Safety Analysis of Panax Ginseng in Randomized Clinical Trials: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
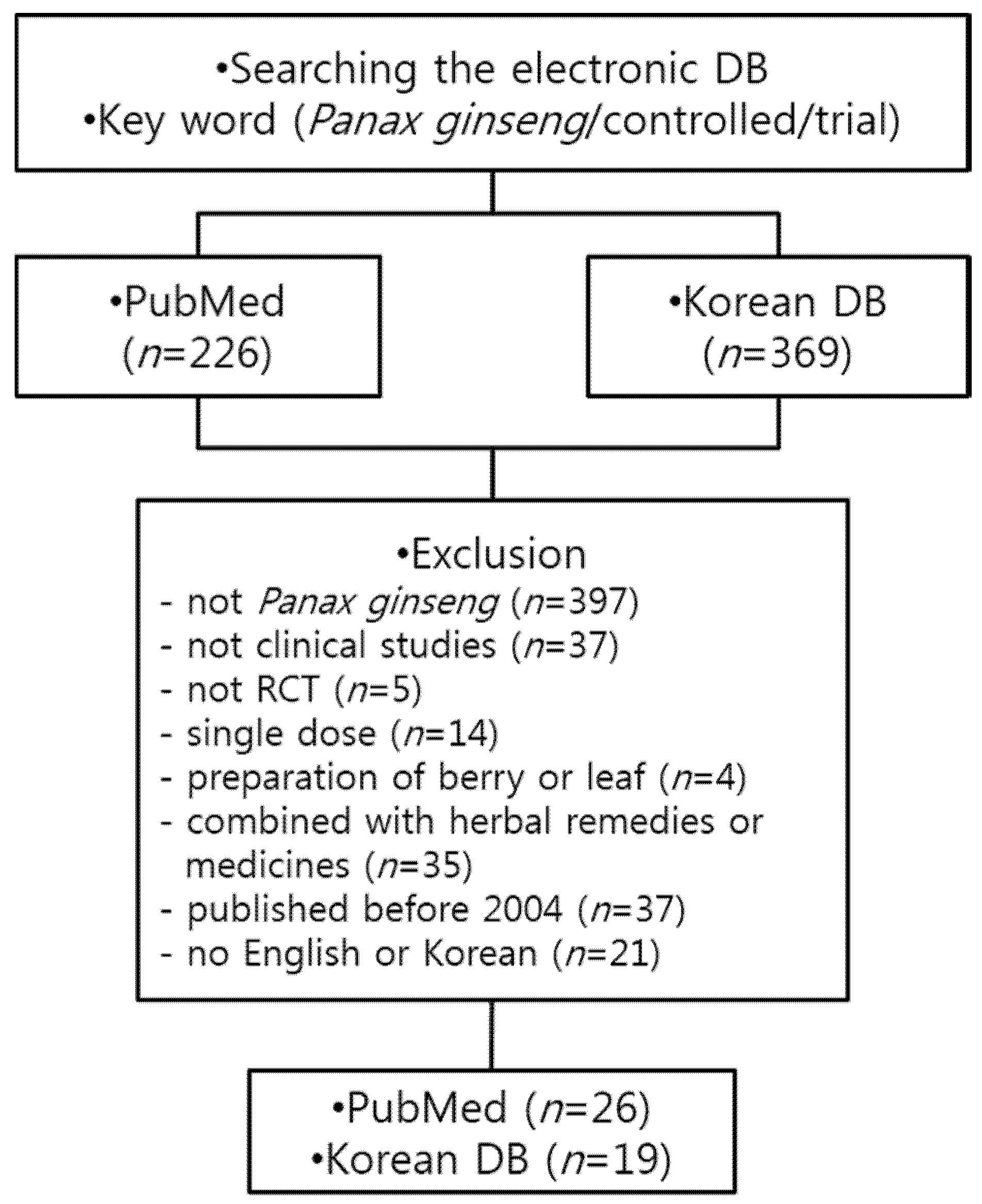
2.1. Data Sources and Selection
2.2. Eligibility of Studies
2.3. Data Extraction
3. Results
3.1. Included Studies
3.2. Participants
3.3. Interventions
| Author (Year) | Design | Condition, Age Range (yr) | No of Subjects C/T | Intervention Dose (g/day) Duration | Main Results | Adverse Events | Adverse Reactions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kang (2013) [10] | DB, parallel | Healthy subjects, 30–50 | C and T:20 | Korean red ginseng powder, 1.5 g, 8 weeks |
| Not reported | - |
| Park (2012) [11] | DB, parallel | Subjects with metabolic syndrome ≥ 20 | C:25 T:23 | Korean red ginseng powder, 5 g, 12 weeks |
| C:1 T:0 | Gastrointestinal disturbance (C:1) |
| Choi (2009) [12] | DB, crossover | Healthy, married women with FSFI score below 25, 30–45 | C and T:23 | Korean red ginseng powder, 3 g, 6 weeks |
| Not reported | - |
| Shin (2007) [13] | DB, parallel | Healthy subjects with cholesterol 180– 250 mg/dL, 20–59 | C:29 T1 (low-dose): 29 T2 (high-dose): 29 | Korean red ginseng extract, 1.5 g, 3 g, 8 weeks |
| T:1 (not clear in dosage) | Cold allergy (T:1) |
| Bang (2014) [14] | DB, parallel | Subjects with IFG (100–125 mg/dL), IGT (2-h OGTT ≥ 140 mg/dL) or newly diagnosed T2DM, 20–70 | C:20 T:21 | Korean red ginseng powder, 5.0 g, 12 weeks |
| Not reported | - |
| Oh (2014) [15] | DB, parallel | Healthy subjects (FBG5.6–7.8 mmol/L), 44–62 | C:21 T:21 | Fermented red ginseng, 2.7 g, 4 weeks |
| C:0 T:1 (exclude the data) | Hypoglycemia (T:1) |
| Lee (2013) [16] | DB, parallel | Post-menopausal women, 52–64 | C:44 T:49 | Fermented red ginseng, 2.1 g, 2 weeks |
| Not reported | - |
| Reed (2011) [17] | DB, parallel | Overweight and/or obese subjects (BMI 34 ± 1 kg/m2) with impaired glucose tolerance or newly diagnosed T2DM 43–49 | C:5 T1:5 T2:5 | T1: Korean red ginseng extract, 3 g/day for 2 weeks→8 g/day for 2 weeks T2: Re, 250 mg/day for 2 weeks→500 mg/day for 2 weeks |
| Not reported | - |
| Reay (2009) [18] | DB, crossover | Healthy subjects, Study 1: 33.4 ± 10.4 Study 2: 38.4 ± 10.6 | Study 1:C and T 23 Study 2:C and T 14 | Study 1: Panax ginseng extract (G115), 200mg, 8 weeks Study 2: Korean red ginseng extract, 200 mg, 8 weeks |
| Not reported | - |
| Yeo (2012) [19] | DB, parallel | Healthy young men, 19–25 | C:7 T:8 | Korean red ginseng 4.5 g, 2 weeks |
| Not reported | - |
| Reay (2010) [20] | DB, crossover | Healthy, young volunteers, 18–26 | C and T:30 | Panax ginseng extract (G115) 200 mg, 8 days |
| Not reported | - |
| Kennedy (2007) [21] | DB, crossover | Healthy, young volunteers, 19–25 | C and T:18 | Korean red ginseng extract, 200 mg, 8 weeks |
| Not reported | - |
| Yun (2010) [22] | DB, parallel 3 years of intervention and 8 years of follow up | Chronic atrophic gastritis patients, 40–69 (no mentioned medication) | C:318 T:325 | Korean red ginseng extract powder, 1 g/week, 3 years |
| General symptom: C:23 (12%) T:19 (9.9%) | Headache (C:4, T:4), Increasing heartbeat (C:2, T:2), Rash (C:4, T:4) Sweating (C:3, T:2), Increasing blood pressure (C:8, T:4), Nasal bleeding (C:2, T:3) |
| Seo (2014) [23] | DB, parallel | Postmenopausal women, 45–60 | C:36 T:35 | Korean red ginseng powder, 3 g, 12 weeks |
| Not reported | - |
| Kim (2012) [24] | DB, parallel | Healthy subjects, 20–65 | C:19 T1 (low-dose): 19 T2 (high-dose):19 | Korean red ginseng powder, 3 g, 6 g, 8 weeks |
| Not reported | - |
| Kim (2011) [25] | DB, parallel | Healthy subjects, 21–61 | C:27 T1 (low-dose): 27 T2 (high-dose):27 | 20% ethanol extract of Panax ginseng 1 g, 2 g, 4 weeks |
| C:0 T1:0 T2:2 (females) | Insomnia and palpitations (T2:1) None-health related reasons (T2:1) |
| Kim (2013) [26] | DB, parallel | Subject with idiopathic chronic fatigue, 20–65 | C:30 T1 (low-dose):30 T2 (high-dose):30 | 20% ethanol extract of Panax ginseng 1 g, 2 g, 4 weeks |
| T1:1 (female) T2:1 (male) | Non-medical reason (T1:1) Allergic response (systemic rash, pruritus) (T2:1) |
| Jung (2011) [27] | DB, Parallel | Healthy male subject, 19–22 | C:9 T:9 | Korean red ginseng extract 60 g, 11 days |
| Not reported | - |
| Yoon (2008) [28] | DB, parallel | Healthy male subject, 19–22 | C:7 (endurance training+placebo) T1:7 (endurance training+ginseng) T2:10 (only ginseng) | Korean red ginseng extract 3 g, 8 weeks |
| Not reported | - |
| Kulaputana (2007) [29] | DB, parallel | Physically active Thai men, 17–22 | C:30 T:30 | Ginseng powder, 3 g, 8 weeks |
| None | - |
| Oh (2010) [30] | DB, crossover | Menopausal women, 40–60 | C and T:28 | Korean red ginseng powder, 3 g, 8 weeks |
| C:0 T: 2 | Vaginal bleeding (T:2) |
| Ham (2009) [31] | DB, parallel | Patient with erectile dysfunction, 40–70 | C:34 T:35 | Korean red ginseng extract powder:total ginsenoside (~90%) (1:1), 0.8 g, 8 weeks |
| C:5 T:8 | Acute nasopharyngitis (C:3) Rhinitis (T:1) Eczema (T:1) Skin disease (T:1) Diarrhea (T:1) Anal bleeding (C:1) Voice disorders (T:1) Ophthalmalgia (T:1) Perineal pain (T:1) Chest pain (T:1) Renal stone (C:1) |
| Kim (2009) [32] | DB, cross-over | Women depressed sexual function 30–45 | C and T:24 | Korean red ginseng powder, 6 g, 6 weeks |
| No significant adverse events related to red ginseng | - |
| Kim (2009) [33] | DB, parallel | Patients with erectile dysfunction 33–79 | C:21 T:65 | Tissue-cultured mountain ginseng extract, 2 g, 8 weeks |
| Not reported | - |
| de Andrade (2007) [34] | DB, parallel | Patients with erectile dysfunction, 26–70 | C:30 T:30 | Korean red ginseng powder, 1 g, 12 weeks |
| C:0 T:3 | Headache, insomnia |
| Kim (2006) [35] | DB, parallel | Patients with erectile dysfunction C: 36.1 ± 5.6 T: 43.6 ± 14.1 | C:12 T:23 | Tissue-cultured mountain ginseng extract, 2 g, 12 weeks |
| C:1 T:0 | Minor dyspepsia (C:1) |
| Kim (2012) [36] | DB, parallel | Menopausal women, 45–60 | C:36 T:36 | Korean red ginseng powder, 3 g, 12 weeks |
| Not reported | - |
| Kim (2009) [37] | DB, parallel | Menopausal women, 45–55 | C:12 T:14 | Korean red ginseng powder, 0.9 g, 8 weeks |
| None | - |
| Cho (2013) [38] | DB, parallel | Non-diabetic healthy subjects with BMI ≥ 23 kg/m2, 20–60 | C:34 T:34 | Korean red ginseng powder, 6 g, 12 weeks |
| C:3 T:0 | Increased appetite (C:3) |
| Kwon (2011, 2012) [7,8] | DB, parallel | Obese women with BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2, 18–65 | C:26 T:24 | Korean red ginseng powder, 6 g, 8 weeks |
| None | - |
| Lee (2012) [39] | DB, parallel | Healthy subjects, 30–70 | C:49 T:50 | Korean red ginseng extract, 3 g, 12 weeks |
| C:7 T:11 | Gastritis (T:5) Arthritis (T:2) Urticarias (C:2) Others (T:4, C:5) |
| Jung (2011) [40] | DB, parallel | Patients with allergic rhinitis, 19–48 | C:29 T:30 | Fermented red ginseng powder, 1.5 g, 4 weeks |
| None | - |
| Han (2013) [41] | DB, crossover | Healthy male subjects, 15–37 | C and T:15 | Korean red ginseng powder, 4.5 g, 7 days |
| Not reported | - |
| Lee (2010) [42] | DB, parallel | Healthy male subjects, 19–25 | C:7 T:8 | Korean red ginseng powder, 4.5 g, 2 weeks |
| Not reported | - |
| Kitaoka (2009) [43] | DB, parallel | Healthy male subjects, 20.69 ± 0.44 | C:8 T:8 | Fermented red ginseng powder, 1.845 g, 8 days |
| Not reported | - |
| Doosti (2014) [44] | DB, parallel | Male textile workers, 28–50 | C:16 T: 6 Drug:16 | Panax ginseng extract (G115) 200 mg, 14 days |
| Not reported | - |
| Braz (2013) [45] | DB, parallel | Patients with fibromyalgia, 27–58 | C:13 T1(ginseng): 12 T2(amitriptyline):13 | Panax ginseng extract, 100 mg, 12 weeks |
| Not reported | - |
| Lee (2012) [46] | DB, parallel | Healthy Korean subjects, 16–60 | C:57 T1(low-dose:56 T2(high-dose):57 | 20% ethanol extract of Panax. ginseng, 1 g, 2 g, 4 weeks |
| C:0 T1:0 T2:2 (female) | Rapid heartbeat and insomnia (T2:1) Rash and nausea (T2:1) |
| Park (2010) [47] | DB, parallel | Xerostomatic patients, 19–76 | C:50 T:50 | Korean red ginseng powder, 6 g, 8 weeks |
| C:9 T:7 | Dyspepsia (C:2,T3) Diarrhea (C:3, T:1) Itching sensation (C:2, T:1) Mild fever (C:1, T:1) Palmar sweating (C:1, T;1)- |
| Kang (2009) [48] | DB, parallel | Normal subjects, C: 25.6 ± 3.8 T: 27.5 ± 5.1 | C:18 T:21 | Korean red ginseng powder, 3 g, 3 weeks |
| Not reported | - |
| Kim (2009) [49] | DB, parallel | Patients with male and female pattern alopecia | C:20 T:20 | Korean red ginseng powder, 3 g, 24 weeks |
| C:0 T:1 | Dyspepsia (T:1) |
| Seo (2005) [50] | DB, parallel | Healthy male Koreans (160) and Chinese (160), 20–29 | C:32 T1 (red ginseng) T2 (white ginseng):32 T3 (American ginseng 4 yrs.):32 T4 (American ginseng 6 yrs.):32 | Korean red ginseng (6 yrs.), Korean white ginseng (6 yrs.), American ginseng (4 or 6 yrs.) 3 g, 4 weeks |
| No significant frequency of adverse events between Koreans and Chinese group | Chest discomfort in Chinese group treated American ginseng |
| Yang (2014) [9] | Single blind, parallel | Healthy women, 21–30 | C:11 T:11 | Korean red ginseng powder, 2.7 g, 2 weeks |
| None | - |
| Lee (2014) [51] | DB, parallel | Postmenopausal women, 50–73 | C:44 T:49 | Fermented red ginseng powder, 2.1 g, 2 weeks |
| Not reported | - |
3.4. Efficacy
3.5. Safety
| Adverse Event | Placebo Control (n = 1381) | P. Ginseng (n = 1711) |
|---|---|---|
| Dyspepsia | 13 (9.6 a , 0.9 b) | 18 (9.4 a, 1.1 b) |
| Hot flash | 19 (14.1 , 1.4) | 34 (17.8, 2.0) |
| Insomnia | 9 (6.7 , 0.7) | 20 (10.5, 1.2) |
| Constipation | 6 (4.4 , 0.4) | 10 (5.2, 0.6) |
| Low energy | 1 (0.7 , 0.1) | 4 (2.1, 0.2) |
| Headache | 10 (7.4 , 0.7) | 11 (5.8, 0.6) |
| Skin disorders | 6 (4.4 , 0.4) | 16 (8.4, 0.9) |
| Dizziness | 7 (5.2 , 0.5) | 6 (3.1, 0.4) |
| Nausea | 1 (0.7 , 0.1) | 2 (1.0, 0.1) |
| Diarrhea | 10 (7.4 , 0.7) | 12 (6.3, 0.7) |
| Abdominal pain | 0 | 2 (1.0, 0.1) |
| Nasal Bleeding | 5 (3.7 , 0.4) | 10 (5.2, 0.6) |
| Rapid heartbeat | 2 (1.5 , 0.1) | 5 (2.6, 0.3) |
| Anorexia | 6 (4.4 , 0.4) | 3 (1.6, 0.2) |
| Increased appetite | 3 (2.2 , 0.2) | 0 |
| Dried mouth | 13 (9.6 , 0.9) | 12 (6.3, 0.7) |
| Chest discomfort | 8 (5.9 , 0.6) | 9 (4.7, 0.5) |
| Eruption on the tongue | 1 (0.7, 0.1) | 0 |
| Allergy (cold allergy, systemic rash) | 0 | 3 (1.6, 0.2) |
| Common cold | 0 | 2 (1.0, 0.1) |
| Itching sensation | 2 (1.5, 0.1) | 2 (1.0, 0.1) |
| Mild fever | 1 (0.7, 0.1) | 1 (0.5, 0.1) |
| Sweating | 4 (3.0, 0.3) | 3 (1.6, 0.2) |
| Increasing blood pressure | 8 (5.9, 0.6) | 4 (2.1, 0.2) |
| Vaginal bleeding | 0 | 2 (1.0, 0.1) |
| Total events | 135 (9.8 b) | 191 (11.2 b) |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Christensen, L.P. Ginsenosides chemistry, biosynthesis, analysis, and potential health effects. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2009, 55, 1–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y. Structure and biological activities of the polysaccharides from the leaves, roots and fruits of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer: An overview. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 85, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Lee, C.S.; Leung, K.M.; Yan, Z.K.; Shen, B.H.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Jiang, Z.H. Quantification of two polyacetylenes in radix ginseng and roots of related Panax species using a gas chromatography-mass spectrometric method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8830–8835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, X.J. Current evaluation of the millennium phytomedicine—Ginseng (II): Collected chemical entities, modern pharmacology, and clinical applications emanated from traditional Chinese medicine. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 2924–2942. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, N.H.; Son, C.G. Systematic review of randomized controlled trials evaluating the efficacy and safety of ginseng. J. Acupunct. Meridian Stud. 2011, 4, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shergis, J.L.; Zhang, A.L.; Zhou, W.; Xue, C.C. Quality and risk of bias Panax ginseng randomized controlled trial: A review. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2013, 41, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, D.H.; Bose, S.; Song, M.Y.; Lee, M.J.; Lim, C.Y.; Kwon, B.S.; Kim, H.J. Efficacy of Korean red ginseng by single nucleotide polymorphism in obese women: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, D.H.; Lee, M.J.; Lim, J.Y.; Bose, S.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, H.J. Efficacy of red ginseng by oriental medical obesity syndrome differentiation on obese women: randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Korean Med. Obes. Res. 2011, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Lee, H.S.; Hwang, M.W.; Jin, M. Effects of Korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng. C.A. Meyer) on bisphenol A exposure and gynecologic complaints: Single blind, randomized clinical trial of efficacy and safety. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.H.; Lee, N.; Ahn, Y.H.; Lee, H. Study on improving blood flow with Korean red ginseng substances using digital infrared thermal imaging and Doppler sonography: Randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial with parallel design. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2013, 33, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, H.R.; Jung, D.H.; Na, H.Y.; Kim, H.B.; Shim, J.Y. Effects of Korean red ginseng on cardiovascular risks in subjects with metabolic syndrome: A double-blind randomized controlled study. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2012, 33, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.S.; Jeong, J.C.; Park, J.K.; Ahn, H.Y.; Kim, D.I. A study on thermal effect and medication compliance of red ginseng extract. J. Oriental Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 22, 223–235. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, K.S.; Lee, J.J.; Jin, Y.R.; Yu, J.Y.; Park, E.S.; Im, J.H.; You, S.H.; Oh, K.W.; Lee, M.K.; Wee, J.J.; et al. Effect of Korean red ginseng extract on blood circulation in healthy volunteers: A randomized, double-blind, pacebo-controlled trial. J. Ginseng Res. 2007, 31, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Bang, H.J.; Kwak, J.H.; Ahn, H.Y.; Shin, D.Y.; Lee, J.H. Korean red ginseng improves glucose control in subjects with impaired fasting glucose, impaired glucose tolerance, or newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Med. Food 2014, 17, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, M.R.; Park, S.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Back, H.I.; Kim, M.G.; Jeon, J.Y.; Ha, K.C.; Na, W.T.; Cha, Y.S.; Park, B.H.; et al. Postprandial glucose-lowering effects of fermented red ginseng in subjects with impaired fasting glucose or type2 diabetes: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Ji, G.E. Diabetes-ameliorating effects of fermented red ginseng and causal effects on hormonal interactions: Testing the hypothesis by multiple group path analysis. J. Med. Food. 2013, 16, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeds, D.N.; Patterson, B.W.; Okunade, A.; Holloszy, J.O.; Polonsky, K.S.; Klein, S. Ginseng and ginsenoside Re do not improve β-cell function or insulin sensitivity in overweight and obese subjects with impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reay, J.L.; Scholey, A.B.; Milne, A.; Fenwick, J.; Kennedy, D.O. Panax ginseng has no effect on indices of glucose regulation following acute or chronic ingestion in healthy volunteers. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 101, 1679–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, H.B.; Yoon, H.K.; Lee, H.J.; Kang, S.G.; Jung, K.Y.; Kim, L. Effects of Korean red ginseng on cognitive and motor function: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reay, J.L.; Scholey, A.B.; Kennedy, D.O. Panax ginseng (G115) improves aspects of working memory performance and subjective ratings of calmness in healthy young adults. Hum. Psychopharmacol. Clin. Exp. 2010, 25, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.O.; Reay, J.L.; Scholey, A.B. Effects of 8 weeks administration of Korean Panax ginseng extract on the mood and cognitive performance of healthy individuals. J. Ginseng Res. 2007, 31, 34–43. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, T.K.; Zheng, S.; Choi, S.Y.; Cai, S.R.; Lee, Y.S.; Liu, X.Y.; Cho, K.J.; Park, K.Y. Non-organ-specific preventive effect of long-term administration of Korean red ginseng extract on incidence of human cancers. J. Med. Food 2010, 13, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, S.K.; Hong, Y.; Yun, B.Y.; Chon, S.J.; Jung, Y.S.; Park, J.H.; Cho, S.; Choi, Y.S.; Lee, B.K. Antioxidative effects of Korean red ginseng in postmenopausal women: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 154, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, O.Y.; Lee, J.H. Beneficial effects of Korean red ginseng on lymphocyte DNA damage, antioxidant enzyme activity, and LDL oxidation in healthy participants: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nutr. J. 2012, 11, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.G.; Yoo, S.R.; Park, H.J.; Lee, N.H.; Shin, J.W.; Sathyanath, R.; Cho, J.H.; Son, C.G. Antioxidant effects of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer in healthy subjects: A randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 2229–2235. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.G.; Cho, J.H.; Yoo, S.R.; Lee, J.S.; Han, J.M.; Lee, N.H.; Ahn, Y.C.; Son, C.G. Antifatigue effects of Panax ginseng C.A Meyer: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.L.; Kwak, H.E.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, Y.C.; Lee, C.D.; Byurn, H.K.; Kang, H.Y. Effects of Panax ginseng supplementation on muscle damage and inflammation after uphill treadmill running in humans. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2011, 39, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.J.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, C.J.; Park, H.C.; Kang, K.H.; Kim, M.J.; Kang, S.M.; Kwak, U.H.; Kim, H.J. Effect of red ginseng supplementation on aerobic.anaerobic performance, central and peripheral fatigue. J. Ginseng Res. 2008, 32, 210–219. [Google Scholar]
- Kulaputana, O.; Thanakomsirichot, S.; Anomasiri, W. Ginseng supplementation does not change lactate threshold and physical performances in physically active Thai man. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2007, 90, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, K.J.; Chae, M.J.; Lee, H.S.; Hong, H.D.; Park, K. Effects of Korean red ginseng on sexual arousal in menopausal women: Placebo-controlled, double-blind crossover clinical study. J. Sex. Med. 2010, 7, 1469–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ham, W.S.; Kim, W.T.; Lee, J.S.; Ju, H.J.; Kang, S.J.; Oh, J.H.; Her, Y.; Chung, J.Y.; Park, K.S.; Choi, Y.D. Efficacy and safety of red ginseng extract powder in patients with erectile dysfunction: Multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Korean J. Urol. 2009, 50, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.I.; Choi, M.S.; Ahn, H.Y. Efficacy and safety of red ginseng on women’s health related quality of life and sexual function. J. Ginseng Res. 2009, 33, 115–126. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.H.; Jeon, S.H.; Hahn, E.J.; Paek, K.Y.; Park, J.K.; Youn, N.Y.; Lee, H.L. Effects of tissue-cultured mountain ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) extract on male patients with erectile dysfunction. Asian J. Androl. 2009, 11, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Andrade, E.; de Mesquita, A.A.; Claro, J.A.; de Andrade, P.M.; Ortiz, V.; Paranhos, M.; Srougi, M. Study of the efficacy of Korean red ginseng in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Asian J. Androl. 2007, 9, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Woo, S.H.; Jo, S.H.; Hahn, E.J.; Youn, N.Y.; Lee, H.L. Double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center study for therapeutic effects of mountain Panax ginseng C.A Meyer extract in men with erectile dysfunction: A preliminary report. Korean J. Androl. 2006, 24, 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.Y.; Seo, S.K.; Choi, Y.M.; Jeon, Y.E.; Lim, K.J.; Cho, S.; Choi, Y.S.; Lee, B.S. Effects of red ginseng supplementation on menopausal symptoms and cardiovascular risk factors in postmenopausal woman: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Menopause 2012, 19, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Yoon, Y.J.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, C.H.; Jang, J.B.; Lee, K.S.; Cho, J.H. A clinical study on the effect of red ginseng for postmenopausal hot flushes. J. Oriental Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 22, 132–139. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, Y.H.; Ahn, S.C.; Lee, S.Y.; Jeong, D.W.; Choi, E.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.G.; Lee, Y.H.; Shin, B.C. Effect of Korean red ginseng on insulin sensitivity in non-diabetic healthy overweight and obese adults. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 22, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.S.; Lee, J.H.; Oh, M.; Choi, K.M.; Jeong, M.R.; Park, J.D.; Kwon, D.Y.; Ha, K.C.; Park, E.O.; Lee, N.; et al. Preventive effect of Korean red ginseng for acute respiratory illness: A randomized and double-blind clinical trial. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2012, 27, 1472–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.W.; Kang, H.R.; Ji, G.E.; Park, M.S.; Song, W.J.; Kim, M.H.; Kwon, J.W.; Kim, T.W.; Park, H.W.; Cho, S.H.; et al. Therapeutic effects of fermented red ginseng in allergic rhinitis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2011, 3, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Choi, J.J.; Ahn, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Oh, K.W.; Kim, S.Y. Effects of red ginseng extract on sleeping behaviors in human volunteers. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 149, 597–599. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.A.; Kang, S.G.; Lee, H.J.; Jung, K.Y.; Kim, L. Effect of Korean red ginseng on sleep: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Sleep Med. Psychophysiol. 2010, 17, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Kitaoka, K.; Uchida, K.; Okamoto, N.; Chikahisa, S.; Miyazaki, T.; Takeda, E.; Sei, H. Fermented ginseng improves the first-night effect in humans. Sleep 2009, 32, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Doosti, A.; Lotfi, Y.; Moossavi, A.; Bakhshi, E.; Talasaz, A.H.; Hoorzad, A. Comparison of the effects of N-actyl-cysteine and ginseng in prevention of noise induced hearing loss in male textile workers. Noise Health 2014, 16, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Braz, A.S.; Morais, L.C.; Paula, A.P.; Diniz, M.F.; Almeida, R.N. Effects of Panax ginseng extract in patients with fibromyalgia: A 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Rev. Bras. Psiquiatr. 2013, 35, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.H.; Yoo, S.R.; Kim, H.G.; Cho, J.H.; Son, C.G. Safety and tolerability of Panax ginseng root extract: A randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial in healthy Korean volunteers. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2012, 18, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.W.; Lee, B.J.; Bu, Y.M.; Yeo, I.W.; Kim, J.S.; Ryu, B.H. Effects of Korean red ginseng on dry mouth: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Ginseng Res. 2010, 34, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.H.; Shin, W.Y.; Song, Y.J.; Yu, B.H. Effect of Korean red ginseng on somatic symptoms in a general population in Korea. J. Ginseng Res. 2009, 33, 219–222. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Yi, S.M.; Choi, J.E.; Son, S.W. Study of the efficacy of Korean red ginseng in the treatment of androgenic alopecia. J. Ginseng Res. 2009, 33, 223–228. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, J.C.; Han, S.W.; Byun, J.S.; An, H.D.; Ha, I.D.; Cho, G.H.; Leem, K.H. The effects of ginseng and American ginseng on general symptom in Koreans and Chineses–double-blind randomized controlled trials. J. Ginseng Res. 2005, 29, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.J.; Ji, G.E. The effect of fermented red ginseng on depression is mediated by lipids. Nutr. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shergis, J.L.; Zhang, A.L.; Zhou, W.; Xue, C.C. Panax ginseng in randomized controlled trials: A systematic review. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 949–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Kim, T.H.; Choi, T.Y.; Lee, M.S. Ginseng for health care: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials in Korean literature. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coon, J.T.; Ernst, E. Panax ginseng a systematic review of adverse effects and drug interactions. Drug Saf. 2002, 25, 323–344. [Google Scholar]
- Izzo, A.A.; Ernst, E. Interactions between herbal medicines and prescribed drugs: An updated systematic review. Drugs 2009, 69, 1777–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Williams, K.M.; Liauw, W.S.; Ammit, A.J.; Roufogalis, B.D.; Duke, C.C.; Day, R.O.; McLachlan, A.J. Effect of St John’s wort and ginseng on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of warfarin in healthy subjects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2004, 57, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Ahn, Y.M.; Ahn, S.Y.; Doo, H.K.; Lee, B.C. Interaction between warfarin and Panax ginseng in ischemic stroke patients. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2008, 14, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H.; Lee, B.K.; Choi, Y.J.; Yoon, I.K.; Chang, B.C.; Gwak, H.S. Interaction between warfarin and Korean red ginseng in patients with cardiac valve replacement. Int. J. Cardiol. 2010, 145, 275–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.-S.; Woo, J.-Y.; Han, C.-K.; Chang, I.-M. Safety Analysis of Panax Ginseng in Randomized Clinical Trials: A Systematic Review. Medicines 2015, 2, 106-126. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines2020106
Kim Y-S, Woo J-Y, Han C-K, Chang I-M. Safety Analysis of Panax Ginseng in Randomized Clinical Trials: A Systematic Review. Medicines. 2015; 2(2):106-126. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines2020106
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Young-Sook, Jung-Yoon Woo, Chang-Kyun Han, and Il-Moo Chang. 2015. "Safety Analysis of Panax Ginseng in Randomized Clinical Trials: A Systematic Review" Medicines 2, no. 2: 106-126. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines2020106
APA StyleKim, Y.-S., Woo, J.-Y., Han, C.-K., & Chang, I.-M. (2015). Safety Analysis of Panax Ginseng in Randomized Clinical Trials: A Systematic Review. Medicines, 2(2), 106-126. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines2020106





