Accuracy and Precision of Model-Based Tracking of a Dynamic Hop Landing Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
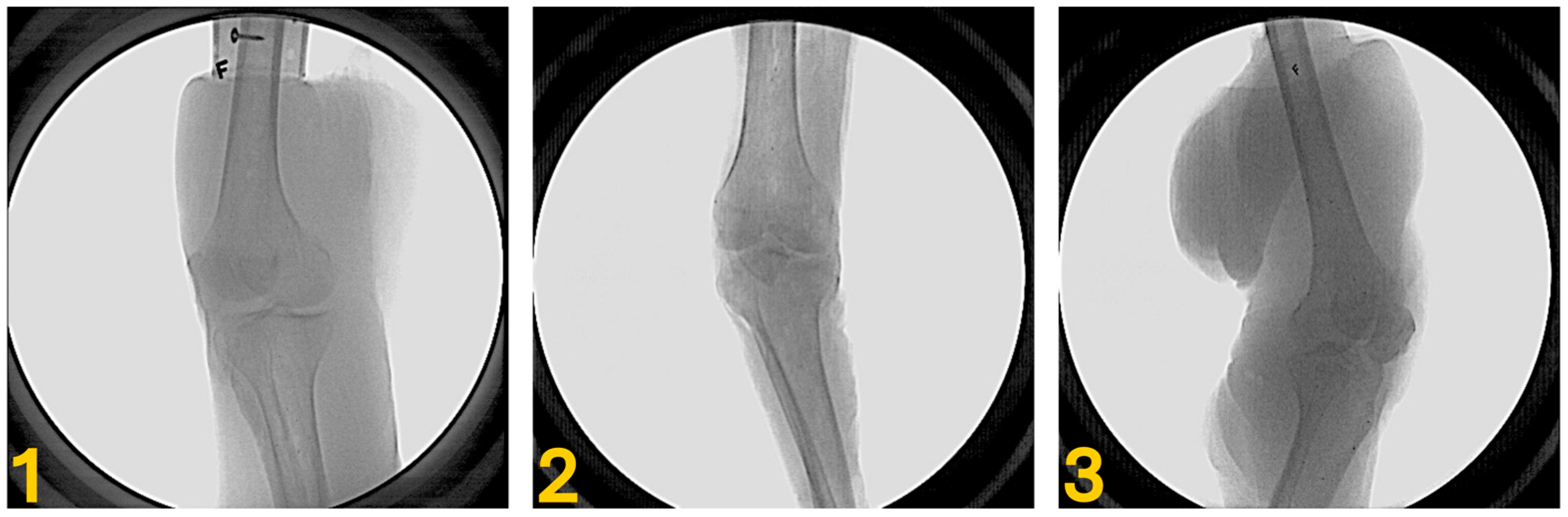
2.1. Specimen Preparation
2.2. Bone Model and Volume Generation
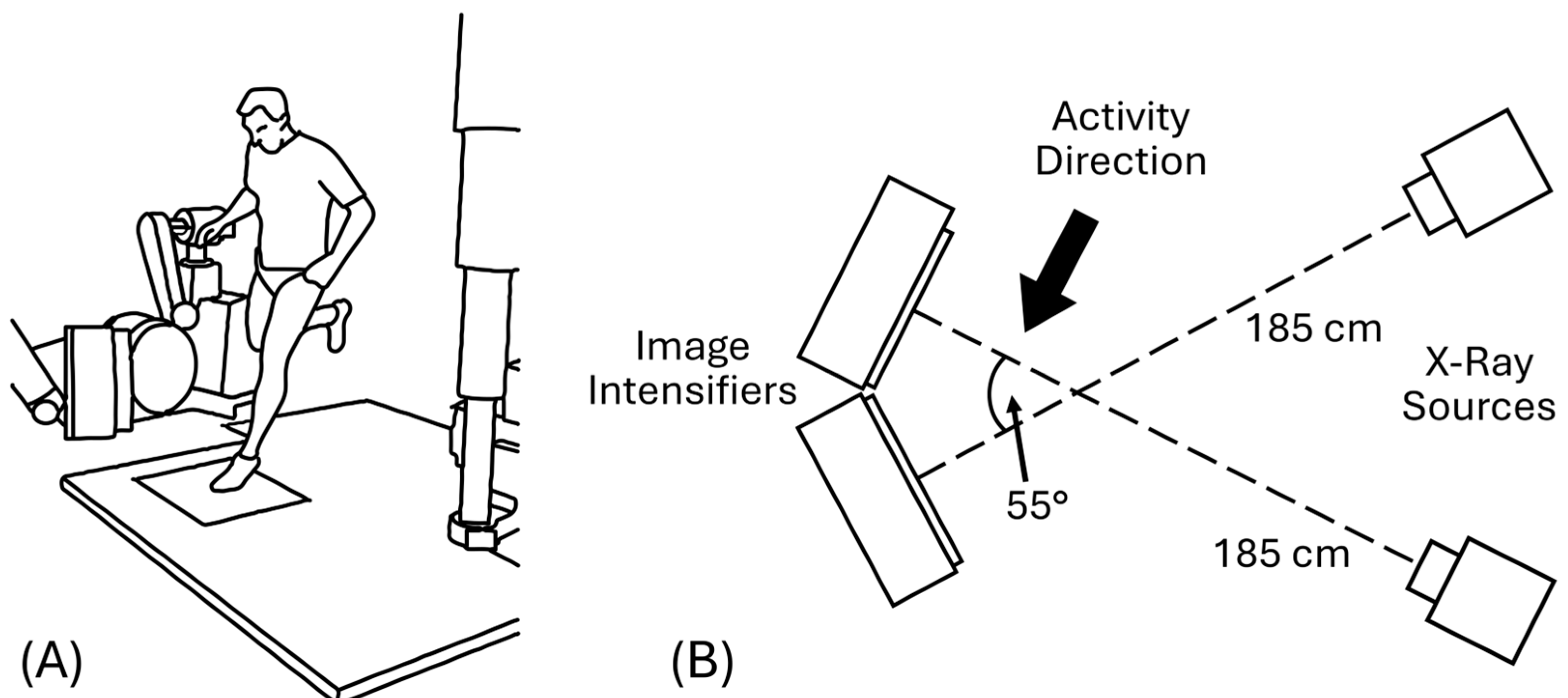
2.3. BVR System Geometry and Recording Parameters
2.4. Data Collection
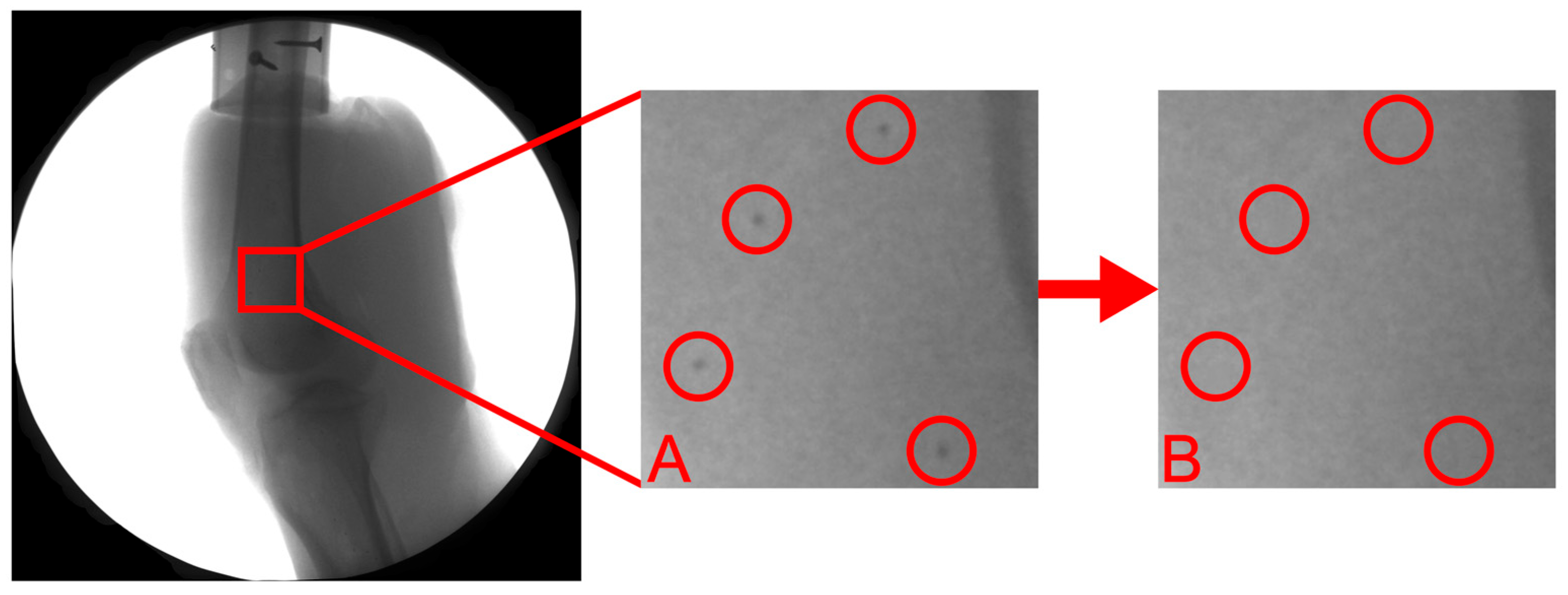
2.5. Marker-Based Tracking
2.6. Model-Based Tracking
2.7. Three-Dimensional Kinematics
2.8. Accuracy, Bias, and Precision
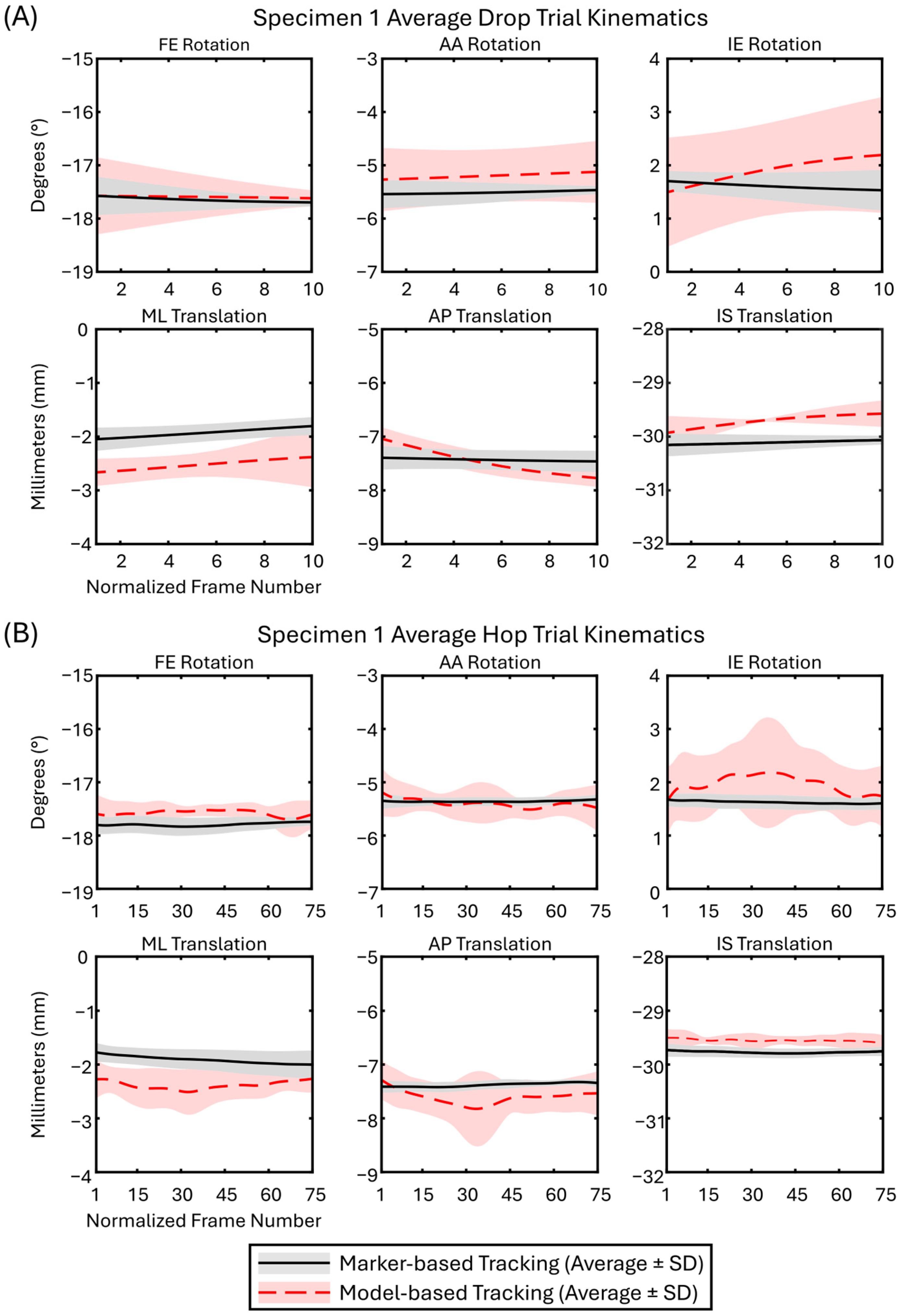
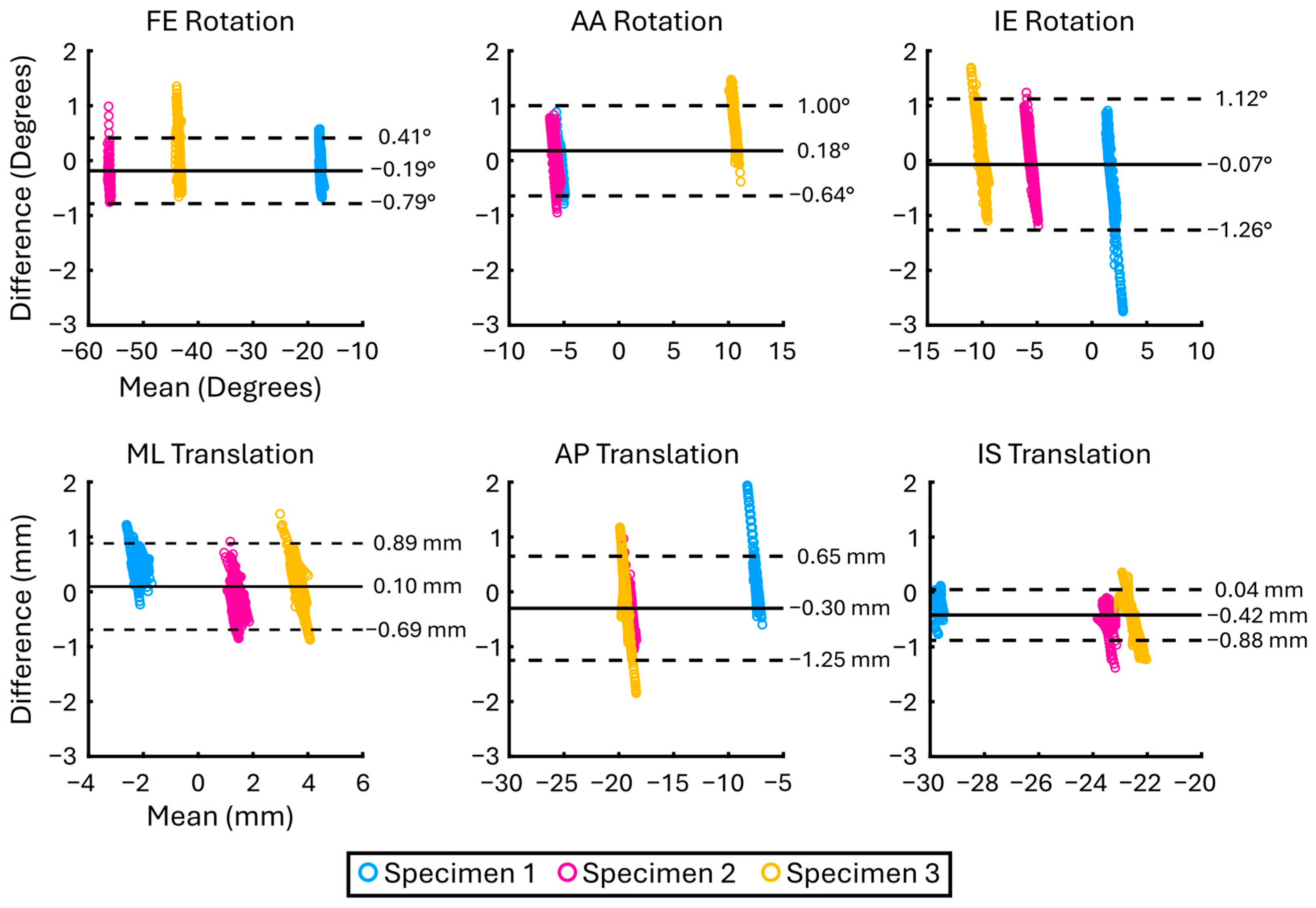
3. Results
| Analysis | DOF | Mean Absolute Difference (±SD) (°/mm) | Bias (°/mm) | LoA (°/mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specimen 1 n = 429 | FE | 0.30 ± 0.17 | −0.22 | 0.52 |
| AA | 0.21 ± 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.52 | |
| IE | 0.66 ± 0.55 | −0.47 | 1.40 | |
| ML | 0.50 ± 0.24 | 0.49 | 0.49 | |
| AP | 0.39 ± 0.35 | 0.33 | 0.80 | |
| IS | 0.23 ± 0.13 | −0.22 | 0.27 | |
| Specimen 2 n = 1095 | FE | 0.29 ± 0.13 | −0.28 | 0.30 |
| AA | 0.22 ± 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.56 | |
| IE | 0.40 ± 0.27 | −0.04 | 0.94 | |
| ML | 0.26 ± 0.19 | −0.09 | 0.62 | |
| AP | 0.53 ± 0.18 | −0.52 | 0.40 | |
| IS | 0.42 ± 0.13 | −0.42 | 0.26 | |
| Specimen 3 n = 450 | FE | 0.35 ± 0.28 | 0.07 | 0.87 |
| AA | 0.72 ± 0.36 | 0.71 | 0.72 | |
| IE | 0.53 ± 0.33 | 0.24 | 1.13 | |
| ML | 0.36 ± 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.79 | |
| AP | 0.53 ± 0.35 | −0.36 | 1.02 | |
| IS | 0.62 ± 0.29 | −0.60 | 0.66 |
| Analysis | DOF | Mean Absolute Difference (±SD) (°/mm) | Bias (°/mm) | LoA (°/mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drop (1.8 m/s) n = 173 | FE | 0.40 ± 0.22 | 0.01 | 0.90 |
| AA | 0.68 ± 0.39 | 0.41 | 1.31 | |
| IE | 0.51 ± 0.34 | −0.02 | 1.21 | |
| ML | 0.30 ± 0.24 | 0.16 | 0.68 | |
| AP | 0.37 ± 0.23 | 0.25 | 0.69 | |
| IS | 0.55 ± 0.30 | −0.54 | 0.63 | |
| Hop (0.9 m/s) n = 1801 | FE | 0.30 ± 0.18 | −0.21 | 0.55 |
| AA | 0.30 ± 0.28 | 0.16 | 0.74 | |
| IE | 0.48 ± 0.38 | −0.08 | 1.19 | |
| ML | 0.34 ± 0.24 | 0.09 | 0.80 | |
| AP | 0.51 ± 0.28 | 0.31 | 0.97 | |
| IS | 0.41 ± 0.21 | −0.41 | 0.44 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BVR | Biplane Videoradiography |
| ACL | Anterior Cruciate Ligament |
| SID | Source-to-image distance |
| ACLR | ACL Reconstruction |
| SAM | SlicerAutoscoperM |
| DOF | Degree-of-freedom |
| FE | Flexion/Extension |
| AA | Abduction/Adduction |
| IE | Internal/External |
| ML | Medial/Lateral |
| AP | Anterior/Posterior |
| IS | Inferior/Superior |
| LoA | Limits of Agreement |
| CI | Confidence Intervals |
| HU | Hounsfield Units |
References
- Beveridge, J.E.; Heard, B.J.; Shrive, N.G.; Frank, C.B. Tibiofemoral centroid velocity correlates more consistently with cartilage damage than does contact path length in two ovine models of stifle injury. J. Orthop. Res. 2013, 31, 1745–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beveridge, J.E.; Heard, B.J.; Brown, J.J.Y.; Shrive, N.G.; Frank, C.B. A new measure of tibiofemoral subchondral bone interactions that correlates with early cartilage damage in injured sheep. J. Orthop. Res. 2014, 32, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setliff, J.C.; Anderst, W.J. A scoping review of human skeletal kinematics research using biplane radiography. J. Orthop. Res. Off. Publ. Orthop. Res. Soc. 2024, 42, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, D.L.; Schwartz, J.B.; Loomis, A.C.; Brainerd, E.L.; Fleming, B.C.; Crisco, J.J. Static and dynamic error of a biplanar videoradiography system using marker-based and markerless tracking techniques. J. Biomech. Eng. 2011, 133, 121002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderst, W.; Zauel, R.; Bishop, J.; Demps, E.; Tashman, S. Validation of three-dimensional model-based tibio-femoral tracking during running. Med. Eng. Phys. 2009, 31, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Gray, H.A.; Keynejad, F.; Pandy, M.G. Mobile biplane x-ray imaging system for measuring 3d dynamic joint motion during overground gait. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Velde, S.K.V.d.; Bingham, J.T. Validation of a non-invasive fluoroscopic imaging technique for the measurement of dynamic knee joint motion. J. Biomech. 2008, 41, 1616–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, G.J.; McCarty, E.; Provencher, M.; Manske, R.C. ACL return to sport guidelines and criteria. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2017, 10, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knörlein, B.J.; Baier, D.B.; Gatesy, S.M.; Laurence-Chasen, J.D.; Brainerd, E.L. Validation of xmalab software for marker-based xromm. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 3701–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, A.M.; Holtgrewe, J.D.; Beveridge, J.E.; Yoon, D.; Rainbow, M.J.; Lopez, C.; Zhao, K.D.; Paniagua, B.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Lombardi, A.J.; et al. An accuracy assessment of slicerautoscoperm−software for tracking skeletal structures in multi-plane videoradiography datasets. J. Biomech. 2025, 189, 112810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beveridge, J.E.; Hague, M.; Parola, L.R.; Costa, M.Q.; Molino, J.; Fleming, B.C. Static and Dynamic Constraint in ACL-Reconstructed Patients at 10-15 Year Follow-up. In Proceedings of the Orthopaedic Research Society Annual Meeting, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2–6 February 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda, D.L.; Fadale, P.D.; Hulstyn, M.J.; Shalvoy, R.M.; Machan, J.T.; Fleming, B.C. Knee biomechanics during a jump-cut maneuver: Effects of sex and acl surgery. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2013, 45, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, D.L.; Rainbow, M.J.; Leventhal, E.L.; Crisco, J.J.; Fleming, B.C. Automatic determination of anatomical coordinate systems for three-dimensional bone models of the isolated human knee. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 1623–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englander, Z.A.; Martin, J.T.; Ganapathy, P.K.; Garrett, W.E.; DeFrate, L.E. Automatic registration of mri-based joint models to high-speed biplanar radiographs for precise quantification of in vivo anterior cruciate ligament deformation during gait. J. Biomech. 2018, 81, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brainerd, E.L.; Baier, D.B.; Gatesy, S.M.; Hedrick, T.L.; Metzger, K.A.; Gilbert, S.L.; Crisco, J.J. X-ray reconstruction of moving morphology (xromm): Precision, accuracy and applications in comparative biomechanics research. J. Exp. Zool. Part Ecol. Genet. Physiol. 2010, 313, 262–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, E. XROMM Autoscoper. Tools. Available online: https://bitbucket.org/xromm/Xromm_autoscopertools/ (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Fedorov, A.; Beichel, R.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Finet, J.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Pujol, S.; Bauer, C.; Jennings, D.; Fennessy, F.; Sonka, M.; et al. 3D slicer as an image computing platform for the quantitative imaging network. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1323–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhbari, B.; Morton, A.M.; Moore, D.C.; Weiss, A.-P.C.; Wolfe, S.W.; Crisco, J.J. Accuracy of biplane videoradiography for quantifying dynamic wrist kinematics. J. Biomech. 2019, 92, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giphart, J.E.; Zirker, C.A.; Myers, C.A.; Pennington, W.W.; LaPrade, R.F. Accuracy of a contour-based biplane fluoroscopy technique for tracking knee joint kinematics of different speeds. J. Biomech. 2012, 45, 2935–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akelman, M.R.; Fadale, P.D.; Hulstyn, M.J.; Shalvoy, R.M.; Garcia, A.; Chin, K.E.; Duryea, J.; Badger, G.J.; Tung, G.A.; Fleming, B.C. Effect of matching or overconstraining knee laxity during anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction on knee osteoarthritis and clinical outcomes: A randomized controlled trial with 84-month follow-up. Am. J. Sports Med. 2016, 44, 1660–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breker, A.N.; Badger, G.J.; Kiapour, A.M.; Costa, M.Q.; Fleming, E.N.; Ferrara, S.L.; Chrostek, C.A.; Fadale, P.D.; Hulstyn, M.J.; Shalvoy, R.M.; et al. Effect of initial graft tension on knee osteoarthritis outcomes after acl reconstruction: A randomized controlled clinical trial with 15-year follow-up. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2025, 13, 23259671251320972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.Q.; Badger, G.J.; Chrostek, C.A.; Carvalho, O.D.; Faiola, S.L.; Fadale, P.D.; Hulstyn, M.J.; Gil, H.C.; Shalvoy, R.M.; Fleming, B.C. Effects of initial graft tension and patient sex on knee osteoarthritis outcomes after acl reconstruction: A randomized controlled clinical trial with 10- to 12-year follow-up. Am. J. Sports Med. 2022, 50, 3510–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markes, A.R.; Knox, J.; Zhong, Q.; Pedoia, V.; Li, X.; Ma, C.B. An abnormal tibial position is associated with alterations in the meniscal matrix: A 3-year longitudinal study after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2019, 7, 2325967118820057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biercevicz, A.M.; Akelman, M.R.; Fadale, P.D.; Hulstyn, M.J.; Shalvoy, R.M.; Badger, G.J.; Tung, G.A.; Oksendahl, H.L.; Fleming, B.C. MRI volume and signal intensity of acl graft predict clinical, functional, and patient-oriented outcome measures after acl reconstruction. Am. J. Sports Med. 2015, 43, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandiyeh, P.; Parola, L.R.; Costa, M.Q.; Hague, M.J.; Molino, J.; Fleming, B.C.; Beveridge, J.E. Long-term bilateral neuromuscular function and knee osteoarthritis after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| DOF | Mean Absolute Difference (±SD) (°/mm) | Bias (°/mm) | LoA (°/mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FE | 0.30 ± 0.19 | −0.19 | 0.60 |
| AA | 0.33 ± 0.31 | 0.18 | 0.82 |
| IE | 0.49 ± 0.37 | −0.07 | 1.19 |
| ML | 0.34 ± 0.24 | 0.10 | 0.79 |
| AP | 0.50 ± 0.28 | −0.30 | 0.95 |
| IS | 0.43 ± 0.23 | −0.42 | 0.46 |
| Analysis | DOF | Mean Absolute Difference (±SD) (°/mm) | Bias (°/mm) | LoA (°/mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Femur n = 1974 | FE | 0.21 ± 0.14 | −0.14 | 0.42 |
| AA | 0.17 ± 0.11 | −0.02 | 0.40 | |
| IE | 0.31 ± 0.22 | −0.10 | 0.72 | |
| ML | 0.37 ± 0.29 | 0.32 | 0.67 | |
| AP | 0.20 ± 0.12 | −0.15 | 0.36 | |
| IS | 0.49 ± 0.10 | −0.49 | 0.20 | |
| Tibia n = 1974 | FE | 0.17 ± 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.44 |
| AA | 0.26 ± 0.23 | −0.13 | 0.64 | |
| IE | 0.42 ± 0.34 | −0.02 | 1.06 | |
| ML | 0.48 ± 0.25 | 0.19 | 1.00 | |
| AP | 0.24 ± 0.16 | 0.06 | 0.56 | |
| IS | 0.18 ± 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Holtgrewe, J.D.; Murray, C.J.; Barnes, D.A.; Fleming, B.C.; Beveridge, J.E. Accuracy and Precision of Model-Based Tracking of a Dynamic Hop Landing Activity. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111168
Holtgrewe JD, Murray CJ, Barnes DA, Fleming BC, Beveridge JE. Accuracy and Precision of Model-Based Tracking of a Dynamic Hop Landing Activity. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(11):1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111168
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoltgrewe, John D., Crystal J. Murray, Dominique A. Barnes, Braden C. Fleming, and Jillian E. Beveridge. 2025. "Accuracy and Precision of Model-Based Tracking of a Dynamic Hop Landing Activity" Bioengineering 12, no. 11: 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111168
APA StyleHoltgrewe, J. D., Murray, C. J., Barnes, D. A., Fleming, B. C., & Beveridge, J. E. (2025). Accuracy and Precision of Model-Based Tracking of a Dynamic Hop Landing Activity. Bioengineering, 12(11), 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111168






