Modulation of Gene Expression in a Sterile Atopic Dermatitis Model and Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus Adhesion by Fucoidan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Materials
2.2. Reconstructed Human Epidermis—RHE
2.3. Induction of the Th2-Inflamed Model
2.4. Treatment of the Epidermis—Gene Expression
2.5. Analysis of Tissue Morphology
2.6. Analysis of Gene Expression Modifications
2.6.1. Total RNA Extraction and Integrity Analysis
2.6.2. cDNA Synthesis
2.6.3. TaqMan Assays
2.7. Analysis of Extracellular Periostin Abundance
2.8. Bacterial Cultures, Adhesion of Bacteria, and CFU Counting
2.8.1. Bacterial Cultures of Staphylococcus epidermis and Staphylococcus aureus
2.8.2. Adhesion of Bacteria and CFU Counting
3. Results
3.1. Effects of the Test Compounds on the Morphology of RHE When Cultured under Conditions Mimicking Atopic Dermatitis
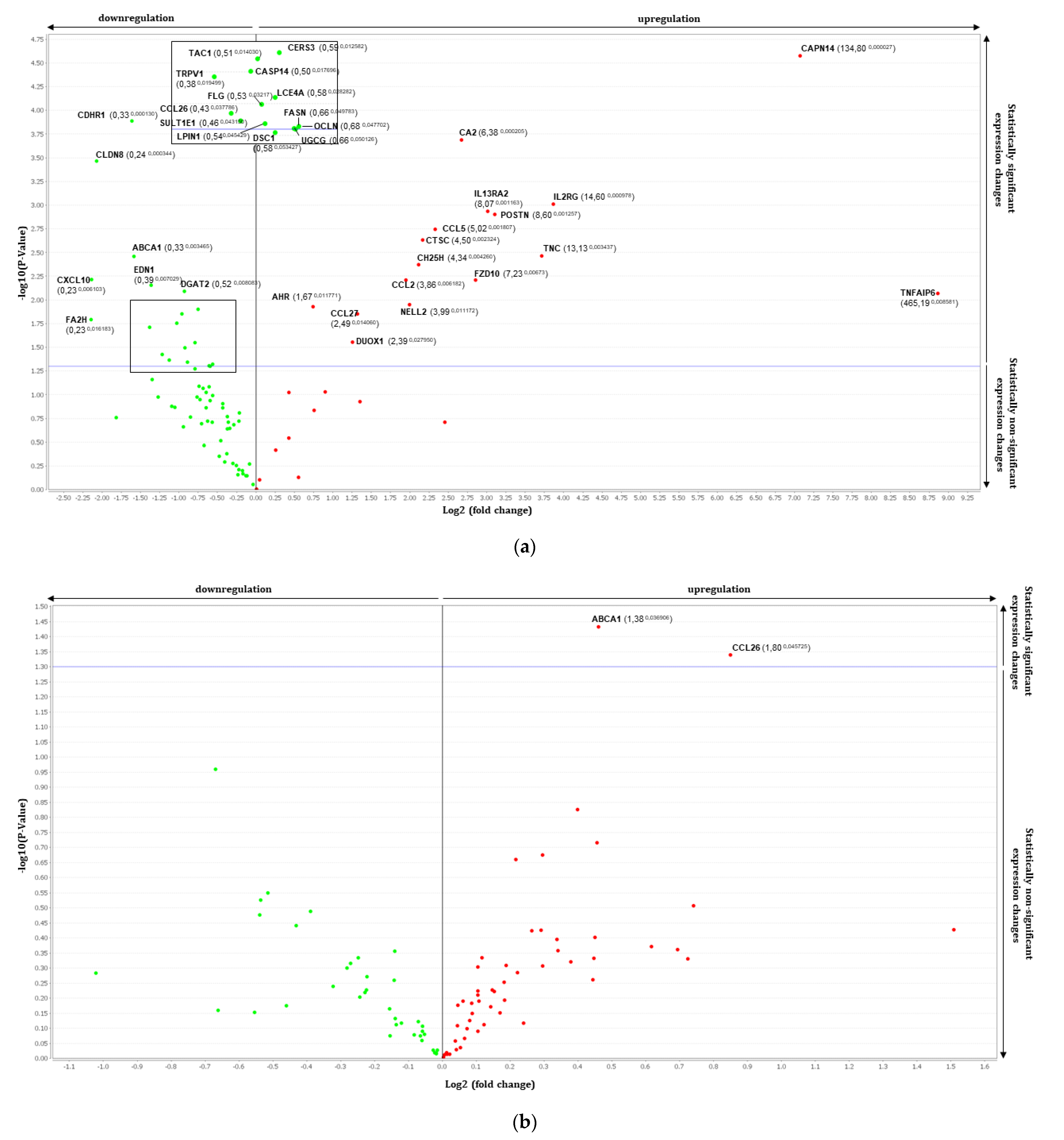
3.2. Gene Expression Analysis by RT-qPCR Using TaqMan Array
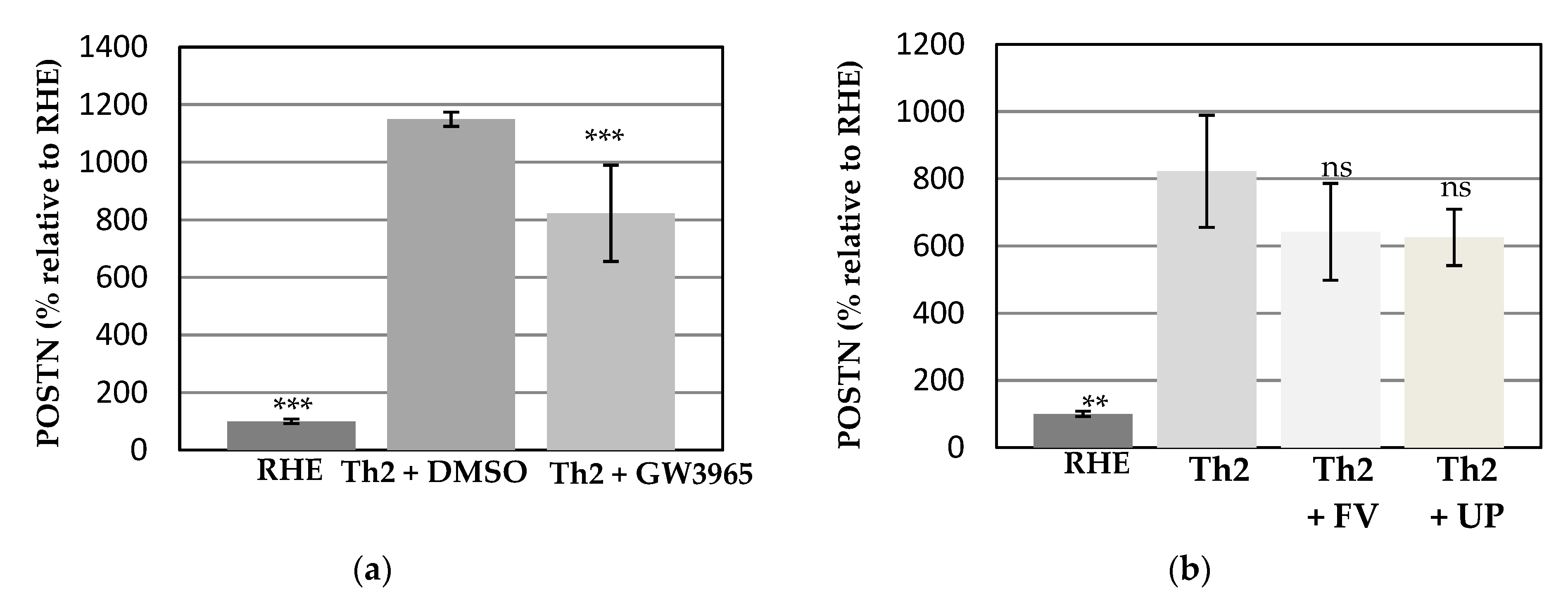
3.3. Effects of the Test Compounds on Periostin Release by RHE When Cultured under Conditions Mimicking Atopic Dermatitis
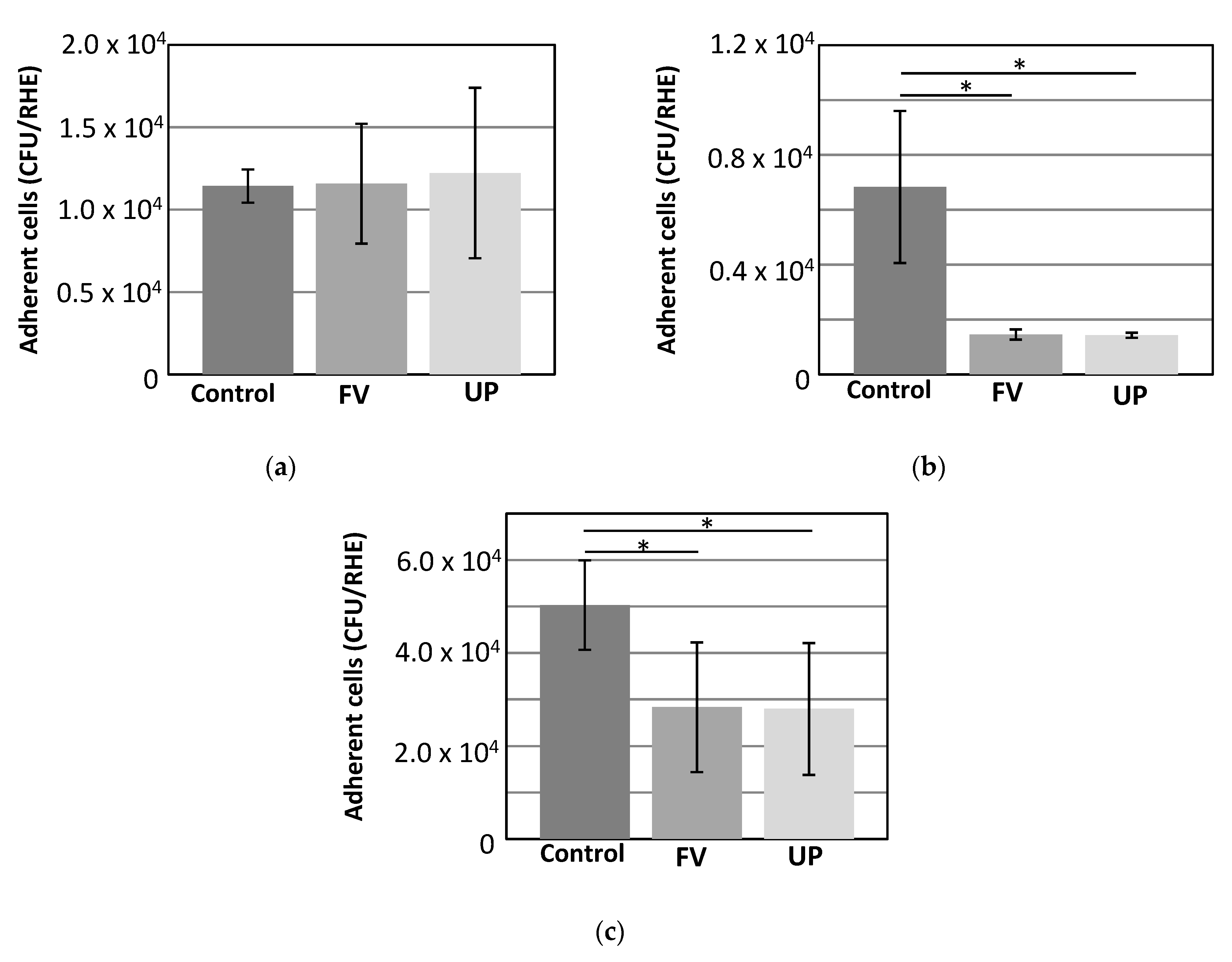
3.4. Adhesion of Bacteria
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, B.W.; Detzel, P.R. Treatment of Childhood Atopic Dermatitis and Economic Burden of Illness in Asia Pacific Countries. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 66 (Suppl. 1), 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitton, H.J.; Stringer, D.S.; Park, A.Y.; Karpiniec, S.N. Therapies from Fucoidan: New Developments. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitton, J.H.; Stringer, D.N.; Karpiniec, S.S. Therapies from Fucoidan: An Update. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 5920–5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Jeong, M.R.; Choi, S.M.; Na, S.S.; Cha, J.D. Synergistic effect of fucoidan with antibiotics against oral pathogenic bacteria. Arch. Oral Biol. 2013, 58, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, S.; Okabe, M.; Tsubura, S.; Mikami, M.; Imai, A. Properties of fucoidans beneficial to oral healthcare. Odontology 2020, 108, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, M.; Snoeck, R.; Pauwels, R.; de Clercq, E. Sulfated polysaccharides are potent and selective inhibitors of various enveloped viruses, including herpes simplex virus, cytomegalovirus, vesicular stomatitis virus, and human immunodeficiency virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1988, 32, 1742–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegami-Kuzuhara, A.; Yoshinaka, T.; Ohmoto, H.; Inoue, Y.; Saito, T. Therapeutic potential of a novel synthetic selectin blocker, OJ-R9188, in allergic dermatitis. Br. J. Pharm. 2001, 134, 1498–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, K.; Hiragun, T.; Takahagi, S.; Yanase, Y.; Morioke, S.; Mihara, S.; Kameyoshi, Y.; Hide, M. Fucoidan suppresses IgE production in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with atopic dermatitis. Arch Derm. Res. 2010, 303, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H. Topical Application of Fucoidan Improves Atopic Dermatitis Symptoms in NC/Nga Mice. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 1898–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, T.; Chang, H.; He, K.; Ni, Y.; Li, C.; Hou, M.; Chen, L.; Xu, Z.; Chen, B.; Ji, M. Fucoidan from seaweed Fucus vesiculosus inhibits 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 75, 105823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankart, A.; Malaisse, J.; De Vuyst, E.; Minner, F.; de Rouvroit, C.L.; Poumay, Y. Epidermal morphogenesis during progressive in vitro 3D reconstruction at the air-liquid interface. Exp. Derm. 2012, 21, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastore, S.; Mascia, F.; Gulinelli, S.; Forchap, S.; Dattilo, C.; Adinolfi, E.; Girolomoni, G.; Di Virgilio, F.; Ferrari, D. Stimulation of purinergic receptors modulates chemokine expression in human keratinocytes. J. Invest. Derm. 2007, 127, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieber, T. Atopic dermatitis. Ann. Derm. 2010, 22, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubaux, R.; Bastin, C.; Salmon, M. On the relevance of an in vitro reconstructed human epidermis model for drug screening in atopic dermatitis. Exp. Derm. 2018, 27, 1403–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.K.; Wheeler, J.J.; Pitake, S.; Ding, H.; Jiang, C.; Fukuyama, T.; Paps, J.S.; Ralph, P.; Coyne, J.; Parkington, M.; et al. Periostin Activation of Integrin Receptors on Sensory Neurons Induces Allergic Itch. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, M.; Lee, K.S.; Ha, E.G.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, M.A.; Lee, S.W.; Jee, H.M.; Sheen, Y.H.; Jung, Y.H.; Han, M.Y. An association of periostin levels with the severity and chronicity of atopic dermatitis in children. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 28, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, K.; Okawa, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Ono, J.; Inoue, Y.; Kohno, M.; Matsukura, S.; Kambara, T.; Ohta, S.; Izuhara, K.; et al. Periostin levels correlate with disease severity and chronicity in patients with atopic dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014, 171, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, H.; Masuoka, M.; Ohta, S.; Suzuki, S.; Arima, K.; Taniguchi, K.; Aoki, S.; Toda, S.; Yoshimoto, T.; Inagaki, N.; et al. Periostin contributes to the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis by inducing TSLP production from keratinocytes. Allergol. Int. 2012, 61, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, D.; Kubo, T.; Kiya, K.; Kawai, K.; Matsuzaki, S.; Kobayashi, D.; Fujiwara, T.; Katayama, T.; Hosokawa, K. Periostin is induced by IL-4/IL-13 in dermal fibroblasts and promotes RhoA/ROCK pathway-mediated TGF-beta1 secretion in abnormal scar formation. J. Plast. Surg. Hand. Surg. 2019, 53, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vuyst, E.; Giltaire, S.; Lambert de Rouvroit, C.; Malaisse, J.; Mound, A.; Bourtembourg, M.; Poumay, Y.; Nikkels, A.F.; Chretien, A.; Salmon, M. Methyl-beta-cyclodextrin concurs with interleukin (IL)-4, IL-13 and IL-25 to induce alterations reminiscent of atopic dermatitis in reconstructed human epidermis. Exp. Derm. 2018, 27, 435–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vuyst, E.; Mound, A.; Lambert de Rouvroit, C.; Poumay, Y. Modelling atopic dermatitis during the morphogenetic process involved in reconstruction of a human epidermis. Curr. Res. Transl. Med. 2016, 64, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vuyst, E.; Salmon, M.; Evrard, C.; Lambert de Rouvroit, C.; Poumay, Y. Atopic Dermatitis Studies through In Vitro Models. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, A.J.; Sheu, M.Y.; Schmuth, M.; Kao, J.; Fluhr, J.W.; Rhein, L.; Collins, J.L.; Willson, T.M.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Elias, P.M.; et al. Liver X receptor activators display anti-inflammatory activity in irritant and allergic contact dermatitis models: Liver-X-receptor-specific inhibition of inflammation and primary cytokine production. J. Invest. Derm. 2003, 120, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmuth, M.; Jiang, Y.J.; Dubrac, S.; Elias, P.M.; Feingold, K.R. Thematic review series: Skin lipids. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and liver X receptors in epidermal biology. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goleva, E.; Berdyshev, E.; Leung, D.Y. Epithelial barrier repair and prevention of allergy. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardesca, E.; Farage, M.; Maibach, H. Sensitive skin: An overview. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2013, 35, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarling, E.J.; de Aguiar Vallim, T.Q.; Edwards, P.A. Role of ABC transporters in lipid transport and human disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 24, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspar, K.; Kukova, G.; Bunemann, E.; Buhren, B.A.; Sonkoly, E.; Szollosi, A.G.; Muller, A.; Savinko, T.; Lauerma, A.I.; Alenius, H.; et al. The chemokine receptor CCR3 participates in tissue remodeling during atopic skin inflammation. J. Derm. Sci. 2013, 71, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rees, P.A.; Greaves, N.S.; Baguneid, M.; Bayat, A. Chemokines in Wound Healing and as Potential Therapeutic Targets for Reducing Cutaneous Scarring. Adv. Wound Care 2015, 4, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, L.; Carraux, P.; Saurat, J.H.; Kaya, G. Increased expression of CD44 and hyaluronate synthase 3 is associated with accumulation of hyaluronate in spongiotic epidermis. J. Invest. Derm. 2012, 132 (Pt 1), 736–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, M.; Elias, P.M.; Man, W.; Wu, Y.; Bourguignon, L.Y.; Feingold, K.R.; Man, M.Q. The role of CD44 in cutaneous inflammation. Exp. Derm. 2009, 18, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaisse, J.; Bourguignon, V.; De Vuyst, E.; Lambert de Rouvroit, C.; Nikkels, A.F.; Flamion, B.; Poumay, Y. Hyaluronan metabolism in human keratinocytes and atopic dermatitis skin is driven by a balance of hyaluronan synthases 1 and 3. J. Investig. Derm. 2014, 134, 2174–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugovic-Mihic, L.; Novak-Bilic, G.; Vucic, M.; Japundzic, I.; Bukvic, I. CD44 expression in human skin: High expression in irritant and allergic contact dermatitis and moderate expression in psoriasis lesions in comparison with healthy controls. Contact Dermat. 2020, 82, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graczyk, A.; Lesniak, W. S100A6 expression in keratinocytes and its impact on epidermal differentiation. Int. J. Biochem Cell Biol 2014, 57, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.Y. Molecular Mechanism of Epidermal Barrier Dysfunction as Primary Abnormalities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, Y. Elucidation of the Synthetic Mechanism of Acylceramide, an Essential Lipid for Skin Barrier Function. Yakugaku Zasshi 2017, 137, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuji, T.; Chen, T.H.; Narala, S.; Chun, K.A.; Two, A.M.; Yun, T.; Shafiq, F.; Kotol, P.F.; Bouslimani, A.; Melnik, A.V.; et al. Antimicrobials from human skin commensal bacteria protect against Staphylococcus aureus and are deficient in atopic dermatitis. Sci. Transl Med. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerebour, G.; Cupferman, S.; Bellon-Fontaine, M.N. Adhesion of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis to the Episkin reconstructed epidermis model and to an inert 304 stainless steel substrate. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 97, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jesumani, V.; Du, H.; Pei, P.; Aslam, M.; Huang, N. Comparative study on skin protection activity of polyphenol-rich extract and polysaccharide-rich extract from Sargassum vachellianum. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, K.; Ravichandran, S.; Muralisankar, T.; Uthayakumar, V.; Chandirasekar, R.; Seedevi, P.; Abirami, R.G.; Rajan, D.K. Application of marine-derived polysaccharides as immunostimulants in aquaculture: A review of current knowledge and further perspectives. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 86, 1177–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.K.; Bhate, K. A global perspective on the epidemiology of acne. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 172 (Suppl. 1), 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claudel, J.P.; Auffret, N.; Leccia, M.T.; Poli, F.; Corvec, S.; Dreno, B. Staphylococcus epidermidis: A Potential New Player in the Physiopathology of Acne? Dermatology 2019, 235, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Fucoidan Extract | Neutral Carbohydrates | Sulfate | Cations (approx.) | Fucoidan | Polyphenol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FV | 43.7% | 10.1% | 3% | 58.6% | 33.7% |
| UP | 48.8% | 27.4% | 9% | 89.6% | <2% |
| Th2-Induced RHE vs. RHE | |||||
| Genes | Fold Change | p Value | Genes | Fold Change | p Value |
| ABCA1 | 0.33 | 0.0035 | AHR | 1.67 | 0.0118 |
| CASP14 | 0.49 | 0.0177 | CA2 | 6.38 | 0.0002 |
| CCL26 | 0.43 | 0.0378 | CAPN14 | 134.80 | 0.0000 |
| CDHR1 | 0.33 | 0.0001 | CCL2/MCP1 | 3.86 | 0.0062 |
| CERS3 | 0.59 | 0.0126 | CCL27 | 2.49 | 0.0141 |
| CLDN8 | 0.24 | 0.0003 | CCL5/RANTES | 5.02 | 0.0018 |
| CNR1 | 0.51 | 0.0346 | CH25H | 4.34 | 0.0043 |
| CXCL10 | 0.23 | 0.0061 | CTSC | 4.50 | 0.0023 |
| DGAT2 | 0.52 | 0.0081 | DUOX1 | 2.39 | 0.0279 |
| EDN1 | 0.39 | 0.007 | FZD10 | 7.23 | 0.0062 |
| FA2H | 0.23 | 0.0162 | IL13RA2 | 8.07 | 0.0012 |
| FASN | 0.66 | 0.0498 | IL2R | 14.60 | 0.001 |
| FLG | 0.53 | 0.0321 | NELL2 | 3.99 | 0.0112 |
| LCE4A | 0.58 | 0.0283 | POSTN | 8.60 | 0.0013 |
| LPIN1 | 0.54 | 0.0454 | TNC | 13.13 | 0.0034 |
| OCLN | 0.68 | 0.0477 | TNFAIP6 | 465.19 | 0.0086 |
| SEMA3A | 0.51 | 0.0336 | |||
| SULT1E1 | 0.46 | 0.0431 | |||
| TAC1 | 0.51 | 0.014 | |||
| TRPV1 | 0.38 | 0.0195 | |||
| Th2 Induced RHE vs. FV Treated | Th2 Induced RHE vs. UP Treated | ||||
| Genes | Fold Change | p Value | Genes | Fold Change | p Value |
| CD44 | 0.71 | 0.0183 | ABCA1 | 1.38 | 0.0369 |
| S100A6 | 0.51 | 0.0425 | CCL26 | 1.80 | 0.0457 |
| UGCG | 1.46 | 0.0444 | |||
| Functions | Genes | Th2 vs NT | Th2 vs Th2 + FV | Th2 vs Th2 + UP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fold Change | p Value | Fold Change | p Value | Fold Change | p Value | ||
| Triglyceride synthesis | GPAT3 | 0.6214 | 0.0861 | 1.3189 | 0.1494 | 1.3213 | 0.1769 |
| Fatty acid synthesis | ACACA | 0.6756 | 0.1961 | 1.2663 | 0.4387 | 1.6682 | 0.1628 |
| FA2H | 0.2267 | 0.0162 | 1.2280 | 0.4934 | 2.0985 | 0.3626 | |
| Cholesterol biosynthesis and transport | ABCA1 | 0.3335 | 0.0035 | 1.3755 | 0.0369 | 1.2663 | 0.0646 |
| HMGCS1 | 0.6389 | 0.1370 | 0.8291 | 0.4831 | 1.8712 | 0.0777 | |
| NR1H3 | 0.7706 | 0.4183 | 1.3721 | 0.1926 | 1.1837 | 0.3636 | |
| SULT1E1 | 0.4577 | 0.0431 | 0.9815 | 0.9404 | 1.7573 | 0.1530 | |
| Ceramide synthesis | CERS3 | 0.5949 | 0.0126 | 1.0840 | 0.4628 | 1.5486 | 0.0728 |
| GBA | 0.7193 | 0.4457 | 1.3629 | 0.4651 | 1.7666 | 0.2421 | |
| SMPD1 | 0.7417 | 0.1241 | 2.8455 | 0.3736 | 1.3497 | 0.1891 | |
| UGCG | 0.6619 | 0.0501 | 0.9075 | 0.4411 | 1.4580 | 0.0444 | |
| AM defense | DEFB4A | 0.3933 | 0.0691 | 1.3601 | 0.5485 | 1.2980 | 0.4851 |
| Epidermal biology | HAS3 | 5.4933 | 0.1958 | 0.4924 | 0.5206 | 0.7897 | 0.8425 |
| Epidermal junction | CLDN25 | 1.4695 | 0.7438 | 0.6323 | 0.6919 | 1.5768 | 0.7407 |
| OCLN | 0.6770 | 0.0477 | 1.0514 | 0.7956 | 1.2521 | 0.1352 | |
| TJP1 | 0.6468 | 0.1899 | 1.6713 | 0.3112 | 1.3790 | 0.5035 | |
| Cornified envelope precursors | CASP14 | 0.4896 | 0.0177 | 0.9058 | 0.5509 | 1.3626 | 0.2183 |
| LCE2A | 0.5544 | 0.1728 | 1.6514 | 0.4677 | 1.5951 | 0.4212 | |
| SPRR2A | 0.5200 | 0.2194 | 1.6174 | 0.4346 | 0.8558 | 0.7255 | |
| ZNF750 | 0.8382 | 0.5563 | 0.9098 | 0.7737 | 1.5126 | 0.3437 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, A.Y.; Bourtembourg, M.; Chrétien, A.; Hubaux, R.; Lancelot, C.; Salmon, M.; Fitton, J.H. Modulation of Gene Expression in a Sterile Atopic Dermatitis Model and Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus Adhesion by Fucoidan. Dermatopathology 2021, 8, 69-83. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology8020012
Park AY, Bourtembourg M, Chrétien A, Hubaux R, Lancelot C, Salmon M, Fitton JH. Modulation of Gene Expression in a Sterile Atopic Dermatitis Model and Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus Adhesion by Fucoidan. Dermatopathology. 2021; 8(2):69-83. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology8020012
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Ah Young, Maureen Bourtembourg, Aline Chrétien, Roland Hubaux, Céline Lancelot, Michel Salmon, and J. Helen Fitton. 2021. "Modulation of Gene Expression in a Sterile Atopic Dermatitis Model and Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus Adhesion by Fucoidan" Dermatopathology 8, no. 2: 69-83. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology8020012
APA StylePark, A. Y., Bourtembourg, M., Chrétien, A., Hubaux, R., Lancelot, C., Salmon, M., & Fitton, J. H. (2021). Modulation of Gene Expression in a Sterile Atopic Dermatitis Model and Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus Adhesion by Fucoidan. Dermatopathology, 8(2), 69-83. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology8020012






