Evaluation of Smile Aesthetics in Dental Students: Perceptions of Tooth Colour Changes Due to Incisor Inclination and Micro- and Mini-Aesthetic Characteristics Assessed by Professionals and Laypersons
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- (1)
- Smile line, classified according to Liebert and Deruelle [25] as very high (>2 mm marginal gingiva visible), high (0–2 mm), average (gingival embrasure only), or low (no gingiva visible);
- (2)
- Smile arch, categorized as parallel, straight, or inverted [26];
- (3)
- Oral corridor width, categorized as wide, average, narrow, or minimal;
- (4)
- Smile width, defined by the most posterior visible tooth (canine, first premolar, second premolar, or first molar) [27];
- (5)
- Smile index, calculated as the ratio of intercommissural width (points 1–2) to interlabial gap (points 3–4);
- (6)
- Dynamic smile symmetry, calculated using the formula [(1 − 3) + (1 − 4)]/[(2 − 3) + (2−4)].
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, C.; Hu, W.J.; Liang, L.Z.; Zhang, Y.L.; Chung, K.H. Esthetics and smile-related characteristics assessed by laypersons. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2017, 30, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, J.T.; Prabhu, N.; Robinson, P.G. The impact of dental appearance on the appraisal of personal characteristics. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2003, 16, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davis, L.G.; Ashworth, P.D.; Spriggs, L.S. Psychological effects of aesthetic dental treatment. J. Dent. 1998, 26, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coachman, C.; Calamita, M. Digital Smile Design: A tool for treatment planning and communication in esthetic dentistry. Quintessence Dent. Technol. 2012, 35, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes, G. The evolutionary psychology of facial beauty. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2021, 57, 199–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffarpour, A.; Ghavam, M.; Saffarpour, A.; Dayani, R.; Fard, M.J.K. Perception of laypeople and dental professionals of smile esthetics. J. Dent. 2016, 13, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Mir, C.; Silva, E.; Barriga, M.I.; Lagravère, M.O.; Major, P.W. Lay person’s perception of smile aesthetics in dental and facial views. J. Orthod. 2004, 31, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charruel, S.; Perez, C.; Foti, B.; Camps, J.; Monnet-Corti, V. Gingival contour assessment: Clinical parameters useful for esthetic diagnosis and treatment. J. Periodontol. 2008, 79, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakroborty, G.; Pal, T.K.; Chakroborty, A. A study on gingival component of smile. J. Int. Clin. Dent. Res. Organ. 2015, 7, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.J.; Tan, J.H.; Stappert, C.F.; Tarnow, D.P. Gingival zenith positions and levels of the maxillary anterior dentition. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2009, 21, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snigdha, G.; Shankar, T.; Chatterjee, S.; Mohanty, P.; Sahoo, N.; Baratam, S. Gingival zenith positions and levels of maxillary anterior dentition in cases of bimaxillary protrusion: A Morphometric Analysis. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2017, 18, 700–704. [Google Scholar]
- Indurkar, M.S.; Abinesh, M. Clinical study of assessment of gingiva in smile designing. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 5, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardarian, A.; Khaledi, A.; Firouzmandi, M.; Nematollahi, H. The effect of varying head tilt on the perceived color from composite resin and porcelain restorations: Simulating the effect of altering torque. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2021, 159, e35–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.A.V.; Nguyen, P.A. Morphological features of smile attractiveness and related factors influence perception and gingival aesthetic parameters. Int. Dent. J. 2022, 72, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrini, S.; Rossini, G.; Castroflorio, T.; Fortini, A.; Deregibus, A.; Debernardi, C. Laypeople’s perception of frontal smile esthetics: A systematic review. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2016, 150, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, J.J.; Anilkumar. Smile Esthetics in Orthodontics—Review of Literature. J. Dent. 2024, 14, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, R.C.B.; Brandão, L.B.C. Finishing procedures in orthodontics: Dental dimensions and proportions (microesthetics). Dent. Press J. Orthod. 2021, 18, 147–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paravina, R.D.; Powers, J.M.; Fay, R.M. Color and appearance in dentistry. J. Dent. 2011, 39 (Suppl. 2), e3–e10. [Google Scholar]
- Ciucchi, P.; Kiliaridis, S. Incisor inclination and perceived tooth colour changes. Eur. J. Orthod. 2019, 39, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joiner, A. Tooth colour: A review of the literature. J. Dent. 2004, 32 (Suppl. 1), 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehl, A.; Gloger, W.; Kunzelmann, K.-H.; Hickel, R. A New Optical 3-D Device for the Detection of Wear. J. Dent. Res. 1997, 76, 1799–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokich, V.O.; Kokich, V.G.; Kiyak, H.A. Perceptions of dental professionals and laypersons to altered dental esthetics: Asymmetric and symmetric situations. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1999, 116, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, N.; Jones, M.L.; Newcombe, R.G.; Bell, R.A. Thresholds for perception of changes in incisor inclination in smiling view. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2013, 144, 648–657. [Google Scholar]
- Fradeani, M. Esthetic Rehabilitation in Fixed Prosthodontics. In Esthetic Analysis; Quintessence Publishing: Chicago, IL, USA, 2004; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Liebart, M.F.; Fouque-Deruelle, C.; Santini, A.; Dillier, F.L.; Monnet-Corti, V.; Glise, J.M.; Borghetti, A. Smile line and periodontium visibility. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2004, 16, 26–35. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, T.; Southard, K.A.; Casko, J.S.; Qian, F.; Southard, T.E. Buccal corridor space and its relationship to smile esthetics. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2005, 127, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frush, J.P.; Fisher, R.D. The dynesthetic interpretation of the dentogenic concept. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1958, 8, 558–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolte, R.A.; Kolte, A.P.; Rathi, P. Association of the gingival line angle with the gingival and interdental smile line: A gender based evaluation. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2019, 31, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolte, A.P.; Kolte, R.A.; Purohit, M.J.; Bajaj, V.A. Proportions in papilla, crestal papilla, and proximal contact area in maxillary anterior teeth: A cross-sectional study. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2022, 26, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haralur, S.B. Effect of age on tooth shade, skin color and skin–tooth color interrelationship in Saudi Arabian subpopulation. J. Int. Oral Health 2015, 7, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Alfaro, F.; Guijarro-Martínez, R.; Molina-Coral, A.; Badía-Escriche, C. Variation between natural head orientation and Frankfort horizontal planes in orthognathic surgery patients: 187 consecutive cases. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 50, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, C.M.; Vasilakos, G.; Halazonetis, D.J.; Gkantidis, N. Standardised anatomical alignment of the head in a clinical photography studio: A comparison between the Frankfort Horizontal and the natural head position. J. Vis. Commun. Med. 2016, 39, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardani, D.E.; Hamid, T.; Narmada, I.B.; Suharwan, M. Frankfort Horizontal Deviation Comparison in Natural Head Position on Discrepancy of Skeletal Pattern (Cephalometry Study). Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2023, 16, 1843–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solow, B.; Tallgren, A. Head posture and craniofacial morphology. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 1971, 35, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Johany, S.S.; Alqahtani, A.S.; Alqahtani, F.Y.; Alzahrani, A.H. Evaluation of different esthetic smile criteria. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2011, 24, 64–70. [Google Scholar]
- Kau, C.H.; Christou, T.; Xie, R.B.; Abou-Saleh, T. Rating of smile attractiveness of patients finished to the American Board of Orthodontics standards. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2020, 81, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, S.; Peck, L. The esthetic smile: Diagnosis and treatment. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 1992, 123, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Gaikwad, S.; Kaur, H.; Vaz, A.C.; Singh, B.; Taneja, L.; Vinod, K.S.; Verma, P. Influence of smile arc and buccal corridors on facial attractiveness: A cross-sectional study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, ZC20–ZC23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, A.W. Smile aesthetics: Perception and influencing factors. Braz. J. Oral Sci. 2010, 9, 441–445. [Google Scholar]
- Ioi, H.; Nakata, S.; Counts, A.L. Effects of buccal corridor space on smile esthetics in Japanese. Angle Orthod. 2009, 79, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, S.M.; Fields, H.W.; Beck, M.; Rosenstiel, S. Attractiveness of variations in the smile arc and buccal corridor space as judged by orthodontists and laymen. Angle Orthod. 2006, 76, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulsey, C.M. An esthetic evaluation of lip–teeth relationships present in the smile. Am. J. Orthod. 1970, 57, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, M.B.; Ackerman, J.L. Smile analysis and design in the digital era. J. Clin. Orthod. 2002, 36, 221–236. [Google Scholar]
- Sarver, D.M. The importance of incisor positioning in the esthetic smile: The smile arc. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2001, 120, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.J.; Tsai, P. Smile analysis and design. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 62, 499–511. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, M.; Ata-Ali, J.; Ata-Ali, F.; Bulsei, M.; Grella, P.; Cobo, T.; Martínez-González, J.M. Evaluation of the maxillary midline, curve of the upper lip, smile line and tooth shape: A prospective study of 140 Caucasian patients. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

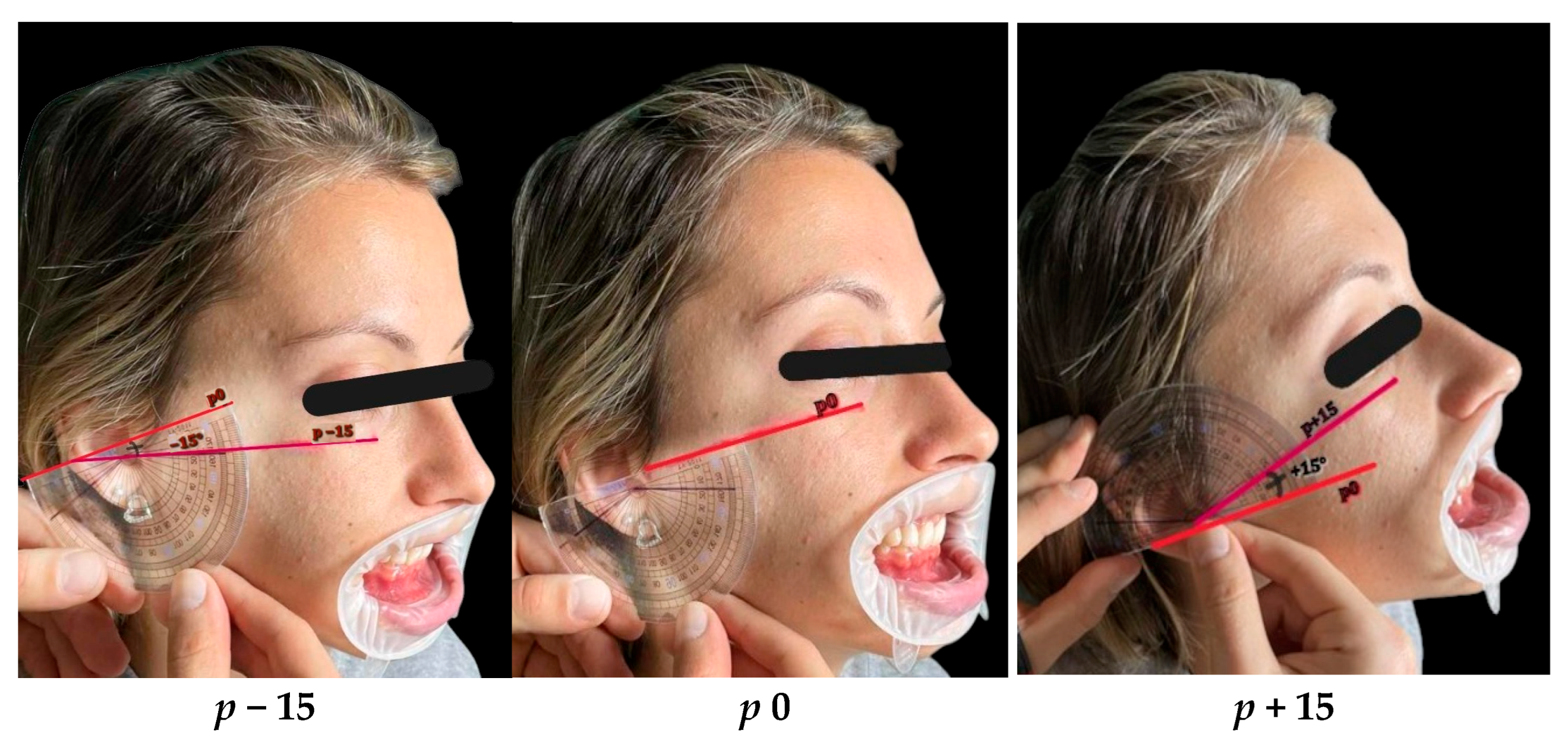
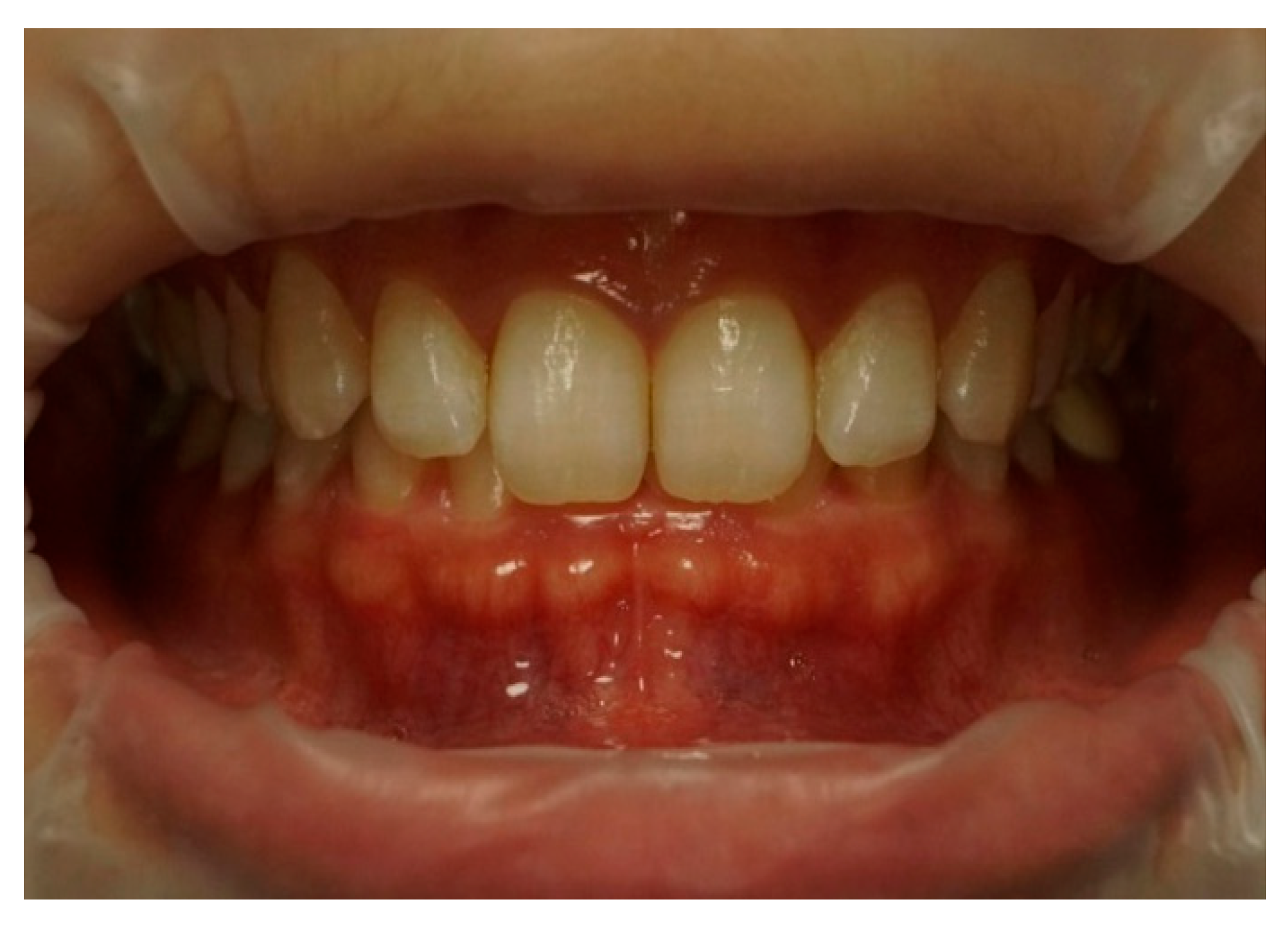
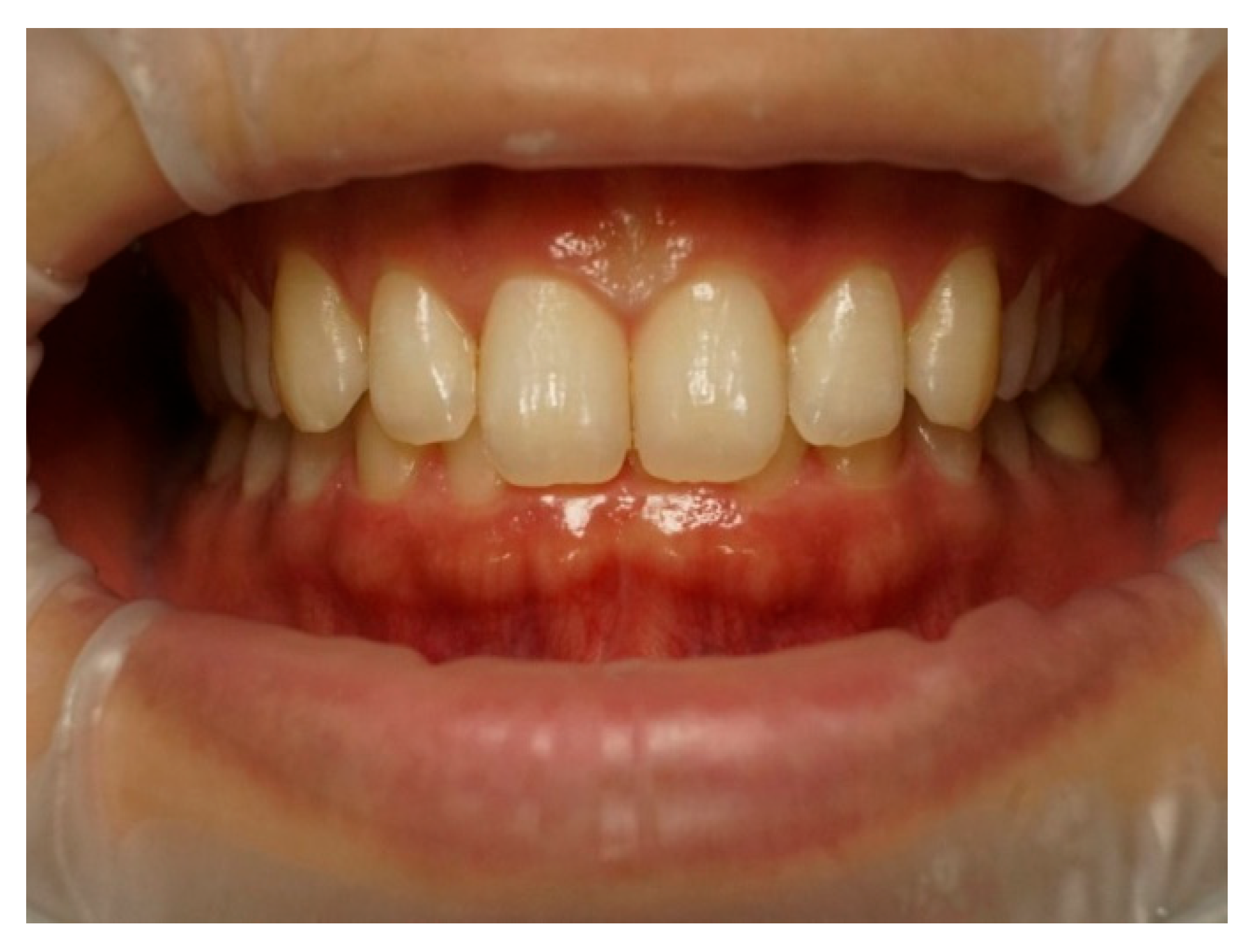
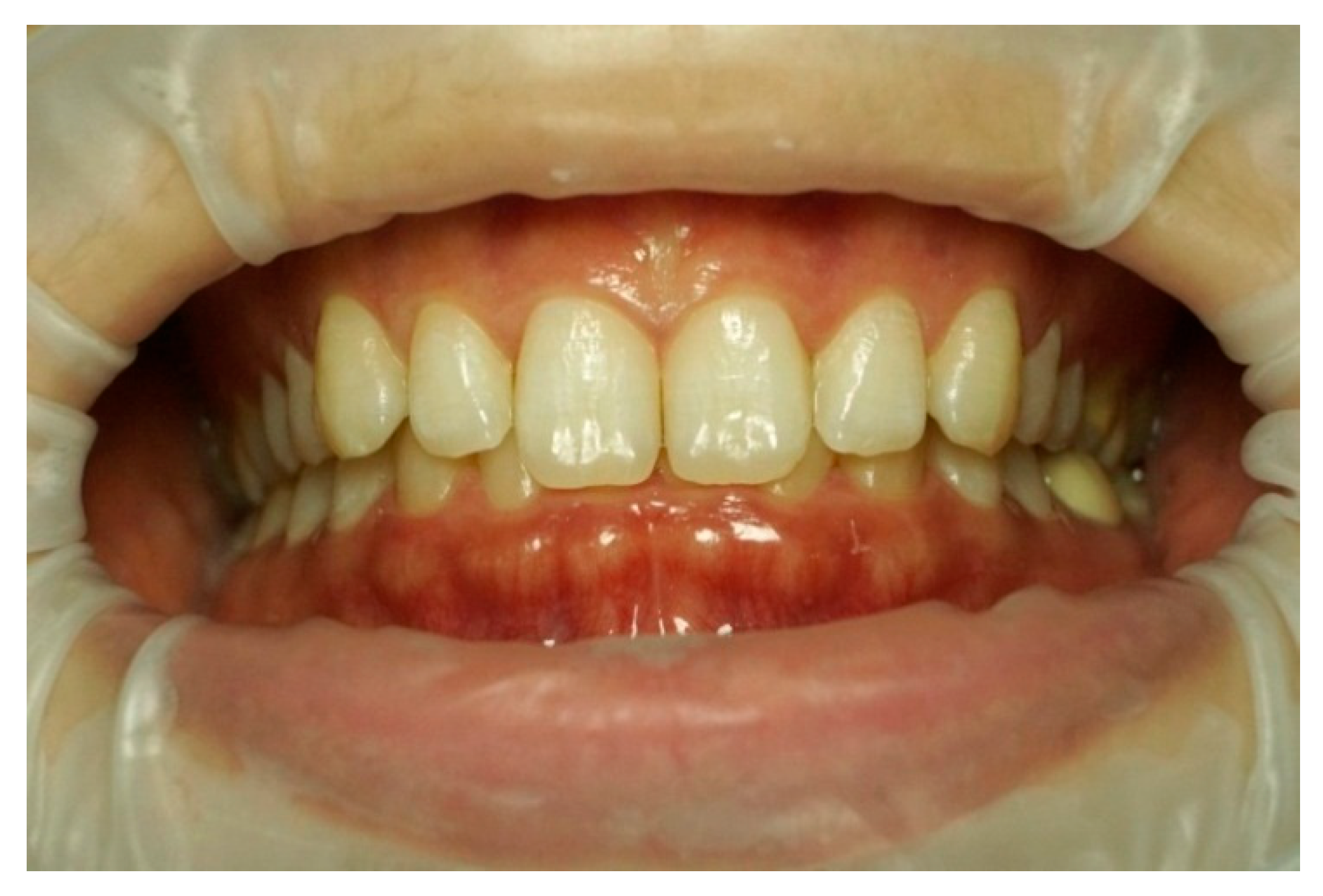

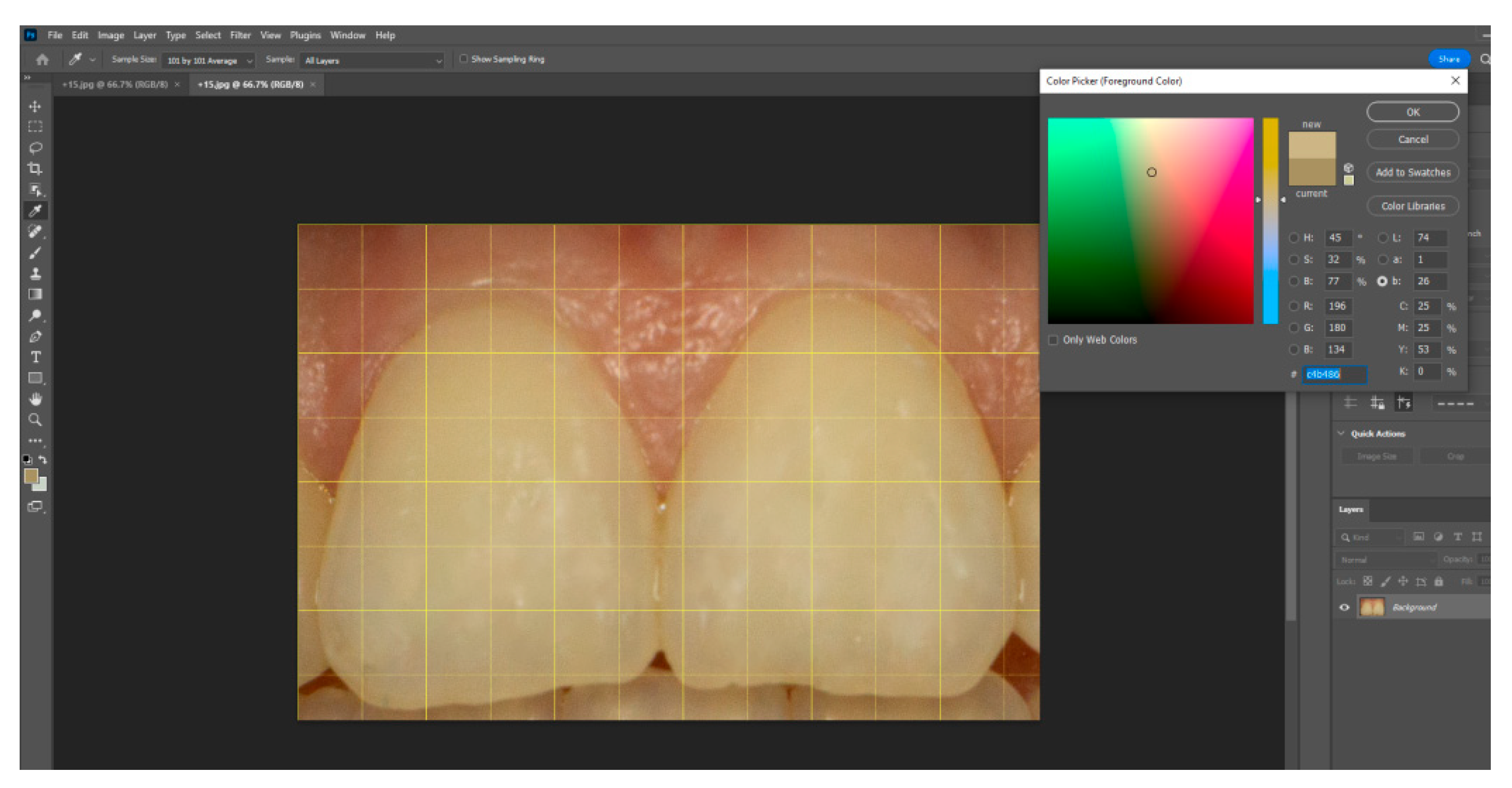
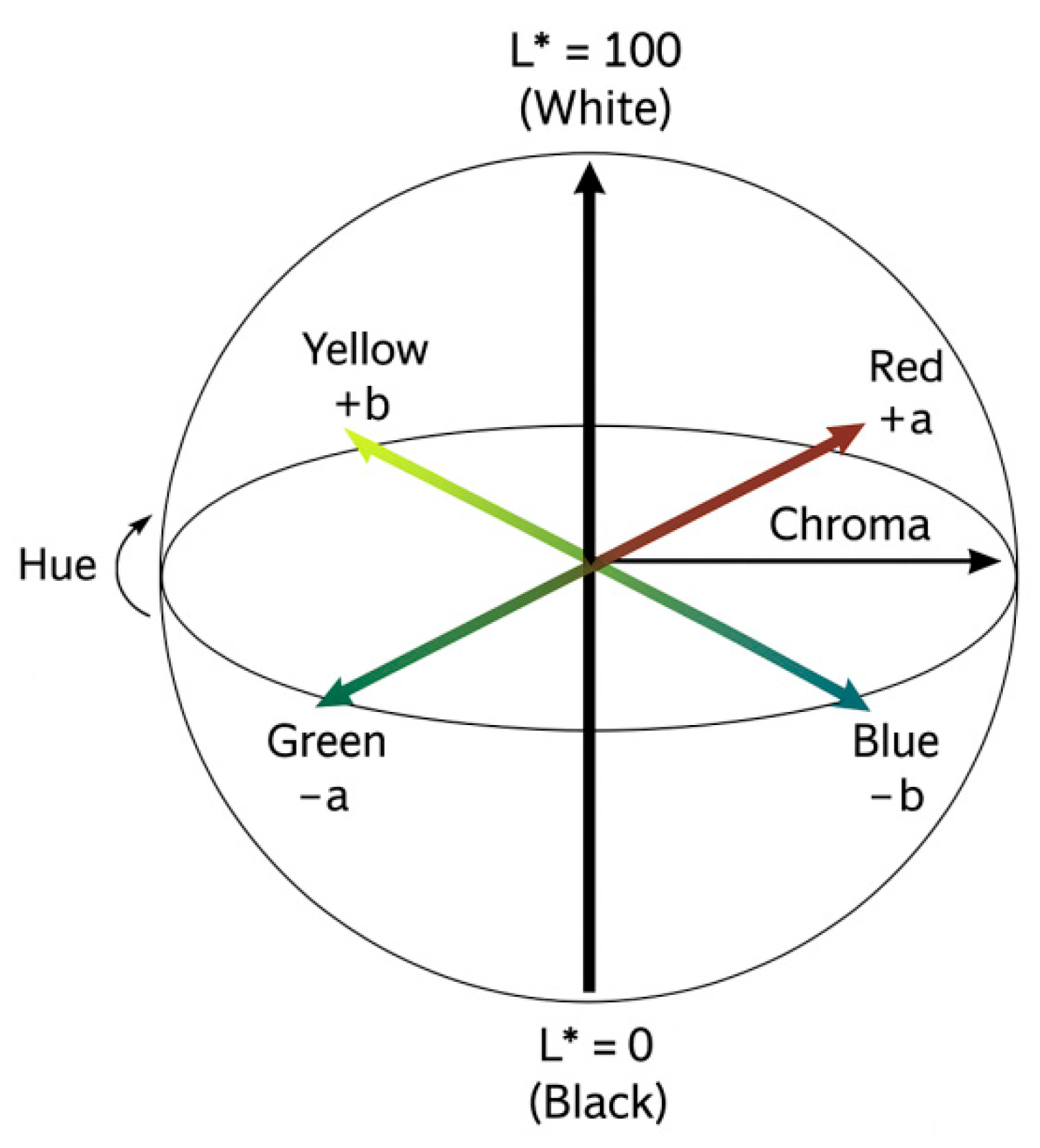
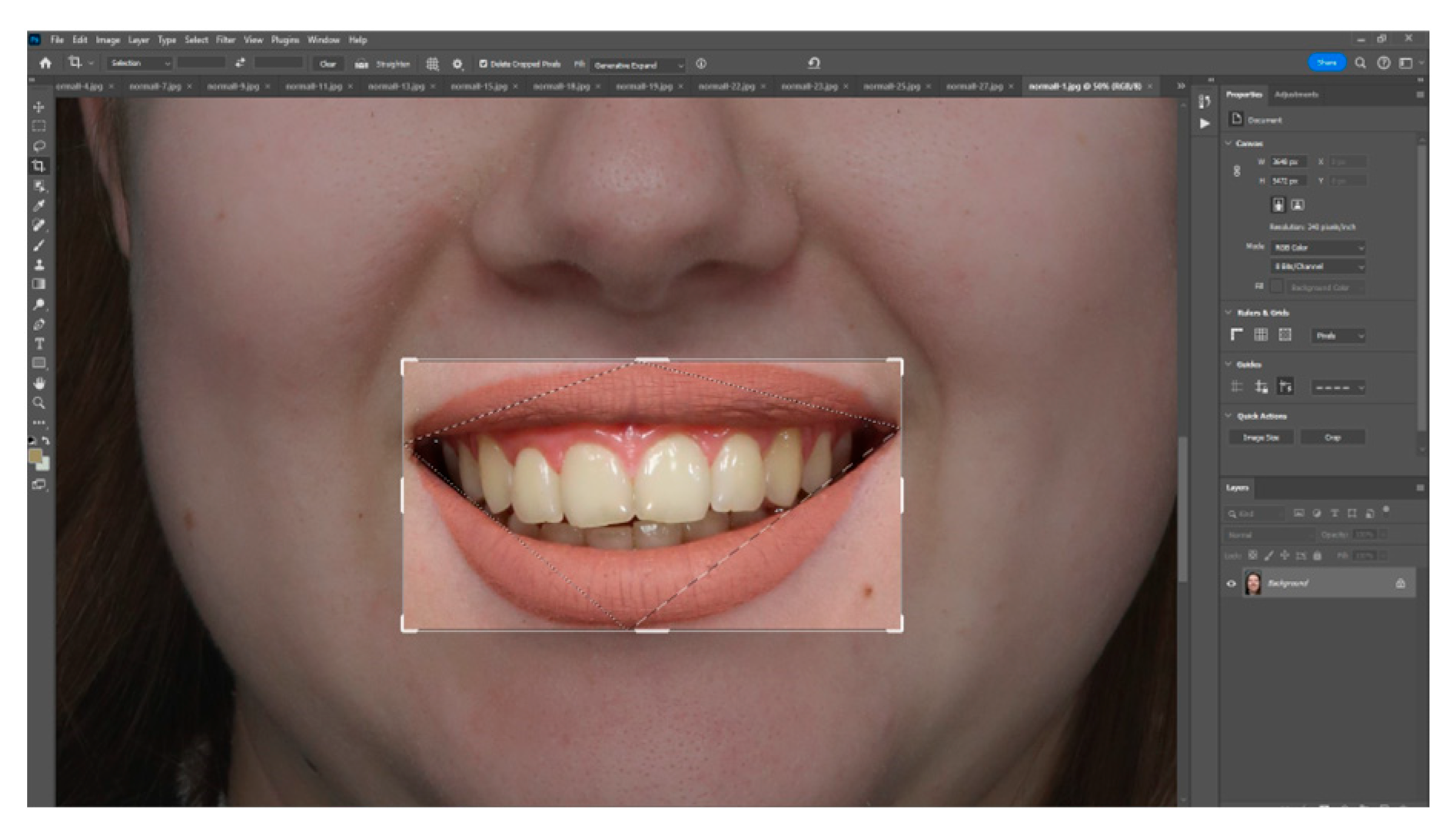
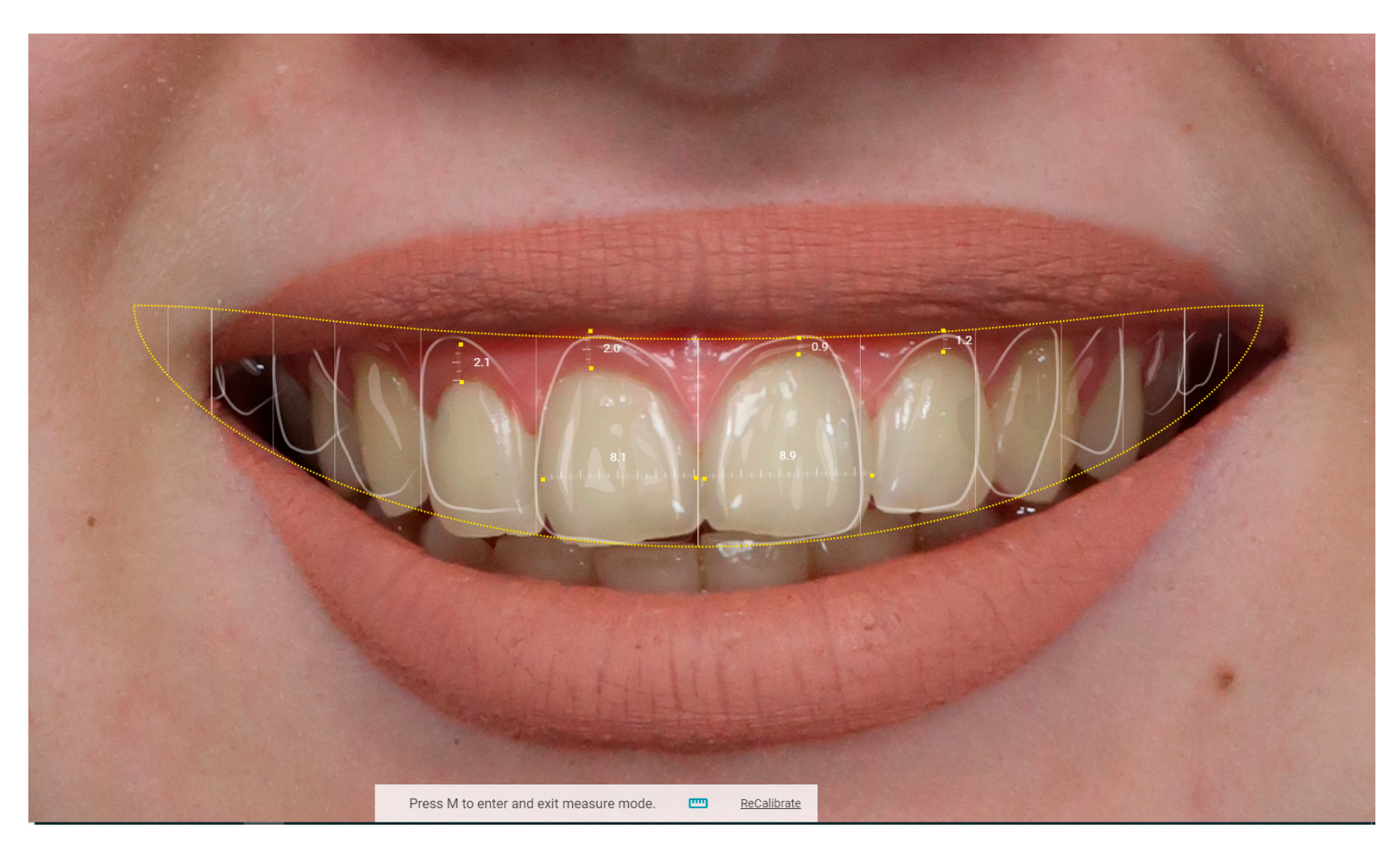
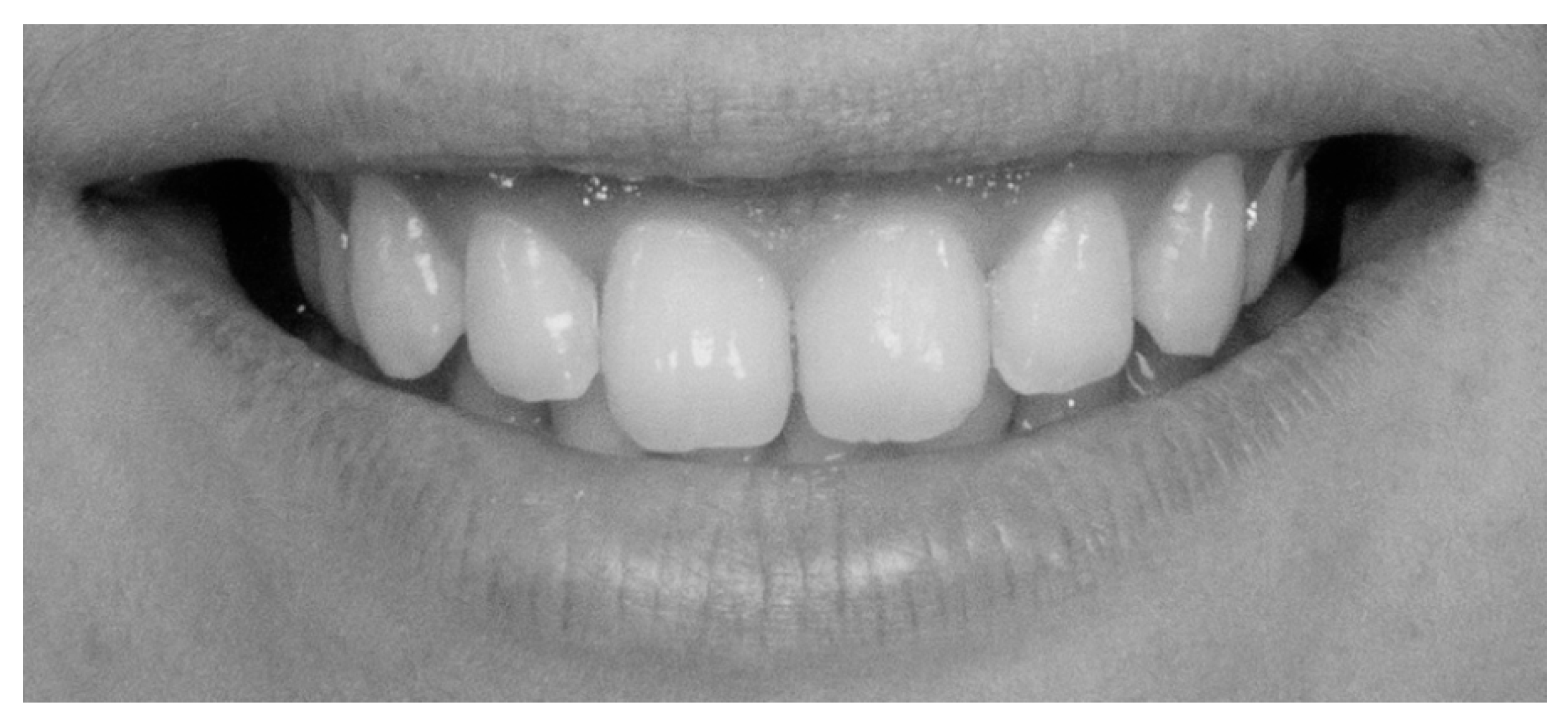
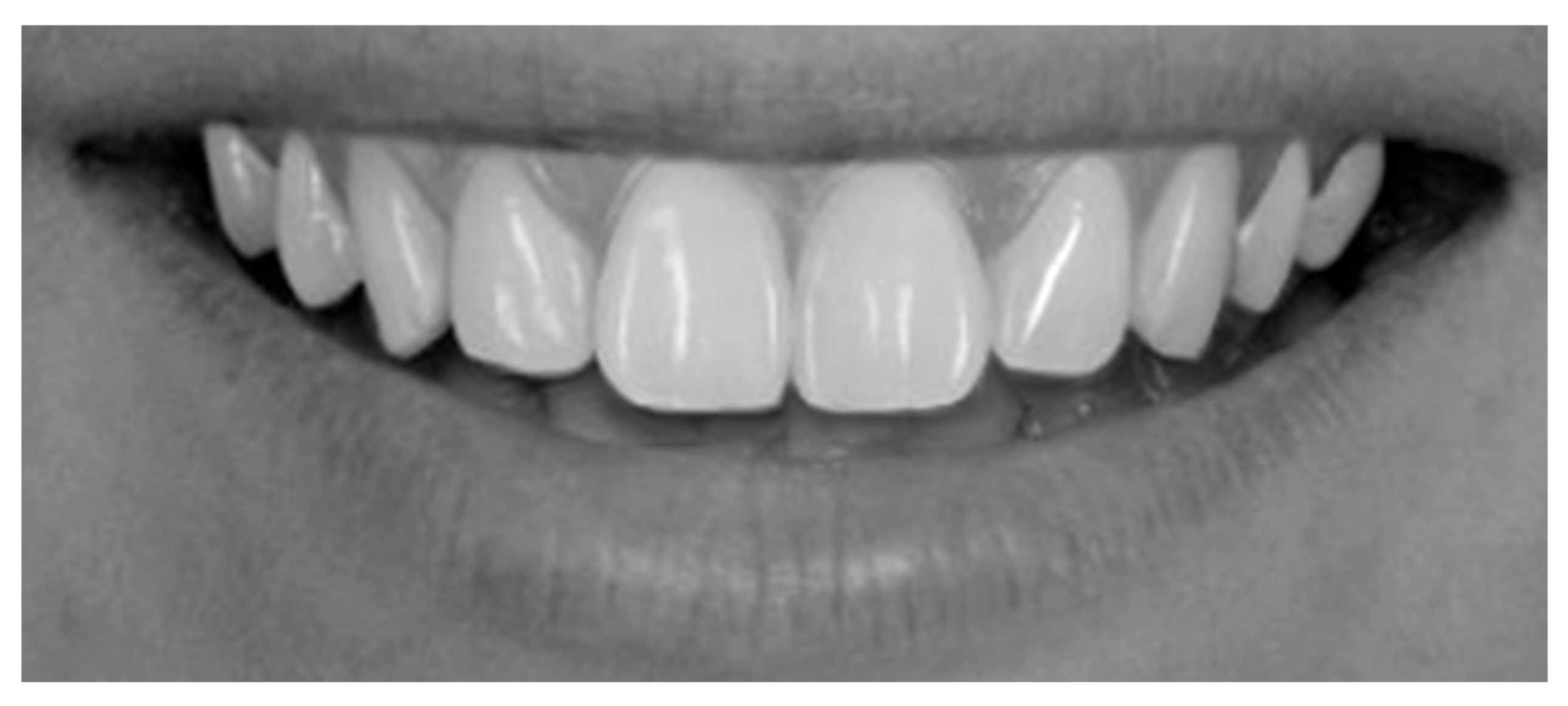
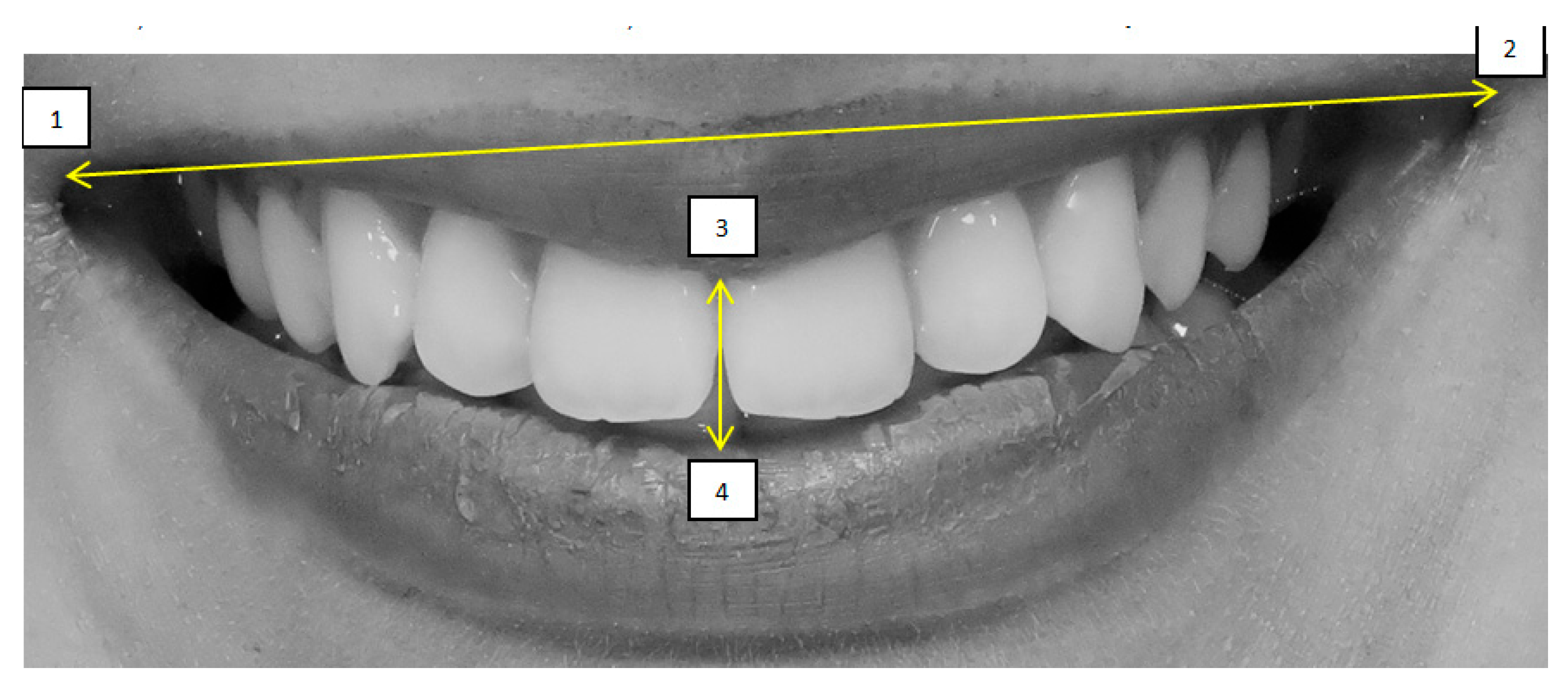

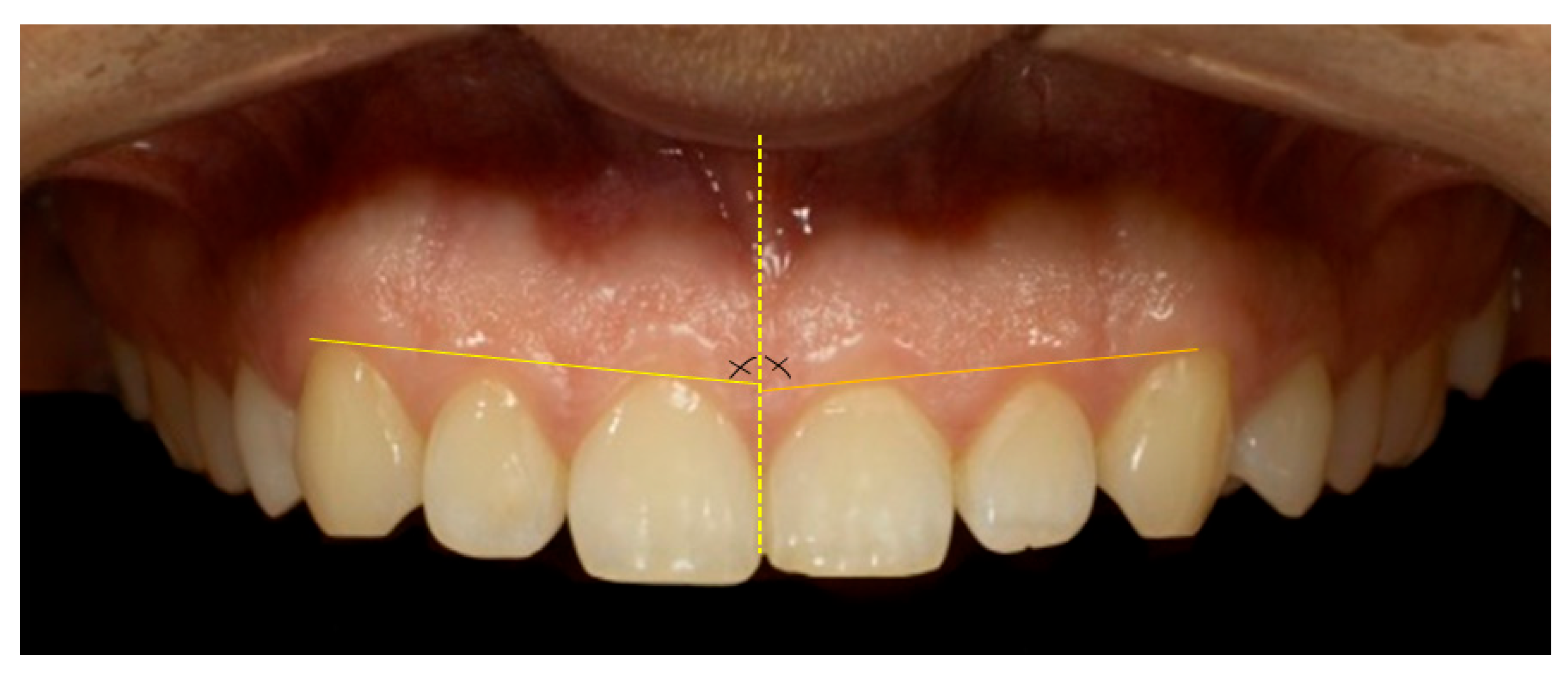



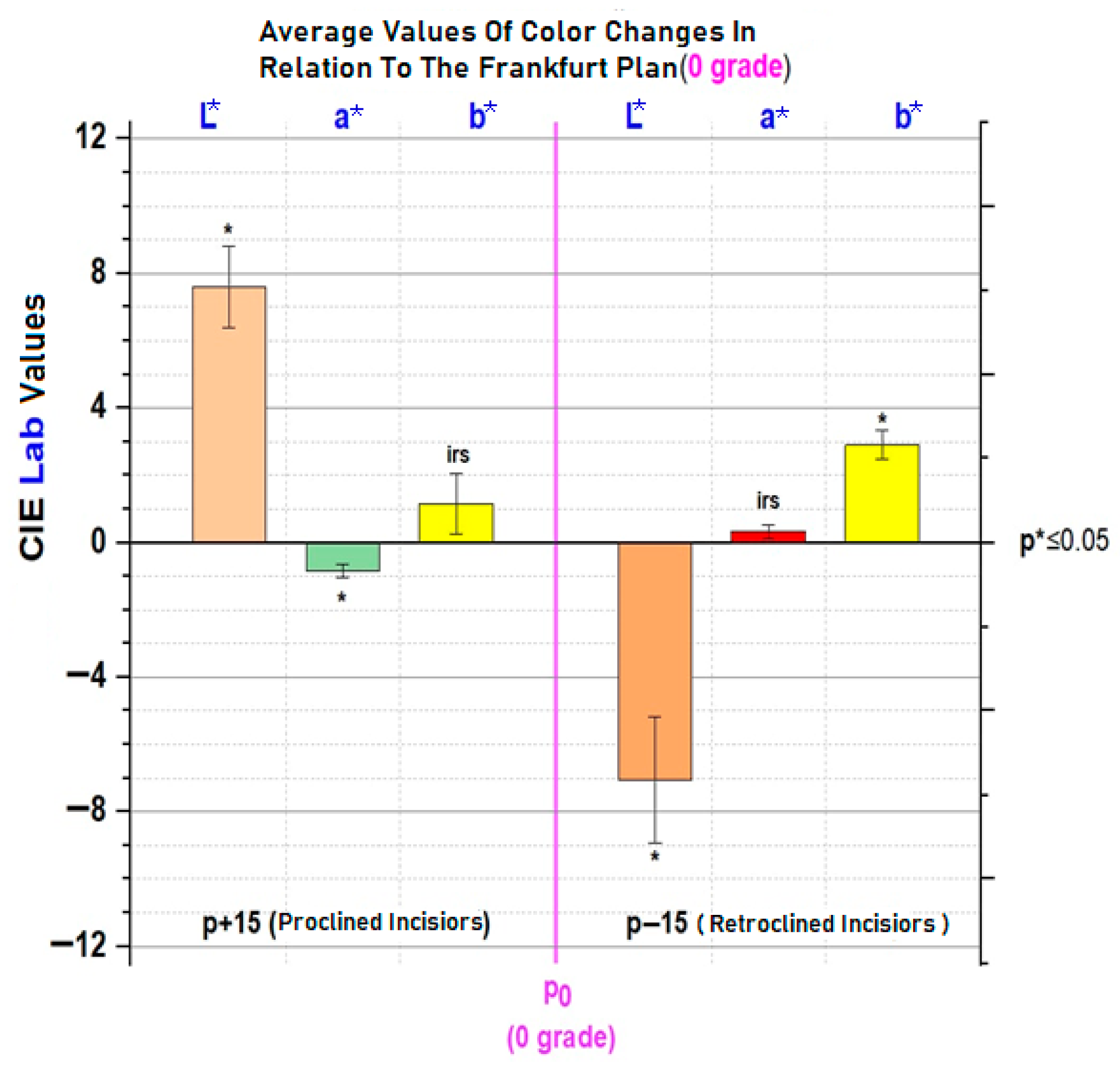
| Characteristics of Smile | Classification | Attractive Smiles | Unattractive Smiles | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dentists p (%) | Laypersons p (%) | p * | Dentists p (%) | Laypersons p (%) | p * | ||
| Smile line | Very high | 0 (0%) | 2 (8%) | 0.255 | 11 (44%) | 11 (44%) | 1 |
| High | 10 (40%) | 13 (52%) | 1 (4%) | 1 (4%) | |||
| Average | 14 (56%) | 10 (40%) | 3 (12%) | 3 (12%) | |||
| Low | 1 (4%) | 0 (0%) | 10 (40%) | 10 (40%) | |||
| Smile arch | Parallel | 21 (84%) | 22 (88%) | 0.683 | 4 (16%) | 7 (28%) | 0.492 |
| Straight | 4 (16%) | 3 (12%) | 12 (48%) | 12 (48%) | |||
| Inverted | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 9 (36%) | 6 (24%) | |||
| Size of the oral corridor | Wide | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0.089 | 15 (60%) | 14 (56%) | 0.478 |
| Average | 2 (8%) | 2 (8%) | 5 (20%) | 4 (16%) | |||
| Narrow | 13 (52%) | 14 (56%) | 5 (20%) | 7 (28%) | |||
| Minimal | 10 (40%) | 9 (36%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |||
| Width of smile | Canine | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0.124 | 6 (24%) | 5 (20%) | 0.689 |
| First premolar | 8 (32%) | 8 (32%) | 11 (44%) | 12 (48%) | |||
| Second premolar | 10 (40%) | 11 (44%) | 3 (12%) | 1 (4%) | |||
| Molar | 7(28%) | 6 (24%) | 5 (20%) | 7 (28%) | |||
| Media ± SD | p ** | Media ± SD | p ** | ||||
| Smile index | 5.46 ± 0.38 | 5.50 ± 0.36 | <0.001 | 4.34 ± 0.43 | 4.31 ± 0.43 | <0.001 | |
| Dynamic smile symmetry | 1.03 ± 0.05 | 1.10 ± 0.08 | <0.001 | 0.89 ± 0.03 | 0.90 ± 0.03 | <0.001 | |
| Characteristics of Smile | Classification | Attractive Smiles | Unattractive Smiles | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men p (%) | Women p (%) | p * | Men p (%) | Women p (%) | p * | ||
| Smile line | Very high | 2 (8%) | 2 (8%) | 0.366 | 11 (44%) | 10 (40%) | 0.736 |
| High | 11 (44%) | 13 (52%) | 1 (4%) | 1 (4%) | |||
| Average | 11 (44%) | 9 (36%) | 3 (12%) | 6 (24%) | |||
| Low | 1 (4%) | 1 (4%) | 10 (40%) | 8 (32%) | |||
| Smile arch | Parallel | 21 (84%) | 19 (76%) | 0.479 | 8 (32%) | 9 (36%) | 0.117 |
| Straight | 4 (16%) | 6 (24%) | 9 (36%) | 8 (32%) | |||
| Inverted | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 8 (32%) | 8 (32%) | |||
| Size of the oral corridor | Wide | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0.355 | 13 (52%) | 15 (60%) | 0.352 |
| Average | 3 (12%) | 4 (16%) | 8 (32%) | 7 (28%) | |||
| Narrow | 14 (56%) | 12 (48%) | 4 (16%) | 3 (12%) | |||
| Minimal | 8 (32%) | 9 (36%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |||
| Width of smile | Canine | 6 (24%) | 5 (20%) | 0.371 | 2 (8%) | 2 (8%) | 0.583 |
| First premolar | 9 (36%) | 8 (32%) | 7 (28%) | 5 (20%) | |||
| Second premolar | 8 (32%) | 10 (40%) | 7 (28%) | 9 (36%) | |||
| First molar | 2 (8%) | 2 (8%) | 9 (36%) | 9 (36%) | |||
| Average ± SD | p ** | Average ± SD | p ** | ||||
| Smile index | 5.49 ± 0.38 | 5.49 ± 0.38 | <0.001 | 4.34 ± 0.44 | 4.29 ± 0.48 | <0.001 | |
| Dynamic smile symmetry | 1.03 ± 0.05 | 1.06 ± 0.05 | <0.001 | 0.89 ± 0.03 | 0.84 ± 0.05 | <0.001 | |
| Quadrant 1 (Average ± SD) | Quadrant 2 (Average ± SD) | p * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GALº | 89.22 ± 3.02 | 85.44 ± 4.48 | <0.001 |
| HPI central incisor (mesial) | 4.206 ± 0.103 | 4.186 ± 0.157 | <0.001 |
| HPI central incisor (distal) | 4.114 ± 0.114 | 4.152 ± 0.115 | <0.001 |
| HPI lateral incisor (mesial) | 3.68 ± 0.127 | 3.717 ± 0.1 | <0.001 |
| HPI lateral incisor (distal) | 3.435 ± 0.104 | 3.476 ± 0.1 | <0.001 |
| HPI canine (mesial) | 4.094 ± 0.127 | 4.166 ± 0.097 | <0.001 |
| HPI canine (distal) | 3.551 ± 0.046 | 3.518 ± 0.119 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bud, E.; Vlasa, A.; Bud, A.; Pacurar, M.; Bucur, S.M.; Esian, D.; Stepco, E.; Cheptanaru, O.; Nenec, B.G.; Nenec, A.C. Evaluation of Smile Aesthetics in Dental Students: Perceptions of Tooth Colour Changes Due to Incisor Inclination and Micro- and Mini-Aesthetic Characteristics Assessed by Professionals and Laypersons. Dent. J. 2025, 13, 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13080380
Bud E, Vlasa A, Bud A, Pacurar M, Bucur SM, Esian D, Stepco E, Cheptanaru O, Nenec BG, Nenec AC. Evaluation of Smile Aesthetics in Dental Students: Perceptions of Tooth Colour Changes Due to Incisor Inclination and Micro- and Mini-Aesthetic Characteristics Assessed by Professionals and Laypersons. Dentistry Journal. 2025; 13(8):380. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13080380
Chicago/Turabian StyleBud, Eugen, Alexandru Vlasa, Anamaria Bud, Mariana Pacurar, Sorana Maria Bucur, Daniela Esian, Elena Stepco, Olga Cheptanaru, Bianca Gabriela Nenec, and Andrei Cosmin Nenec. 2025. "Evaluation of Smile Aesthetics in Dental Students: Perceptions of Tooth Colour Changes Due to Incisor Inclination and Micro- and Mini-Aesthetic Characteristics Assessed by Professionals and Laypersons" Dentistry Journal 13, no. 8: 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13080380
APA StyleBud, E., Vlasa, A., Bud, A., Pacurar, M., Bucur, S. M., Esian, D., Stepco, E., Cheptanaru, O., Nenec, B. G., & Nenec, A. C. (2025). Evaluation of Smile Aesthetics in Dental Students: Perceptions of Tooth Colour Changes Due to Incisor Inclination and Micro- and Mini-Aesthetic Characteristics Assessed by Professionals and Laypersons. Dentistry Journal, 13(8), 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13080380







