Abstract
Introduction: The salmonelloses are among the commonest, most widespread human zoonotic infections. They have generated international networks to attempt their control, since they cause a spectrum of ailments, ranging from inapparent carrier states to full-blown, severe, sometimes deadly diarrheal and systemic disease. Rapid diagnosis is needed for a number of reasons. The aim of this study was to standardize and validate a phage amplification test for the identification of salmonellosis to be applied to infections of Cavia porcellus. Methods: Native bacteriophages were isolated from infected cavies and environmental residues from commercial cavy-breeding facilities. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium ATCC 14028 was used to detect, isolate and propagate the bacteriophages, and to standardize a phage amplification assay to detect S. Typhimurium from rectal swabs of cavies. The phage amplification assay was tested using 2 antiviral agents, MgSO4·7H2O (MAS) and pomegranate rind extract (PRE) plus ferrous sulfate (PRE–FeSO4). Results: The final assay format chosen used PRE–FeSO4 and allowed detection of S. Typhimurium in 90 min from culture, 5 h from clinical samples, with a limit of detection at 103 pfu; sensitivity was 98.2%, specificity 98%, negative predictive value (NPV) 96.1%, and positive predictive value (PPV) 99.1%. Conclusion: Bacteriophage amplification is therefore an appropriate, fast procedure for detection of this pathogen in clinical samples.
Introduction
Salmonellosis is a common bacterial infection in humans [1], Salmonella enterica, the etiologic agent, can cause different clinical conditions which vary according to the pathogenic serovar [2].
Diagnosis of salmonellosis is performed by culture, which takes too long, between 3 and 5 days [3]. Molecular methods, which exhibit high sensitivity, specificity and speed, are expensive and require especially trained personnel, which prevents their application in basic level laboratories. There is a need for new methods for rapid, appropriate and economical diagnosis of Salmonella infections.
Several studies have demonstrated the use of bacteriophages for bacterial identification [4,5]. Some of the methods described use genetically modified bacteriophages, or bacteriophages labelled with fluorescent substances or the luciferin-luciferase enzyme system. These highly sensitive and specific methods have other disadvantages, such as complicated implementation, high costs, and reagent instability, which hinder their application in low-complexity diagnostic laboratories [4].
This paper describes a technically simple and affordable procedure, based on bacteriophage amplification, which is readily applicable by laboratories of different complexity levels.
Bacteriophage amplification involves the infection of the target bacteria by specific phages, followed by destruction of the bacteriophages which did not enter the host bacteria [6], using an active antiviral substance which should be harmless for the target bacteria, and is usually neutralized at the end of this step. The genetic material inoculated by the phages is amplified within the bacterial host cells, producing a large amount of copies which lyse the bacteria. The progeny phages are identified by the lysis plaques they produce on indicator plates seeded with the target bacteria. This method exponentially multiplies the viral load, and allows designing an end-point assay, with qualitative and quantitative quick results [6,7]. An important advantage of working with phages is their harmlessness to humans, being unable to penetrate the eukaryotic cell [4].
The aim of this study was to standardize and validate a phage amplification test for the identification of salmonellosis to be applied to infections of cavies, Cavia porcellus, or guinea pigs [8] which are commercially bred in Andean countries for food. Salmonellosis, mainly caused by serovar Typhimurium, is a major, often lethal disease for this animal [9,10,11].
Methods
Type of study
Standardization and validation of a diagnostic test.
Bacteriophages
Salmonella bacteriophages were isolated by the multiple enrichment method from clinical samples (fecal and rectal swabs) of cavies with signs of acute infection and organic waste from farms in the province of Lima.
Cavia porcellus
For the determination of sensitivity, specificity and other validation parameters, 156 cavies from breeding facilities in the districts of Lurín, Cieneguilla, Pachacamac and San Martín de Porras, all in Lima, were used.
Antiviral agents
Two antiviral agents were evaluated: magnesium sulfate heptahydrate MgSO4·7H2O (MAS) and pomegranate (Punica granatum) husk extract plus ferrous sulfate (PRE–FeSO4). PRE extract was prepared as described by Stewart et al. [7]. Prior to the tests, their antibacterial activity was evaluated against S. enterica serovar Typhimurium ATCC 14028. Serial dilutions of MAS and PRE–FeSO4 (1/10, 1/100, 1/1000, 1/10,000) were performed in 20 mL TSA agar (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) tempered to 40 °C. Then 1 mL of bacterial strain and 1 mL of the MAS or PRE–FeSO4 dilutions were added to separate tubes; the contents were homogenized for 2 min and then poured onto sterile Petri dishes with LB nutrient agar (Merck) and incubated at 37 °C overnight. As a control, growth medium inoculated with Salmonella alone at the same concentrations as in the experiments were used. The antibacterial activity was determined by a decrease of plaque forming units per mL (pfu/mL) counts in media with MAS or PRE–FeSO4 when compared to control, a difference greater than 20% in the bacterial count between control plates and plates with MAS or PRE was considered as antibacterial activity.
Standardization of the bacteriophage amplification test
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium ATCC 14028 was used as a positive control and Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 as a negative control. These strains were incubated for 18 to 24 h, then diluted in 4 mL of LB broth (Merck) to a turbidity of 0.5 McFarland scale, determined with a Densicheck plus (Biomérieux, Marcy l’Étoile, France) densitometer. The suspensions of Salmonella and Escherichia coli (500 µL) were added separately to tubes with 4 mL of LB broth; 250 µL of phage suspension at a concentration of 109 pfu/mL and the tubes were incubated at 37 °C for 2 h. A volume of 100 µL of MAS or PRE solution was added to the two tubes, which were incubated at room temperature for 5 min. The antiviral effect of MAS or PRE–FeSO4 was neutralized with 100 μL of Tween-80 at 2%. The tubes were centrifuged at 2500 rpm for 10 min; 1 mL of supernatant from each tube was added into tubes containing 4 mL of selenite broth (Merck); each tube was inoculated with 250 µL of S. Typhimurium ATCC 14028, incubated for 18 to 24 h and diluted to a turbidity of 0.5 McFarland scale. The contents were homogenized and a reading of the tubes was performed with the densitometer considering this result as zero time (0). The tubes were incubated for 5 h, with densitometer readings every half hour; a total of 11 readings were made.
The indicator Salmonella in the original samples showed absence or minimal growth in the test, while bacteriophage-negative samples allowed its growth. The procedure was repeated with the 42 isolates of S. enterica serovar Typhimurium from our laboratory collection.
Determination of the limit of detection
S. ATCC 14028 was incubated for 18 to 24 h and diluted to a turbidity 0.5 on the McFarland scale in 4 mL of saline (1.5 × 108 cfu/mL). From this, serial dilutions in sterile saline were made, obtaining the bacterial concentrations from 1.5 × 107, 1.5 × 106, 1.5 × 105, 1.5 × 104, 1.5 × 103, 1.5 × 102 to 1.5 × 101. The same dilutions were performed with the negative control (E. coli ATCC 25922).
The bacteriophage amplification test was performed for each bacterial dilution with both Salmonella and E. coli.
Validation of the methodology
The sample size for validation was calculated with the EPIDAT 4.0 program, considering an expected sensitivity of 97.0%, a ratio of healthy to sick animals of 2.0, a confidence level of 95% and an accuracy of 5%; a total of 45 sick and 90 healthy animals was obtained, with a minimum of 135 cavies for the test. To calculate the predictive values a disease prevalence of 33% in the study population was considered.
The clinical samples used were rectal swabs on Cary and Blair medium (Merck) from 156 cavies. Each swab was incubated for 18 to 24 h at 37 °C in 4 mL of selenite broth. After the incubation the samples were subjected in parallel to conventional culture and to the phage amplification test. The cultures were performed on Rambach agar, Hektoen enteric (HE) agar and Salmonella and Shigella (SS) agar (Merck). Lactose negative “suspicious” colonies were picked and identified using the VITEK-2® system (Biomérieux); serological confirmation was done with polyvalent serum for somatic antigen (Probac, São Paulo, Brazil).
The phage amplification test was performed following the procedures standardized through this study. The antiviral agent used was only the MAS solution. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value were determined using conventional culture as the gold standard.
Ethical aspects
The project was approved by the Animal Institutional Ethics Committee of the Universidad Peruana Cayetano Heredia, through record N° 051-06-17 dated 10 August 2016.
Results
Bacteriophage isolation
Six bacteriophages with lytic capacity against Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium were isolated. One bacteriophage was selected because of its greater capacity (larger plaques) and spectrum (more Salmonella isolates susceptible) of lytic activity. This was called “phage 10”.
Evaluation of the antibacterial activity of MAS and PRE against Salmonella
Counts of S. Typhimurium ATCC 14028 in the control plate and the plates with the 2 virucidal agents, MAS and PRE-FeSO4 were very similar, showing no significant difference.
Bacteriophage amplification
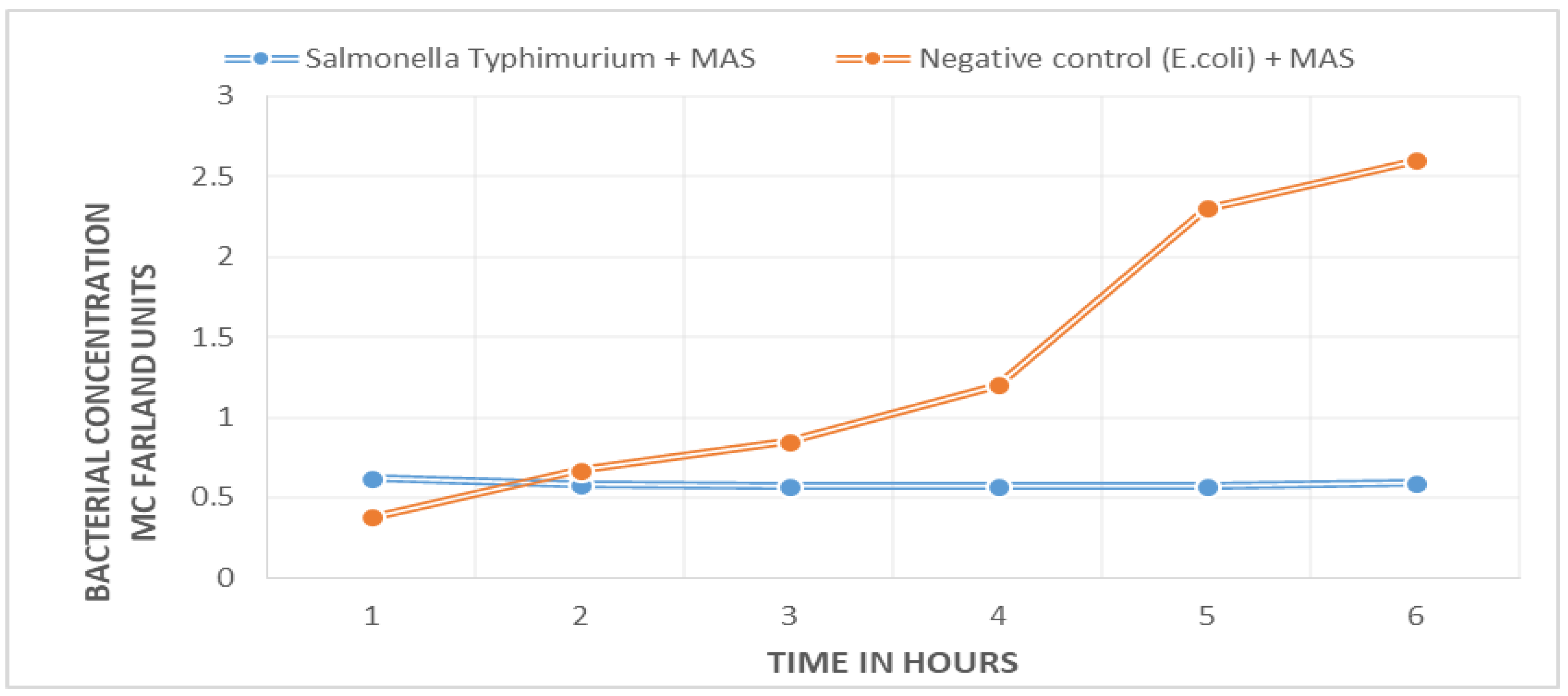
A marked difference between the bacterial growth curve of the negative control (E. coli ATCC 25922) and the sample with target bacteria (S. Typhimurium ATCC 14028) was found. Figure 1 shows that there is no bacterial growth in the positive sample; the curve remains unchanged during the 5.5 h of the experiment. The negative control shows exponential growth. The difference between the two curves can be appreciated from the first hour into the experiment.
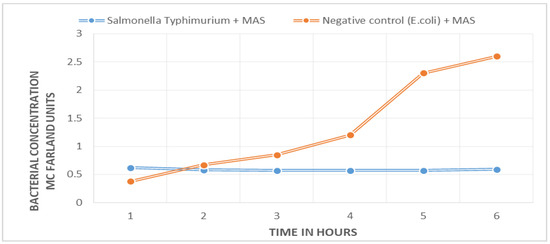
Figure 1.
Results of bacteriophage amplification. The positive sample (blue line), which contains the target Salmonella, shows no change in bacterial concentration: absence of growth; the negative control (orange line), which contains E. coli, shows exponential growth.
The 42 Salmonella enterica isolates showed the same behavior pattern.
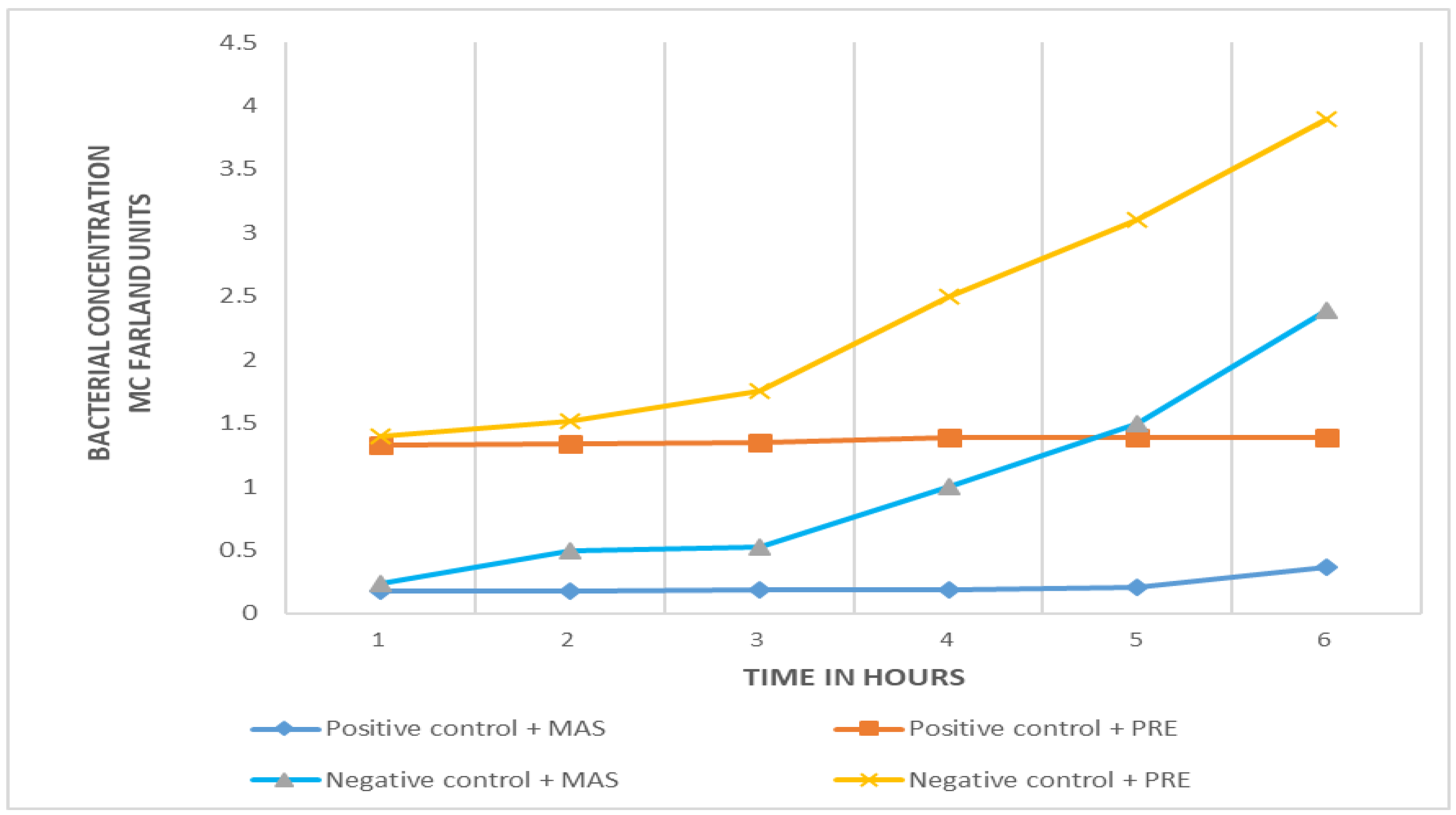
Comparison of efficiency between PRE-FeSO4 and MAS in phage amplification
Both virucidal substances are effective in eliminating the bacteriophages from samples with no target (Salmonella) bacteria. The growth curves of negative controls and positive samples are clearly differentiated with the two virucidal substances (Figure 2), no growth in the positive sample and exponential bacterial growth in the negative (E. coli) control. However, the initial turbidity of samples (positive and negative) with MAS is less than that obtained with PRE-FeSO4. In the initial phase of microbial growth (time zero), there is a difference of more than one unit of turbidity in the McFarland scale (Figure 2).
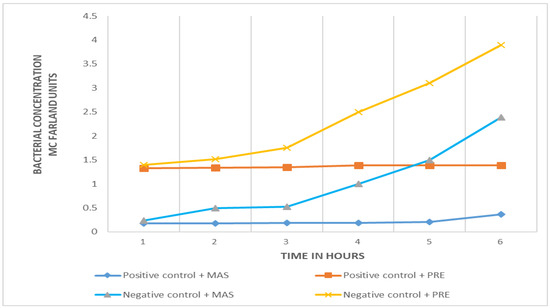
Figure 2.
Comparison of the efficiency of MAS and PRE in the phage amplification test. The positive samples (dark blue and red lines), which contain the target Salmonella, show no change in bacterial concentration (absence of growth); the negative controls (orange and light blue lines), which contain E. coli, show exponential growth.
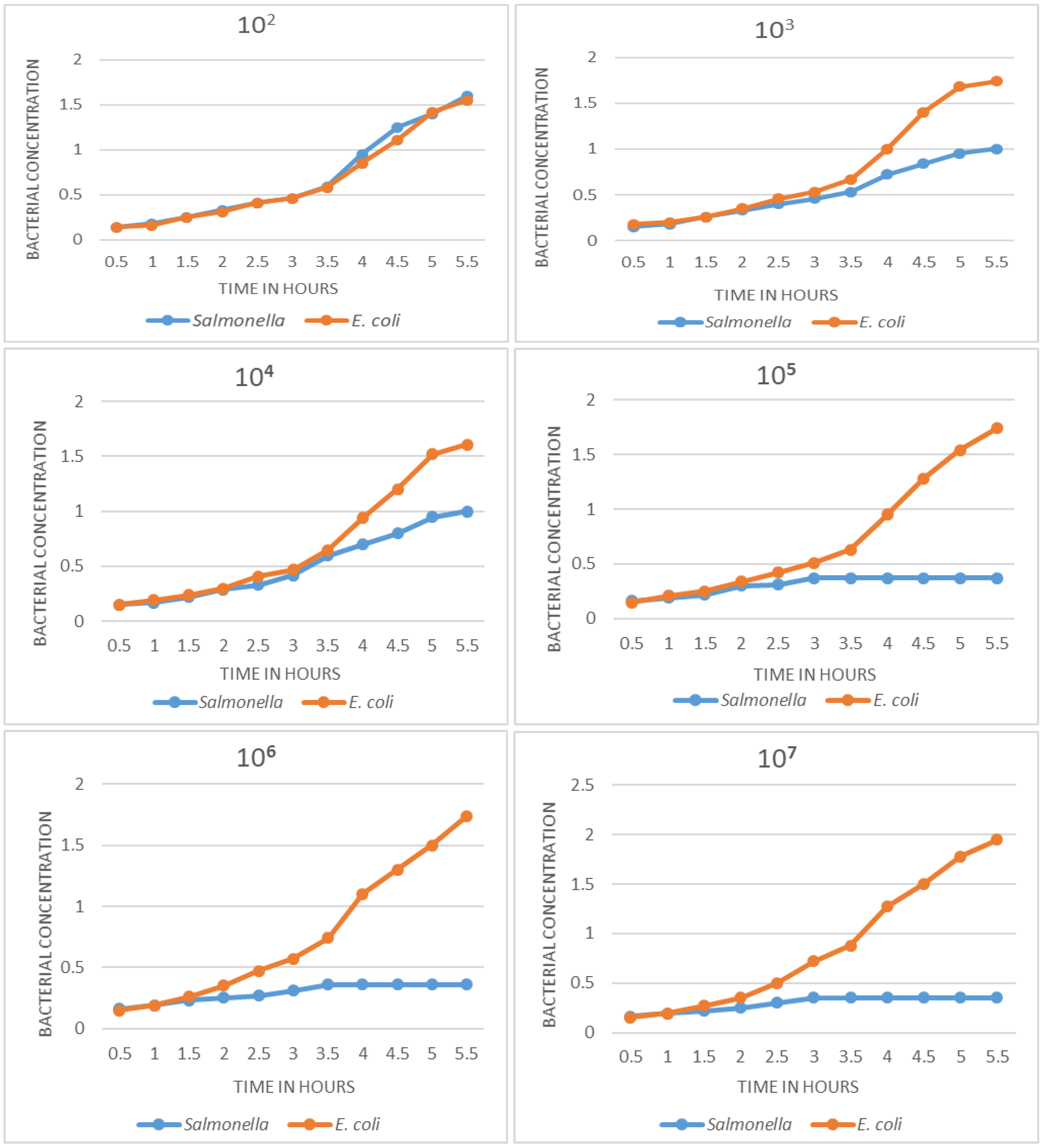
Determination of limit of detection
In Figure 3, the growth curves obtained with decreasing concentrations of Salmonella and E. coli are observed. Dilutions with 107, 106, 105 cfu/mL show very well differentiated growth curves: absence of growth in the sample with target bacteria and an exponential curve in the negative control. The difference can be appreciated from 2.5 h. At concentrations of 104 and 103 cfu/mL, a difference can also be seen in growth curves, although in these cases the differentiation occurs later; the curves are still different at 3.5 to 4 h; the curves of samples containing Salmonella show slow growth at first, but then increase exponentially, becoming indistinguishable from the negative control. In this sense, the detection limit of the method was determined to be at 103 cfu.
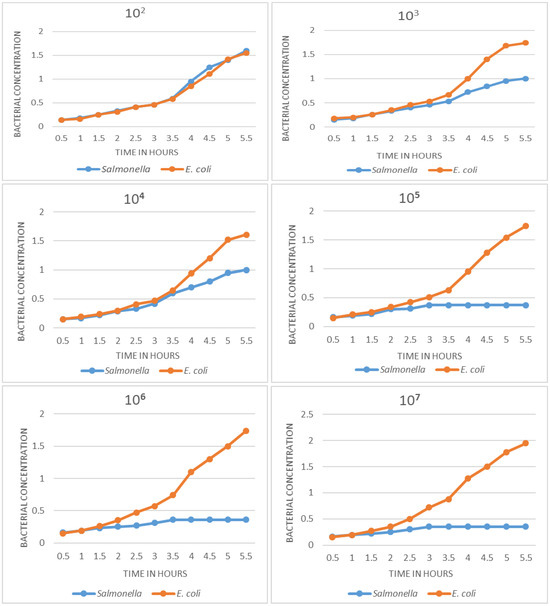
Figure 3.
Salmonella detection limit by the phage amplification method. Differences in growth curves can be shown up to dilution 103; at dilution 102 the curves cannot be differentiated. A similar result was obtained at dilution 101 (not shown in the graph).
Validation of the methodology
A sensitivity of 98.18%, a specificity of 98.02%, a positive predictive value of 96.07% and a negative predictive value of 99.09% were obtained. The results are shown in the Table 1.

Table 1.
Results obtained in the identification of Salmonella enterica by culture and phage.
Discussion
The need for rapid, simple and economical methods to identify bacterial pathogens has increased significantly in the medical field, agriculture, food industry and livestock [3,4,13,14,15]. Conventional methods lack practicality mainly due to slowness and lack of cost effectiveness. As a consequence, a series of methods such as immunoassays and molecular methods have emerged [4]. These require, in most cases, the initial microbial culture, DNA extraction, amplification and sequencing, they usually require sophisticated and expensive equipment as well as highly specialized personnel. Immunoassays are less reliable because of sensitivity or specificity problems.
The positive sample (blue line), which contains the target Salmonella, shows no change in bacterial concentration: absence of growth; the negative control (orange line), which contains E. coli, shows exponential growth.
There is an increased interest in the development of faster, operationally simpler methods that do not require sophisticated and costly equipment or highly specialized technical personnel.
The ability of bacteriophages to infect and propagate only in a specific bacterium makes them ideal tools for the detection of pathogens. This marked specificity, plus their capacity of propagating on a large scale within their specific host, provides an opportunity to increase the sensitivity of the assay. Phage diversity and abundance in nature and the ease of their isolation and identification with current technical tools, makes methods using them economically accessible [6,7,13,14,15,16]. Therefore phages are considered very promising for the development of quick, easy, effective and economic identification tools for bacterial pathogens.
The present study sought to standardize and validate a method for the identification of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, a clinically important pathogen in our environment, both in humans and other mammals, and whose isolation and identification by conventional microbiological methods still pose several problems.
Cavia porcellus use has several advantages in our country, such as ease of access and work, reduced study time, and importance of the species as a food animal. In addition, this species is significantly affected by this Salmonella in particular, as considerable levels of infection are registered in cavy breeding facilities [8,9,10,11].
Two virucidal agents, MAS and PRE-FeSO4, were evaluated in the standardization process. The results show similar antiviral activity in both, but the PRE-FeSO4, which at the beginning of the study was shown as an innovative, practical and ecologically sound alternative, had high levels of staining and turbidity, which altered initial readings of the bacterial concentrations; that, and some instability to light, led us to opt for the MAS.
Time to detection of the pathogen, as seen when standardizing the method from isolated bacteria in culture (Figure 1), may be as low as 1.5 h. The results of detection limit determination show that the time to detect a pathogen is inversely related to its initial bacterial concentration, so the time to detection varies between 2 to 4 h.
If we add the primary isolation time (18 h) to the 4 h that the amplification test takes, it is possible to have the final identification of the pathogen in less than 22 h. This is a difference of at least 2 days as compared to conventional culture. The time to detection could be decreased further if the growth of Salmonella is promoted by incorporating an agitation system, removing inhibitory components of selenite broth, or other simple means. Those changes could be evaluated in later studies.
On the detection limit, as shown in Figure 3, the standardized phage amplification method is able to identify the pathogen even at a concentration of 103 cfu/mL of the target Salmonella. At the concentrations of 107, 106 and 105 cfu, detection is more evident because the curves are clearly differentiated; when evaluating concentrations of 104 and 103 cfu/mL, it is still possible to differentiate the growth curves, but using a longer time for their evaluation. The limit of detection determined is quite appropriate for the case of Salmonella, since the amount of bacteria that are eliminated in the feces of an affected individual is high [1].
The validation shows the high efficiency of the bacteriophage amplification test, a sensitivity of 98.10% and a specificity of 98%. It is necessary to consider that the identification of the pathogen both in culture and in phage amplification, are based on the viability of the bacterium. Molecular tools may improve efficiency of detection even more.
Conclusion
The methodology standardized is one of the most basic and simple phage-based alternatives. Various studies combine phage methods with modern and sophisticated detection tools. The aim of the study, which was attained, was to test a rapid, effective and simple method to identify S. enterica serovar Typhimurium, which would be accessible to laboratories with basic implementation, and that does not require specialized personnel or highly sophisticated equipment.
Author Contributions
JT contributed to the conception, design of the work, analysis and interpretation of data, and granted final approval of the version to be published. VG contributed to the acquisition and analysis of data. HG contributed to the drafting of the work and revising it critically for important intellectual content and granted final approval of the version to be published. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Peruvian “Programa Nacional de Innovación para la Competitividad y Productividad—PNICP” grant number: 234-FINCyT-IA-2013.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors—none to disclose.
References
- Murray, P.R.; Baron, E.J.; Jorgensen, J.H.; Landry, M.L.; Pfaller, M.A. Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 9th ed.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fàbrega, A.; Vila, J. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium skills to succeed in the host: Virulence and regulation. Clin Microbiol Rev 2013, 26, 308–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isenberg, H.D. Clinical Microbiology Procedures Handbook, 2nd ed.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sabour, P.M.; Griffiths, M.W. Bacteriophages in the Control of Food-And Waterborne Pathogens; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mandeville, R.; Griffiths, M.W.; Goodridge, L.; McIntyre, L.; Ilenchuk, T.T. Diagnostic and therapeutic applications of lytic phages. Anal Lett 2003, 36, 3241–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, G.S.A.B.; Jassim, S.A.A.; Denyer, S.P.; Rees, C.E.D.; Park, S.; Rostas-Mulligan, K. Methods for Rapid Microbial Detection. PCT Patent WO 92/02633, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, G.S.; Jassim, S.A.; Denyer, S.P.; Newby, P.; Linley, K.; Dhir, V.K. The specific and sensitive detection of bacterial pathogens within 4 h using phage amplification. J Appl Microbiol 1988, 84, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministerio de Agricultura del Perú. Buenas Prácticas Pecuarias Para la Crianza Comercial de Cuyes. Manual Para el Productor. 2010. Available online: http://www.minagri.gob.pe/portal/download/pdf/direc cionesyoficinas/dgca/crianza/cuyes.pdf (accessed on 4 September 2018).
- Matsuura, S.; Morales, S.; Calle, S.; Ara, M. Susceptibilidad a antimicrobianos in vitro de Salmonella enterica aislada de cuyes de crianza familiar-comercial en la provincia de Carhuaz, Ancash. Rev Inv Vet Perú 2010, 21, 93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Layme, A.; Perales, R.; Chavera, A.; Gavidia, C.; Calle, S. Lesiones anatomopatológicas en cuyes (Cavia porcellus) con diagnóstico bacteriológico de Salmonella sp. Rev Inv Vet Perú 2011, 22, 376–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez Vallejos. La Salmonelosis en Cobayos (Cavia Porcellus): Aspectos Epidemiológicos; Asociación de Investigadores Agrícolas y Pecuarios del Perú: Lima, Peru, 1974; p. 176. [Google Scholar]
- Caballero, R. Caracterización Fenotípica y Genotípica de Salmonelosis en Cavia porcellus (Cuyes) en las Provincias de Cajamarca, Lima y Moquegua. Tesis para optar el Título Profesional de Médico Veterinario Zootecnista, Universidad Peruana Cayetano Heredia, Lima, Peru, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Petty, N.K.; Evans, T.J.; Fineran, P.C.; Salmond, G.P. Biotechnological exploitation of bacteriophage research. Trends Biotechnol 2007, 25, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rees, C.E.D.; Dodd, C.E.R. Phage for rapid detection and control of bacterial pathogens in food. Adv Appl Microbiol 2006, 59, 159–186. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lakshmanan, R.S.; Guntupalli, R.; Hu, J.; et al. Phage immobilized magnetoelastic sensor for the detection of Salmonella typhimurium. J Microbiol Methods 2007, 71, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagens, S.; Loessner, M.J. Application of bacteriophages for detection and control of foodborne pathogens. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2007, 76, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).