Epithelioid Fibrous Histiocytoma with CARS-ALK Fusion: First Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
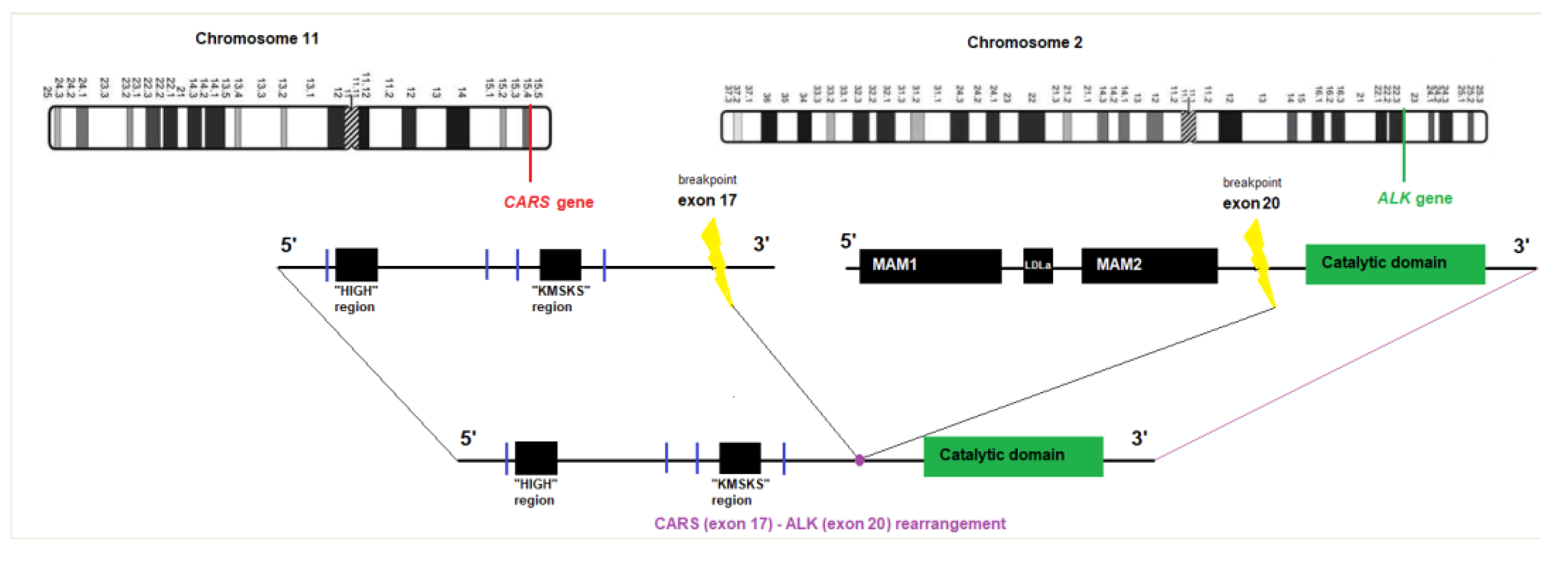
2. Case Report
3. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Debelenko, L.V.; Arthur, D.C.; Pack, S.; Helman, L.J.; Schrump, D.S.; Tsokos, M. Identification of CARS-ALK Fusion in Primary and Metastatic Lesions of an Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor. Lab. Investig. 2003, 83, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cools, J.; Wlodarska, I.; Somers, R.; Mentens, N.; Pedeutour, F.; Maes, B.; De Wolf-Peeters, C.; Pauwels, P.; Hagemeijer, A.; Marynen, P. Identification of novel fusion partners of ALK, the anaplastic lymphoma kinase, in anaplastic large-cell lymphoma and inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2002, 34, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanatani, Y.; Ogawa, K.; Shinkuma, S.; Mitsui, Y.; Miyagawa, F.; Ando, J.; Kuwahara, M.; Takeda, M.; Fujii, T.; Fukumoto, T.; et al. An unusual case of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor harboring ALK-CARS fusion with few inflammatory cells: A potential diagnostic pitfall. J. Dermatol. 2022. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollum, K.J.; Jour, G.; Al-Rohil, R.N. Cutaneous inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor with CARS-ALK fusion: Case report and literature review. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2022. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, S.W.; Xue, L.; Ma, Z.; Kinney, M.C. Alk+ CD30+ lymphomas: A distinct molecular genetic subtype of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2001, 113, 275–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgantzoglou, N.; Green, D.; Winnick, K.N.; Sumegi, J.; Charville, G.W.; Bridge, J.A.; Linos, K. Molecular investigation of ALK-rearranged epithelioid fibrous histiocytomas identifies CLTC as a novel fusion partner and evidence of fusion-independent transcription activation. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2022, 61, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazlouskaya, V.; Ho, J.; Jedrych, J.; Karunamurthy, A.; Kazlouskaya, V. Spindle cell variant of epithelioid cell histiocytoma (spindle cell histiocytoma) with ALK gene fusions: Cases series and review of the literature. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2020, 48, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazakov, D.V.; Kyrpychova, L.; Martinek, P.; Grossmann, P.; Steiner, P.; Vanecek, T.; Pavlovsky, M.; Bencik, V.; Michal, M. ALK Gene Fusions in Epithelioid Fibrous Histiocytoma: A Study of 14 Cases, with New Histopathological Findings. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2018, 40, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidrine, D.W.; Berry, J.F.; Garbuzov, A.; Falcon, C.; Tubbs, R.S.; Bui, C.J. DCTN1-ALK gene fusion in inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT) of the CNS. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2021, 37, 2147–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, B.; Perez-Atayde, A.; Hibbard, M.K.; Rubin, B.P.; Cin, P.D.; Pinkus, J.L.; Pinkus, G.S.; Xiao, S.; Yi, E.S.; Fletcher, C.D.; et al. TPM3-ALK and TPM4-ALK Oncogenes in Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumors. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; He, X.; Cui, L.; Qiu, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H. Case Report: Early Distant Metastatic Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor Harboring EML4-ALK Fusion Gene: Study of Two Typical Cases and Review of Literature. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 826705. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, K.; Ramalingam, P.; Euscher, E.D.; Reques Llanos, A.; García, A.; Malpica, A. Uterine Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Neoplasms with Aggressive Behavior, Including an Epithelioid Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Sarcoma: A Clinicopathologic Study of 9 Cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2022, 46, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szablewski, V.; Laurent-Roussel, S.; Rethers, L.; Rommel, A.; Vaneechout, P.; Camboni, A.; Willocz, P.; Copie-Bergman, C.; Ortonne, N. Atypical fibrous histiocytoma of the skin with CD30 and p80/ALK1 positivity and ALK gene rearrangement. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2014, 41, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, L.A.; Mariño-Enriquez, A.; Fletcher, C.D.M.; Hornick, J. ALK rearrangement and overexpression in epithelioid fibrous histiocytoma. Mod. Pathol. 2015, 28, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Fibrous Histiocytoma | Epithelioid Fibrous Histiocytoma | Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency in skin | Frequent | Uncommon | Rare |
| Location | Limbs, trunk Head and neck uncommon | Limbs Trunk, head and neck uncommon | Head and neck Soft tissues |
| Histopathology Architecture | Rounded to wedge-shaped dermal-based nodule with epidermal hyperplasia | Nodule with exophytic growth, epidermal collarette | Nodular or multinodular |
| Cellularity | Fibroblastic cells with round to elongated nuclei | Plump epithelioid cells with vesicular nuclei and small nucleoli | Myofibroblastic and fibroblastic spindle cells |
| Stroma | Coarse collagen Macrophages | Numerous small capillaries | Inflammatory infiltrate (plasma cells, lymphocytes) within myxoid or collagenized background |
| Immunohistochemistry | Positivity for CD68 and factor XIIIa, sometimes SMA | SMA and desmin negative | CD68 positive in histiocytic-like cells |
| CD30 or EMA may be expressed | Desmin and SMA variably positive | ||
| ALK negative | ALK positive | ALK positive | |
| Molecular alterations | Non recurrent karyotypic alterations | ALK gene fusions | ALK gene fusions |
| Most common ALK gene fusion partners | VCL, SQSTM1, EML4, TMP3, PRKAR2A, MLPH, DCTN1, CLTC, PPFIBP1 | TPM3, TPM4, RANBP2, CARS, ATIC LMNA, PRKAR1A, CLTC, FN1, EML4, DCTN1, PPFIBP1 | |
| Recurrence or distant metastasis | Rarely | Rarely | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Secco, L.-P.; Libbrecht, L.; Seijnhaeve, E.; Eggers, S.; Dekairelle, A.-F.; De Roo, A.-K. Epithelioid Fibrous Histiocytoma with CARS-ALK Fusion: First Case Report. Dermatopathology 2023, 10, 25-29. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology10010003
Secco L-P, Libbrecht L, Seijnhaeve E, Eggers S, Dekairelle A-F, De Roo A-K. Epithelioid Fibrous Histiocytoma with CARS-ALK Fusion: First Case Report. Dermatopathology. 2023; 10(1):25-29. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology10010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleSecco, Léo-Paul, Louis Libbrecht, Elsa Seijnhaeve, Silke Eggers, Anne-France Dekairelle, and An-Katrien De Roo. 2023. "Epithelioid Fibrous Histiocytoma with CARS-ALK Fusion: First Case Report" Dermatopathology 10, no. 1: 25-29. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology10010003
APA StyleSecco, L.-P., Libbrecht, L., Seijnhaeve, E., Eggers, S., Dekairelle, A.-F., & De Roo, A.-K. (2023). Epithelioid Fibrous Histiocytoma with CARS-ALK Fusion: First Case Report. Dermatopathology, 10(1), 25-29. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology10010003






