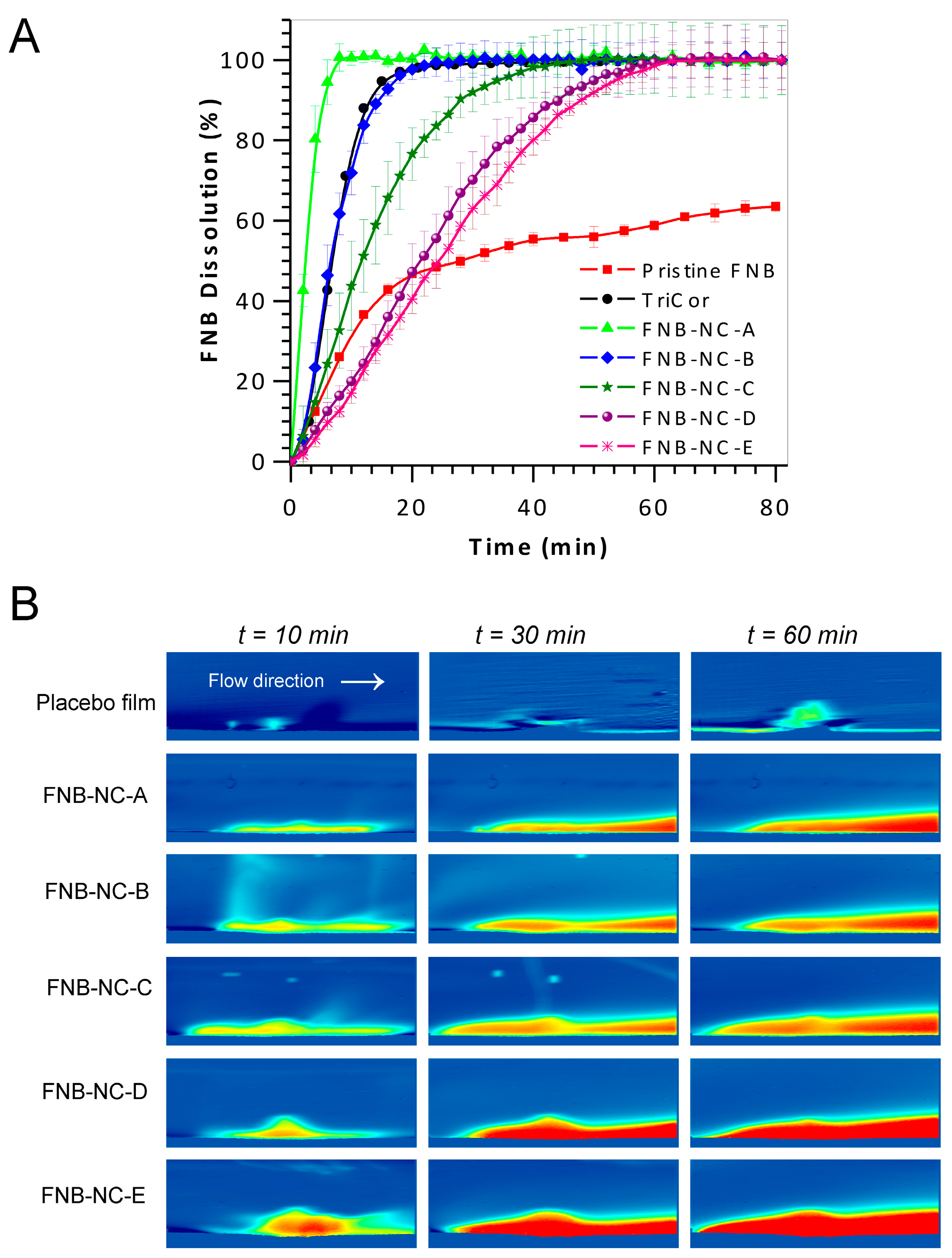
3.5. In Vitro Dissolution Studies
3.6. In Situ Real-Time Drug Dissolution Analysis
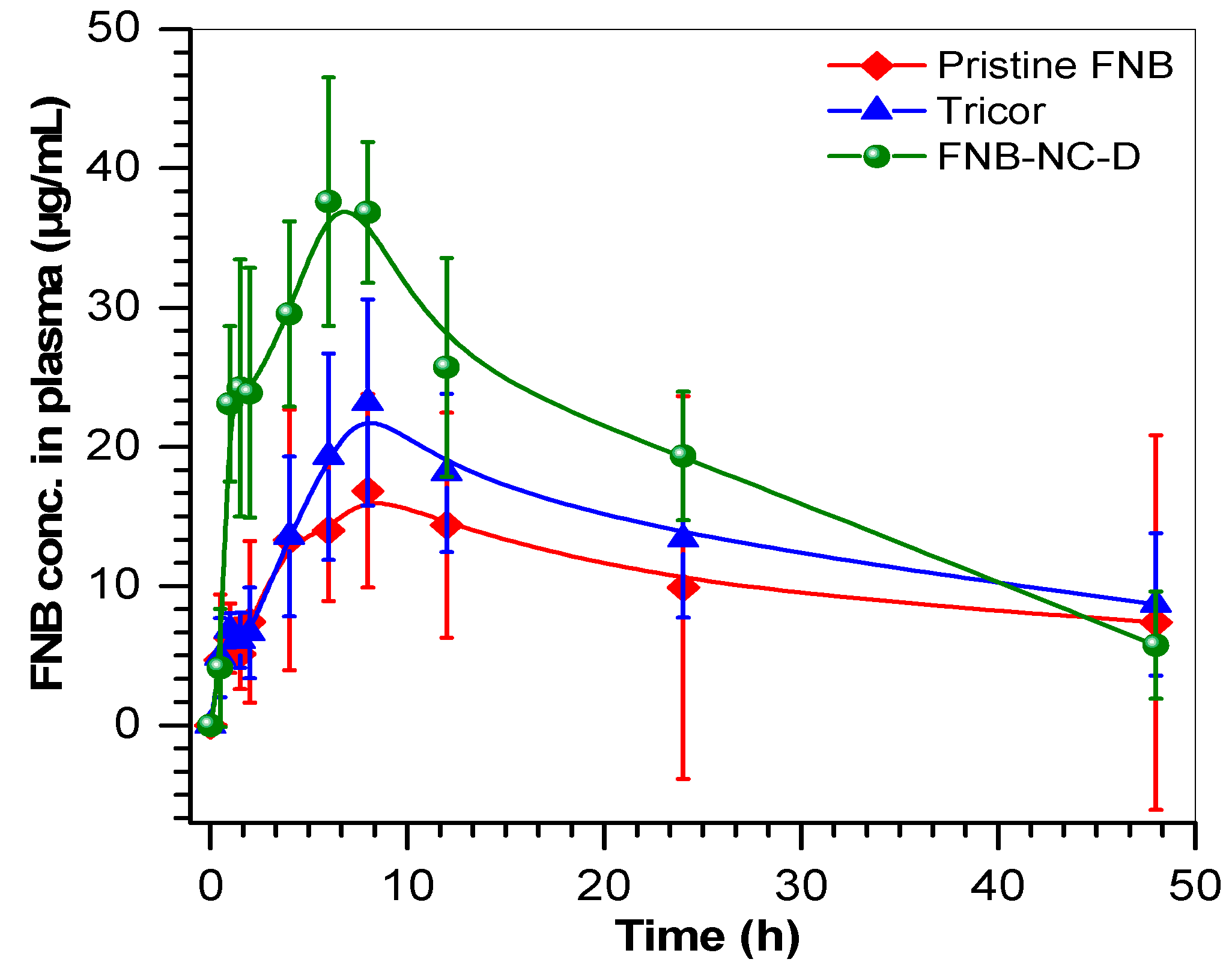
3.7. Pharmacokinetic Parameters
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tziomalos, K.; Athyros, V.G. Fenofibrate: A novel formulation (triglide™) in the treatment of lipid disorders: A review. Int. J. Nanomed. 2006, 1, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.; Luoma, J.T.; Hilleman, D. A review of currently available fenofibrate and fenofibric acid formulations. Cardiol. Res. 2013, 4, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthelsen, R.; Sjögren, E.; Jacobsen, J.; Kristensen, J.; Holm, R.; Abrahamsson, B.; Müllertz, A. Combining in vitro and in silico methods for better prediction of surfactant effects on the absorption of poorly water soluble drugs—A fenofibrate case example. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 473, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Lin, P.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q. A novel nanomatrix system consisted of colloidal silica and ph-sensitive polymethylacrylate improves the oral bioavailability of fenofibrate. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 79, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, M.; Kunath, K.; Dressman, J.B. Dissolution improvement of four poorly water soluble drugs by cogrinding with commonly used excipients. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 68, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, Y.; Chen, J.; Lai, J.; Sun, J.; Hu, F.; Wu, W. Enhanced bioavailability of the poorly water-soluble drug fenofibrate by using liposomes containing a bile salt. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 376, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, K.-H.; Cho, K.-J.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, J.-S.; Park, H.J.; Park, J.; Cho, W.; Park, J.-S.; Hwang, S.-J. Enhancement of the dissolution rate and bioavailability of fenofibrate by a melt-adsorption method using supercritical carbon dioxide. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5565–5575. [Google Scholar]
- Uejo, F.; Limwikrant, W.; Moribe, K.; Yamamoto, K. Dissolution improvement of fenofibrate by melting inclusion in mesoporous silica. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 8, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, R.J.; Hanrahan, J.P.; Tobin, J.M.; Ryan, K.B.; Crean, A.M. Comparison of fenofibrate–mesoporous silica drug-loading processes for enhanced drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 50, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.G.; Poudel, B.K.; Marasini, N.; Lee, D.W.; Hiep, T.T.; Yang, K.Y.; Kim, J.O.; Yong, C.S.; Choi, H.-G. Enhancement of oral bioavailability of fenofibrate by solid self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.-D.; Ho, H.-O.; Chen, C.-H.; Ke, W.-T.; Chen, E.T.-H.; Sheu, M.-T. Characterisation of fenofibrate dissolution delivered by a self-microemulsifying drug-delivery system. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 1685–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanganwar, G.P.; Gupta, R.B. Dissolution-rate enhancement of fenofibrate by adsorption onto silica using supercritical carbon dioxide. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 360, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vialpando, M.; Martens, J.A.; Van den Mooter, G. Potential of ordered mesoporous silica for oral delivery of poorly soluble drugs. Ther. Deliv. 2011, 2, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Yun, H.-S.; Kim, S.-H. The comparative effects of mesoporous silica nanoparticles and colloidal silica on inflammation and apoptosis. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9434–9443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.; Liu, T.; Li, L.; Liu, H.; Chen, D.; Tang, F. The absorption, distribution, excretion and toxicity of mesoporous silica nanoparticles in mice following different exposure routes. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2565–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievens-Figueroa, L.; Bhakay, A.; Jerez-Rozo, J.I.; Pandya, N.; Romañach, R.J.; Michniak-Kohn, B.; Iqbal, Z.; Bilgili, E.; Davé, R.N. Preparation and characterization of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose films containing stable bcs class ii drug nanoparticles for pharmaceutical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 423, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Gu, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y. Preparation of fenofibrate nanosuspension and study of its pharmacokinetic behavior in rats. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2009, 35, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanafy, A.; Spahn-Langguth, H.; Vergnault, G.; Grenier, P.; Tubic Grozdanis, M.; Lenhardt, T.; Langguth, P. Pharmacokinetic evaluation of oral fenofibrate nanosuspensions and sln in comparison to conventional suspensions of micronized drug. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesisoglou, F.; Panmai, S.; Wu, Y. Nanosizing—Oral formulation development and biopharmaceutical evaluation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ige, P.P.; Baria, R.K.; Gattani, S.G. Fabrication of fenofibrate nanocrystals by probe sonication method for enhancement of dissolution rate and oral bioavailability. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 108, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, A.; Breyer, S.; Geissler, S.; Mier, W.; Haberkorn, U.; Weigandt, M.; Mäder, K. How do in-vitro release profiles of nanosuspensions from alzet® pumps correspond to the in-vivo situation? A case study on radiolabeled fenofibrate. J. Control. Release 2013, 168, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Huey, B.D.; Burgess, D.J. Scanning probe microscopy method for nanosuspension stabilizer selection. Langmuir 2009, 25, 12481–12487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, I.; Schenck, D.; Bose, S.; Ruegger, C. Optimization of formulation and process parameters for the production of nanosuspension by wet media milling technique: Effect of vitamin e tpgs and nanocrystal particle size on oral absorption. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 47, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, D. Stability of nanosuspensions in drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 1126–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinow, B.E. Nanosuspensions in drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Kumar, S.; Gokhale, R.; Burgess, D.J. Physical stability of nanosuspensions: Investigation of the role of stabilizers on ostwald ripening. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 406, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, D.; Tao, J.; He, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, D.; Yu, M.; Cui, F.; Gan, Y. Enhanced transport of nanocage stabilized pure nanodrug across intestinal epithelial barrier mimicking listeria monocytogenes. Biomaterials 2015, 37, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhakay, A.; Azad, M.; Vizzotti, E.; Dave, R.N.; Bilgili, E. Enhanced recovery and dissolution of griseofulvin nanoparticles from surfactant-free nanocomposite microparticles incorporating wet-milled swellable dispersants. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2014, 40, 1509–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhakay, A.; Azad, M.; Bilgili, E.; Dave, R. Redispersible fast dissolving nanocomposite microparticles of poorly water-soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 461, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.-D.; Shen, C.-Y.; Yuan, X.-D.; Bai, J.-X.; Lv, Q.-Y.; Xu, H.; Dai, L.; Yu, C.; Han, J.; Yuan, H.-L. Development and characterization of an orodispersible film containing drug nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuhrmann, K.; Fuhrmann, G. Recent advances in oral delivery of macromolecular drugs and benefits of polymer conjugation. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 31, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susarla, R.; Sievens-Figueroa, L.; Bhakay, A.; Shen, Y.; Jerez-Rozo, J.I.; Engen, W.; Khusid, B.; Bilgili, E.; Romañach, R.J.; Morris, K.R.; et al. Fast drying of biocompatible polymer films loaded with poorly water-soluble drug nano-particles via low temperature forced convection. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 455, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, F.; Franceschini, I.; Corrias, F.; Sala, M.C.; Cilurzo, F.; Sinico, C.; Pini, E. Maltodextrin fast dissolving films for quercetin nanocrystal delivery. A feasibility study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 121, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, S.; Ibrahim, H.K.; Mohamed, M.I.; El-Milligi, M.F. Fast-dissolving sublingual films of terbutaline sulfate: Formulation and in vitro/in vivo evaluation. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 2942–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afolabi, A.; Akinlabi, O.; Bilgili, E. Impact of process parameters on the breakage kinetics of poorly water-soluble drugs during wet stirred media milling: A microhydrodynamic view. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 51, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ying, Y.; Pielecha-Safira, B.; Bilgili, E.; Ramachandran, R.; Romañach, R.; Davé, R.N.; Iqbal, Z. Raman spectroscopy for in-line and off-line quantification of poorly soluble drugs in strip films. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 475, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knieke, C.; Azad, M.A.; Davé, R.N.; Bilgili, E. A study of the physical stability of wet media-milled fenofibrate suspensions using dynamic equilibrium curves. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2013, 91, 1245–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Srinivasan, K.K.; Gowthamarajan, K.; Singare, D.S.; Prakash, D.; Gaikwad, N.B. Investigation of preparation parameters of nanosuspension by top-down media milling to improve the dissolution of poorly water-soluble glyburide. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 78, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devadasu, V.R.; Bhardwaj, V.; Kumar, M.N.V.R. Can controversial nanotechnology promise drug delivery? Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 1686–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglund, K.D.; Przybycien, T.M.; Tilton, R.D. Coadsorption of sodium dodecyl sulfate with hydrophobically modified nonionic cellulose polymers. 1. Role of polymer hydrophobic modification. Langmuir 2003, 19, 2705–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoreishi, S.M.; Li, Y.; Bloor, D.M.; Warr, J.; Wyn-Jones, E. Electromotive force studies associated with the binding of sodium dodecyl sulfate to a range of nonionic polymers. Langmuir 1999, 15, 4380–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Tao, X.; Tian, B.; Tang, Y.; Shao, Y.; Kou, L.; Gou, J.; Li, X.; Yin, T.; Tang, X. Improved oral bioavailability of core–shell structured beads by redispersion of the shell-forming nanoparticles: Preparation, characterization and in vivo studies. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 113, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmuga Priya, D.; Suriyaprabha, R.; Yuvakkumar, R.; Rajendran, V. Chitosan-incorporated different nanocomposite hpmc films for food preservation. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, H.; Grelier, S.; Pardon, P.; Coma, V. Antimicrobial and physicochemical properties of chitosan−hpmc-based films. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 6585–6591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somashekarappa, H.; Prakash, Y.; Hemalatha, K.; Demappa, T.; Somashekar, R. Preparation and characterization of hpmc/pvp blend films plasticized with sorbitol. Indian J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 2013, 307514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, R.B.; da Silva, A.B.F.; Pimentel, A.S. Infrared spectroscopy of anionic, cationic, and zwitterionic surfactants. Adv. Phys. Chem. 2012, 2012, 903272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Waard, H.; De Beer, T.; Hinrichs, W.L.J.; Vervaet, C.; Remon, J.-P.; Frijlink, H.W. Controlled crystallization of the lipophilic drug fenofibrate during freeze-drying: Elucidation of the mechanism by in-line raman spectroscopy. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tipduangta, P.; Takieddin, K.; Fábián, L.; Belton, P.; Qi, S. A new low melting-point polymorph of fenofibrate prepared via talc induced heterogeneous nucleation. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 5011–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Østergaard, J.; Meng-Lund, E.; Larsen, S.W.; Larsen, C.; Petersson, K.; Lenke, J.; Jensen, H. Real-time uv imaging of nicotine release from transdermal patch. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 2614–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, N.; Wang, K.; Schlindwein, W.; Davies, A.; Li, M. In situ monitoring of carbamazepine–nicotinamide cocrystal intrinsic dissolution behaviour. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 83, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boetker, J.P.; Savolainen, M.; Koradia, V.; Tian, F.; Rades, T.; Müllertz, A.; Cornett, C.; Rantanen, J.; Østergaard, J. Insights into the early dissolution events of amlodipine using uv imaging and raman spectroscopy. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 1372–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Østergaard, J.; Wu, J.X.; Naelapää, K.; Boetker, J.P.; Jensen, H.; Rantanen, J. Simultaneous uv imaging and raman spectroscopy for the measurement of solvent-mediated phase transformations during dissolution testing. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S.; Naelapää, K.; Rantanen, J.; Selen, A.; Müllertz, A.; Østergaard, J. Real-time dissolution behavior of furosemide in biorelevant media as determined by uv imaging. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2013, 18, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

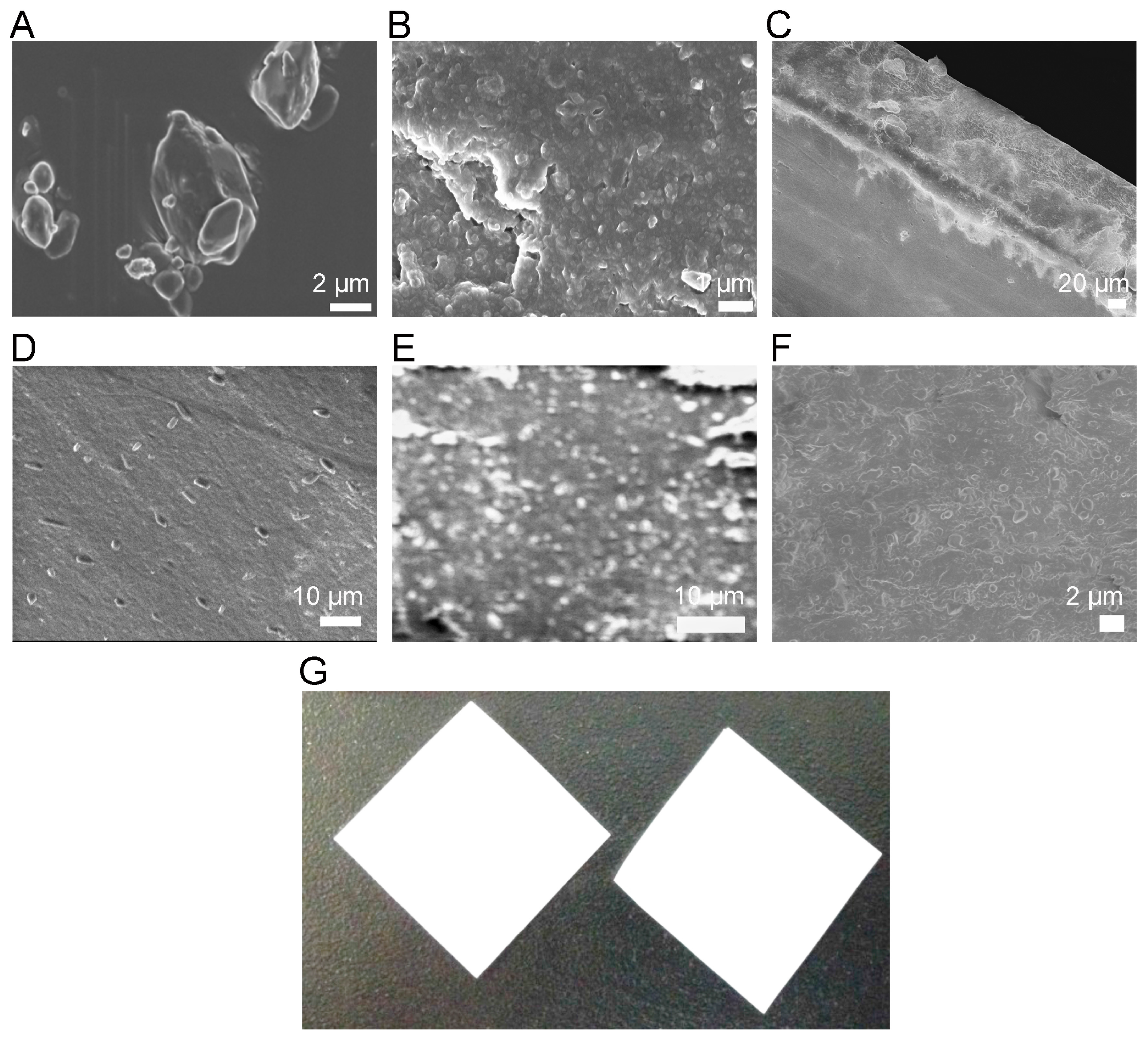
| Formulations | Film Thickness (µm) | wt FNB (%) | FNB Conc. (mg/cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FNB-NC-A | 45.90 ± 2.7 | 37.07 ± 1.4% | 2.24 |
| FNB-NC-B | 84.5 ± 8.0 | 36.87 ± 0.9% | 3.47 |
| FNB-NC-C | 115.8 ± 4.7 | 36.00 ± 0.7% | 4.46 |
| FNB-NC-D | 151.2 ± 5.7 | 33.15 ± 0.3% | 5.20 |
| FNB-NC-E | 165.0 ± 5.5 | 31.43 ± 1.5% | 5.28 |
| PK Parameters | FNB | Tricor | FNB-NC-D (OSF) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax (µg/mL) | 16.8 ± 12.2 | 23.1 ± 8.8 | 37.6 ± 10.6 * | 0.01 |
| Tmax (h) | 8.0 ± 5.8 | 8.0 ± 3.0 | 6.0 ± 1.7 | 0.6 |
| AUC 0–∞ (µg·h/mL) | 514.8 ± 374 | 654.6 ± 251 | 931.2 ± 263 | 0.08 |
| MRT (h) | 21.6 ± 15.7 | 21.4 ± 8.2 | 17.4 ± 4.9 | 0.7 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kevadiya, B.D.; Barvaliya, M.; Zhang, L.; Anovadiya, A.; Brahmbhatt, H.; Paul, P.; Tripathi, C. Fenofibrate Nanocrystals Embedded in Oral Strip-Films for Bioavailability Enhancement. Bioengineering 2018, 5, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering5010016
Kevadiya BD, Barvaliya M, Zhang L, Anovadiya A, Brahmbhatt H, Paul P, Tripathi C. Fenofibrate Nanocrystals Embedded in Oral Strip-Films for Bioavailability Enhancement. Bioengineering. 2018; 5(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering5010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleKevadiya, Bhavesh D., Manish Barvaliya, Lu Zhang, Ashish Anovadiya, Harshad Brahmbhatt, Parimal Paul, and Chandrabhanu Tripathi. 2018. "Fenofibrate Nanocrystals Embedded in Oral Strip-Films for Bioavailability Enhancement" Bioengineering 5, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering5010016
APA StyleKevadiya, B. D., Barvaliya, M., Zhang, L., Anovadiya, A., Brahmbhatt, H., Paul, P., & Tripathi, C. (2018). Fenofibrate Nanocrystals Embedded in Oral Strip-Films for Bioavailability Enhancement. Bioengineering, 5(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering5010016