ARROW: Allele-Specific Recombined gRNA Design for Reduced Off-Target with Enhanced Specificity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
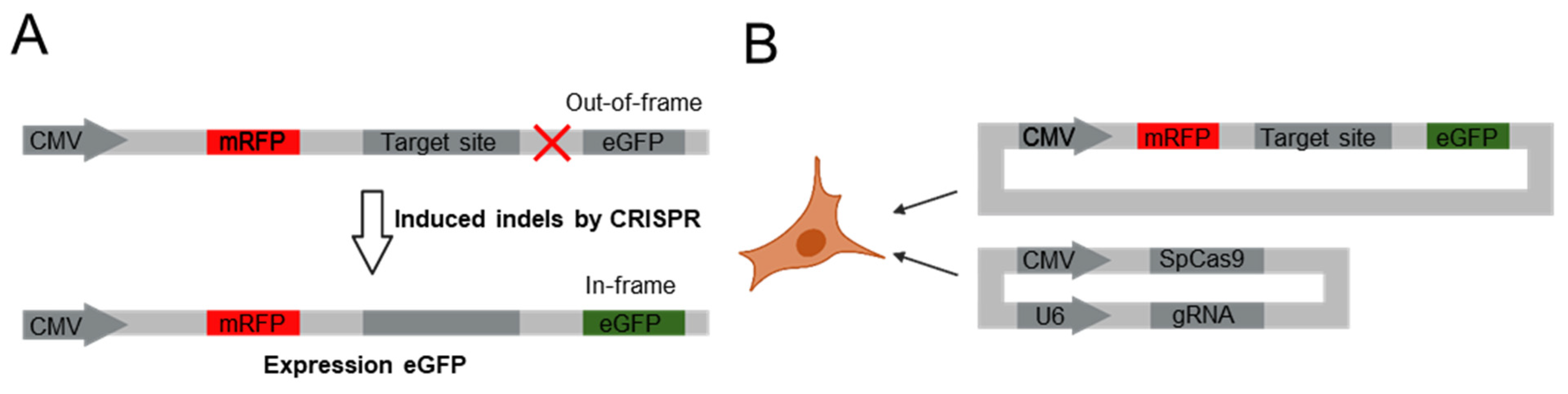
2.1. Cell Subculture and Transfection of Dual Fluorescence Reporter Vector System
2.2. Generation of Mismatched gRNAs
2.3. Targeted Deep Sequencing
2.4. T7E1 Assay for Potential Off-Target Sites
3. Results
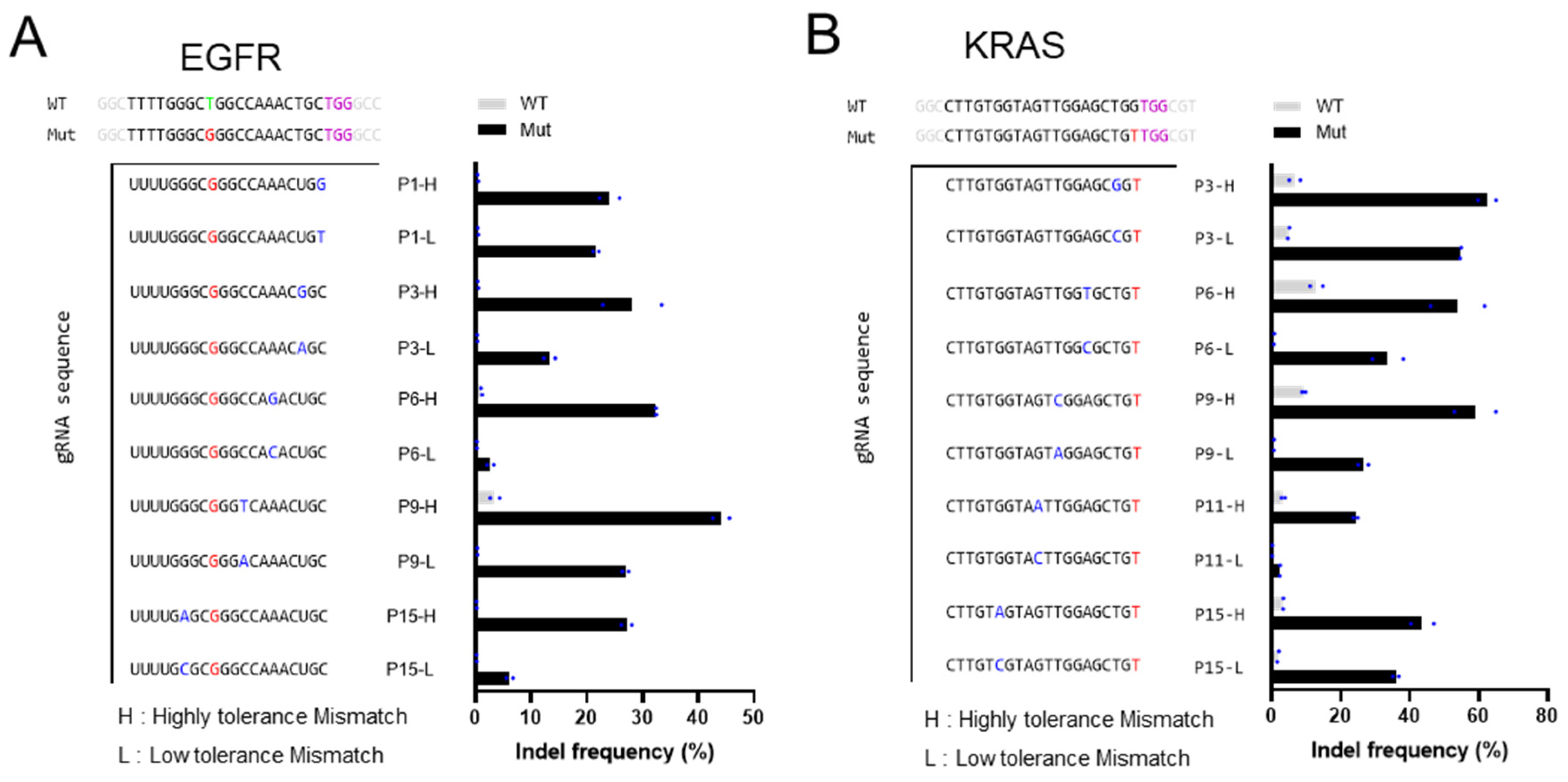
3.1. Characterization of the Insertion and Deletion Rates of gRNA Variants on EGFR L858R and KRAS G12V Mutations
3.2. Intentionally Mismatched gRNA Can Discriminate Between Mutant and Wild-Type Alleles
3.3. Intentionally Mismatched gRNAs Enhance Specificity in Mammalian Cells
3.4. Intentionally Mismatched KRAS G12V gRNAs for Decreasing Potential Off-Target Effects
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jinek, M.; Chylinski, K.; Fonfara, I.; Hauer, M.; Doudna, J.A.; Charpentier, E. A Programmable Dual-RNA-Guided DNA Endonuclease in Adaptive Bacterial Immunity. Science 2012, 337, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinek, M.; East, A.; Cheng, A.; Lin, S.; Ma, E.B.; Doudna, J. RNA-programmed genome editing in human cells. Elife 2013, 2, e00471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, L.; Ran, F.A.; Cox, D.; Lin, S.L.; Barretto, R.; Habib, N.; Hsu, P.D.; Wu, X.B.; Jiang, W.Y.; Marraffini, L.A.; et al. Multiplex Genome Engineering Using CRISPR/Cas Systems. Science 2013, 339, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.X.; Yang, Y.Y.; Qi, H.Z.; Cui, W.G.; Zhang, L.; Fu, X.X.; He, X.Q.; Liu, M.X.; Li, P.F.; Yu, T. CRISPR/Cas9 therapeutics: Progress and prospects. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.P.; Bui, T.A.; Mei, H.Q.; Aksoy, Y.A.; Deng, F.; Hutvagner, G.; Deng, W. Exploring the Potential and Challenges of CRISPR Delivery and Therapeutics for Genetic Disease Treatment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2402630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehelgerdi, M.; Chehelgerdi, M.; Khorramian-Ghahfarokhi, M.; Shafieizadeh, M.; Mahmoudi, E.; Eskandari, F.; Rashidi, M.; Arshi, A.; Mokhtari-Farsani, A. Comprehensive review of CRISPR-based gene editing: Mechanisms, challenges, and applications in cancer therapy. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.D.; Scott, D.A.; Weinstein, J.A.; Ran, F.A.; Konermann, S.; Agarwala, V.; Li, Y.Q.; Fine, E.J.; Wu, X.B.; Shalem, O.; et al. DNA targeting specificity of RNA-guided Cas9 nucleases. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.N.; Cradick, T.J.; Brown, M.T.; Deshmukh, H.; Ranjan, P.; Sarode, N.; Wile, B.M.; Vertino, P.M.; Stewart, F.J.; Bao, G. CRISPR/Cas9 systems have off-target activity with insertions or deletions between target DNA and guide RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 7473–7485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.X.H.; Onge, R.P.S.; Fire, A.Z.; Smith, J.D. Distinct patterns of Cas9 mismatch tolerance and. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 5365–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, T.; Hou, Y.Z.; Zhang, P.J.; Zhang, Z.X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L.T.; Niu, L.L.; Yang, Y.; Liang, D.; Yi, F.; et al. Profiling single-guide RNA specificity reveals a mismatch sensitive core sequence. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Song, C.Q.; Suresh, S.; Kwan, S.Y.; Wu, Q.Q.; Walsh, S.; Ding, J.M.; Bogorad, R.L.; Zhu, L.J.; Wolfe, S.A.; et al. Partial DNA-guided Cas9 enables genome editing with reduced off-target activity. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2018, 14, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, K.; Amrani, N.; Jiang, W.; Yogesha, S.D.; Nguyen, R.; Qin, P.Z.; Rajan, R. Bridge Helix of Cas9 Modulates Target DNA Cleavage and Mismatch Tolerance. Biochemistry 2019, 58, 1905–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, J.P.; Tan, J.; Gascoigne, K.E.; Haverty, P.M.; Forrest, W.F.; Costa, M.R.; Martin, S.E. Multiple-gene targeting and mismatch tolerance can confound analysis of genome-wide pooled CRISPR screens. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huston, N.C.; Tycko, J.; Tillotson, E.L.; Wilson, C.J.; Myer, V.E.; Jayaram, H.; Steinberg, B.E. Identification of Guide-Intrinsic Determinants of Cas9 Specificity. CRISPR J. 2019, 2, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, B.P.; Hsu, R.V.; Medrano, M.A.; Zewde, N.T.; Narkhede, Y.B.; Palermo, G. Spontaneous Embedding of DNA Mismatches Within the RNA:DNA Hybrid of CRISPR-Cas9. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.; Park, J.; Min, S.; Choi, J.W.; Huang, T.P.; Yoon, S.; Liu, D.R.; Kim, H.H. High-throughput analysis of the activities of xCas9, SpCas9-NG and SpCas9 at matched and mismatched target sequences in human cells. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.B.; Guo, J.H.; Wang, T.M.; Zhang, C.; Xing, X.H. Guide-target mismatch effects on dCas9-sgRNA binding activity in living bacterial cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 1263–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.J.; He, W.; Dou, J.Z.; Villarreal, O.D.; Bedford, E.; Wang, H.E.; Hou, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.L.; Ma, D.C.; et al. Systematic decomposition of sequence determinants governing CRISPR/Cas9 specificity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimi, K.; Kaneko, T.; Voigt, B.; Mashimo, T. Allele-specific genome editing and correction of disease-associated phenotypes in rats using the CRISPR-Cas platform. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquet, D.; Kwart, D.; Chen, A.; Sproul, A.; Jacob, S.; Teo, S.; Olsen, K.M.; Gregg, A.; Noggle, S.; Tessier-Lavigne, M. Efficient introduction of specific homozygous and heterozygous mutations using CRISPR/Cas9. Nature 2016, 533, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteys, A.M.; Ebanks, S.A.; Keiser, M.S.; Davidson, B.L. CRISPR/Cas9 Editing of the Mutant Huntingtin Allele In Vitro and In Vivo. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabai, A.; Reisser, L.; Reina-San-Martin, B.; Mamchaoui, K.; Cowling, B.S.; Nicot, A.S.; Laporte, J. Allele-Specific CRISPR/Cas9 Correction of a Heterozygous Mutation Rescues Centronuclear Myopathy Cell Phenotypes. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 16, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- György, B.; Nist-Lund, C.; Pan, B.F.; Asai, Y.; Karavitaki, K.D.; Kleinstiver, B.P.; Garcia, S.P.; Zaborowski, M.P.; Solanes, P.; Spataro, S.; et al. Allele-specific gene editing prevents deafness in a model of dominant progressive hearing loss. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, T.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, S.H.; Ham, B.J.; Hur, J.K. Specificity Assessment of CRISPR Genome Editing of Oncogenic EGFR Point Mutation with Single-Base Differences. Molecules 2020, 25, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, T.; Yoon, A.R.; Cho, H.Y.; Bae, S.; Yun, C.O.; Kim, J.S. Selective disruption of an oncogenic mutant allele by CRISPR/Cas9 induces efficient tumor regression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 7897–7908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.; Abalde-Atristain, L.; He, C.X.; Brodsky, B.R.; Braunstein, E.M.; Chaudhari, P.; Jang, Y.Y.; Cheng, L.Z.; Ye, Z.H. Efficient and Allele-Specific Genome Editing of Disease Loci in Human iPSCs. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bae, T.; Been, K.W.; Kang, S.; Hong, S.; Hur, J.K.; Hwang, W. ARROW: Allele-Specific Recombined gRNA Design for Reduced Off-Target with Enhanced Specificity. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111237
Bae T, Been KW, Kang S, Hong S, Hur JK, Hwang W. ARROW: Allele-Specific Recombined gRNA Design for Reduced Off-Target with Enhanced Specificity. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(11):1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111237
Chicago/Turabian StyleBae, Taegeun, Kyung Wook Been, Seunghun Kang, Sumin Hong, Junho K. Hur, and Woochang Hwang. 2025. "ARROW: Allele-Specific Recombined gRNA Design for Reduced Off-Target with Enhanced Specificity" Bioengineering 12, no. 11: 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111237
APA StyleBae, T., Been, K. W., Kang, S., Hong, S., Hur, J. K., & Hwang, W. (2025). ARROW: Allele-Specific Recombined gRNA Design for Reduced Off-Target with Enhanced Specificity. Bioengineering, 12(11), 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111237





