Exploring the Effects of EEG-Based Alpha Neurofeedback on Working Memory Capacity in Healthy Participants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
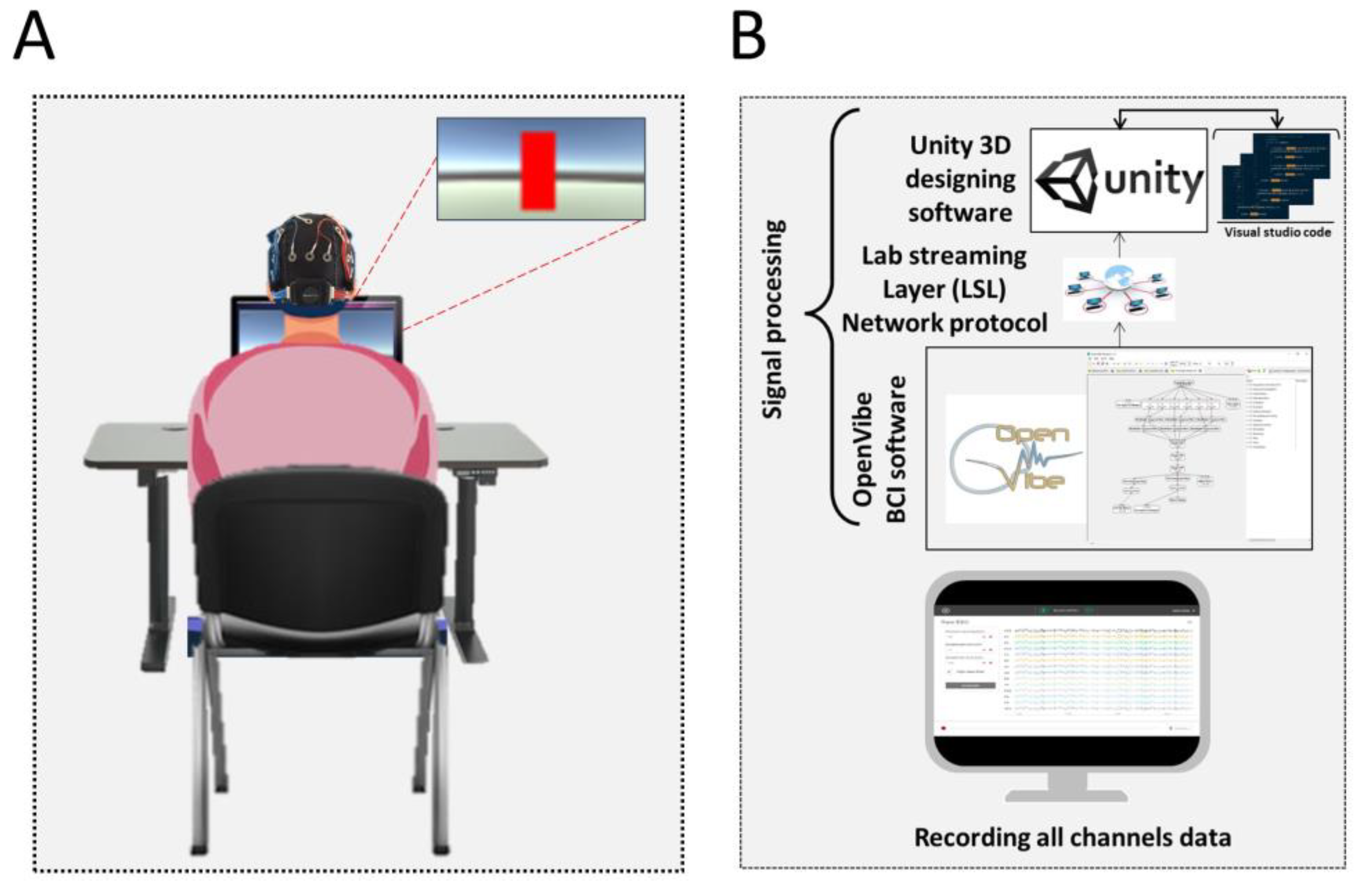
2.2. Neurofeedback Training
2.3. Experimental Protocol
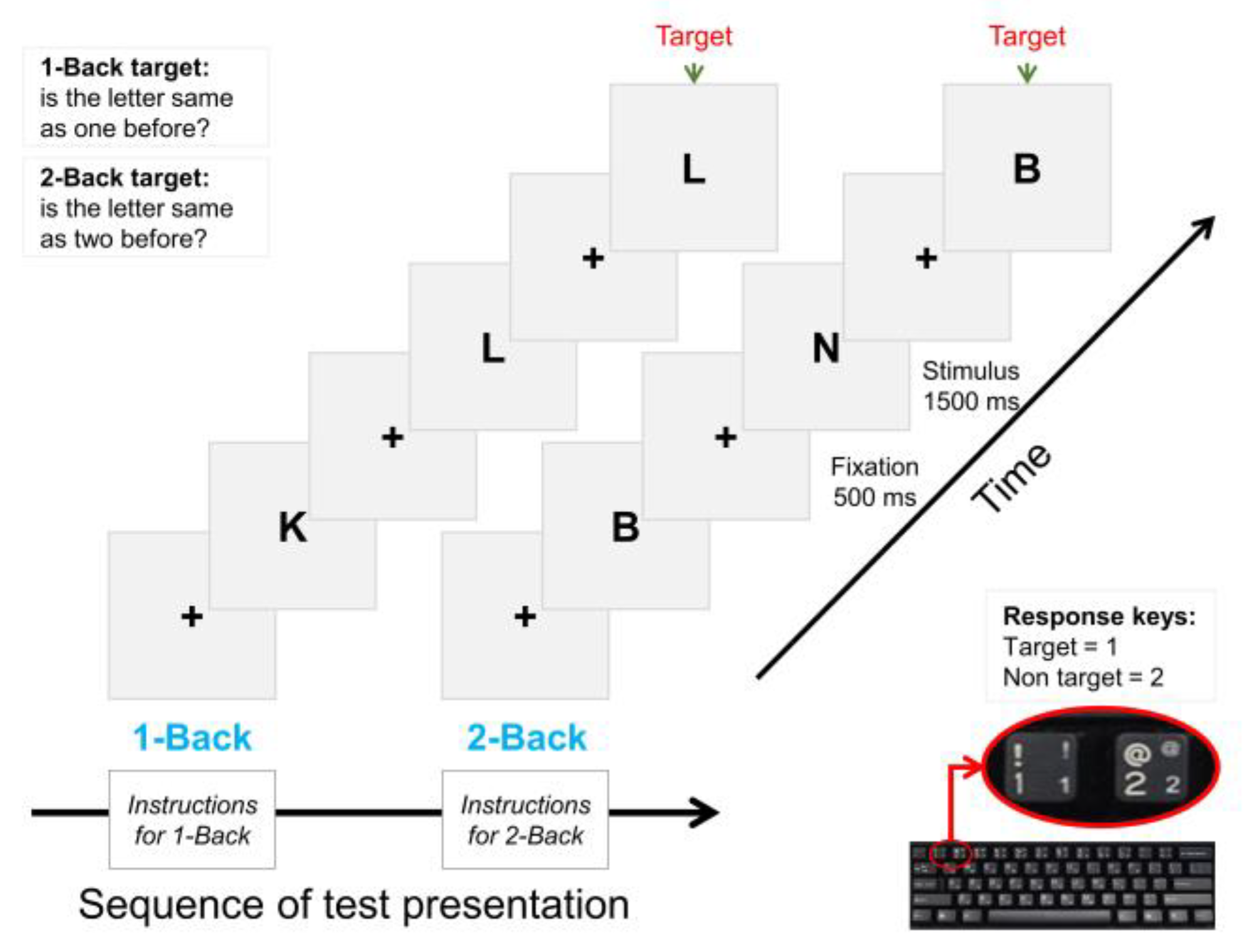
2.4. Task-Based Data
2.4.1. EEG Recordings and Processing
2.4.2. Time–Frequency Decomposition
2.4.3. Power Computation
2.4.4. Functional Connectivity Measurement
2.5. EEG Data Collected during the NFT Sessions
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
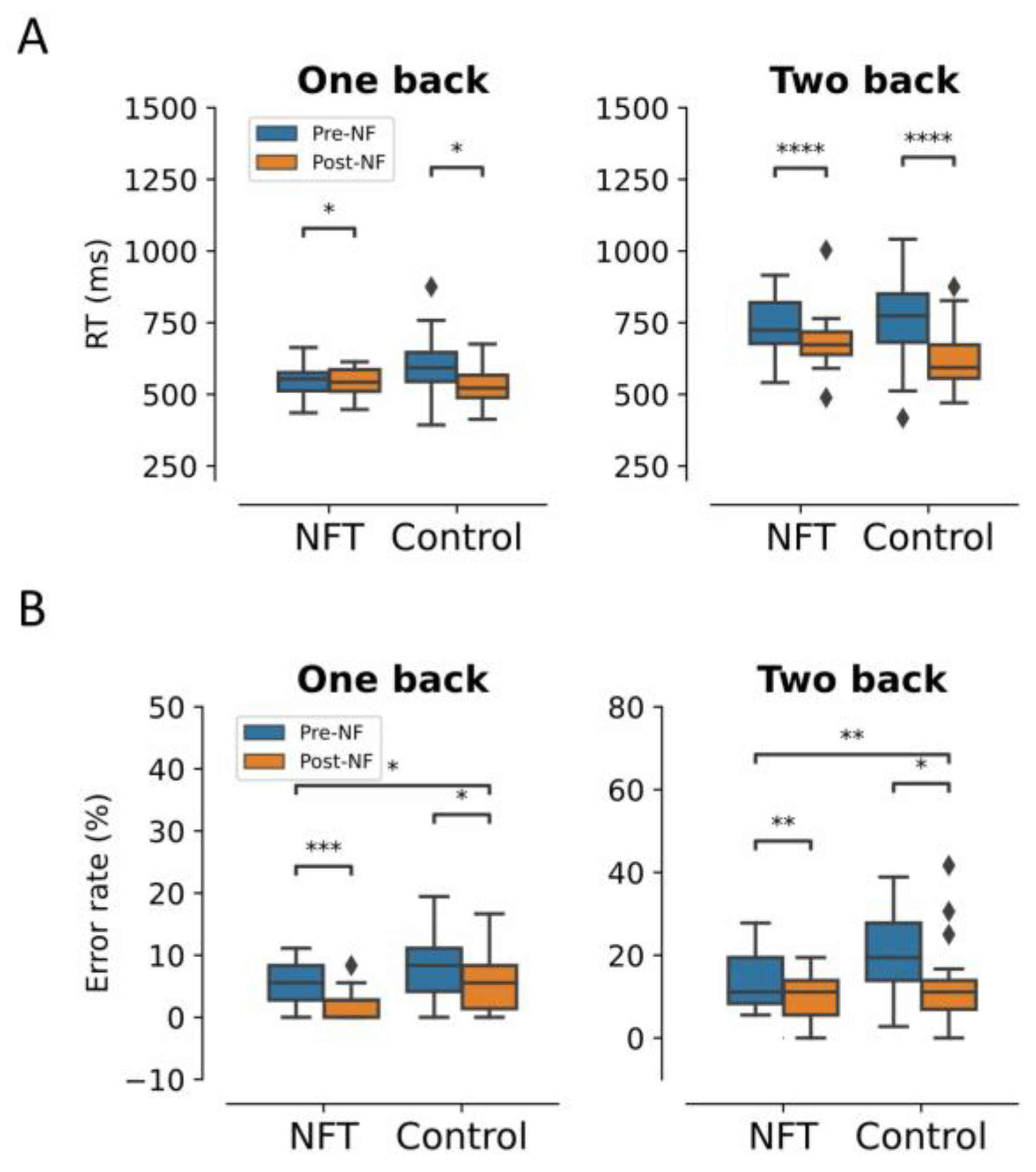
3.1. Behavioural Results (Response Time and Error Rate)
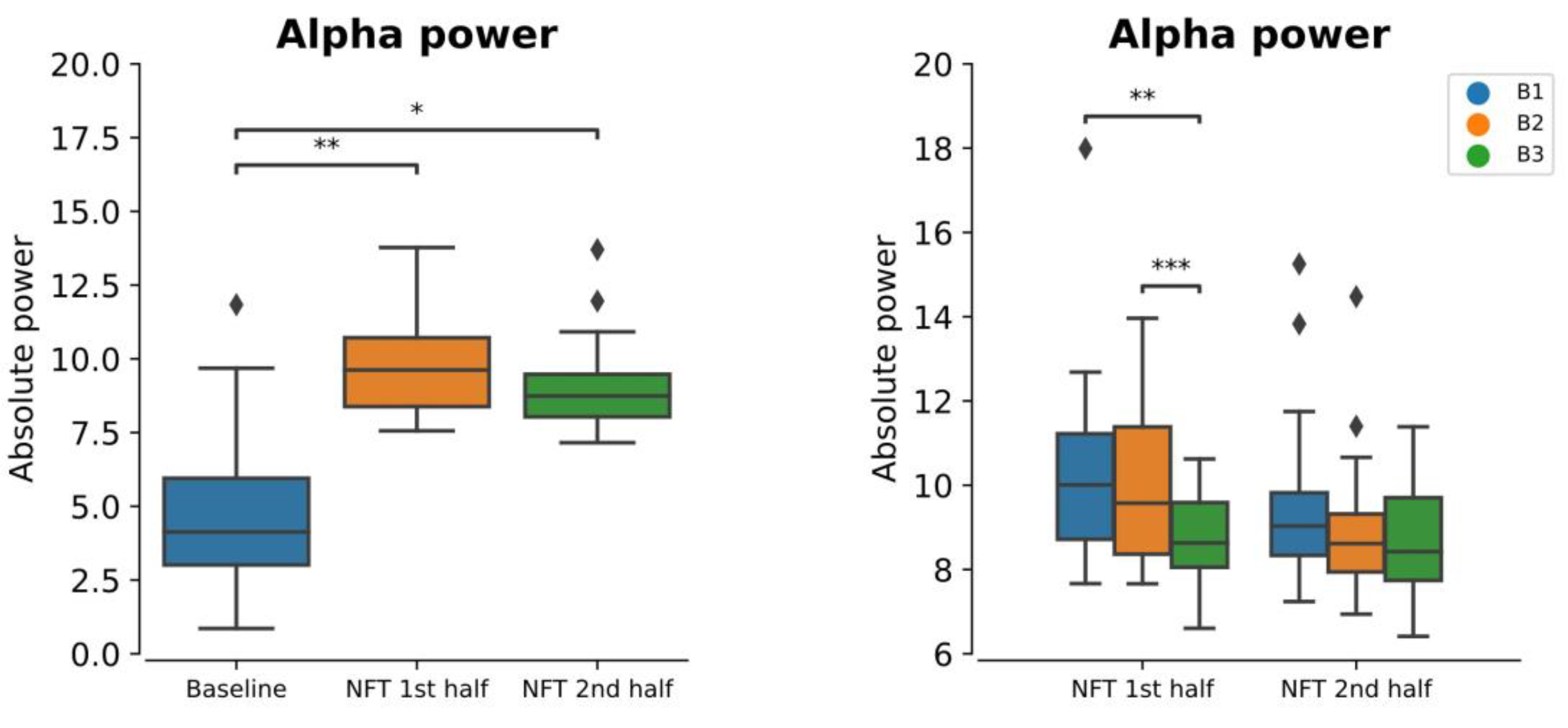
3.2. Within-Session Alpha Power
3.3. EEG Post-Stimulus Power
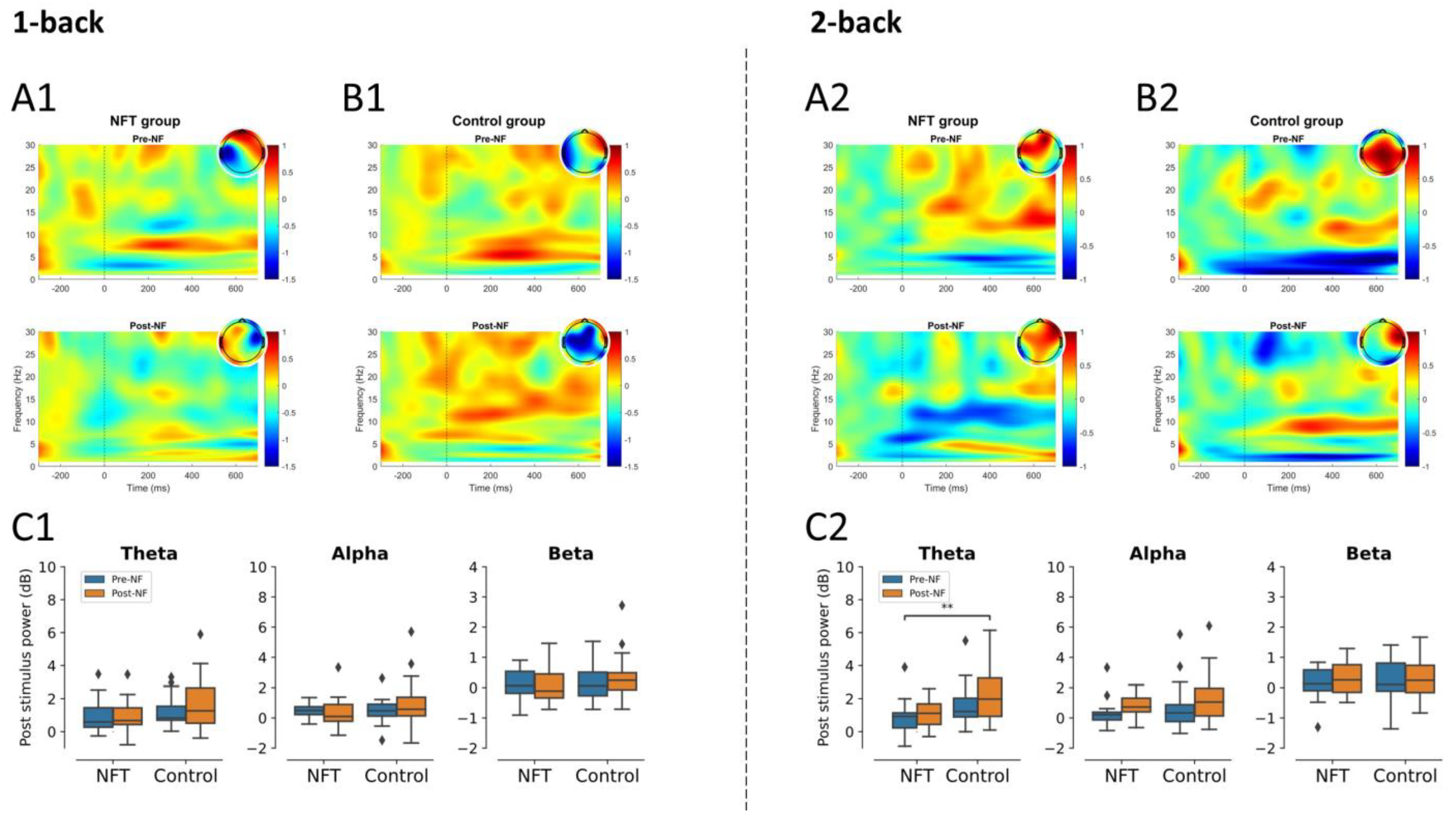
3.3.1. Frontal Lobe
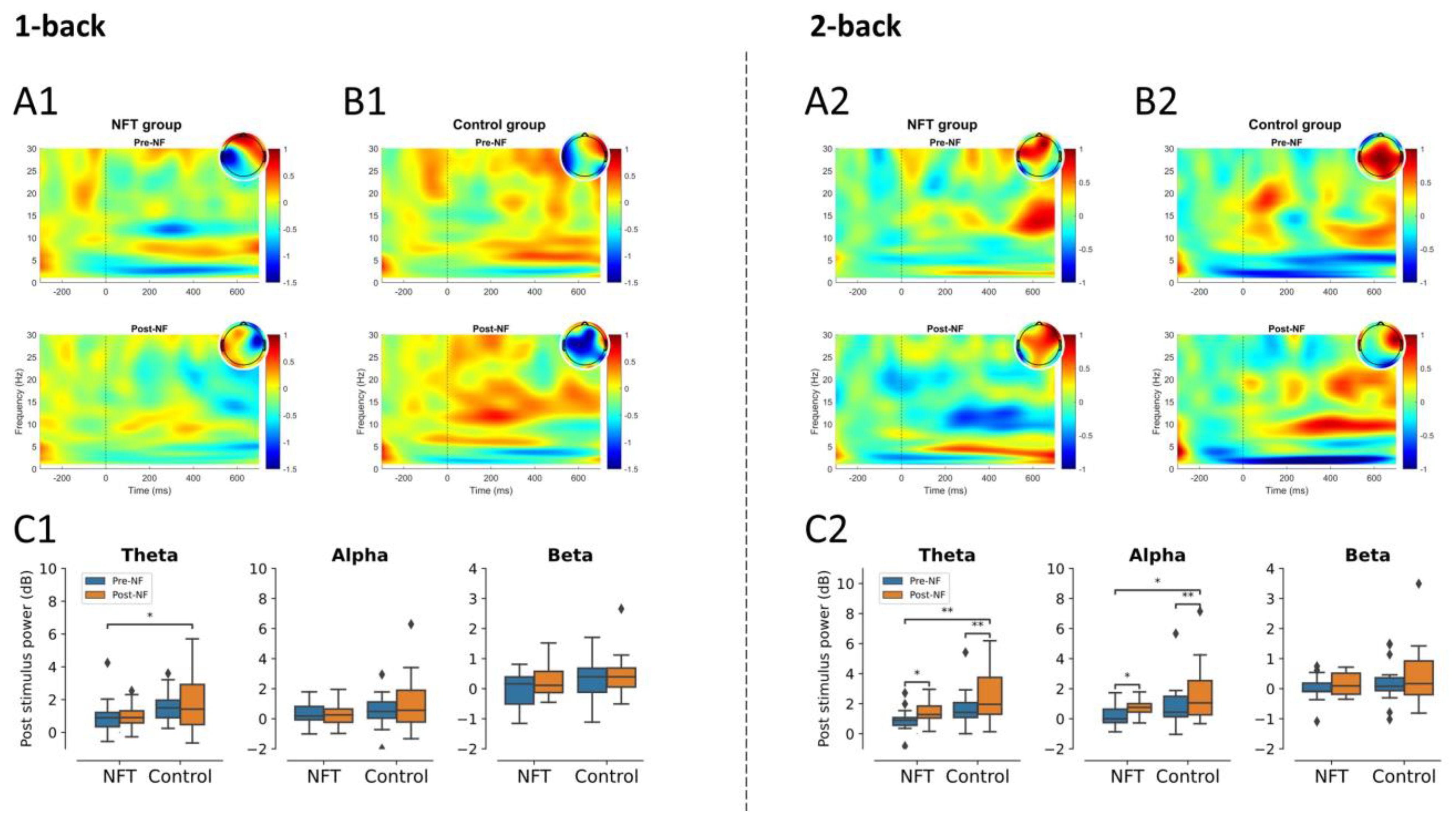
3.3.2. Fronto-Central Lobe
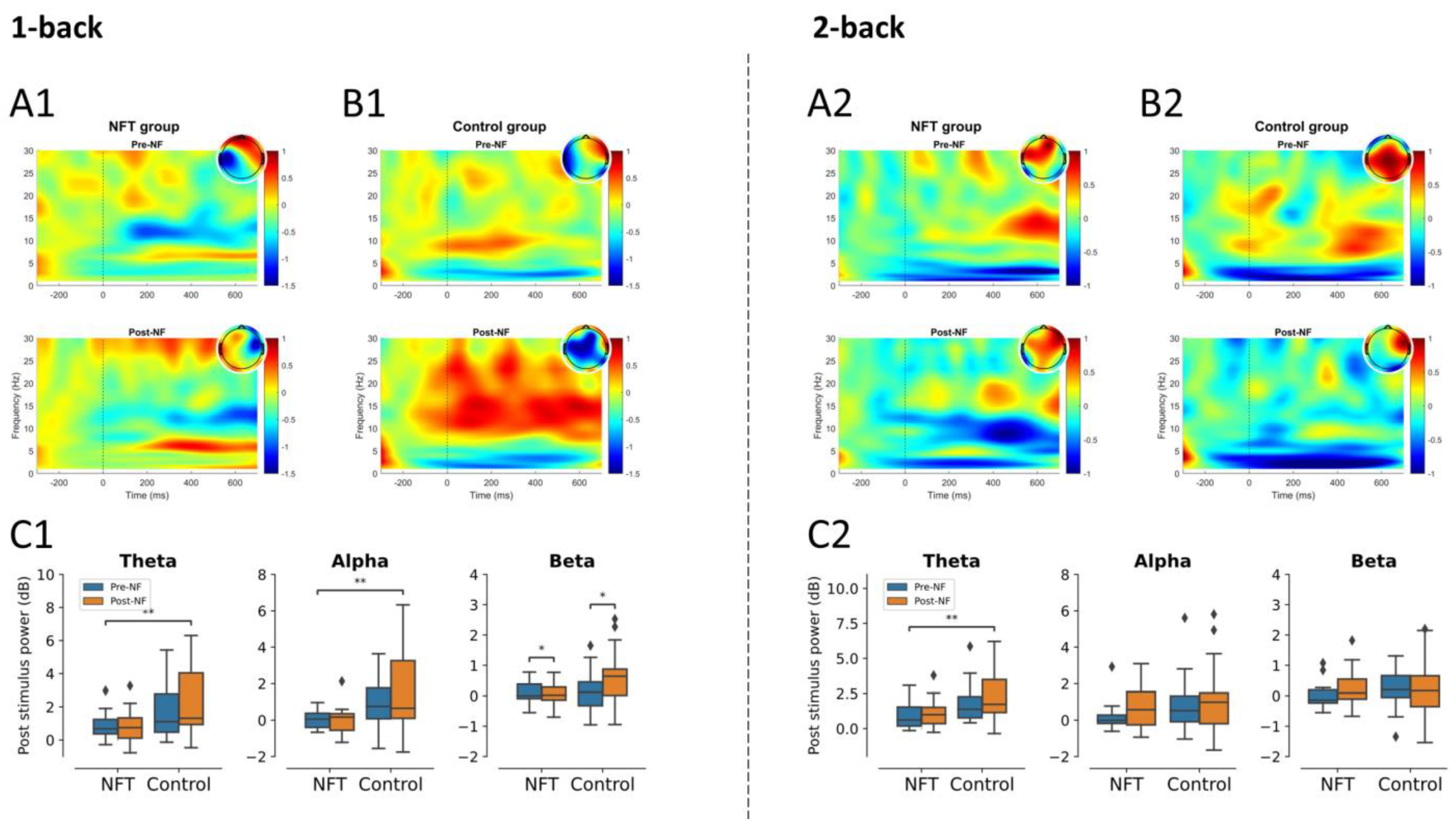
3.3.3. Parietal Lobe
3.3.4. Occipital Lobe
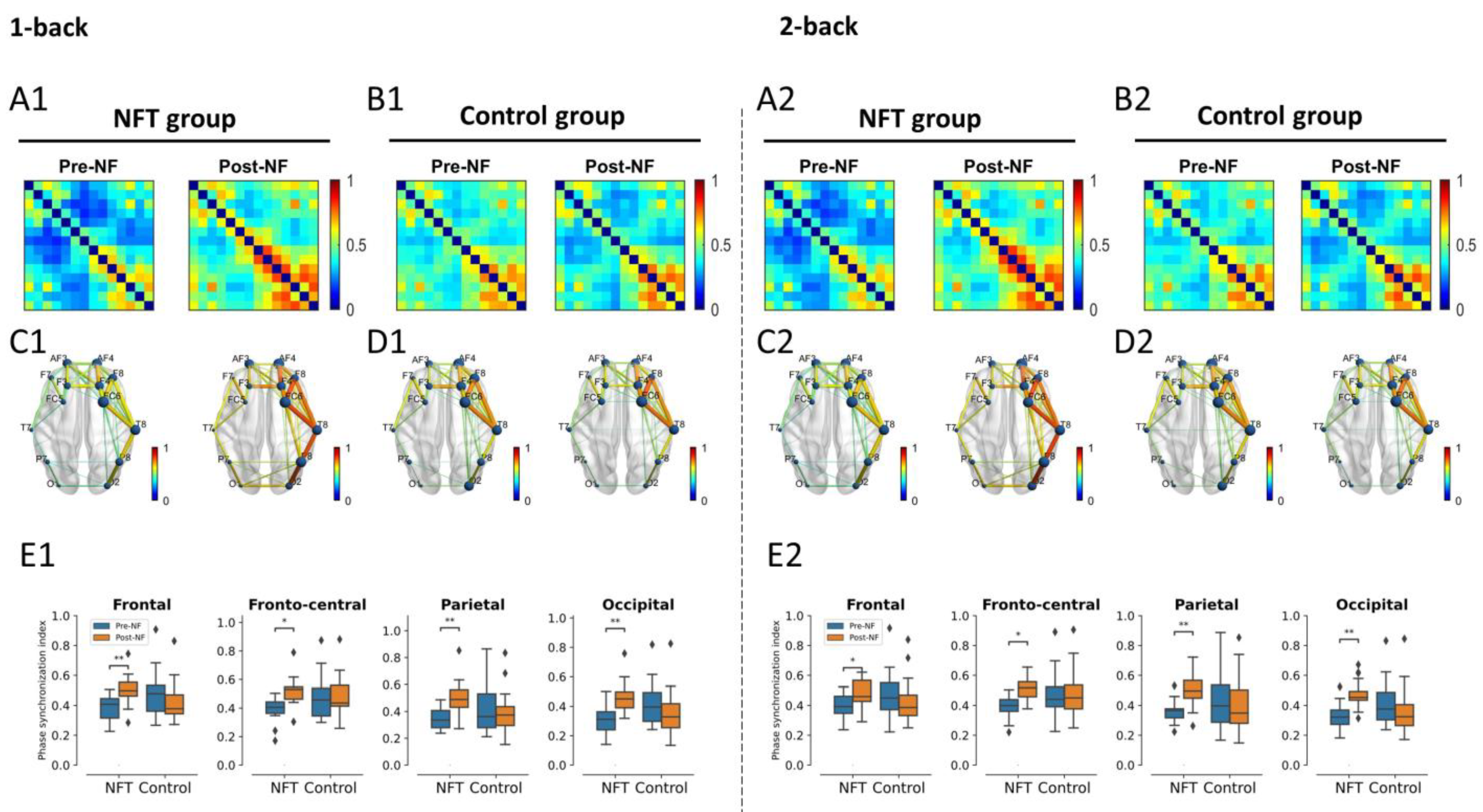
3.4. EEG Functional Connectivity
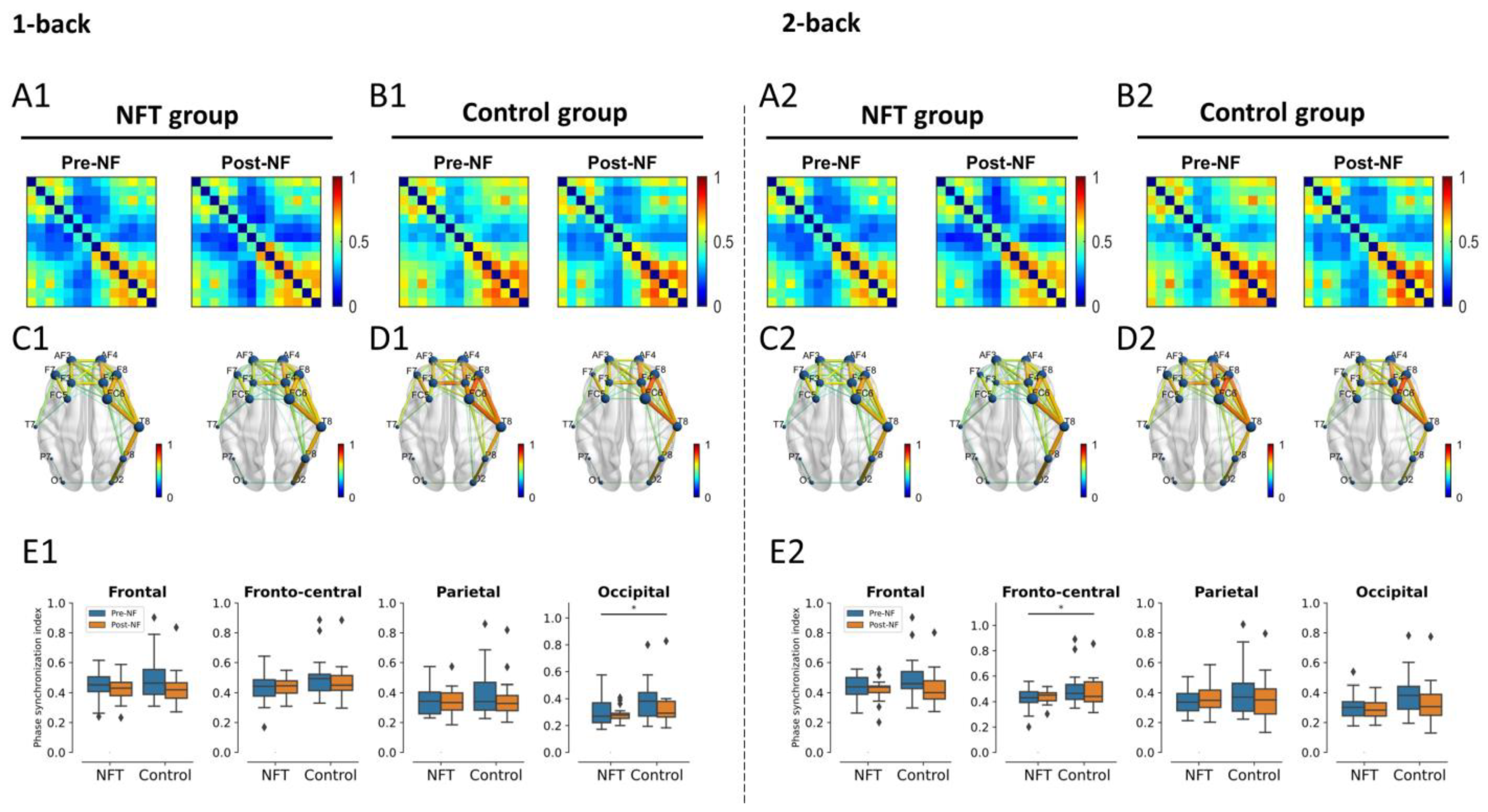
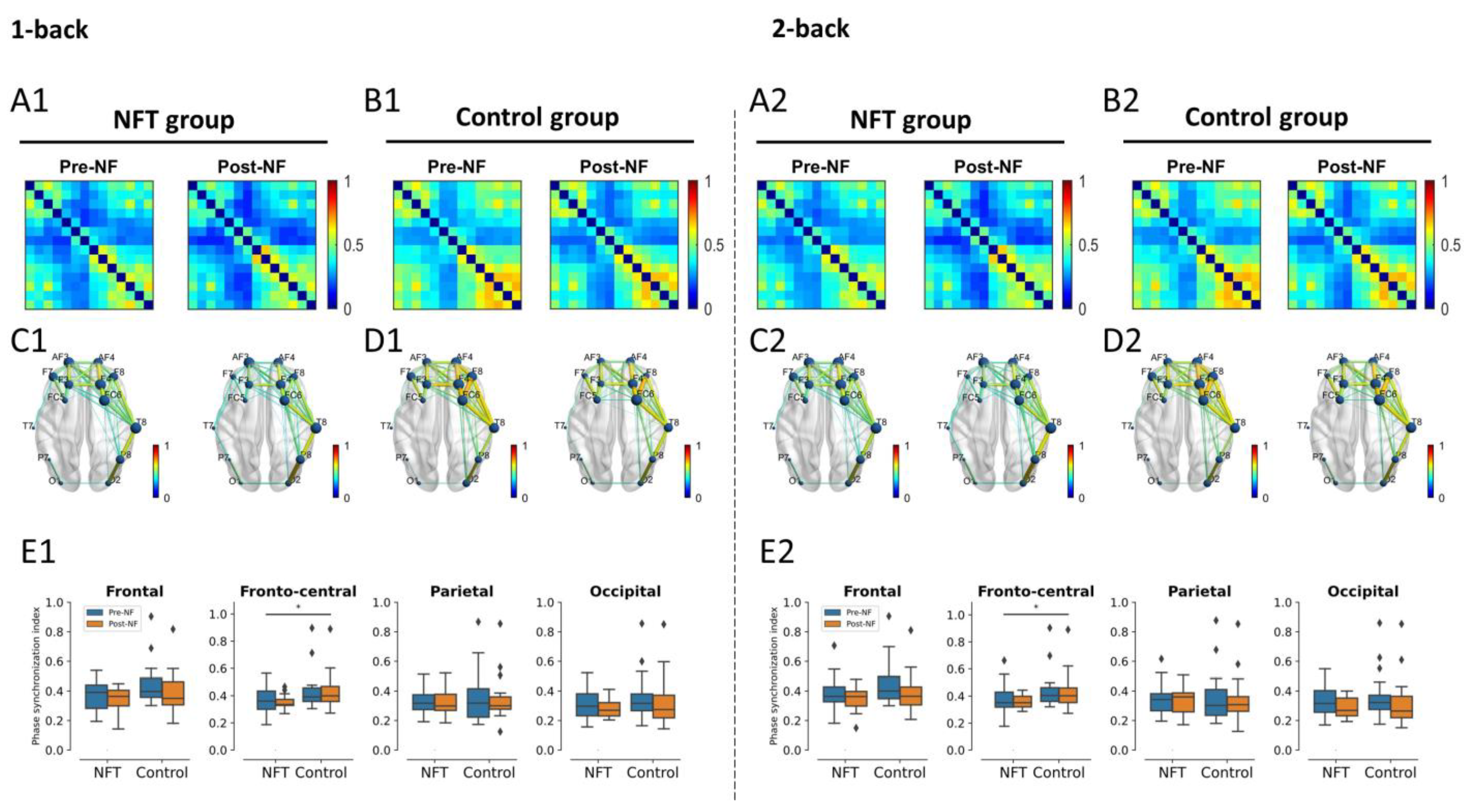
3.4.1. Theta Band
3.4.2. Alpha Band
3.4.3. Beta Band
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sterman, M.B.; Howe, R.C.; Macdonald, L.R. Facilitation of spindle-burst sleep by conditioning of electroencephalographic activity while awake. Science 1970, 167, 1146–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropotov, J.D. Quantitative EEG, Event-Related Potentials and Neurotherapy; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gruzelier, J.H. EEG-neurofeedback for optimising performance. III: A review of methodological and theoretical considerations. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 44, 159–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazanova, O.M.; Aftanas, L.I. Individual EEG alpha activity analysis for enhancement neurofeedback efficiency: Two case studies. J. Neurother. 2010, 14, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palva, S.; Palva, J.M. New vistas for alpha-frequency band oscillations. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimesch, W. Memory processes, brain oscillations and EEG synchronization. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 1996, 24, 61–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimesch, W.; Doppelmayr, M.; Hanslmayr, S. Upper alpha ERD and absolute power: Their meaning for memory performance. Prog. Brain Res. 2006, 159, 151–165. [Google Scholar]
- Klimesch, W. EEG alpha and theta oscillations reflect cognitive and memory performance: A review and analysis. Brain Res. Rev. 1999, 29, 169–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.R.; Hsieh, S. Neurofeedback training improves attention and working memory performance. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2013, 124, 2406–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoefel, B.; Huster, R.J.; Herrmann, C.S. Neurofeedback training of the upper alpha frequency band in EEG improves cognitive performance. Neuroimage 2011, 54, 1427–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, W.; Rodrigues, J.P.; Ma, J.; Qu, X.; Wan, F.; Mak, P.I.; Mak, P.U.; Vai, M.I.; Rosa, A. Individual alpha neurofeedback training effect on short term memory. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2012, 86, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kober, S.E.; Schweiger, D.; Witte, M.; Reichert, J.L.; Grieshofer, P.; Neuper, C.; Wood, G. Specific effects of EEG based neurofeedback training on memory functions in post-stroke victims. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2015, 12, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavy, Y.; Dwolatzky, T.; Kaplan, Z.; Guez, J.; Todder, D. Neurofeedback improves memory and peak alpha frequency in individuals with mild cognitive impairment. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2019, 44, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsueh, J.-J.; Chen, T.-S.; Shaw, F.-Z. Neurofeedback training on memory enhancement in humans. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), Hsinchu, Taiwan, 28–30 November 2012; pp. 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kober, S.E.; Witte, M.; Stangl, M.; Väljamäe, A.; Neuper, C.; Wood, G. Shutting down sensorimotor interference unblocks the networks for stimulus processing: An SMR neurofeedback training study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ros, T.; Enriquez-Geppert, S.; Zotev, V.; Young, K.D.; Wood, G.; Whitfield-Gabrieli, S.; Wan, F.; Vuilleumier, P.; Vialatte, F.; Van De Ville, D.; et al. Consensus on the reporting and experimental design of clinical and cognitive-behavioural neurofeedback studies (CRED-nf checklist). Brain 2020, 143, 1674–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, R.; Nisar, H.; Voon, Y.V. Changes in Spectral Power and Functional Connectivity of Response-Conflict Task after Neurofeedback Training. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 139444–139459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Cox, S.R.; Adams, M.J.; Howard, D.M.; Lawrie, S.M.; Ritchie, S.J.; Bastin, M.E.; Deary, I.J.; McIntosh, A.M.; Whalley, H.C. Resting-state connectivity and its association with cognitive performance, educational attainment, and household income in the UK Biobank. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2018, 3, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, M.; Kazui, H.; Tanaka, T.; Ishii, R.; Canuet, L.; Pascual-Marqui, R.D.; Aoki, Y.; Ikeda, S.; Kanemoto, H.; Yoshiyama, K.; et al. Functional connectivity assessed by resting state EEG correlates with cognitive decline of Alzheimer’s disease--An eLORETA study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, T.; Théberge, J.; Frewen, P.A.; Kluetsch, R.; Densmore, M.; Calhoun, V.D.; Lanius, R.A. Mind over chatter: Plastic up-regulation of the fMRI salience network directly after EEG neurofeedback. Neuroimage 2013, 65, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munivenkatappa, A.; Rajeswaran, J.; Indira Devi, B.; Bennet, N.; Upadhyay, N. EEG Neurofeedback therapy: Can it attenuate brain changes in TBI? NeuroRehabilitation 2014, 35, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datko, M.C. Functional and Structural Connectivity, and the Effects of Neurofeedback Training, in Imitation-Related Brain Networks in Autism. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, San Diego, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka, Y.; Osaka, N.; Osaka, M. Functional asymmetry of superior parietal lobule for working memory in the elderly. Neuroreport 2008, 19, 1355–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, M.; Manenti, R.; Ferrari, C.; Cotelli, M. Better together: Left and right hemisphere engagement to reduce age-related memory loss. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 293, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirzadi, S.; Einalou, Z.; Dadgostar, M. Investigation of Functional Connectivity During Working Memory Task and Hemispheric Lateralization in Left-and Right-Handers Measured by fNIRS. Optik 2020, 221, 165347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielson, K.A.; Langenecker, S.A.; Garavan, H. Differences in the functional neuroanatomy of inhibitory control across the adult life span. Psychol. Aging 2002, 17, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.C.; Zacks, R.T.; Slade, J.M. Brain activation during interference resolution in young and older adults: An fMRI study. Neuroimage 2010, 50, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuter-Lorenz, P.A.; Jonides, J.; Smith, E.E.; Hartley, A.; Miller, A.; Marshuetz, C.; Koeppe, R.A. Age differences in the frontal lateralization of verbal and spatial working memory revealed by PET. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, M.; Magalhães, R.; Marques, P.; Castanho, T.C.; Portugal-Nunes, C.; Soares, J.M.; Almeida, A.; Santos, N.C.; Sousa, N.; Leite-Almeida, H. Functional hemispheric (A) symmetries in the aged brain—Relevance for working memory. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renard, Y.; Lotte, F.; Gibert, G.; Congedo, M.; Maby, E.; Delannoy, V.; Bertrand, O.; Lécuyer, A. Openvibe: An open-source software platform to design, test, and use brain--computer interfaces in real and virtual environments. Presence teleoperators virtual Environ. 2010, 19, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naas, A.; Rodrigues, J.; Knirsch, J.-P.; Sonderegger, A. Neurofeedback training with a low-priced EEG device leads to faster alpha enhancement but shows no effect on cognitive performance: A single-blind, sham-feedback study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzbani, H.; Marateb, H.R.; Mansourian, M. Neurofeedback: A comprehensive review on system design, methodology and clinical applications. Basic Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 143. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, J.; Portugal, A.M.; Fernandes, L.; Afonso, N.; Pereira, M.; Sousa, N.; Dias, N.S. An alpha and theta intensive and short neurofeedback protocol for healthy aging working-memory training. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, R.; Nisar, H.; Yap, V.V.; Tsai, C.-Y. The Effect of Alpha Neurofeedback Training on Cognitive Performance in Healthy Adults. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, R.; Nisar, H.; Voon, Y.V. The effect of music on human brain; Frequency domain and time series analysis using electroencephalogram. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 45191–45205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.C.; Thropp, J.E. Review of low frame rate effects on human performance. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. A Syst. Humans 2007, 37, 1063–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.L.; Suk, H.J.; Kang, J.H.; Jung, J.M.; Laine, T.H.; Westlin, J. Using Unity 3D to facilitate mobile augmented reality game development. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 6–8 March 2014; pp. 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Nobili, L.; Khatami, R.; Loddenkemper, T.; Cajochen, C.; Dijk, D.-J.; Eriksson, S.H. Circadian rhythm and epilepsy. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 1098–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-Y.; Hsu, S.-H.; Pion-Tonachini, L.; Jung, T.-P. Evaluation of artifact subspace reconstruction for automatic artifact components removal in multi-channel EEG recordings. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 67, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pion-Tonachini, L.; Hsu, S.-H.; Chang, C.-Y.; Jung, T.-P.; Makeig, S. Online automatic artifact rejection using the real-time EEG source-mapping toolbox (REST). In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018; pp. 106–109. [Google Scholar]
- Pergher, V.; Wittevrongel, B.; Tournoy, J.; Schoenmakers, B.; Van Hulle, M.M. N-back training and transfer effects revealed by behavioral responses and EEG. Brain Behav. 2018, 8, e01136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-W.; Girolami, M.; Sejnowski, T.J. Independent component analysis using an extended infomax algorithm for mixed subgaussian and supergaussian sources. Neural Comput. 1999, 11, 417–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, W.R.; Nunez, P.L.; Ding, J.; Srinivasan, R. Comparison of the effect of volume conduction on EEG coherence with the effect of field spread on MEG coherence. Stat. Med. 2007, 26, 3946–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.; Winter, W.R.; Ding, J.; Nunez, P.L. EEG and MEG coherence: Measures of functional connectivity at distinct spatial scales of neocortical dynamics. J. Neurosci. Methods 2007, 166, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haufe, S. Towards EEG source connectivity analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 9, e105041. [Google Scholar]
- Perrin, F.; Pernier, J.; Bertrand, O.; Echallier, J.F. Spherical splines for scalp potential and current density mapping. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1989, 72, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.X. A better way to define and describe Morlet wavelets for time-frequency analysis. Neuroimage 2019, 199, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rac-Lubashevsky, R.; Kessler, Y. Oscillatory correlates of control over working memory gating and updating: An EEG study using the reference-back paradigm. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2018, 30, 1870–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, A.M.; Schoffelen, J.-M. A tutorial review of functional connectivity analysis methods and their interpretational pitfalls. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Tong, Y.; Heng, X. Phase-locking value based graph convolutional neural networks for emotion recognition. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 93711–93722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losonczi, L.; Bako, L.; Brassai, S.-T.; Marton, L.-F. Hilbert-Huang transform used for EEG signal analysis. In Proceedings of the The International Conference Interdisciplinarity in Engineering INTER-ENG; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; p. 361. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, M.; Wang, J.; He, Y. BrainNet Viewer: A network visualization tool for human brain connectomics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurewicz, K.; Paluch, K.; Kublik, E.; Rogala, J.; Mikicin, M.; Wróbel, A. EEG-neurofeedback training of beta band (12--22 Hz) affects alpha and beta frequencies--A controlled study of a healthy population. Neuropsychologia 2018, 108, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Singh, U.; Pandey, C.M.; Mishra, P.; Pandey, G. Application of student’s t-test, analysis of variance, and covariance. Ann. Card. Anaesth. 2019, 22, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallat, R. Pingouin: Statistics in Python. J. Open Source Softw. 2018, 3, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinidis, C.; Klingberg, T. The neuroscience of working memory capacity and training. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Paz, V.K.C.; Tomaz, C. Neurofeedback Training on Aging: Prospects on Maintaining Cognitive Reserve. In Neurological and Mental Disorders; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, O.; Gelfand, J.; Kounios, J.; Lisman, J.E. Oscillations in the alpha band (9--12 Hz) increase with memory load during retention in a short-term memory task. Cereb. cortex 2002, 12, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, L.-T.; Ekstrom, A.D.; Ranganath, C. Neural oscillations associated with item and temporal order maintenance in working memory. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 10803–10810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meltzer, J.A.; Zaveri, H.P.; Goncharova, I.I.; Distasio, M.M.; Papademetris, X.; Spencer, S.S.; Spencer, D.D.; Constable, R.T. Effects of working memory load on oscillatory power in human intracranial EEG. Cereb. Cortex 2008, 18, 1843–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, O.; Tesche, C.D. Frontal theta activity in humans increases with memory load in a working memory task. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 15, 1395–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onton, J.; Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. Frontal midline EEG dynamics during working memory. Neuroimage 2005, 27, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Dong, Q.; Xia, X.; Tian, X.; Li, X. Theta oscillation and functional connectivity alterations related to cerebral small vessel disease with working memory impairment. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2022, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukrishnan, S.P.; Soni, S.; Sharma, R. Brain networks communicate through theta oscillations to encode high load in a visuospatial working memory task: An EEG connectivity study. Brain Topogr. 2020, 33, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klados, M.A.; Paraskevopoulos, E.; Pandria, N.; Bamidis, P.D. The impact of math anxiety on working memory: A cortical activations and cortical functional connectivity EEG study. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 15027–15039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauseng, P.; Griesmayr, B.; Freunberger, R.; Klimesch, W. Control mechanisms in working memory: A possible function of EEG theta oscillations. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010, 34, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lett, T.A.; Voineskos, A.N.; Kennedy, J.L.; Levine, B.; Daskalakis, Z.J. Treating working memory deficits in schizophrenia: A review of the neurobiology. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 75, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruzelier, J. A theory of alpha/theta neurofeedback, creative performance enhancement, long distance functional connectivity and psychological integration. Cogn. Process. 2009, 10, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheloyannis, S.; Pachou, E.; Stam, C.J.; Breakspear, M.; Bitsios, P.; Vourkas, M.; Erimaki, S.; Zervakis, M. Small-world networks and disturbed functional connectivity in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2006, 87, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastin, C.; Yakushev, I.; Bahri, M.A.; Fellgiebel, A.; Eustache, F.; Landeau, B.; Scheurich, A.; Feyers, D.; Collette, F.; Chételat, G.; et al. Cognitive reserve impacts on inter-individual variability in resting-state cerebral metabolism in normal aging. Neuroimage 2012, 63, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moezzi, B.; Lavrencic, L.M.; Goldsworthy, M.R.; Coussens, S.; Keage, H.A.D. Associations between EEG functional brain connectivity and a cognitive reserve proxy in healthy older adults. bioRxiv 2019, 625608. [Google Scholar]
- Sauseng, P.; Hoppe, J.; Klimesch, W.; Gerloff, C.; Hummel, F.C. Dissociation of sustained attention from central executive functions: Local activity and interregional connectivity in the theta range. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 25, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, P.S.; Wong, A.S.W.; Fulham, W.R.; Thienel, R.; Mansfield, E.; Michie, P.T.; Karayanidis, F. Theta frontoparietal connectivity associated with proactive and reactive cognitive control processes. Neuroimage 2015, 108, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabeza, R.; Albert, M.; Belleville, S.; Craik, F.I.M.; Duarte, A.; Grady, C.L.; Lindenberger, U.; Nyberg, L.; Park, D.C.; Reuter-Lorenz, P.A.; et al. Maintenance, reserve and compensation: The cognitive neuroscience of healthy ageing. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 19, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Loyo, J.; González-Garrido, A.A.; Llamas-Alonso, L.A.; Sequeira, H. Sex differences in cognitive processing: An integrative review of electrophysiological findings. Biol. Psychol. 2022, 172, 108370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nawaz, R.; Wood, G.; Nisar, H.; Yap, V.V. Exploring the Effects of EEG-Based Alpha Neurofeedback on Working Memory Capacity in Healthy Participants. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020200
Nawaz R, Wood G, Nisar H, Yap VV. Exploring the Effects of EEG-Based Alpha Neurofeedback on Working Memory Capacity in Healthy Participants. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(2):200. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020200
Chicago/Turabian StyleNawaz, Rab, Guilherme Wood, Humaira Nisar, and Vooi Voon Yap. 2023. "Exploring the Effects of EEG-Based Alpha Neurofeedback on Working Memory Capacity in Healthy Participants" Bioengineering 10, no. 2: 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020200
APA StyleNawaz, R., Wood, G., Nisar, H., & Yap, V. V. (2023). Exploring the Effects of EEG-Based Alpha Neurofeedback on Working Memory Capacity in Healthy Participants. Bioengineering, 10(2), 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020200





