Asymmetric Lip Hyperpigmentation in a Transplant Patient
Abstract
1. Introduction
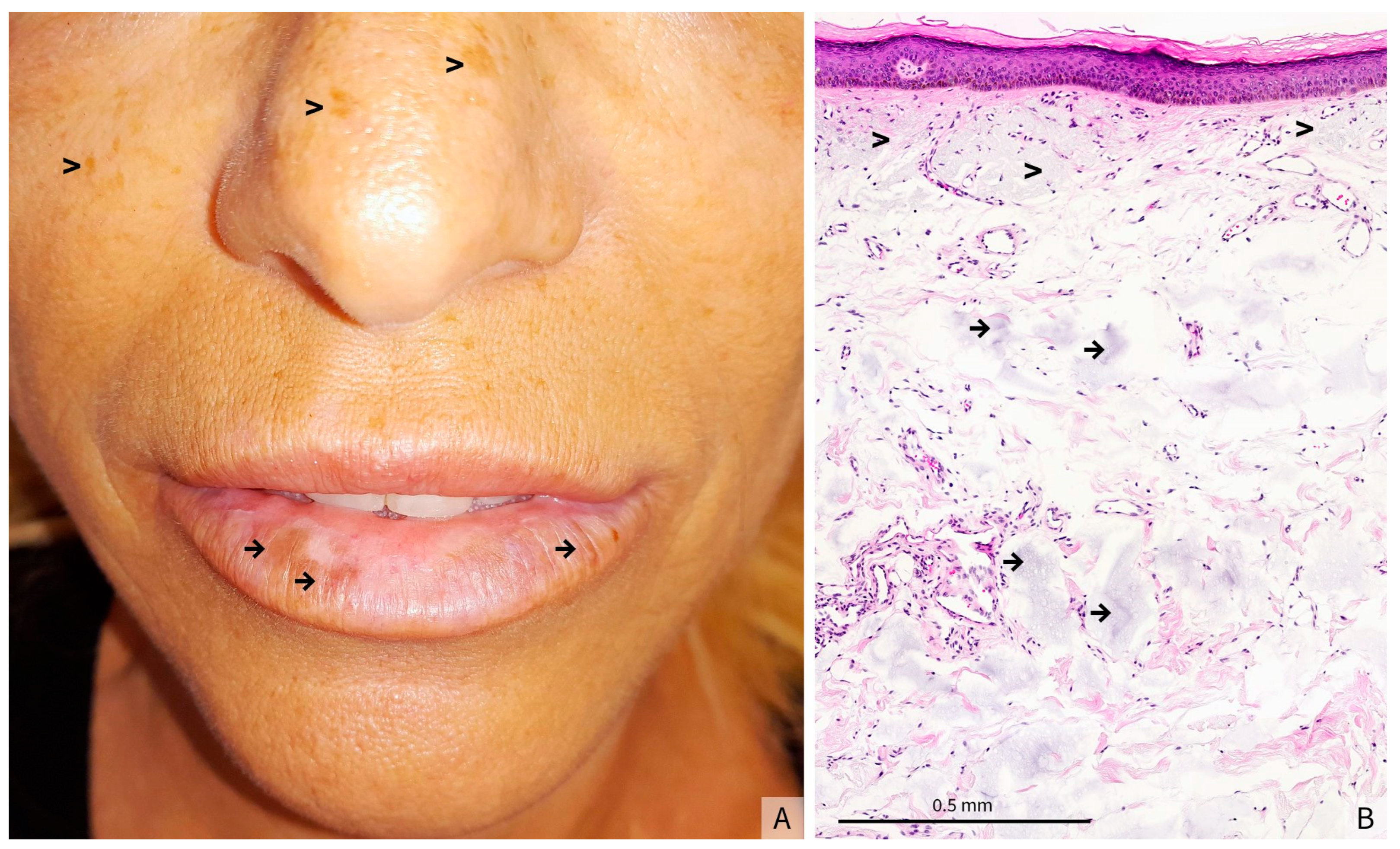
2. What Is the Diagnosis?
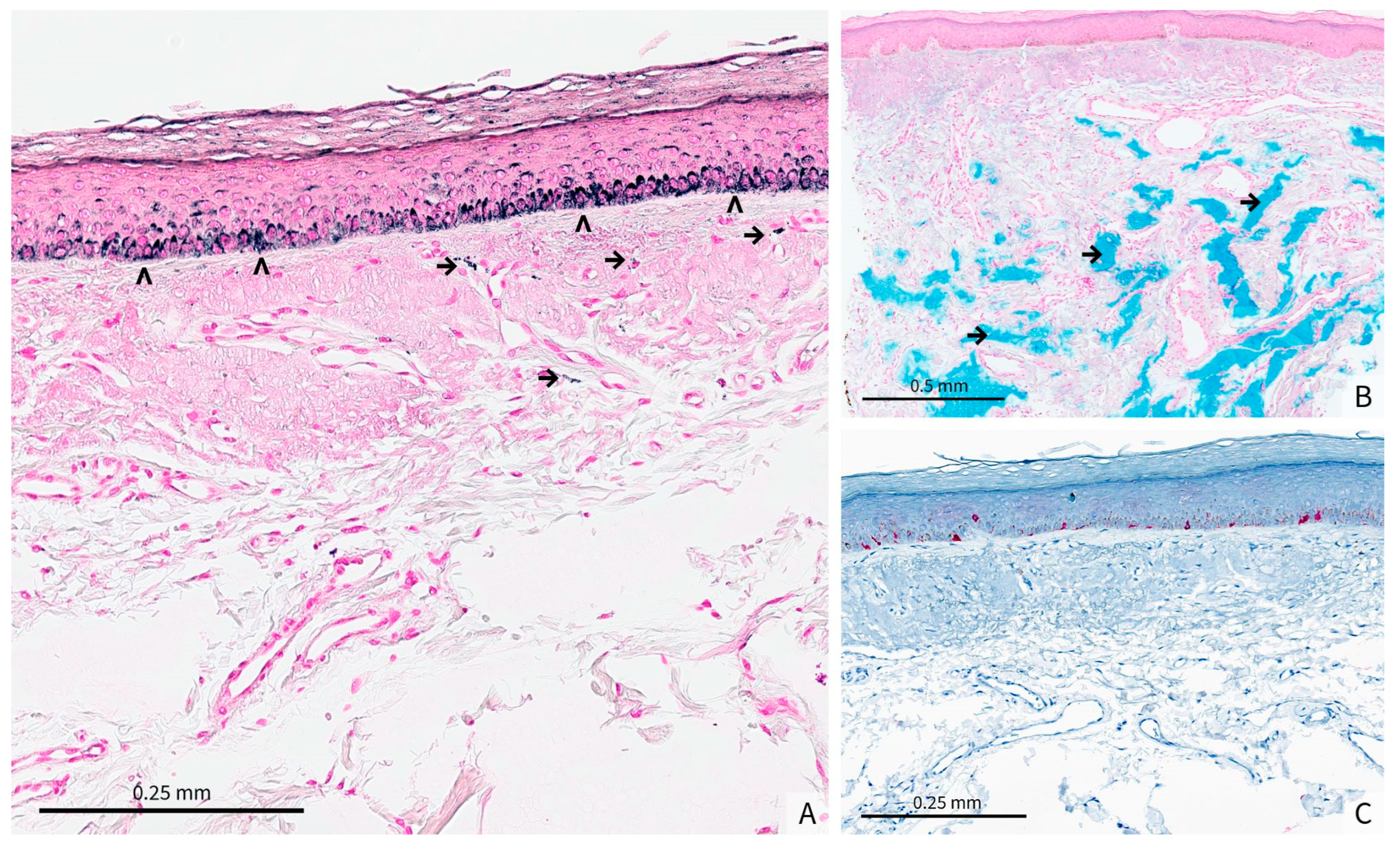
3. Diagnosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HA | Hyaluronic Acid |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| LMW-HA | Low Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid |
| IL-1α | Interleukin-1 alpha |
References
- Krause, W. Drug-Induced Hyperpigmentation: A Systematic Review. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. J. Ger. Soc. Dermatol. JDDG 2013, 11, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahhas, A.F.; Braunberger, T.L.; Hamzavi, I.H. An Update on Drug-Induced Pigmentation. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2019, 20, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbagci, Z. Amlodipine Associated Hyperpigmentation. Saudi Med. J. 2004, 25, 103–105. [Google Scholar]
- Harper, H.E.; DaCunha, M.; Fraga, G.; Hall, J.C. Amlodipine-Induced Hyperpigmentation. Dermatol. Arch. 2021, 5, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addo, H.A.; Ferguson, J.; Frain-Bell, W. Thiazide-induced Photosensitivity: A Study of 33 Subjects. Br. J. Dermatol. 1987, 116, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuoka, E.; Bito, T.; Shimizu, H.; Nishigori, C. Dysfunction of Melanocytes in Photoleukomelanoderma Following Photosensitivity Caused by Hydrochlorothiazide. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2011, 27, 328–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozzi, F.; Di Raimondo, C.; Lanna, C.; Diluvio, L.; Mazzilli, S.; Garofalo, V.; Dika, E.; Dellambra, E.; Coniglione, F.; Bianchi, L.; et al. Latest Evidence Regarding the Effects of Photosensitive Drugs on the Skin: Pathogenetic Mechanisms and Clinical Manifestations. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.; Nooreyezdan, S. Nonvascular Complications of Injectable Fillers-Prevention and Management. Indian J. Plast. Surg. Off. Publ. Assoc. Plast. Surg. India 2020, 53, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funt, D.; Pavicic, T. Dermal Fillers in Aesthetics: An Overview of Adverse Events and Treatment Approaches. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 6, 295–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Yoo, K.H. One-Year Safety Evaluation of New Hyaluronic Acid Fillers (YYS Series): A Prospective, Multicenter, Observational Study. Dermatol. Surg. 2024, 50, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, O.; Overman, J.; Arndt, K.A.; Dover, J.S. Filler Nodules: Inflammatory or Infectious? A Review of Biofilms and Their Implications on Clinical Practice. Dermatol. Surg. 2018, 44, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bootun, R. Effects of Immunosuppressive Therapy on Wound Healing. Int. Wound J. 2013, 10, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Boulle, K.; Heydenrych, I. Patient Factors Influencing Dermal Filler Complications: Prevention, Assessment, and Treatment. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 8, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, D.K.; Bai, X.L.; Liang, T. Dermatological Disorders Following Liver Transplantation: An Update. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 2019, 9780952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kang, W.H. Effect of Cyclosporin A on Melanogenesis in Cultured Human Melanocytes. Pigment Cell Res. 2003, 16, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willems, M.C.M.; van der Vliet, J.A.; de Man, B.M.; van der Laak, J.A.W.M.; Lomme, R.M.L.M.; Hendriks, T. Persistent Effects of Everolimus on Strength of Experimental Wounds in Intestine and Fascia. Wound Repair Regen. Off. Publ. Wound Health Soc. Eur. Tissue Repair Soc. 2010, 18, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.K.; Shin, S.H.; Mun, S.K.; Kim, B.J. Delayed Skin Discoloration Spreading in the Direction of Gravity after Injection of Hyaluronic Acid Dermal Fillers in Both Nasolabial Folds. Med. Lasers Eng. Basic Res. Clin. Appl. 2022, 11, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khalawany, M.; Fawzy, S.; Saied, A.; Al Said, M.; Amer, A.; Eassa, B. Dermal Filler Complications: A Clinicopathologic Study with a Spectrum of Histologic Reaction Patterns. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 19, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadzie, O.E.; Mahalingam, M.; Parada, M.; El Helou, T.; Philips, T.; Bhawan, J. Adverse Cutaneous Reactions to Soft Tissue Fillers—A Review of the Histological Features. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2008, 35, 536–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Feature | Drug-Induced Hyperpigmentation | Filler-Related PIH | Solar Lentigo |
|---|---|---|---|
| Distribution | Often patchy; can be widespread or mucosal | Focal, at injection site; irregular, asymmetric | Localized to chronically sun-exposed sites |
| Onset | Weeks–months after exposure | Weeks–months after injection (may be delayed) | Gradual over months–years |
| Colour/appearance | Variable (gray-blue to brown) | Light brown to grayish, localized | Light to dark brown macules |
| Key histology | Variable: dermal deposition, melanosis or pigment incontinence | Epidermal melanosis ± mild pigment incontinence; possible extracellular HA deposits | Epidermal hyperplasia with clubbing, Basal hyperpigmentation, solar elastosis |
| Prevention/treatment | — | Technical prevention; topical agents, peels, lasers; hyaluronidase if indicated | Photoprotection; topical lightening agents; cryotherapy or superficial chemical peels; pigment-targeted lasers |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the European Society of Dermatopathology. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kimpe, V.; Alvarez Martinez, D.; Menzinger, S.; Kaya, G. Asymmetric Lip Hyperpigmentation in a Transplant Patient. Dermatopathology 2025, 12, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12040041
Kimpe V, Alvarez Martinez D, Menzinger S, Kaya G. Asymmetric Lip Hyperpigmentation in a Transplant Patient. Dermatopathology. 2025; 12(4):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12040041
Chicago/Turabian StyleKimpe, Vincent, David Alvarez Martinez, Sébastien Menzinger, and Gürkan Kaya. 2025. "Asymmetric Lip Hyperpigmentation in a Transplant Patient" Dermatopathology 12, no. 4: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12040041
APA StyleKimpe, V., Alvarez Martinez, D., Menzinger, S., & Kaya, G. (2025). Asymmetric Lip Hyperpigmentation in a Transplant Patient. Dermatopathology, 12(4), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12040041







