Histopathologic Features and Molecular Markers of Encephalocraniocutaneous Lipomatosis (ECCL)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
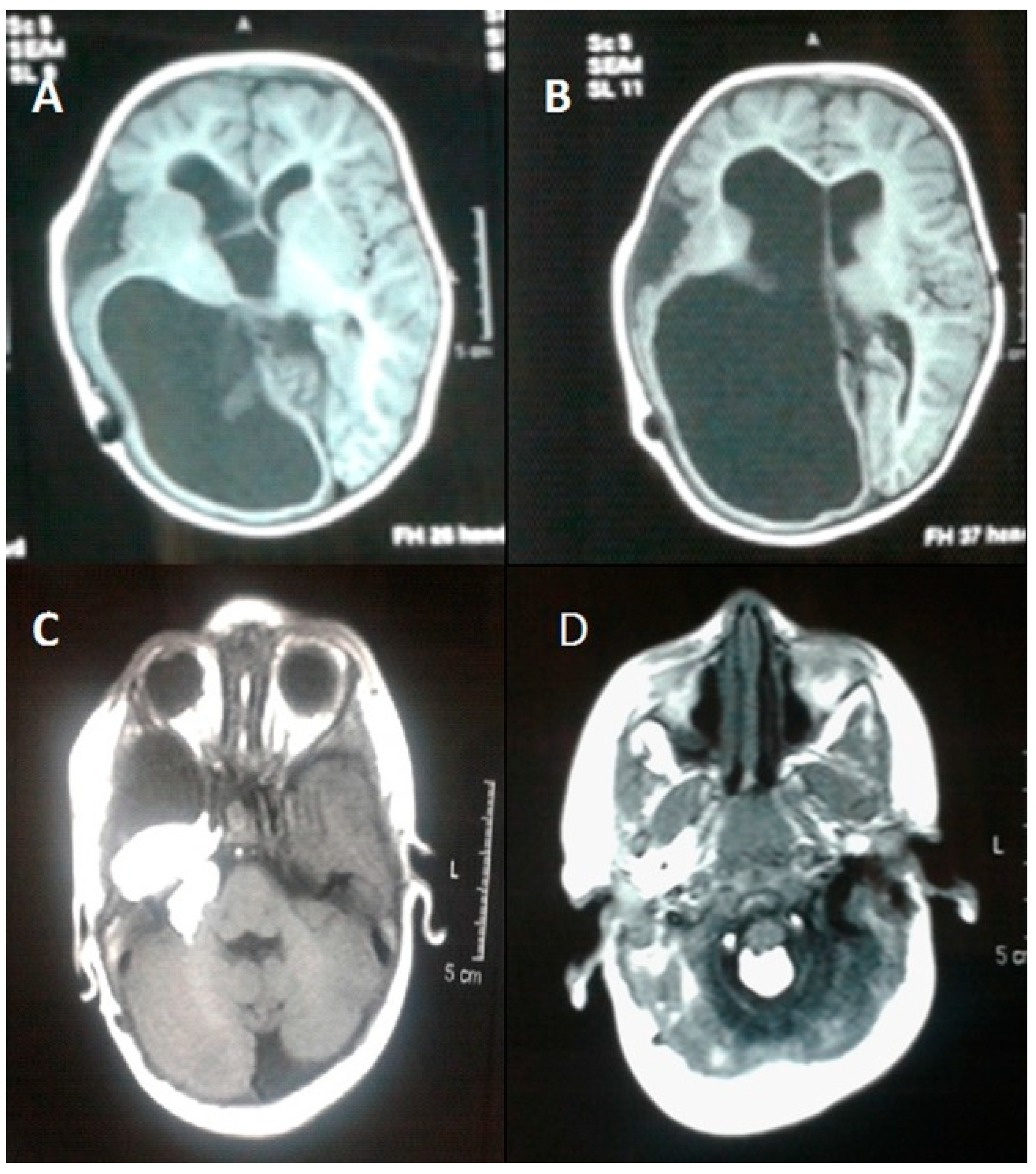
3. Results
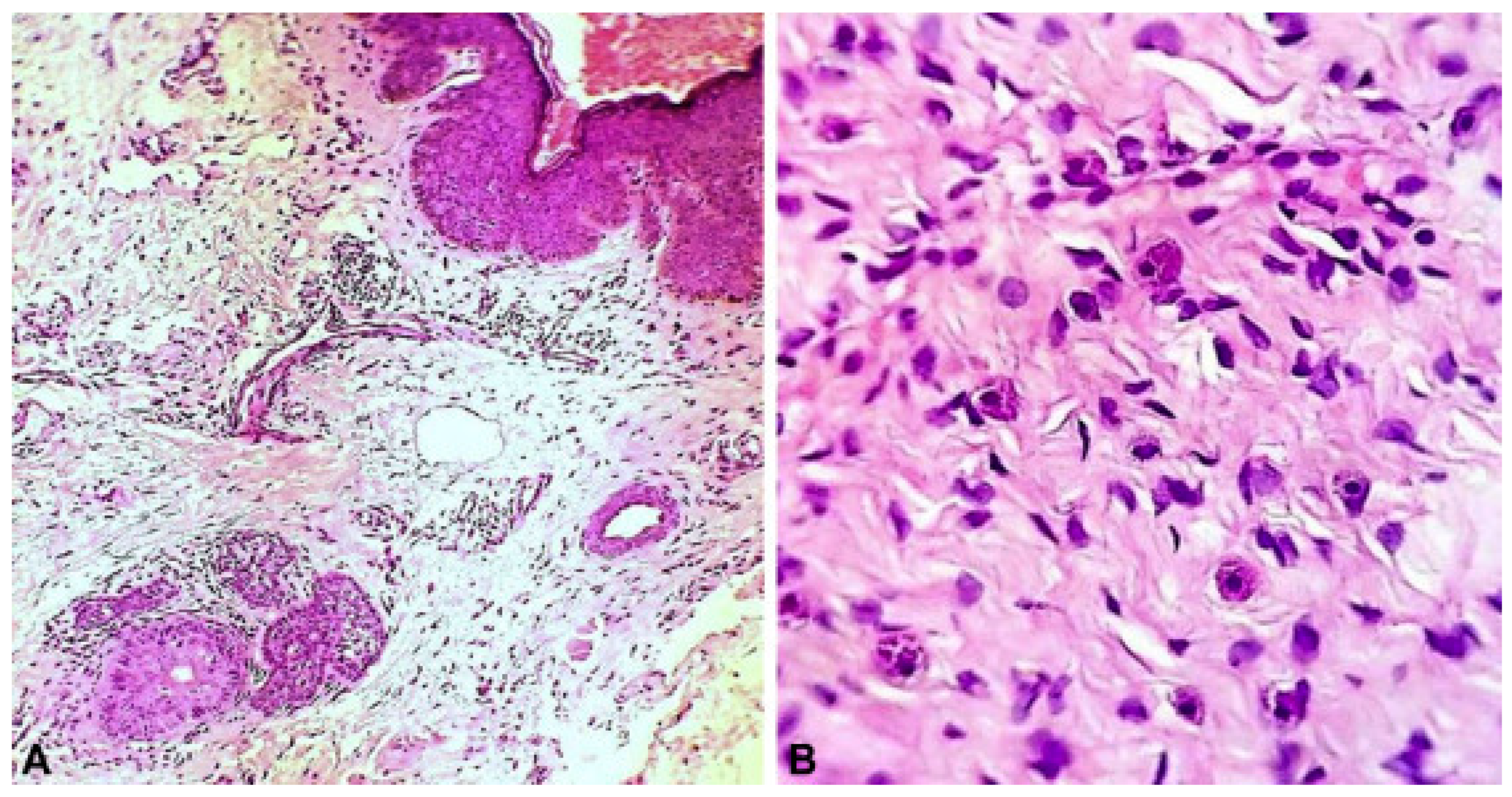
3.1. Histopathologic Features
3.1.1. Nevus Psiloliparus
3.1.2. Vascular Hyperplasia and Inflammatory Infiltrates
3.2. Molecular Markers and Pathways
Oculoectodermal Syndrome (OES)
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moog, U.; Dobyns, W.B. Encephalocraniocutaneous Lipomatosis. In GeneReviews(®); Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, F.C.P.S.; Schroeder, C.; Patel, B.; Levy, M.L. Review of encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2024, 52, 101166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.L.; Massey, C. Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2015, 132, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moog, U. Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis. J. Med. Genet. 2009, 46, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavanello, M.; Piro, L.; Roggero, A.; Rossi, A.; Cataldi, M.; Piatelli, G. Navigating the complexities of encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis: A case series and review. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2024, 40, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romiti, R.; Rengifo, J.A.; Arnone, M.; Sotto, M.N.; Valente, N.Y.; Jansen, T. Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis: A new case report and review of the literature. J. Dermatol. 1999, 26, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, J.T.; Tan, T.Y.; Alcantara, D.; Tétrault, M.; Timms, A.E.; Jensen, D.; Collins, S.; Nowaczyk, M.J.; Lindhurst, M.J.; Christensen, K.M.; et al. Mosaic Activating Mutations in FGFR1 Cause Encephalocraniocutaneous Lipomatosis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 98, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Park, S.B.; Lee, Y.; Im, M.; Seo, Y.J.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, J.-H. Encephalocraniocutaneous Lipomatosis without Neurologic Anomalies. Ann. Dermatol. 2012, 24, 476–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alakad, R.; Nofal, A.; Assaf, M.; Gharib, K.; Albalat, W.; Tantawy, E.; Ashour, W. An Egyptian boy with Haberland syndrome: Case report with observations on the histopathology. JAAD Case Rep. 2015, 1, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rubegni, P.; Risulo, M.; Sbano, P.; Buonocore, G.; Perrone, S.; Fimiani, M. Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis (Haberland syndrome) with bilateral cutaneous and visceral involvement. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2003, 28, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happle, R.; Küster, W. Nevus psiloliparus: A distinct fatty tissue nevus. Dermatology 1998, 197, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses, M.; Galdeano, A.F.; Garay, M.; Moreno, S. Nevus Psiloliparus: Case Series. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2022, 113, 319–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagati, A.; Shah, B.J.; Joshi, R.; Gajjar, T. Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis (Haberland syndrome): A rare case report. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2016, 7, 523–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happle, R.; Horster, S. Nevus psiloliparus: Report of two nonsyndromic cases. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2004, 14, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boppudi, S.; Bögershausen, N.; Hove, H.B.; Percin, E.F.; Aslan, D.; Dvorsky, R.; Kayhan, G.; Li, Y.; Cursiefen, C.; Tantcheva-Poor, I.; et al. Specific mosaic KRAS mutations affecting codon 146 cause oculoectodermal syndrome and encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis. Clin. Genet. 2016, 90, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, N.P.; Rhodes, A.R.; Mandell, F.; Mihm, M.C. Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis: A new neurocutaneous syndrome. Br. J. Dermatol. 1981, 104, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauber, K.; Warmuth-Metz, M.; Rose, C.; Bröcker, E.B.; Hamm, H. Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis: A case with unilateral odontomas and review of the literature. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2003, 162, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant’Anna, G.D.; Saffer, M.; Mauri, M.; Facco, S.; Raupp, S. Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis with otolaryngologic manifestations: A rare neurocutaneous syndrome. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 1999, 49, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, I.A.S.; Nicolas, M.E.O. A Filipino male with encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis (Haberland’s syndrome). J. Dermatol. Case Rep. 2013, 7, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodsi, S.R.; Bloom, K.E.; Egbert, J.E.; Holland, E.J.; Cameron, J.D. Ocular and systemic manifestations of encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1994, 118, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, S.; Naaz, S.; Ahmad, M.; Khan, Z.A.; Wahab, S.; Rashid, B.A. Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis: A case report with review of literature. Neuroradiol. J. 2017, 30, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koti, K.; Bhimireddy, V.; Dandamudi, S.; Gunnamreddy, R. Encephalocraniocutaneous Lipomatosis (Haberl and syndrome): A case report and review of literature. Indian. J. Dermatol. 2013, 58, 232–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgognoni, L.; Brandani, P.; Reali, F.; Gerlini, G.; Sestini, S.; Maio, V.; Reali, U.M. Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis: Congenital alopecia treatment in a rare neurocutaneous syndrome. J. Plast. Surg. Hand Surg. 2014, 48, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, A.G.W. Oculocerebrocutaneous and encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis syndromes: Blind men and an elephant or separate syndromes? Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2006, 140, 709–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordacka, J.; Zakrzewski, K.; Gruszka, R.; Witusik-Perkowska, M.; Taha, J.; Sikorska, B.; Liberski, P.P.; Zakrzewska, M. Sensitive detection of FGFR1 N546K mosaic mutation in patient with encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis and pilocytic astrocytoma. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2019, 179, 1622–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, K.K.; Liang, M.G.; Balkin, D.M.; Srivastava, S.; Church, A.J.; Eng, W. Next generation sequencing aids diagnosis and management in a case of encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2024, 41, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valera, E.T.; McConechy, M.K.; Gayden, T.; Rivera, B.; Jones, D.T.W.; Wittmann, A.; Han, H.; Bareke, E.; Nikbakht, H.; Mikael, L.; et al. Methylome analysis and whole-exome sequencing reveal that brain tumors associated with encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis are midline pilocytic astrocytomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 136, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morren, M.A.; Fodstad, H.; Brems, H.; Bedoni, N.; Guenova, E.; Jacot-Guillarmod, M.; Busiah, K.; Giuliano, F.; Gilliet, M.; Atallah, I. Mosaic RASopathies concept: Different skin lesions, same systemic manifestations? J. Med. Genet. 2024, 61, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaworski, E.; Gruber, E.; Regent-Smith, A.; Jones, K.L.; Chalhoub, M.S.; Lin, K. Encephalocraniocutaneous Lipomatosis: A Case Report. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2024, 92, e29–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturgis, M.R.; Wrobel, K.E.; Bosco, G.N.; Jones, C.H. Utility of Neonatal Findings in Early Diagnosis of a Case of Haberland Syndrome. J. Pediatr. Genet. 2023, 12, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damar, Ç.; Yaman, A.; Ali İkidağ, M.; Pekpak, E.; Olgaç, A. Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis with Wilms’ tumor. Pediatr. Int. 2017, 59, 835–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binișor, I.; Baniță, I.M.; Alexandru, D.; Mehedinți, M.C.; Jurja, S.; Andrei, A.M.; Pisoschi, C.G. Progranulin: A proangiogenic factor in visceral adipose tissue in tumoral and non-tumoral visceral pathology. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, H.; Kaisa, K.; Kristiina, A.; Sirpa, K.; Leila, J.; Sinikka, S.; Päivi, S.; Katariina, H. Mosaic KRAS Mutation in Schimmelpenning-Feuerstein-Mims Syndrome With Overlapping Oculoectodermal Syndrome and Encephalocraniocutaneous Lipomatosis Features. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2025, 42, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonell, L.M.; Leung, G.K.C.; Daoud, H.; Ip, J.; Chim, S.; Luk, H.M.; Lan, L. Mosaic KRAS mutation in a patient with encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis and renovascular hypertension. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2018, 176, 2523–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richters, R.J.H.; Seyger, M.M.B.; Meeuwis, K.A.P.; Rinne, T.; Eijkelenboom, A.; Willemsen, M.A. Oculoectodermal Syndrome- Encephalocraniocutaneous Lipomatosis Associated with NRAS Mutation. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2020, 100, adv00103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azrak, O.; Hung, S.C.; Wooten, N.G.; Hildebrandt, C.C. A New Case Linking a Somatic NRAS Variant to Encephalocraniocutaneous Lipomatosis. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2025, e64202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeijers, S.; Brems, H.; Verhaeghe, A.; van Paesschen, W.; van Loon, J.; Van der Auweraer, S.; Sciot, R.; Thal, D.R.; Lagae, L.; Legius, E.; et al. Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis phenotype associated with mosaic biallelic pathogenic variants in the NF1 gene. J. Med. Genet. 2024, 61, 904–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayer, R.E.; Zouros, A. Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis: A review of its clinical pathology and neurosurgical indications. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2011, 8, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naous, A.; Shatila, A.R.; Naja, Z.; Naja, A.S.; Rajab, M. Encephalocraniocutaneous Lipomatosis: A Rare Association With Tethered Spinal Cord Syndrome With Review of Literature. Child. Neurol. Open. 2015, 2, 2329048X14553297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimalt, R.; Ermacora, E.; Mistura, L.; Russo, G.; Tadini, G.L.; Triulzi, F.; Cavicchini, S.; Rondanini, G.F.; Caputo, R. Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis: Case report and review of the literature. Pediatr. Dermatol. 1993, 10, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Wang, J.; Kanwar, N.; Villani, A.; Ajani, O.; Fleming, A.; Patil, V.; Mamatjan, Y.; Wei, Q.; Malkin, D.; et al. A primary DICER1-sarcoma with KRAS and TP53 mutations in a child with suspected ECCL. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2022, 39, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fărcaş-Berechet, C.M.; Berechet, E.M.; Crăiţoiu, Ş.; Mehedinţi, M.C.; Osman, A.; Eremia, I.A.; Popescu, C.; Iacov-Craitoiu, M.-M. Clinical, statistical, histological and immunohistochemical aspects of periodontal changes in patients with diabetes mellitus. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2019, 60, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Clinical Cutaneous Findings | Reported Associated Histopathological Features |
|---|---|
| Alopecic scalp lesion | Absent hair follicles, lobular fat infiltration of the dermis, and isolated arrector pilli muscles [8] Fibrovascular stroma [9] Degenerated muscle fibers of arrector pilli muscles [9] Potential for complex hamartomous structures such as fibrolipomas or angiolipomas [10] Retification of the epidermis and hair follicles surrounded by fibrosis and absent elastin fiber network [6] Lack of adnexal structures [11] Irregularly shaped collagen fibers in the dermis [16] Inflammatory infiltrate including mast cells [16] Diffuse adipocytes separated by congested capillaries [13] |
| Facial and eyelid papules | Fibrovascular stroma [9,17] Vascular hyperplasia [9,16] Inflammatory infiltrate [9,18] Dermal fibrosis in a lamellar array [16] Connective tissue nevi including bands of hyperelastic tissue fibers mixed with collagen bundles [6,20] Cluster of adipocytes in the dermis bordered by bundles of collagen fibers and fibrosis [19,21,22] |
| Skin tags | Hamartoma with disorganized elements of fibrous tissue and fat [21,22] Vascular hyperplasia [23] |
| Gene. | Pathogenic Variant | Sequencing Technique Used |
|---|---|---|
| FGFR-1 | p.Asn546Lys [7,25,27] p.Lys656Glu [7,26,27] | Single molecular inversion probes (smMIPs) [7] Exome Sequencing [7,27] Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction (ddPCR) technique [25] Sanger sequencing [7,25] Next generation sequencing [26] |
| KRAS | p.Ala146Val [15] p.Ala146Thr [15,34] | Sanger sequencing [15,34] High throughput sequencing [34] |
| NF1 | K2375N [27] (c.5234C>G; p.(Ser1745*)) [37] (c.3916C>T; p.(Arg1306*)) [37] | Whole exome sequencing [27] Sanger sequencing [37] |
| PTPN11 | E69K [27] | Whole exome sequencing [27] |
| NRAS | p.(Gln61Arg). [35] p.Gly13Arg [36] | Single molecular inversion probe (smMIP) [35] Next generation sequencing [36] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the European Society of Dermatopathology. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Venigalla, S.; Dhaliwal, T.K.; Anumolu, A.; Rafey, L.; Saavedra, A.P.; Limbrick, D.D. Histopathologic Features and Molecular Markers of Encephalocraniocutaneous Lipomatosis (ECCL). Dermatopathology 2025, 12, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12040039
Venigalla S, Dhaliwal TK, Anumolu A, Rafey L, Saavedra AP, Limbrick DD. Histopathologic Features and Molecular Markers of Encephalocraniocutaneous Lipomatosis (ECCL). Dermatopathology. 2025; 12(4):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12040039
Chicago/Turabian StyleVenigalla, Siddharth, Tanvir K. Dhaliwal, Anvita Anumolu, Lena Rafey, Arturo P. Saavedra, and David D. Limbrick. 2025. "Histopathologic Features and Molecular Markers of Encephalocraniocutaneous Lipomatosis (ECCL)" Dermatopathology 12, no. 4: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12040039
APA StyleVenigalla, S., Dhaliwal, T. K., Anumolu, A., Rafey, L., Saavedra, A. P., & Limbrick, D. D. (2025). Histopathologic Features and Molecular Markers of Encephalocraniocutaneous Lipomatosis (ECCL). Dermatopathology, 12(4), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12040039






