Use of End-to-End Tool for the Analysis of the Digital Governance of Ports
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. State of the Art
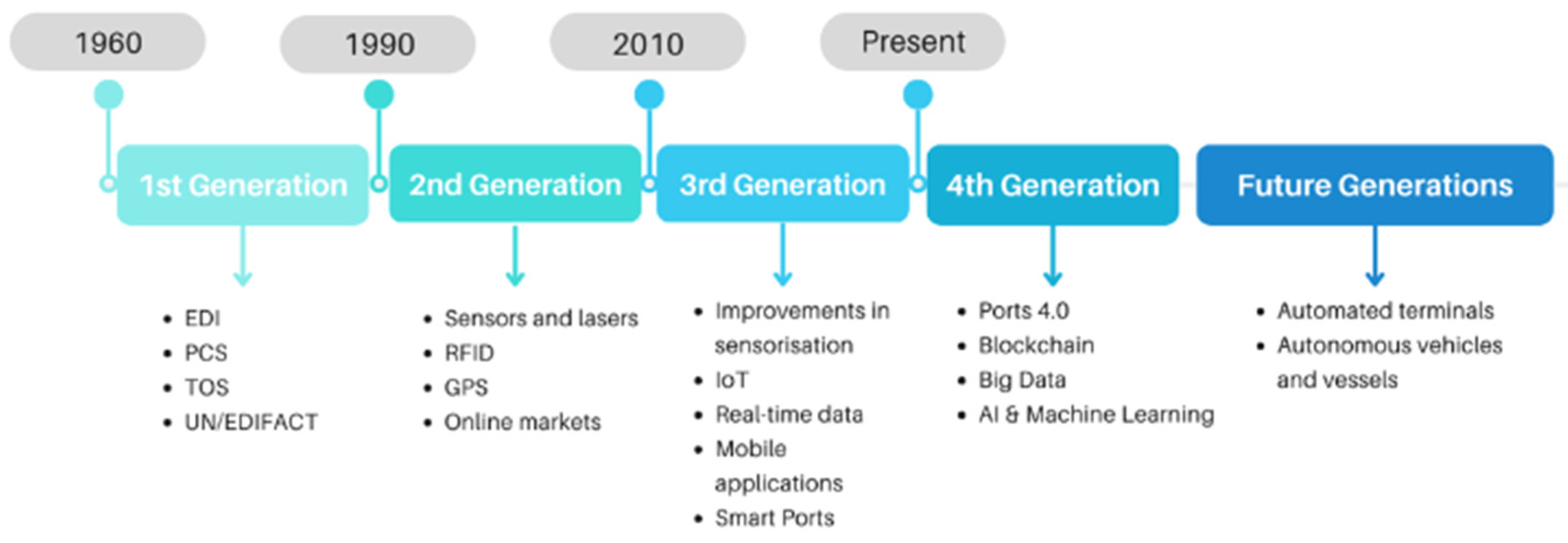
2.1. The Digital Governance of Ports: Evolution to the Present
2.2. Digital Governance: Contributions and Benefits to Ports
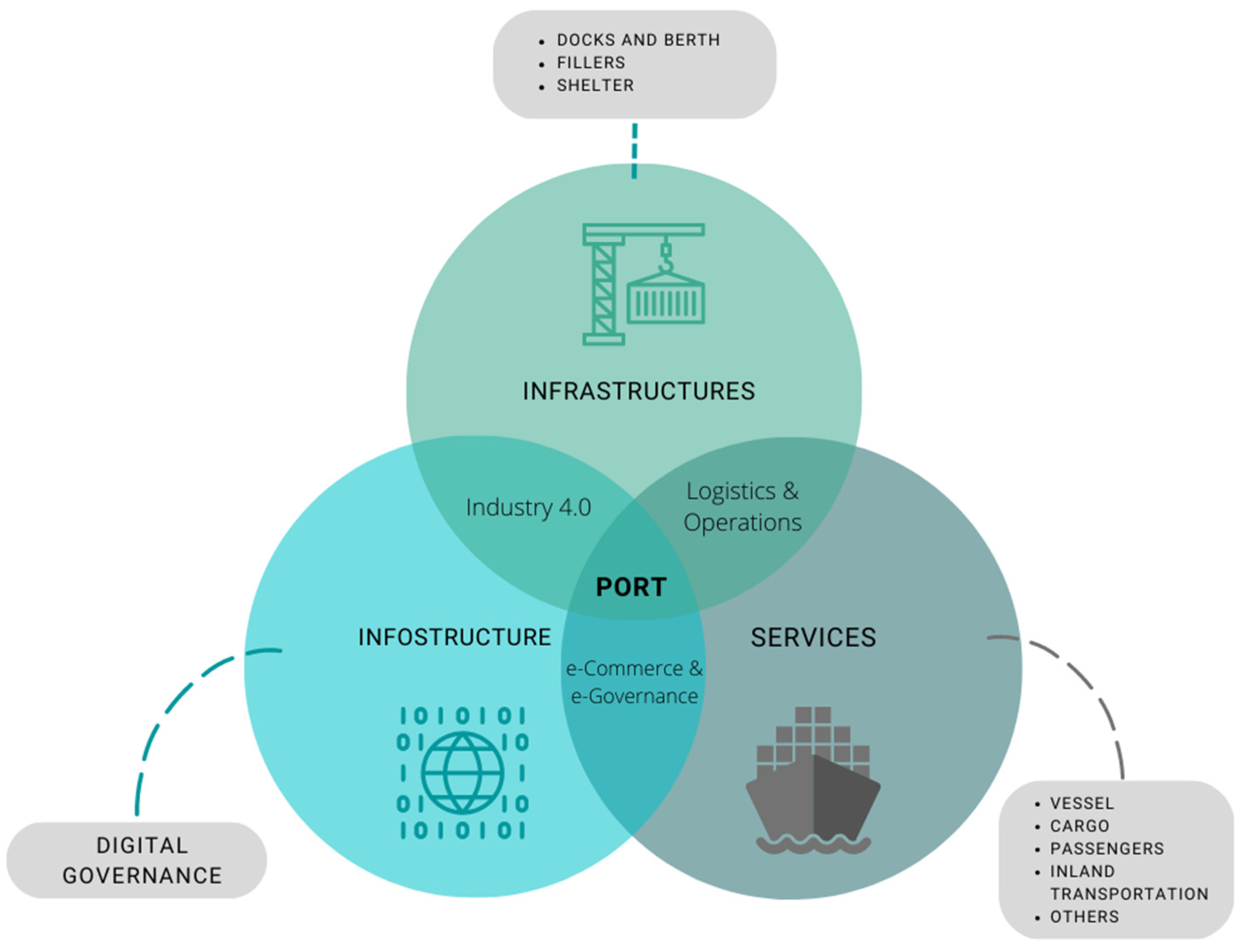
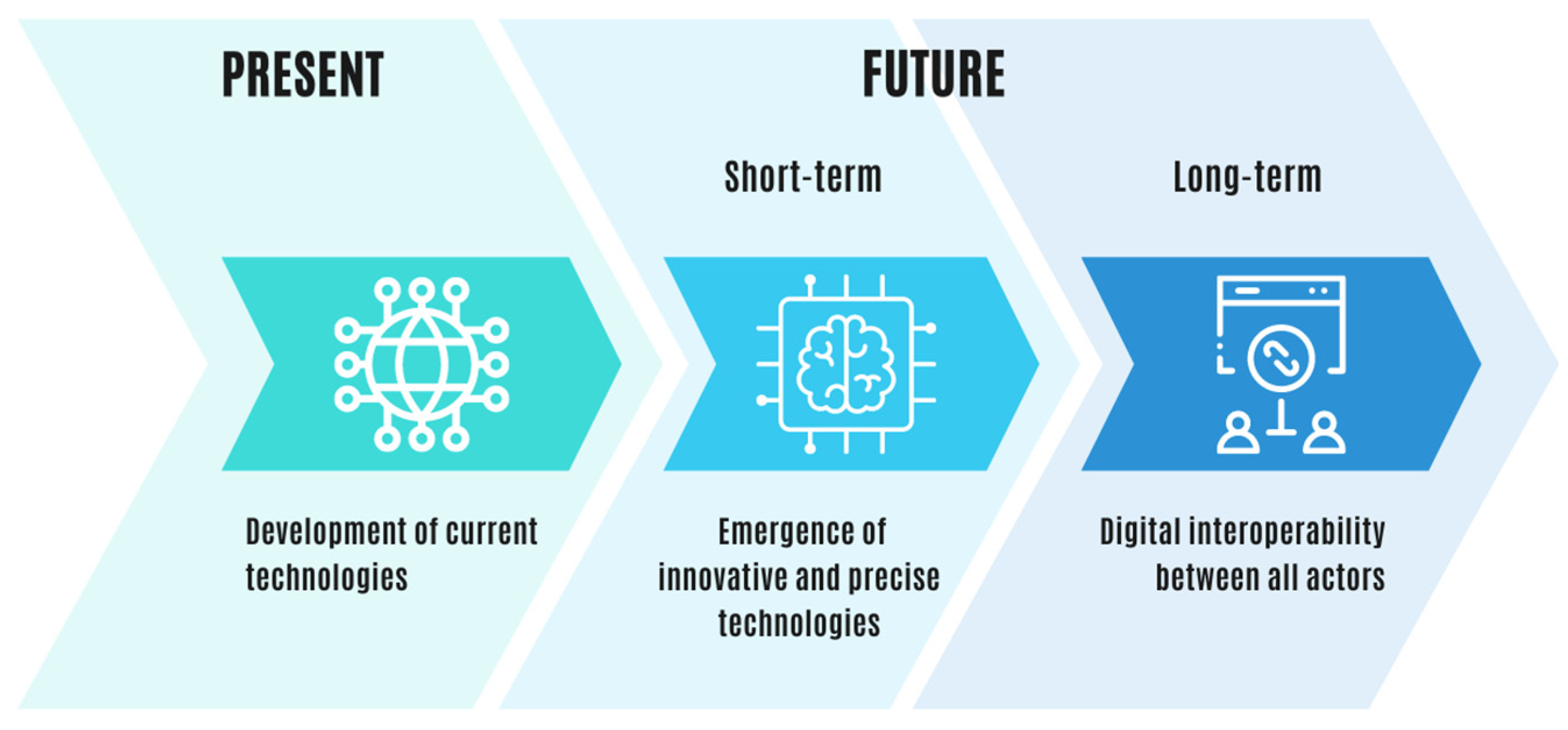
2.3. Digital Governance: Contributions and Benefits of End-to-End Tool
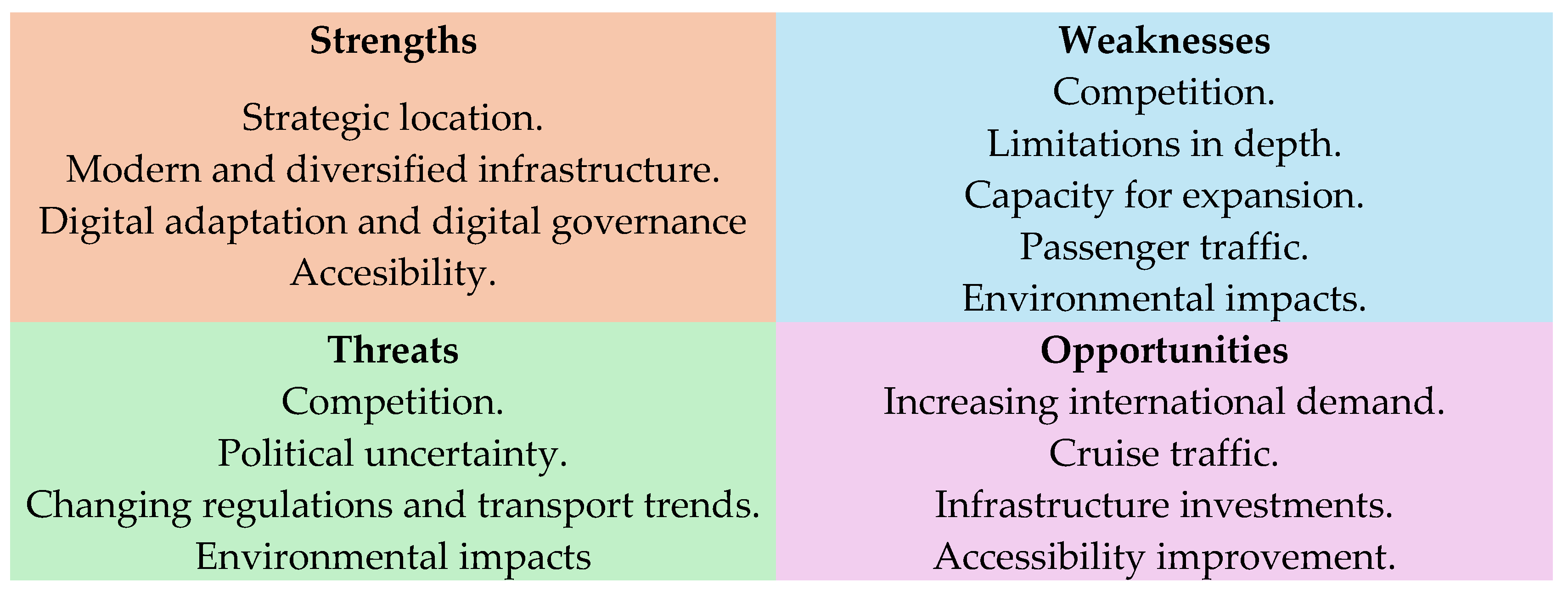
3. Methodology and Results
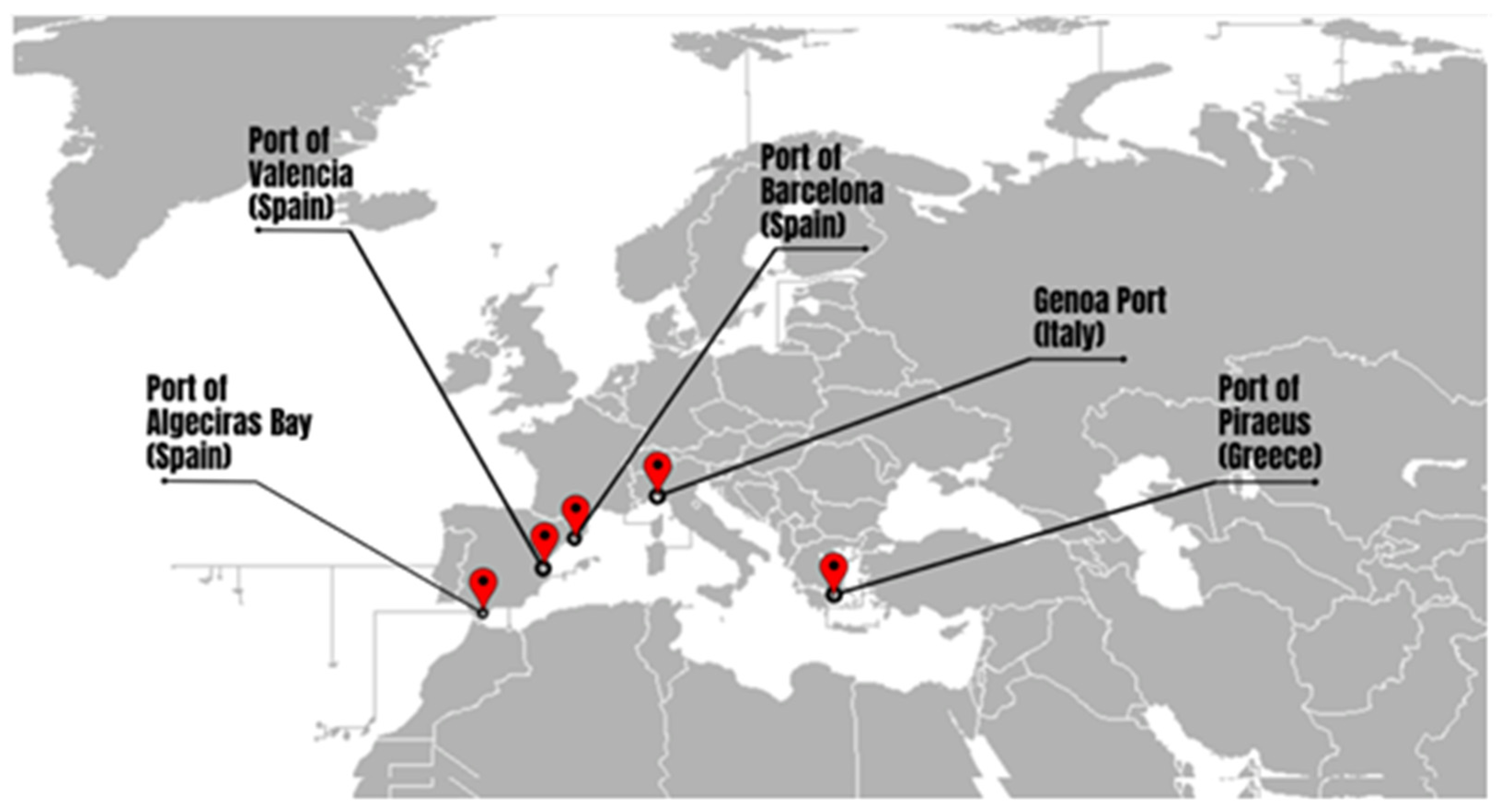
3.1. Approach to the Application Case
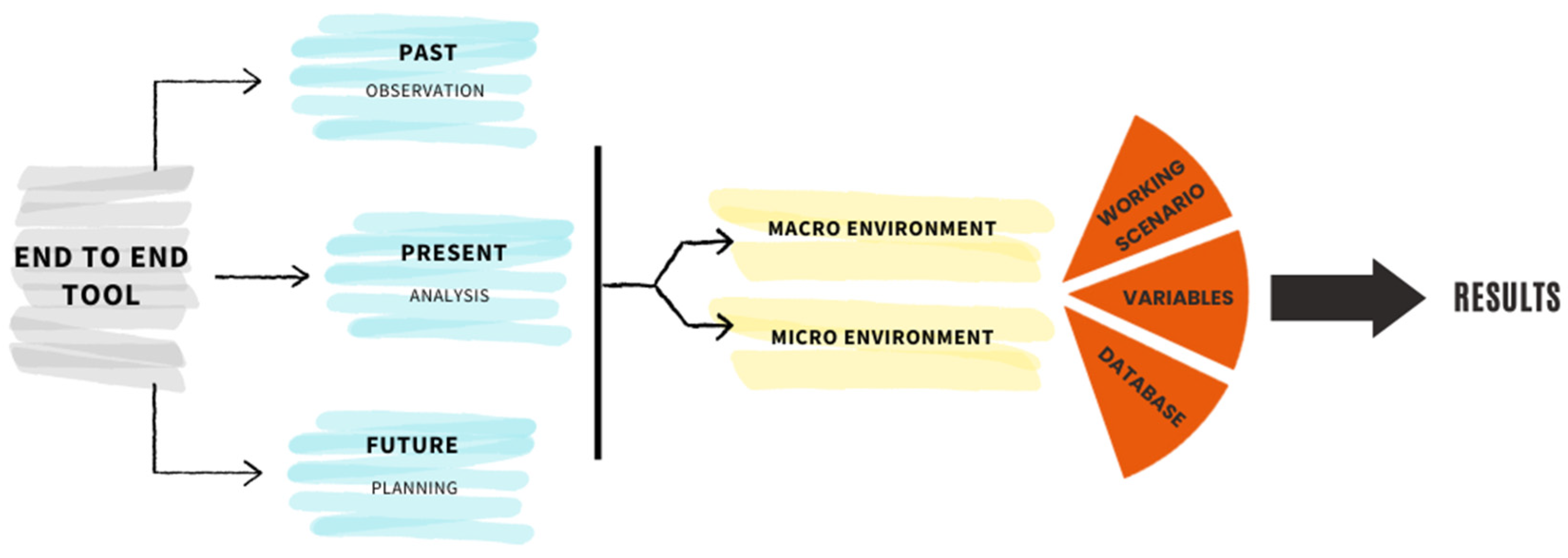
3.2. Method: Applying End-to-End Tool
3.2.1. Past
- Historical experience
- Main activity
- Strategy
- International relations
- Technological evolution
3.2.2. Present
- Level of digitalization and digital governance.
- Environmental impacts
- Competitiveness and connectivity between ports
- Infrastructure development
3.2.3. Macroenvironment
3.2.4. Microenvironment
4. Analysis of Results
5. Conclusions
- Public policies and private initiatives are essential to foster the adoption of digital governance and enhance the competitiveness of the sector.
- The receipt by the ports of fiscal incentives and the promotion of public–private collaborations with continuous training and reskilling programs.
- The proclamation and adoption of standards and protocols for the interoperability of port management systems.
- The promotion of a business culture that promotes the innovation and adoption of digital technologies for the correct management of data or infostructure.
- Access to necessary financing due to the presence of high costs associated with the implementation of the measures in question.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| EDI | Electronic data interchange |
| PCS | Port community system |
| TOS | Terminal Operator system |
| ONU/EDIFACT | Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Trade and Transport. |
| RFID | Radio Frequency Identification |
| GPS | geographic position system |
| IoT | Internet of things |
References
- Gómez Díaz, C.; González-Cancelas, N.; Camarero Orive, A.; Soler Flores, F. Digital Governance Approach to the Spanish Port System: Proposal for a Port. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarero, A.; Cancelas, N.G.; Verdesoto, V. Impact of COVID-19 on the cost of technical services in European ports. In Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Maritime Engineering, Online, 24 March 2022; Thomas Telford Ltd.: London, UK, 2022; pp. 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Port Economics, Management and Policy. Routledge & CRC Press: London, UK. Available online: https://www.routledge.com/Port-Economics-Management-and-Policy/Notteboom-Notteboom-Pallis-Pallis-Rodrigue-Rodrigue/p/book/9780367331559 (accessed on 29 April 2024).
- González-Cancelas, N.; Serrano, B.M.; Flores, F.S.; C-Majolero, N. Diagnosis of the digilatization of the Spanish ports: End to End tool. World Sci. News 2021, 155, 47–64. [Google Scholar]
- Clemente, D.; Cabral, T.; Rosa-Santos, P.; Taveira-Pinto, F. Blue Seaports: The Smart, Sustainable and Electrified Ports of the Future. Smart Cities 2023, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancelas, N.G.; Cabrero, J.V.; Orive, A.C. Metaverse in Spanish ports as a high impact solution. World Sci. News 2023, 181, 145–163. [Google Scholar]
- Cancelas, N.G.; Serrano, B.M.; Flores, F.S. Federated Learning for Spanish Ports as an Aid to Digitization. J. KONBiN 2021, 51, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaia, G.; Arkhipova, D.; DeLone, W. Digital governance mechanisms and principles that enable agile responses in dynamic competitive environments. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 2022, 31, 662–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmoukari, B.; Audy, J.-F.; Forget, P. Smart port: A systematic literature review. Eur. Transp. Res. Rev. 2023, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijan, E.; Jović, M.; Aksentijević, S.; Pucihar, A. Digital transformation in the maritime transport sector. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 170, 120879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H. Developing a smart port architecture and essential elements in the era of Industry 4.0. Marit. Econ. Logist. 2022, 24, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lun, Y.V.; Lai, K.; Cheng, T.E.; Yang, D. New Technology Development in the Shipping Industry. In Shipping and Logistics Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 257–279. [Google Scholar]
- Notteboom, T.; Pallis, T.; Rodrigue, J.-P. Disruptions and resilience in global container shipping and ports: The COVID-19 pandemic versus the 2008–2009 financial crisis. Marit. Econ. Logist. 2021, 23, 179–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acciaro, M.; Renken, K.; El Khadiri, N. Technological change and logistics development in European ports. In European Port Cities in Transition; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 73–88. [Google Scholar]
- Senyo, P.K.; Effah, J.; Osabutey, E.L.C. Digital platformisation as public sector transformation strategy: A case of Ghana’s paperless port. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 162, 120387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, A.; El-gazzar, S.; Knez, M. A framework for adopting a sustainable smart sea port index. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapkaeva, N.; Gurzhiy, A.; Maydanova, S.; Levina, A. Digital Platform for Maritime Port Ecosystem: Port of Hamburg Case. Transp. Res. Procedia 2021, 54, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wu, L.; Wang, S.; Jia, H.; Li, K.X. How big data enriches maritime research—A critical review of Automatic Identification System (AIS) data applications. Transp. Rev. 2019, 39, 755–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secinaro, S.; Brescia, V.; Iannaci, D.; Jonathan, G.M. Does Citizen Involvement Feed on Digital Platforms? Int. J. Public Adm. 2022, 45, 708–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dev, N.K.; Shankar, R.; Qaiser, F.H. Industry 4.0 and circular economy: Operational excellence for sustainable reverse supply chain performance. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 153, 104583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attaran, M. Digital technology enablers and their implications for supply chain management. Supply Chain Forum. Int. J. 2020, 21, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlitz, L.; Meyer, C. Small and Medium-Sized Ports in the TEN-T Network and Nexus of Europe’s Twin Transition: The Way towards Sustainable and Digital Port Service Ecosystems. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.W.; Hasan, H.; Jayaraman, R.; Salah, K.; Omar, M. Blockchain applications and architectures for port operations and logistics management. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2021, 41, 100620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inkinen, T.; Helminen, R.; Saarikoski, J. Port Digitalization with Open Data: Challenges, Opportunities, and Integrations. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2019, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, Z.; Woxenius, J.; Vural, C.A.; Lind, M. Digital transformation of maritime logistics: Exploring trends in the liner shipping segment. Comput. Ind. 2023, 145, 103811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inkinen, T.; Helminen, R.; Saarikoski, J. Technological trajectories and scenarios in seaport digitalization. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2021, 41, 100633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijan, E.; Jović, M.; Panjako, A.; Žgaljić, D. The Role of Port Authority in Port Governance and Port Community System Implementation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappalainen, A.; Rosenberg, C. Bridging the digital divide: Success depends on content provider and application developer involvement [point of view]. Proc. IEEE 2021, 109, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orive, A.C.; Santiago, J.I.P.; Corral, M.M.E.-I.; González-Cancelas, N. Strategic Analysis of the Automation of Container Port Terminals through BOT (Business Observation Tool). Logistics 2020, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, E.R.; González-Cancelas, N.; Orive, A.C.; Díaz-Gutiérrez, D. Green Ports Analysis Using an End-to-End Tool Application in the Fishing Port of Vigo. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelona es el Principal Puerto de Cruceros del Mediterráneo y de Europa con 2.68 Millones de Cruceristas y 758 Escalas en 2016|Red Social de Cruceros|Nudoss.com. Available online: http://nudoss.com/barcelona-principal-puerto-de-cruceros-del-mediterraneo-y-de-europa/ (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Amministrazione Trasparente Autorita’ Di Sistema Portuale Del Mar Ligure Occidentale—Gazzetta Amministrativa. Available online: https://ww2.gazzettaamministrativa.it/opencms/opencms/_gazzetta_amministrativa/amministrazione_trasparente/_liguria/_autorita___di_sistema_portuale_del_mar_ligure_occidentale/ (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Platias, C.; Spyrou, D. EU-Funded Energy-Related Projects for Sustainable Ports: Evidence from the Port of Piraeus. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
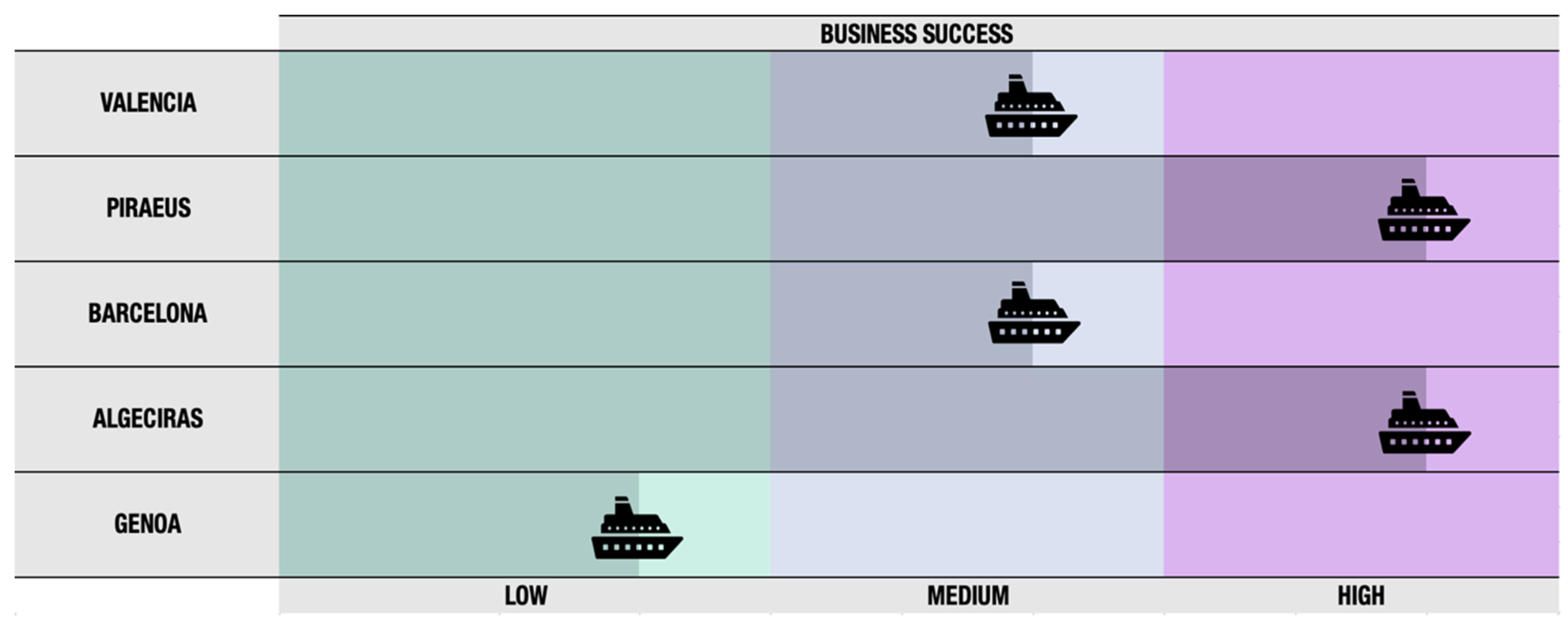


| INDICATORS | Port of Valencia | Port of Piraeus | Port of Barcelona | Port of Algeciras | Genoa Port | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Historical experience | Middle Ages | S. V b.C. | Middle Ages | 1894 | Middle Ages | |||||
| Principal activity | ||||||||||
| Container |  |  |  |  |  | |||||
| Passengers |  |  |  |  | ||||||
| Bulk |  |  | ||||||||
| Strategy | ||||||||||
| Efficiency |  |  |  | |||||||
| Specialization |  |  |  | |||||||
| Diversification |  | |||||||||
| Intermodality |  |  |  | |||||||
| International relations | Italy, France, Morocco | Italy, Spain, Turkey | Italy, France, Morocco | Africa, Latin America, Mediterranean Sea, Northern Europe | Spain, France, Greece | |||||
| Technological evolution | 5 out of 5 | 2 out of 5 | 4 out of 5 | 3 out of 5 | 3 out of 5 | |||||
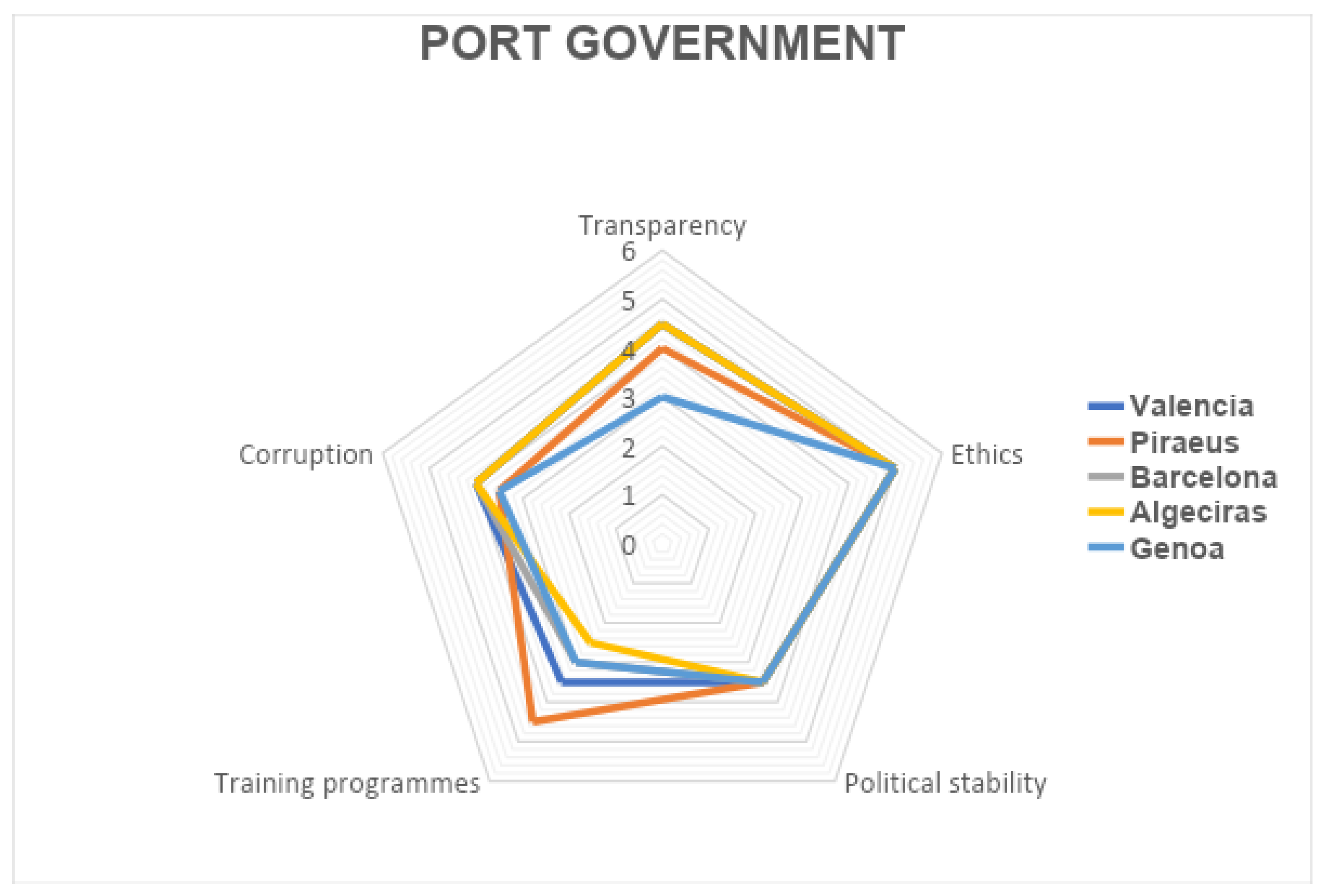
| Category | Subcategory | ID | Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Past | Pa_1 | Historical experience | |
| Pa_2 | Principal activity | ||
| Pa_3 | Strategy | ||
| Pa_4 | International relations | ||
| Pa_5 | Technological evolution | ||
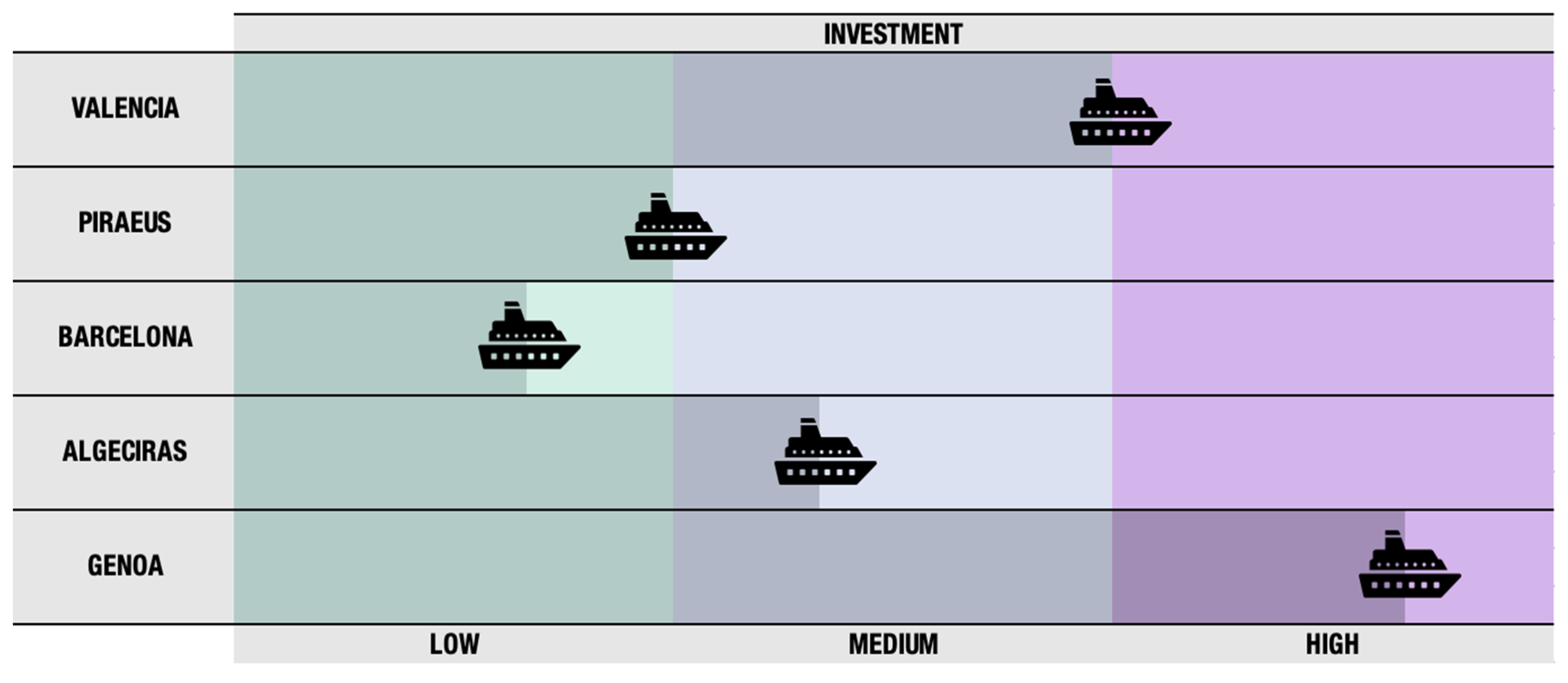
| Present | Economic | MaE_1 | Cargo volume |
| Macro Environment | MaE_2 | Number of berths | |
| MaE_3 | Infrastructure investment | ||
| MaE_4 | Total traffic | ||
| Institutional | MaI_1 | Government investment | |
| MaI_2 | Political stability of a country | ||
| MaI_3 | Regional competitiveness | ||
| MaI_4 | Transparency | ||
| MaI_5 | Protection of the national port brand | ||
| Sociocultural | MaSC_1 | Employability | |
| MaSC_2 | Employee training programmes | ||
| MaSC_3 | Gender Inclusiveness | ||
| Sustainability | MaS_1 | Greenhouse gas emissions | |
| MaS_2 | Energy consumption | ||
| MaS_3 | Water consumption | ||
| MaS_4 | Biodiversity and habitat | ||
| MaS_5 | Reduction of water consumption (compared to 2019) | ||
| MaS_6 | Reduction in energy consumption (compared to 2019) | ||
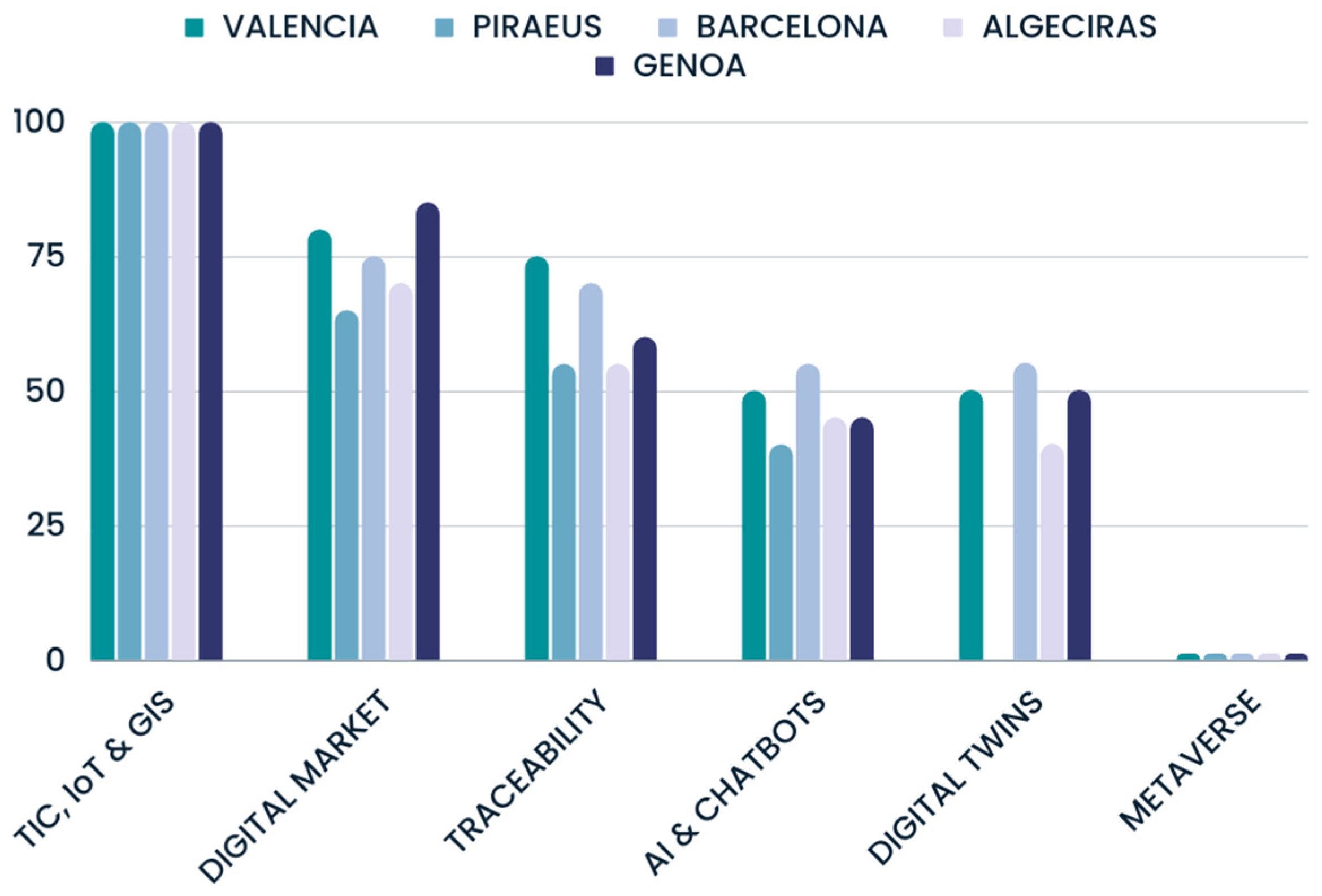
| Technological | MaT_1 | Use of ICTs | |
| MaT_2 | Use of AI | ||
| MaT_3 | Use of Digital Twins | ||
| MaT_4 | Use of chatbots | ||
| MaT_5 | Metaverse | ||
| MaT_6 | Digital competitiveness | ||
| MaT_7 | Ports using GIS | ||
| Legal | MaL_1 | Code of Ethics for Port Agencies | |
| MaL_2 | IMO Compendium Regulations | ||
| MaL_3 | Corruption Perception Index | ||
| Present | Customers | MiCu_1 | Digital market |
| Micro Environment | MiCu_2 | Hinterland | |
| Suppliers | MiS_1 | Data management system | |
| MiS_2 | Digital logistics | ||
| MiS_3 | Fleet | ||
| Products | MiP_1 | Traceability technologies | |
| MiP_2 | Merchandise | ||
| Competitors | MiCo_1 | Port performance index | |
| MiCo_2 | Port capacity |
| INDICATORS | Port of Valencia | Port of Piraeus | Port of Barcelona | Port of Algeciras | Genoa Port |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customers | |||||
| Digital market | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Hinterland | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Providers | |||||
| Data management systems | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| Digital logists | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Fleet | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 |
| Product | |||||
| Traceability technologies | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| Mercandise | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Competitors | |||||
| Port performance index | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 1 |
| Port capacity | 4 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-Cancelas, N.; Camarero Orive, A.; Vilarchao, A.R.; Vaca-Cabrero, J. Use of End-to-End Tool for the Analysis of the Digital Governance of Ports. Logistics 2024, 8, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8020058
González-Cancelas N, Camarero Orive A, Vilarchao AR, Vaca-Cabrero J. Use of End-to-End Tool for the Analysis of the Digital Governance of Ports. Logistics. 2024; 8(2):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8020058
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-Cancelas, Nicoletta, Alberto Camarero Orive, Alberto Rivas Vilarchao, and Javier Vaca-Cabrero. 2024. "Use of End-to-End Tool for the Analysis of the Digital Governance of Ports" Logistics 8, no. 2: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8020058
APA StyleGonzález-Cancelas, N., Camarero Orive, A., Vilarchao, A. R., & Vaca-Cabrero, J. (2024). Use of End-to-End Tool for the Analysis of the Digital Governance of Ports. Logistics, 8(2), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8020058








