Comparative Evaluation of Customized CAD/CAM vs. Stock Titanium Abutments for Immediate Implant Placement in Class II Extraction Sockets: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Sample Size Calculation
2.3. Randomization and Blinding
2.4. Patient Selection
2.5. Patients Grouping
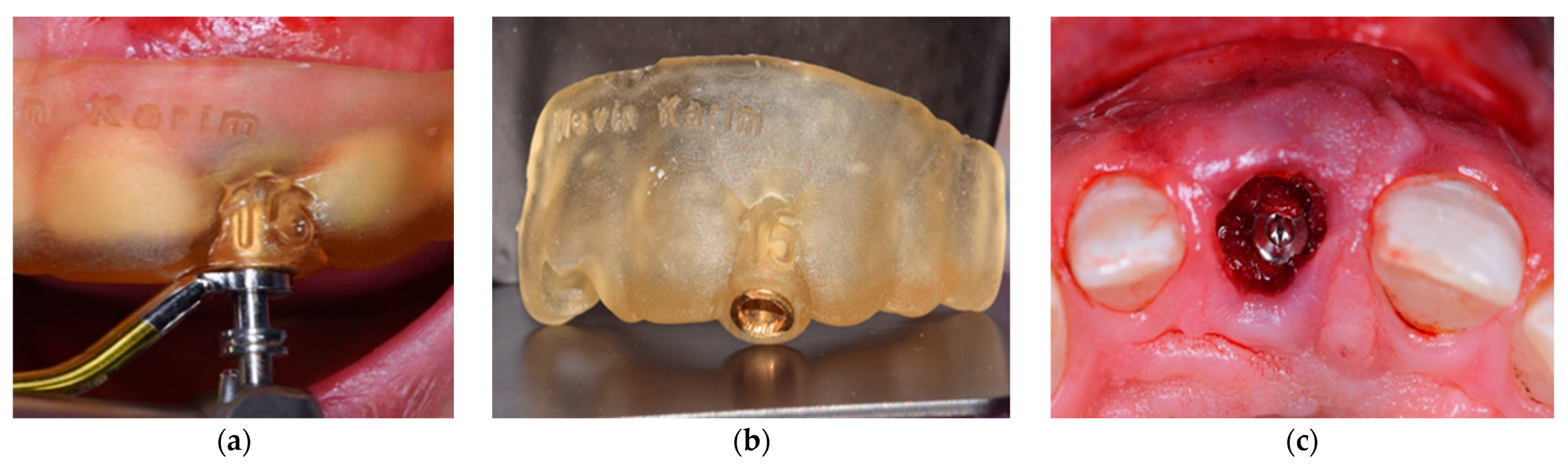
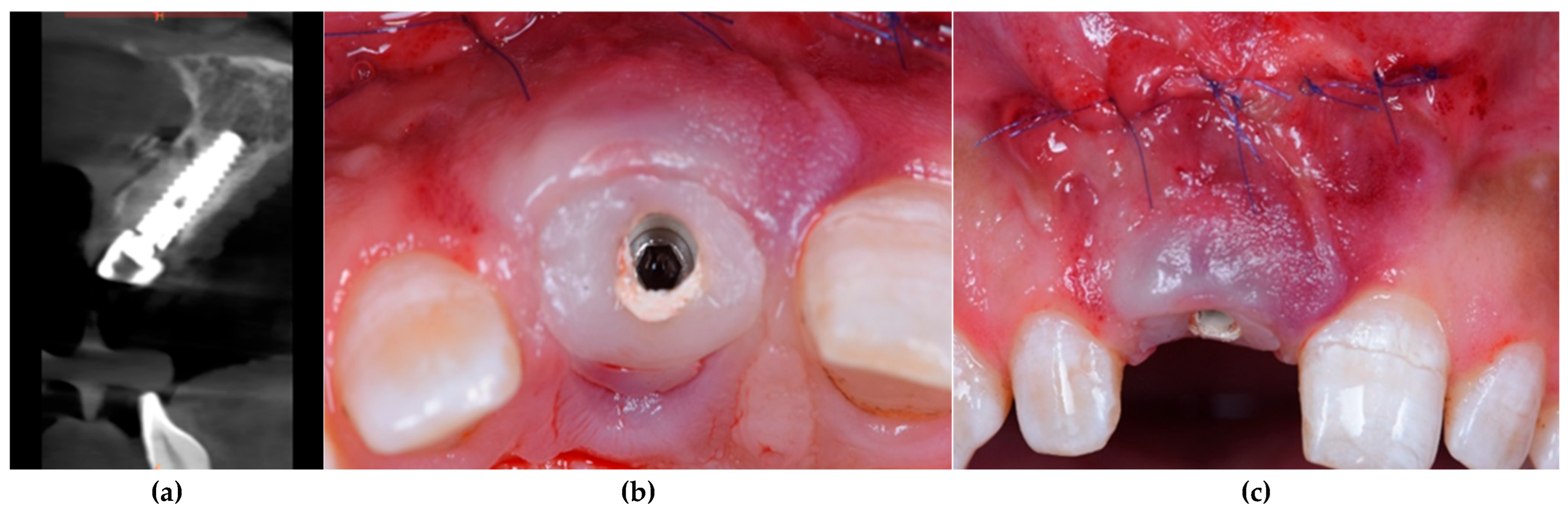
2.6. Surgical and Implant Procedures
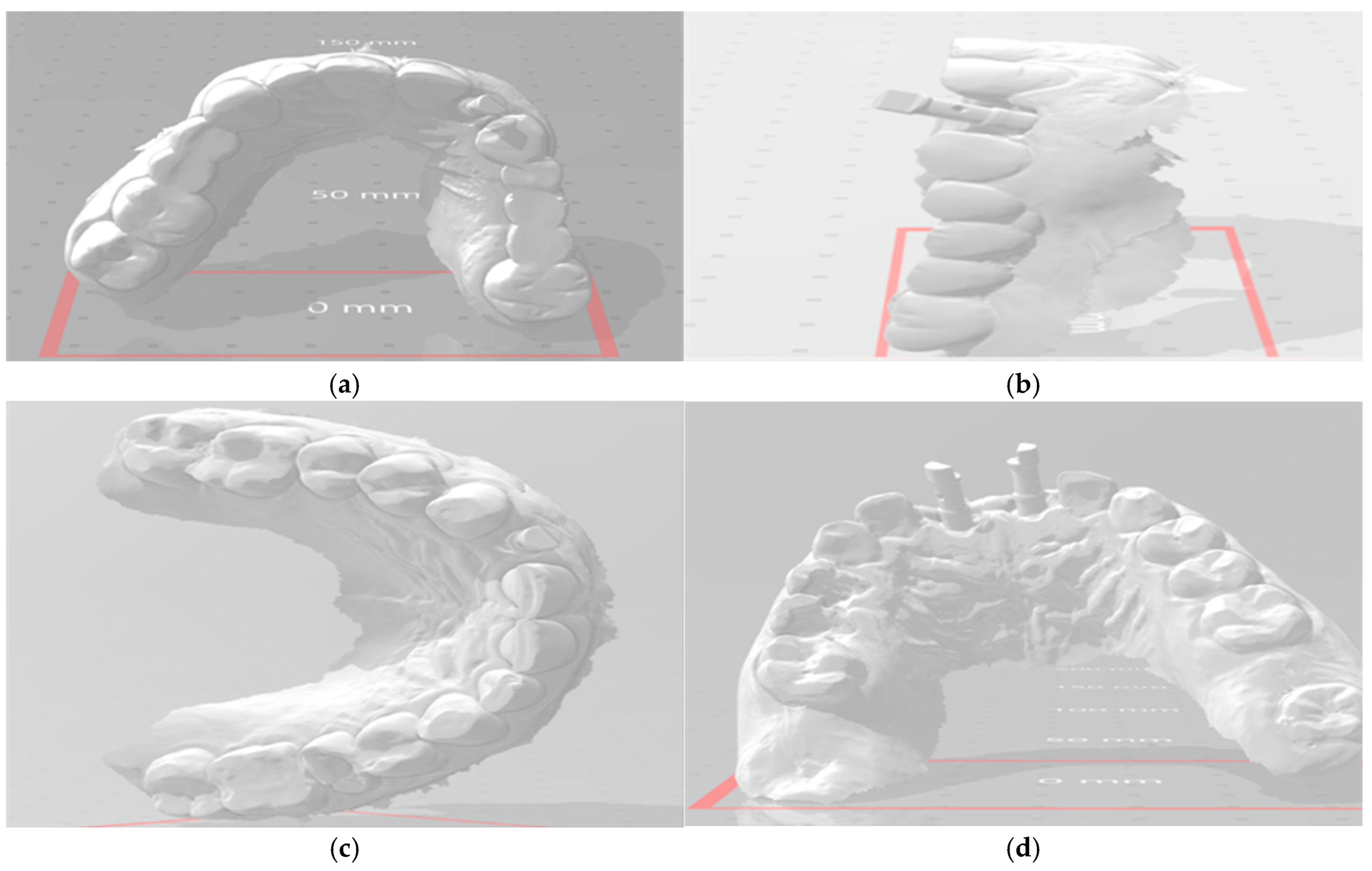
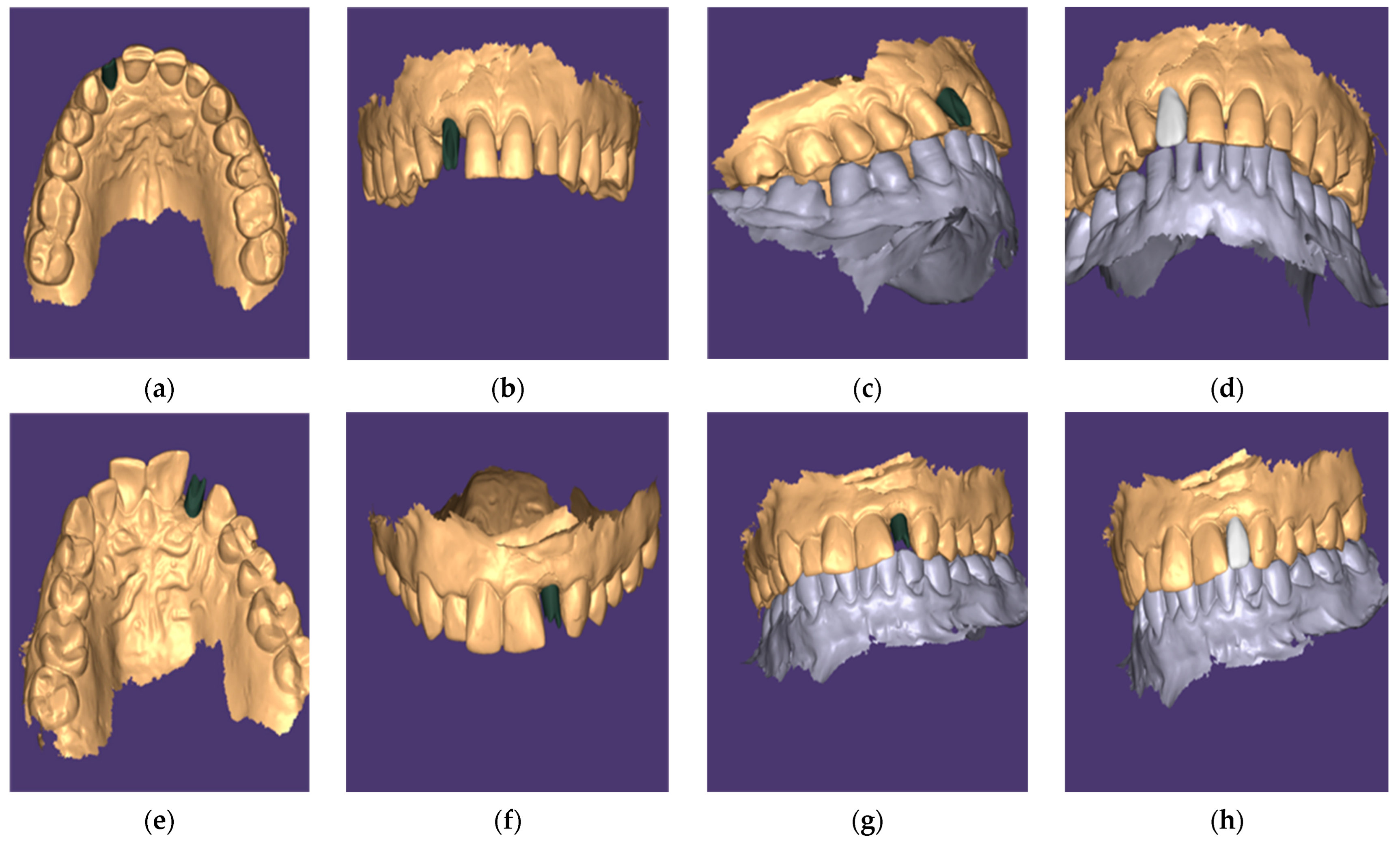
2.7. Abutment Fabrication Workflow
2.8. Standardized Polishing and Cleaning Protocol
2.9. Prosthetic and Postoperative Protocol
2.10. Outcome Assessments
2.11. Clinical Assessment
- Probing Depth (PD): Peri-implant PD was measured using a UNC-15 probe at two aspects (mesial and distal) for each implant. Baseline PD was recorded prior to extraction at the corresponding tooth sites, and implant PD was measured at T1 and T2.
- Peri-implant Mucosal Level: Changes in soft tissue level were assessed by measuring the height of the mesial papilla, mid-facial mucosa, and distal papilla at T1 and T2 relative to baseline. The average change of these three points represented overall peri-implant mucosal level change.
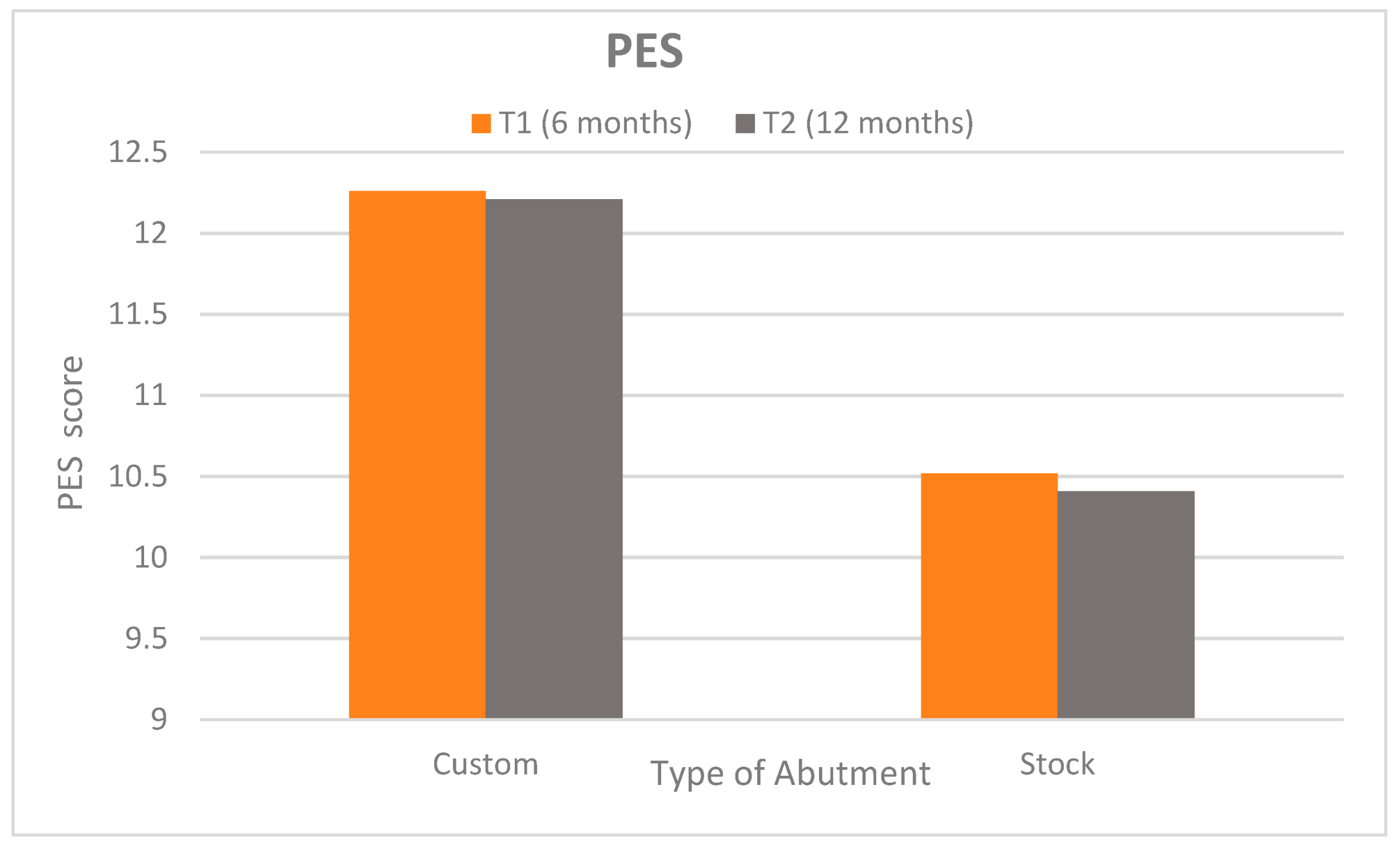
- The Pink Esthetic Score (PES): The PES was evaluated at T1 and T2 to rate the peri-implant soft tissue esthetics. Seven PES criteria (mesial/distal papilla fill, soft tissue level, contour, ridge morphology, soft tissue color, and texture) were scored 2 (best) to 0 (worst). The maximum PES is 14, indicating ideal tissue esthetics around the implant crown [28].
2.12. Radiographic Assessment
2.13. Patient Satisfaction
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Demographic Data
3.2. Clinical Assessment
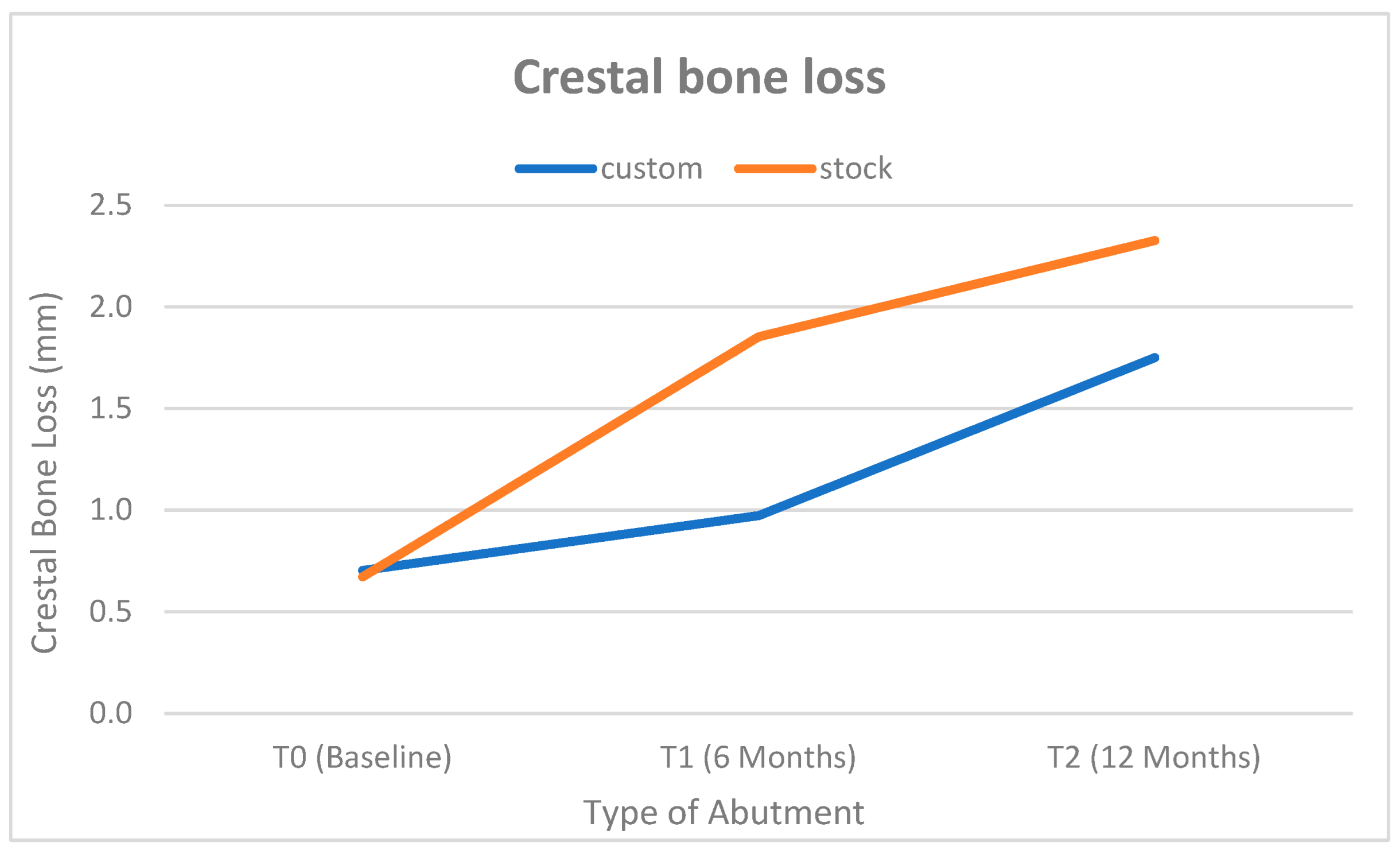
3.3. Radiographic Assessment
3.4. Patient Satisfaction
4. Discussion
5. Limitation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaviria, L.; Salcido, J.P.; Guda, T.; Ong, J.L. Current trends in dental implants. J. Korean Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 40, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, S.; Reddy, V.; Kumar, R.; Kudlure, S.; Gomasani, S.; Ali, S. Tooth loss prevalence and risk indicators among adult people visiting community health centers in Nellore district, Andhra Pradesh: A cross-sectional study. J. Indian Assoc. Public Health Dent. 2016, 14, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, J.Y.; Rungcharassaeng, K.; Morimoto, T.; Lozada, J. Facial gingival tissue stability after connective tissue graft with single immediate tooth replacement in the esthetic zone: Consecutive case report. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 67 (Suppl. S11), 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elian, N.; Cho, S.C.; Froum, S.; Smith, R.B.; Tarnow, D.P. A simplified socket classification and repair technique. Pract. Proced. Aesthet. Dent. 2007, 19, 99–104, quiz 106. [Google Scholar]
- Ahamed, S.K.; Menchini-Fabris, G.B.; Alqarni, A.; Alarabi, S.M.; Alharbi, A.A.; Alshamrani, A.; Covani, U.; Cosola, S. Insights into the Current Management Techniques for Peri-Implant Gaps: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, S.; Pascadopoli, M.; Pellegrini, M.; Pulicari, F.; Manfredini, M.; Zampetti, P.; Spadari, F.; Maiorana, C.; Scribante, A. CAD/CAM Abutments versus Stock Abutments: An Update Review. Prosthesis 2022, 4, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepke, U.; Gresnigt, M.M.M.; Browne, W.R.; Abdolahzadeh, S.; Nijkamp, J.; Cune, M.S. Phase transformation and fracture load of stock and CAD/CAM-customized zirconia abutments after 1 year of clinical function. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2019, 30, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, J.A.; Tan, W.C.; Balmer, T.E.; Salvi, G.E.; Lang, N.P. Bleeding on probing and pocket probing depth in relation to probing pressure and mucosal health around oral implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2009, 20, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Wang, X.; Chen, S. Vertical and horizontal dimensional changes of peri-implant facial bone following immediate placement and provisionalization with customized definite abutment in maxillary anterior single implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2019, 30, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, S.; Ahmed, Y.; El-Anwar, M.I.; Elddamony, E.; Ashraf, R. Influence of different polymeric materials of implant and attachment on stress distribution in implant-supported overdentures: A three-dimensional finite element study. BMC Oral Health 2025, 25, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giner, S.; Bartolomé, J.F.; Gomez-Cogolludo, P.; Castellote, C.; Pradíes, G. Fatigue fracture resistance of titanium and chairside CAD-CAM zirconia implant abutments supporting zirconia crowns: An in vitro comparative and finite element analysis study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 125, 503.e1–503.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vautrin, A.; Zysset, P.; Varga, P. Influence of key modeling assumptions on the finite element prediction of dental implant primary stability. Comput. Biol. Med. 2025, 195, 110587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taymour, N.; Abdul Hameed, S.M.; AlGhamdi, M.A.; El Sharkawy, Z.R.; Farid, Z.S.; Ahmed, Y. Accuracy of New-Generation Intraoral Scanners in Digitizing All-on-Four Implant Models with Varying Posterior Implant Angulations: An In Vitro Trueness and Precision Evaluation. Prosthesis 2025, 7, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokaree, P.; Poovarodom, P.; Chaijareenont, P.; Rungsiyakull, P. Effect of Customized and Prefabricated Healing Abutments on Peri-Implant Soft Tissue and Bone in Immediate Implant Sites: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Danasory, M.B.; Khamis, M.M.; Abdel Hakim, A.A.; Fahmy, R.A. Outcomes of bio-esthetic single implant-supported restorations after peri-implant soft tissue conditioning with two prosthetic techniques: A 1-year randomized clinical trial. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2025, 133, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelivan, I.; Šeparović, I.; Vuletić, M.; Dulcic, N.; Gabrić, D. Radiological and Periodontal Evaluation of Stock and Custom CAD/CAM Implant Abutments—A One-Year Follow-Up Study. Prosthesis 2023, 5, 437–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lops, D.; Romeo, E.; Mensi, M.; Troiano, G.; Zhurakivska, K.; Del Fabbro, M.; Palazzolo, A. CAD/CAM Abutments in the Esthetic Zone: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Soft Tissue Stability. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paek, J.; Woo, Y.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Pae, A.; Noh, K.; Lee, H.; Kwon, K.-R. Comparative Analysis of Screw Loosening With Prefabricated Abutments and Customized CAD/CAM Abutments. Implant. Dent. 2016, 25, 770–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Târtea, D.A.; Ionescu, M.; Manolea, H.O.; Mercuț, V.; Obădan, E.; Amărăscu, M.O.; Mărășescu, P.C.; Dăguci, L.; Popescu, S.M. Comparative Study of Dental Custom CAD-CAM Implant Abutments and Dental Implant Stock Abutments. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elleuch, S.; Jrad, H.; Wali, M.; Dammak, F. Agglomeration effect on biomechanical performance of CNT-reinforced dental implant using micromechanics-based approach. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2023, 145, 106023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belloni, A.; Argentieri, G.; Orilisi, G.; Notarstefano, V.; Giorgini, E.; D’Addazio, G.; Orsini, G.; Caputi, S.; Sinjari, B. New insights on collagen structural organization and spatial distribution around dental implants: A comparison between machined and laser-treated surfaces. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Han, X.; Zhang, D.; Wu, J.; Huang, S. Buccal plate preservation with immediate post-extraction implant placement and provisionalization in anterior maxillary tooth: Preliminary results of a new technique using Teruplug collagen. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 124 (Suppl. S6), 101536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.C.; den Hartog, L.; van Heereveld, C.; Jagdale, A.; Dilbaghi, A.; Cune, M.S. Comparison of two different abutment designs on marginal bone loss and soft tissue development. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2014, 29, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hua, F.; Zhang, H.; Hu, J. Influence of using collagen on the soft and hard tissue outcomes of immediate dental implant placement: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 124 (Suppl. S1), 101385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Rezk, F.; Trimpou, G.; Lauer, H.C.; Weigl, P.; Krockow, N. Response of soft tissue to different abutment materials with different surface topographies: A review of the literature. Gen. Dent. 2018, 66, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Canullo, L.; Penarrocha Oltra, D.; Pesce, P.; Zarauz, C.; Lattanzio, R.; Penarrocha Diago, M.; Iezzi, G. Soft tissue integration of different abutment surfaces: An experimental study with histological analysis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2021, 32, 928–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh Ismail, H.; Ibrahim Ali, A. The Effect of Finishing and Polishing Systems on Surface Roughness and Microbial Adhesion of Bulk Fill Composites: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Dent. 2023, 20, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fürhauser, R.; Florescu, D.; Benesch, T.; Haas, R.; Mailath, G.; Watzek, G. Evaluation of soft tissue around single-tooth implant crowns: The pink esthetic score. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2005, 16, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, C.; Lam, O.; Lang, N. An evidence-based review of patient-reported outcome measures in dental implant research among dentate subjects. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2012, 39, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; González-Martín, O.; Weisgold, A.S.; Lee, E.A. Considerations of implant abutment and crown contour: Critical contour and subcritical contour. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2010, 30, 335–343. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Y.; Koo, K.-T.; Schwarz, F.; Ben Amara, H.; Heo, S.-J. Association of prosthetic features and peri-implantitis: A cross-sectional study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2020, 47, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binon, P.P. Implants and components: Entering the new millennium. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2000, 15, 76–94. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Chen, J.; Pei, X.; Han, J.; Wang, J. Network meta-analysis of survival rate and complications in implant-supported single crowns with different abutment materials. J. Dent. 2019, 88, 103115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Martín, O.; Lee, E.; Weisgold, A.; Veltri, M.; Su, H. Contour Management of Implant Restorations for Optimal Emergence Profiles: Guidelines for Immediate and Delayed Provisional Restorations. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2020, 40, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.-T.; Lin, J.; Salamanca, E.; Dorj, O.; Pan, Y.-H.; Wu, Y.-F.; Hsu, Y.-S.; Fang, C.-Y.; Chang, W.-J. Marginal Bone Level Evaluation of Fixed Partial Dental Prostheses Using Preformed Stock versus CAD/CAM Customized Abutments. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.C.; Liang, C.H.; Shen, Y.F.; Hsu, K.W. Retrospective comparison of posterior fixed dental prostheses supported by two different titanium abutments on tissue level implants. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 125, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, A.; Khater, A.G.A.; Gehrke, S.A.; Serra, P.; Francesco, I.; Di Carmine, M.; Tari, S.R.; Leo, L.; Lorusso, F. Current Status of Peri-Implant Diseases: A Clinical Review for Evidence-Based Decision Making. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, D.; Grandin, H.M.; Ofec, R. Retrospective cohort study of 4,591 dental implants: Analysis of risk indicators for bone loss and prevalence of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis. J. Periodontol. 2019, 90, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsan, I.M.; Pauna, M.R.; Petre, A.E.; Oancea, L. Biologic and Esthetic Outcome of CAD/CAM Custom Ceramic Implant Abutment: A Clinical Report. Maedica 2021, 16, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lops, D.; Bressan, E.; Parpaiola, A.; Sbricoli, L.; Cecchinato, D.; Romeo, E. Soft tissues stability of cad-cam and stock abutments in anterior regions: 2-year prospective multicentric cohort study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2015, 26, 1436–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menchini-Fabris, G.B.; Cosola, S.; Toti, P.; Hwan Hwang, M.; Crespi, R.; Covani, U. Immediate Implant and Customized Healing Abutment for a Periodontally Compromised Socket: 1-Year Follow-Up Retrospective Evaluation. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, C.C.; Lemos, C.A.A.; de Luna Gomes, J.M.; Verri, F.R.; Pellizzer, E.P. CAD/CAM vs Conventional Technique for Fabrication of Implant-Supported Frameworks: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of In Vitro Studies. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 32, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menchini-Fabris, G.B.; Toti, P.; Covani, U.; Trasarti, S.; Cosola, S.; Crespi, R. Volume assessment of the external contour around immediate implant with or without immediate tooth-like crown provisionalization: A digital intraoral scans study. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 124, 101418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveau, A.; Rignon-Bret, C.; Wulfman, C. Zirconia abutments in the anterior region: A systematic review of mechanical and esthetic outcomes. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 121, 775–781.e771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Holanda Cavalcanti Pereira, A.K.; de Oliveira Limirio, J.P.J.; Cavalcanti do Egito Vasconcelos, B.; Pellizzer, E.P.; Dantas de Moraes, S.L. Mechanical behavior of titanium and zirconia abutments at the implant-abutment interface: A systematic review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2024, 131, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albarghouti, G.; Sadi, H.A.S. Recent Modifications of Zirconia in Dentistry. In Zirconia—New Advances, Structure, Fabrication and Applications; Al-Naib, U.M.B., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- de Moura, A.J.; Burgoa, S.; Rayes, A.; da Silva, R.L.B.; Ayres, A.P.; Cortes, A.R.G. Digital Workflow for Designing CAD-CAM Custom Abutments of Immediate Implants Based on the Natural Emergence Profile of the Tooth to be Extracted. J. Oral Implantol. 2023, 49, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borzangy, S. A Comparison of Zirconia CAD/CAM to Conventionally Fabricated Single Implant Restorations in the Esthetic Zone; Harvard University: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, R.; Gresnigt, M.M.M.; Mahesh, K.; Dilbaghi, A.; Cune, M.S. Esthetic Evaluation of Anterior Single-Tooth Implants with Different Abutment Designs-Patients’ Satisfaction Compared to Dentists’ Observations. J. Prosthodont. 2017, 26, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halim, F.; Pesce, P.; De Angelis, N.; Benedicenti, S.; Menini, M. Comparison of the Clinical Outcomes of Titanium and Zirconia Implant Abutments: A Systematic Review of Systematic Reviews. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laleman, I.; Lambert, F.; Gahlert, M.; Bacevic, M.; Woelfler, H.; Roehling, S. The effect of different abutment materials on peri-implant tissues—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2023, 34, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | CAD-CAM Titanium Milled Abutments | Stock Abutment | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.041 ns | ||
| Male | 11 (46%) | 12 (50%) | |
| Female | 13 (54%) | 12 (50%) | |
| Age in years | 30 ± 6.2 | 28.4 ± 7.5 | 0.338 ns |
| Site | 0.582 ns | ||
| Central incisor | 8 (33%) | 7 (29%) | |
| Lateral incisor | 10 (42%) | 8 (33%) | |
| Canine | 6 (25%) | 9 (38) | |
| Insertion torque in N/cm | 46.25 ± 6.3 | 45.5 ± 7.3 | 0.685 ns |
| Parameter | Customized | Customized | Stock | Stock | p-Value | Cohen’s d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | 95% CI | Mean ± SD | 95% CI | |||
| Mesial PD—T0 | 3.589 mm ± 0.552 mm | 3.356–3.822 | 4.118 mm ± 0.591 mm | 3.868–4.367 | 0.242 ns | 0.34 |
| Mesial PD—T1 | 1.790 mm ± 0.430 mm | 1.609–1.972 | 2.542 mm ± 0.525 mm | 2.320–2.763 | <0.0001 * | 1.56 |
| Mesial PD—T2 | 1.745 mm ± 0.489 mm | 1.538–1.951 | 2.592 mm ± 0.408 mm | 2.420–2.764 | <0.0001 * | 1.86 |
| Distal PD—T0 | 3.985 mm ± 0.605 mm | 3.729–4.240 | 3.794 mm ± 0.625 mm | 3.530–4.058 | 0.275 ns | 0.31 |
| Distal PD—T1 | 1.726 mm ± 0.409 mm | 1.553–1.899 | 3.299 mm ± 0.472 mm | 3.099–3.498 | <0.0001 * | 3.56 |
| Distal PD—T2 | 1.691 mm ± 0.487 mm | 1.485–1.896 | 3.202 mm ± 0.424 mm | 3.023–3.381 | <0.0001 * | 3.31 |
| Time | Custom | Stock | p-Value | Cohen’s d | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Mean ± SD) | 95% CI | (Mean ± SD) | ||||
| T1 | 0.645 mm ± 0.063 mm | 0.618–0.672 mm | 0.606 mm ± 0.057 mm | 0.582–0.630 mm | 0.031 * | 0.65 |
| T2 | 0.649 mm ± 0.054 mm | 0.626–0.672 mm | 0.602 mm ± 0.051 mm | 0.580–0.624 mm | 0.004 * | 0.89 |
| Variable | Time | Custom Abutment (n = 22) | Stock Abutment (n = 22) | p-Value | Effect Size (d) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (Range) | Mean (SD) | Median (Range) | Mean (SD) | ||||
| Gum appearance | Baseline | 9 (8, 10) | 8.95 (0.55) | 6 (5, 7) | 6.2 (0.85) | <0.001 * | 2.9 |
| 12 months | 10 (9, 10) | 9.20 (0.50) | 7 (6, 7) | 6.7 (0.90) | <0.001 * | 3 | |
| p-value | 0.16 ns | 0.6 ns | |||||
| Effect size (w) | 0.943 ns | 0.353 ns | |||||
| Phonetics | Baseline | 9 (8, 10) | 8.95 (0.55) | 10 (9, 11) | 9.75 (0.52) | 0.4 ns | 0.3 |
| 12 months | 9 (8, 10) | 8.95 (0.55) | 10 (9, 11) | 9.75 (0.52) | 0.4 ns | 0.3 | |
| p-value | Not computed because the variable is constant | Not computed because the variable is constant | |||||
| Effect size (w) | |||||||
| Chewing comfort | Baseline | 9 (8, 10) | 8.82 (0.4) | 7 (6, 8) | 7.10 (1.1) | 0.005 * | 1.3 |
| 12 months | 9 (8, 10) | 8.82 (0.4) | 7 (6, 8) | 7.10 (1.1) | 0.005 * | 1.3 | |
| p-value | Not computed because the variable is constant | Not computed because the variable is constant | |||||
| Effect size (w) | |||||||
| Overall satisfaction | Baseline | 9 (8, 10) | 8.25 (0.2) | 7 (6, 8) | 7.05 (0.25) | <0.001 * | 2.361 |
| 12 months | 9 (8, 10) | 8.5 (0.24) | 7 (6, 8) | 7.25 (0.26) | <0.001 * | 2.361 | |
| p-value | 0.23 ns | 0.6 ns | |||||
| Effect size (w) | 0.73 ns | 0.4 ns | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Robaian, A.; Hamed, M.M.; Ahmed, Y.; Hassanein, F.E.A. Comparative Evaluation of Customized CAD/CAM vs. Stock Titanium Abutments for Immediate Implant Placement in Class II Extraction Sockets: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Dent. J. 2025, 13, 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13080371
Robaian A, Hamed MM, Ahmed Y, Hassanein FEA. Comparative Evaluation of Customized CAD/CAM vs. Stock Titanium Abutments for Immediate Implant Placement in Class II Extraction Sockets: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Dentistry Journal. 2025; 13(8):371. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13080371
Chicago/Turabian StyleRobaian, Ali, Mohamed Mofreh Hamed, Yousra Ahmed, and Fatma E. A. Hassanein. 2025. "Comparative Evaluation of Customized CAD/CAM vs. Stock Titanium Abutments for Immediate Implant Placement in Class II Extraction Sockets: A Randomized Controlled Trial" Dentistry Journal 13, no. 8: 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13080371
APA StyleRobaian, A., Hamed, M. M., Ahmed, Y., & Hassanein, F. E. A. (2025). Comparative Evaluation of Customized CAD/CAM vs. Stock Titanium Abutments for Immediate Implant Placement in Class II Extraction Sockets: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Dentistry Journal, 13(8), 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13080371







