Antigenic Distribution of Streptococcus agalactiae Isolates from Pregnant Women at Garankuwa Hospital—South Africa
Abstract
Introduction
Methods
Sample collection
Capsular typing
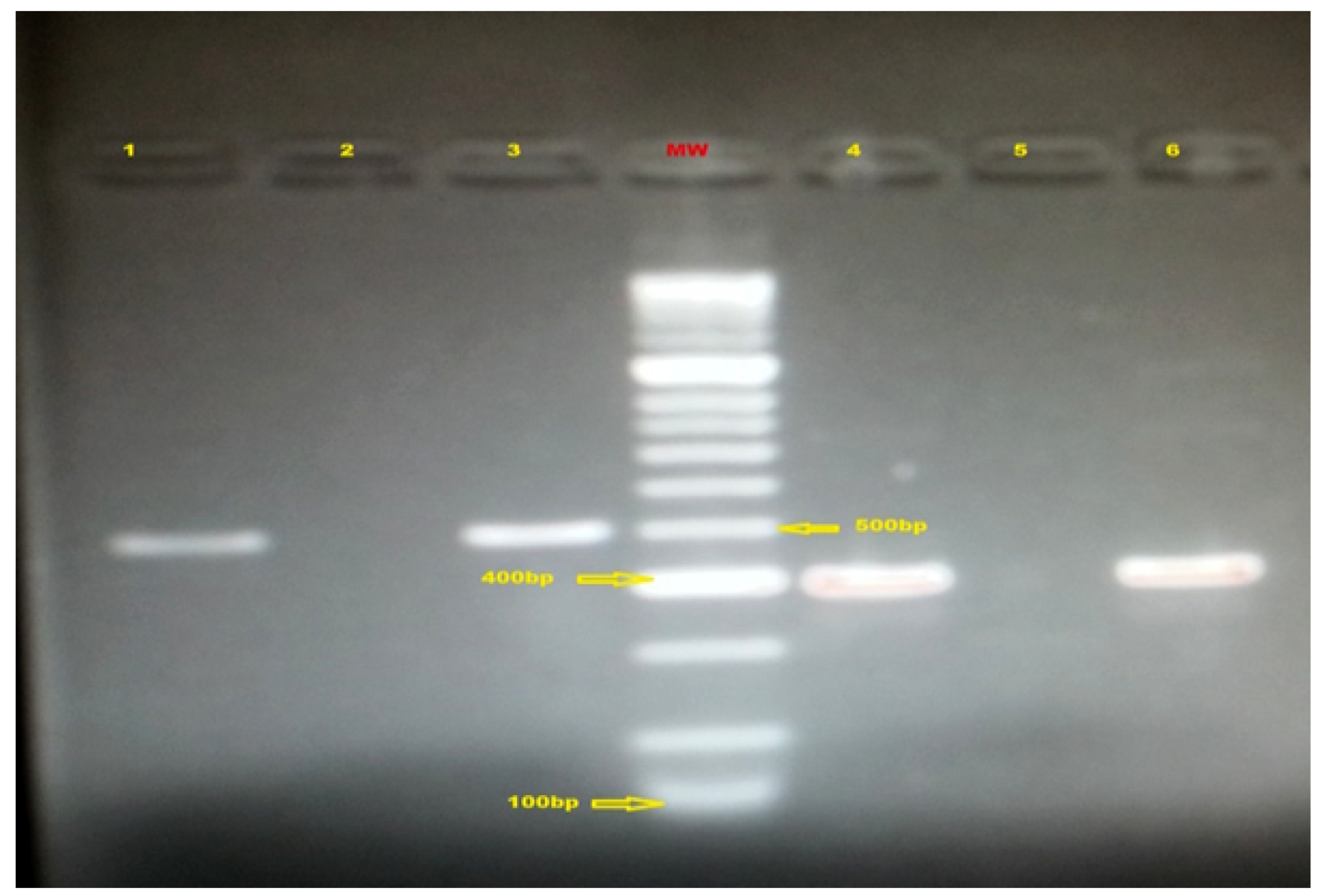
Molecular typing
Subtypes of GBS isolates
Ethical considerations
Results
Capsular type distribution
Molecular typing
Antigenic subtypes of GBS detected
Discussion
Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Edwards, M.S.; Baker, C.J. Group B streptococcal infections in elderly adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2005, 6, 839–847. [Google Scholar]
- Skoff, T.H.; Farley, M.M.; Petit, S.; et al. Increasing burden of invasive group B streptococcal disease in nonpregnant adults, 1990-2007. Clin Infect Dis. 2009, 49, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.M.; Uldbjerg, N.; Kilian, M.; Sørensen, U.B. Dynamics of Streptococcus agalactiae colonization in women during and after pregnancy and in their infants. J Clin Microbiol. 2004, 42, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavenyengwa, R.T.; Afset, J.E.; Schei, B.; et al. Group B Streptococcus colonization during pregnancy and maternalfetal transmission in Zimbabwe. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2010, 89, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spellerberg, B. Pathogenesis of neonatal Streptococcus agalactiae infections. Microbes Infect 2000, 2, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotved, H.C.; Kong, F.; Lambertsen, L.; Sauer, S.; Gilbert, G.L. Serotype IX, a proposed new Streptococcus agalactiae serotype. J Clin Microbiol. 2007, 45, 2929–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, S.Y.; Seki, C.; Sakata, H.; et al. Capsular type and antibiotic resistance in Streptococcus agalactiae isolates from patients, ranging from newborns to the elderly, with invasive infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2009, 53, 2650–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Kong, F.; Zeng, X.; Gidding, H.F.; Morgan, J.; Gilbert, G.L. Distribution of genotypes and antibiotic resistance genes among invasive Streptococcus agalactiae (group B streptococcus) isolates from Australasian patients belonging to different age groups. Clin Microbiol Infect 2008, 14, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creti, R.; Michel, J.; Orefici, L.G. Genetic variability of the locus encoding alpha-C like proteins in Streptococcus agalactiae. In Streptococci and streptococcal diseases: Entering the new millennium, Proceedings of the XIV Lancefield international symposium on streptococci and streptococcal diseases. Securacopy, Porirua, New Zealand; Martin, D.R., Tagg, J., Eds.; 2000; pp. 397–399. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, F.; Gowan, S.; Martin, D.; James, G.; Gilbert, G.L. Molecular profiles of group B streptococcal surface protein antigen genes: relationship to molecular serotypes. J Clin Microbiol 2002, 40, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madoff, L.C.; Michel, J.L.; Gong, E.W.; Kling, D.E.; Kasper, D.L. Group B streptococci escape host immunity by deletion of tandem repeat elements of the alpha C protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1996, 93, 4131–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachenauer CS, Madoff LC. . A protective surface protein from type V group B streptococci shares N-terminal sequence homology with the alpha C protein. Infect Immun 1996, 64, 4255–4260.
- Slotved, H.C.; Elliott, J.; Thompson, T.; Konradsen, H.B. Latex assay for serotyping of group B streptococcus isolates. J Clin Microbiol 2003, 41, 4445–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creti, R.; Fabretti, F.; Orefici, G.; von Hunolstein, C. Multiplex PCR assay for direct identification of group B streptococcal alpha-protein-like protein genes. J Clin Microbiol 2004, 42, 1326–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolukaoto, J.Y.; Monyama, C.M.; Chukwu, M.O.; et al. Antibiotic resistance of Streptococcus agalactiae isolated from pregnant women in Garankuwa, South Africa. BMC Res Notes 2015, 8, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchardt, S.M.; Foxman, B.; Chaffin, D.O.; et al. Comparison of DNA dot blot hybridization and Lancefield capillary precipitin methods for group B streptococcal capsular typing. J Clin Microbiol 2004, 42, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Ma, L.; Gilbert, G.L. Simultaneous detection and serotype identification of Streptococcus agalactiae using multiplex PCR and reverse line blot hybridization. J Med Microbiol 2005, 54, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madzivhandila, M.; Adrian, P.V.; Cutland, C.L.; Kuwanda, L.; Schrag, S.J.; Madhi, S.A. Serotype distribution and invasive potential of group B streptococcus isolates causing disease in infants and colonizing maternal-newborn dyads. PLoS One 2011, 6, e17861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyo, S.R.; Mudzori, J.; Tswana, S.A.; Maeland, J.A. Prevalence, capsular type distribution, anthropometric and obstetric factors of group B Streptococcus (Streptococcus agalactiae) colonization in pregnancy. Cent Afr J Med 2000, 46, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Ippolito, D.L.; James, W.A.; Tinnemore, D.; et al. Group B streptococcus serotype prevalence in reproductive-age women at a tertiary care military medical center relative to global serotype distribution. BMC Infect Dis 2010, 10, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.K.; Song, Y.R.; Kim, M.Y.; et al. Epidemiology of group B streptococcus in Korean pregnant women. Epidemiol Infect 2010, 138, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phares, C.R.; Lynfield, R.; Farley, M.M.; et al. Epidemiology of invasive group B streptococcal disease in the United States, 1999-2005. JAMA 2008, 299, 2056–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.A.; Thompson, T.A.; Facklam, R.R.; Slotved, H.C. Increased sensitivity of a latex agglutination method for serotyping group B streptococcus. J Clin Microbiol 2004, 42, 3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, K.J.; Bennett, S.L.; French, N.; Phiri, A.J.; Graham, S.M. Invasive group B streptococcal infection in infants, Malawi. Emerg Infect Dis 2007, 13, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhi, S.A.; Radebe, K.; Crewe-Brown, H.; et al. High burden of invasive Streptococcus agalactiae disease in South African infants. Ann Trop Paediatr 2003, 23, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyo, S.R.; Maeland, J.A.; Bergh, K. Typing of human isolates of Streptococcus agalactiae (group B streptococcus, GBS) strain from Zimbabwe. J Med Microbiol 2002, 51, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavenyengwa, R.T.; Maeland, J.A.; Moyo, S.R. Distinctive features of surface-anchored proteins of Streptococcus agalactiae strains from Zimbabwe revealed by PCR and dot blotting. Clin Vaccine Immunol 2008, 15, 1420–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavenyengwa, R.T.; Maeland, J.A.; Moyo, S.R. Serotype markers in a Streptococcus agalactiae strain collection from Zimbabwe. Indian J Med Microbiol 2010, 28, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, E.; Berg, S.; Trollfors, B.; et al. Serotypes and infections in western Sweden 1998–2001. Clin Microbiol clinical manifestations of invasive group B streptococcal Infect. 2004, 10, 791–796. [Google Scholar]

| Capsular type | Primer | Expected amplicon size | Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ia | IacpsHS1-R | 354 | 5’-GGC CTG CTGGGA TTA ATG AAT ATA GTT CCA GGT TTG C-3’ |
| Ia and III | CpsIA-F | - | 5’-GTA TAA CTT CTA TCA ATG GAT GAG TCT GTT GTAGTACGG-3’ |
| Ib | IbcpsIS-F | 523 | 5’-GAT AAT AGT GGA GAA ATT TGT GAT AAT TTA TCT CAA AAA GAC G-3’ |
| Ib | IbcpsIA1-R | - | 5’-CCT GAT TCA TTG CAG AAG TCT TTA CGA TGC GAT AGG TG-3’ |
| III | IIIcpsHS-F | 641 | 5’-GAA TAC TAT TGG TCT GTA TGT TGG TTT TAT TAG CAT CGC-3’ |
| II | cpsIIK-F | 526 | 5’-CCA ACG GCA ATA AAA TAC AT-3’ |
| II | cpsIIK-R | - | 5’-GCATTGAGATTAGAGTAGTC-3’ |
| IV | IVcpsHS1-F | 379 | 5’-CCC AAG TAT AGT TAT GAA TAT TAG TTG GAT GGT TTT TGG-3’ |
| IV | VcpsMA-R | - | 5’-GGG TCA ATT GTA TCGTCGCTG TCA ACA AAA CCA ATC AAA TC-3’ |
| V | VcpsHS2-F | 374 | 5’-CCC AGT GTG GTA ATG AAT ATT AGT TGG CTA GTT TTT GG-3’ |
| V | VcpsMA-R | - | 5’-CCC CCC ATA AGT ATA AATAATATC CAA TCT TGC ATA GTC AG-3’ |
| Surface protein gene | Primer | Expected amplicon size | Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Universal | Universal-F | - | 5’-TGA TAC TTC ACA GAC GAA ACA ACG-3’ |
| bca | Alpha-C-R | 398 | 5’-TAC ATG TGG TAG TCC ATC TTC ACC-3’ |
| rib | Rib-R | 295 | 5’-CAT ACT GAG CTT TTA AAT CAG GTG A-3’ |
| epsilon | Epsilon-R | 200 | 5’-CCA GAT ACA TTT TTTACT AAA GCG G-3’ |
| alp2/3 | Alp2/3-R | 334 | 5’-CAC TCG GAT TAC TAT AAT ATT TAG CAC-3’ |
| alp4 | Alp4-R | 110 | 5’-TTA ATT TGC ACC GGA TTA ACA CCA C-3’ |
| Serotypes | Latex, no. (%) | PCR, no. (%) | Total, no. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ia | 25 (25.0) | 8 (22.9) | 33 (25.8) |
| Ib | 7 (6.0) | 4 (11.4) | 11 (8.6) |
| II | 18 (18.0) | 2 (5.7) | 20 (15.6) |
| III | 26 (26.0) | 12 (34.3) | 38 (29.7) |
| V | 9 (9.0) | 5 (14.3) | 14 (10.9) |
| IV | 8 (8.0) | 3 (8.5) | 11 (8.6) |
| Nontypeable | 7 (7.0) | 1 (2.8) | |
| Total | 100 | 35 | 128 |
| Surface protein gene | Serotypes/number of surface protein genes possessed | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ia | Ib | II | III | IV | V | NT | Total | ||
| alp4 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 6 | |
| epsilon | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 10 | |
| alp2/3 | 2 | 2 | 8 | 2 | 1 | 8 | 0 | 23 | |
| bca | 19 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 31 | |
| rib | 0 | 2 | 6 | 36 | 8 | 5 | 0 | 57 | |
| Total | 32 | 10 | 18 | 38 | 13 | 16 | 1 | 128 | |
© GERMS 2015.
Share and Cite
O Chukwu, M.; Mavenyengwa, R.T.; Monyama, C.M.; Bolukaoto, J.Y.; Lebelo, S.L.; Maloba, M.R.; Nchabeleng, M.; Moyo, S.R. Antigenic Distribution of Streptococcus agalactiae Isolates from Pregnant Women at Garankuwa Hospital—South Africa. GERMS 2015, 5, 125-133. https://doi.org/10.11599/germs.2015.1080
O Chukwu M, Mavenyengwa RT, Monyama CM, Bolukaoto JY, Lebelo SL, Maloba MR, Nchabeleng M, Moyo SR. Antigenic Distribution of Streptococcus agalactiae Isolates from Pregnant Women at Garankuwa Hospital—South Africa. GERMS. 2015; 5(4):125-133. https://doi.org/10.11599/germs.2015.1080
Chicago/Turabian StyleO Chukwu, Martina, Rooyen Tinago Mavenyengwa, Charles M Monyama, John Y Bolukaoto, Sogolo L Lebelo, Motlatji RB Maloba, Maphoshane Nchabeleng, and Sylvester Rogers Moyo. 2015. "Antigenic Distribution of Streptococcus agalactiae Isolates from Pregnant Women at Garankuwa Hospital—South Africa" GERMS 5, no. 4: 125-133. https://doi.org/10.11599/germs.2015.1080
APA StyleO Chukwu, M., Mavenyengwa, R. T., Monyama, C. M., Bolukaoto, J. Y., Lebelo, S. L., Maloba, M. R., Nchabeleng, M., & Moyo, S. R. (2015). Antigenic Distribution of Streptococcus agalactiae Isolates from Pregnant Women at Garankuwa Hospital—South Africa. GERMS, 5(4), 125-133. https://doi.org/10.11599/germs.2015.1080




