Abstract
Introduction: Pseudomonas aeruginosa produces many exotoxins which are essential for the bacterial pathogenesis. The aim of this study was to identify Pseudomonas aeruginosa from clinical specimens, detect the sensitivity pattern, biofilm production, and the frequency of exogenes. Methods: Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates were identified by conventional and genotypic methods. Antibiotic susceptibility patterns and biofilm production were performed. Molecular detection of exotoxin genes exoS, exoT, exoU, and exoY in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates was performed by PCR. Results: Seventy-five Pseudomonas aeruginosa were identified in 400 clinical specimens. Sixty-six (88%) isolates were carbapenem-resistant. A total of 25 (33.3%) isolates were extensively drug resistant, 18 (24%) were multidrug resistant, and 11 (14.7%) were pandrug resistant. Sixty-three (84%) isolates were biofilm producers. Biofilm formation was detected in 56 (85%) of carbapenem-resistant isolates. Totally, 70 (93.3%) isolates carried exoS, 68 (90.7%) carried exoY, 65 (86.7%) carried exoT, and 28 (37.3%) carried exoU. Exogenes were highly expressed in carbapenem-resistant isolates. Coexistence of more than one gene was detected in nearly all isolates. Conclusions: Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates were resistant to many anti-pseudomonal antibiotics. Most of isolates were biofilm-producers. The genes exoT, exoS and exoY were identified in almost all P. aeruginosa strains and are considered an inevitable component of P. aeruginosa virulence.
Introduction
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, is Gram-negative bacteria of the Pseudomonadaceae bacterial family. It is a ubiquitous organism in hospital settings and the environment. The bacterium has the ability to cause severe morbidities especially in immunocompromised patients [1]. Multidrug-resistant (MDR) P. aeruginosa can develop from the natural resistance to numerous antibiotics and the additional resistance that developed during treatment. Drug resistance of Pseudomonas may be innate in nature. The bacterium is a biofilm-producer, which is an essential for bacterial virulence and antibiotic resistance [2]. Combined resistance to antibiotics may develop due to the simultaneous existence of many mechanisms. One of the most pathogenic factors is exotoxin production including ExoS, ExoT, ExoU, and ExoY [1]. ExoU is a phospholipase, ExoY is an adenylate cyclase; and ExoS and ExoT are bi-functional proteins. Almost all strains code for ExoY and ExoT, which highlights the inevitability of these toxins as virulent agents [3]. ExoS and ExoU also play major role in pathogenesis [1].
We aimed in this study to isolate and identify P. aeruginosa from different clinical specimens, detect the sensitivity pattern, biofilm production, and the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) for carbapenems, and the frequency of the exogenes (exoS, exoT, exoU, and exoY) in P. aeruginosa clinical isolates.
Methods
Study design, study participants, and ethical approval
This was a cross-sectional study that was conducted from May 2022 to February 2023 and included 400 patients attending different units at Assiut University Hospitals.tble Patients were included when they showed manifestations of bacterial infection including fever, purulent discharge, and high white blood cell count over 10,000/mL [3]. Patients were excluded when they were under antibiotic therapy or diagnosed to have viral or fungal infections. All patients received a written clear consent form explaining the aim of the study, and their freedom to participate or withdraw at any time without obligation. Patients were assigned with code numbers to ensure confidentiality. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the Faculty of Medicine, Assiut University (IRB no: 17101935). Patients’ data, clinical evaluation, and laboratory data were collected according to a pre-designed questionnaire.
Sample size calculation and clinical specimens
Sample size was calculated using the G power program based on the proportion of resistant and sensitive strains of Pseudomonas to carbapenems. The total Pseudomonas isolates to be taken was calculated to be 60 at a power of 80% and error of 0.05. Different clinical specimens were obtained from patients including pus, sputum, urine, and blood.
Bacterial isolation and identification
Clinical specimens were examined for motility, stained with Gram stain, and cultured on nutrient, blood, MacConkey’s (HiMedia, India), Triple sugar iron (TSI), and Cetrimide agars (Sigma-Aldrich, USA). Colonies were identified as P. aeruginosa by conventional methods and the ability to grow at 42ºC. Isolates were subjected for biochemical reactions including oxidase, catalase, and citrate tests.
Molecular identification of P. aeruginosa isolates by PCR
Extraction of DNA was done as mentioned previously [1]. To amplify the 16S rRNA of P. aeruginosa isolates conventional PCR was performed using the following species specific primers: F 5′-GGGGGATCTTCGGACCTCA-3′ and R 5′-TCCTTAGAGTGCCCACCCG-3′) as recommended [4]. The reaction was performed in 20 μL volume (10 µL master mix, 1.25 µL (10 mM) F primer, 1.25 µL R primer (10 mM), 1 µL template DNA, and 6.5 µL molecular grade H2O. PCR was performed in the thermocycler (Biometra, Germany) as follows: denaturation at 95°C for 2 min, 25 cycles each consisting of denaturation at 94°C for 30 sec, annealing at 58°C for 30 sec and extension at 72°C for 50 sec, and final extension at 72°C for 5 min. Agarose gel electrophoresisand UV transilluminator of 366 nm wavelength were used to detect the amplicon of DNA at a size of 956 bp. The reference P. aeruginosa strain ATCC 27853 was used as positive control.
Antibiotic sensitivity tests
In vitro susceptibility of P. aeruginosa isolates to different antibiotics was preformed according to modified Kirby-Bauer disk method. The used antibiotic discs were ceftazidime (30 μg), aztreonam (30 μg), cefepime (30 μg), meropenem (10 μg), ceftriaxone (30 μg), ciprofloxacin (5 μg), imipenem (10 μg), levofloxacin (5 μg), gentamicin (10 μg), ofloxacin (5 μg), amikacin (30 μg), and piperacillin/tazobactam (TZP) (100/10 μg). The results of the disc diffusion method were reported as susceptible, intermediate, or resistant. The broth microdilution method was used for determination of MIC of meropenem to detect carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa isolates. Interpretation was performed in accordance to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). The reference P. aeruginosa strain ATCC 27853 was used as positive control.
Biofilm assay
The biofilm quantification assay of P. aeruginosa isolates was performed using the microtiter plate technique as recommended [1]. Each sample was done in triplicate and the average of optical density was considered. Absorbance reading was taken in an ELISA reader (BioRad, model 550, USA) at wave length of 570 nm.
Molecular detection of exotoxin genes in P. aeruginosa isolates by conventional PCR
The template DNA was prepared by the boiling method as reported [5]. P. aeruginosa isolates were tested for exotoxin genes using the conventional PCR. The forward and reverse oligonucleotide primer sequences used for detection of these genes, their annealing temperature, and the amplified product sizes were as follows, respectively: exoS: F 5′-ATCCTCAGGCGTACATCC-3′, R 5′-CGACGGCTATCTCTCCAC-3′, 48°C, 328 bp, exoT: F 5′-ATCATCTCAGCAGAACC-3′, R 5′-GTCGTAGAGGATCTCCTG-3′, 48°C, 1158 bp, exoY: F 5′-CGGATTCTATGGCAGGGAGG-3′, R 5′-GCCCTTGATGCACTCGACCA-3′, 52°C, 289 bp [6], and exoU: F 5′-ATGCATATCCAATCGTTG-3′, R 5′-TCATGTGAACTCCTTATT-3′, 45°C, 2000 bp [7]. The reaction was performed in a volume of 25 μL. The master mix consisted of 4.2 µL, 0.5 µL F Primer (10 mM), 0.5 µL R Primer (10 mM), 5 µL template DNA, and 14.8 µL molecular grade H2O in the thermocycler (Biometra, Germany). Amplification was as follows: denaturation at 97°C for 3 min, 35 amplification cycles (30 cycles for exoT and exoU) as following: denaturation at 94°C for 45 sec, annealing at suitable temperature for each gene for 45 sec and extension at 72°C for 30 sec and final extension step at 72°C for 10 min. Agarose gel electrophoresis and UV transilluminator of 366 nm wavelength were used to detect the amplicon.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed by the SPSS 22.0 program. Data were statistically described as frequencies (number of cases), and relative frequencies (percentages). Chi-square and Fisher’s Exact tests were used to test differences between categorical data. Significance was considered for p-value ≤0.05.
Results
Patient characteristics, clinical specimens, and isolation of P. aeruginosa
A total of 75 (18.8%) P. aeruginosa isolates were detected in 400 nonrepetitive clinical specimens confirmed by the conventional and genotypic methods (Figure 1) that were obtained from patients attending different departments at Assiut University Hospitals including in a decreasing order: 14 (18.7%) from Intensive Care units (ICUs), 11 (14.7%) from Chest department, 10 (13.3%) from Internal Medicine department, 10 (13.3%) from the Burn unit, 7 (9.3%) from the Orthopedic septic unit, 6 (8%) from the Nephrology unit, 5 (6.7%) from the Urology department, 4 (5.3%) from the Plastic surgery department, 4 (5.3%) from the General Surgery department, 2 (2.7%) from the Rheumatology and Rehabilitation department, and 2 (2.7%) from the Diabetic Foot outpatient clinic.
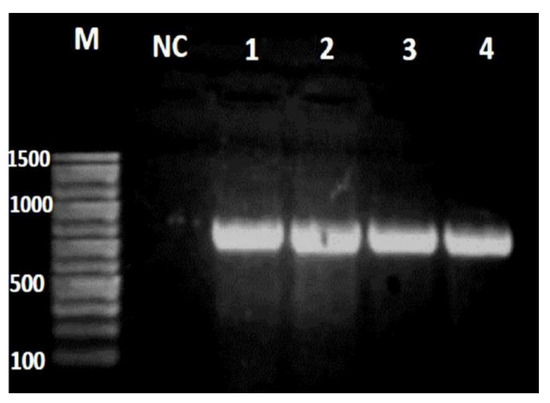
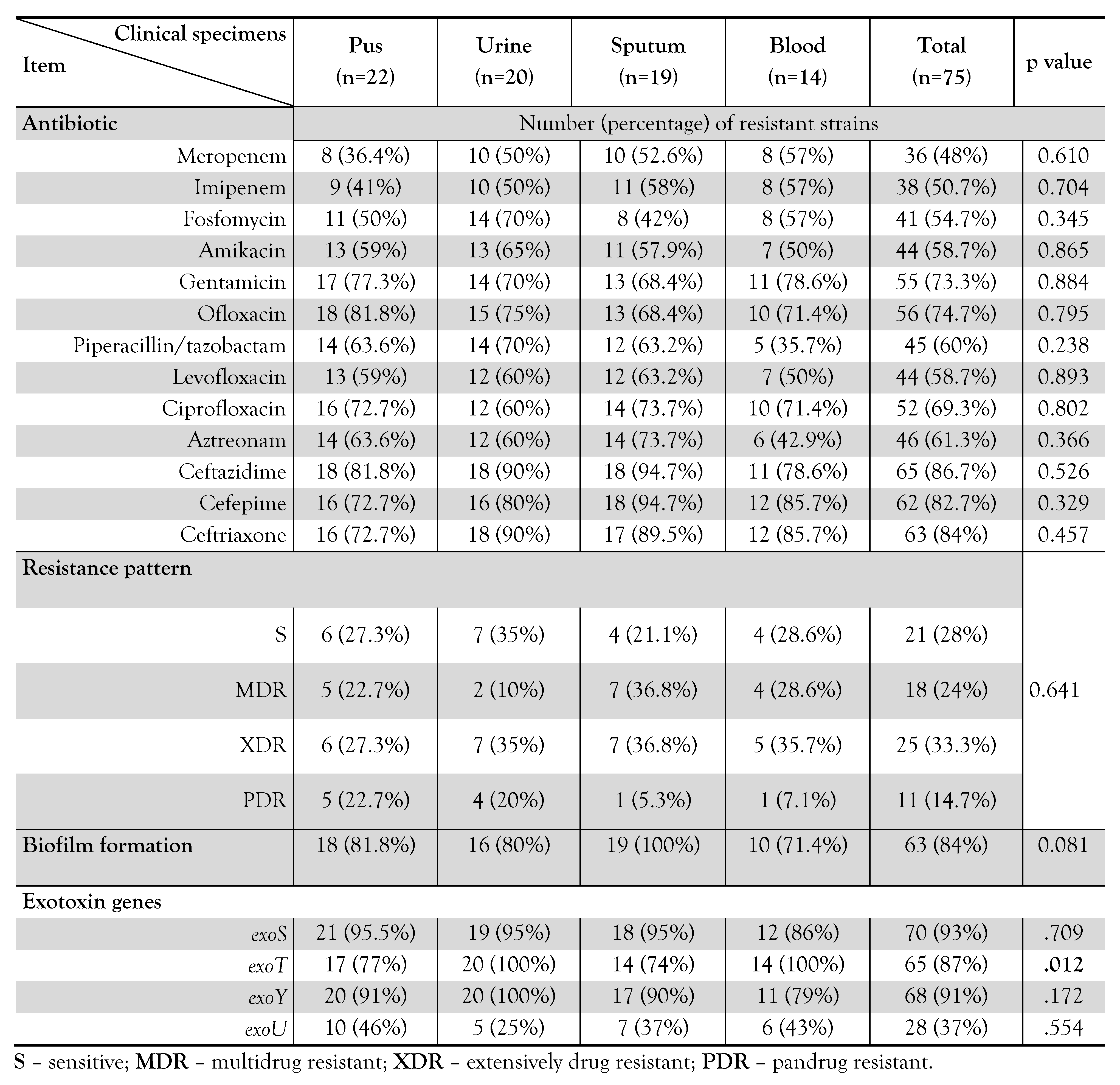
Figure 1.
Gel electrophoresis of species specific 16S rRNA gene. M: 100-1500bp DNA ladder, NC: negative control (distilled water), and lanes 1-4 are amplified DNA products of P. aeruginosa isolates at 956 bp.
Patients were 203 (50.8%) males and 197 (49.2%) females and were 18-78 years old. Clinical specimens were 127 pus and wound swabs, 120 urine, 111 sputum, and 42 blood specimens. P. aeruginosa was detected in 22 (17.3%) pus specimens, 20 (16.7%) urine specimens, 19 (17.0%) sputum specimens, and 14 (33.3%) blood specimens. A total of 66 (88%) of the confirmed P. aeruginosa isolates were carbapenem-resistant, and were detected in 20 (15.7%) pus specimens, 17 (14.2%) urine specimens, 18 (16.2%) sputum specimens, and 11 (26.2%) blood specimens.
Antibiotic sensitivity tests and biofilm formation
In vitro susceptibility of P. aeruginosa isolates showed the highest resistance rate to ceftazidime, ceftriaxone, and cefepime antibiotics (86.7%, 84.0% and 82.7%, respectively) while the lowest resistance was to meropenem and imipenem (48.0% and 50.7%, respectively). Biofilm quantification assay showed that 63 (84.0%) P. aeruginosa isolates were biofilm-producers (weakly adherent +) and the remaining 12 (16.0%) isolates were non producers. Higher resistance rates were detected among biofilm-producers compared to non-producer strains. By Fisher’s Exact test, such differences reached significant level only for aztreonam (Chi-square, p=0.024) – Figure 2. MIC of meropenem revealed that 66 (88.0%) P. aeruginosa isolates were resistant to meropenem. Fifty-six (85%) carbapenem-resistant strains were biofilm-producers (weakly adherent) in contrast to 10 (15%) strains which were non-producers with a statically significant difference between both groups regarding biofilm formation [Fisher’s Exact test, p=0.043; odds ratio 5.07, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.14-22.5] where most of carbapenem-resistant isolates were biofilm-producers, while non-producers were mostly carbapenem-sensitive isolates. Table 1 shows the antibiotic resistance patterns of P. aeruginosa in different clinical specimens. Isolates from sputum specimens showed the highest resistance rates to levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, cephalosporins, and aztreonam. Most of the P. aeruginosa isolates had difficult-to-treat resistance (DTR) being resistant to many anti-pseudomonal antibiotics including piperacillin/tazobactam, ceftazidime, cefepime, aztreonam, ciprofloxacin, and levofloxacin.
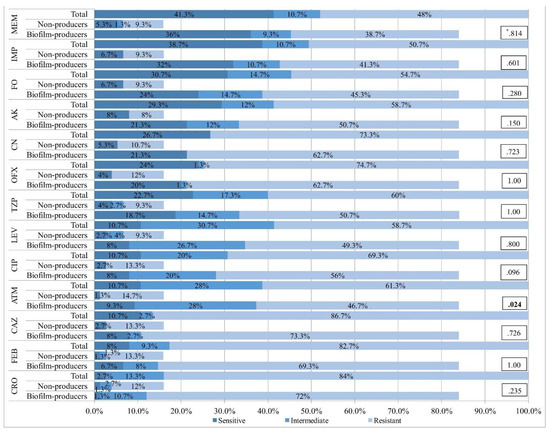
Figure 2.
In vitro susceptibility pattern of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates, biofilm-producer and non-producer strains to various antibiotics. MEM – meropenem; IMP – imipenem; FO – fosfomycin; AK – amikacin; CN – gentamicin; OFX – ofloxacin; TZP – piperacillin/tazobactam; LEV – levofloxacin; CIP – ciprofloxacin; ATM – aztreonam; CAZ – ceftazidime; FEP – cefepime; CRO – ceftriaxone. *p values were calculated by Fisher's Exact test and represent difference in resistance rate between biofilm-producer and non-producer strains.

Table 1.
Resistance patterns, biofilm formation, and exotoxin genes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical.
Isolates from urine, pus, and blood were highly resistant to cephalosporins, ofloxacin, and gentamicin. Isolates from all clinical specimens showed relatively lower resistance rates to the carbapenem group. Twenty-five (33.3%) isolates were XDR, 18 (24.0%) isolates were MDR, and 11 (14.7%) isolates were pandrug resistant (PDR). MDR and XDR isolates were detected in 50.0%, 45.0%, 73.6%, and 64.3% of pus, urine, sputum, and blood specimens, respectively. PDR were found in considerable numbers of pus and urine specimens. Difference in resistance patterns among clinical samples did not reach significant levels (Chi-square test, p=0.641) – Table 1.
Biofilm production in various clinical specimens is shown in Table 1. All sputum isolates were biofilm-producers. Most pus, urine, and blood isolates were biofilm-producers. No significant differences were detected among clinical isolates regarding biofilm production (Fisher's Exact test, p=0.081). Twenty-three (92%) XDR strains were biofilm-producers, 15 (83.3%) MDR strains were biofilm-producers, 6 (54.5%) PDR strains were biofilm-producers with statistically significant differences in resistance patterns according to biofilm production (Chi-square test, p=0.027). No significant differences were found in carbapenem resistance or biofilm production in relation to the site of admission (Chi-square test, p=0.782 and p=0.094, respectively).
Molecular detection of exotoxin genes in P. aeruginosa clinical isolates
Detected exogenes are shown in Figure 3 (A-D). The genes exoS, exoY, and exoT were detected in most P. aeruginosa isolates where 70 (93.3%) isolates carried exoS, 68 (90.7%) isolates carried exoY, and 65 (86.7%) isolates carried exoT while 28 (37.3%) isolates carried exoU. Carbapenem-resistant isolates were 62 (94%) isolates carried exoS, 60 (91%) isolates carried exoY, 57 (86%) isolates carried exoT, and 26 (39%) isolates carried exoU. No significant differences were found between carbapenem-sensitive and resistant strains regarding the expression of exogenes (p>0.05 by Chi-square test). Table 1 shows the frequency of genes in various clinical specimens. The exoT gene was found in all urine and blood isolates with significant differences compared to pus and sputum isolates (Fisher’s Exact test, p=0.012). The gene exoY was found in all urine isolates. The frequency of exoS, exoT, and exoY among other clinical specimens was relatively high. The frequency of exoU was relatively higher among pus and blood isolates than urine and sputum isolates. The frequency distribution of exoS, exoY, and exoU genes did not reach significant differences among various clinical isolates (p>0.05 by Chi-square test). Figure 4A shows the frequency distribution of exogenes among carbapenem-sensitive and resistant isolates. Coexistence of more than one exotoxin gene was detected in 73 (97%) P. aeruginosa isolates. Most frequently, exoS, exoT, and exoY genes coexisted in 38 (51%) isolates. Coexistence of the four exogenes was found in 19 (25.3%) isolates. Frequency distribution of exogenes did not show significant differences between carbapenem-sensitive and resistant isolates (Chi-square test; p=0.158). Coexistence of exoS, exoT, and exoY genes was detected in 33 (52.4%) biofilm-producers. Coexistence of the four exogenes was detected in 16 (25.4%) biofilm-producers. Five (8%) biofilm-producers expressed exoS and exoY genes. Two (3.2%) biofilm-producers carried exoS, exoY, and exoU genes (Figure 4B). No significant differences were found between biofilm producers and non-producers regarding coexisting genes (Chi-square test, p>0.05).
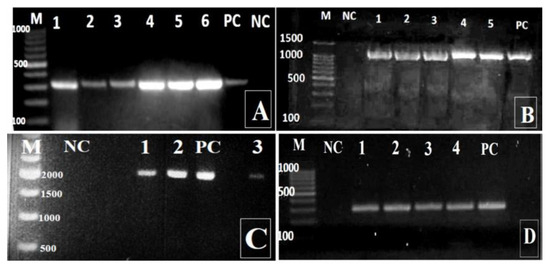
Figure 3.
Amplified PCR products of P. aeruginosa by agarose electrophoresis. A: exoS (amplicon size is 328 bp; lanes 1-6); B: exoT (amplicon size is 1158 bp; lanes 1-5); C: exoU (amplicon size is 2000 bp; lanes 1-3); D: exoY (amplicon size is 289 bp; lanes 1-4). M - DNA ladder; PC - positive control (reference P. aeruginosa strain ATCC 27853); NC - negative control (distilled water).
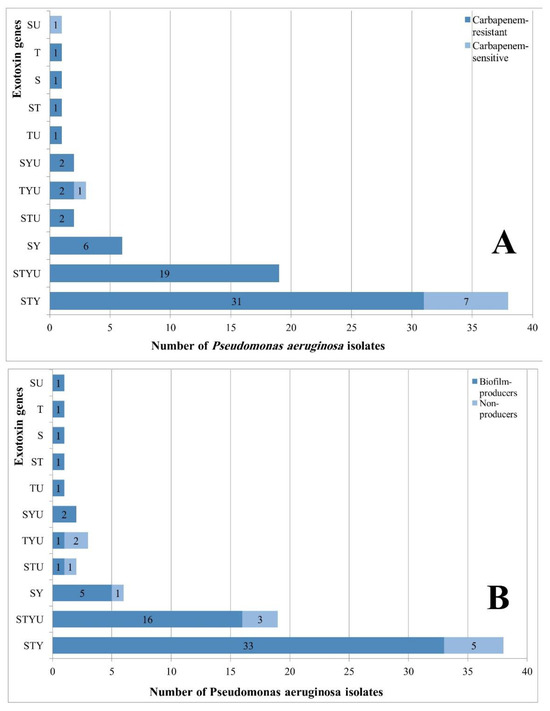
Figure 4.
A. Coexistence of exotoxin genes in carbapenem-sensitive and carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates; B. Coexistence of exotoxin genes in biofilm-producing and non-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates. S – exoS; T – exoT; U – exoU; Y – exoY; p-values did not show significant differences between carbapenem-sensitive or resistant isolates or regarding biofilm production in gene expression.
Discussion
This study was a hospital based cross sectional study that aimed to isolate and identify P. aeruginosa from different clinical samples, to detect the sensitivity pattern of P. aeruginosa to different types of antibiotics using disc diffusion method, to determine the MIC for carbapenems, to investigate the biofilm formation, and to determine the frequency of the exogenes (exoS, exoT, exoU, and exoY) in P. aeruginosa clinical isolates. This study included 400 patients attending different units of Assiut University Hospitals.
In this study, the detection rate of P. aeruginosa was 18.8% which is similar to previous studies in Egypt, India, and Iraq [2,8,9]. P. aeruginosa in this study were detected from all types of clinical specimens in considerable numbers where the highest percentage was found in blood followed by pus, sputum, and lastly urine. Our results are partly similar to previous reports in Nepal and Islamabad [10,11]. We could explain the highest isolation of P. aeruginosa from blood in our study due to many risk factors in ICUs and the Burn unit from where many blood samples were obtained. Other causing factors are the underlying disease, the severity of systemic inflammatory response syndrome, inadequate antibiotic treatment, other infections, older age, and MDR strains [10]. A previous report detected increased incidence of bloodstream infections in hospitalized patients, that are caused by P. aeruginosa primarily MDR or XDR strains as detected in our study [12]. Our findings are identical to the study of Tang et al. who detected that P. aeruginosa bacteremia occurs in patients with serious underlying diseases and the organism is frequently acquired in healthcare facilities, and has been associated with increased lengths of stay, cost of hospitalization, and mortality [13]. As reported previously, P. aeruginosa is still a major cause of blood infections with considerable mortality rate [14]. In our study, MDR and XDR isolates were detected in a great majority of our clinical specimens and PDR isolates were found in a considerable number. Results of our study are comparable to many previous reports where P. aeruginosa showed high resistance rates to most used anti-pseudomonal drugs [11]. The highest resistance rates in Pseudomonas in this study were to cephalosporins, which is similar to other previous studies. In a study by Parmar et al., they found high resistance rate against cephalosporins [9]. In another study in Yemen, the authors found P. aeruginosa strains that were highly resistant to cephalosporins [15]. In this study, MIC testing detected 66 (88%) carbapenem resistant P. aeruginosa isolates. These results are similar to Kakeya et al. who stated that, although carbapenems are the best antibiotics to treat MDR P. aeruginosa, the improper drug usage and incongruous dose results in emergence of antibiotic-resistant isolates in clinical settings [16]. In this study, the highest resistance rates were detected in P. aeruginosa isolates from sputum especially to levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, cephalosporins, and aztreonam. Urine isolates also expressed high resistance rates, followed by blood and pus isolates. Relatively lower resistance rates were identified to the carbapenem group. In another recent study, they found higher resistance rates in P. aeruginosa isolated from the respiratory tract (particularly in patients admitted to ICU) compared to isolates from other sites [17]. For biofilm formation, we detected that most of our P. aeruginosa isolates were biofilm-producers and the majority of these biofilm forming isolates were carbapenem resistant. This result matches with the fact that biofilm provides a protective lifestyle for bacteria and is extremely challenging and costly to treat by antimicrobial compounds [11]. Also consistent to our results, in a meta-analysis conducted by Mirzahosseini et al. they found that biofilm-producing P. aeruginosa isolates showed higher antibiotic resistance rates than non-producers [18]. Abdelraheem et al. reported that biofilm production in P. aeruginosa could reach up to 90% and biofilm-producing isolates have higher resistance rate to many antibiotics [19]. In our study, most MDR and XDR and more than half of PDR strains were biofilm-producers. In this work, all sputum isolates were biofilm-producers. Most pus, urine, and blood isolates were biofilm-producers.
Concerning occurrence of exotoxin genes, exoT and exoY genes were detected by conventional PCR in most of the strains, which is greatly matching with Horna et al. who stated that all P. aeruginosa strains code for exoY and exoT, so they are crucial genes for bacterial virulent ability [7]. On the other hand, exoS was detected in nearly all strains, while exoU was detected only in about one third of the isolates. This is in agreement with Horna et al. who stated that exoS and exoU highly enhance pathogenicity and exoU is accountable for cytotoxicity, cell death, and severity of infections [7] and with Rangel et al. who stated that P. aeruginosa coding for exoS evidenced bad prognosis in patients [20]. Our results also are in agreement with that of Feltman et al. where they found 72% of P. aeruginosahad exoS, 28% had exoU, and 89% had exoY genes, which is greatly similar to our findings [21]. Previous reports detected that the exoS gene evidenced bad prognosis in patients [20]. Our results are in agreement with those of Feltman et al. where they found that 72% of P. aeruginosa had exoS, 28% had exoU, and 89% had exoY genes, which is similar to our results [21]. Our study detected that there was no significant association between coexistence of exogenes in P. aeruginosa and carbapenem resistance. Bahador et al. declared that these proteins impair cell function [22]. Comparable to our results, Gajdács et al. detected no association between detected virulence factors and resistance in P. aeruginosa strains [23]. In another study, by Zarei et al., the authors did not find relations between resistance rate and expression of virulence genes in Pseudomonas strains [3]. In contrast to our findings, other studies declared a relation between exogenes and antimicrobial resistance in P. aeruginosa. Yousefi-Avarvand et al. detected increased numbers of exogenes within isolates with observed high antibiotic resistance [24]. In another study, by Mitov et al., the authors found more prevalence of exogenes in MDR strains [25]. This debate in results requires more future both in vivo and in vitro studies to declare whether there is a relationship between existence of exogenes and drug resistance in P. aeruginosa strains.
Conclusions
We concluded that P. aeruginosa represents an important opportunistic pathogen that we detected in different clinical specimens with the highest percentage found in blood. Most of our P. aeruginosa isolates had DTR being resistant to many anti-pseudomonal antibiotics. Most of P. aeruginosa isolates were biofilm-producers, which is directly related to marked drug resistance of isolates especially to carbapenems. The genes exoT, exoS and exoY were encoded by almost all P. aeruginosa strains and therefore might be considered an inevitable component of P. aeruginosa virulence. Despite the lower detection of exoU compared to other exogenes, it may be responsible for a highly cytotoxic phenotype. A statistically insignificant relationship between coexistence of exogenes and carbapenem resistance was detected.
Author Contributions
AGT contributed to design and the decision to submit the report for publication. MNS contributed to collection of the materials and laboratory performance. MSEM contributed to analysis of data, writing the report. All authors read and approved the final version of the article.
Funding
None to declare.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Prof. Sherine Aly (Prof. of Medical Microbiology and Immunology, Faculty of Medicine, Assiut University, University Street 71515 Assiut, Egypt) and Dr. Safy Hadiya (Assiut International Center of Nanomedicine, Al-Rajhy Liver Hospital, Assiut University, University Street 71515 Assiut, Egypt) for kindly providing Pseudomonas aeruginosa reference strain 27853.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors – none to declare.
References
- Azimi, S.; Kafil, H.S.; Baghi, H.B.; et al. Presence of exoY, exoS, exoU and exoT genes, antibiotic resistance and biofilm production among Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates in Northwest Iran. GMS Hyg Infect Control. 2016, 11, Doc04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.A.; Bakir, S.H.; Haji, S.H.; Hussen, B.M. Evaluation of blaGES-5 and blaVEB-1 genes with multidrug-resistant extend, pandrug resistance patterns (MDR, XDR, PDR), and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates. Cell Mol Biol. 2021, 67, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, O.; Shokoohizadeh, L.; Hossainpour, H.; Alikhani, M.Y. Molecular analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from clinical, environmental and cockroach sources by ERIC-PCR. BMC Res Notes. 2018, 11, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spilker, T.; Coenye, T.; Vandamme, P.; LiPuma, J.J. PCR-based assay for differentiation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from otherPseudomonas species recovered from cystic fibrosis patients. J Clin Microbiol. 2004, 42, 2074–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akrami, S.; Ekrami, A.; Avarvand, A.Y. Biofilm generation and antibiotic resistant profile of extensive and multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa from burn patients in Ahvaz: a cross-sectional study. Health Sci Rep. 2024, 7, e2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhkhari, P.; Tajeddin, E.; Azimirad, M.; et al. Involvement of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the occurrence of community and hospital acquired diarrhea, and its virulence diversity among the stool and the environmental samples. Int J Environ Health Res. 2022, 32, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horna, G.; Amaro, C.; Palacios, A.; Guerra, H.; Ruiz, J. High frequency of the exoU+/exoS+ genotype associated with multidrug-resistant "high-risk clones" of Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates from Peruvian hospitals. Sci Rep. 2019, 9, 10874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gad, G.F.; El-Domany, R.A.; Zaki, S.; Ashour, H.M. Characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from clinical and environmental samples in Minia, Egypt: prevalence, antibiogram and resistance mechanisms. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007, 60, 1010–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, H.; Dholakia, A.; Vasavada, D.; Singhala, H. The current status of antibiotic sensitivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from various clinical samples. Int J Res Med. 2013, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Anjum, F.; Mir, A. Susceptibility pattern of Pseudomonas aeruginosa against various antibiotics. Afr J Microbiol Res. 2010, 4, 1005–12. [Google Scholar]
- Anil, C.; Shahid, R.M. Antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates at a tertiary care hospital in Kathmandu, Nepal. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2013, 6, 235–38. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera, S.; Bodro, M.; Soriano, A. Predictors of multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa involvement in bloodstream infections. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2021, 34, 686–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.C.; Lee, C.C.; Li, C.W.; Li, M.C.; Ko, W.C.; Lee, N.Y. Time-to-positivity of blood culture: an independent prognostic factor of monomicrobial Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2017, 50, 486–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Delden, C. Pseudomonas aeruginosa bloodstream infections: how should we treat them? Int J Antimicrob Agents 2007, 30 (Suppl. 1), S71–S75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyahawi, A.; Alhomidi, A.M.; Al-Henhena, N. Prevalence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns at a private hospital in Sana'a, Yemen. Univ J Pharm Res. 2018, 3, 12–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kakeya, H.; Yamada, K.; Nakaie, K.; et al. [A comparison of susceptibility ofPseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates to carbapenem antibiotics in our hospital]. Jpn J Antibiot. 2014, 67, 241–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tsujimoto, H.; Fujikura, Y.; Hamamoto, T.A.; et al. Drug resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa based on the isolation sites and types of gastrointestinal diseases: an observational study. Fukushima J Med Sci. 2025, 71, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karballaei Mirzahosseini, H.; Hadadi-Fishani, M.; Morshedi, K.; Khaledi, A. Meta-analysis of biofilm formation, antibiotic resistance pattern, and biofilm-related genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from clinical samples. Microb Drug Resist. 2020, 26, 815–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelraheem, W.M.; Abdelkader, A.E.; Mohamed, E.S.; Mohammed, M.S. Detection of biofilm formation and assessment of biofilm genes expression in different Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates. Meta Gene. 2020, 23, 100646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, S.M.; Logan, L.K.; Hauser, A.R. The ADP-ribosyltransferase domain of the effector protein ExoS inhibits phagocytosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa during pneumonia. MBio. 2014, 5, e01080-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feltman, H.; Schulert, G.; Khan, S.; Jain, M.; Peterson, L.; Hauser, A.R. Prevalence of type III secretion genes in clinical and environmental isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology. 2001, 147, 2659–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahador, N.; Shoja, S.; Faridi, F.; et al. Molecular detection of virulence factors and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa obtained from different clinical specimens in Bandar Abbas. Iran J Microbiol. 2019, 11, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdács, M.; Baráth, Z.; Kárpáti, K.; et al. No correlation between biofilm formation, virulence factors, and antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: results from a laboratory-based in vitro study. Antibiotics. 2021, 10, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi-Avarvand, A.; Khashei, R.; Ebrahim-Saraie, H.S.; Emami, A.; Zomorodian, K.; Motamedifar, M. The frequency of exotoxin A and exoenzymes S and U genes among clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Shiraz, Iran. Int J Mol Cell Med. 2015, 4, 167–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mitov, I.; Strateva, T.; Markova, B. Prevalence of virulence genes among Bulgarian nosocomial and cystic fibrosis isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Braz J Microbiol. 2010, 41, 588–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© GERMS 2025.