Linoleic Acid Acts as a Potential Anti-Virulence Agent in Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
Introduction
Methods
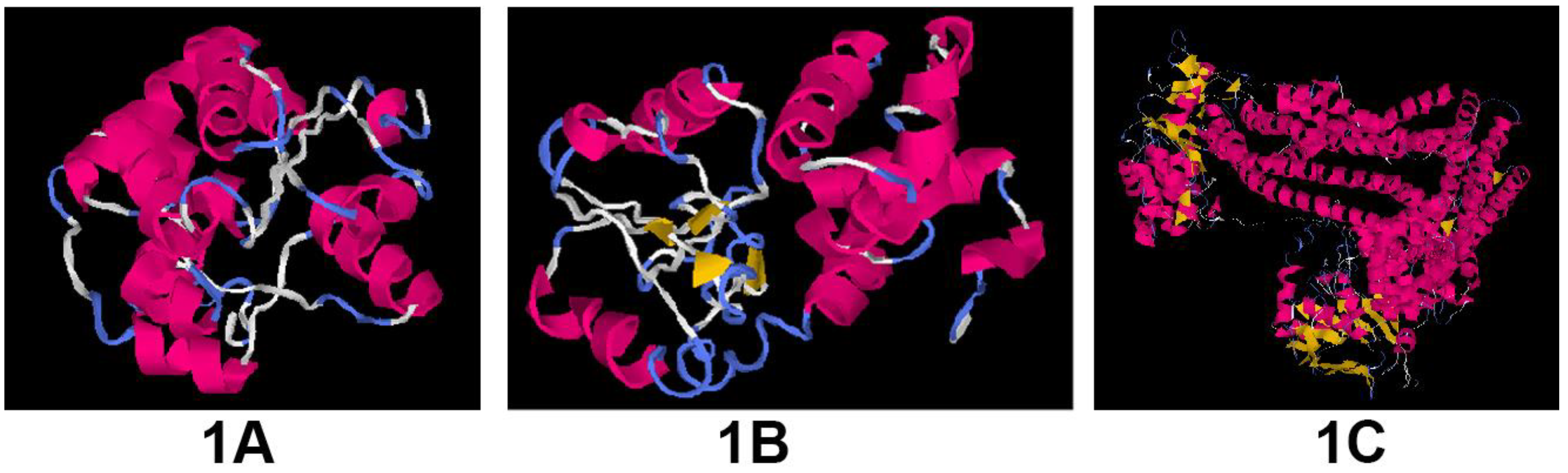
Modeling of the proteins
Ligands
Molecular docking studies
Bacterial strains and identification
Assessment of inhibitory activity of selected anti-virulence compounds
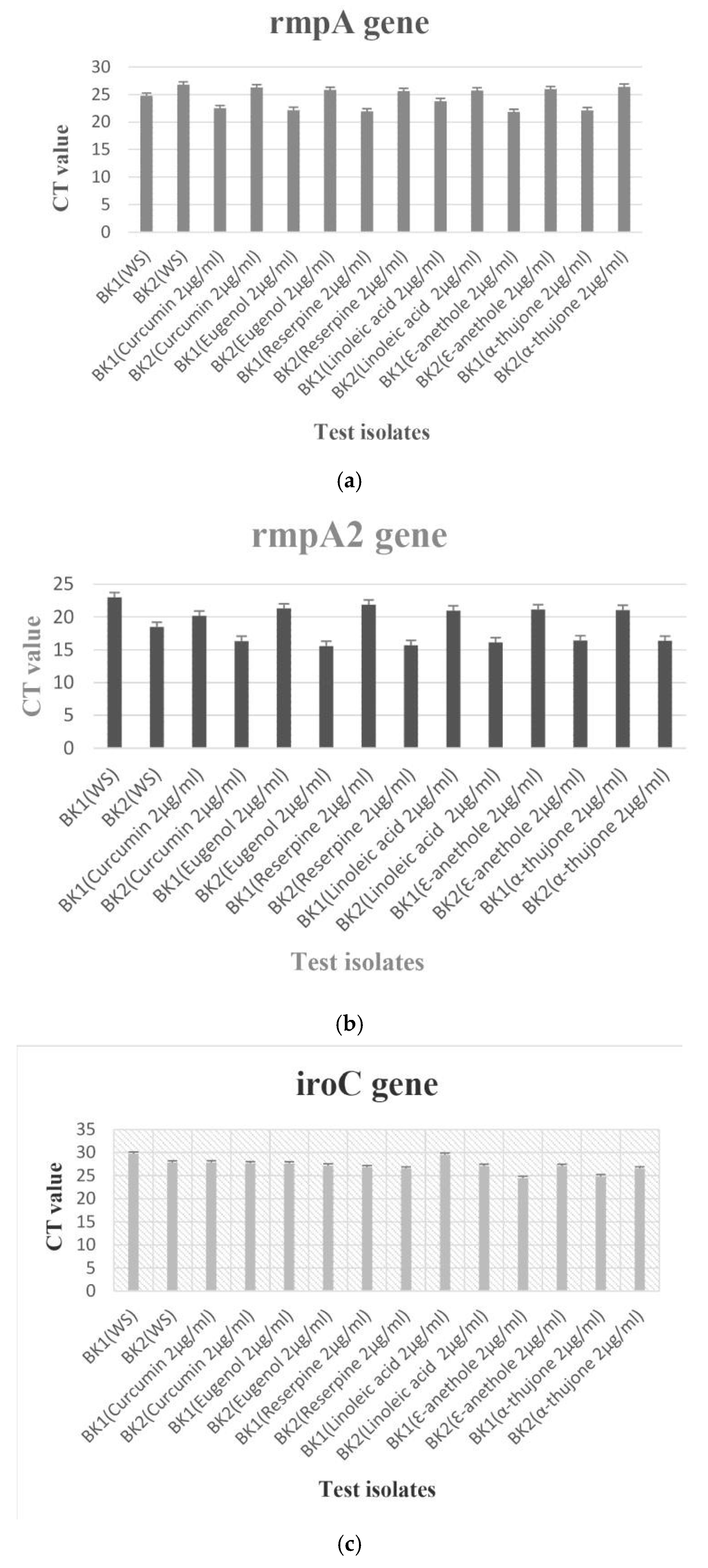
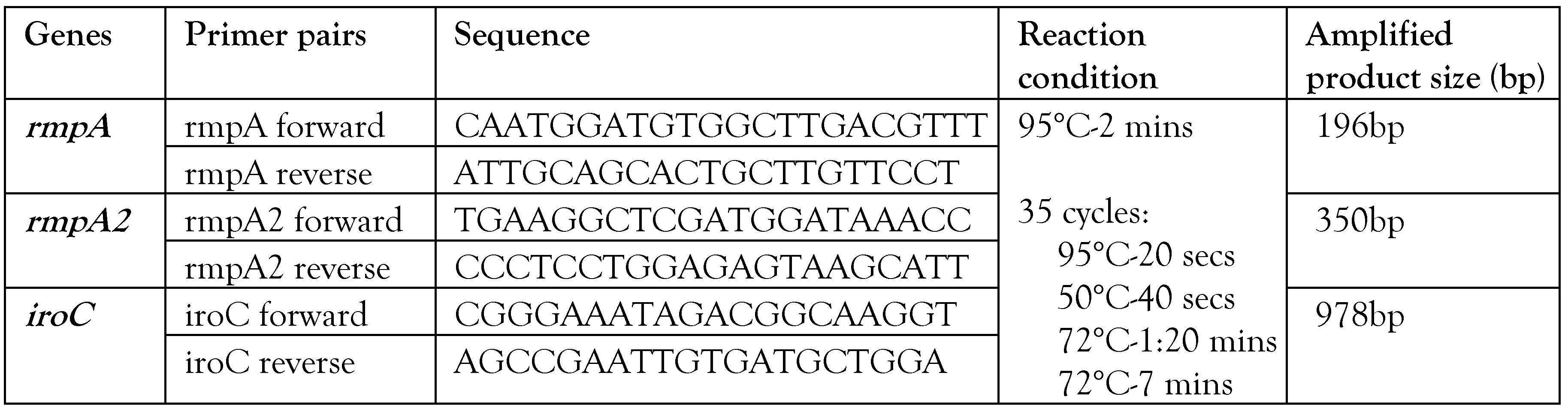
Transcriptional analysis of hypervirulence genes with and without anti-virulence compounds
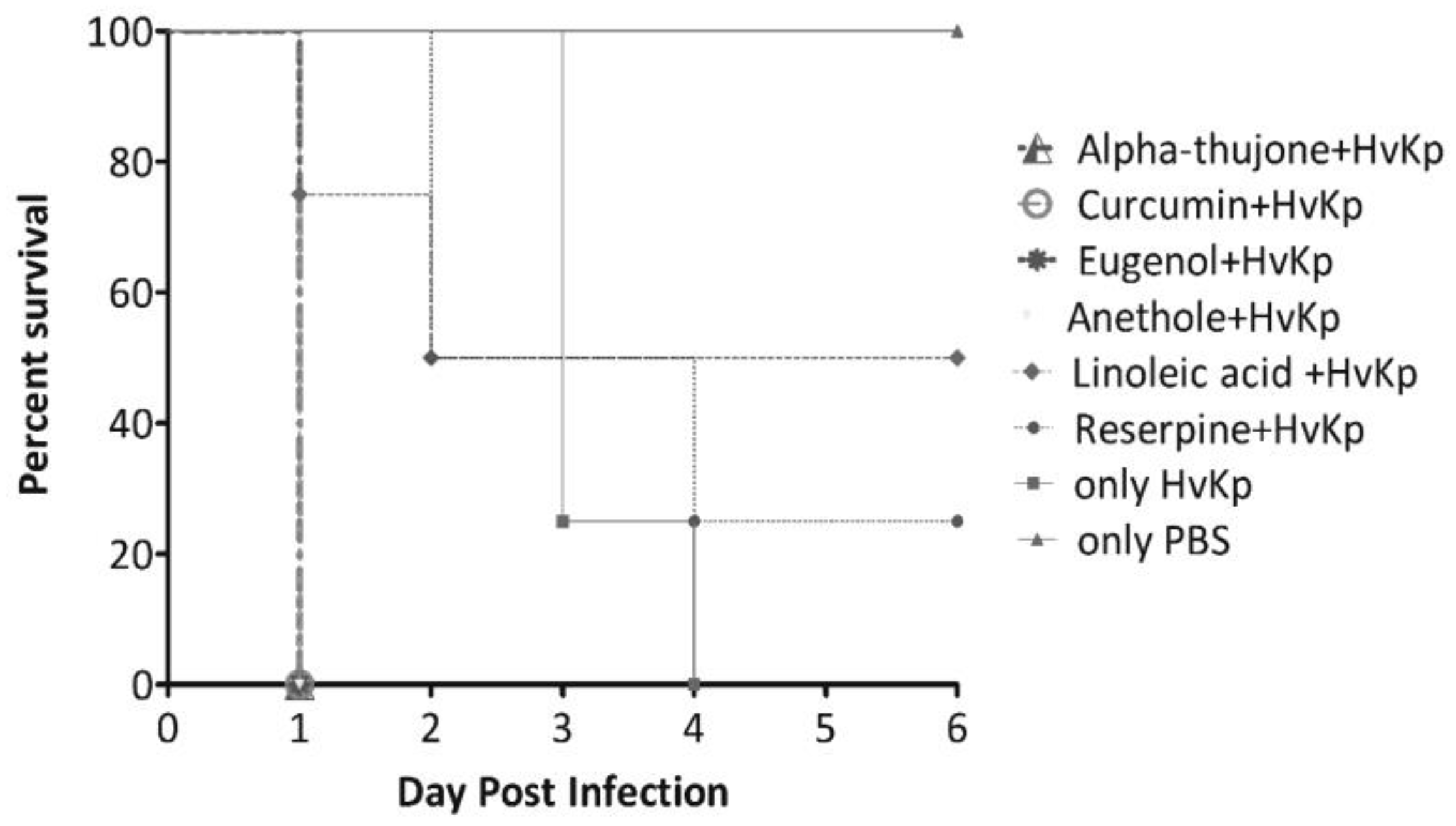
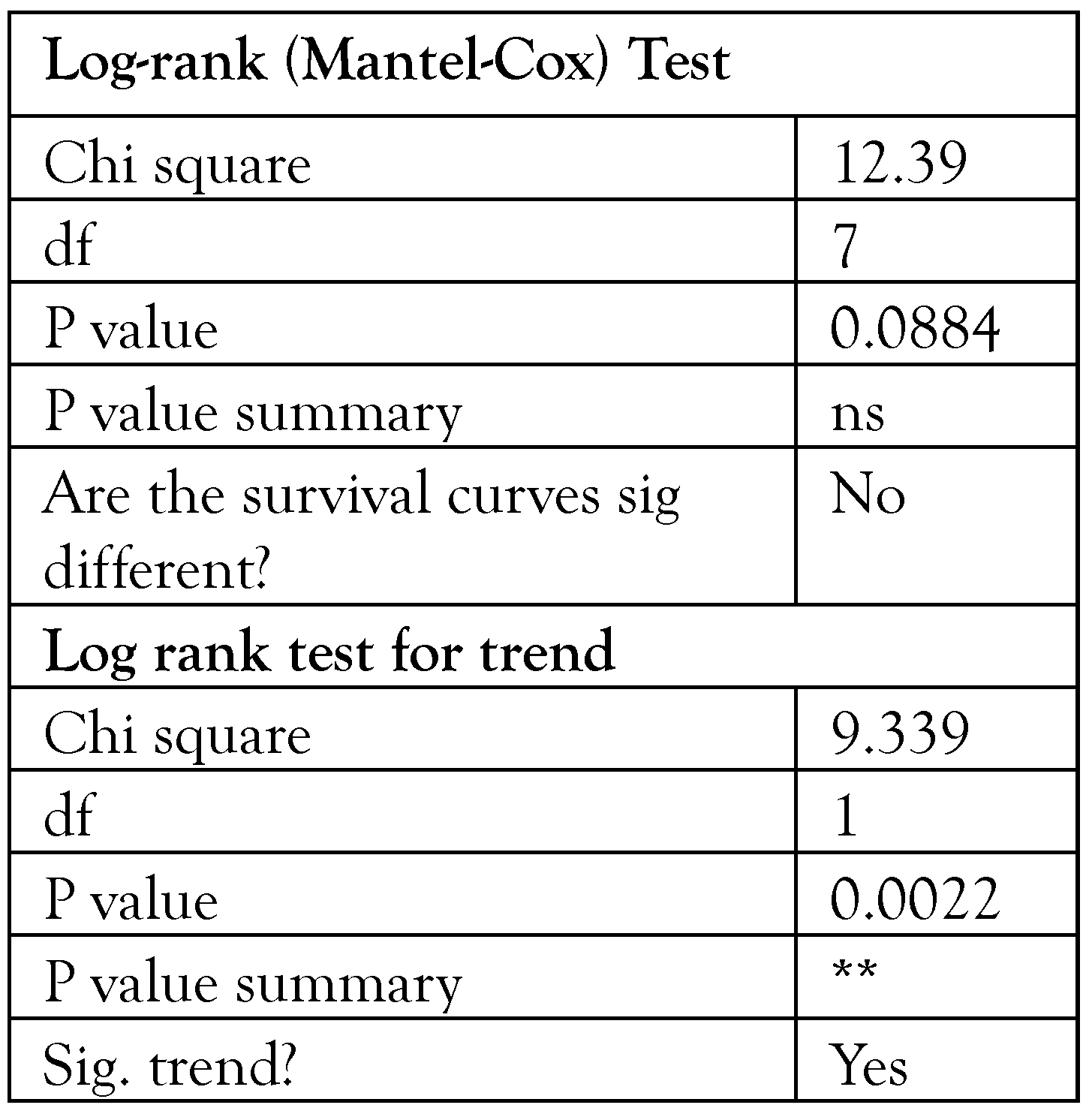
In-vivo analysis of anti-virulence in Galleria mellonella infection model
Statistical analysis
Results
Discussion
Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria to guide research, discovery, and development of new antibiotics; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Choby, J.E.; Howard-Anderson, J.; Weiss, D.S. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical and molecular perspectives. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 287, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyres, K.L.; Nguyen, T.N.T.; Lam, M.M.C.; et al. Genomic surveillance for hypervirulence and multi-drug resistance in invasive Klebsiella pneumoniae from South and Southeast Asia. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buroni, S.; Chiarelli, L.R. Antivirulence compounds: A future direction to overcome antibiotic resistance? Future Microbiol. 2020, 155, 299–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, T.; Wangkheimayum, J.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, A.; Bhattacharjee, A. Extensively drug resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae from a series of neonatal sepsis in a tertiary care hospital, India. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 645955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Country Office for India, Department of Biotechnology, Government of India. Indian Priority Pathogen List to Guide research, discovery, and development of new antibiotics in India. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Crouch, M.L.; Castor, M.; Karlinsey, J.E.; Kalhorn, T.; Fang, F.C. Biosynthesis and IroC-dependent export of the siderophore salmochelin are essential for virulence of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 67, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.C.; Peng, H.L.; Chang, H.Y. RmpA2, an activator of capsule biosynthesis in Klebsiella pneumoniae CG43, regulates K2 cps gene expression at the transcriptional level. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, C.; Basu, S.; Lal, B.; et al. Aerobactin seems to be a promising marker compared with unstable RmpA2 for the identification of hypervirulent carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: In silico and in vitro evidence. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 709681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, V.L.; Hansen, D.S.; Ko, W.C.; et al. Virulence characteristics of Klebsiella and clinical manifestations of K. pneumoniae bloodstream infections. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open Babel: An open chemical toolbox. J. Cheminform. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.C.; Chang, F.Y.; Fung, C.P.; et al. High prevalence of phagocytic-resistant capsular serotypes of Klebsiella pneumoniae in liver abscess. Microbes Infect. 2004, 6, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, B.F.; Ferreira, M.L.; Campos, P.A.; et al. Hypervirulence and biofilm production in KPC-2producing Klebsiella pneumoniae CG258 isolated in Brazil. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.C.; Liu, F.; Zhu, K.; Shen, J.Z. Natural products that target virulence factors in antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13195–13211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitencourt-Ferreira, G.; de Azevedo, W.F., Jr. Molegro Virtual Docker for docking. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 2053, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, R.; Christensen, M.S. MolDock: A new technique for high-accuracy molecular docking. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3315–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.S.; Kim, K.; Huh, J.Y.; Jung, B.; Kang, M.S.; Hong, S.G. Multiplex PCR for rapid detection of genes encoding class A carbapenemases. Ann. Lab. Med. 2012, 32, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Walsh, T.R.; Cuvillier, V.; Nordmann, P. Multiplex PCR for detection of acquired carbapenemase genes. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 70, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, S.D.; Nahar, L.; Kumarasamy, Y. Microtitre platebased antibacterial assay incorporating resazurin as an indicator of cell growth, and its application in the in vitro antibacterial screening of phytochemicals. Methods 2007, 42, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, A.C.; Thompson, M.G.; Black, C.C.; et al. AB5075, a highly virulent isolate of Acinetobacter baumannii, as a model strain for the evaluation of pathogenesis and antimicrobial treatments. mBio 2014, 5, e01076-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Lv, Y.; Yuan, M.; et al. Genetic basis of high-level aminoglycoside resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii from Beijing, China. Acta Pharm. Sin. B. 2014, 4, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumaningrum, S.; Budianto, E.; Kosela, S.; Sumaryono, W.; Juniarti, F. The molecular docking of 1,4naphthoquinone derivatives as inhibitors of Polo-like kinase 1 using Molegro Virtual Docker. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 4, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, G.M.; Lim-Wilby, M. Molecular docking. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 443, 365–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami-Zarandi, M.; Ghale, H.E.; Ranjbar, R. Characterization of virulence factors and antibacterial activity of curcumin in hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Future Microbiol. 2022, 17, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effah, C.Y.; Sun, T.; Liu, S.; Wu, Y. Klebsiella pneumoniae: An increasing threat to public health. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2020, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, K.E.; Wertheim, H.; Zadoks, R.N.; et al. Genomic analysis of diversity, population structure, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae, an urgent threat to public health. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2015, 112, E3574-81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.N.; Zimmer, K.R.; Macedo, A.J.; Trentin, D.S. Plant natural products targeting bacterial virulence factors. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 9162–9236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.S.; Awasthi, S.P.; Asakura, M.; et al. Suppression of virulence of toxigenic Vibrio cholerae by anethole through the cyclic AMP (cAMP)-cAMP receptor protein signaling system. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.C.; Liu, F.; Zhu, K.; Shen, J.Z. Natural products that target virulence factors in antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13195–13211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, D.; Paul, D.; Ghosh, A.S.; et al. Effect of singledose carbapenem exposure on transcriptional expression of blaNDM-1 and mexA in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2016, 7, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami-Zarandi, M.; Rahdar, H.A.; Esmaeili, H.; Ranjbar, R. Klebsiella pneumoniae: An update on antibiotic resistance mechanisms. Future Microbiol. 2023, 18, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 |
 |
© GERMS 2024.
Share and Cite
Wangkheimayum, J.; Banerjee, T.; Baishya, S.; Sharma, S.; Choudhury, M.D.; Laskar, M.A.; Bhattacharjee, A. Linoleic Acid Acts as a Potential Anti-Virulence Agent in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Germs 2024, 14, 136-148. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2024.1426
Wangkheimayum J, Banerjee T, Baishya S, Sharma S, Choudhury MD, Laskar MA, Bhattacharjee A. Linoleic Acid Acts as a Potential Anti-Virulence Agent in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Germs. 2024; 14(2):136-148. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2024.1426
Chicago/Turabian StyleWangkheimayum, Jayalaxmi, Tuhina Banerjee, Somorita Baishya, Swati Sharma, Manabendra Dutta Choudhury, Monjur Ahmed Laskar, and Amitabha Bhattacharjee. 2024. "Linoleic Acid Acts as a Potential Anti-Virulence Agent in Klebsiella pneumoniae" Germs 14, no. 2: 136-148. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2024.1426
APA StyleWangkheimayum, J., Banerjee, T., Baishya, S., Sharma, S., Choudhury, M. D., Laskar, M. A., & Bhattacharjee, A. (2024). Linoleic Acid Acts as a Potential Anti-Virulence Agent in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Germs, 14(2), 136-148. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2024.1426




