Oronasal Fistula and Complete Edentulism: What to Do?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Etiology
1.1.1. Infectious
1.1.2. Iatrogenic
1.1.3. Traumatic
1.1.4. Patient Compliance
1.1.5. Tumor and Cystic Resection
| Tumors Involving Palate | |
|---|---|
| Common | Uncommon |
| Basal cell carcinoma | Squamous papilloma |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | Verrucous carcinoma |
| Pleomorphic adenoma | Verruciformxanthoma |
| Mucoepidermoid carcinoma | Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma |
| Adenoid cystic carcinoma | Chondroma |
| Polymorphous low grade adenocarcinoma | Liposarcoma |
| Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma | Myoepithelioma |
| Oral hemangioma | Basal cell adenocarcinoma |
| Oral fibroma | Intraductal papilloma |
| Giant cell fibroma | Extramedullary plasmacytoma |
| Torus palatines | Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor |
1.1.6. Rhinolithiasis
1.1.7. Congenital
1.2. Causes of Persistence of Fistula
1.3. Diagnosis
1.3.1. Diagnostic Criterias
- Air escape from the opening when patient blows his/her nose;
- An obvious communication between the opening and floor of the nasal cavity;
- Unobstructed penetration of Gutta percha through the opening into the nasal cavity;
- Occlusal radiographs;
- Apart from these, symptoms associated with ONF also help in its diagnosis.
1.3.2. Signs and Symptoms
- Hypernasality of voice due to audible nasal air escape during speech;
- Nasal regurgitation of fluids;
- Food lodgement into nasal cavity with risk of rhinitis and tonsillitis.
1.4. Surgical Closure
1.4.1. Preoperative Clinical Assessment
1.4.2. Surgical Closure Methods
1.4.3. Flap Selection Factors [22,31,32]
| Patient | Defect | Surgeon |
|---|---|---|
| Age | Location | Familiarity with surgical methods surgical methods |
| General condition | Size | Experience |
| Economical status | Etiology | Dexterity |
| Willingness | Severity | |
| Associated scarring | ||
| Duration |
1.4.4. Surgical Contraindications
1.4.5. Surgical Closure in Traumatic and Iatrogenic ONF
2. Case Presentation
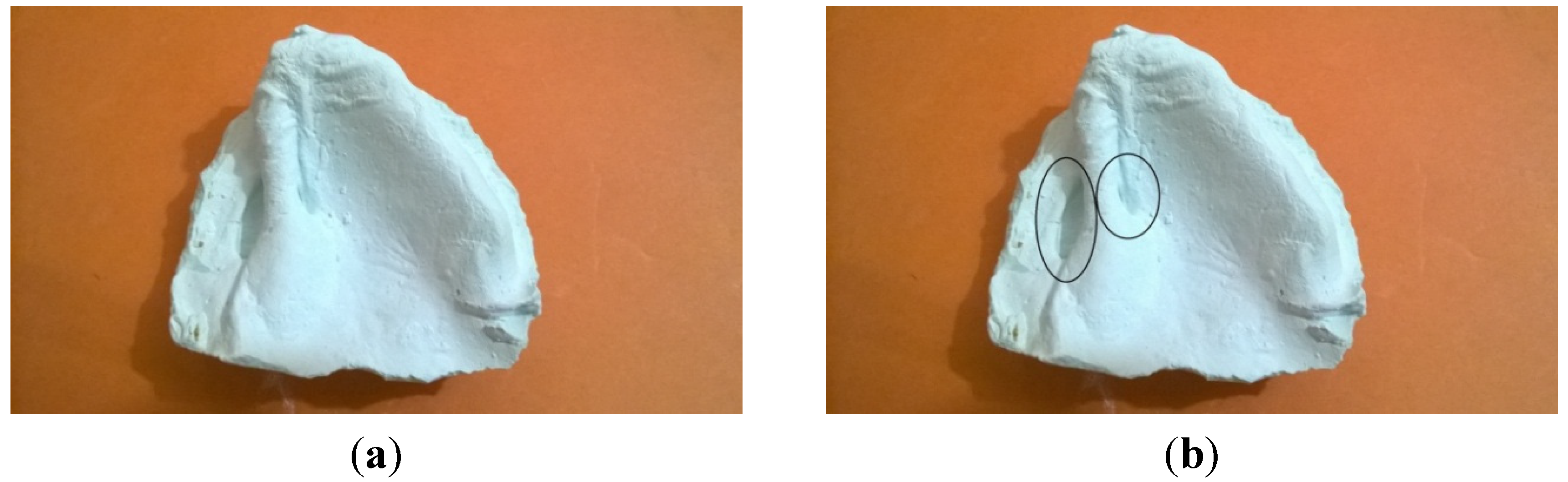
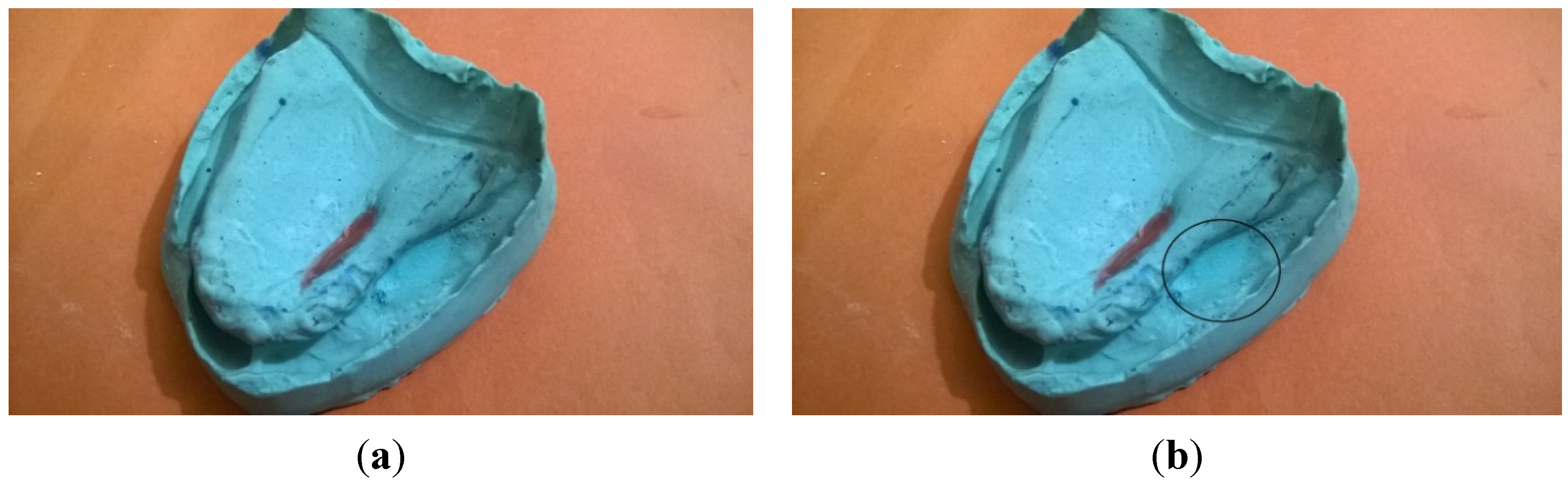
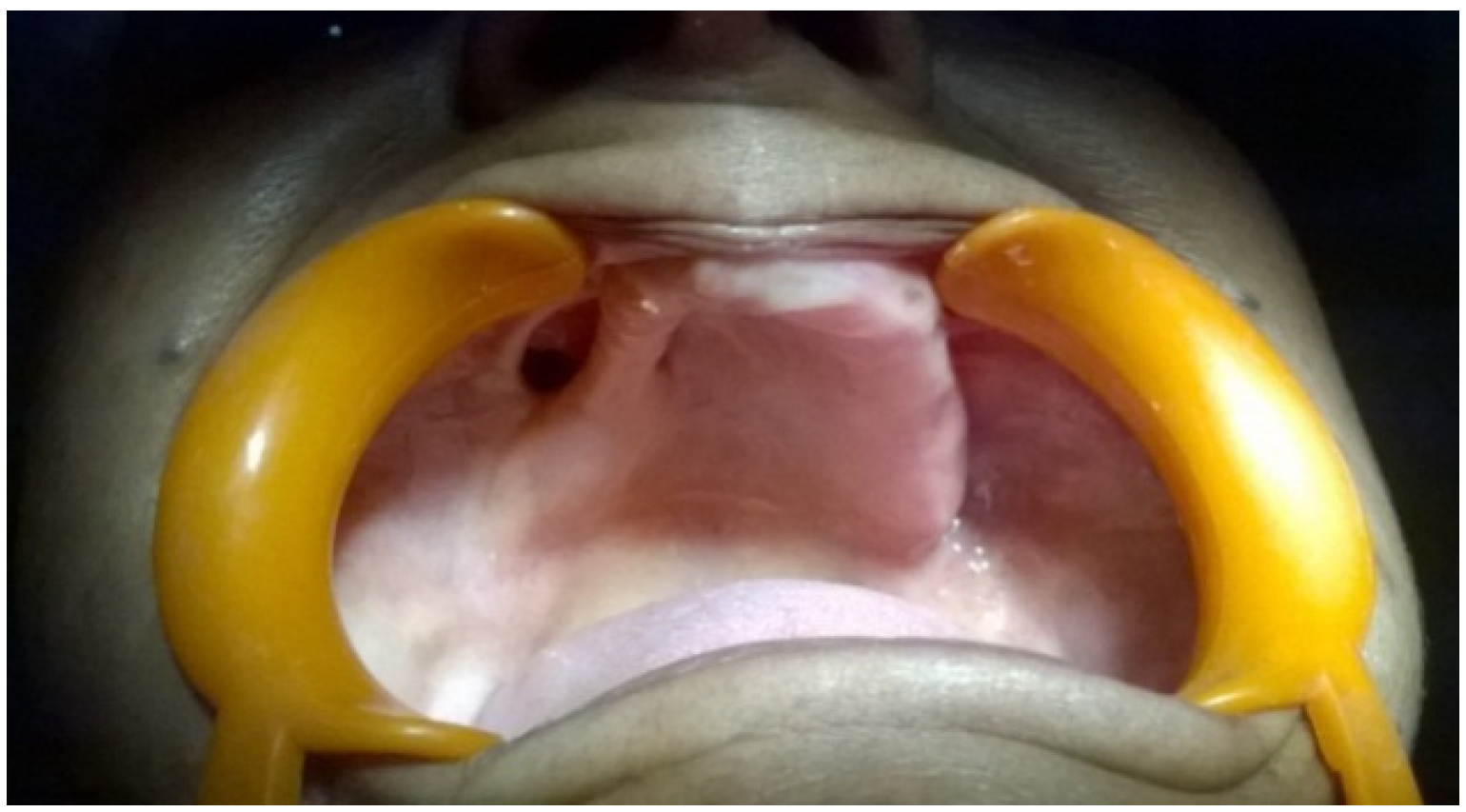
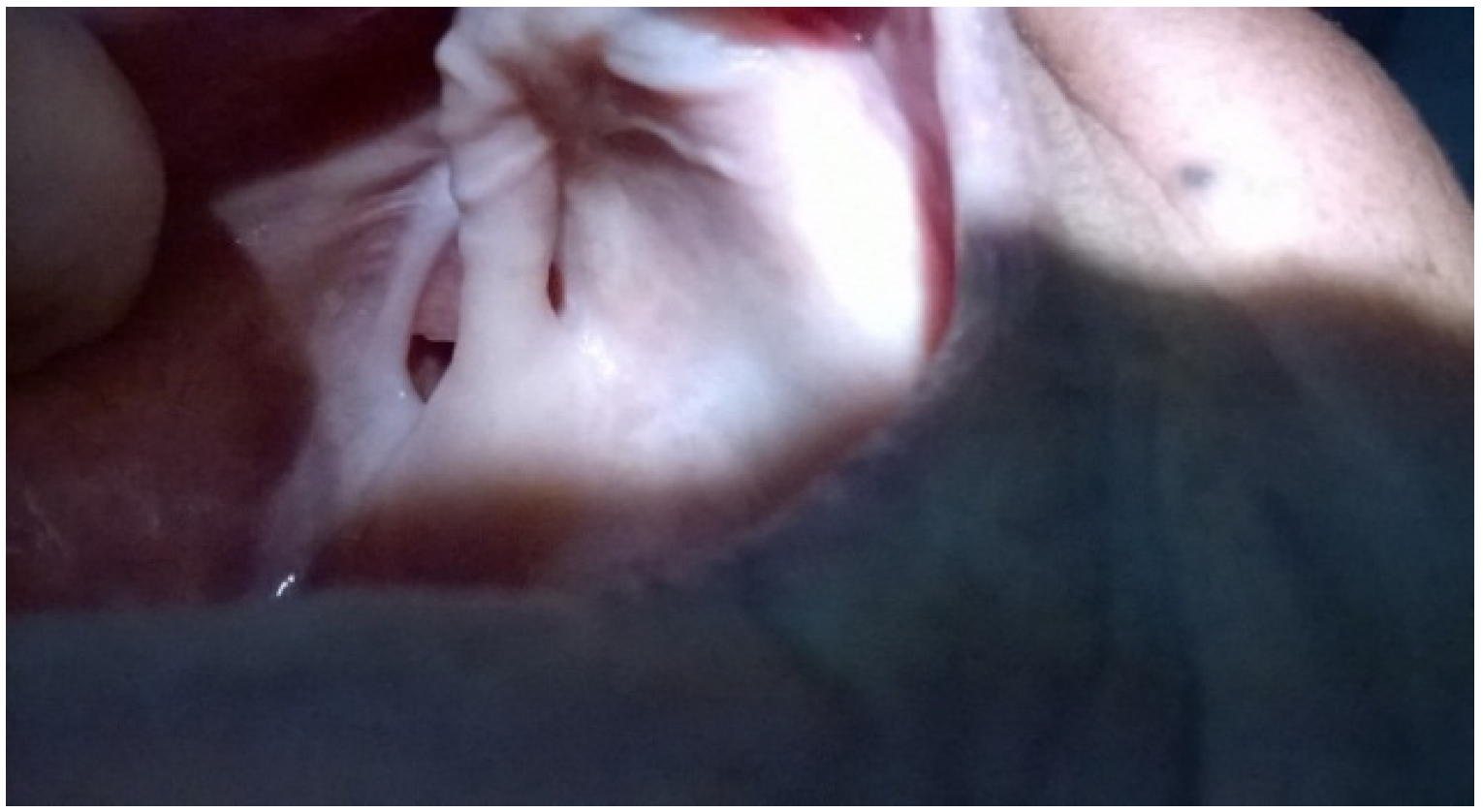


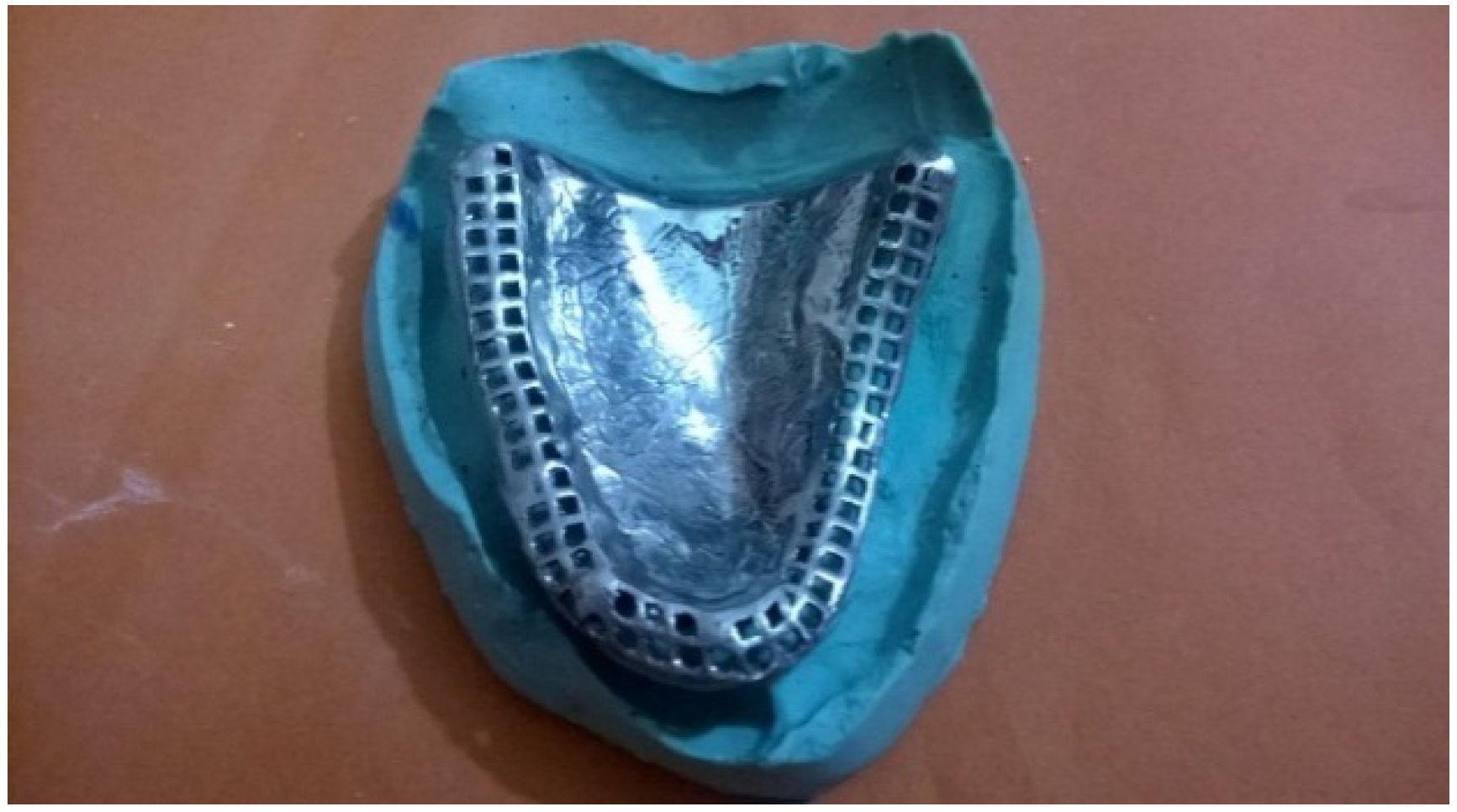
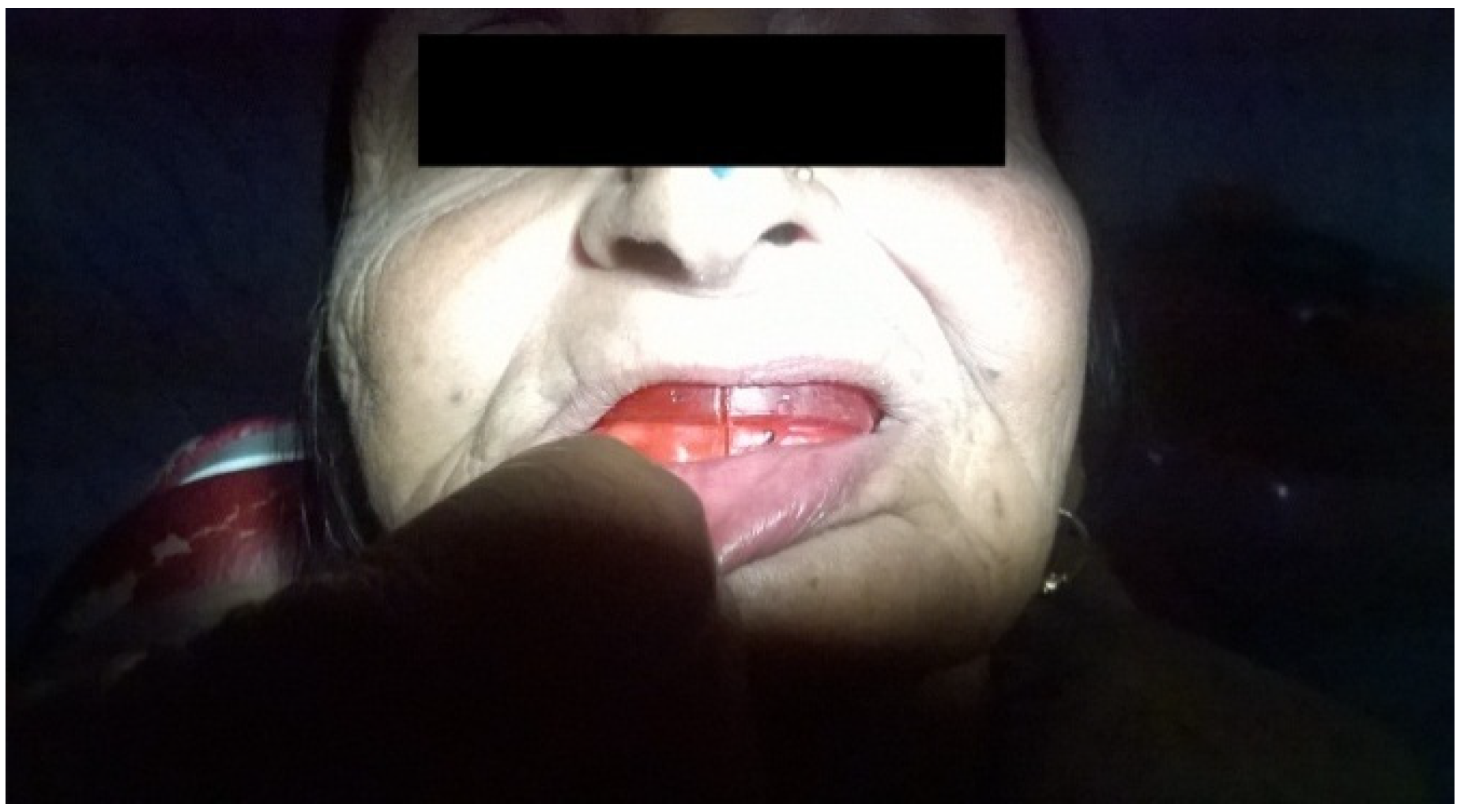
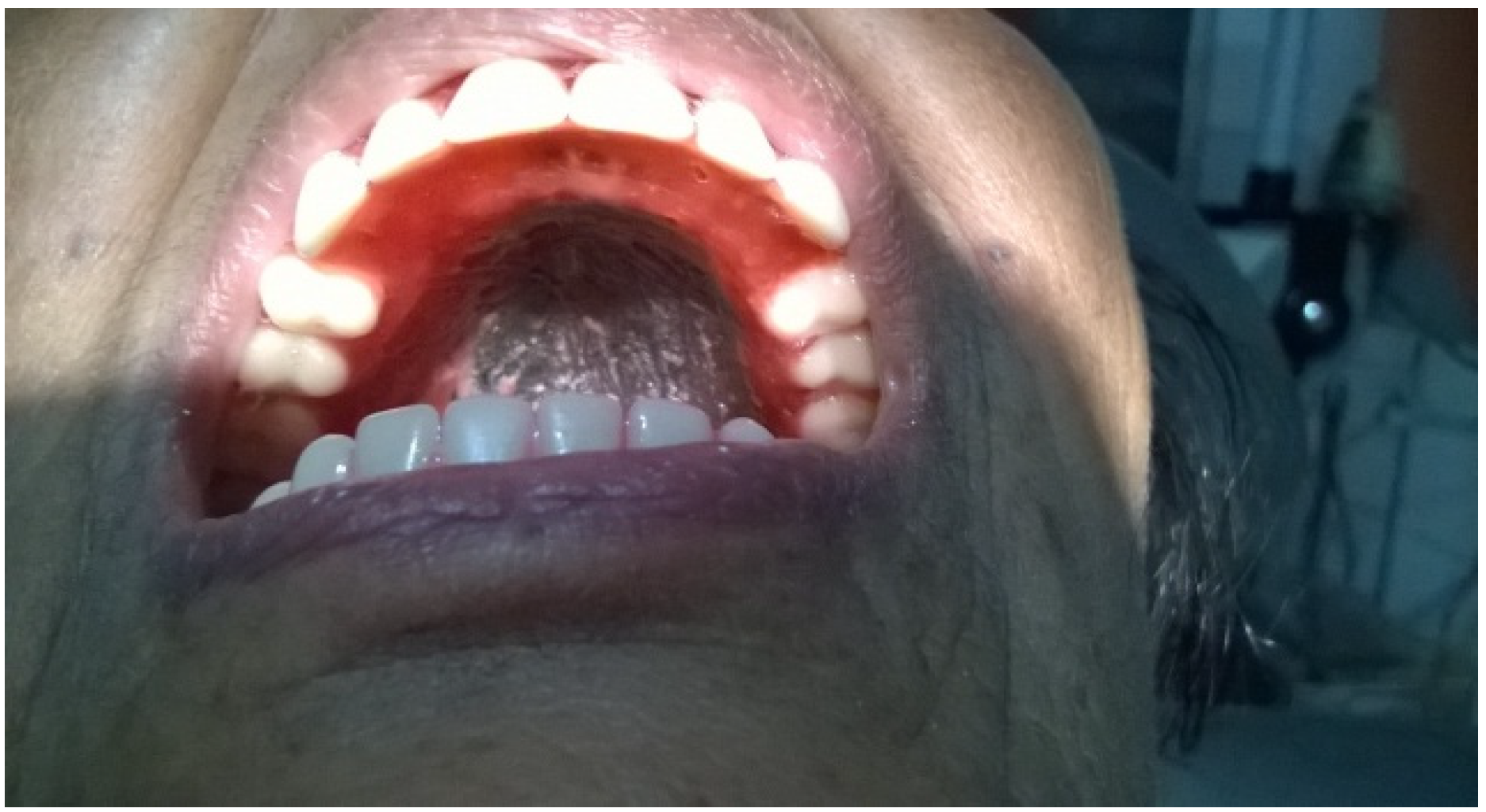
3. Discussion
3.1. Surgical Closure of the Defect
3.2. Prosthodontic Rehabilitation
3.2.1. Implant Supported Denture
3.2.2. Prosthesis Incorporating Magnets
- Cases with large sized defects where the weight of single piece prosthesis is over the limit and counteracts retentive force of denture thus compromising its success.
- When volume of prosthesis is large enough to interfere with its removal from mouth.
- When the defect is in or near center compared to off center position as seen in this case making it difficult to manage.
3.2.3. Conventional Denture
3.3. Prosthetic Rehabilitation
4. Conclusion
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Das, S. Examination of a Sinus or a Fistula. In A manual on Clinical Surgery, 5th ed.; Old Mayors Court: Calcutta, India, 2001; p. 55. [Google Scholar]
- Stammberger, H.; Jaske, R.; Beaufort, F. Aspergillosis of the paranasal sinuses, X-ray diagnosis, histopathology of clinical aspects. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1984, 93, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikawa, H.; Egusa, H.; Makihira, S.; Yamashiro, H.; Fukushima, H.; Jin, C.; Nishimura, M.; Pudji, R.R.; Hamada, T. Alteration of the coadherence of candida albicans with oral bacteria by dietary sugars. Oral Microbiol. Immun. 2001, 16, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, I.S.; Bull, T.R. Rhinology. In Scott-Brown’s Otolaryngology, 6th ed.; Butterworth Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1997; Volume 4, pp. 39–49. [Google Scholar]
- Martinson, F.D. Zygomycosis in otorhinolaryngology practice. Prog. Oto. Rhino. Laryngol. 1983, 29, 224–230. [Google Scholar]
- Eppley, B.; Sclaroff, A. Oronasal fistula secondary to maxillary augmentation. Int. J. Oral. Surg. 1984, 13, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emory, R.E.; Clay, R.P.; Bite, U.; Jackson, I.T. Fistula formation and repair after palatal closure: An institutional perspective. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1997, 99, 1535–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.R.; Kalinowski, J.; LaRossa, D.; Randall, P. Cleft palate fistulas: A multivariate statistical analysis of prevalence, etiology and surgical management. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1991, 87, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, D.A.C. Fistula in the hard palate following cleft palate surgery. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1962, 15, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClelland, R.M.A.; Patterson, T.J.S. The influence of penicillin on the complication rate after repair of clefts of the lip and palate. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1963, 16, 144–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathog, R.H.; Arden, R.I.; Marks, S.C. Maxillary Trauma. In Trauma of the Nose and Paranasal Sinuses; Thieme: New York, NY, USA, 1995; p. 55. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, S.; Waldron, C.A. Primary intra osseous squamous carcinoma. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1991, 20, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiro, R.H.; Strong, E.W.; Shah, J.P. Maxillectomy and its classification. Head Neck. 1997, 19, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, C. Carcinomas of the Head and Neck; Jacobs, C., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 83–113. [Google Scholar]
- Thawley, S.E.; Batsakis, J.G.; Lindberg, R.D.; Panje, W.R.; Donley, S. Comprehensive Management of Head and Neck Tumors, 2nd ed.; Thawley, S.E., Batsakis, J.G., Lindberg, R.D., Panje, W.R., Donley, S., Eds.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1998; pp. 526–527. [Google Scholar]
- Aksungur, E.H.; Binokay, F.B.; Biçakçi, K.; Apaydin, D.; Oguz, M.; Aydogan, B. A rhinolith which is mimicking a nasal benign tumor. Eur. J. Radiol. 1999, 31, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.G.; Sahni, R.C. Unilateral rhinolithiasis. Australas. Radiol. 1981, 25, 132–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, H.I.; Batnitzky, S.; Karlin, C.A.; Norris, C.W. Giant nasal rhinolith. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1981, 2, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Celikkanat, S.; Turgut, S.; Özcan, I.; Balyan, A.R.; Ozdem, C. Rhinolithiasis. Rhinology 1997, 53, 39–40. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, J. Nasal cavity. In Clinical Anatomy of the Nose, Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses; Thieme: New York, NY, USA, 1989; p. 46. [Google Scholar]
- Abadi, B.; Johnson, J.D. The prosthodontic management of cleft palate patients. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1982, 48, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.V.; Naz, F.; Chand, M.A.U.H.; Tambuwala, A.; Kaul, D. Repair of iatrogenic oronasal fistula after periapical surgery. Univ. Res. J. Dent. 2012, 2, 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- EL-Leathy, M.M.; Attia, M.F. Closure of palatal fistula with bucco-labial myomucosal pedicled flap. Ann. Pediatr. Surg. 2009, 5, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Muzzafar, A.R.; Byrd, H.S.; Rohrich, R.J.; Johns, D.F.; LeBlanc, D.; Beran, S.J.; Anderson, C.; Papaioannoua, A.A. Incidence of cleft palate fistula: An institutional experience with two stage palate repair. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2001, 108, 1515–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henningson, G.; Isberg, A. Oronasal fistulas and speech production. In Multidisciplinary Management of Cleft Lip and Palate, 1st ed.; Bardach, J., Morris, H.L., Eds.; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1990; pp. 787–791. [Google Scholar]
- Riski, J.E. Evaluation and management of speech, language, and articulation disorders. In Cleft Lip and Palate from Origin to Treatment; Wyszynski, D.F., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 354–367. [Google Scholar]
- Rintala, A.E. A double, overlapping hinge flap to close palatal fistulae. Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1971, 5, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakakita, N.; Maeda, K.; Ando, S.; Ojimi, H.; Utsugi, R. Use of a buccal musculomucosal flap to close palatal fistulae after cleft palate repair. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1990, 43, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argamaso, R.V. The tongue flap: Placement and fixation for closure of post palatoplasty fistulae. Cleft Palate J. 1990, 27, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, R.B. Cleft palate. In Plastic Surgery of the Head and Neck; Churchill Livingstone: New York, NY, USA, 1987; pp. 1300–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.A.; Naqash, T.A.; Abdullah, S.; Zargar, N.M.; Jangral, S. Prosthetic rehabilitation of a patient with limited mouth opening consequent to partial maxillectomy: A clinical report. Int. J. Health Sci. Res. 2013, 3, 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Diah, E.; Lu, L.J.; Yun, C.; Wang, R.; Wahyuni, L.K.; Chen, Y.R. Cleft oronasal fistula: A review of treatment results and surgical management algorithm proposal. Chang. Gung Med. J. 2007, 30, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meechan, J.G. Oronasal fistula occurring after simple dental extraction. Br. J. Oral. Surg. 1983, 2, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukohyama, H.; Haraguchi, M.; Sumita, Y.I.; Iida, H.; Hata, Y.; Kishimoto, S.; Taniguchi, H. Rehabilitation of a bilateral maxillectomy patient with a free fibula osteocutaneous flap. J. Oral Rehabil. 2005, 32, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anantharaju, A.; Kamath, G.; Mody, P.; Nooji, D. Prosthetic rehabilitation of oro-nasal defect. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2011, 11, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaur, P.; Kaur, J. Oronasal Fistula and Complete Edentulism: What to Do? Dent. J. 2014, 2, 142-154. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj2040142
Kaur P, Kaur J. Oronasal Fistula and Complete Edentulism: What to Do? Dentistry Journal. 2014; 2(4):142-154. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj2040142
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaur, Pushappreet, and Jaspinder Kaur. 2014. "Oronasal Fistula and Complete Edentulism: What to Do?" Dentistry Journal 2, no. 4: 142-154. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj2040142
APA StyleKaur, P., & Kaur, J. (2014). Oronasal Fistula and Complete Edentulism: What to Do? Dentistry Journal, 2(4), 142-154. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj2040142




