A Self-Polymerizing Mesh of Nano-Tethers for the Mechanical Constraint of Degraded Intervertebral Discs—A Review of 25 Years of Pre-Clinical and Early Clinical Research
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. The Role of Mechanical Strength Deterioration in the Pathogenesis of IDD
3.2. The Reaction Kinetics of Genipin in Collagenous Tissues
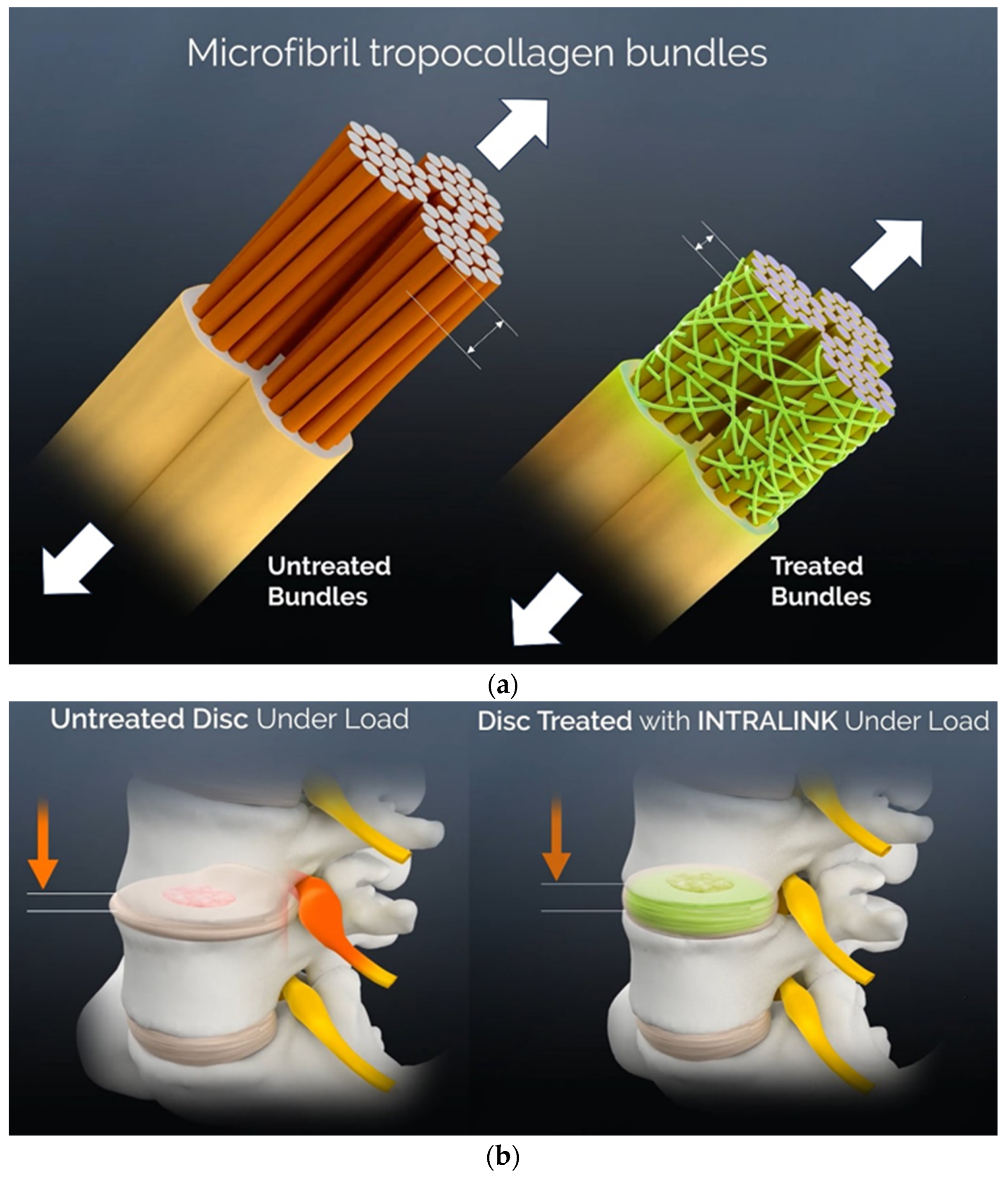
3.3. A Mechanical Effects Review
| Pain or Degeneration-Related Mechanical Factor | Effect Size |
|---|---|
| Resistance to tissue degradation from repetitive loading [33,40] | 3-fold increase |
| Joint stability, neutral zone reductions [33,41,42,43,44] † | Up to 4-fold increase |
| Annulus mechanical properties such as tensile strength, yield strength, resilience and toughness [32,36,37] | 50% or more improvement |
| Disc bulging under a load [32,38] | 38% reduction |
| Resistance to tear propagation, delamination [39,40] | Up to 70% increase |
| Tensile stress levels in annulus [47] | 3- to 8-fold lower |
| Annular sealing, disc pressure restoration [49,50] | 5- to 7-fold increase |
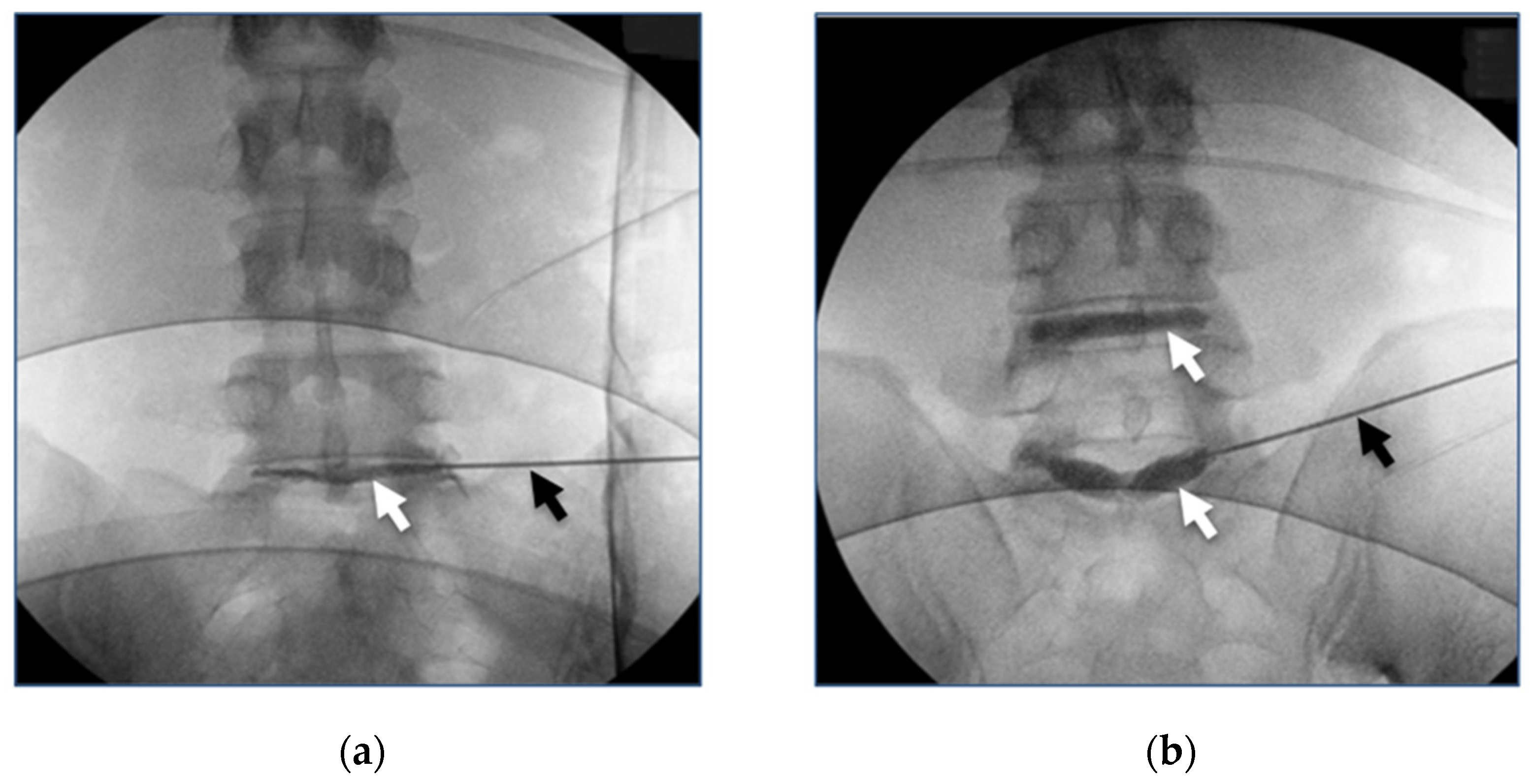
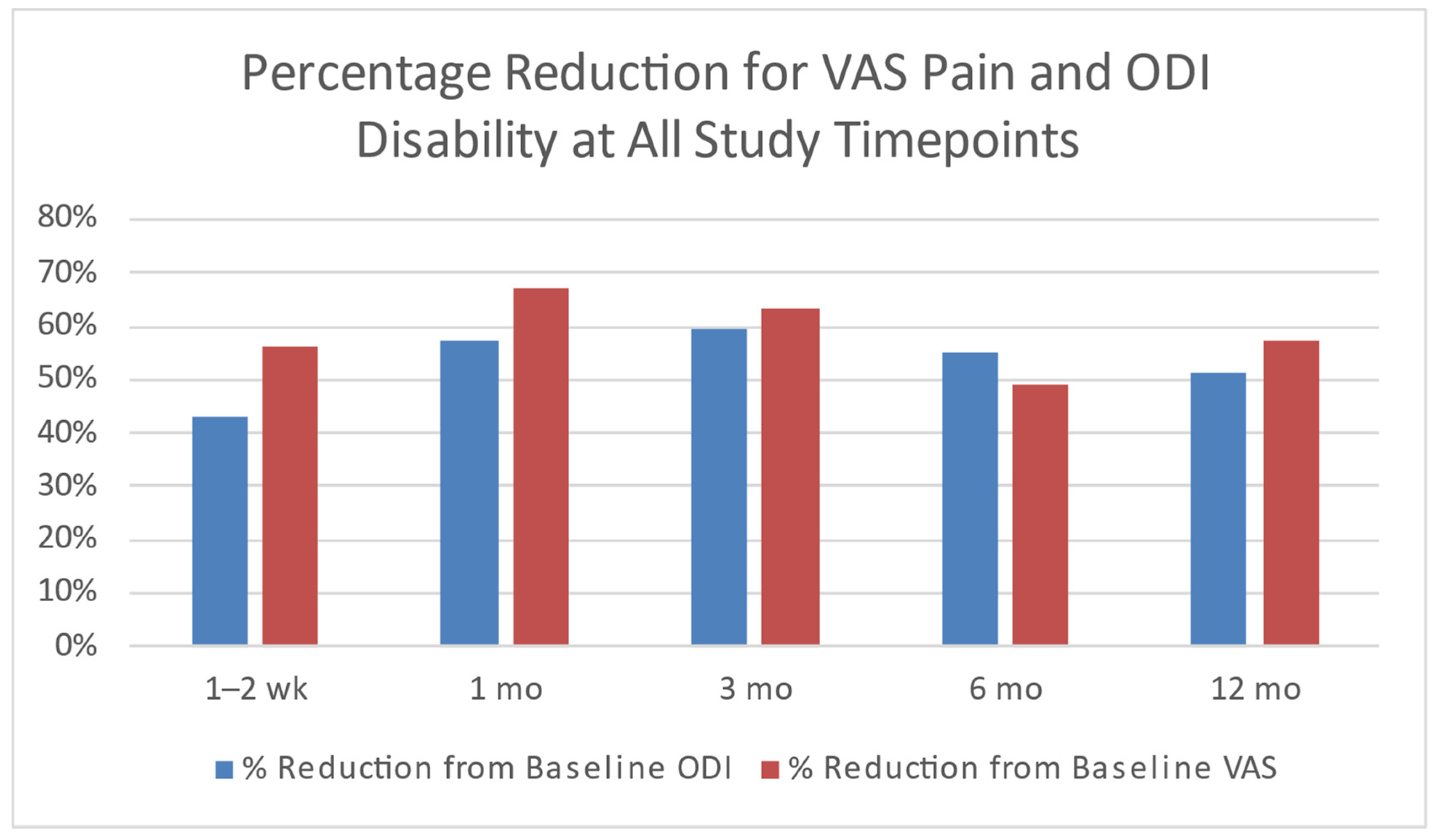
3.4. Clinical Studies Review
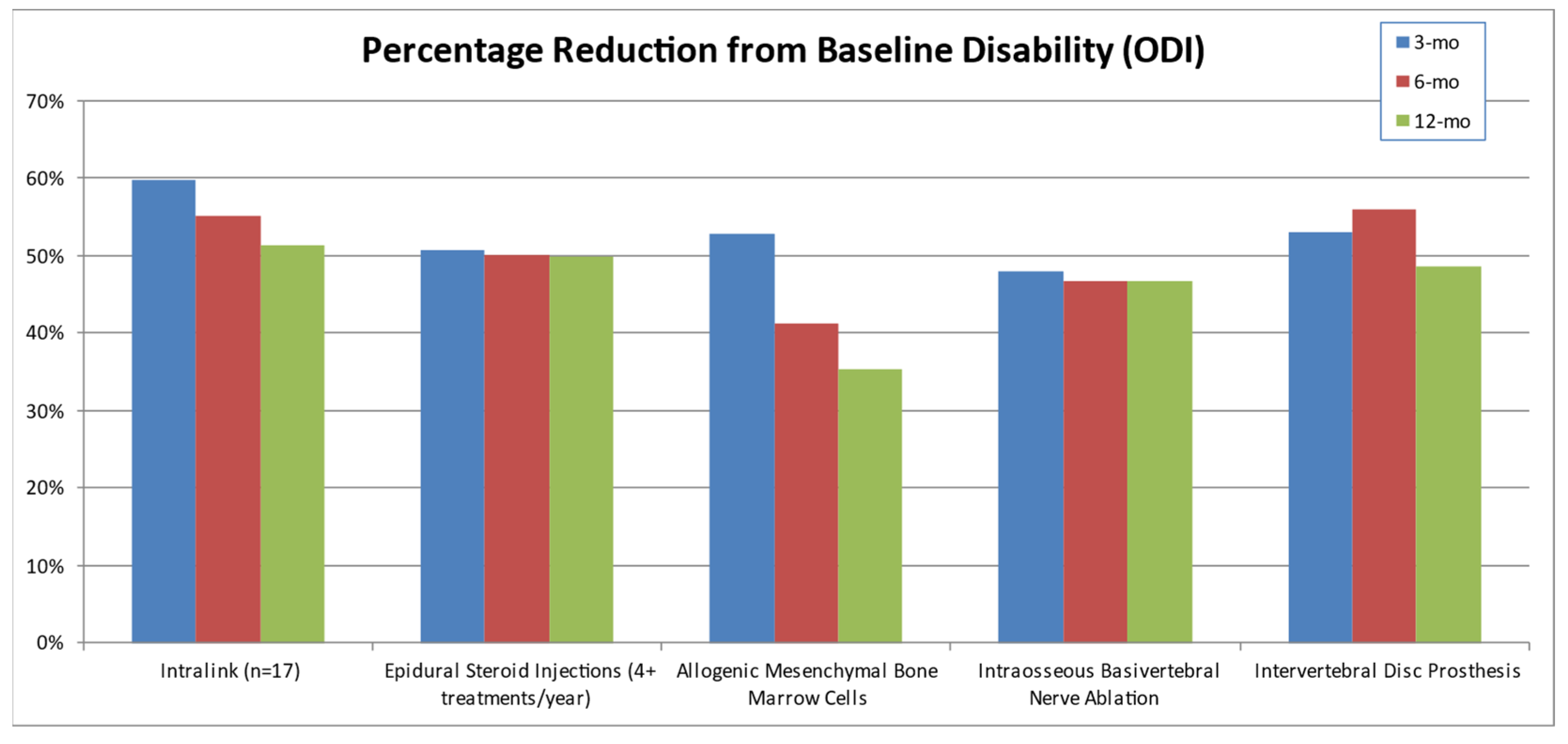
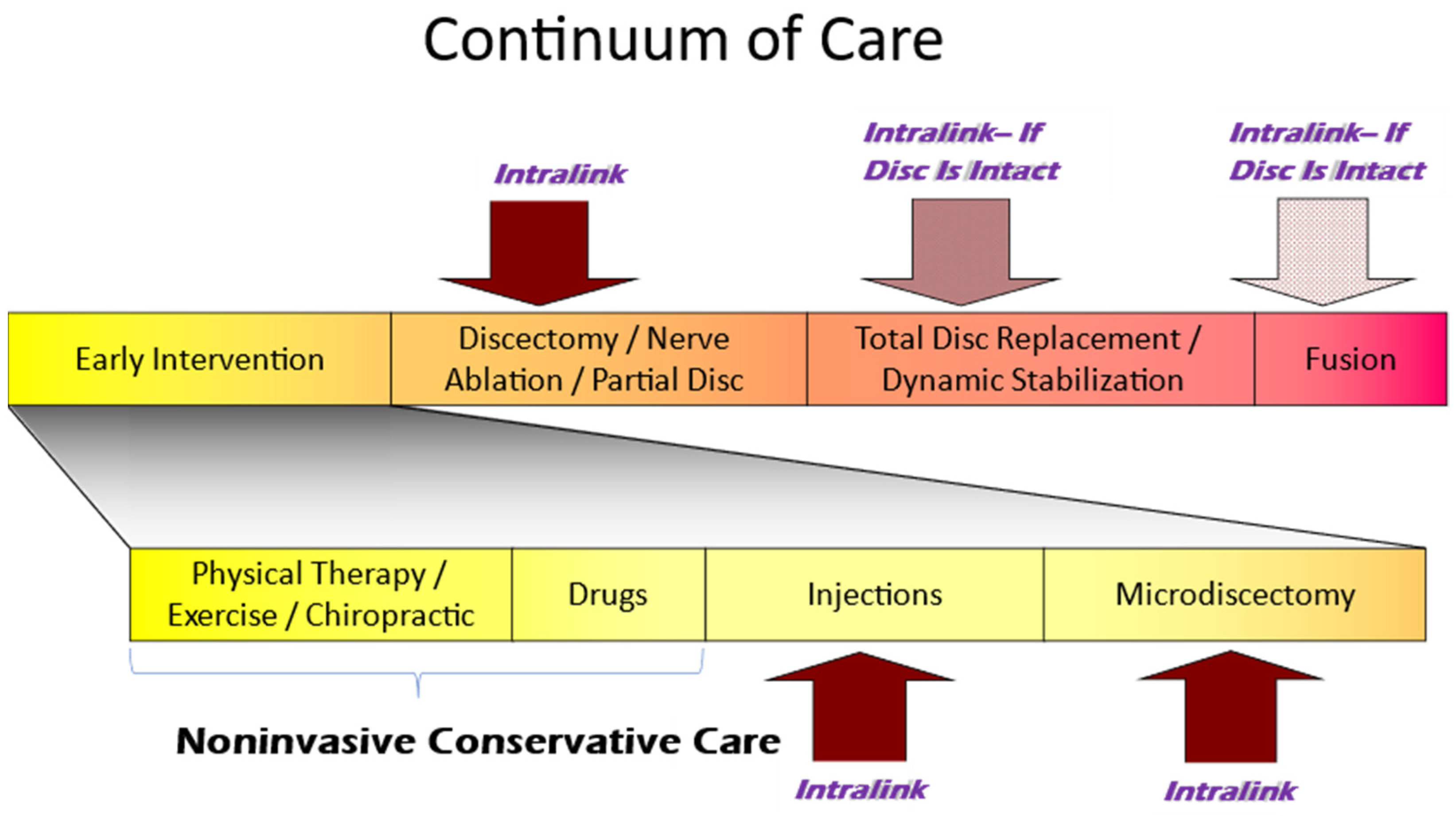
3.5. The Current Continuum of Care for Discogenic LBP
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adams, M.A.; Roughley, P.J. What is intervertebral disc degeneration, and what causes it? Spine 2006, 31, 2151–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, J.P.; Smith, S.; Fairbank, J.C. Nutrition of the intervertebral disc. Spine 2004, 29, 2700–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, J.P.G.; Roberts, S. Degeneration of the intervertebral disc. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2003, 5, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Adams, M.; Bogduk, N.; Burton, K.; Dolan, P. The Biomechanics of Back Pain; Churchill Livingstone: London, UK, 2002; ISBN 0-443-06207-2. [Google Scholar]
- Buckwalter, J.A. Aging and degeneration of the human intervertebral disc. Spine 1995, 20, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iatridis, J.C.; Laible, J.P.; Krag, M.H. Influence of fixed charge density magnitude and distribution on the intervertebral disc: Applications of a poroelastic and chemical electric (PEACE) model. J. Biomech. Eng. 2003, 125, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, M.A.; Freeman, B.J.C.; Morrison, H.P.; Nelson, I.W.; Dolan, P. Mechanical initiation of intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine 2000, 25, 1625–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Pollintine, P.; Hole, B.D.; Dolan, P.; Adams, M.A. Discogenic origins of spinal instability. Spine 2005, 30, 2621–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, D.; Trafimow, J.H.; Andersson, G.B.; McNeill, T.W.; Huckman, M.S. Discs degenerate before facets. Spine 1990, 15, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckwalter, J.A.; Woo, S.L.; Goldberg, V.M.; Hadley, E.C.; Booth, F.; Oegema, T.R.; Eyre, D.R. Soft-tissue aging and musculoskeletal function. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1993, 75, 1533–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koes, B.W.; van Tulder, M.W.; Thomas, S. Diagnosis and treatment of low back pain. BMJ 2006, 332, 1430–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, C.; Underwood, M.; Buchbinder, R. Non-specific low back pain. Lancet 2017, 389, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartynski, W.S.; Dejohn, L.M.; Rothfus, W.E.; Gerszten, P.C. ‘Progressive-Onset’ versus injury-associated discogenic low back pain: Features of disc internal derangement in patients studied with provocation lumbar discography. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2013, 19, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panjabi, M.M. Clinical spina instability and low back pain. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2003, 13, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Korff, M.; Deyo, R.A.; Cherkin, D.; Barlow, W. Back pain in primary care—Outcomes at 1 year. Spine 1993, 18, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Korff, M. Studying the natural history of back pain. Spine 1994, 19, 2041S–2046S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniadakis, N.; Gray, A. The economic burden of back pain in the UK. Pain 2000, 84, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balague, F.; Mannion, A.F.; Pellise, F.; Cedraschi, C. Non-specific low back pain. Lancet 2012, 379, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haldemann, S.; Dagenais, S. A supermarket approach to the evidence-informed management of chronic low back pain. Spine J. 2008, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deyo, R.A.; Mirza, S.K.; Martin, B.I. Back pain prevalence and visit rates—Estimates from US National Surveys—2002. Spine 2006, 31, 2724–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagenais, S.; Caro, J.; Haldemann, S. A systematic review of low back pain cost of illness studies in the United States and international. Spine J. 2008, 8, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, F.L.; Shyu, S.S.; Peng, C.K. Characterization of ring-opening polymerization of genipin and pH-dependent cross-linking reactions between chitosan and genipin. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2005, 43, 1985–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.F.; Ng, Y.F.; Pudney, P.D.A. Mechanism and Kinetics of the Crosslinking Reaction between Biopolymers Containing Primary Amine Groups and Genipin. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2003, 41, 3941–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slusarewicz, P.; Zhu, K.; Hedman, T. Kinetic analysis of genipin degradation in aqueous solution. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 1853–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Slusarewicz, P.; Hedman, T. Thermal Analysis Reveals Differential Effects of Various Crosslinkers on Bovine Annulus Fibrosis. J. Orthop. Res. 2011, 29, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battie, M.C.; Videman, T.; Parent, E. Lumbar disc degeneration: Epidemiology and genetic influences. Spine 2004, 29, 2679–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roughley, P.J. Biology of intervertebral disc aging and degeneration: Involvement of the extracellular matrix. Spine 2004, 29, 2691–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokes, I.A.; Iatridis, J.C. Mechanical conditions that accelerate intervertebral disc degeneration: Overload versus immobilization. Spine 2004, 29, 2724–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotz, J.C.; Ulrich, J.A. Innervation, inflammation, and hypermobility may characterize pathologic disc degeneration: Review of animal model data. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2006, 88 (Suppl. S2), 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slusarewicz, P.; Zhu, K.; Hedman, T. Kinetic characterization and comparison of various protein crosslinking reagents for matrix modification. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, H. The natural history of disc herniation and the influence of intervention. Spine 1994, 19, 2234–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slusarewicz, P.; Zhu, K.; Kirking, B.; Toungate, J.; Hedman, T. Optimization of protein crosslinking formulations for the treatment of degenerative disc disease. Spine 2011, 36, E7–E13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedman, T.P.; Chuang, S.Y.; Syed, B.G.D. Biomechanical benefits of crosslink augmentation in spinal discs. In Proceedings of the IMECE, Washington, DC, USA, 16–21 November 2003; Volume 43256. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.; Racadio, J.; Sundararaj, S.; Hedman, T. Long Term Biocompatibility of Intradiscal Injections with Genipin in Ovine Model. Orthop. Trans. 2016, 41, 0871. [Google Scholar]
- Hedman, T.; Yu, J.; Singh, H.; Deer, T. Early clinical results of intervertebral joint stabilization by injectable load-sharing polymers. J. Pain Res. 2023, 16, 2777–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, S.Y.; Odono, R.M.; Hedman, T.P. Effects of exogenous crosslinking on in vitro tensile and compressive moduli of lumbar intervertebral discs. Clin. Biomech. 2007, 22, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirking, B.; Toungate, J.; Slusarewicz, P.; Zhu, K.; Hedman, T. The effects of different crosslinking agents on the tensile properties of the annulus fibrosus. Orthop. Trans. 2009, 34, 1676. [Google Scholar]
- Kirking, B.; Toungate, J.; Slusarewicz, P.; Zhu, K.; Hedman, T. The effect of chemical crosslinking agent injection on intervertebral disc bulge. Orthop. Trans. 2010, 35, 1560. [Google Scholar]
- Kirking, B.; Hedman, T.; Criscione, J. Changes in the interfacial shear resistance of disc annulus fibrosus from genipin crosslinking. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fessel, G.; Wernli, J.; Li, Y.; Gerber, C.; Snedeker, J.G. Exogenous collagen cross-linking recovers tendon functional integrity in an experimental model of partial tear. J. Orthop. Res. 2012, 30, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedman, T.P.; Saito, H.; Vo, C.; Chuong, S.Y. Exogenous cross-linking increases the stability of spinal motion segments. Spine 2006, 31, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerramalli, C.S.; Chou, A.I.; Miller, G.J.; Nicoll, S.B.; Chin, K.R.; Elliott, D.M. The effect of nucleus pulposus crosslinking and glycosaminoglycan degradation on disc mechanical function. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2007, 6, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbir, A.; Michalek, A.J.; Abbott, R.D.; Iatridis, J.C. Effects of enzymatic digestion on compressive properties of rat intervertebral discs. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirking, B.C.; Toungate, J.K.; Hedman, T.P. The dose response relationship between intervertebral disc flexion-extension neutral zone metrics and injected genipin concentration. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2013, 11, e73–e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, S.Y.; Lin, L.C.; Hedman, T.P. The influence of exogenous cross-linking and compressive creep loading on intradiscal pressure. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2010, 9, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedman, T.P.; Chen, W.P.; Lin, L.C.; Lin, H.J.; Chuang, S.Y. Effects of Collagen Crosslink Augmentation on Mechanism of Compressive Load Sharing in Intervertebral Discs. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2017, 37, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, S.Y.; Popovich, J.M.; Lin, S.Y.; Hedman, T.P. The Effects of Exogenous Crosslinking on Hydration and Fluid Flow in the Intervertebral Disc Subjected to Compressive Creep Loading and Unloading. Spine 2010, 35, E1362–E1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovich, J.M.; Yau, D.; Chuang, S.Y.; Hedman, T.P. Exogenous Collagen Crosslinking of the Intervertebral Disc Restores Joint Stability following Lumbar Posterior Decompression Surgery. Spine 2011, 36, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, S.Y.; Lin, L.C.; Tsai, Y.C.; Wang, J.L. Exogenous crosslinking recovers the functional integrity of intervertebral disc secondary to stab injury. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 92, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.J.; Lin, L.C.; Hedman, T.P.; Chen, W.P.; Chuang, S.Y. Exogenous Crosslinking Restores Intradiscal Pressure of Injured Porcine Intervertebral Discs: An In Vivo Examination Using Quantitative Discomanometry. Spine 2015, 40, 1572–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beall, D.P.; Amirdelfan, K.; Nunley, P.D.; Phillips, T.R.; Navarro, L.C.I.; Spath, A. Hydrogel Augmentation of the Lumbar Intervertebral Disc: An Early Feasibility Study of a Treatment for Discogenic Low Back Pain. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2024, 35, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalek, A.J.; Buckley, M.R.; Bonassar, L.J.; Cohen, I.; Iatridis, J.C. The effects of needle puncture injury on microscale shear strain in the intervertebral disc annulus fibrosus. Spine J. 2010, 10, 1098–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carragee, E.J.; Don, A.S.; Hurwitz, E.L.; Cuellar, J.M.; Carrino, J.; Herzog, R. Does Discography Cause Accelerated Progression of Degeneration Changes in the Lumbar Disc: A Ten-Year Cohort Study. Spine 2009, 34, 2338–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manchikanti, L.; Pampati, V.; Benyamin, R.M.; Boswell, M.V. Analysis of efficacy differences between caudal and lumbar interlaminar epidural injections in chronic lumbar axial discogenic pain: Local anesthetic alone vs. local combined with steroids. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 12, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noriega, D.C.; Ardura, F.; Hernandez-Ramajo, R.; Martin-Ferrero, M.A.; Sanches-Lite, I.; Toribio, B.; Alberca, M.; Garcia, V.; Moraleda, J.M.; Sanches, A.; et al. Intervertebral Disc Repair by Allogeneic Mesenchymal Bone Marrow Cells: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Transplantation 2017, 101, 1945–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischgrund, J.S.; Rhyne, A.; Franke, J.; Sasso, R.; Kitchel, S.; Bae, H.; Yeung, C.; Truumees, E.; Shaufele, M.; Yuan, P.; et al. Intraosseous basivertebral nerve ablation for the treatment of chronic low back pain: A prospective randomized double-blind sham-controlled multi-center study. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siepe, C.J.; Heider, F.; Haas, E.; Hitzl, W.; Szeimies, U.; Stabler, A.; Weiler, C.; Nerlich, A.G.; Mayer, M.H. Influence of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration on the outcome of total lumbar disc replacement: A prospective clinical, histological, X-ray and MRI investigation. Eur. Spine J. 2012, 21, 2287–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proietti, L.; Scaramuzzo, L.; Schiro, G.R.; Sessa, S.; Logroscino, C.A. Complications in lumbar spine surgery: A retrospective analysis. Indian J. Orthop. 2013, 47, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, J.; McGregor, A.; Jones, F.; Mullane, J.; Hurley, M. Rehabilitation Following Lumbar Fusion Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Spine 2016, 41, E28–E36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanford, Z.; Broda, A.; Taylor, H.; Turcotte, J.; Patton, C.M. Predictive Risk Factors Associated with Increased Opioid Use among Patients Undergoing Elective Spine Surgery. Int. J. Spine Surg. 2020, 14, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karhade, A.V.; Cha, T.D.; Fogel, H.A.; Hershman, S.H.; Tobert, D.G.; Schoenfeld, A.J.; Bono, C.M.; Schwab, J.H. Predicting prolonged opioid prescriptions in opioid-naive lumbar spine surgery patients. Spine J. 2020, 20, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Ugiliweneza, B.; Aljuboori, Z.; Boakkye, M. Health care utilization and overall costs based on opioid dependence in patients undergoing surgery for degenerative spondylolisthesis. Neurosurg. Focus 2018, 44, E14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, R. Pharmacological management of low back pain. Drugs 2010, 70, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorio, M.P.; Beall, D.P.; Calodney, A.K.; Lewandrowski, K.-U.; Block, J.E.; Mekhail, N. Defining the Patient with Lumbar Discogenic Pain: Real-World Implications for Diagnosis and Effective Clinical Management. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorio, M.P.; Tate, J.L.; Myers, T.J.; Block, J.E.; Beall, D.P. Perspective on Intradiscal Therapies for Lumbar Discogenic Pain: State of the Science, Knowledge Gaps, and Imperatives for Clinical Adoption. J. Pain Res. 2024, 17, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gornet, M.G.; Peacock, J.; Ryken, T.; Schranck, F.W.; Eastlack, R.K.; Lotz, J.C. Establishing a Gold Standard for Noninvasive Identification of Painful Lumbar Discs: Prospective Comparison of Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy vs Low-Pressure Provocation Discography. Int. J. Spine Surg. 2024, 18, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braunstein, J.; Hipp, J.A.; Browning, R.; Grieco, T.F.; Reitman, C.A. Analysis of translation and angular motion in loaded and unloaded positions in the lumbar spine. N. Am. Spine Soc. J. 2020, 4, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatprem, T.; Puntumetakul, R.; Kanpittaya, J.; Selfe, J.; Yeowell, G. A diagnostic tool for people with lumbar instability: A criterion-related validity study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasai, Y.; Morishita, K.; Kawakita, E.; Kondo, T.; Uchida, A. A New Evaluation Method for Lumbar Spinal Instability: Passive Lumbar Extension Test. Phys. Ther. 2006, 86, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, D.; Grider, J.; Strand, N.; Hagedorn, J.M.; Falowski, S.; Lam, C.M.; Francio, V.T.; Beall, D.P.; Tomycz, N.D.; Davanzo, J.R.; et al. The American Society of Pain and Neuroscience (ASPN) Evidence-Based Clinical Guideline of Interventional Treatments for Low Back Pain. J. Pain Res. 2022, 15, 3729–3832. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hedman, T.; Rogers, A.; Beall, D. A Self-Polymerizing Mesh of Nano-Tethers for the Mechanical Constraint of Degraded Intervertebral Discs—A Review of 25 Years of Pre-Clinical and Early Clinical Research. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060535
Hedman T, Rogers A, Beall D. A Self-Polymerizing Mesh of Nano-Tethers for the Mechanical Constraint of Degraded Intervertebral Discs—A Review of 25 Years of Pre-Clinical and Early Clinical Research. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(6):535. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060535
Chicago/Turabian StyleHedman, Thomas, Adam Rogers, and Douglas Beall. 2024. "A Self-Polymerizing Mesh of Nano-Tethers for the Mechanical Constraint of Degraded Intervertebral Discs—A Review of 25 Years of Pre-Clinical and Early Clinical Research" Bioengineering 11, no. 6: 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060535
APA StyleHedman, T., Rogers, A., & Beall, D. (2024). A Self-Polymerizing Mesh of Nano-Tethers for the Mechanical Constraint of Degraded Intervertebral Discs—A Review of 25 Years of Pre-Clinical and Early Clinical Research. Bioengineering, 11(6), 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060535








