Evaluation of Clinicians’ Reporting Proficiency and Their Risk Perceptions of Ebola Virus Disease in Ebonyi State, Nigeria
Abstract
Introduction
Methods
Study setting
Study design
Instrument
Data analysis
Ethical approval
Results
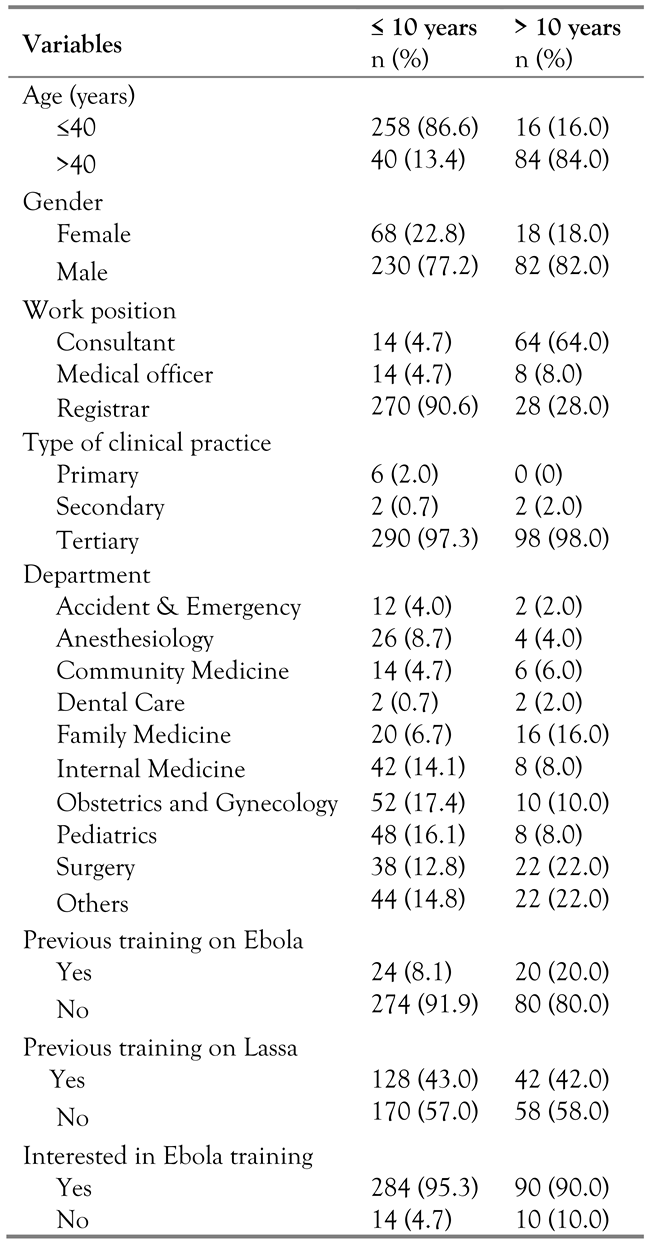
Characteristics of the respondents
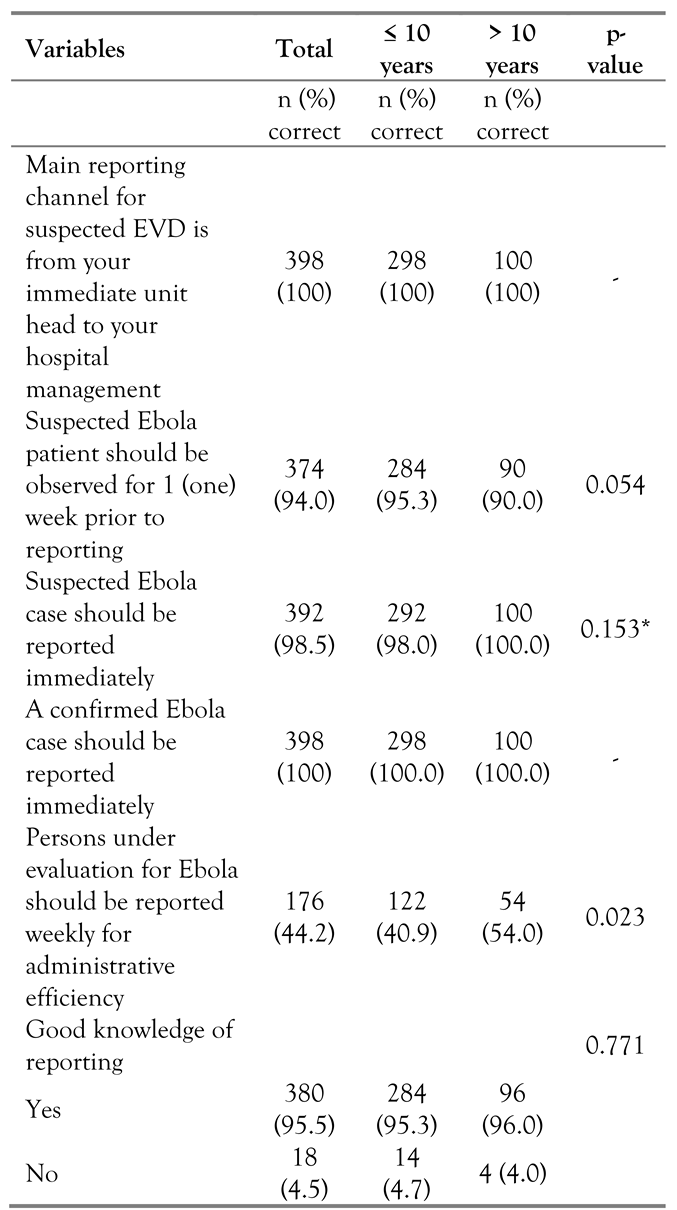
Knowledge of reporting of probable EVD cases
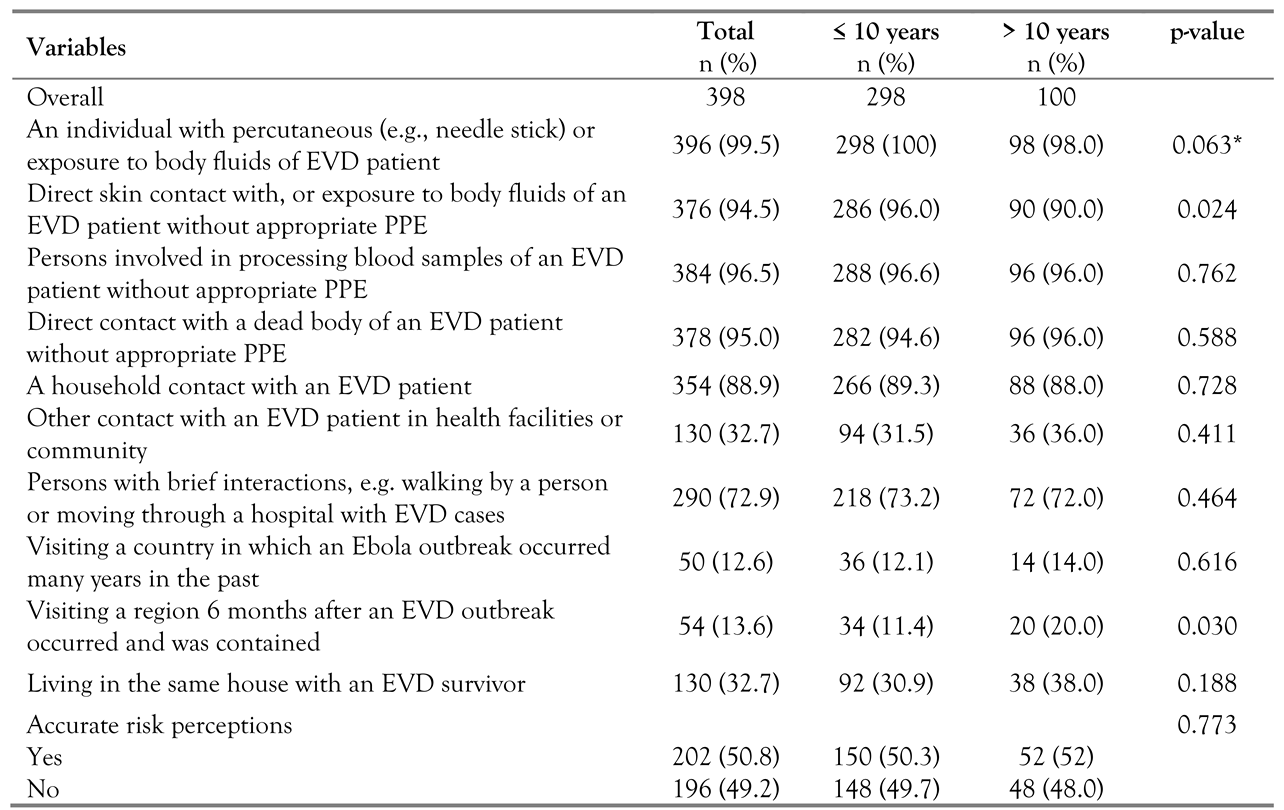
Risk perceptions of EVD
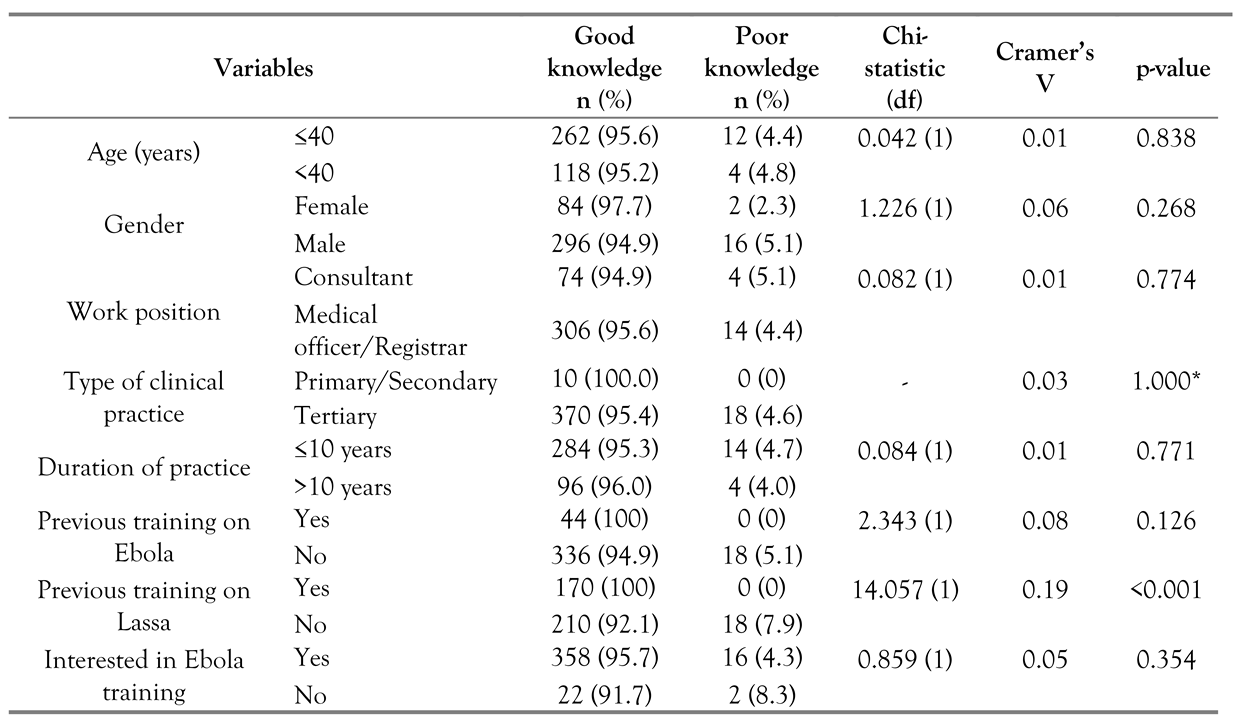
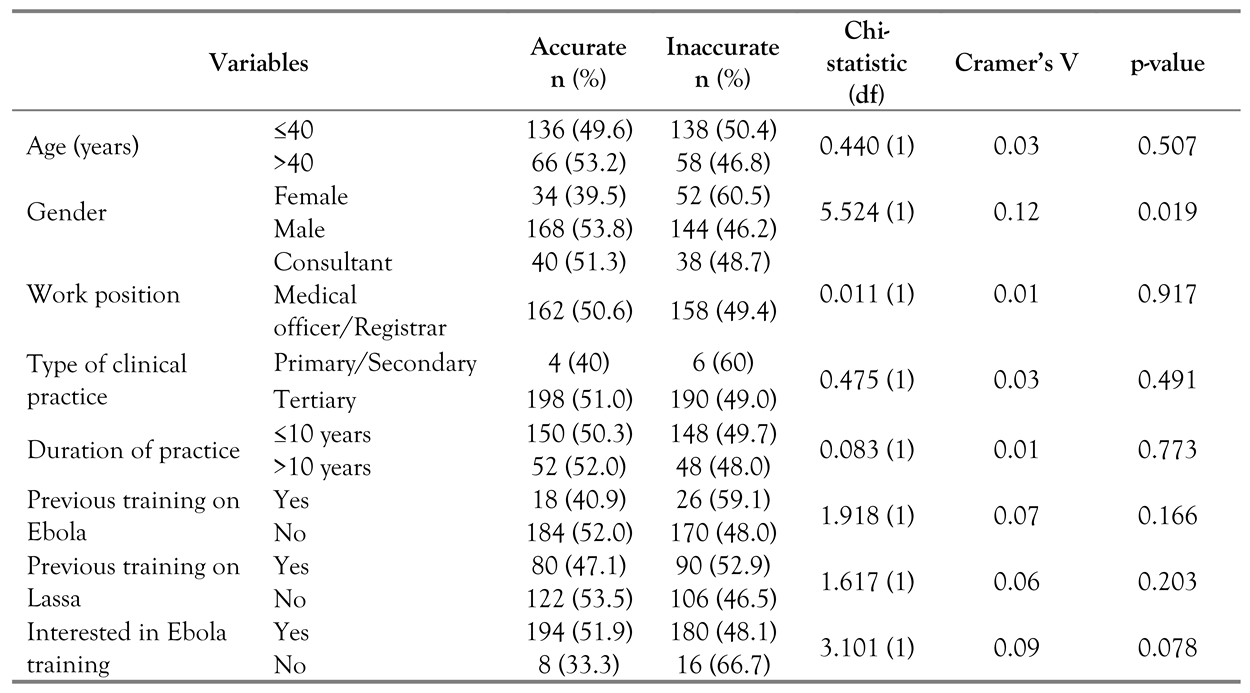
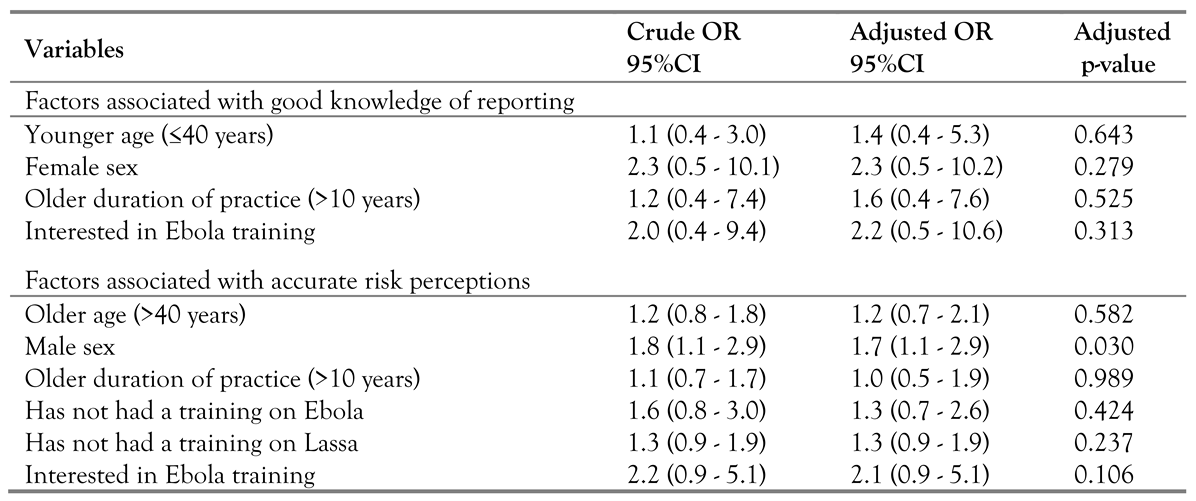
Relationships between knowledge of notification modalities and risk perceptions to EVD, and the characteristics of the respondents
Discussion
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Ebola virus disease: Situation reports. Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/208883/1/ebolasitrep_10Jun2016_eng.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 14 January 2017).
- World Health Organization. Ebola virus disease: Fact sheet January 2016. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs103/en/ (accessed on 12 January 2017).
- Almutairi, K.M.; Alodhayani, A.A.; Moussa, M.; Aboshaiqah, A.E.; Tumala, R.B.; Vinluan, J.M. Ebola outbreak preparedness and preventive measures among healthcare providers in Saudi Arabia. J Infect Dev Ctries 2016, 10, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Khan, M.U.; Jamshed, S.Q.; et al. Are healthcare workers ready for Ebola? An assessment of their knowledge and attitude in a referral hospital in South India. J Infect Dev Ctries 2016, 10, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfaki, M.M.; Salih, A.M.; Elhuda, D.A.; Egail, M.S. Knowledge, attitude and practice of health care providers toward Ebola virus disease in hotspots in Khartoum and White Nile states, Sudan, 2014. Am J Infect Control 2016, 44, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Health worker Ebola infections in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone: A preliminary report. (WHO/EVD/SDS/REPORT/2015.1); World Health Organization: Geneva, 21 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, W.A., 2nd; Hynes, N.A.; Perl, T.M. Protecting health care workers from Ebola: Personal protective equipment is critical but is not enough. Ann Intern Med 2014, 161, 753–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matanock, A.; Arwady, M.A.; Ayscue, P.; et al. Ebola virus disease cases among health care workers not working in Ebola treatment units—Liberia, June-August 2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2014, 63, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, D.K.; Sittig, D.F.; Singh, H. Ebola US Patient Zero: Lessons on misdiagnosis and effective use of electronic health records. Diagnosis (Berl) 2014, 1, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliyasu, G.; Ogoina, D.; Otu, A.A.; et al. A multi-site knowledge attitude and practice survey of Ebola virus disease in Nigeria. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazekas, B.; Fazekas, J.; Moledina, M.; Fazekas, B.; Karolyhazy, K. Ebola virus disease: Awareness among junior doctors in England. J Hosp Infect 2015, 90, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, S.; Brouqui, P.; Fontaine, J.; et al. Risk perceptions of MSF healthcare workers on the recent Ebola epidemic in West Africa. New Microbes New Infect 2016, 12, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igonoh, A.K. My experience as an Ebola patient. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2015, 92, 221–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Cirilo, L.; Martín-Ríos, M.D.; de Las Casas-Cámara, G.; Andrés-Prado, M.J.; Rodríguez-Caravaca, G. [Notifiable infectious diseases: Knowledge and notification among hospital physicians]. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin 2013, 31, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brabazon, E.D.; O’Farrell, A.; Murray, C.A.; Carton, M.W.; Finnegan, P. Under-reporting of notifiable infectious disease hospitalizations in a health board region in Ireland: Room for improvement? Epidemiol Infect 2008, 136, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spedding, R.L.; Jenkins, M.G.; O’Reilly, S.A. Notification of infectious diseases by junior doctors in accident and emergency departments. J Accid Emerg Med 1998, 15, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinson, L. From clinician to suspect case: My experience after a needle stick in an Ebola treatment unit in Sierra Leone. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2015, 92, 225–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santibañez, S.; Polgreen, P.M.; Beekmann, S.E.; Rupp, M.E.; Del Rio, C. Infectious Disease physicians’ perceptions about Ebola preparedness early in the US response: A qualitative analysis and lessons for the future. Health Secur 2016, 14, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC). Ebola Virus Disease. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/vhf/ebola/index.html (accessed on 12 January 2017).
- Federal Ministry of Health Nigeria. Technical guidelines for Integrated Disease Surveillance and Response in Nigeria. Available online: http://www.ncdc.gov.ng/themes/common/docs/protocols/4_1476085948.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2017).
- Ajayi, N.A.; Nwigwe, C.G.; Azuogu, B.N.; et al. Containing a Lassa fever epidemic in a resource-limited setting: Outbreak description and lessons learned from Abakaliki, Nigeria (January-March 2012). Int J Infect Dis 2013, 17, e1011–e1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olowookere, S.A.; Fatiregun, A.A.; Gbolahan, O.O.; Adepoju, E.G. Diagnostic proficiency and reporting of Lassa fever by physicians in Osun State of Nigeria. BMC Infect Dis 2014, 14, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davtyan, M.; Brown, B.; Folayan, M.O. Addressing Ebola-related stigma: Lessons learned from HIV/AIDS. Glob Health Action 2014, 7, 26058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karafillakis, E.; Jalloh, M.F.; Nuriddin, A.; et al. ‘Once there is life, there is hope’ Ebola survivors’ experiences, behaviours and attitudes in Sierra Leone, 2015. BMJ Global Health 2016, 1, e000108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
© GERMS 2017.
Share and Cite
Ajayi, N.A.; Ojide, C.K.; Ajayi, I.A.; Ukwaja, K.N. Evaluation of Clinicians’ Reporting Proficiency and Their Risk Perceptions of Ebola Virus Disease in Ebonyi State, Nigeria. Germs 2017, 7, 140-148. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2017.1119
Ajayi NA, Ojide CK, Ajayi IA, Ukwaja KN. Evaluation of Clinicians’ Reporting Proficiency and Their Risk Perceptions of Ebola Virus Disease in Ebonyi State, Nigeria. Germs. 2017; 7(3):140-148. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2017.1119
Chicago/Turabian StyleAjayi, Nnennaya Anthony, Chiedozie Kingsley Ojide, Immanuel Anthony Ajayi, and Kingsley Nnanna Ukwaja. 2017. "Evaluation of Clinicians’ Reporting Proficiency and Their Risk Perceptions of Ebola Virus Disease in Ebonyi State, Nigeria" Germs 7, no. 3: 140-148. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2017.1119
APA StyleAjayi, N. A., Ojide, C. K., Ajayi, I. A., & Ukwaja, K. N. (2017). Evaluation of Clinicians’ Reporting Proficiency and Their Risk Perceptions of Ebola Virus Disease in Ebonyi State, Nigeria. Germs, 7(3), 140-148. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2017.1119




