Does Diabetes Matter? The Efficacy of PRP on the Quality of Life in Stress Urinary Incontinence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Participants
2.3. Intervention Protocol
2.4. Outcome Measures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. KHQ Scores and Domains
- (a)
- Question 1
- (b)
- Question 2
- (c)
- Question 3
- (d)
- Question 4
- (e)
- Question 5
- (f)
- Question 6
- (g)
- Question 7
- (h)
- Question 8
- (i)
- Question 9
- (j)
- Question 10
- (k)
- Overall score
3.2. Stamey Scale
- ○
- Among diabetic patients, PRP treatment resulted in a significant decrease in Stamey scores (p = 0.0027).
- ○
- Among non-diabetic patients, a similarly significant reduction was observed (p < 0.001).
3.3. Safety Profile
4. Discussion
4.1. Biological Rationale for Differential PRP Response in Diabetes
4.2. Limitations of the Study and Future Directives
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| KHQ Item | Non-D Pre | Non-D PRP1 | Non-D PRP2 | Non-D PRP3 | D Pre | D PRP1 | D PRP2 | D PRP3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 General health | 45.00 | 30.31 | 20.31 | 15.94 | 47.73 | 35.23 | 32.95 | 26.14 |
| Q2 Incontinence impact | 62.50 | 47.92 | 33.33 | 27.50 | 77.27 | 53.03 | 45.45 | 42.42 |
| Q3 Role limitations | 47.29 | 32.92 | 22.50 | 16.46 | 52.27 | 38.64 | 40.15 | 29.55 |
| Q4 Physical limitations | 34.38 | 24.17 | 13.96 | 9.38 | 34.09 | 22.73 | 17.43 | 12.12 |
| Q5 Social limitations | 31.39 | 21.25 | 13.33 | 10.97 | 40.40 | 25.76 | 22.73 | 16.67 |
| Q6 Personal relationships | 66.87 | 63.54 | 57.92 | 57.50 | 95.45 | 90.91 | 92.42 | 89.39 |
| Q7 Emotions | 47.78 | 35.00 | 23.19 | 17.64 | 58.59 | 35.35 | 30.30 | 24.24 |
| Q8 Sleep/energy | 24.37 | 17.29 | 11.25 | 7.71 | 45.45 | 31.82 | 25.00 | 20.45 |
| Q9 Symptom severity (domain) | 55.94 | 46.35 | 37.40 | 32.71 | 65.15 | 53.41 | 42.05 | 36.74 |
| Q10 Symptom severity scale | 23.51 | 20.46 | 18.06 | 16.65 | 25.27 | 21.18 | 19.45 | 17.59 |
| Total KHQ score | 416.12 | 339.21 | 251.26 | 212.45 | 510.63 | 408.05 | 367.94 | 315.32 |
Appendix B
| Diabetics | N | Stamey Pre (Mean ± SD) | Stamey Post (Mean ± SD) | Mean Change (Mean ± SD) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With insulin | 9 | 1.33 ± 0.50 | 1 | 0.33 ± 0.50 | 0.083 |
| No insulin | 13 | 1.62 ± 0.65 | 1.15 ± 0.38 | 0.46 ± 0.52 | 0.014 |
| Mann–Whitney U comparison | 22 | p = 0.58 | |||
References
- Grigoriadis, T.; Kalantzis, C.; Zacharakis, D.; Kathopoulis, N.; Prodromidou, A.; Xadzilia, S.; Athanasiou, S. Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence—A Randomized Trial. Urogynecology 2024, 30, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed-Ahmed, R.; Taithongchai, A.; Da Silva, A.S.; Robinson, D.; Cardozo, L. Treating and Managing Urinary Incontinence: Evolving and Potential Multicomponent Medical and Lifestyle Interventions. Res. Rep. Uro. 2023, 15, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, P.-M.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Hsu, K.C.P.; Shen, Y.-C.; Liu, S.-P. Impact of Female Stress Urinary Incontinence on Quality of Life, Mental Health, Work Limitation, and Healthcare Seeking in China, Taiwan, and South Korea (LUTS Asia): Results from a Cross-Sectional, Population-Based Study. Int. J. Womens Health 2022, 14, 1871–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, U.J.; Godecker, A.L.; Giles, D.L.; Brown, H.W. Updated Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence in Women: 2015–2018 National Population-Based Survey Data. Female Pelvic Med. Reconstr. Surg. 2022, 28, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borislavschi, A.; Petca, A. Between Promise and Proof: Evaluating PRP’s Role in Modern Gynecology. Medicina 2025, 61, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.-H.; Lee, P.-J.; Kuo, H.-C. Therapeutic Efficacy of Urethral Sphincter Injections of Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence Due to Intrinsic Sphincter Deficiency: A Proof-of-Concept Clinical Trial. Int. Neurourol. J. 2021, 25, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boswell, S.G.; Cole, B.J.; Sundman, E.A.; Karas, V.; Fortier, L.A. Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Milieu of Bioactive Factors. Arthroscopy: J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2012, 28, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boț, M.; Vlădăreanu, R.; Vlădăreanu, S.; Zvâncă, M.; Petca, A. Stress urinary incontinence (SUI) due to causes other than parturition. In Proceedings of the 13th National Congress of Urogynecology, UROGYN, Brasov, Romania, 29 September–1 October 2016; pp. 56–62, ISBN 978-88-95922-78-2. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, C.-H.; Kuo, H.-C. The Efficacy and Mid-Term Durability of Urethral Sphincter Injections of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Treatment of Female Stress Urinary Incontinence. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 847520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dankova, I.; Pyrgidis, N.; Tishukov, M.; Georgiadou, E.; Nigdelis, M.P.; Solomayer, E.-F.; Marcon, J.; Stief, C.G.; Hatzichristou, D. Efficacy and Safety of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections for the Treatment of Female Sexual Dysfunction and Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Systematic Review. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamey, T.A. Endoscopic suspension of the vesical neck for urinary incontinence. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1973, 136, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinney, J.L.; Keyser, L.E.; Pulliam, S.J.; Ferzandi, T.R. Female Urinary Incontinence Evidence-Based Treatment Pathway: An Infographic for Shared Decision-Making. J. Women’s Health 2022, 31, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleher, C.J.; Cardozo, L.D.; Khullar, V.; Salvatore, S. A new questionnaire to assess the quality of life of urinary incontinent women. Br. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 1997, 104, 1374–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Løwenstein, E.; Jepsen, R.; Andersen, L.L.; Laigaard, J.; Møller, L.A.; Gæde, P.; Bonde, L.; Gimbel, H. Prevalence of urinary incontinence among women with diabetes in the Lolland-Falster Health Study, Denmark. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2021, 40, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syafira, F.; Iman, M.B.; Pariyana; Sriwulandari, R. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) as therapy for diabetic foot ulcer (DFU): A systematic review and meta-analysis of the latest randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Epidemiol. Manag. 2024, 13, 100178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.G. Current Overview of Surgical Options for Female Stress Urinary Incontinence. Int. Neurourol. J. 2020, 24, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-fattah, M.; Rizk, D.E.E. Diabetes mellitus and female urinary incontinence: A time for change. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2012, 23, 1481–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micussi, M.T.; Freitas, R.; Angelo, P.; Soares, E.; Lemos, T.; Maranhão, T. Evaluation of the relationship between the pelvic floor muscles and insulin resistance. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2015, 8, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbesen, M.H.; Hannestad, Y.S.; Midthjell, K.; Hunskaar, S. Diabetes and urinary incontinence—prevalence data from Norway. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2007, 86, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.S.; Vittinghoff, E.; Lin, F.; Nyberg, L.M.; Kusek, J.W.; Kanaya, A.M. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Urinary Incontinence in Women With Type 2 Diabetes and Impaired Fasting Glucose. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1307–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subak, L.L.; Whitcomb, E.; Shen, H.; Saxton, J.; Vittinghoff, E.; Brown, J.S. Weight Loss: A Novel And Effective Treatment For Urinary Incontinence. J. Urol. 2005, 174, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Hafez, S.M.N.; Zenhom, N.M.; Abdel-Hamid, H.A. Effects of platelet rich plasma on experimentally induced diabetic heart injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 96, 107814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, L.; Nakatsuka, H.; Johnson, C.M.; Kenne, K.; Kreder, K.J.; Kruse, R.; Wendt, L.; Takacs, E.B.; Vollstedt, A.J. A Single Injection of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection for the Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence in Females: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Urology 2024, 193, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirzargar, M.A.; Jafari, M.; Mohamadi, B.; Moradi, A. Comparison of Platelet Rich Plasma in Combination with Autologous Fat Injection Versus Injection of Autologous Fat in Bladder Neck for Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence of Women. J. Res. Urol. 2016, 1, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Samy Tahoon, A.; El-Din Hussein Salem, H.; Anwar Abdo Mousa, A. The Role of Platelet Rich Plasma Injections in Cases of Stress Incontinence. Qeios 2022, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apolikhina, I.A.; Sokolova, A.V.; Saidova, A.S.; Gorbunova, E.A. Autologous Platelet-rich plasma combined with hyaluronic acid is a new method of minimally invasive treatment of stress urinary incontinence in women. Med. Sov. 2018, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasiou, S.; Kalantzis, C.; Zacharakis, D.; Kathopoulis, N.; Pontikaki, A.; Grigoriadis, T. The Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma as a Novel Nonsurgical Treatment of the Female Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Prospective Pilot Study. Female Pelvic Med. Reconstr. Surg. 2021, 27, e668–e672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.-Y.; Lin, K.-L.; Shen, C.-R.; Ker, C.-R.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Loo, Z.-X.; Hsiao, H.-H.; Lee, Y.-C. A Pilot Study: Effectiveness of Local Injection of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma in Treating Women with Stress Urinary Incontinence. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshpajooh, A.; Mirzaei, M.; Farsinejad, A.; NaghibzadehTahami, A.; Eslami, A. The Effect of Periurethral Injection of Pure Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Urinary Incontinence in Female Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Kerman Univ. Med. Sci. 2021, 28, 330–337. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Zhu, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, X.; Chen, H.; Zhou, Q.; Xie, L. Hyperglycemia-reduced platelet-derived growth factor–BB expression impairs corneal wound healing in diabetic mice. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2025, 66, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Giri, B.; Dey, S.; Das, T.; Sarkar, M.; Banerjee, J.; Dash, S.K. Chronic hyperglycemia mediated physiological alteration and metabolic distortion leads to organ dysfunction, infection, cancer progression and other pathophysiological consequences: An update on glucose toxicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 306–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, I.-K.; King, G.L. New perspectives on diabetic vascular complications: The loss of endogenous protective factors induced by hyperglycemia. Diabetes Metab. J. 2011, 35, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kolluru, G.K.; Bir, S.C.; Kevil, C.G. Endothelial dysfunction and diabetes: Effects on angiogenesis, vascular remodeling, and wound healing. Int. J. Vasc. Med. 2012, 2012, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, D.-R.; Wang, M.-Y.; Zhang, C.-L.; Wang, Y. Endothelial Dysfunction in vascular complications of diabetes: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and implications. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1359255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Huang, K.; Mi, B.; Xiong, Y.; Fu, Z.; Zhou, W.; Liu, W.; Liu, G.; Dai, G. Angiogenesis during diabetic wound repair: From mechanism to therapy opportunity. Burn. Trauma 2025, 13, tkae052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrini, V.; La Grotta, R.; Carreras, F.; Giuliani, A.; Sabbatinelli, J.; Olivieri, F.; Berra, C.C.; Ceriello, A.; Prattichizzo, F. Inflammatory trajectory of type 2 diabetes: Novel opportunities for early and late treatment. Cells 2024, 13, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Jeon, Y.; Lee, C.-H.; Yang, J.M.; Kim, S.G. Dysregulation of extracellular matrix in diabetic complications: Clinical impacts and new molecular targets. Innov. Acupunct. Med. 2025, 18, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; He, X.; Long, C.; Luo, Z. Hypothesis: Platelet-rich plasma accelerate diabetic wound healing via dynamic modulation of multiple signaling pathways. Med. Hypotheses 2023, 176, 111097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.; Rai, V. Platelet-rich plasma in diabetic foot ulcer healing: Contemplating the facts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.R.; Purita, J.; Martins, R.; Costa, B.; De Oliveira, L.V.; Huber, S.C.; Santos, G.S.; Pires, L.; Azzini, G.; Kruel, A.; et al. Not all platelets are created equal: A review on platelet aging and functional quality in regenerative medicine. Cells 2025, 14, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelem, A.; Adane, T.; Shiferaw, E. Insulin resistance-induced platelet hyperactivity and a potential biomarker role of platelet parameters: A narrative review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2023, 16, 2843–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karina; Wahyuningsih, K.A.; Sobariah, S.; Rosliana, I.; Rosadi, I.; Widyastuti, T.; Afini, I.; Wanandi, S.I.; Soewondo, P.; Wibowo, H.; et al. Evaluation of platelet-rich plasma from diabetic donors shows increased platelet vascular endothelial growth factor release. Stem Cell Investig. 2019, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hassanien, M.; Elawamy, A.; Kamel, E.Z.; Khalifa, W.A.; Abolfadl, G.M.; Roushdy, A.S.I.; El Zohne, R.A.; Makarem, Y.S. Perineural platelet-rich plasma for diabetic neuropathic pain: Could it make a difference? Pain Med. 2020, 21, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, P.J.; Nag, S.; Baria, M.; Rice, E.; Moore, A.M. A systematic review of the clinical application of platelet-rich plasma for peripheral neuropathic pain. J. Orthop. Rep. 2025, 100725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Sinha, M.K.; Sahoo, J.; Viswanath, A. The benefit of platelet-rich plasma injection over institution-based physical therapy program in adhesive capsulitis patients with diabetes mellitus: Prospective observational cohort study. Clin. Shoulder Elb. 2021, 24, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shunmuga, P.D.; Tadepalli, A.; Parthasarathy, H.; Ponnaiyan, D.; Cholan, P.K.; Ramachandran, L. Clinical evaluation of the combined efficacy of injectable platelet-rich fibrin along with scaling and root planing in the non-surgical periodontal therapy of stage iii and grade c periodontitis patients having type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Adv. Periodontics 2024, 14, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.-H.; Lee, K.-H.; Chung, S.-D.; Chen, K.-C.; Praveen Rajneesh, C.; Chen, B.-H.; Cheng, J.-H.; Lin, W.-Y.; Chiang, H.-S.; Wu, Y.-N. Intracavernous injection of platelet-rich plasma therapy enhances erectile function and decreases the mortality rate in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zaghloul, A.S.; El-Nashaar, A.M.; Said, S.Z.; Osman, I.A.; Mostafa, T. Assessment of the intracavernosal injection platelet-rich plasma in addition to daily oral tadalafil intake in diabetic patients with erectile dysfunction non-responding to on-demand oral PDE5 inhibitors. Andrologia 2022, 54, e14421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
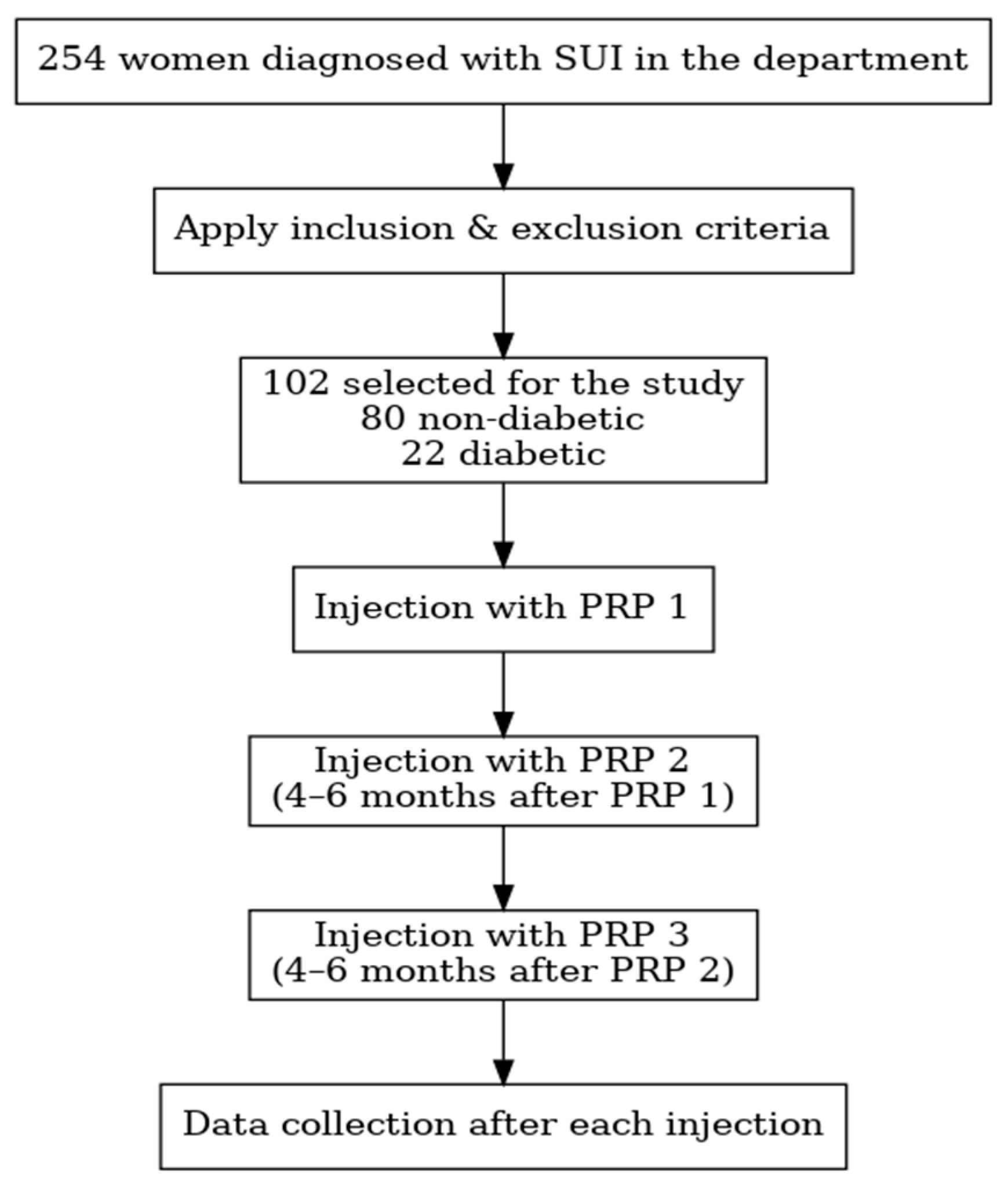
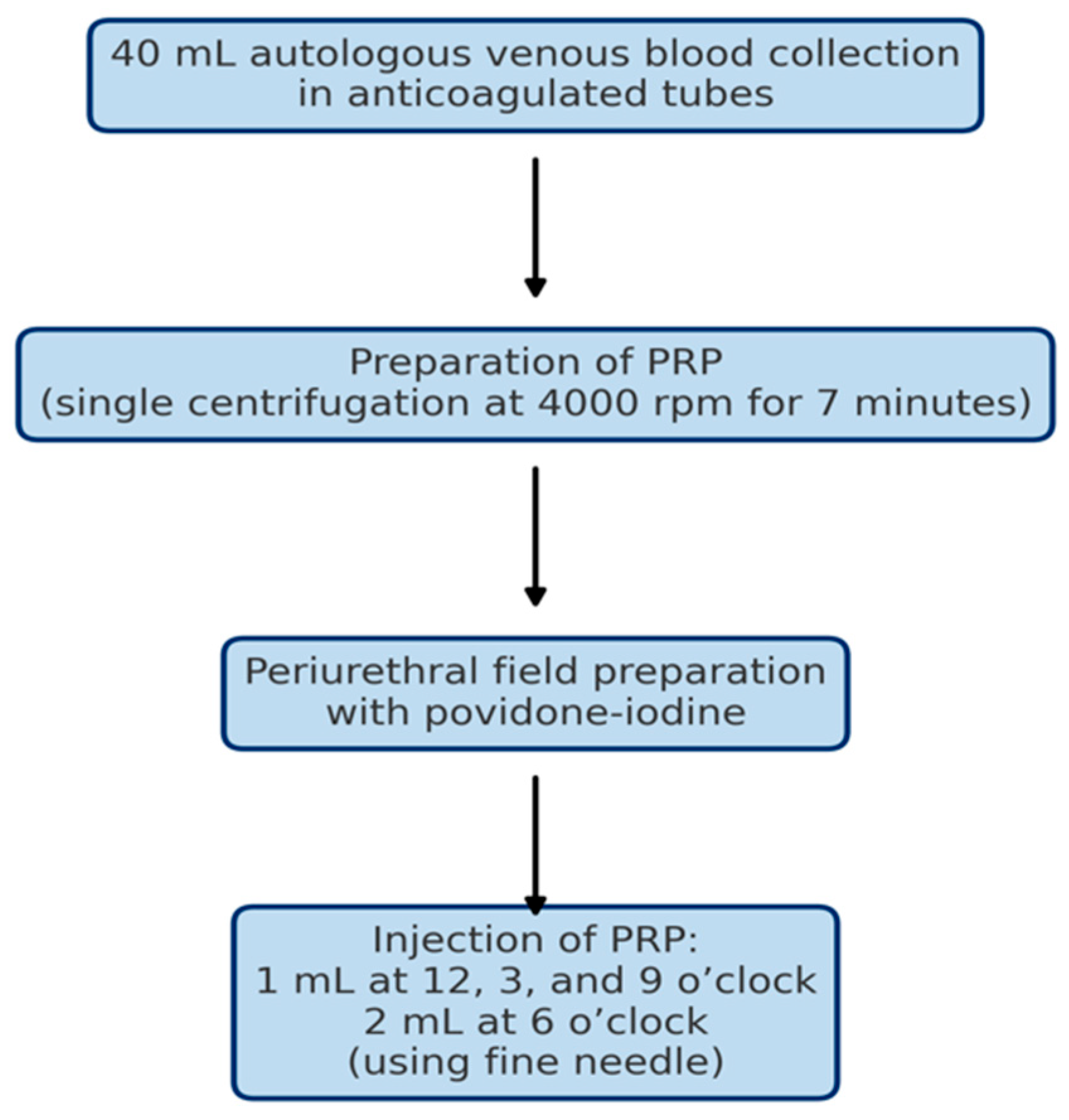

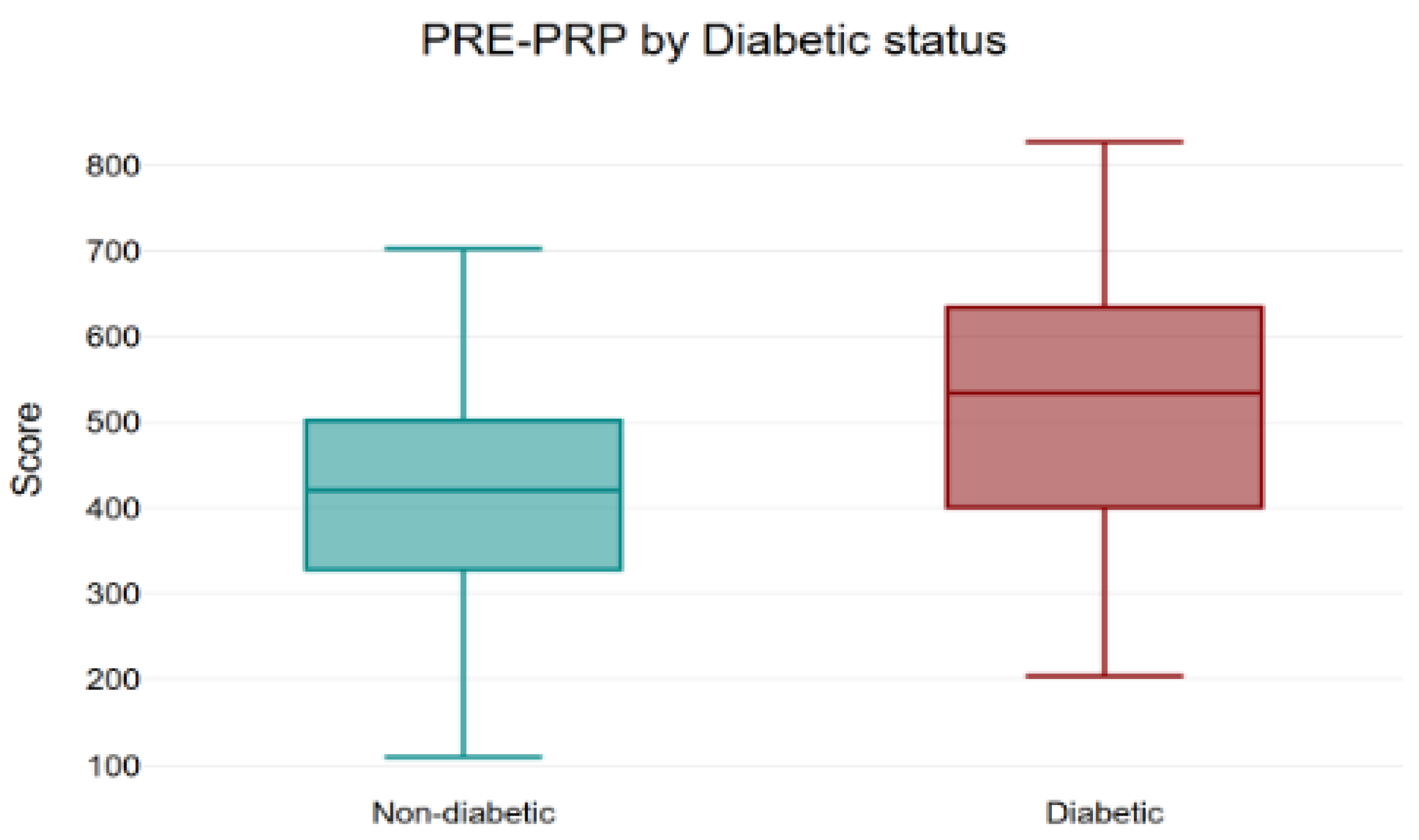



| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Stress urinary incontinence reported by the patient and confirmed by gynecological examination (all degrees of SUI: mild, moderate, and severe) | Anatomical defect (anterior and/or central compartment prolapse > stage 1) |
| Contraindications for surgical treatment | Platelet disorders (qualitative or quantitative) |
| Patient’s preference for a non-surgical treatment | Sepsis |
| Neoplasia | |
| Chronic treatment with NSAIDs |
| Objectives | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Objective | To compare treatment outcomes using KHQ between diabetic and non-diabetic women treated with PRP for SUI. To compare the treatment outcomes using the Stamey scale. |
| Secondary Objectives | To evaluate overall symptom improvement and assess the occurrence of adverse events. Mean change in KHQ score within each group. Observe the difference in Stamey score between diabetics treated with insulin and diabetics without insulin. |
| Variable | Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 58.63 | 10.77 | 38 | 82 |
| Number of births | 1.89 | 0.94 | 0 | 4 |
| Group | Pre-PRP Mean | Post-PRP3 Mean | Absolute Change | Percent Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-diabetic (n = 80) | 416.12 | 212.45 | −203.67 | −48.9% |
| Diabetic (n = 22) | 510.63 | 315.32 | −195.31 | −38.3% |
| Entire cohort (n = 102) | 436.50 | 234.64 | −201.87 | −46.2% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borislavschi, A.; Petca, R.-C.; Petca, A. Does Diabetes Matter? The Efficacy of PRP on the Quality of Life in Stress Urinary Incontinence. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111179
Borislavschi A, Petca R-C, Petca A. Does Diabetes Matter? The Efficacy of PRP on the Quality of Life in Stress Urinary Incontinence. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(11):1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111179
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorislavschi, Andreea, Răzvan-Cosmin Petca, and Aida Petca. 2025. "Does Diabetes Matter? The Efficacy of PRP on the Quality of Life in Stress Urinary Incontinence" Bioengineering 12, no. 11: 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111179
APA StyleBorislavschi, A., Petca, R.-C., & Petca, A. (2025). Does Diabetes Matter? The Efficacy of PRP on the Quality of Life in Stress Urinary Incontinence. Bioengineering, 12(11), 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111179






