Dentinogenesis Imperfecta and Caries in Osteogenesis Imperfecta among Vietnamese Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participant Recruitment
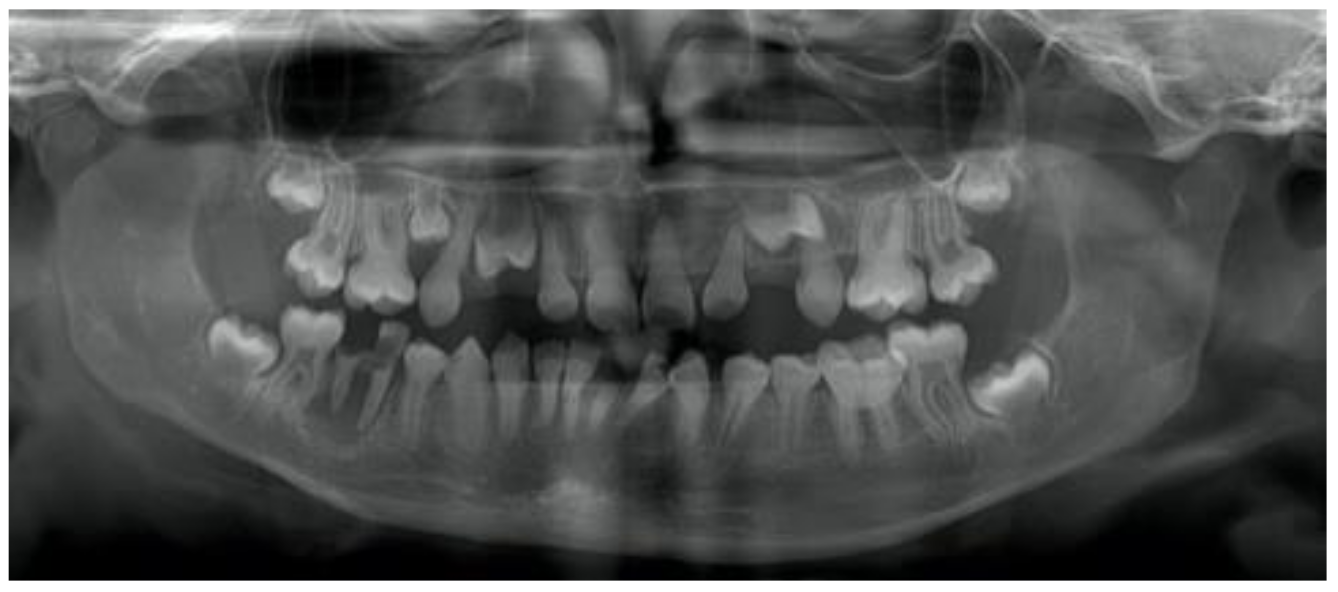
2.2. Clinical and Radiographic Examinations
2.2.1. Caries Diagnosis
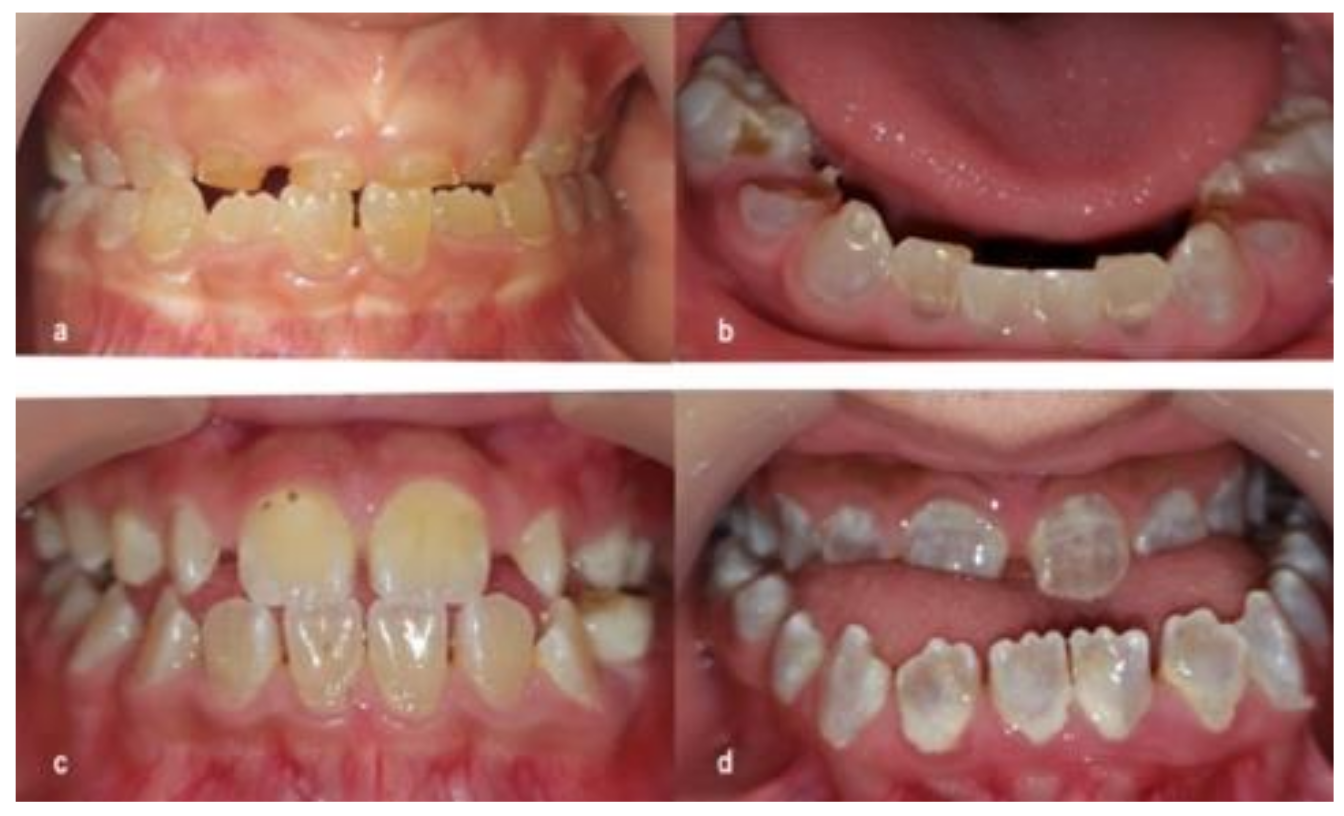
2.2.2. Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Diagnosis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
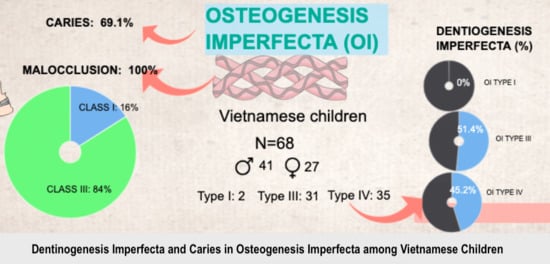
3. Results
3.1. Dentinogenesis Imperfecta
3.2. Caries
3.3. Occlusion, Eruption, Impacted and Missing Teeth
4. Discussion
4.1. Dentinogenesis Imperfecta
4.2. Caries
4.3. Occlusion, Eruption, Impaction and Missing Teeth
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rauch, F.; Glorieux, F.H. Osteogenesis imperfecta. Lancet 2004, 363, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, J.R.; Stover, M.L.; Burn, V.E.; McKinstry, M.B.; Burshell, A.L.; Chipman, S.D.; Rowe, D.W. An osteopenic nonfracture syndrome with features of mild osteogenesis imperfecta associated with the substitution of a cysteine for glycine at triple helix position 43 in the pro alpha 1(I) chain of type I collagen. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 89, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sillence, D.; Senn, A.; Danks, D. Genetic heterogeneity in osteogenesis imperfecta. J. Med. Genet. 1979, 16, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.M.; Nagamani, S.C.; Cuthbertson, D.; Campeau, P.M.; Krischer, J.P.; Shapiro, J.R.; Steiner, R.D.; Smith, P.A.; Bober, M.B.; Byers, P.H. A cross-sectional multicenter study of osteogenesis imperfecta in North America–results from the linked clinical research centers. Clin. Genet. 2015, 87, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, M.J.; McDonnell, S.T.; Mackie, I.; Dixon, M.J. Hereditary dentine disorders: Dentinogenesis imperfecta and dentine dysplasia. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2008, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opsahl Vital, S.; Gaucher, C.; Bardet, C.; Rowe, P.S.; George, A.; Linglart, A.; Chaussain, C. Tooth dentin defects reflect genetic disorders affecting bone mineralization. Bone 2012, 50, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, E.; Bixler, D.; El-Kafrawy, A. A proposed classification for heritable human dentine defects with a description of a new entity. Arch. Oral Biol. 1973, 18, 543–553, IN7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sæves, R.; Wekre, L.L.; Ambjørnsen, E.; Axelsson, S.; Nordgarden, H.; Storhaug, K. Oral findings in adults with osteogenesis imperfecta. Spec. Care Dent. 2009, 29, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnagdy, G.M.H.A.; ElRefaiey, M.I.; Aglan, M.; Ibrahim, R.O.; Badry, T.H.M. Oro-dental manifestations in different types of osteogenesis imperfecta. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2012, 6, 464–473. [Google Scholar]
- Thuesen, K.J.; Gjørup, H.; Hald, J.D.; Schmidt, M.; Harsløf, T.; Langdahl, B.; Haubek, D. The dental perspective on osteogenesis imperfecta in a Danish adult population. BMC Oral Health 2018, 18, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, K.; Dahllöf, G.; Lindahl, K.; Kindmark, A.; Grigelioniene, G.; Åström, E.; Malmgren, B. Mutations in COL1A1 and COL1A2 and dental aberrations in children and adolescents with osteogenesis imperfect—A retrospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.; Wetzel, W.-E. Recent findings in classification of osteogenesis imperfecta by means of existing dental symptoms. J. Dent. Child. 1998, 65, 305–309. [Google Scholar]
- O’Connell, A.C.; Marini, J.C. Evaluation of oral problems in an osteogenesis imperfecta population. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 1999, 87, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Simmer, J.P. Hereditary dentin defects. J. Dent. Res. 2007, 86, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindau, B.; Dietz, W.; Lundgren, T.; Storhaug, K.; Noren, J. Discrimination of morphological findings in dentine from osteogenesis imperfecta patients using combinations of polarized light microscopy, microradiograhpy and scanning electron microscopy. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 1999, 9, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, B.W.; Damm, D.D.; Allen, C.M.; Chi, A.C. 2—Pathology of Teeth. In Color Atlas of Oral and Maxillofacial Diseases; Neville, B.W., Damm, D.D., Allen, C.M., Chi, A.C., Eds.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 41–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.S.; Najirad, M.; Taqi, D.; Retrouvey, J.-M.; Tamimi, F.; Dagdeviren, D.; Glorieux, F.H.; Lee, B.; Sutton, V.R.; Rauch, F.; et al. Caries prevalence and experience in individuals with osteogenesis imperfecta: A cross-sectional multicenter study. Spec. Care Dent. 2019, 39, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmgren, B.; Norgren, S. Dental aberrations in children and adolescents with osteogenesis imperfecta. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2002, 60, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenvik, A.; Larheim, T.; Storhaug, K. Incisor and jaw relationship in 27 persons with osteogenesis imperfecta. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 1985, 93, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.A. Osteogenesis imperfecta. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2007, 103, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isshiki, Y. Morphological studies on osteogenesis imperfecta, especially in teeth, dental arch and facial cranium. Bull. Tokyu Dent. Coll. 1966, 7, 31–69. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, P.-C.; Lin, S.-Y.; Hsu, K.-H. The craniofacial characteristics of osteogenesis imperfecta patients. Eur. J. Orthod. 2007, 29, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukinmaa, P.; Ranta, H.; Ranta, K.; Kaitila, I.; Hietanen, J. Dental findings in osteogenesis imperfecta: II. Dysplastic and other developmental defects. J. Craniofac. Genet. Dev. Biol. 1987, 7, 127–135. [Google Scholar]
- Waltimo-Sirén, J.; Kolkka, M.; Pynnönen, S.; Kuurila, K.; Kaitila, I.; Kovero, O. Craniofacial features in osteogenesis imperfecta: A cephalometric study. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part. A 2005, 133, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, B.L.; Lund, A.M. Osteogenesis imperfecta: Clinical, cephalometric, and biochemical investigations of OI types I, III, and IV. J. Craniofac. Genet. Dev. Biol. 1997, 17, 121–132. [Google Scholar]
- Biggin, A.; Munns, C. Long-term bisphosphonate therapy in osteogenesis imperfecta. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2017, 15, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giudice, A.; Barone, S.; Diodati, F.; Antonelli, A.; Nocini, R.; Cristofaro, M.G. Can surgical management improve resolution of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw at early stages? A prospective cohort study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 78, 1986–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudice, A.; Antonelli, A.; Muraca, D.; Fortunato, L. Usefulness of advanced-platelet rich fibrin (A-PRF) and injectable-platelet rich fibrin (i-PRF) in the management of a massive medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ): A 5-years follow-up case report. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2020, 31, 813. [Google Scholar]
- Contaldo, M.; Luzzi, V.; Ierardo, G.; Raimondo, E.; Boccellino, M.; Ferati, K.; Bexheti-Ferati, A.; Inchingolo, F.; Di Domenico, M.; Serpico, R. Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws and dental surgery procedures in children and young people with osteogenesis imperfecta: A systematic review. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 121, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luder, H.U.; Steinman, B. Teeth in osteogenesis imperfecta: A mirror of genetic collagen defects. In Studies in Stomatology and Craniofacial Biology; Cohen, M.M., Jr., Baum, B.J., Eds.; IOS Press: Oxford, UK, 1995; pp. 209–228. [Google Scholar]
- Sillence, D.O.; Rimoin, D.L.; Rimoin, D.M. Clinical variability in osteogenesis imperfecta-variable expressivity or genetic heterogeneity. Birth Defects 1979, 15, 113–129. [Google Scholar]
- Forlino, A.; Marini, J.C. Osteogenesis imperfecta. Lancet 2016, 387, 1657–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forlino, A.; Cabral, W.A.; Barnes, A.M.; Marini, J.C. New perspectives on osteogenesis imperfecta. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, R.; Roberts, G.; Scully, C. ABC of oral health: Oral health and disease. BMJ Br. Med. J. 2000, 320, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, A.I.; Sohn, W.; Tellez, M.; Amaya, A.; Sen, A.; Hasson, H.; Pitts, N.B. The International Caries Detection and Assessment System (ICDAS): An integrated system for measuring dental caries. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 2007, 35, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iranzo-Cortés, J.; Almerich-Silla, J. Caries diagnosis: Agreement between WHO and ICDAS II criteria in epidemiological surveys. Community Dent. Health 2013, 30, 108–111. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Oral Health Surveys: Basic Methods; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Majorana, A.; Bardellini, E.; Brunelli, P.C.; Lacaita, M.; Cazzolla, A.P.; Favia, G. Dentinogenesis imperfecta in children with osteogenesis imperfecta: A clinical and ultrastructural study. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2010, 20, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binh, H.D.; Maasalu, K.; Dung, V.C.; Ngoc, C.T.B.; Hung, T.T.; Nam, T.V.; Nhan, L.N.T.; Prans, E.; Reimann, E.; Zhytnik, L.; et al. The clinical features of osteogenesis imperfecta in Vietnam. Int. Orthop. 2017, 41, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Rios, D.; Vieira, A.L.; Tenuta, L.M.; Machado, M.A. Osteogenesis imperfecta and dentinogenesis imperfecta: Associated disorders. Quintessence Int. 2005, 36, 695–701. [Google Scholar]
- Lund, A.M.; Jensen, B.L.; Nielsen, L.A.; Skovby, F. Dental manifestations of osteogenesis imperfecta and abnormalities of collagen I metabolism. J. Craniofac. Genet. Dev. Biol. 1998, 18, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbard, P.D. The management of children and adolescents suffering from amelogenesis imperfecta and dentinogenesis imperfecta. Int. J. Orthod. 1974, 12, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranta, H.; Lukinmaa, P.L.; Waltimo, J. Heritable dentin defects: Nosology, pathology, and treatment. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1993, 45, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Y.H.T.; Ueno, M.; Zaitsu, T.; Nguyen, T.; Kawaguchi, Y. Early Childhood Caries and Risk Factors in Vietnam. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2018, 42, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, N.T.H.; Kanchanakhan, N. Prevalence and factors related to dental caries among 6 year-old children in Nha Trang City, Khanh Hoa Province, Vietnam. J. Health Res. 2015, 29, 251–258. [Google Scholar]
- Khanh, L.N.; Ivey, S.L.; Sokal-Gutierrez, K.; Barkan, H.; Ngo, K.M.; Hoang, H.T.; Vuong, I.; Thai, N. Early Childhood Caries, Mouth Pain, and Nutritional Threats in Vietnam. Am. J. Public Health 2015, 105, 2510–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.M.; Nguyen, M.K.; Saag, M.; Jagomagi, T. The Need for Orthodontic Treatment among Vietnamese School Children and Young Adults. Int. J. Dent. 2014, 2014, 132301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ormiston, I.; Tideman, H. Orthognathic surgery in osteogenesis imperfecta: A case report with management considerations. J. Cranio Maxillofac. Surg. 1995, 23, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizkallah, J.; Schwartz, S.; Rauch, F.; Glorieux, F.; Vu, D.-D.; Muller, K.; Retrouvey, J.-M. Evaluation of the severity of malocclusions in children affected by osteogenesis imperfecta with the peer assessment rating and discrepancy indexes. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2013, 143, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retrouvey, J.-M.; Schwartz, S.; Hartsfield, J.K. Oral-facial aspects of osteogenesis imperfecta. In Osteogenesis Imperfecta; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 313–327. [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel, R.; Kim, E.; Tuncer, F.B.; Siddiqi, F.; Gociman, B. Maxillary Distraction Osteogenesis in a Patient with Osteogenesis Imperfecta. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2019, 30, 2530–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, S.; Morice, A.; Picard, A.; Giudice, A. Surgery-first orthognathic approach vs conventional orthognathic approach: A systematic review of systematic reviews. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 122, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartsfield, J.K.; Hohlt, W.F.; Roberts, W.E. Orthodontic Treatment and Orthognathic Surgery for Patients with Osteogenesis Imperfecta. Semin. Orthod. 2006, 12, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Viana, M.A.G.; Graber, T.M.; Omerza, F.F.; BeGole, E.A. The effectiveness of protraction face mask therapy: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1999, 115, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| OI Type | Total | Gender | Age (year) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | 3–5 | 6–12 | 13–17 | ||
| Type I | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Type III | 35 | 24 | 11 | 2 | 21 | 12 |
| Type IV | 31 | 15 | 16 | 8 | 19 | 4 |
| OI Type | Dentition | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | I (n = 2) | III (n = 35) | IV (n = 31) | pa | Primary (n = 50) | Permanent (n = 54) | p-value | |
| DI | 47.1% | 0% | 51.4% | 45.2% | 0.61 | 52% | 44.4% | 0.44 |
| Yellow-brown | - | - | - | - | - | 13 | 14 | 0.55 |
| Opalescent-gray | - | - | - | - | - | 13 | 10 | |
| Caries | 69.1% | 100% | 71.4% | 64.5% | 0.55 | 86% | 51.9% | <0.001 |
| Dentition | dt | ft | dft | DT | FT | DFT | Dft + DFT | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary (n = 14) | 6.2 ± 5.9 | 1.3 ± 2.8 | 7.5 ± 6.8 | - | - | - | 7.5 ± 6.8 | 0.04 |
| Mixed (n = 36) | 4.4 ± 5.5 | 0.2 ± 1.1 | 4.6 ± 5.7 | 1.1 ± 1.9 | 0.2 ± 0.7 | 1.3 ± 2.1 | 5.9 ± 6.0 | |
| Permanent (n = 18) | - | - | - | 2.5 ± 2.5 | 0.2 ± 0.5 | 2.7 ± 2.6 | 2.7 ± 2.6 |
| Findings | Type I | Type III | Type IV | pa-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 2 | n = 28 | n = 20 | |||
| Malocclusion | Class I | 0 | 10.8% | 25% | 0.19 |
| Class II | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Class III | 100% | 89.2% | 75% | ||
| Open bite | Anterior | 100% | 42.9% | 40% | 0.84 |
| Posterior | 100% | 39.3% | 15% | 0.07 | |
| Cross bite | Anterior | 100% | 82.1% | 60% | 0.09 |
| Posterior | 100% | 71.4% | 25% | 0.002 | |
| n = 2 | n = 35 | n = 31 | |||
| Eruption | Early | 0 | 5.7% | 3.2% | 0.63 |
| Normal | 2 | 74.3% | 96.8% | 0.01 | |
| Late | 0 | 20% | 0 | - | |
| Impacted tooth n, (%) | Tooth 17 | 0 | 5, (14.3%) | 0 | |
| Tooth 27 | 2 | 4, (11.4%) | 2, (6.5%) | ||
| Missing tooth | 0 | 1, (2.9%) | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, H.T.T.; Vu, D.C.; Nguyen, D.M.; Dang, Q.D.; Tran, V.K.; Le, H.; Tong, S.M. Dentinogenesis Imperfecta and Caries in Osteogenesis Imperfecta among Vietnamese Children. Dent. J. 2021, 9, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj9050049
Nguyen HTT, Vu DC, Nguyen DM, Dang QD, Tran VK, Le H, Tong SM. Dentinogenesis Imperfecta and Caries in Osteogenesis Imperfecta among Vietnamese Children. Dentistry Journal. 2021; 9(5):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj9050049
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Huong Thi Thu, Dung Chi Vu, Duc Minh Nguyen, Quang Dinh Dang, Van Khanh Tran, Hung Le, and Son Minh Tong. 2021. "Dentinogenesis Imperfecta and Caries in Osteogenesis Imperfecta among Vietnamese Children" Dentistry Journal 9, no. 5: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj9050049
APA StyleNguyen, H. T. T., Vu, D. C., Nguyen, D. M., Dang, Q. D., Tran, V. K., Le, H., & Tong, S. M. (2021). Dentinogenesis Imperfecta and Caries in Osteogenesis Imperfecta among Vietnamese Children. Dentistry Journal, 9(5), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj9050049