Is the Impact of Sodium–Glucose Co-Transporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors on Bone Metabolism and Fracture Incidence a Class or Drug Effect? A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Search
3. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Bone Metabolism
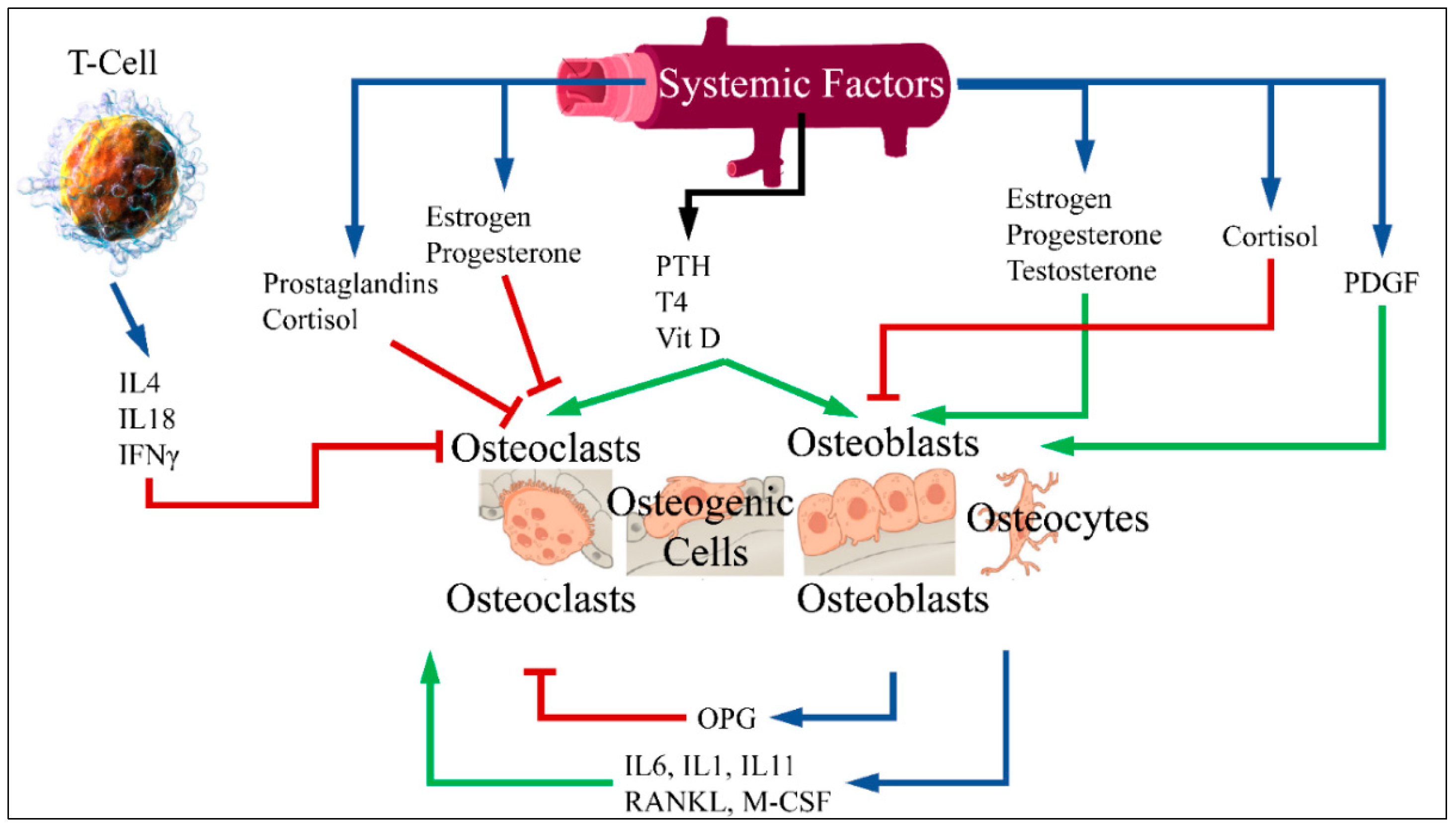
3.1. Bone Metabolism
3.2. Antidiabetic Treatments and Bone Metabolism
4. Insights into SGLT2 Inhibitors and Bone Metabolism
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMD | Bone mineral density |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CT | Computer tomography |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| DXA | Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry |
| FGF23 | Fibroblast growth factor 23 |
| GLP1RAs | Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists |
| IDF | International Diabetes Federation |
| IFNγ | Interferon gamma |
| M-CSF | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| OPG | Osteoprotegerin |
| PDGF | Platelet-Derived Growth Factor |
| PPARγ | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ |
| PTH | Parathormone |
| RANKL | Receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand |
| SGLT2 | Sodium–glucose co-transporter 2 |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| T4 | Thyroxine |
| TNF | Tumor Necrosis Factor |
| TRACP-5b | Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase-5b |
| TZD | Thiazolidinedione |
| Vit D | Vitamin D |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- World Health Organization. Therapeutic Patient Education: Continuing Education Programmes for Health Care Providers in the Field of Prevention of Chronic Diseases: Report of a WHO Working Group. 1998. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/108151/E63674.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Non-Communicable Diseases 2010. 2011. Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/44579 (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- O’Connell, J.M.; Manson, S.M. Understanding the Economic Costs of Diabetes and Prediabetes and What We May Learn About Reducing the Health and Economic Burden of These Conditions. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1609–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IDF. IDF Diabetes Atlas; IDF: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization; International Diabetes Federation. Definition and Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus and Intermediate Hyperglycaemia: Report of a WHO/IDF Consultation; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 1. Improving Care and Promoting Health in Populations: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care 2024, 48, S14–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Summary of Revisions: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care 2024, 48, S6–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, M.; Sharma, R.; Mubarik, S.; Aashima, A.; Zhang, K. Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM): Spatial-temporal Patterns of Incidence, Mortality and Attributable Risk Factors from 1990 to 2019 among 21 World Regions. Endocrine 2022, 77, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagnani, A.; Gonnelli, S. Antidiabetic therapy effects on bone metabolism and fracture risk. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2013, 15, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Office of the Surgeon General. Reports of the Surgeon General. In Bone Health and Osteoporosis: A Report of the Surgeon General; Office of the Surgeon General (US): Rockville, MD, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, G.; Liu, H.; Lu, H. Glucagon-like peptide-1(GLP-1) receptor agonists: Potential to reduce fracture risk in diabetic patients? Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 81, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjidakis, D.J.; Androulakis, I.I. Bone remodeling. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1092, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniilopoulou, I.; Vlachou, E.; Lambrou, G.I.; Ntikoudi, A.; Dokoutsidou, E.; Fasoi, G.; Govina, O.; Kavga, A.; Tsartsalis, A.N. The Impact of GLP1 Agonists on Bone Metabolism: A Systematic Review. Medicina 2022, 58, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsartsalis, A.N.; Dokos, C.; Kaiafa, G.D.; Tsartsalis, D.N.; Kattamis, A.; Hatzitolios, A.I.; Savopoulos, C.G. Statins, bone formation and osteoporosis: Hope or hype? Hormones 2012, 11, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosenzon, O.; Wei, C.; Davidson, J.; Scirica, B.M.; Yanuv, I.; Rozenberg, A.; Hirshberg, B.; Cahn, A.; Stahre, C.; Strojek, K.; et al. Incidence of Fractures in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes in the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 2142–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, A.K.; Rosenthal, R.S.; Cao, X.; Saag, K.G. The effect of thiazolidinediones on BMD and osteoporosis. Nat. Clin. Pract. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 4, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.H.; Horng, M.H.; Yeh, S.Y.; Lin, I.C.; Yeh, C.J.; Muo, C.H.; Sung, F.C.; Kao, C.H. Glycemic Control with Thiazolidinedione Is Associated with Fracture of T2DM Patients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonopoulou, M.; Bahtiyar, G.; Banerji, M.A.; Sacerdote, A.S. Diabetes and bone health. Maturitas 2013, 76, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, A.; D’Onofrio, L.; Eastell, R.; Schwartz, A.V.; Pozzilli, P.; Napoli, N. Oral anti-diabetic drugs and fracture risk, cut to the bone: Safe or dangerous? A narrative review. Osteoporos. Int. 2015, 26, 2073–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Liang, J.; Yu, M.; Qu, X. Effect of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors on Bone Metabolism and the Possible Underlying Mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, A.; Vickneson, K.; Singh, J.S. SGLT2-inhibitors; more than just glycosuria and diuresis. Heart Fail. Rev. 2021, 26, 623–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, I.; Rashid, T.; Jaikaransingh, V.; Heilig, C.; Abdel-Rahman, E.M.; Awad, A.S. SGLT2 inhibitors: Beyond glycemic control. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 2024, 35, 100335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Lv, R.; Wang, J.; Che, L.; Wang, Z.; Huai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L. The Extraglycemic Effect of SGLT-2is on Mineral and Bone Metabolism and Bone Fracture. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 918350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Zhao, C.; Liang, J.; Yang, Y.; Yu, M.; Qu, X. Effect of Sodium-Glucose Co-transporter 2 Inhibitors on Bone Metabolism and Fracture Risk. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshizaka, M.; Ishikawa, K.; Ishibashi, R.; Takahashi, S.; Sakamoto, K.; Yokoh, H.; Baba, Y.; Ide, S.; Ide, K.; Ishikawa, T.; et al. Comparison of Visceral Fat Reduction by Ipragliflozin and Metformin in Elderly Type 2 Diabetes Patients: Sub-Analysis of a Randomized-Controlled Study. Diabetes Ther. Res. Treat. Educ. Diabetes Relat. Disord. 2021, 12, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blau, J.E.; Bauman, V.; Conway, E.M.; Piaggi, P.; Walter, M.F.; Wright, E.C.; Bernstein, S.; Courville, A.B.; Collins, M.T.; Rother, K.I.; et al. Canagliflozin triggers the FGF23/1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D/PTH axis in healthy volunteers in a randomized crossover study. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e99123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Guo, A.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, H. The effect of empagliflozin (sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor) on osteoporosis and glycemic parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes: A quasi-experimental study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2024, 25, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, T.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, Y.; Xue, M.; Xu, L.; Liu, X.; Yu, X.; Sun, B.; Chen, L. Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on fractures and bone mineral density in type 2 diabetes: An updated meta-analysis. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2019, 35, e3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sheng, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, Y. Effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on fractures, BMD, and bone metabolism markers in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos. Int. 2023, 34, 2013–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimadhyam, S.; Lee, T.A.; Calip, G.S.; Smith Marsh, D.E.; Layden, B.T.; Schumock, G.T. Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors and the risk of fractures: A propensity score-matched cohort study. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2019, 28, 1629–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, K.; Moseley, K.F. Diabetes and Bone Fragility: SGLT2 Inhibitor Use in the Context of Renal and Cardiovascular Benefits. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2020, 18, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.J.; Ha, K.H.; Lee, N.; Kim, D.J. Effectiveness and safety of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors compared with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in older adults with type 2 diabetes: A nationwide population-based study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, A.; Shigeno, R.; Horie, I.; Morimoto, S.; Ito, A.; Chiba, K.; Kawazoe, Y.; Tashiro, S.; Miyamoto, J.; Sato, S.; et al. The effect of luseogliflozin on bone microarchitecture in older patients with type 2 diabetes: Study protocol for a randomized controlled pilot trial using second-generation, high-resolution, peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT). Trials 2020, 21, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masajtis-Zagajewska, A.; Hołub, T.; Pęczek, K.; Makówka, A.; Nowicki, M. Different Effects of Empagliflozin on Markers of Mineral-Bone Metabolism in Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Patients with Stage 3 Chronic Kidney Disease. Medicina 2021, 57, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islek, T.; Mirioglu, S.; Gursu, M.; Kazancioglu, R.; Demirel, M.; Selek, S.; Elcioglu, O.C. Short-term effects of dapagliflozin on biomarkers of bone and mineral metabolism in patients with diabetic kidney disease: A prospective observational study. Nefrologia 2024, 44, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Lei, C. Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on bone metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2024, 24, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zibellini, J.; Seimon, R.V.; Lee, C.M.; Gibson, A.A.; Hsu, M.S.; Shapses, S.A.; Nguyen, T.V.; Sainsbury, A. Does Diet-Induced Weight Loss Lead to Bone Loss in Overweight or Obese Adults? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2015, 30, 2168–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napolitano, A.; Miller, S.; Murgatroyd, P.R.; Hussey, E.; Dobbins, R.L.; Bullmore, E.T.; Nunez, D.J.R. Exploring glycosuria as a mechanism for weight and fat mass reduction. A pilot study with remogliflozin etabonate and sergliflozin etabonate in healthy obese subjects. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 2014, 1, e3–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, W.P.; Wang, R.; Ang, L.W.; Heng, D.; Yuan, J.M.; Yu, M.C. Diabetes and risk of hip fracture in the Singapore Chinese Health Study. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1766–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppolino, G.; Bolignano, D.; De Paola, L.; Giulino, C.; Mannella, A.; Riccio, M.; Mascaro, M.A.; Lombardi, G.; Fuiano, G.; Lombardi, L.; et al. Parathyroid hormone and mobilization of circulating bone marrow-derived cells in uremic patients. J. Investig. Med. 2011, 59, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, G.; Di Somma, C.; Rubino, M.; Faggiano, A.; Vuolo, L.; Guerra, E.; Contaldi, P.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A. The roles of parathyroid hormone in bone remodeling: Prospects for novel therapeutics. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2011, 34, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Z.; Wang, R.; Ang, L.W.; Yuan, J.M.; Koh, W.P. Dietary B vitamin intake and risk of hip fracture: The Singapore Chinese Health Study. Osteoporos. Int. 2013, 24, 2049–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lambrou, G.I.; Samartzi, A.; Vlachou, E.; Tsartsalis, A.N. Is the Impact of Sodium–Glucose Co-Transporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors on Bone Metabolism and Fracture Incidence a Class or Drug Effect? A Narrative Review. Medicines 2025, 12, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines12020010
Lambrou GI, Samartzi A, Vlachou E, Tsartsalis AN. Is the Impact of Sodium–Glucose Co-Transporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors on Bone Metabolism and Fracture Incidence a Class or Drug Effect? A Narrative Review. Medicines. 2025; 12(2):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines12020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleLambrou, George I., Athanasia Samartzi, Eugenia Vlachou, and Athanasios N. Tsartsalis. 2025. "Is the Impact of Sodium–Glucose Co-Transporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors on Bone Metabolism and Fracture Incidence a Class or Drug Effect? A Narrative Review" Medicines 12, no. 2: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines12020010
APA StyleLambrou, G. I., Samartzi, A., Vlachou, E., & Tsartsalis, A. N. (2025). Is the Impact of Sodium–Glucose Co-Transporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors on Bone Metabolism and Fracture Incidence a Class or Drug Effect? A Narrative Review. Medicines, 12(2), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines12020010







