Abstract
Genitourinary tuberculosis (TB) is infrequently reported in the United States, but is a common form of extrapulmonary TB that often goes unnoticed due to its insidious and sometimes asymptomatic presentation. Prostate involvement and the development of tuberculous prostatic abscesses have been reported in the literature largely in association with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). We report a case of disseminated TB involving tuberculous prostatic abscesses in a patient without HIV/AIDS, presenting with sepsis and urinary symptoms. This patient had simultaneous prostatic, peritoneal, pulmonary, and likely renal TB, serving as a reminder to clinicians that multi-organ presentations of TB do occur in patients without overt immunosuppressive conditions. This case also highlights the importance of considering the diagnosis of genitourinary TB in patients with risk factors for TB presenting with vague, long-standing urinary symptoms.
Introduction
A significant resurgence of tuberculosis (TB) has taken place in recent years due to the AIDS epidemic, the emergence of drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) bacilli, population migration patterns, and worldwide poverty levels [1]. Genitourinary TB is a significant, yet uncommon, form of TB that develops in 2- 20% of patients with pulmonary TB [1,2]. It is responsible for approximately 30-40% of all cases of extrapulmonary TB worldwide [1,2]. In the United States, genitourinary TB accounted for 5% of all cases of extrapulmonary TB in 2011 [3].
Tuberculosis of the prostate is a rare form of genitourinary TB that is most often diagnosed incidentally following transurethral resections, prostatectomies, or during post-mortem examinations [1,4,5]. Prostatic TB often presents as diffuse caseous necrosis with calcifications and the development of fibrosis with gland hardening; however, it is usually asymptomatic [1,6]. Tuberculous abscesses of the prostate are infrequent, and generally found only in immunocompromised patients [1,2,7]. We report a case of tuberculosis of the prostate in an immunocompetent patient presenting with sepsis and multiple tuberculous prostatic abscesses.
Case History
A 43-year-old man who was born in Peru presented with 2 weeks of progressively worsening abdominal pain and distention. He also noted fever, dysuria, dyschezia, and weight loss.
Two years prior, he had presented to our institution with two weeks of fever, fatigue, night sweats, and scant cough. His chest radiograph had revealed a right lower lobe consolidation. He had 3 negative sputum smears for acid-fact bacilli (AFB), and sputum cultures were negative for MTB. A tuberculin skin test was not performed. He was treated for community-acquired pneumonia with cefpodoxime and azithromycin. His symptoms resolved completely until 1.5 years later, when he presented to the emergency room with fever, abdominal pain, dysuria, and dyschezia, accompanied by a tender prostate on physical exam. He was diagnosed with prostatitis and treated with an empiric 4-week course of ciprofloxacin, with minimal improvement in symptoms. He presented to the emergency room 6 months later with similar symptoms and again was given a 4-week course of ciprofloxacin, which he had completed 2 weeks prior to his current presentation. He reported some improvement in symptoms while taking ciprofloxacin but noted rapid recurrence of dysuria and new-onset abdominal distention in the 2 weeks after completing his course of antibiotics.
He denied any past medical or surgical history. He was not taking any medications and had no known drug allergies. He had moved to the United States from Peru 3 years prior to his presentation, having previously lived in California before moving to New York. He worked various odd jobs. He was heterosexual, denied any sexually transmitted infections, and had not been sexually active for 8 months. He denied any significant risk factors for HIV infection, including injection drug use. He had an unknown neonatal BCG vaccination history. Ten years prior to the current presentation, he had been a close contact to his brother who had been diagnosed at the time with active pulmonary TB.
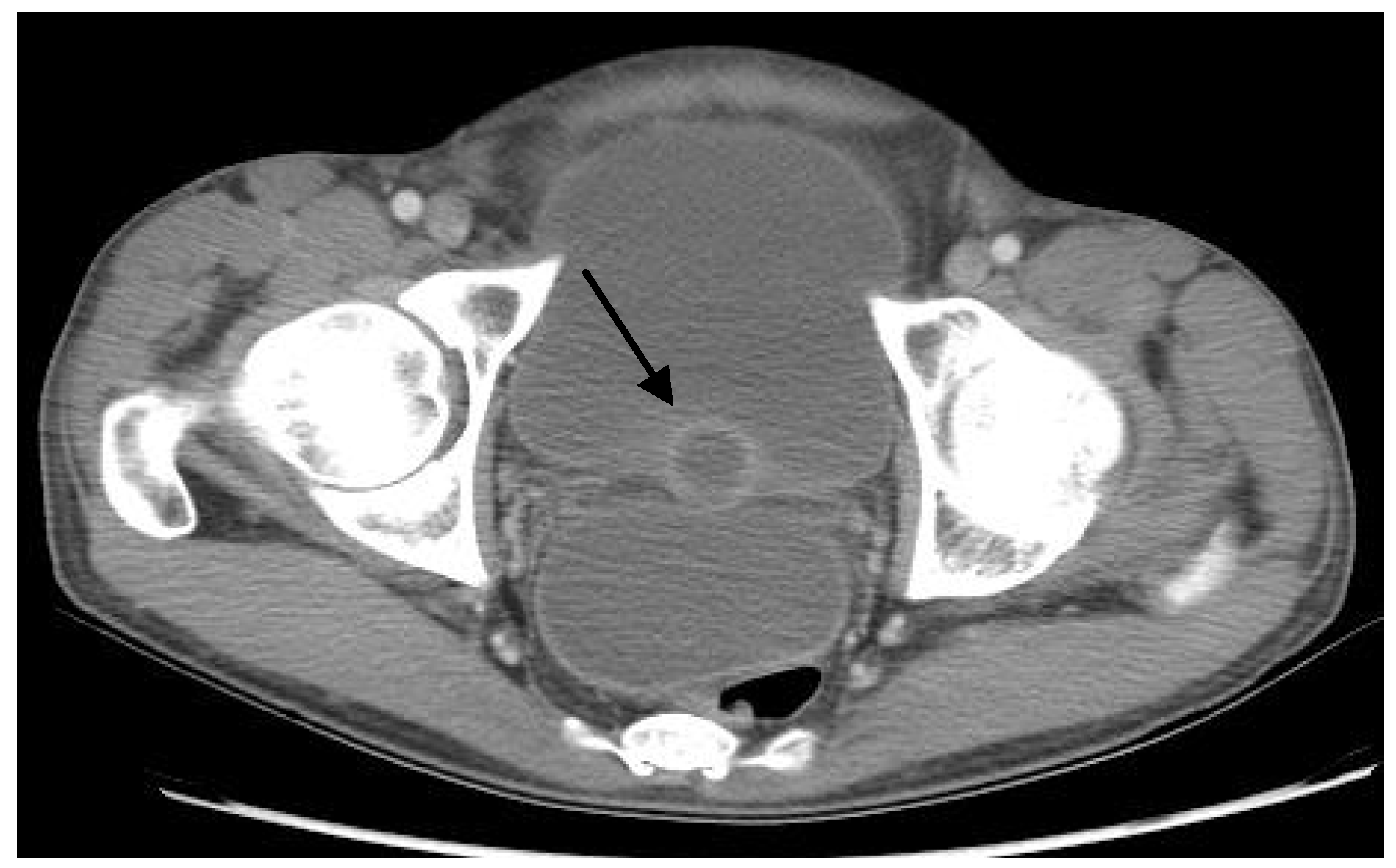
Physical exam was notable for a temperature of 100.9°F (38.3°C) and blood pressure of 80/54 mmHg. His abdomen was firm, tender, and distended. He refused a digital rectal exam. He was HIV negative on the rapid HIV immunoassay. Urinalysis was notable for pyuria; urine bacterial culture demonstrated no growth, and urine AFB smears were negative. His chest radiograph was unremarkable. Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis with intravenous and oral contrast revealed large- volume ascites, diffuse peritonitis, multiple prostatic abscesses (largest 3.5 cm) (Figure 1), and possible focal pyelonephritis in the left kidney.
Figure 1.
Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis with intravenous and oral contrast demonstrating prostatic abscess (arrow).
He underwent a diagnostic paracentesis that was negative for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and consistent with a lymphocytic exudative process (white blood cell count 60 cmm with 62% lymphocytes, ascites fluid albumin 2.8 g/dL, serum albumin 3.7 g/dL, serum-ascites albumin gradient of 0.9). Ascites fluid Gram stain and AFB smears were negative, but the adenosine deaminase level was elevated at 29 U/L (reference range <9.2 U/L). He also had intra- abdominal hypertension, based on an intra- abdominal pressure ≥12 mmHg as measured with a manometer. He had a tuberculin skin test with purified protein derivative (PPD) that was negative, but his QuantiFERON®-TB Gold (QFT- G, Cellestis Limited, Carnegie, Victoria, Australia) test was positive. He was initially treated for sepsis with intravenous fluids and broad-spectrum antibiotics, and urology consultation was obtained for sampling of the prostatic abscesses.
The patient underwent a non-contrast chest CT the following day, which was notable for small-moderate bilateral pleural effusions, left lower lobe collapse due to atelectasis, and numerous ill-defined “tree-in-bud” nodular opacities in the right upper and middle lobes. Sputum induction for AFB smears was performed, and 3 of 3 specimens were smear- negative for AFB.
On hospital day 5, while awaiting prostatic abscess sampling, the patient developed oliguria and acute kidney injury (AKI) with a creatinine level that peaked at 9.8 mg/dL on hospital day 11. His AKI was attributed to a combination of possible factors including a post-renal uropathy from the obstructing prostate abscesses or tuberculous bladder involvement, intra- abdominal hypertension from tense ascites, contrast nephropathy from the CT examination, or acute interstitial nephritis from the administration of piperacillin-tazobactam. His urine output improved after Foley urinary catheter placement and a therapeutic paracentesis, but his renal function did not return to baseline until hospital day 30.
Cystoscopy with transurethral aspiration of a prostate abscess was performed on hospital day 14. Bladder and prostate biopsies were also obtained. Gram stains and AFB smears from the abscess fluid were negative, but mycobacterial cultures grew MTB 2 weeks later. Subsequent to the prostate biopsy, 3 of 5 urine cultures, 1 of 3 sputum cultures, and the ascitic fluid culture returned as positive for pan-sensitive MTB. The bladder biopsy showed focal acute inflammation without granulomas or AFB. The prostate tissue biopsy showed granulomatous inflammation and focal necrosis; no AFB were seen and caseous necrosis was not noted.
The patient was started on a 4-drug regimen of isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol. His TB treatment was complicated by severe transaminitis (aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase >7 times the upper limit of normal) requiring discontinuation of pyrazinamide. He completed 9 months of directly observed therapy with rifampin, isoniazid, and ethambutol without further complication, and has remained clinically well in the 4 years since treatment.
Discussion
Genitourinary TB is thought to be caused by the hematogenous spread of MTB during the initial pulmonary infection; the primary organ infected is typically the kidney, and the infection is spread to adjacent organs by direct extension [4]. Prostatic TB, in particular, can result from hematogenous seeding of the prostate at the time of initial TB infection, or from urinary seeding after renal involvement [4]. A long latency period exists of approximately 22 years between initial pulmonary infection and the potential development of genitourinary TB [1,2]. Autopsy studies have revealed that 25% of genitourinary TB cases do not have any urinary symptoms [8]. Due to its insidious and often asymptomatic progression, genitourinary TB is associated with a high rate of delay in diagnosis and treatment [2].
This patient had a multi-organ presentation of TB involving the lungs, peritoneum, and genitourinary system. Tuberculous prostate abscesses are unusual, especially in immunocompetent individuals. He likely developed genitourinary TB after exposure to his brother who was treated for pulmonary TB over 10 years ago. Given the characteristically slow progression of genitourinary TB, it is even possible that he may have had an earlier TB exposure.
The patient was an immigrant from Peru and a close contact to a TB case. He had chronic constitutional symptoms including fever and weight loss. Sterile pyuria, the classic urinary finding for genitourinary TB, was present. However there was no microhematuria, which is present in up to 50% of patients with genitourinary TB [4]. He presented with severe sepsis with peritonitis, ascites, multiple prostatic abscesses, possible focal pyelonephritis, and tree- in-bud opacities in the lungs. Our suspicion for TB was high, and we had several diagnostic testing and management options.
Urine mycobacterial cultures are the gold standard for diagnosing genitourinary TB because of the poor sensitivity of urine AFB smears [4]. Ideally, 3-6 first morning midstream urine specimens should be sent for MTB culture to maximize yield. Because bacilli are shed into the urine intermittently, only 30-40% of single urine specimens are positive in patients with active genitourinary TB. Furthermore, broad-spectrum antibiotic use may inhibit the growth of mycobacteria from urine, which would lead to false-negative results [4,9]. But even with sensitivities of 80-90% for the diagnosis of genitourinary TB, serial urine MTB cultures may take up to 8 weeks to grow [4]. Thus, in some cases where the diagnosis is uncertain, tissue or fluid sampling from multiple sites may be necessary when extrapulmonary TB is suspected [10].
The patient had received 2 separate courses of ciprofloxacin therapy in the 6 months before presenting to our institution. Fluoroquinolones have been shown to delay and confound the diagnosis of TB due to their antimicrobial activity against MTB. Among TB patients who were empirically treated with fluoroquinolones for presumed bacterial pneumonia prior to their hospitalization, the median time until initiation of appropriate anti-tuberculosis therapy was 21 days; among those not treated, the median time was 5 days [11]. Fluoroquinolone exposure prior to TB diagnosis has been associated with fluoroquinolone-resistant TB as well as an increased risk of death [12,13]. As always, fluoroquinolones should be used cautiously in anyone suspected of TB [13].
In our case, while AFB culture results from sputum, urine, and ascitic fluid were pending, the patient was deteriorating. Prompt treatment was a priority. Because the patient was from Peru where rates of drug-resistant TB are high, concern existed regarding initiation of empiric TB therapy without specimens for drug susceptibility testing, especially in the setting of prior fluoroquinolone exposure. Thus, tissue sampling was undertaken to confirm the diagnosis pathologically and obtain microbiology specimens for susceptibility testing [14]. Our options included prostate biopsy or abscess aspiration, laparoscopic peritoneal biopsy, or bronchoscopic lymph node or parenchymal lung tissue biopsy. After much discussion among the consultation teams, cystoscopy with transurethral aspiration of one of the prostate abscesses was deemed the safest means to obtain tissue. He tolerated the procedure well, and the diagnosis of TB was confirmed with abscess fluid culture.
An alternative approach, especially given the high suspicion for extrapulmonary TB and the patient’s septic presentation, would have been to initiate empiric TB therapy after several morning urine specimens as well as sputum and ascites fluid specimens were sent for MTB culture. With sensitivities of 80-90% for serial urine specimens, there was a high likelihood of cultures returning as positive even with a potentially reduced yield due to prior fluoroquinolone use. In this case, urine, sputum, and ascites fluid were ultimately positive for MTB. Given that the first positive culture returned only 4 days after the prostate biopsy was performed, an early empiric treatment approach would have obviated the need for biopsy without a significant delay in definitive diagnosis and drug susceptibility results.
In addition, nucleic acid amplification (NAA) testing can provide same-day results and confirm the diagnosis of TB while culture results are pending [15]. NAA testing is often reserved for respiratory tract specimens but has been shown to be effective in diagnosing extrapulmonary TB as well; sensitivity and specificity vary by type of specimen tested [15]. CDC recommends NAA testing on at least 1 respiratory specimen when TB is suspected but not yet established [16]. If NAA testing, particularly of sputum, had been performed in our patient, it could have prompted earlier TB diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion
This report describes a multi-organ presentation of pulmonary, peritoneal, and genitourinary TB involving multiple tuberculous prostatic abscesses in an immunocompetent patient. Genitourinary TB should always be considered in patients with risk factors for TB who present with vague, long-standing urinary symptoms [4]. Diagnostic persistence, along with a high index of suspicion, is essential in identifying genitourinary and other types of extrapulmonary TB.
Author Contributions
MJ: patient care, idea, writing; MM: patient care, idea, review; CC: review.
Acknowledgments
The authors are solely responsible for the work with no additional contributors or funders. This case was presented at our institution as part of our clinical resident report series.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors – none to declare.
References
- Figueiredo, A.A.; Lucon, A.M. Urogenital tuberculosis: update and review of 8961 cases from the world literature. Rev Urol. 2008, 10, 207–17. [Google Scholar]
- Figueiredo, A.A.; Lucon, A.M.; Junior, R.F.; Srougi, M. Epidemiology of urogenital tuberculosis worldwide. Int J Urol. 2008, 15, 827–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Reported Tuberculosis in the United States, 2011. Atlanta, GA: US. Department of Health and Human Services, CDC, October 2012. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/tb/statistics/reports/2011/pdf/re port2011.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2012).
- McAleer, S.J.; Johnson, C.W.; Johnson, W.D. Tuberculosis and parasitic and fungal infections of the genitourinary system. In Campbell-Walsh Urology, 9th ed.; Wein, A.J., Kavoussi, L.R., Novick, A.C., et al., Eds.; Campbells’ Urology: WB Saunders, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 436–70. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, N.; Mandal, A.K.; Singh, S.K. Tuberculosis of the prostate and urethra: A review. Indian J Urol. 2008, 24, 388–91. [Google Scholar]
- Matos, M.J.; Bacelar, M.T.; Pinto, P.; Ramos, I. Genitourinary tuberculosis. Eur J Radiol. 2005, 55, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, L.E. Tuberculous abscess of the prostate in AIDS. Ann Intern Med. 1996, 125, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medlar, E.M.; Spain, D.M.; Holliday, R.W. Post-mortem compared with clinical diagnosis of genitourinary tuberculosis in adult males. J Urol. 1949, 61, 1078–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Thoracic Society and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Diagnostic Standards and Classification of Tuberculosis in Adults and Children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000, 161, 1376–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Langston, A.A.; Gallis, H.A. Miliary tuberculosis: epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and outcome. Rev Infect Dis. 1990, 12, 583–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dooley, K.E.; Golub, J.; Goes, F.S.; Merz, W.G.; Sterling, T.R. Empiric treatment of community-acquired pneumonia with fluoroquinolones, and delays in the treatment of tuberculosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2002, 34, 1607–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devasia, R.A.; Blackman, A.; Gebretsadik, T.; et al. Fluoroquinolone resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: the effect of duration and timing of fluoroquinolone exposure. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009, 180, 365–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Heijden, Y.F.; Maruri, F.; Blackman, A.; et al. Fluoroquinolone exposure prior to tuberculosis diagnosis is associated with an increased risk of death. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2012, 16, 1162–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, R.; Jain, P.; Sud, R.; et al. EUS-guided drainage of an isolated primary tubercular prostatic abscess. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010, 71, 425–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laraque, F.; Griggs, A.; Slopen, M.; Munsiff, S.S. Performance of nucleic adic amplification tests for diagnosis of tuberculosis in a large urban setting. Clin Infect Dis. 2009, 49, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated guidelines for the use of nucleic acid amplification tests in the diagnosis of tuberculosis. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009, 58, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
© GERMS 2014.