Abstract
This paper investigates last-mile delivery and explores hybrid distributed computational models for routing and scheduling delivery services and assigning delivery-points to deliverymen over multiple time periods. The objective of these models is to minimize the number of deliverymen hired for providing delivery services over multiple periods while satisfying predetermined time limits. This paper describes the development of multiple traveling deliverymen approaches, multi-period optimization models, and a multi-period distributed algorithm, to optimize routing and scheduling for last-mile deliveries. This paper utilizes a computer-aided modeling system to facilitate the proposed distributed approach, which offers an optimization model for large numbers of delivery-points and helps in performing limited computation as required to minimize the memory usage and provide efficiently solvable models within acceptable durations of execution. To illustrate the solvability of the proposed approach and scalability to large instances, 26 case problems are presented for last-mile delivery services. The key results include optimized routing and scheduling, a minimum number of deliverymen, and a significant reduction in computational effort and time.
1. Introduction
Considering the vast distribution and delivery network in supply chains, the term miles delivery can be used to define the distances traveled in the supply chain network, which includes the set of firms and individuals to deliver goods to end customers through an engineered flow of physical distribution. The first-mile relates to the distance traveled to deliver raw materials and semi-finished products from upstream suppliers. In contrast, the last-mile is related to the distance traveled to deliver goods to downstream customers. In this research, however, our focus is only on the latter. We describe the last-mile as the last distance traveled in the distribution and delivery network through which the customer receives the delivery. Therefore, the last-mile delivery service can be defined as the service of delivering a product to the final delivery destination from a depot, warehouse, or distribution center. Last-mile distribution has become a popular area of interest for distributors due to its growing demand across multi-channel distribution networks. Such networks involve a larger number of delivery destinations to be served by the minimum number of deliverymen over multiple periods. The final delivery destination considered in this research work could typically be a sales-point or delivery-point of a personal residence.
Deliverymen play a vital role in the last-mile delivery of goods to end-users and customers, serving as the primary means of distributing products and achieving distributors’ strategic goals.
Deliverymen assignment, routing, and scheduling are crucial activities in last-mile delivery management. Distributors who deliver goods to numerous delivery-points must carefully analyze distribution routes and assign deliverymen in order to maintain an efficient delivery force and minimize overall delivery costs. Routing deliverymen is a fundamental function in last-mile distribution management, involving the determination of the most optimal geographic path for a deliveryman to follow when delivering goods to a specific set of delivery-points. In the context of last-mile delivery management, planners often encounter the challenge of routing and scheduling individual deliverymen. They must find an efficient approach to route and schedule deliveries in order to minimize the number of deliverymen needed to serve a given set of locations. In real-life scenarios, distributors must assign multiple deliverymen to serve specific delivery-points, while also determining the sequence in which customers are served within each route across multiple periods, typically spanning several days.
Our focus with respect to last-mile service is to model the routes, schedules, and assignments of given delivery-points to the minimum possible number of deliverymen required to deliver all items over multiple periods. By focusing on the modeling of last-mile delivery assignments and routing, distributors can provide satisfactory service levels to their delivery-points with minimum delivery costs.
The multiple traveling deliverymen problem addressed here in last-mile delivery resembles the multiple traveling salesmen problem (mTSP), which is a broader view of the traveling salesman problem (TSP) in which more than one salesman are considered [1].
This paper focuses on suggesting and implementing effective methods for last-mile delivery, specifically tailored toward the extended versions of the classical traveling salesmen problem. These extensions are significant in relation to the multiple salesmen problem. What differentiates the mTSP is that salesmen take longer service times at delivery-points compared to the time spent by deliverymen at delivery-points. Every delivery-point can be visited and served multiple times, but cannot be visited more than once in the same period (day).
We primarily aim to develop a general distributed approach for resolving the multi-deliverymen problem in last-mile delivery that resembles the mTSP. This problem involves a set of delivery-points, the main distribution center, traveling times between different delivery-points, and a time limit for individual deliverymen to provide delivery services to different delivery-points. The proposed approach optimizes the schedules, routes, and delivery-points assigned to individual deliverymen while satisfying the time-limit constraints they face. Each route has to begin and end at the same distribution center, and every delivery-point can be visited and served multiple times, but cannot be visited more than once in the same period (day); the amount of time needed to provide delivery service at every delivery-point is predetermined according to the type of customer. Like the mTSP, the importance of the problem we address here is described by the vast savings that are made by minimizing the number of deliverymen hired and optimizing their routes and schedules.
In this context, computer-aided systems facilitating optimization methods have emerged as effective techniques for investigating and optimizing real-life problems, including the mTSP and last-mile delivery service problems. Such tools allow one to investigate operations in a risk-free and flexible manner to route and schedule deliveries, assign delivery-points to deliverymen, and enable the optimization of last-mile services through optimized planning and routing procedures. However, among hundreds of well-known and useful problems, the mTSP has been revealed to be NP-hard. NP-hard problems are computational problems that cannot be solved in polynomial time, as the elapsed time to obtain a solution increases exponentially with the size of the problem. It is not yet known whether the solutions to these problems can be computed in a reasonable running time [2]. Despite all the efforts in the last few decades, no published work has found an algorithm or made any attempts in practice to effectively produce an optimal or near-optimal solution for any of those problems in reasonable running times.
The primary contribution of this research is the formulation of a distributed novel approach, an algorithm that uses a computer-aided system to facilitate embedded mathematical optimization models to ease the pain of solving mTSP-like problems on a widespread scale in a reasonable amount of time (CPU), which is illustrated by solving 26 case problems. Nonetheless, as far as we know, there is no published work that both presents the problem addressed in this paper and suggests a method to optimize the number of deliverymen in a distributed approach with optimization models subject to their work time limit and service and traveling times.
The remainder of this manuscript is organized as follows: Section 2 surveys in brief the research work linked to the multiple traveling salesmen problem. Section 3 defines the problem addressed in this paper. Section 4 describes the development details of the proposed approaches for tackling the problem. Section 5 demonstrates the proposed approaches and their application to 26 case problems and reports results. Finally, Section 6 summarizes the paper and provides some conclusions.
2. A Review of Relevant Research on Multiple Traveling Salesmen Problems
Extensive literature is available about various approaches proposed for solving the traveling salesman problems (TSPs) and multiple traveling salesmen problems (mTSPs). The methods have mainly been proposed based on the application areas. The TSP arises in main real-world applications, including the drilling problem of printed circuit boards in actual production environment, overhauling gas turbine engines of aircrafts, the analysis of the structure of crystals presented by Bland and Shallcross [3], the connection of components on a computer board, order-picking, and material handling in warehouses proposed by Ratliff and Rosenthal [4].
Whereas the mTSP has numerous real-life applications, refs. [5,6,7] reported a comprehensive review on various applications of the mTSP. The main applications of the mTSP include production scheduling presented by [8,9,10], school bus routing reported by [11], crew scheduling described by [12], mission planning presented by [13], designing system networks suggested by [14], security service investigated by [15,16], and vehicle routing (VRP) discussed by [17,18,19,20].
With regard to mathematical formulations of the TSP and mTSP, many approaches are reported in the literature. Refs. [21,22] have provided surveys on several formulations of the problem. Among these, formulations are proposed by [12,23,24,25,26,27]. Besides the mathematical formulations, several authors have proposed heuristic methods for solving TSPs and mTSPs. Refs. [28,29,30] have presented surveys of algorithms for the problems. Several well-known heuristic approaches have been developed to solve these problems, which include the algorithms presented by [29,31,32,33]. Bagagiolo and Benetton [34] applied the dynamic programming technique in order to characterize the value function of the TSP as the unique viscosity solution of a suitable Hamilton–Jacobi equation. Vairaktarakis [35] reconsidered a version of the TSP and found applications in machine scheduling and workforce planning. Kalczynski and Kamburowski [36] showed that the problem of minimizing the expected makespan in a two-machine flow shop is equivalent to the TSP. However, the best available algorithm for the symmetric TSP was developed by Applegate et al. [37], which is the culmination of a line of research including [38,39,40].
Furthermore, Bektas [1] listed several variations on the mTSP; instead of one depot, the multi-depot mTSP has multiple depots, with multiple salesmen at every depot. In the first version, salesmen return to the source terminal/depot from which they began. In the second version, salesmen are not required to get back to their source depots, but depots must receive an exact number of salesmen. Bektas [1] listed a third variation that has the number of salesmen be a constant number, or the solution may determine it to be bounded by an upper limit. Bektas [1] also reported another variation based on an inconstant number of salesmen, but with a fixed cost for initiating a salesman. Zhang et al. [41] proposed a discrete mayfly algorithm for solving the asymmetric traveling salesman problem, as a branch of the traveling salesman problem, when a salesman travels a group of cities at the minimum cost and returns to the starting city.
In the mTSP version with a fixed charge, the fixed charges and tour costs for the salesmen are minimized. There is one more mTSP variation based on a time window for visiting different nodes.
Groba et al. [42] discussed the mTSP to prove that integrating forecasting within a metaheuristic evolutionary-based method, such as genetic algorithms, can yield better results in a dynamic scenario than their simple non-predictive version. Zhou et al. [43] proposed genetic algorithms to solve the min-sum mTSP with multiple depots, a closed path, and the requirement for minimizing the number of locations served by individual salesmen. They also adopted a particle swarm optimization algorithm to solve the mTSP. They found out that the suggested algorithms for solving the mTSP are feasible with room for improving their efficiency. Lei et al. [44] proposed an indefinite period, but for a single TSP, in which customer nodes need to be visited an unknown or an infinite number of times, but cannot be visited more than once on the same trip. They proposed exact and heuristic approaches for solving the problem for certain sizes. The authors concluded that better algorithms are to be developed in the future for a very large number of nodes, like 100 nodes or more. Guilherme et al. [45] considered a genetic local search procedure that incorporated a variable neighborhood search method for solving the mTSP. Their outputs demonstrated that the distributed approach provided better results. Zhang et al. [46] proposed a logistics collaboration model to address the collaborative vehicle routing problem that involves shared carriers and depots to decrease transportation distances and improve capacity utilization. Hassanpour et al. [47] proposed a robust optimization model integrated with a vehicle routing problem for solving hazmat location-routing problems. Kuo et al. [48] presented a mixed-integer programming model to minimize the total traveling costs and explored the cooperation of the vehicle routing problem with drones.
Nonetheless, as far as we know, there is no published work that presents the problem addressed in this paper or suggests a method to optimize the number of deliverymen in a distributed manner, subject to their work time limit and service and traveling times.
3. Problem Definition
The mTSP-like problem addressed in this paper is very challenging since the last-mile deliveries are to be assigned, scheduled, and routed in an optimal manner that engages the smallest number of deliverymen. Thus far, no published research work has been found for routing and scheduling large-scale last-mile deliveries to more than 100 delivery-points, with the objective to minimize the number of deliverymen. This is achieved in this paper using a well-modeled distributed optimization approach.
The primary contribution of this research is the formulation of a distributed novel approach, an algorithm that uses a computer-aided system to facilitate embedded mathematical optimization models to ease the pain of solving problems on a widespread scale in a reasonable amount of time (CPU), which is illustrated by solving 26 case problems.
4. Proposed Approaches for Last-Mile Multiple Traveling Deliverymen Problem (mTDP)
4.1. Multi-Period MIP Model for mTDP
An assignment-based MIP formulation is developed for solving the mTSP over multiple periods (mP-mTD). The proposed mP-mTD is based on a graph R = (I, A), where I is the set of |I| nodes, and A is the set of ½*|I|*|I − 1| bidirectional arcs. Visiting node i requires service time Sj, and traversing each arc i-j requires traveling time Tij, where i and j ∈ I. It is assumed that node 1 is the depot or main distribution center. Also, the main distribution center operates with m deliverymen.

Table 1.
mP-mTD model notations.
The objective function and functional constraints of the proposed mP-mTD model are detailed as follows.
Objective Function:
Subject to the following:
Objective function (1) is to minimize the number of employed deliverymen to serve different delivery-points over multiple periods. It also maximizes the utilization of individual deliverymen by minimizing their unutilized time. Constraints (2) and (3) ensure that, if a deliveryman is hired in a given period, he must have at least one delivery-point to visit. Constraints (4) and (5) assume that each delivery-point is to be visited no more than once per period by a deliveryman coming from the main distribution center or another delivery-point. Constraints (6) and (7) ensure that each delivery-point is to be visited as many times as required over the given multiple periods. Constraint (8) confirms that, if a deliveryman is hired and allocated in a given period (day), s/he must visit a delivery-point from the main distribution center. While Constraint (9) ensures that, if a deliveryman is hired in a given period, they must return to the distribution center from the delivery-point last served. Constraint (10) executes the rule of net flow that the deliveryman inflowing from each delivery-point must outflow from it in any given period. This constraint also ensures that all deliverymen who leave the main distribution center must return to it on any given day. Constraint (11) guarantees that each deliveryman does not exceed the allowable daily working time (time limit) to visit and travel between delivery-points on a given day. Constraint (12) computes the total traveling and service time for individual deliverymen over multiple periods. We also adopted the elimination of subtours [49] in Constraint (13). The declarations of xdkij, ydk, and Yk as binary decision variables are given in Constraint (14), (15), and (16), while Constraint (17) states that udk is a non-negative variable.
For the mP-mTDP model, we compute the number of constraints as [2*|I − 1| + 2*|K| + 6*|K|*|D| + 2*|D|*|I − 1| + |I − 1|2*|D| + |K|*|I − 1|2 *|D|+ |K|*|I|*|D|], and the number of variables is [|K| + |K|*|D| + |K|*|I|*|I − 1|*|D|], where the cardinality of sets is denoted by |·|. For example, for |D| = 5 periods, and |I’| = |I − 1|= 40, 80, and 100 delivery-points, the number of variables and constraints, and solutions including the optimal number of salesmen, CPU time in seconds, and memory usage in megabytes, are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
mP-mTD model size and outputs.
The proposed mP-mTD model yields optimal solutions in a reasonable memory size and CPU time for problems with small numbers of delivery-points. However, it is expected that, for large and moderate numbers of delivery-points, the mP-mTD model would not return a solution, as it exceeds the resource, the CPLEX time limit, and the solver terminates the run. Furthermore, the mP-mTD model requires an upper bound on the number of available deliverymen to be given before the model can be implemented. It is challenging to give tight bounds to the number of available deliverymen by simple approaches.
4.2. Decomposed Computational Optimization for Solving mP-mTDP
This distributed computational method (DC-2mPTD) is developed to overcome the limitations of the mP-mTD model. This proposed DC-2mPTD is based on a distributed algorithm that is partitioned by both the deliverymen and multiple periods. It optimizes the periodic routes and schedules for individual deliverymen to minimize the number of deliverymen hired while minimizing the unutilized time of individual deliverymen.
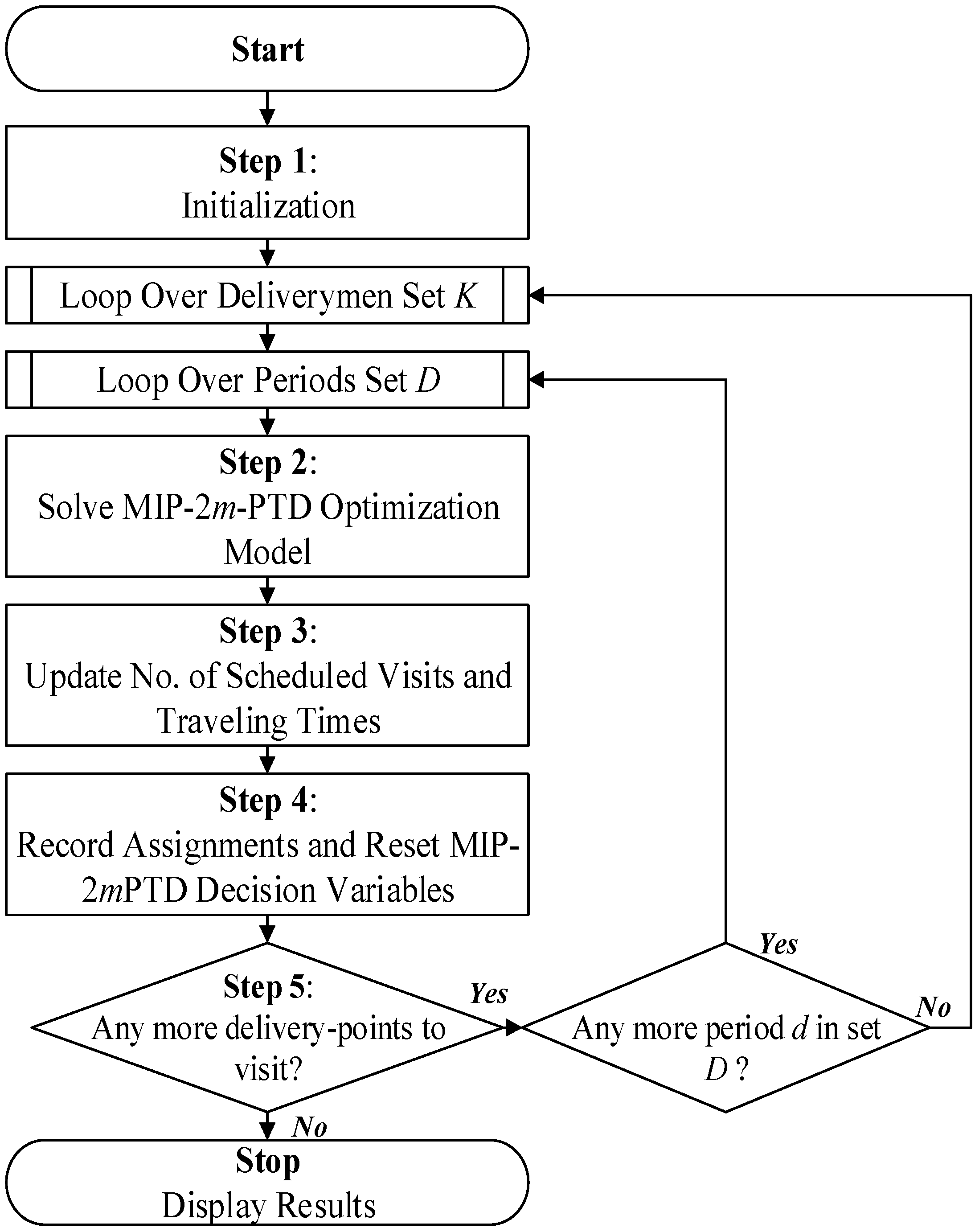
The iterative routing and scheduling for individual deliverymen over multiple periods are to be achieved while meeting the time-limit constraints. The basic framework of DC-2mPTD is outlined in Figure 1, which utilizes an iterative technique for solving this multi-period multiple traveling deliverymen problem.
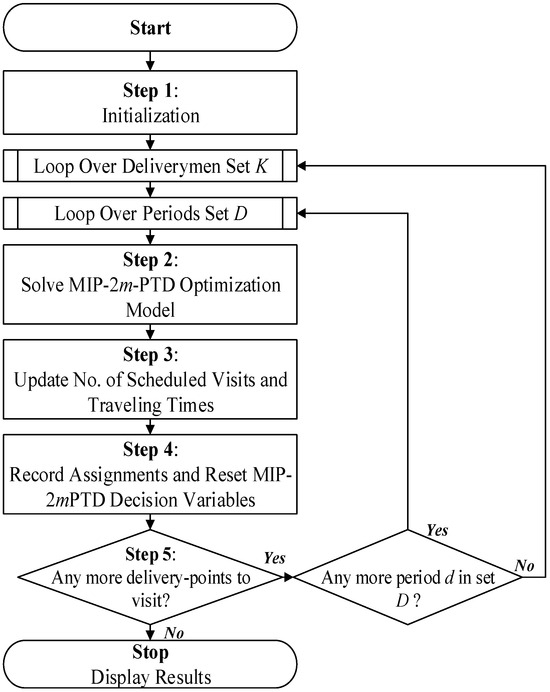
Figure 1.
DC-2mPTD framework.
Given a set of delivery-points with their estimated delivery/service times, the number of required visits to each delivery-point over multiple periods, over which services can be provided to delivery-points, and estimated traveling times between multiple delivery-points and between each delivery-point and the main distribution center, the DC-2mPTD uses an iterative approach for solving the problem of multi-period multiple traveling deliverymen.
Step 1 of DC-2mPTD is an initial stage where the input data are declared, and the DC-2mPTD solution procedure begins. This procedure includes setting the number of scheduled visits to individual delivery-points to zero. Then, DC-2mPTD loops over two sets, the deliverymen set and the period set. Each loop or iteration includes repetitive steps. Moreover, the available time of individual deliverymen is to be assigned to an unsuperscripted parameter H.
In Step 2, the multi-period multiple traveling deliverymen optimization model (MIP-2mPTD) is solved to find routes and schedules for individual deliverymen, and this includes assigning delivery-points to individual deliverymen over a given period. The MIP-2mPTD optimization model is solved separately for each deliveryman-period combination.
Next, DC-2mPTD updates the number of scheduled visits to delivery-points and traveling times in Step 3. If a delivery-point has been served with the required number of visits, then an arbitrarily long traveling time to and from that given delivery-point would be assigned to avoid considering it in the next iterations. In Step 4, DC-2mPTD retains and records the assignment of delivery-points to deliverymen by assigning the values of MIP-2mPTD decision variables xij to the DC-2mPTD variables xdkij superscripted with index k and d and then resetting the MIP-2mPTD decision variable to zero. The DC-2mPTD compares the number of scheduled versus required visits to all delivery-points; if all delivery-points were assigned for visits as required, then DC-2mPTD stops. Otherwise, the algorithmic procedure continues to loop over the period set and deliverymen set until the terminating condition has been satisfied.
4.2.1. DC-2mPTD Pseudo Code
The DC-2mPTD approach we propose in this paper assumes that all input parameters are deterministically identified. Before presenting the steps of the DC-2mPTD algorithm, we report the new notation in Table 3.

Table 3.
DC-2mPTD new and updated notations.
Given set I, which includes all delivery-points and the main distribution center, and the subset I’ of delivery-points that should be visited by deliverymen in set K over a set of multiple periods D, the main steps of the distributed DC-2mPTD approach are formulated as follows:

4.2.2. Multi-Period Multiple Traveling-Salesmen Optimization Model
Step 2 in the DC-2mPTD approach solves the mathematical formulation of the multi-period multiple traveling deliverymen optimization model (MIP-2mPTD). This model is solved iteratively for individual deliverymen over multiple periods.
Objective Functions:
Subject to the following:
The objective function (18) is to be achieved while satisfying functional constraints (19)–(28) in each iteration for individual deliverymen over multiple periods. The objective function (18) minimizes the unutilized time for individual deliverymen on a given day. Constraints (19) and (20) assume that each delivery-point is to be visited no more than once on that iterated day. Constraint (21) ensures that the assigned deliveryman must return to the main distribution center in any iterated period. In contrast, Constraint (22) confirms that the assigned deliveryman must begin from the main distribution center. Constraint (23) imposes the net flow rule introduced in Constraint (10). Constraints (24)–(26) are a modified version of Constraints (11)–(13) after removing superscripts d and k. Constraint (27) states that Xij is a binary decision variable, while Constraint (28) states that U is a non-negative variable.
5. Computational Work and Analysis
We conducted computational work for 26 scaled-up case problems, each with a different number of delivery-points to be visited and served over five business days. Given the number of delivery-points for every case problem, we created random integers between two numbers for the service/delivery times, number of required service visits, and traveling times as following: service times between 5 and 45 min, number of required visits between 1 and 3, and travel times between delivery-points and between the main distribution center and delivery-points between 10 and 40 min. Table 4 provides an example of this random generation process for case problem 1 with 20 delivery-points.

Table 4.
Generated number of visits and service and traveling times (in min) for 20 delivery-points.
The other raw data are not presented here; however, the descriptive summaries for the 26 case problems are reported in Table 5.

Table 5.
Number of delivery-points and required visits and service and traveling times (in min).
The DC-2mPTD method was coded and executed in the General Algebraic Modeling System (GAMS 24.8.5) with the CPLEX solver. The computer used for solving all case problems is a Dell with a 64-bit OS, Intel(R) Xeon(R), x64-based processor @ 3.60 GHz, a 700 GB hard drive, and 16.0 GB of RAM.
We solved the 26 case problems using DC-2mPTD and reported the computational outputs. Three primary metrics are used; these solution metrics are the optimal number of salesmen, memory usage, and total CPU time. The solution metrics obtained for solving the 26 case problems are given in Table 6.

Table 6.
Solution Metrics for DC-2mPTD Approach.
DC-2mPTD revealed to be a promising distributed approach; it is a more efficient business approach that has originated from the last-mile delivery settings. The summary of results shown in Table 6 provides evidence that DC-2mPTD is a promising method that offers competitive solutions to large-scale multi-period multiple traveling deliverymen problems, defined in this research, and enables the efficient last-mile distribution of goods.
To demonstrate that the proposed distributed approach provides a good benefit in CPU computing time and memory usage, we extend this section by comparing the results of the two solved case problems in Section 4.2 using mP-mTD with those obtained using the DC-2mPTD approach. This comparison, in Table 7, shows that the DC-2mPTD distributed approach significantly reduced the CPU computing time by an average of 98% and memory usage by an average of 63%. These percentages of reduction will increase proportionately with the number of delivery-points.

Table 7.
Comparison of mP-mTD and DC-2mPTD outputs.
6. Conclusions
This paper addressed the problem of multiple traveling deliverymen over multiple periods in last-mile delivery, which is considered as a version of the mTSP, where a set of delivery-points, with their service times, number of required visits, and traveling among these locations, and the time limit for individual deliverymen, are involved. We proposed a decomposed or distributed computational approach with embedded mixed-integer programming models. The proposed approach finds routes, schedules deliveries, and assigns delivery-points to individual deliverymen over multiple periods. The aim was to achieve the minimum delivery cost by minimizing the number of deliverymen hired and optimizing delivery routes and schedules. To demonstrate the suitability and applicability of the proposed methods, we solved 26 case problems with a different number of delivery-points. The results of solving the 26 case problems revealed that the proposed distributed approach offered a promising business tool for finding the optimal routes, schedules, and assignments of a large number of delivery-points and the minimum number of deliverymen. These results are especially noteworthy because the proposed distributed approaches are heuristic-based methods, but they can yield optimal deliveryman assignments with effective routing and scheduling of delivery services.
The main contribution of the proposed decomposition approach comes through its applicability as a novel business method to solve the multi-period multiple traveling deliverymen problem in last-mile delivery with time-limit restrictions. Overall, this research work opens up potential for a great variety of real-world states; for instance, the proposed distributed model can be used for solving a version of the mTSP over multiple periods.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the author.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Correction Statement
This article has been republished with a minor correction to the Data Availability Statement. This change does not affect the scientific content of the article.
References
- Bektas, T. The multiple traveling salesman problem: An overview of formulations and solution procedures. OMEGA Int. J. Manag. Sci. 2006, 34, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reus, B. How to Solve NP-Complete Problems. In Limits of Computation; Undergraduate Topics in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bland, R.E.; Shallcross, D.E. Large traveling salesman problem arising from experiments in X-ray crystallography: A preliminary report on computation. Oper. Res. Lett. 1989, 8, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratliff, H.D.; Rosenthal, A.S. Order-Picking in a Rectangular Warehouse: A Solvable Case for the Travelling Salesman Problem. Oper. Res. 1983, 31, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Elnagar, A.; Al-Hajj, A. Efficient coordinated motion. Math. Comput. Model. 2000, 31, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macharis, C.; Bontekoning, Y.M. Opportunities for OR in intermodal freight transport research: A review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2004, 153, 400–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Regan, A.C. Local truckload pickup and delivery with hard time window constraints. Transp. Res. Part B 2002, 36, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, A.E.; Ragsdale, C.T. Scheduling pre-printed newspaper advertising inserts using genetic algorithms. Omega 2002, 30, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorenstein, S. Printing press scheduling for multi-edition periodicals. Manag. Sci. 1970, 16, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Liu, J.; Rong, A.; Yang, Z. A multiple traveling salesman problem model for hot rolling scheduling in Shangai Baoshan Iron & Steel Complex. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2000, 124, 267–282. [Google Scholar]
- Angel, R.D.; Caudle, W.L.; Noonan, R.; Whinston, A. Computer assisted school bus scheduling. Manag. Sci. 1972, 18, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svestka, J.A.; Huckfeldt, V.E. Computational experience with an m-salesman traveling salesman algorithm. Manag. Sci. 1973, 19, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummit, B.; Stentz, A. GRAMMPS: A generalized mission planner for multiple mobile robots. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Leuven, Belgium, 16–20 May 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, H.A.; Chelouah, R. The design of the global navigation satellite system surveying networks using genetic algorithms. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2004, 17, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, R.W.; Cordone, R. A heuristic approach to the overnight security service problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2003, 30, 1269–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Park, Y. A crane scheduling method for port container terminals. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2004, 156, 752–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granado, I.; Hernando, L.; Galparsoro, I.; Gabiña, G.; Groba, C.; Prellezo, R.; Fernandes, J. Towards a framework for fishing route optimization decision support systems: Review of the state-of-the-art and challenges. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 320, 128661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrović-Minić, S.; Krishnamurti, R.; Laporte, G. Double-horizon based heuristics for the dynamic pickup and delivery problem with time windows. Transp. Res. 2004, 28, 669–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mole, R.H.; Johnson, D.G.; Wells, K. Combinatorial analysis for route first-cluster second vehicle routing. Omega 1983, 11, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralphs, T.K. Parallel branch and cut for capacitated vehicle routing. Parallel Comput. 2003, 29, 607–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öncan, T.; Altınel, I.K.; Laporte, G. A comparative analysis of several asymmetric traveling salesman problem formulations. Comput. Oper. Res. 2009, 36, 637–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orman, A.J.; Williams, H.P. A Survey of Different Integer Programming Formulations of the Travelling Salesman Problem; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 91–104. [Google Scholar]
- Applegate, D.L.; Bixby, R.E.; Chvátal, V.; Cook, W.J. Implementing the Dantzig–Fulkerson–Johnson algorithm for large scale traveling salesman problems. Math. Program. Ser. B 2003, 97, 91–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christofides, N.; Mingozzi, A.; Toth, P. Exact algorithms for the vehicle routing problem, based on spanning tree and shortest path relaxations. Math. Program. 1981, 20, 255–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantzig, G.B.; Fulkerson, D.R.; Johnson, S.M. Solution of a large-scale traveling salesman problem. Oper. Res. 1954, 2, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, R.V.; Bhave, P.R. Integer programming formulations of vehicle routing problems. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1985, 20, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laporte, G.; Nobert, Y. A cutting planes algorithm for the m-salesmen problem. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1980, 31, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balas, E.; Toth, P. Branch and bound methods. The Traveling Salesman Problem: A Guided Tour of Combinatorial Optimization; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1985; pp. 361–401. [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti, M.; Toth, P. An additive bounding procedure for the asymmetric traveling salesman problem. Math. Program. Ser. A B 1992, 53, 173–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laporte, G. The vehicle routing problem: An overview of exact and approximate algorithms. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1992, 59, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpaneto, G.; Dell’Amico, M.; Toth, P. Exact solution of large-scale, asymmetric travelling salesman problems. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 1995, 21, 394–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Amico, M.; Toth, P. Algorithms and codes for dense assignment problems: The state of the art. Discret. Appl. Math. 2000, 100, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, K.; Hofstra, R. A New Multiperiod Multiple Traveling Salesman Problem with Heuristic and Application to a Scheduling Problem. Decis. Sci. 1992, 32, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagagiolo, F.; Benetton, M. About an Optimal Visiting Problem. Appl. Math. Optim. 2012, 65, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vairaktarakis, G.L. Simple Algorithms for Gilmore–Gomory’s Traveling Salesman and Related Problems. J. Sched. 2003, 6, 499–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalczynski, P.J.; Kamburowski, J. Two-Machine Stochastic Flow Shops with Blocking and the Traveling Salesman Problem. J. Sched. 2005, 8, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applegate, D.L.; Bixby, R.E.; Chvátal, V.; Cook, W.J. The Traveling Salesman Problem: A Computational Study; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-691-12993-8. [Google Scholar]
- Padberg, M.W.; Hong, S. On the symmetric travelling salesman problem: A computational study. Math. Program. Study 1980, 12, 78–107. [Google Scholar]
- Padberg, M.; Grötschel, M. Polyhedral computations. In The Traveling Salesman Problem: A Guided Tour of Combinatorial Optimization; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1985; pp. 307–360. [Google Scholar]
- Padberg, M.; Rinaldi, G. A branch-and-cut algorithm for the resolution of largescale symmetric traveling salesman problems. SIAM Rev. 1991, 33, 60–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, G.; Deng, W.; Luo, Q. Discrete Mayfly Algorithm for spherical asymmetric traveling salesman problem. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 221, 119765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groba, C.; Antonio, S.; Xosé, V. Integrating forecasting in metaheuristic methods to solve dynamic routing problems: Evidence from the logistic processes of tuna vessels. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2018, 76, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Song, M.; Pedrycz, W. A comparative study of improved GA and PSO in solving multipletraveling salesmen problem. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 64, 564–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Mark, K.; Moustapha, D. The indefinite period traveling salesman problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 270, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilherme, D.; Alberto, F.; Olinto, C. The Multiple Traveling Salesman Problem with Backup Coverage. Electron. Notes Discret. Math. 2018, 66, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; Yang, S.; Cai, Y. Composite multi-objective optimization on a new collaborative vehicle routing problem with shared carriers and depots. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 122593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour, S.; Ke, G.; Tulett, D. A time-dependent location-routing problem of hazardous material transportation with edge unavailability and time window. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 322, 128951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, R.; Lu, S.; Lai, P.; Mara, S. Vehicle routing problem with drones considering time windows. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 191, 116264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.; Tucker, A.; Zemlin, R. Integer programming formulations and travelling salesman problems. J. Assoc. Comput. Mach. 1960, 7, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).