Time-Frequency Distribution of Seismocardiographic Signals: A Comparative Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
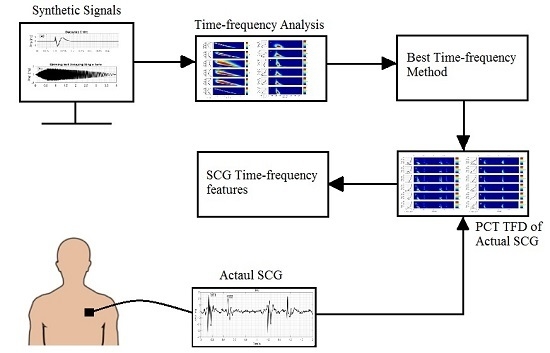
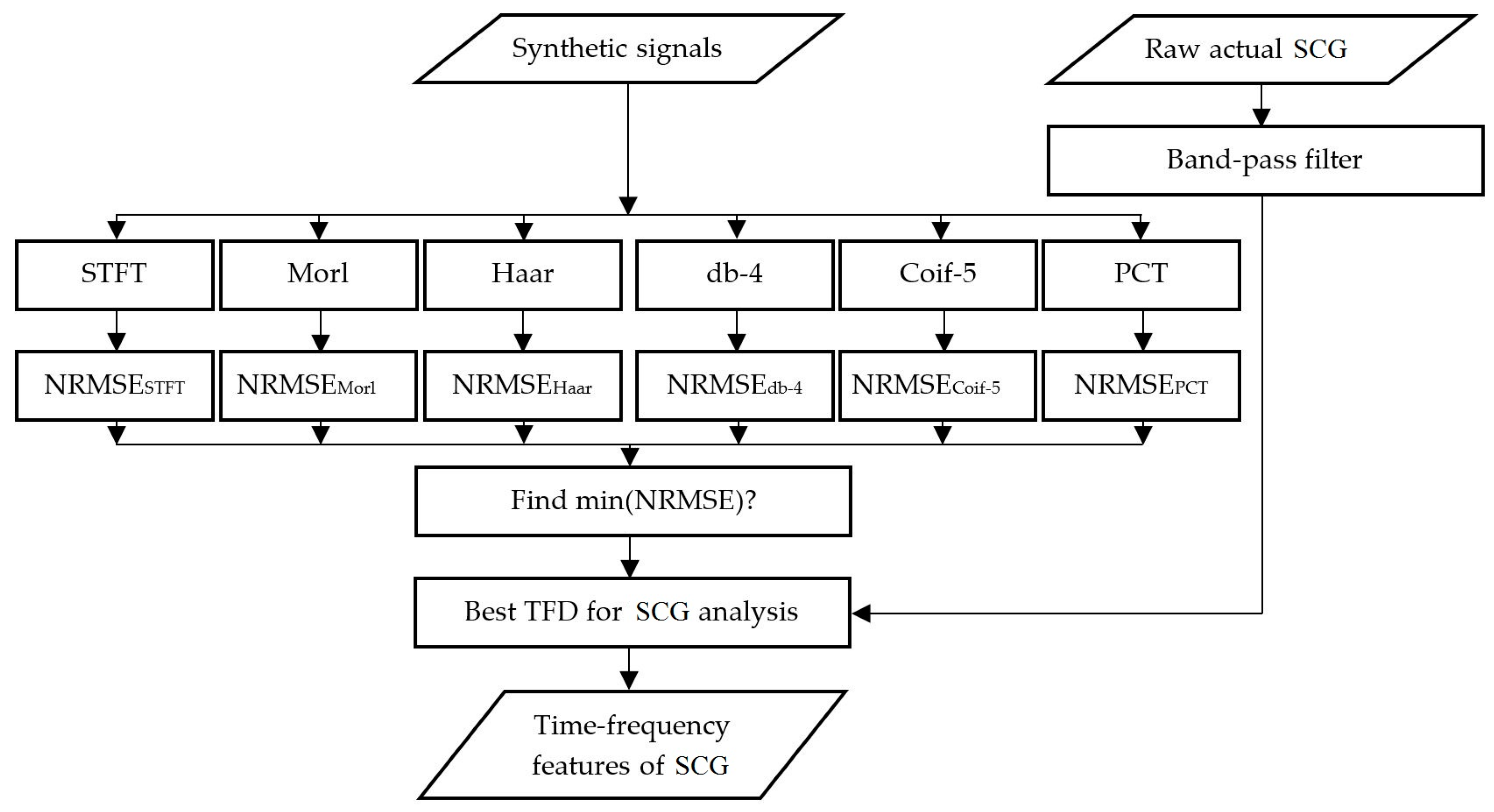
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Time-Frequency Distributions (TFD) Methods
2.1.1. Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT)
2.1.2. Continuous Wavelet Transform (CWT)
2.1.3. Chirplet Transform (CT) and Polynomial CT (PCT)
2.2. Test Signals
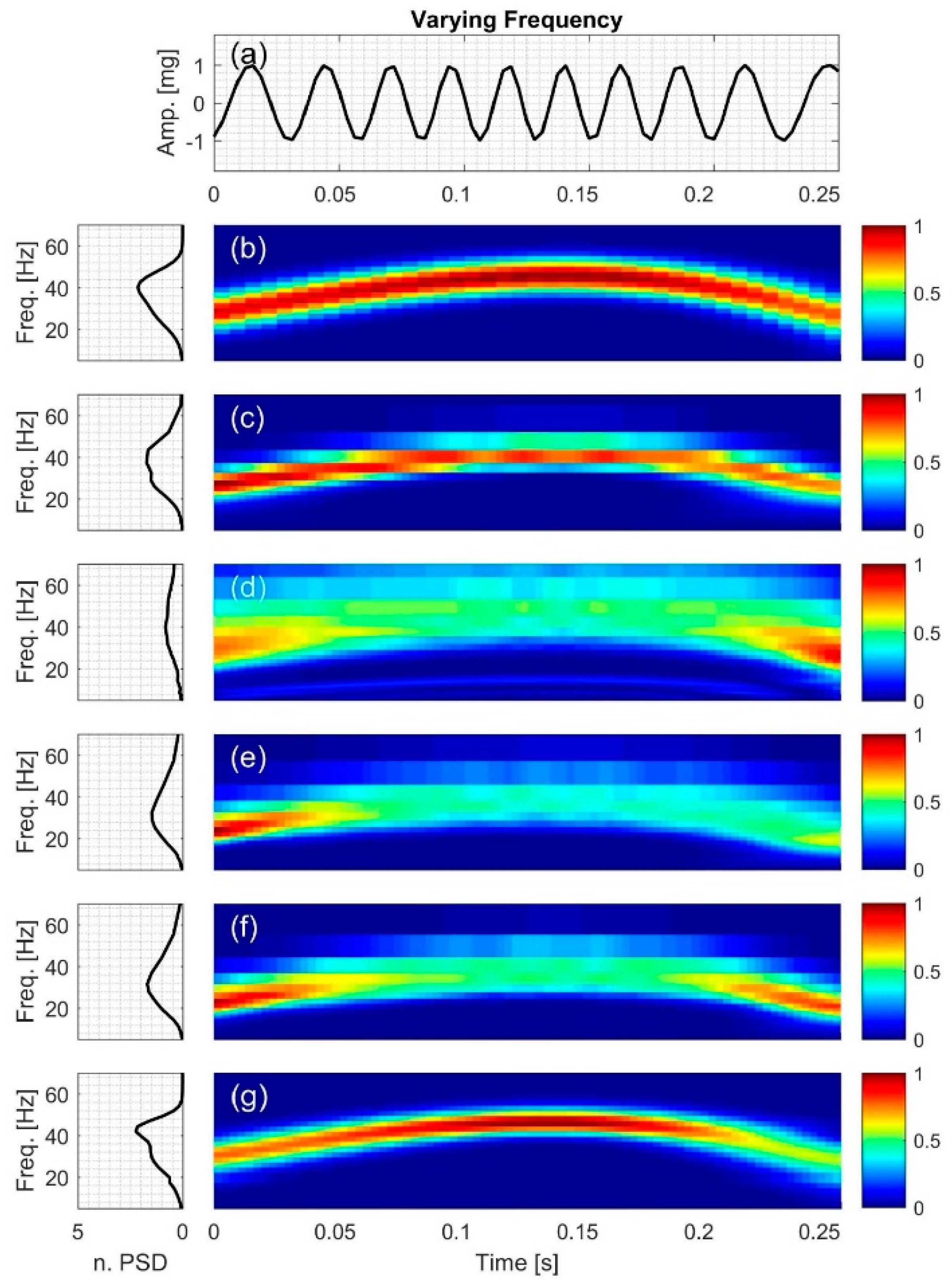
2.2.1. Signal with Varying Frequency
2.2.2. Exponentially Decaying Sinusoid
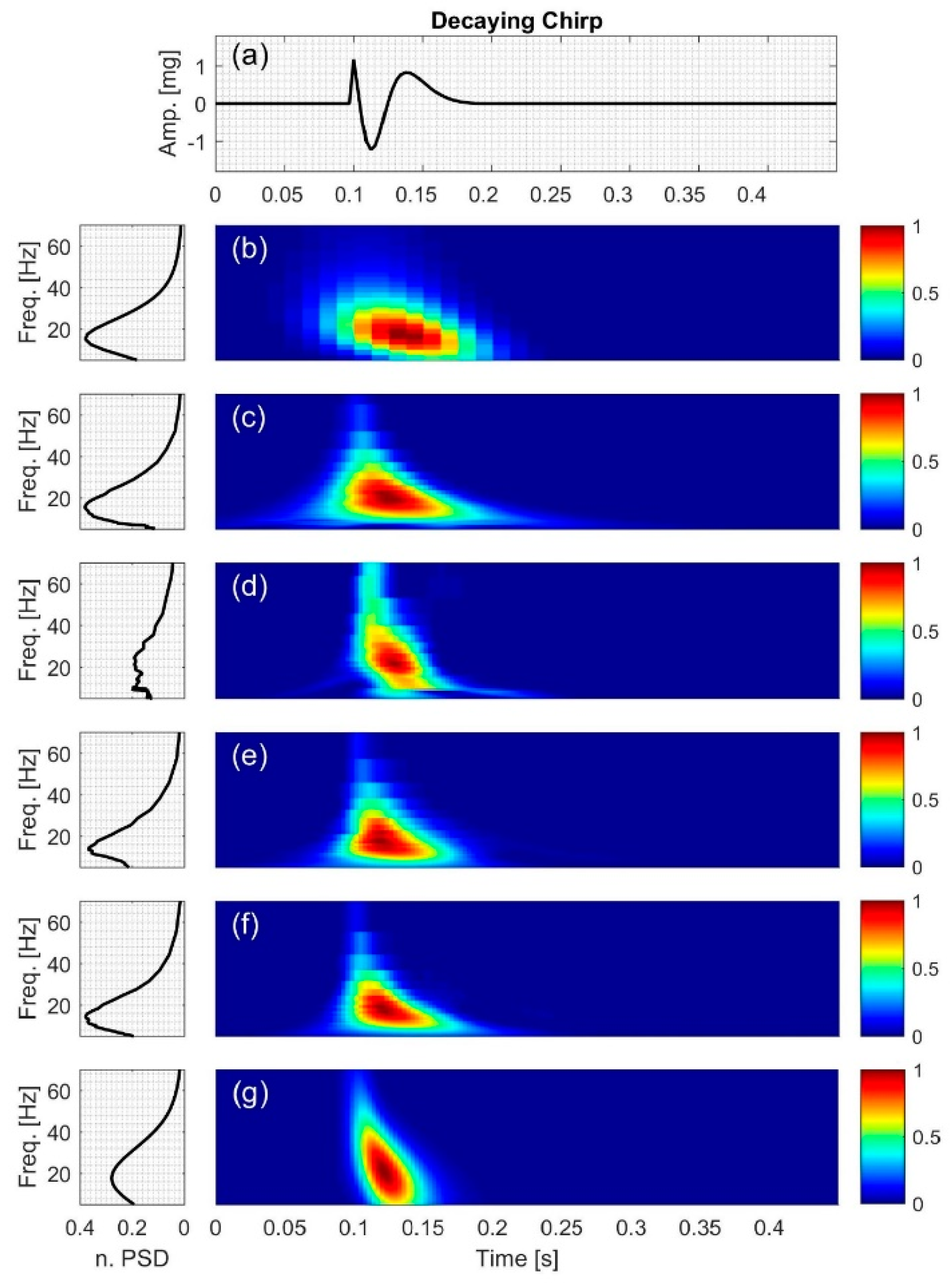
2.2.3. Decaying Chirp
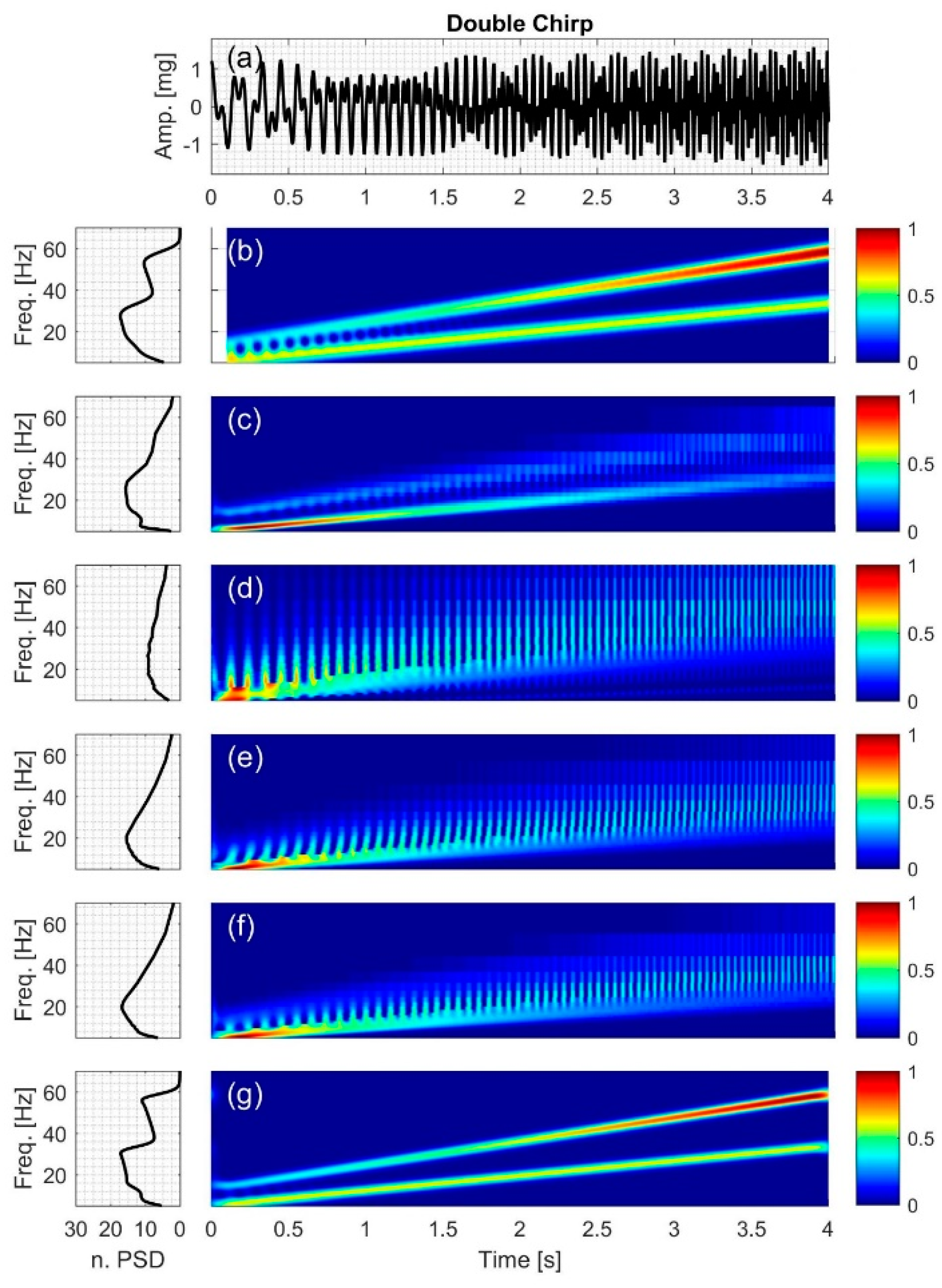
2.2.4. Double Chirp
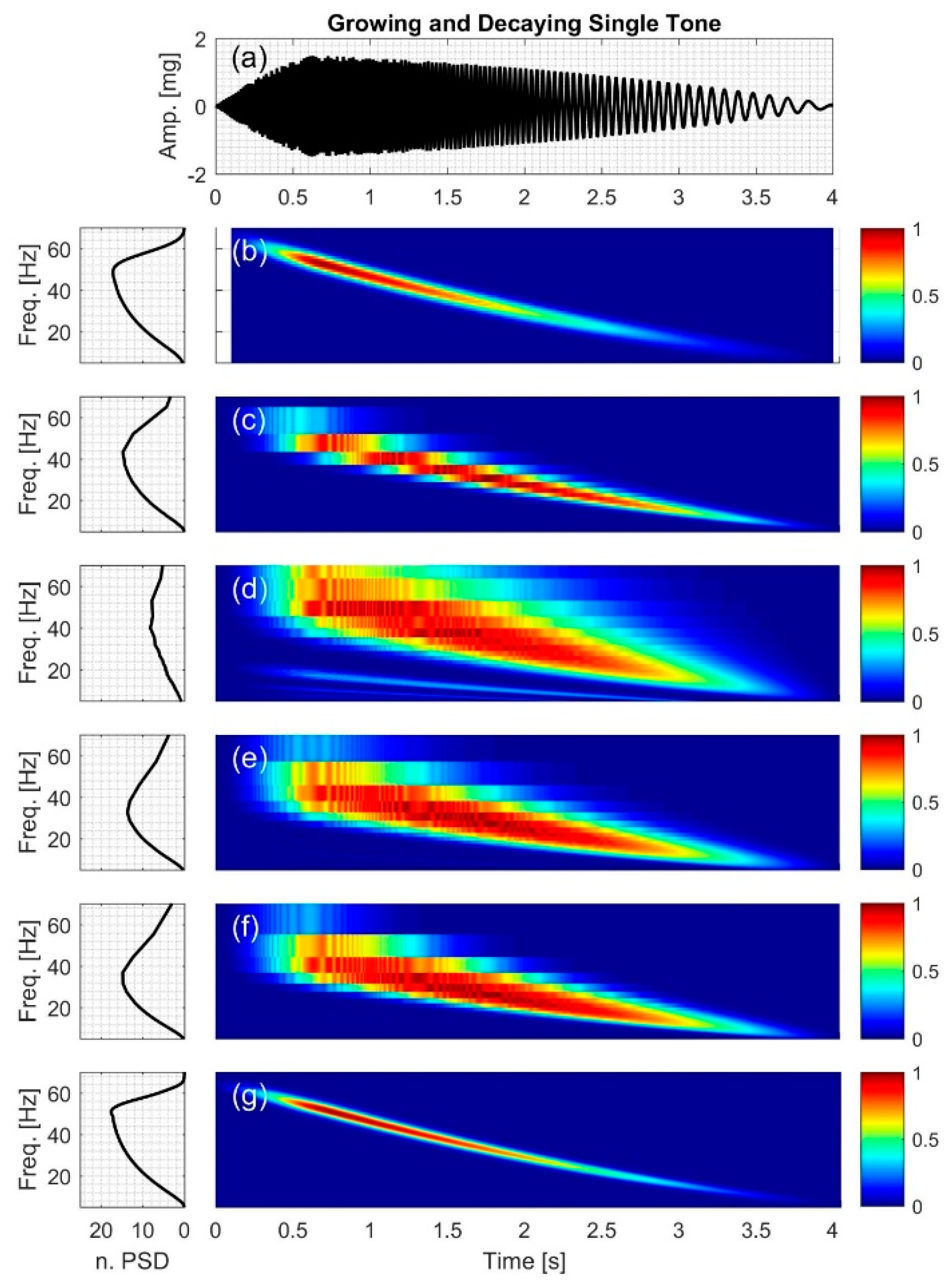
2.2.5. Growing and Decaying Single Tone with Varying Frequency
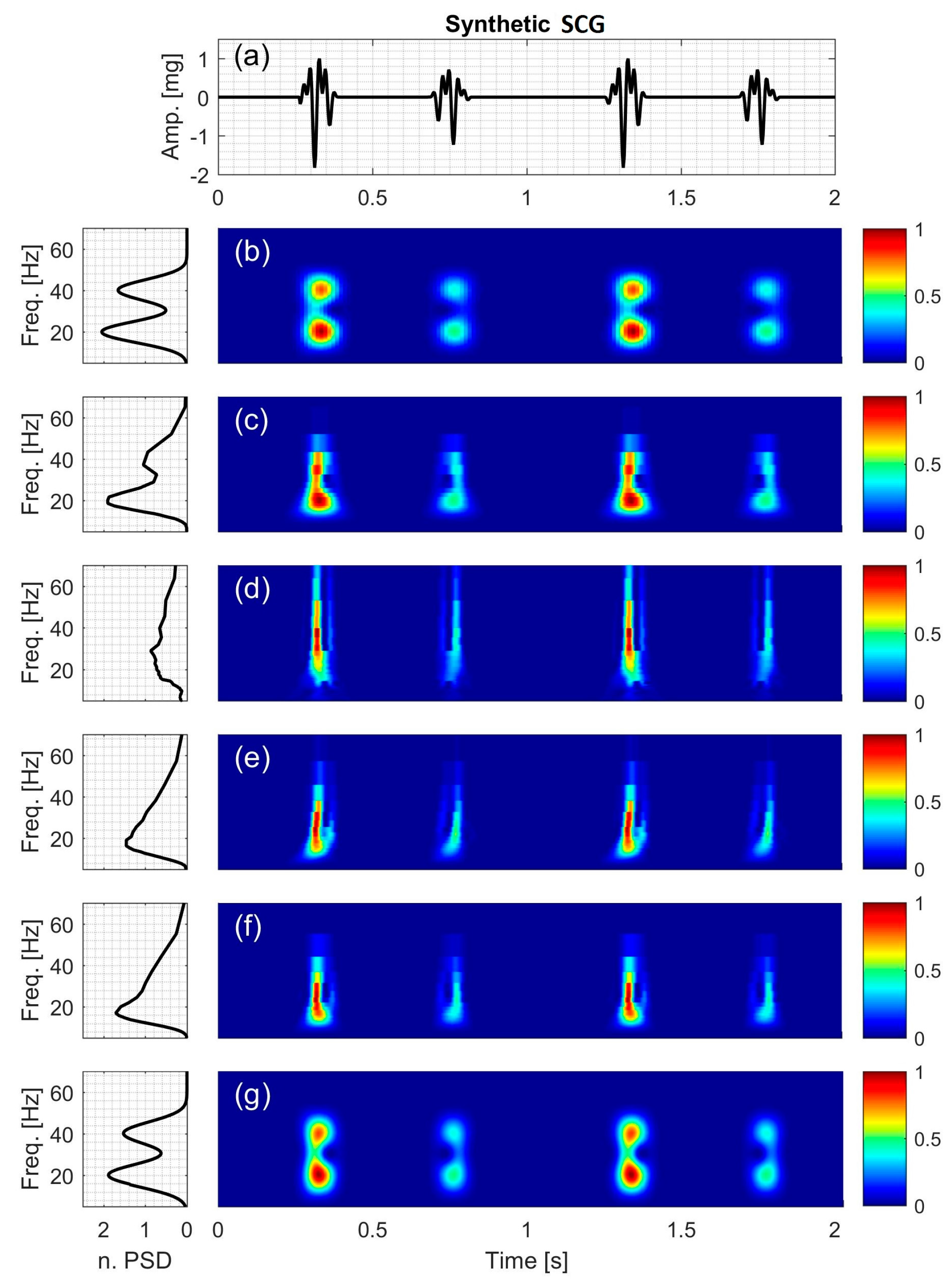
2.2.6. Synthetic Seismocardiographic (SCG) Signal
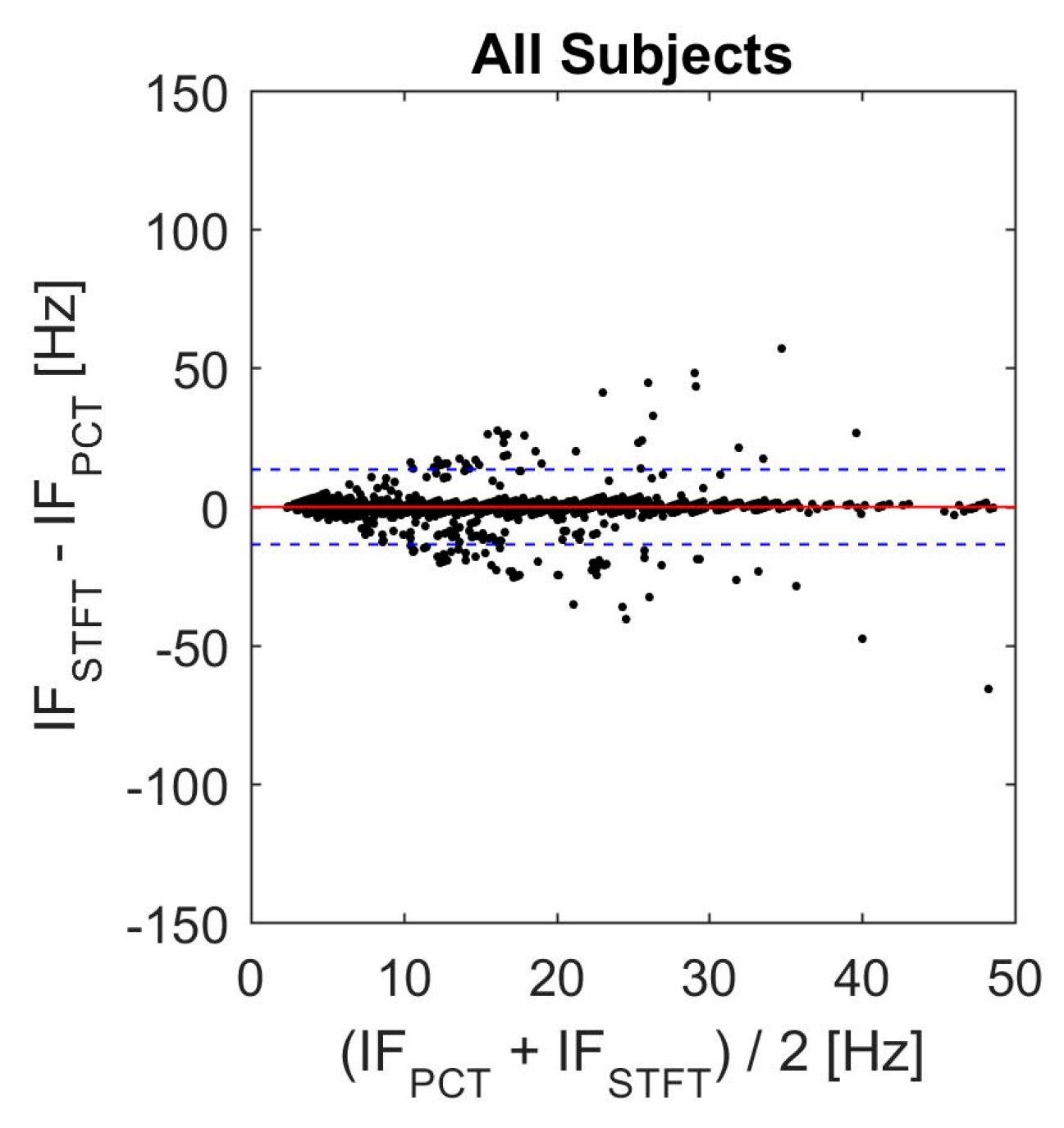
2.3. Instantaneous Frequency (IF) Error Analysis
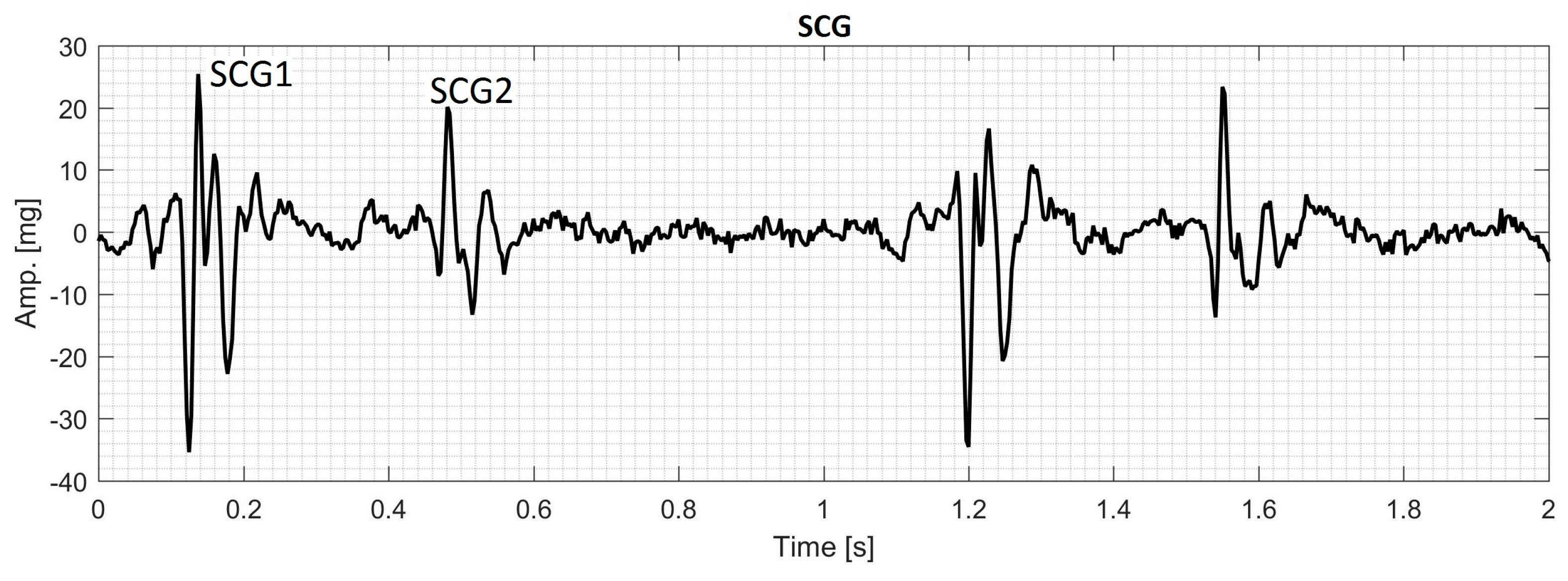
2.4. Data Acquisition of Human SCG
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Signal with Varying Frequency
3.2. Exponentially Decaying Sinusoid
3.3. Decaying Chirp
3.4. Double Chirp
3.5. Growing and Decaying Single Tone with Varying Frequency
3.6. Synthetic SCG Signal
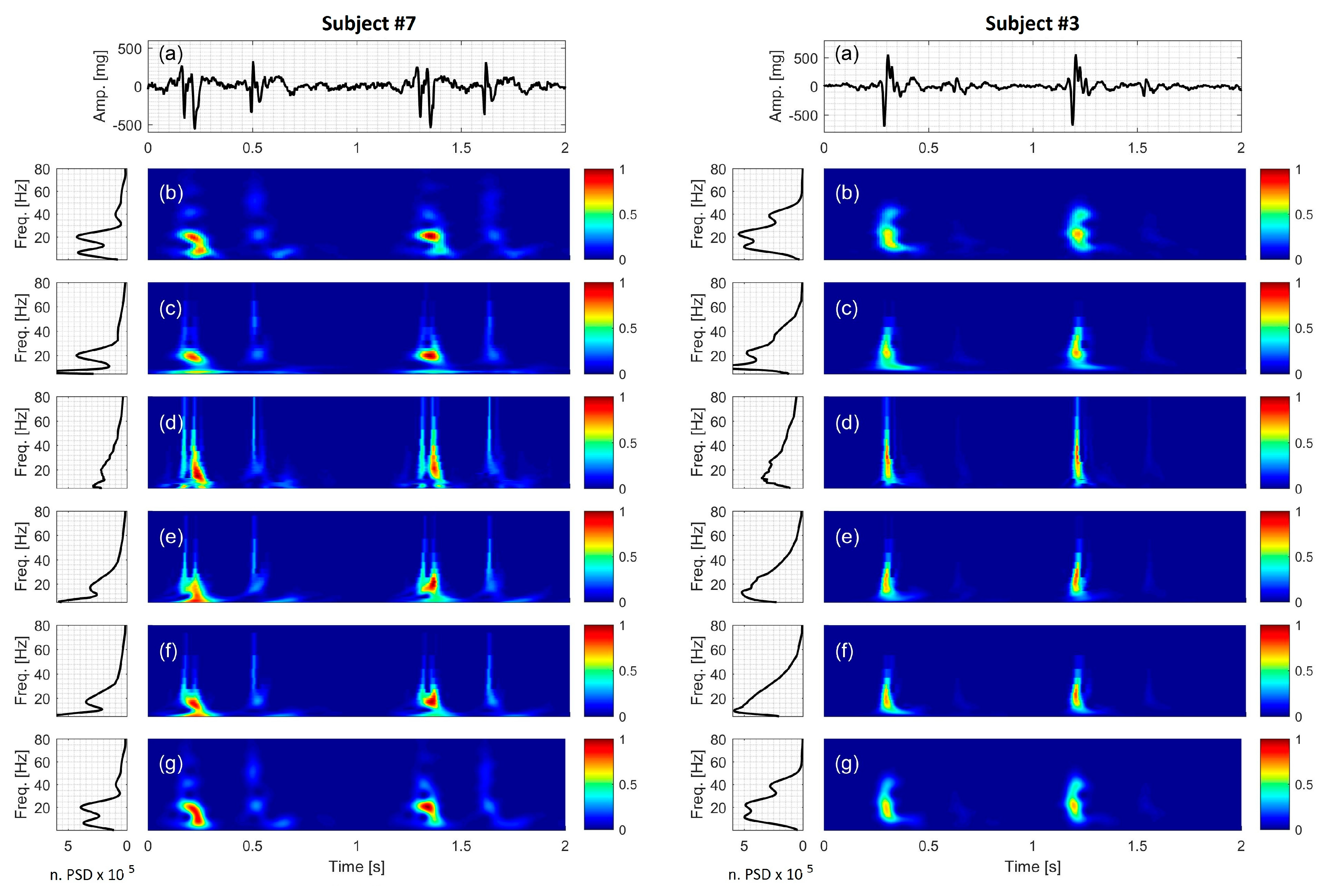
3.7. Actual SCG Signal
3.8. Limitations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murphy, S.L.; Xu, J.; Kochanek, K.D. Deaths: Final data for 2010. Natl. Vital Stat. Rep. 2013, 61, 1–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salerno, D.M.; Zanetti, J.M.; Green, L.A.; Mooney, M.R.; Madison, J.D.; van Tassel, R.A. Seismocardiographic changes associated with obstruction of coronary blood flow during balloon angioplasty. Am. J. Cardiol. 1991, 68, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadi, M.J.; Lehtonen, E.; Hurnanen, T.; Koskinen, J.; Eriksson, J.; Pänkäälä, M.; Teräs, M.; Koivisto, T. A real-time approach for heart rate monitoring using a Hilbert transform in seismocardiograms. Physiol. Meas. 2016, 37, 1885–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salerno, D.M.; Zanetti, J. Seismocardiography for monitoring changes in left ventricular function during ischemia. Chest 1991, 100, 991–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandia, K.; Inan, O.T.; Kovacs, G.T.A.; Giovangrandi, L. Extracting respiratory information from seismocardiogram signals acquired on the chest using a miniature accelerometer. Physiol. Meas. 2012, 33, 1643–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bifulco, P.; Gargiulo, G.D.; D’Angelo, G.; Liccardo, A.; Romano, M.; Clemente, F.; Cesarelli, M.; Angelo, G.; Liccardo, A.; Romano, M.; et al. Monitoring of respiration, seismocardiogram and heart sounds by a PVDF piezo film sensor. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on ADC and DAC Modelling and Testing (IWADC 2014), Benevento, Italy, 15–17 September 2014; pp. 786–789. [Google Scholar]
- Starr, I.; Rawson, J.; Schroeder, H.; Joseph, N. Studies on the estimation of cardiac ouptut in man, and of abnormalities in cardiac function, from the heart’s recoil and the blood’s impacts; the Ballistocardiogram. Am. J. Physiol 1939, 127, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzaki, T. Calibrated low frequency acceleration vibrocardiography. Jpn. Heart J. 1972, 13, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morbiducci, U.; Scalise, L.; de Melis, M.; Grigioni, M. Optical vibrocardiography: A novel tool for the optical monitoring of cardiac activity. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 35, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalise, L.; Morbiducci, U. Non-contact cardiac monitoring from carotid artery using optical vibrocardiography. Med. Eng. Phys. 2008, 30, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosoli, G.; Casacanditella, L.; Pietroni, F.; Calvaresi, A.; Revel, G.M.; Scalise, L. A novel approach for features extraction in physiological signals. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), Torino, Italy, 7–9 May 2015; pp. 380–385. [Google Scholar]
- Benchimol, A.; Dimond, E.; Carson, J. The value of the apexcardiogram as a reference tracing in phonocardiography. Am. Heart J. 1961, 61, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddleman, E.; Willis, K.; Reeves, T.; Harrison, T. The kinetocardiogram. Circulation 1953, 8, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, F.; Overy, D. Vibrations of low frequency over the precordium. Circulation 1951, 3, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounsey, P. Praecordial ballistocardiography. Br. Heart J. 1957, 19, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, H.; Klunhaar, E. Precordial low frequency displacements of the thoracic wall. Method of recording and registration. Am. Heart J. 1961, 61, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, H.; Dobayashi, T.; Sato, C.; Sakamoto, T. Precordial low frequency vibrocardiography. Method of recording. Jpn. Heart J. 1962, 3, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berson, A.; Pipberger, H. Measurement of chest wall vibrations due to the activity of the heart. J. Appl. Physiol. 1966, 21, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taebi, A.; Mansy, H.A. Time-frequency Analysis of Vibrocardiographic Signals. In Proceedings of the 2015 BMES Annual Meeting, Tampa, FL, USA, 7–10 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Eddleman, E. Kinetocardiographic Changes in Ischemic Heart Disease. Circulation 1965, 32, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starr, I.; Wood, E. Twenty-year studies with the ballistocardiograph, the relation between the amplitude of the first record of “health” adults and eventual mortality and morbidity form heart disease. Circulation 1961, 23, 714–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, I.; Noordegroaf, A. Ballistocardiography in Cardiovascular Research; Lippincott: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Phibbs, B.; Lowe, C.; Holmes, R. The ultra lowfrequency force ballistocardiograph in acute cardiomyopathy. Circulation 1967, 36, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherhag, A.W.; Pfleger, S.; Ceconi, C.; Voelker, W.; Gehring, J.; Staedt, U.; Heene, D.L. Evaluation of signal-averaged cardiokymography for the detection of ischaemic left ventricular dysfunction. Int. J. Cardiol. 1997, 59, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Hagisawa, K.; Ishizuka, T.; Takase, B.; Ishihara, M.; Kikuchi, M. A Novel Method to Prevent Secondary Exposure of Medical and Rescue Personnel to Toxic Materials Under Biochemical Hazard Conditions Using Microwave Radar and Infrared Themography. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 51, 2184–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakolian, K.; Vaseghi, A.; Kaminska, B. Improvement of ballistocardiogram processing by inclusion of respiration information. Physiol. Meas. 2008, 29, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, D.C.; Patrie, J.T.; Suratt, P.M.; Felder, R.A.; Alwan, M. Development and preliminary validation of heart rate and breathing rate detection using a passive, ballistocardiography-based sleep monitoring system. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2009, 13, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosoli, G.; Casacanditella, L.; Tomasini, E.; Scalise, L. Heart Rate assessment by means of a novel approach applied to signals of different nature. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 778, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, J.; Salerno, D. Seismocardiography: A new technique for recording cardiac vibrations. Concept, method, and initial observations. J. Cardiovasc. Technol. 1990, 9, 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Gurev, V.; Tavakolian, K.; Constantino, J.; Kaminska, B.; Blaber, A.P.; Trayanova, N.A. Mechanisms underlying isovolumic contraction and ejection peaks in seismocardiogram morphology. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2012, 32, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inan, O.T.; Migeotte, P.F.; Park, K.S.; Etemadi, M.; Tavakolian, K.; Casanella, R.; Zanetti, J.; Tank, J.; Funtova, I.; Prisk, G.K.; et al. Ballistocardiography and Seismocardiography: A Review of Recent Advances. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2015, 19, 1414–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadi, M.; Koivisto, T.; Pankaala, M.; Paasio, A.; Knuutila, T.; Teras, M.; Hanninen, P. A new algorithm for segmentation of cardiac quiescent phases and cardiac time intervals using seismocardiography. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Graphic and Image Processing (ICGIP 2014), Beijing, China, 24 October 2014; p. 94432K. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.; Chou, W.; Chang, P.; Chou, C.; Wen, M.; Ho, M.; Lee, M. Identification of Location Specific Feature Points in a Cardiac Cycle Using a Novel Seismocardiogram Spectrum System. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanetti, J.; Tavakolian, K. Seismocardiography: Past, present and future. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 7004–7007. [Google Scholar]
- Taebi, A.; Mansy, H.A. Noise Cancellation from Vibrocardiographic Signals Based on the Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition. J. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, A.; Pahwa, V. Evaluating the Performance of State of the Art Algorithms for Enhancement of Seismocardiogram Signals. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Communication; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Feigen, L.P. Physical characteristics of sound and hearing. Am. J. Cardiol. 1971, 28, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luisada, A.A. The Sounds of the Normal Heart; Warren H. Green: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, R.H.; Mansy, H.A. Vibro-Acoustic Detection of Cardiac Conditions. U.S. Patent 20,110,295,127, 1 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Taebi, A.; Mansy, H.A. Time-frequency Description of Vibrocardiographic Signals. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Orlando, FL, USA, 17–20 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Taebi, A.; Mansy, H.A. Effect of Noise on Time-frequency Analysis of Vibrocardiographic Signals. J. Bioeng. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramatikov, B.; Brinker, J.; Yi-Chun, S.; Thakor, N.V. Wavelet analysis and time-frequency distributions of the body surface ECG before and after angioplasty. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2000, 62, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, J.A.; Gibson, N.M.; Woolfson, M.S.; Somekh, M.G. Wavelet transform as a potential tool for ECG analysis and compression. J. Biomed. Eng. 1992, 14, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, S.; Figliola, A.; Quiroga, R.Q.; Rosso, O.A.; Serrano, E. Time-frequency analysis of electroencephalogram series. III. Wavelet packets and information cost function. Phys. Rev. E 1998, 57, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celka, P.; Boashash, B.; Colditz, P. Preprocessing and time-frequency analysis of newborn EEG seizures. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2001, 20, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obaidat, M.S. Phonocardiogram signal analysis: Techniques and performance comparison. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 1993, 17, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, P.; Collis, W.; Salmon, A. Analysing heart murmurs using time-frequency methods. Proc. IEEE-SP Int. Symp. Time-Freq. Time-Scale Anal. 1996, 2, 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Debbal, S.M.; Bereksi-Reguig, F. Time-frequency analysis of the first and the second heartbeat sounds. Appl. Math. Comput. 2007, 184, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherif, L.H.; Debbal, S.M.; Bereksi-Reguig, F. Choice of the wavelet analyzing in the phonocardiogram signal analysis using the discrete and the packet wavelet transform. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, S.; Yu, J.; Akay, M. Time-frequency analysis of myoelectric signals during dynamic contractions: A comparative study. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 47, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.K.; Meng, G.; Chu, F.L.; Lang, Z.Q.; Zhang, W.M.; Yang, Y. Polynomial chirplet transform with application to instantaneous frequency estimation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2011, 60, 3222–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auger, F.; Flandrin, P.; Gonçalvès, P.; Lemoine, O. Time-Frequency Toolbox; CNRS, University of La Rochelle: La Rochelle, France, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hadjileontiadis, L.J.; Panas, S.M. A wavelet-based reduction of heart sound noise from lung sounds. Int. J. Med. Inform. 1998, 52, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourazad, M.T.; Moussavi, Z.; Thomas, G. Heart sound cancellation from lung sound recordings using time-frequency filtering. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2006, 44, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Carvalho, P.; Antunes, M.; Henriques, J.; e Melo, A.S.; Schmidt, R.; Habetha, J. Third heart sound detection using wavelet transform-simplicity filter. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2007, 2007, 1277–1281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mazomenos, E.B.; Biswas, D.; Acharyya, A.; Chen, T.; Maharatna, K.; Rosengarten, J.; Morgan, J.; Curzen, N. A Low-Complexity ECG Feature Extraction Algorithm for Mobile Healthcare Applications. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2013, 17, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergen, B.; Tatar, Y.; Gulcur, H.O. Time-frequency analysis of phonocardiogram signals using wavelet transform: A comparative study. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 15, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, S.; Haykin, S. Adaptive chirplet transform: An adaptive generalization of the wavelet transform. Opt. Eng. 1992, 31, 1243–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, S.; Haykin, S. The Chirplet Transform: Physical Considerations. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1995, 43, 2745–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abry, P. Ondelettes et Turbulences: Multirésolutions, Algorithmes de Décomposition, Invariance D’échelle et Signaux de Pression; Diderot Multimédia: Paris, France, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Tavakolian, K. Charachterization and Analysis of Seismocardiogram for Estimation of Hemodynamic Parameters; Simon Fraser University: Burnaby, BC, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mansy, H.A.; Royston, T.J.; Balk, R.A.; Sandler, R.H. Pneumothorax detection using computerised analysis of breath sounds. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2002, 40, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kail, E.; Khoor, S.; Fugedi, K.; Kovacs, I.; Khoor, B.; Kail, B.; Kecskemethy, P.; Balogh, N.; Domijan, E.; Domijan, M. Expert system for phonocardiographic monitoring of heart failure patients based onwavelet analysis. Comput. Cardiol. 2005 2005, 833–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inan, O.T.; Etemadi, M.; Wiard, R.M.; Giovangrandi, L.; Kovacs, G.T.A. Robust ballistocardiogram acquisition for home monitoring. Physiol. Meas. 2009, 30, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castiglioni, P.; Faini, A.; Parati, G.; Di Rienzo, M. Wearable seismocardiography. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Lyon, France, 22–26 August 2007; pp. 3954–3957. [Google Scholar]


| Wavelet | Morlet | Haar | Daubechies4 | Coiflet5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Center frequency (Hz) | 0.8125 | 0.9961 | 0.7143 | 0.6897 |
| Signal Description | Frequency Range (Hz) | Peak-to-Peak Amplitude (V) | Signal Length above 5% of Peak to Peak Amplitude (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Varying frequency, | 23 to 45 | 2.0 | 250 |
| Exp. decaying sinusoid, | 30 | 2.3 | 230 |
| decaying chirp, | 0 to 33 | 2.4 | 75 |
| double chirp, | 7 to 33 | 3.2 | 4000 |
| growing and decaying single tone, | 7 to 66 | 3.0 | 4000 |
| synthetic SCG, | 20 and 40 | 2.8 | 112 |
| Resolution | Signal | STFT | Morl | Haar | db4 | Coif5 | PCT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temporal resolution (ms) | All signals, | 12.5 | 3.1 | 3.1 | 3.1 | 3.1 | 3.1 |
| Spectral resolution (Hz) | varying frequency, | 2.5000 | 0.4000–13.0000 | 0.3213–15.9377 | 0.4517–19.0476 | 0.4361–18.3908 | 0.2133 |
| exponentially decaying sinusoid, | 2.5000 | 0.4000–13.0000 | 0.3213–15.9377 | 0.4517–19.0476 | 0.4361–18.3908 | 0.2036 | |
| decaying chirp, | 2.5000 | 0.4000–13.0000 | 0.3213–15.9377 | 0.4517–19.0476 | 0.4361–18.3908 | 0.2036 | |
| double chirp, | 0.6250 | 0.4000–13.0000 | 0.3213–15.9377 | 0.4517–19.0476 | 0.4361–18.3908 | 0.2462 | |
| growing and decaying single tone with varying frequency, | 1.2500 | 0.4000–13.0000 | 0.3213–15.9377 | 0.4517–19.0476 | 0.4361–18.3908 | 0.2462 | |
| synthetic SCG, | 0.6250 | 0.4000–13.0000 | 0.3213–15.9377 | 0.4517–19.0476 | 0.4361–18.3908 | 0.2462 |
| Signal | STFT | Morl | Haar | db4 | Coif5 | PCT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| varying frequency, | 0.0248 | 0.0477 | 0.2958 | 0.1954 | 0.1411 | 0.0069 |
| exp. decaying sinusoid, | 0.1857 | 0.5393 | 0.6463 | 0.4848 | 0.3599 | 0.0056 |
| decaying chirp, | 0.5737 | 0.4717 | 0.3733 | 0.4081 | 0.3736 | 0.0850 |
| double chirp, | 0.1232 | 0.7467 | 0.5651 | 0.6612 | 0.7507 | 0.0671 |
| growing and decaying single tone, | 0.0109 | 0.1666 | 0.1756 | 0.1393 | 0.1706 | 0.0179 |
| synthetic SCG, | 0.0199 | 0.1084 | 0.4876 | 0.3419 | 0.2370 | 0.0214 |
| Subject No. | Heart Rate (bpm) | f1 (Hz) | f2 (Hz) | f3 (Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 78 | 6.15 | 22.89 | 56.12 |
| 2 | 72 | 11.08 | 30.52 | 71.38 |
| 3 | 70 | 11.32 | 21.91 | 38.65 |
| 4 | 60 | 8.86 | 17.23 | 26.09 |
| 5 | 58 | 5.41 | 28.31 | 53.17 |
| 6 | 62 | 7.63 | 32.98 | 61.05 |
| 7 | 62 | 6.15 | 19.94 | 40.12 |
| 8 | 69 | 16.98 | 32.98 | 59.08 |
| Bias (Hz) | Upper LOV (Hz) | Lower LOV (Hz) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.7593 | 17.32 | −15.80 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taebi, A.; Mansy, H.A. Time-Frequency Distribution of Seismocardiographic Signals: A Comparative Study. Bioengineering 2017, 4, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering4020032
Taebi A, Mansy HA. Time-Frequency Distribution of Seismocardiographic Signals: A Comparative Study. Bioengineering. 2017; 4(2):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering4020032
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaebi, Amirtaha, and Hansen A. Mansy. 2017. "Time-Frequency Distribution of Seismocardiographic Signals: A Comparative Study" Bioengineering 4, no. 2: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering4020032
APA StyleTaebi, A., & Mansy, H. A. (2017). Time-Frequency Distribution of Seismocardiographic Signals: A Comparative Study. Bioengineering, 4(2), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering4020032