CHRIST: CD44-Incorporated Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk Index Scoring Tool—A Novel Prognostic Scoring System for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development and Aggressiveness
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
2.4. CHRIST: CD44-Incorporated HCC Risk Index Scoring Tool
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of the Four Studied Groups in Relation to CD44 Gene Polymorphism and Allele Frequency
3.2. Correlation between Different Genotypes Based on Tumor Behavior and Imaging Findings (CT/MRI)
3.3. CHRIST Scoring System for Evaluation of HCC Development and Aggressiveness
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFP | Alpha-fetoprotein |
| AMUH | Alexandria Main University Hospital |
| BCLC | Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer |
| CLIP | Cancer of the liver Italian program |
| CSCs | Cancer stem cells |
| CHRIST | CD44-incorporated hepatocellular carcinoma risk-index scoring tool |
| CP score | Child-Pugh score |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CD | Cluster of differentiation |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| EMT | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition |
| ESR | Erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| MELD | Modified end-stage liver disease |
| NPV | Negative predictive value |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| PVT | Portal vein thrombosis |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| PPV | Positive predictive value |
| PNI | Prognostic nutritional index |
| ROC curve | Receiver operating characteristic curve |
| UTR | Untranslated region |
References
- Hofmeister, M.G.; Rosenthal, E.M.; Barker, L.K.; Rosenberg, E.S.; Barranco, M.A.; Hall, E.W.; Edlin, B.R.; Mermin, J.; Ward, J.W.; Ryerson, A.B.; et al. Estimating Prevalence of Hepatitis C Virus Infection in the United States, 2013–2016. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1020–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrick, J.L.; Kelly, S.P.; Altekruse, S.F.; McGlynn, K.A.; Rosenberg, P.S. Future of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Incidence in the United States Forecast through 2030. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, S.; Di Marco, V.; Iavarone, M.; Roffi, L.; Boccaccio, V.; Crosignani, A.; Cabibbo, G.; Rossi, S.; Calvaruso, V.; Aghemo, A.; et al. Improved survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and compensated hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis who attained sustained virological response. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 1526–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Lisi, S.; Crosignani, A.; Roffi, L.; Rossi, S.; Boccaccio, V.; Zermiani, P.; Maisonneuve, P.; Bruno, S. SVR is associated with no risk reduction of HCC development in patients with HCV-related cirrhosis. A prospective, up-to 23 years, cohort follow-up study. Dig. Liver Dis. 2014, 46, e33–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Wang, X.W. Clinical implications of cancer stem cell biology in hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Oncol. 2012, 39, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, W.; Frenette, P.S. Alternative CD44 splicing in intestinal stem cells and tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2014, 33, 537–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoller, M. CD44: Can a cancer-initiating cell profit from an abundantly expressed molecule? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, M.E.; Sivanandan, R.; Kaczorowski, A.; Wolf, G.T.; Kaplan, M.J.; Dalerba, P.; Weissman, I.L.; Clarke, M.F.; Ailles, L.E. Identification of a subpopulation of cells with cancer stem cell properties in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clevers, H. The cancer stem cell: Premises, promises and challenges. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyak, K.; Weinberg, R.A. Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states: Acquisition of malignant and stem cell traits. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.-H.; Chen, C.-L.; Chau, G.-Y.; Chiou, S.-H.; Su, C.-W.; Chou, T.-Y.; Peng, W.-L.; Wu, J.-C. Comprehensive analysis of the independent effect of twist and snail in promoting metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1464–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Chan, T.H.M.; Yuan, Y.-F.; Chiou, S.-H.; Su, C.-W.; Chou, T.-Y.; Peng, W.-L.; Wu, J.-C. CHD1L promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis in mice and is associated with these processes in human patients. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 1178–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.J.; Bourguignon, L.Y. Role of hyaluronan-mediated CD44 signaling in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression and chemoresistance. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marhaba, R.; Klingbeil, P.; Nuebel, T.; Nazarenko, I.; Buechler, M.W.; Zoeller, M. CD44 and EpCAM: Cancer-initiating cell markers. Curr. Mol. Med. 2008, 8, 784–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, R.; Wilson, G.D. The Importance of CD44 as a Stem Cell Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 2087204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Houseini, M.E.; Ismail, A.; Abdelaal, A.A.; El-Habashy, A.H.; Abdallah, Z.F.; Mohamed, M.Z.; El-Hadidi, M.; Cho, W.C.S.; Ahmed, H.; Al-Shafie, T.A. Role of TGF-beta1 and C-Kit Mutations in the Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Patients: In vitro Study. Biochemistry 2019, 84, 941–953. [Google Scholar]
- Shirasaki, T.; Honda, M.; Yamashita, T.; Nio, K.; Shimakami, T.; Shimizu, R.; Nakasyo, S.; Murai, K.; Shirasaki, N.; Okada, H.; et al. The osteopontin-CD44 axis in hepatic cancer stem cells regulates IFN signaling and HCV replication. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Child, C.G.; Turcotte, J.G. Surgery and portal hypertension. Major Probl. Clin. Surg. 1964, 1, 1–85. [Google Scholar]
- Kamath, P.S.; Kim, W.R. The model for end-stage liver disease (MELD). Hepatology 2007, 45, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Brú, C.; Bruix, J. Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: The BCLC staging classification. Semin Liver Dis. 1999, 19, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.Q.; Abdullah, K.G.; Wang, Q.K. The TaqMan method for SNP genotyping. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 578, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Beaugrand, M. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Present status and future prospects. J. Hepatol. 2003, 38 (Suppl. 1), S136–S149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozeik, M.S.; Hammam, O.A.; Ali, A.I.; Magdy, M.; Khalil, H.; Anas, A.; el Hassan, A.A.A.; Rahim, A.A.; El-Shabasy, A.I. Evaluation of CD44 and CD133 as markers of liver cancer stem cells in Egyptian patients with HCV-induced chronic liver diseases versus hepatocellular carcinoma. Electron. Phys. 2017, 9, 4708–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Endo, K.; Terada, T. Protein expression of CD44 (standard and variant isoforms) in hepatocellular carcinoma: Relationships with tumor grade, clinicopathologic parameters, p53 expression, and patient survival. J. Hepatol. 2000, 32, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, Y.E.; Hsieh, M.J.; Chiou, H.L.; Lee, H.-L.; Yang, S.-F.; Chen, T.-Y. CD44 gene polymorphisms on hepatocellular carcinoma susceptibility and clinicopathologic features. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 231474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Q.; Cao, Y.; Wang, G.; Hu, A.; Ruan, L.; Wang, S.; Bo, Q.; Chen, W.; et al. Prognostic value of the expression of cancer stem cell-related markers CD133 and CD44 in hepatocellular carcinoma: From patients to patient-derived tumor xenograft models. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 47431–47443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Tan, Y. Prognostic value of CD44 expression in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: Meta-analysis. Cancer Cell Int. 2016, 16, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nozoe, T.; Ninomiya, M.; Maeda, T.; Cao, Y.; Wang, G.; Hu, A.; Ruan, L.; Wang, S.; Bo, Q.; Chen, W. Prognostic nutritional index: A tool to predict the biological aggressiveness of gastric carcinoma. Surg. Today 2010, 40, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, M.J.; Morrison, D.S.; Talwar, D.; Balmer, S.M.; Fletcher, C.D.; O’Reilly, D.S.; Foulis, A.K.; Horgan, P.G.; McMillan, D. A comparison of inflammation-based prognostic scores in patients with cancer. A Glasgow Inflammation Outcome Study. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 2633–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniele, B.; Annunziata, M.; Barletta, E.; Tinessa, V.; Di Maio, M. Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) score for staging hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2007, 37 (Suppl. 2), S206–S209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nault, J.C.; De Reynies, A.; Villanueva, A.; Calderaro, J.; Rebouissou, S.; Couchy, G.; Decaens, T.; Franco, D.; Imbeaud, S.; Rousseau, F. A hepatocellular carcinoma 5-gene score associated with survival of patients after liver resection. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Hepatocellular Carcinoma | p-Value (For TT, CT, and CT) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Metastatic (n = 19) | Metastatic (n = 21) | ||
| Infiltrating malignancy | 1 (5.3%) | 15 (71.4%) | <0.001 |
| Portal vein thrombosis | 0 (0%) | 15 (71.4%) | <0.001 |
| Porta hepatis metastasis | 0 (0%) | 16 (76.2%) | <0.001 |
| BCLC | |||
| 0 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0.001 |
| A | 2 (10.5%) | 1 (4.8%) | |
| B | 8 (42.1%) | 1 (4.8%) | |
| C | 0 (0%) | 9 (42.9%) | |
| D | 9 (47.4%) | 10 (47.6%) | |
| Multicentric tumor | 6 (31.6%) | 9 (42.9%) | 0.462 |
| Tumor size | |||
| <5 | 15 (78.9%) | 6 (28.6%) | 0.001 |
| ≥5 | 4 (21.1%) | 15 (71.4%) | |
| Hepatocellular Carcinoma | Cirrhotic (n = 40) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Metastatic (n = 19) | Metastatic (n = 21) | |||
| Child-Pugh score | ||||
| A | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 9 (22.5%) | 0.033 |
| B | 9 (47.4%) | 11 (52.4%) | 13 (32.5%) | |
| C | 10 (52.6%) | 10 (47.6%) | 18 (45%) | |
| MELD | ||||
| Mean ± SD | 15.26 ± 3.45 | 13.52 ± 4.55 | 13.83 ± 5.15 | 0.170 |
| TNM | ||||
| I | 13 (%) | 0 (0%) | - | <0.001 |
| II | 2 (%) | 0 (0%) | - | |
| IIIa | 4 (%) | 0 (0%) | - | |
| IIIb & c | 0 (0%) | 11 (52.4%) | - | |
| IVa | 0 (0%) | 5 (23.8%) | - | |
| IVb | 0 (0%) | 5 (23.8%) | - | |
| Hepatocellular Carcinoma | Cirrhotic (n = 40) | Control (n = 40) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Metastatic (n = 19) | Metastatic (n = 21) | ||||
| CD44 | |||||
| TT | 10 (52.6%) | 0 (0%) | 11 (27.5%) | 8 (20%) | <0.001 |
| CT | 9 (47.4%) | 12 (57.1%) | 23 (57.5%) | 24 (60%) | |
| CC | 0 (0%) | 9 (42.9%) | 6 (15%) | 8 (20%) | |
| Pcontrol | 0.013 * | 0.033 * | 0.677 * | ||
| Significance between groups | p1 < 0.001 *, p2 = 0.077, p3 = 0.006 * | ||||
| Allele frequency | |||||
| T | 29 (76.3%) | 12 (28.6%) | 45 (56.3%) | 40 (50%) | <0.001 |
| C | 9 (23.7%) | 30 (71.4%) | 35 (43.8%) | 40 (50%) | |
| Pcontrol | 0.007 * | 0.023 * | 0.428 * | ||
| Significance between groups | p1 < 0.001 **, p2 = 0.035 ***, p3 = 0.004 **** | ||||
| CD44 | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TT (n = 10) | CT + CC (n = 30) | ||||
| Child-Pugh score | |||||
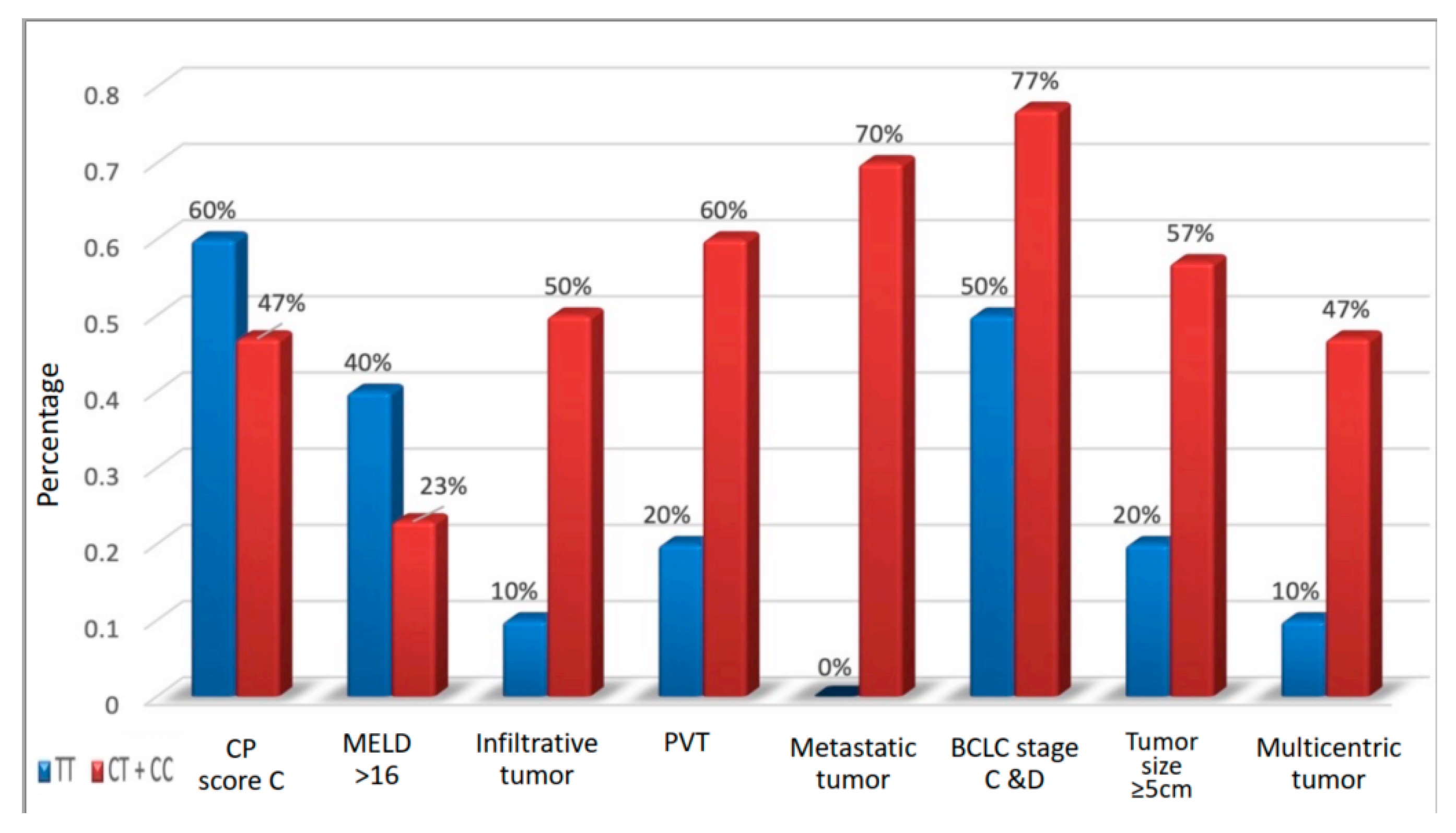
| B 7,8,9 | 4 (40%) | 16 (53.3%) | 0.465 | 0.583 (0.136–2.49) | 0.119 (0.01–1.313) |
| C ≥ 10 | 6(60%) | 14 (46.7%) | |||
| MELD | |||||
| <17 | 6 (60%) | 23 (76.7%) | 0.307 | 0.457 (0.10–2.091) | 0.147 (0.02–1.92) |
| ≥17 | 4 (40%) | 7 (23.3%) | |||
| BCLC | |||||
| 0 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0.160 | ||
| A | 1 (10%) | 2 (6.7%) | |||
| B | 4 (40%) | 5 (16.7%) | - | - | |
| C | 0 (0%) | 9 (30%) | |||
| D | 5 (50%) | 14 (46.7%) | |||
| A + B | 5 (50%) | 7 (23.3%) | 0.111 | 3.28 (0.73–14.73) | 2.5 (0.27–23.54) |
| C + D | 5 (50%) | 23 (76.7%) | |||
| TNM | |||||
| I | 8 (80%) | 5 (16.7%) | 0.002 | ||
| II | 1 (10%) | 1 (3.3%) | |||
| IIIa | 1 (10%) | 3 (10%) | - | - | |
| IIIb & c | 0 (0%) | 11 (36.7%) | |||
| IVa | 0 (0%) | 5 (16.7%) | |||
| IVb | 0 (0%) | 5 (16.7%) | |||
| I, II, IIa | 10 (100%) | 9 (30%) | <0.001 | - | - |
| IIIb & c, IVa, IVb | 0 (0%) | 21 (70%) | |||
| Infiltrative tumor | |||||
| No | 9 (90%) | 15 (50%) | 0.025 | 9.0 (1.011–80.13) | 10.1 (1.07–104.3) |
| Yes | 1 (10%) | 15 (50%) | |||
| Portal vein thrombosis | |||||
| No | 8 (80%) | 12 (40%) | 0.028 | 6.0 (1.08–33.27) | 4.58 (0.74–28.36) |
| Yes | 2 (20%) | 18 (60%) | |||
| Metastasis | |||||
| No | 10 (100%) | 9 (30%) | 0.010 | 8.0 (1.4–44.9) | 6.71 (1.09–41.51) |
| Yes | 0 (0%) | 21 (70%) | |||
| Tumor size | |||||
| <5 | 8 (80%) | 13 (43.3%) | 0.044 | 5.23 (1.04–28.91) | 11.78 (1.12–123.3) |
| ≥5 | 2 (20%) | 17 (56.7%) | |||
| Multicentricity | |||||
| No | 9 (90%) | 16 (53.3%) | 0.038 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khalifa, A.A.; Abdeen, N.; Mikhael, N.L.; Elmalah, S.; Elshayeb, A. CHRIST: CD44-Incorporated Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk Index Scoring Tool—A Novel Prognostic Scoring System for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development and Aggressiveness. Medicines 2022, 9, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines9020014
Khalifa AA, Abdeen N, Mikhael NL, Elmalah S, Elshayeb A. CHRIST: CD44-Incorporated Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk Index Scoring Tool—A Novel Prognostic Scoring System for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development and Aggressiveness. Medicines. 2022; 9(2):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines9020014
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhalifa, Ahmed Ali, Nermeen Abdeen, Neveen L. Mikhael, Sawsan Elmalah, and Ayman Elshayeb. 2022. "CHRIST: CD44-Incorporated Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk Index Scoring Tool—A Novel Prognostic Scoring System for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development and Aggressiveness" Medicines 9, no. 2: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines9020014
APA StyleKhalifa, A. A., Abdeen, N., Mikhael, N. L., Elmalah, S., & Elshayeb, A. (2022). CHRIST: CD44-Incorporated Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk Index Scoring Tool—A Novel Prognostic Scoring System for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development and Aggressiveness. Medicines, 9(2), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines9020014





