Flow Diverter Performance Comparison of Different Wire Materials for Effective Intracranial Aneurysm Treatment
Abstract
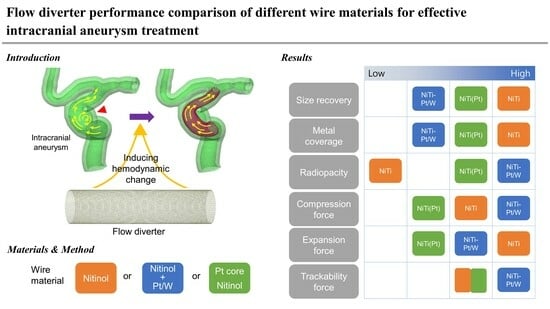
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Flow Diverter Preparation
2.2. Flow Diverter Size Variation
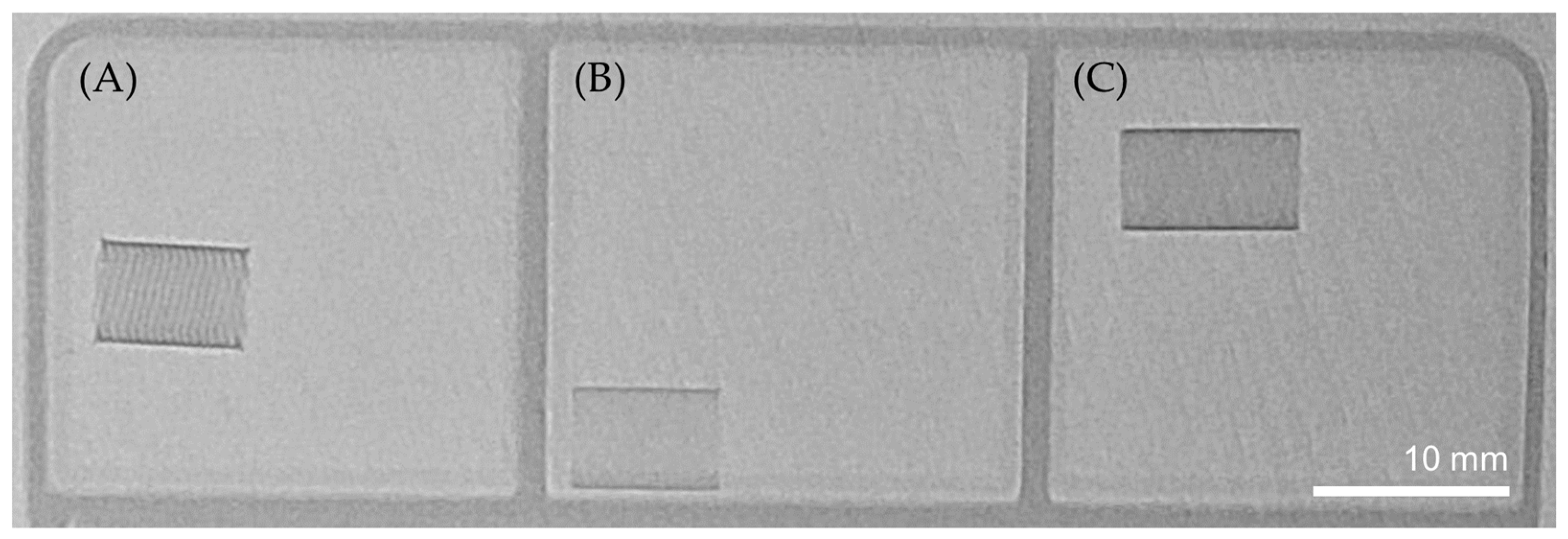
2.3. Radiopacity
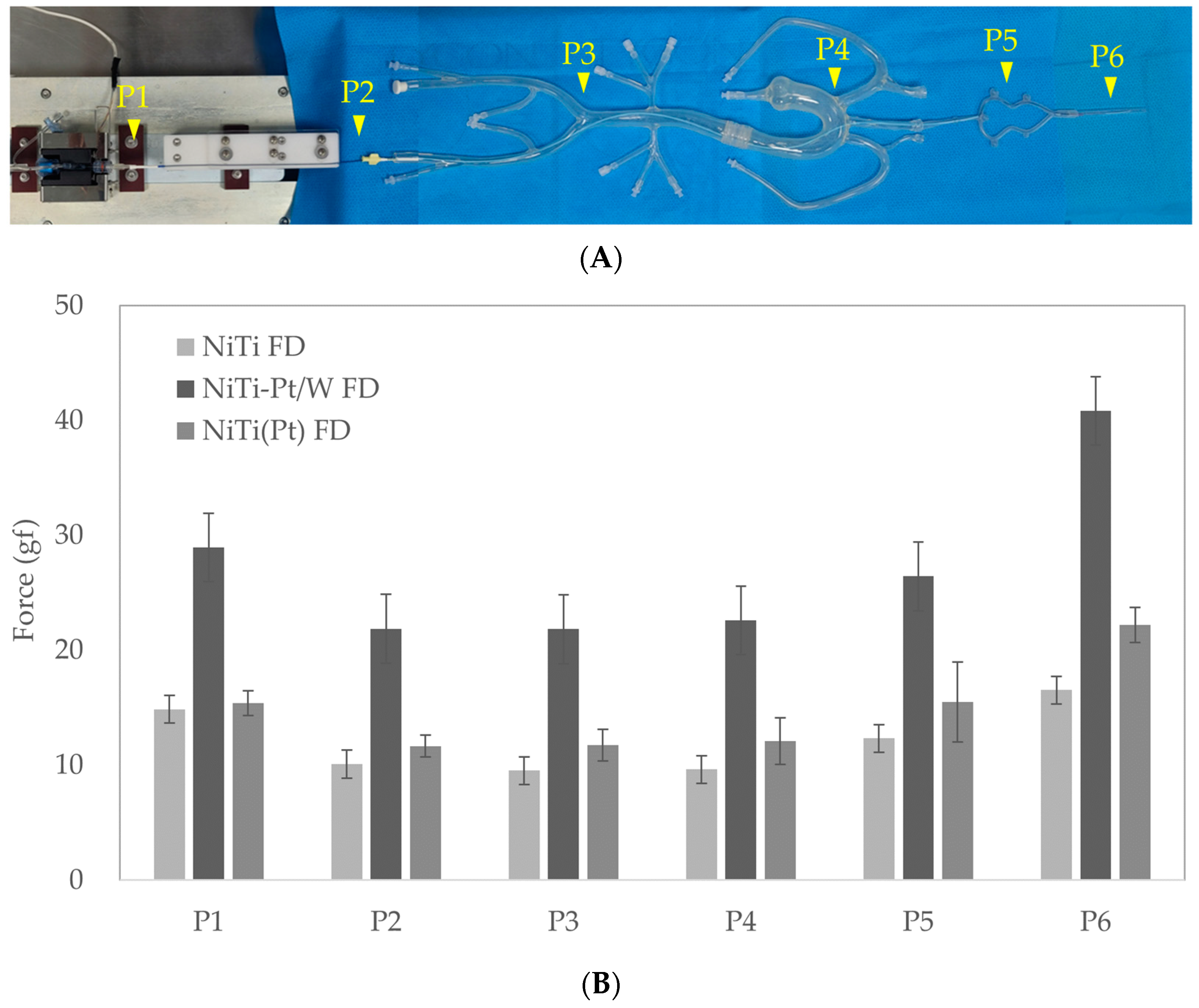
2.4. Radial force
2.5. Trackability and Deployment Force
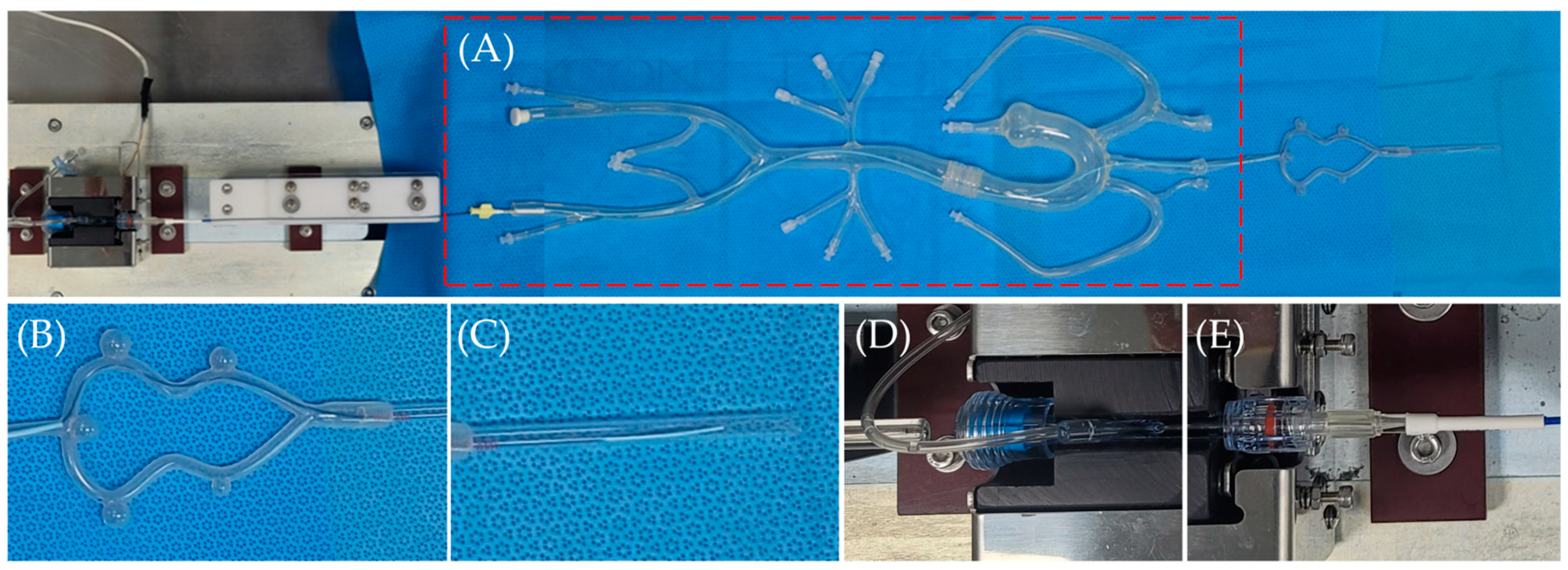
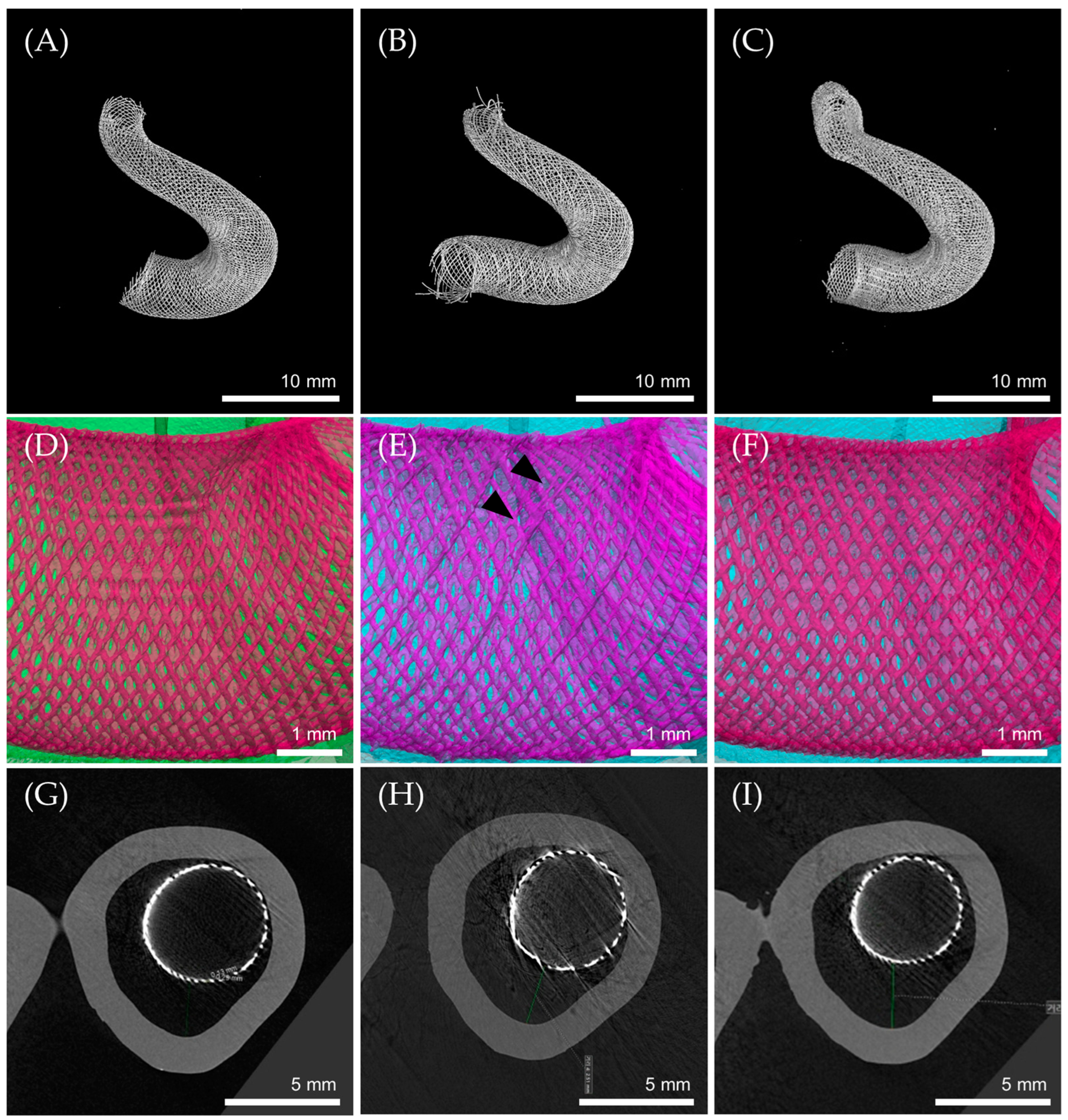
2.6. Flow Diverter Deployment in a 3D-Printed ICA Aneurysm Model
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results & Discussion
3.1. Flow Diverter Stent Size
3.1.1. Diameter Change before and after Delivery Loading
3.1.2. Cell Area Change before and after Delivery Loading
3.2. Radiopacity
3.3. Radial Force
3.4. Trackability and Deployment Force
3.5. Flow Diverter Deployment in 3D Printed ICA Aneurysm Model
3.6. Limitations and Future Work
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jakubowski, J.; Kendall, B. Coincidental aneurysms with tumours of pituitary origin. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1978, 41, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K. Pathology of intracerebral hemorrhage. Zent. Neurochir. 1977, 38, 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kassell, N.F.; Torner, J.C.; Jane, J.A.; Haley, E.C., Jr.; Adams, H.P. The International Cooperative Study on the Timing of Aneurysm Surgery. Part 2: Surgical results. J. Neurosurg. 1990, 73, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, D.B., Jr.; Joseph, P.B. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: Epidemiology, natural history, management options, and familial screening. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bor, A.S.; Rinkel, G.J.; van Norden, J.; Wermer, M.J. Long-term, serial screening for intracranial aneurysms in individuals with a family history of aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage: A cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.Y.; Bin Shi, H.; Miyachi, S.; Hwang, S.M.; Sheen, J.J.; Song, Y.S.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, D.H.; Suh, D.C. Development of New Endovascular Devices for Aneurysm Treatment. J. Stroke 2018, 20, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmi, G.; Viñuela, F.; Dion, J.; Duckwiler, G. Electrothrombosis of saccular aneurysms via endovascular approach. Part 2: Preliminary clinical experience. J. Neurosurg. 1991, 75, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmi, G.; Viñuela, F.; Duckwiler, G.; Dion, J.; Lylyk, P.; Berenstein, A. Endovascular treatment of posterior circulation aneurysms by electrothrombosis using electrically detachable coils. J. Neurosurg. 1992, 77, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmi, G.; Viñuela, F.; Sepetka, I.; Macellari, V. Electrothrombosis of saccular aneurysms via endovascular approach. Part 1: Electrochemical basis, technique, and experimental results. J. Neurosurg. 1991, 75, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.S.; Carroll, C.P.; Elghareeb, M.; Hoh, B.L.; Kim, B.T. The Evolution of Flow-Diverting Stents for Cerebral Aneurysms; Historical Review, Modern Application, Complications, and Future Direction. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2020, 63, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, D.L.; Alleyne, C. Natural history of giant intracranial aneurysms and indications for intervention. Clin. Neurosurg. 1995, 42, 214–244. [Google Scholar]
- Gruber, A.; Killer, M.; Bavinzski, G.; Richling, B. Clinical and angiographic results of endosaccular coiling treatment of giant and very large intracranial aneurysms: A 7-year, single-center experience. Neurosurgery 1999, 45, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluzewski, M.; Menovsky, T.; van Rooij, W.J.; Wijnalda, D. Coiling of very large or giant cerebral aneurysms: Long-term clinical and serial angiographic results. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2003, 24, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeeb, N.; Griessenauer, C.J.; Shallwani, H.; Shakir, H.; Foreman, P.M.; Moore, J.M.; Dmytriw, A.A.; Gupta, R.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Levy, E.I.; et al. Pipeline Embolization Device in treatment of 50 unruptured large and giant aneurysms. World Neurosurg. 2017, 105, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiebers, D.O. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: Natural history, clinical outcome, and risks of surgical and endovascular treatment. Lancet 2003, 362, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiebers, D.O. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: Natural history and clinical management. Update on the international study of unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2006, 16, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, J.; Guilbert, F.; Weill, A.; Georganos, S.A.; Juravsky, L.; Lambert, A.; Lamoureux, J.; Chagnon, M.; Roy, D. Long-term angiographic recurrences after selective endovascular treatment of aneurysms with detachable coils. Stroke 2003, 34, 1398–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campi, A.; Ramzi, N.; Molyneux, A.J.; Summers, P.E.; Kerr, R.S.C.; Sneade, M.; Yarnold, J.A.; Rischmiller, J.; Byrne, J.V. Retreatment of ruptured cerebral aneurysms in patients randomized by coiling or clipping in the International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT). Stroke 2007, 38, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molyneux, A.J. Indications for treatment of cerebral aneurysms from an endovascular perspective: The creation of an evidence base for interventional techniques. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2005, 16, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molyneux, A.J.; Kerr, R.S.; Birks, J.; Ramzi, N.; Yarnold, J.; Sneade, M.; Rischmiller, J. Risk of recurrent subarachnoid haemorrhage death, or dependence and standardized mortality ratios after clipping or coiling of an intracranial aneurysm in the International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT): Long-term follow-up. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc, R.; Weill, A.; Piotin, M.; Ross, I.B.; Moret, J. Delayed stroke secondary to increasing mass effect after endovascular treatment of a giant aneurysm by parent vessel occlusion. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2001, 22, 1841–1843. Available online: https://www.ajnr.org/content/22/10/1841 (accessed on 20 September 2023). [PubMed]
- Brisman, J.L.; Song, J.K.; Newell, D.W. Cerebral aneurysms. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molyneux, A.J.; Kerr, R.S.; Yu, L.M.; Clarke, M.; Sneade, M.; Yarnold, J.A.; Sandercock, P. International subarachnoid aneurysm trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: A randomised comparison of effects on survival, dependency, seizures, rebleeding, subgroups, and aneurysm occlusion. Lancet 2005, 366, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyik, S.; Ertugrul, O.; Yavuz, K.; Geyik, P.; Saatci, I.; Cekirge, H.S. Comparison of bioactive coils and bare platinum coils for treatment of intracranial aneurysms: A matched-pair analysis. J. Neurosurg. 2010, 112, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linfante, I.; DeLeo, M.J.; Gounis, M.J.; Brooks, C.S.; Wakhloo, A.K. Cerecyte versus platinum coils in the treatment of intracranial aneurysms: Packing attenuation and clinical and angiographic midterm results. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 1496–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierot, L.; Leclerc, X.; Bonafé, A.; Bracard, S.; French Matrix Registry Investigators. Endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms with matrix detachable coils: Midterm anatomic follow-up from a prospective multicenter registry. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 29, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, M.; Becske, T.; Sahlein, D.; Babb, J.; Nelson, P.K. Stent-supported aneurysm coiling: A literature survey of treatment and follow-up. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorella, D.; Kelly, M.E.; Albuquerque, F.C.; Nelson, P.K. Curative reconstruction of a giant midbasilar trunk aneurysm with the pipeline embolization device. Neurosurgery 2009, 64, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becske, T.; Kallmes, D.F.; Saatci, I.; McDougall, C.G.; Szikora, I.; Lanzino, G.; Moran, C.J.; Woo, H.H.; Lopes, D.K.; Berez, A.L.; et al. Pipeline for Uncoilable or Failed Aneurysms: Results from a Multicenter Clinical Trial. Radiology 2013, 267, 858–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byung Moon, K.; Keun Young, P.; Jae Whan, L.; Joonho, C.; Dong Joon, K.; Dong Ik, K. A Newly-Developed Flow Diverter (FloWise) for Internal Carotid Artery Aneurysm: Results of a Pilot Clinical Study. Korean J. Radiol. 2019, 20, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Summary of Safety and Effectiveness Data (SSED). Pipeline™ Flex Embolization Device. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf10/P100018S015B.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2024).
- FDA. Summary of Safety and Effectiveness Data (SSED). Surpass Streamline Flow Diverter. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf17/P170024B.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2024).
- José, M.P.; Antonio, M.; Jorge, O.; Claudio, R.F.; Pedro, V.; Eva, G.D. Treatment of Intracranial Aneurysms Using the New Silk Vista Flow Diverter: Safety Outcomes at Short-Term Follow-Up. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 713389. [Google Scholar]
- FDA. Summary of Safety and Effectiveness Data (SSED). Flow Re-Direction Endoluminal Device (FRED®) System. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf18/P180027B.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2024).
- Pierot, L.; Wakhloo, A.K. Endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms: Current status. Stroke 2013, 44, 2046–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubicz, B.; Collignon, L.; Raphaeli, G.; Pruvo, J.P.; Bruneau, M.; De Witte, O.; Leclerc, X. Flow-diverter stent for the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms: A prospective study in 29 patients with 34 aneurysms. Stroke 2010, 41, 2247–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühn, A.L.; Wakhloo, A.K.; Gounis, M.J.; Kan, P.; Rodrigues, K.d.M.; Lozano, J.D.; Marosfoi, M.G.; Perras, M.; Brooks, C.; Howk, M.C.; et al. Use of self-expanding stents for better intracranial flow diverter wall apposition. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2017, 23, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeremy, E.S.; Richard, G. Engineering characteristics of drawn filled nitinol tube. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Shape Memory and Superelastic Technologies; SMST-2003 edition; Alan, R.P., Ed.; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2004; pp. 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Byung Moon, K.; Dong Joon, K.; Dong Ik, K. A New Flow-Diverter (the FloWise): In-Vivo Evaluation in an Elastase-Induced Rabbit Aneurysm Model. Korean J. Radiol. 2016, 17, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzin, B.; Brosseau, L.; Jamali, S.; Salazkin, I.; Jack, A.; Darsaut, T.E.; Raymond, J. Flow diverters: Inter and intra-rater reliability of porosity and pore density measurements. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2015, 7, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su Hee, C.; Won Il, J.; Ye Eun, J.; Ku Hyun, Y.; Jung Cheol, P.; Deok Hee, L. Bench-top Comparison of Physical Properties of 4 Commercially-Available Self-Expanding Intracranial Stents. Neurointervention 2017, 12, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, M.; Raz, E.; Becske, T.; Nelson, P.K. Variable Porosity of the Pipeline Embolization Device in Straight and Curved Vessels: A Guide for Optimal Deployment Strategy. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, P.F.; Fang, Y.B.; Xu, Y.; Hong, B.; Zhao, W.Y.; Li, Q.; Zhao, R.; Huang, Q.H.; Liu, J.M. A Novel Flow-Diverting Device (Tubridge) for the Treatment of 28 Large or Giant Intracranial Aneurysms: A Single-Center Experience. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 2326–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunghan, K.; Hyeondong, Y.; Ineui, H.; Je Hoon, O.; Yong Bae, K. Computational Study of Hemodynamic Changes Induced by Overlapping and Compacting of Stents and Flow Diverter in Cerebral Aneurysms. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 705841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jun, Y.J.; Hwang, D.K.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, B.M.; Park, K.D. Flow Diverter Performance Comparison of Different Wire Materials for Effective Intracranial Aneurysm Treatment. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010076
Jun YJ, Hwang DK, Lee HS, Kim BM, Park KD. Flow Diverter Performance Comparison of Different Wire Materials for Effective Intracranial Aneurysm Treatment. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(1):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010076
Chicago/Turabian StyleJun, Yeo Jin, Doo Kyung Hwang, Hee Sun Lee, Byung Moon Kim, and Ki Dong Park. 2024. "Flow Diverter Performance Comparison of Different Wire Materials for Effective Intracranial Aneurysm Treatment" Bioengineering 11, no. 1: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010076
APA StyleJun, Y. J., Hwang, D. K., Lee, H. S., Kim, B. M., & Park, K. D. (2024). Flow Diverter Performance Comparison of Different Wire Materials for Effective Intracranial Aneurysm Treatment. Bioengineering, 11(1), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010076