Novel PKD2 Missense Mutation p.Ile424Ser in an Individual with Multiple Hepatic Cysts: A Case Report
Abstract
:1. Introduction
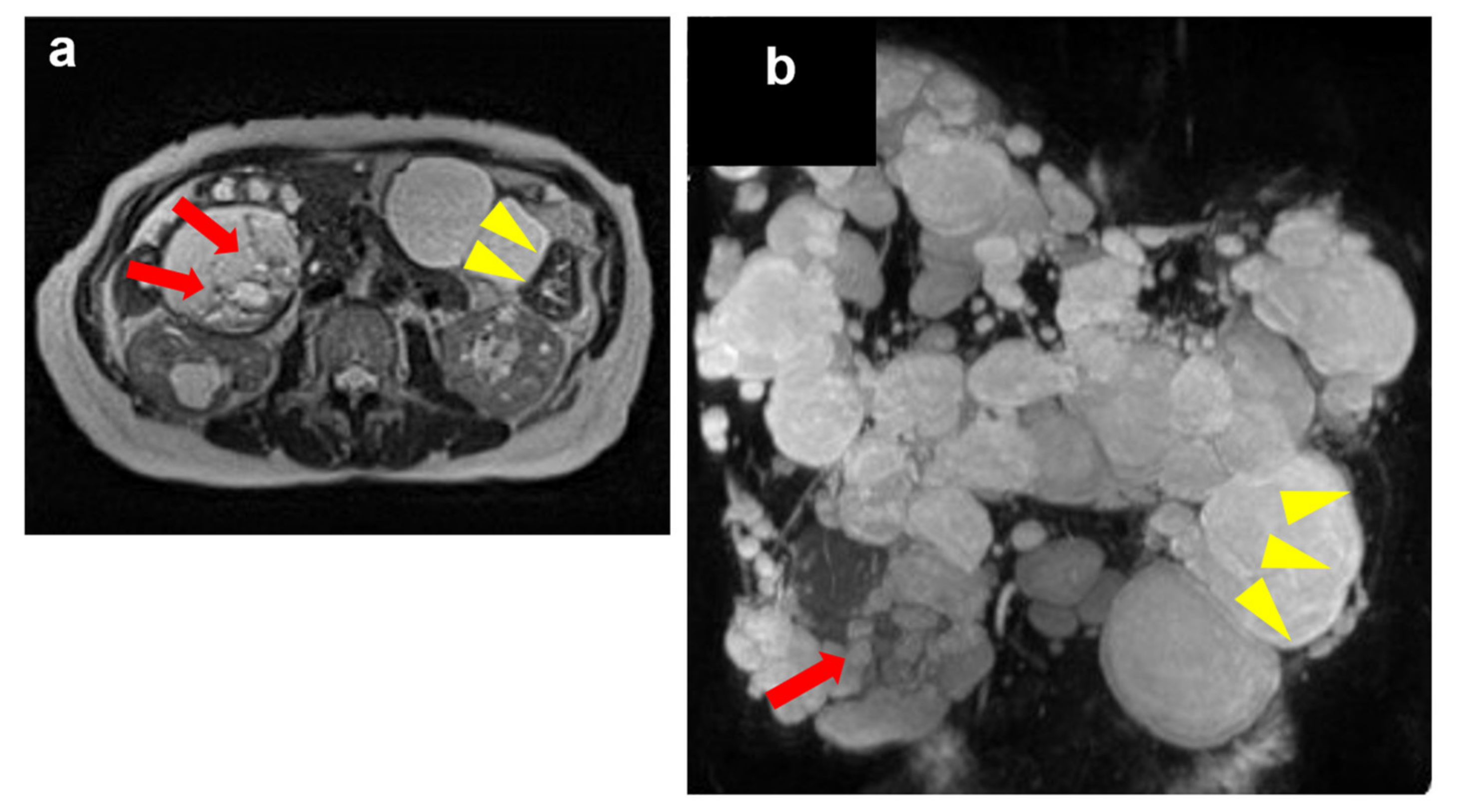
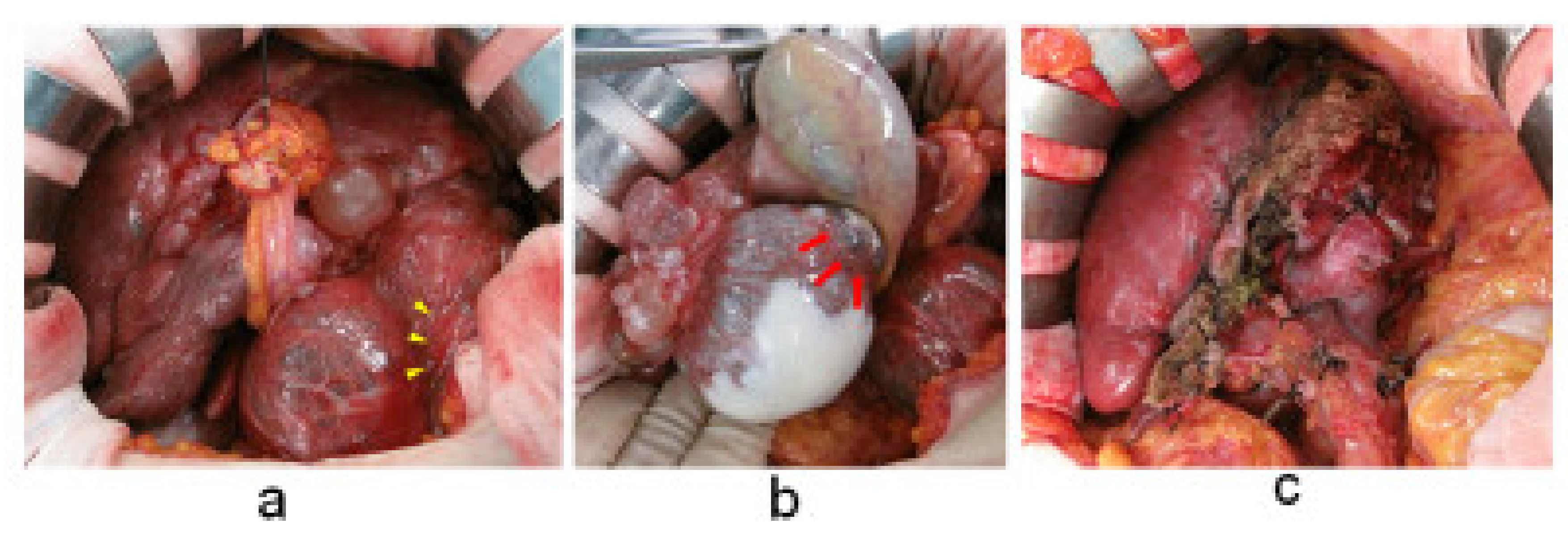
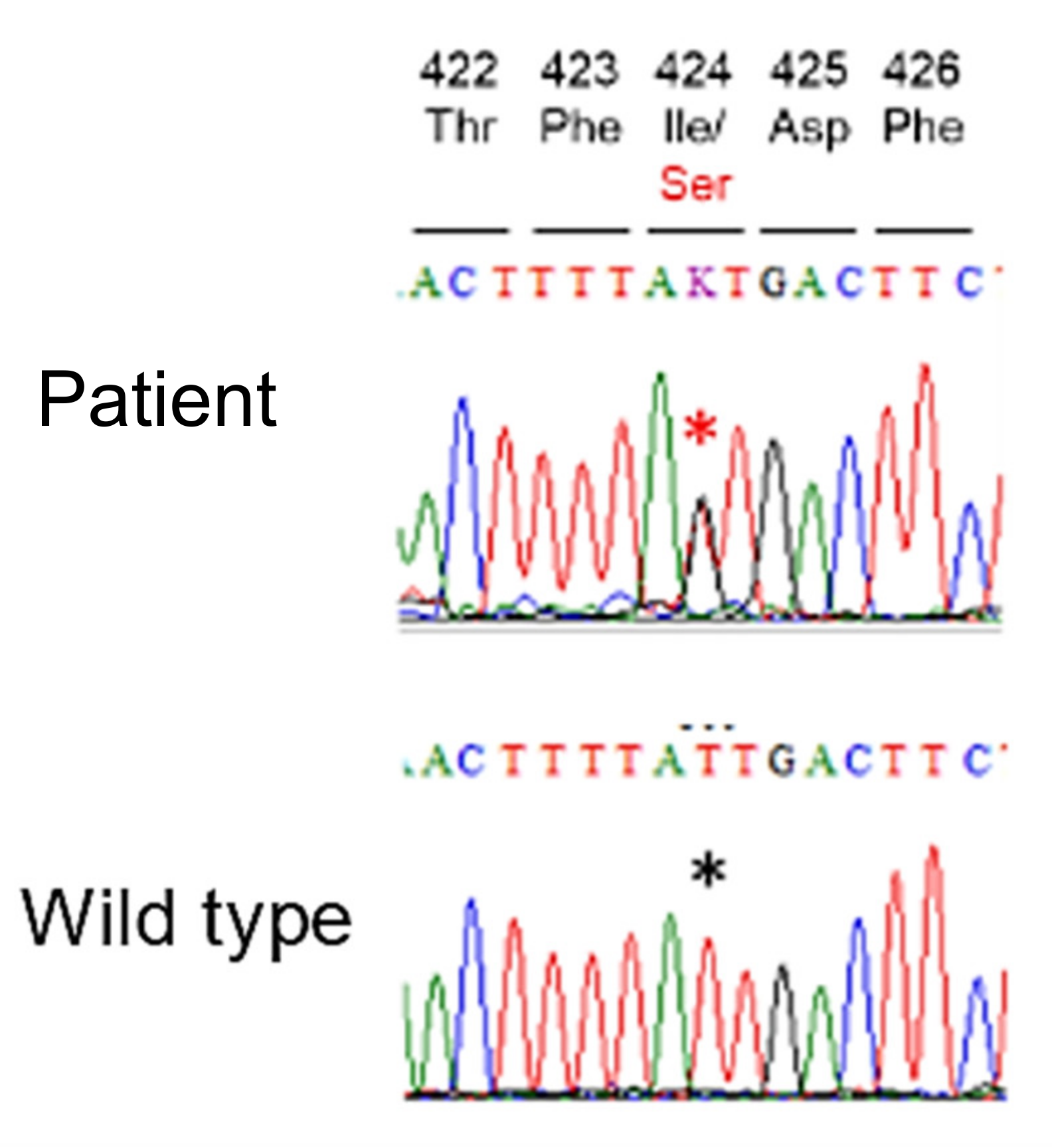
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grantham, J.J. Clinical practice. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1477–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.S.; Yang, X.; DeCaen, P.G.; Liu, X.; Bulkley, D.; Clapham, D.E.; Cao, E. The Structure of the Polycystic Kidney Disease Channel PKD2 in Lipid Nanodiscs. Cell 2016, 167, 763–773.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Togi, S.; Ura, H.; Niida, Y. Optimization and Validation of Multimodular, Long-Range PCR-Based Next-Generation Sequencing Assays for Comprehensive Detection of Mutation in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. J. Mol. Diagn. 2021, 23, 424–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bear, J.C.; McManamon, P.; Morgan, J.; Payne, R.H.; Lewis, H.; Gault, M.H.; Churchill, D.N.; Opitz, J.M. Age at clinical onset and at ultrasonographic detection of adult polycystic kidney disease: Data for genetic counselling. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1984, 18, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravine, D.; Gibson, R.N.; Walker, R.G.; Sheffield, L.J.; Kincaid-Smith, P.; Danks, D.M. Evaluation of ultrasonographic diagnostic criteria for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease 1. Lancet 1994, 343, 824–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Obaji, J.; Dupuis, A.; Paterson, A.D.; Magistroni, R.; Dicks, E.; Parfrey, P.; Cramer, B.; Coto, E.; Torra, R. Unified criteria for ultrasonographic diagnosis of ADPKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Evidence-Based Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) Practice Guidelines 2020. Available online: https://minds.jcqhc.or.jp/docs/gl_pdf/G0001221/4/polycystic_kidney_disease.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- Garcea, G.; Rajesh, A.; Dennison, R. Surgical management of cystic lesions in the liver. ANZ J. Surg. 2016, 83, E3–E20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, C.; von Bothmer, J.; Brüchle, N.O.; Venghaus, A.; Frank, V.; Fehrenbach, H.; Hampel, T.; Pape, L.; Buske, A.; Jonsson, J. Mutations in multiple PKD genes may explain early and severe polycystic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 2047–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leonhard, W.N.; Zandbergen, M.; Veraar, K.; van den Berg, S.; van der Weerd, L.; Breuning, M.; de Heer, E.; Peters, D.J. Scattered deletion of PKD1 in kidneys causes a cystic snowball effect and recapitulates polycystic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1322–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hughes, J.; Ward, C.J.; Peral, B.; Aspinwall, R.; Clark, K.; San Millán, J.L.; Gamble, V.; Harris, P.C. The polycystic kidney disease 1 (PKD1) gene encodes a novel protein with multiple cell recognition domains. Nat. Genet. 1995, 10, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, M.C.; Manganelli, L.; Woollard, J.R.; Masyuk, A.I.; Masyuk, T.V.; Tammachote, R.; Huang, B.Q.; Leontovich, A.A.; Beito, T.G.; Madden, B.J. Characterization of PKD protein-positive exosome-like vesicles. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karihaloo, A.; Koraishy, F.; Huen, S.C.; Lee, Y.; Merrick, D.; Caplan, M.J.; Somlo, S.; Cantley, L.G. Macrophages promote cyst growth in polycystic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1809–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karaosmanoglu, A.D.; Arslan, S.; Akata, D.; Ozmen, M.; Haliloglu, M.; Oguz, B.; Karcaaltincaba, M. Congenital and hereditary cystic diseases of the abdomen. Insights Imaging 2020, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caroli, A.; Antiga, L.; Cafaro, M.; Fasolini, G.; Remuzzi, A.; Remuzzi, G.; Ruggenenti, P. Reducing polycystic liver volume in ADPKD: Effects of somatostatin analogue octreotide. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gevers, T.J.; Inthout, J.; Caroli, A.; Ruggenenti, P.; Hogan, M.C.; Torres, V.E.; Nevens, F.; Drenth, J.P. Young women with polycystic liver disease respond best to somatostatin analogues: A pooled analysis of individual patient data. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 357–365.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherstha, R.; McKinley, C.; Russ, P.; Scherzinger, A.; Bronner, T.; Showalter, R.; Everson, G.T. Postmenopausal estrogen therapy selectively stimulates hepatic enlargement in women with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Hepatology 1997, 26, 1282–1286. [Google Scholar]
- Everson, G.T.; Helmke, S.M. Somatostatin, estrogen, and polycystic liver disease. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Gene Analysis Soft Ware | SIFT | PolyPhe-2 HumDiv | PolyPhe-2 HumVar | Mutation Taster | Mutation Assessor | Likelihood Ratio Test (LRT) | CADD PHRED Like Scaled C-Score (>20) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| result | Damaging (0.000) | Possibly damaging (0.897) | Probably damaging (0.990) | Disease Causing (0.9998) | Medium (3.02) | Deleterious (0.000209) | 29.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miura, S.; Niida, Y.; Hashizume, C.; Fujii, A.; Takagaki, Y.; Kusama, K.; Akazawa, S.; Minami, T.; Mukai, T.; Furuichi, K.; et al. Novel PKD2 Missense Mutation p.Ile424Ser in an Individual with Multiple Hepatic Cysts: A Case Report. Medicines 2022, 9, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines9040025
Miura S, Niida Y, Hashizume C, Fujii A, Takagaki Y, Kusama K, Akazawa S, Minami T, Mukai T, Furuichi K, et al. Novel PKD2 Missense Mutation p.Ile424Ser in an Individual with Multiple Hepatic Cysts: A Case Report. Medicines. 2022; 9(4):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines9040025
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiura, Seiko, Yo Niida, Chieko Hashizume, Ai Fujii, Yuta Takagaki, Kahoru Kusama, Sumiyo Akazawa, Tetsuya Minami, Tsuyoshi Mukai, Kengo Furuichi, and et al. 2022. "Novel PKD2 Missense Mutation p.Ile424Ser in an Individual with Multiple Hepatic Cysts: A Case Report" Medicines 9, no. 4: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines9040025
APA StyleMiura, S., Niida, Y., Hashizume, C., Fujii, A., Takagaki, Y., Kusama, K., Akazawa, S., Minami, T., Mukai, T., Furuichi, K., Tsuchishima, M., Ueda, N., Takamura, H., Koya, D., & Ito, T. (2022). Novel PKD2 Missense Mutation p.Ile424Ser in an Individual with Multiple Hepatic Cysts: A Case Report. Medicines, 9(4), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines9040025







