Arbovirus and Its Potential to Lead the Next Global Pandemic from Sub-Saharan Africa: What Lessons Have We Learned from COVID-19?
Abstract
Introduction
Diversity of arboviruses in sub-Saharan Africa
Family Togaviridae
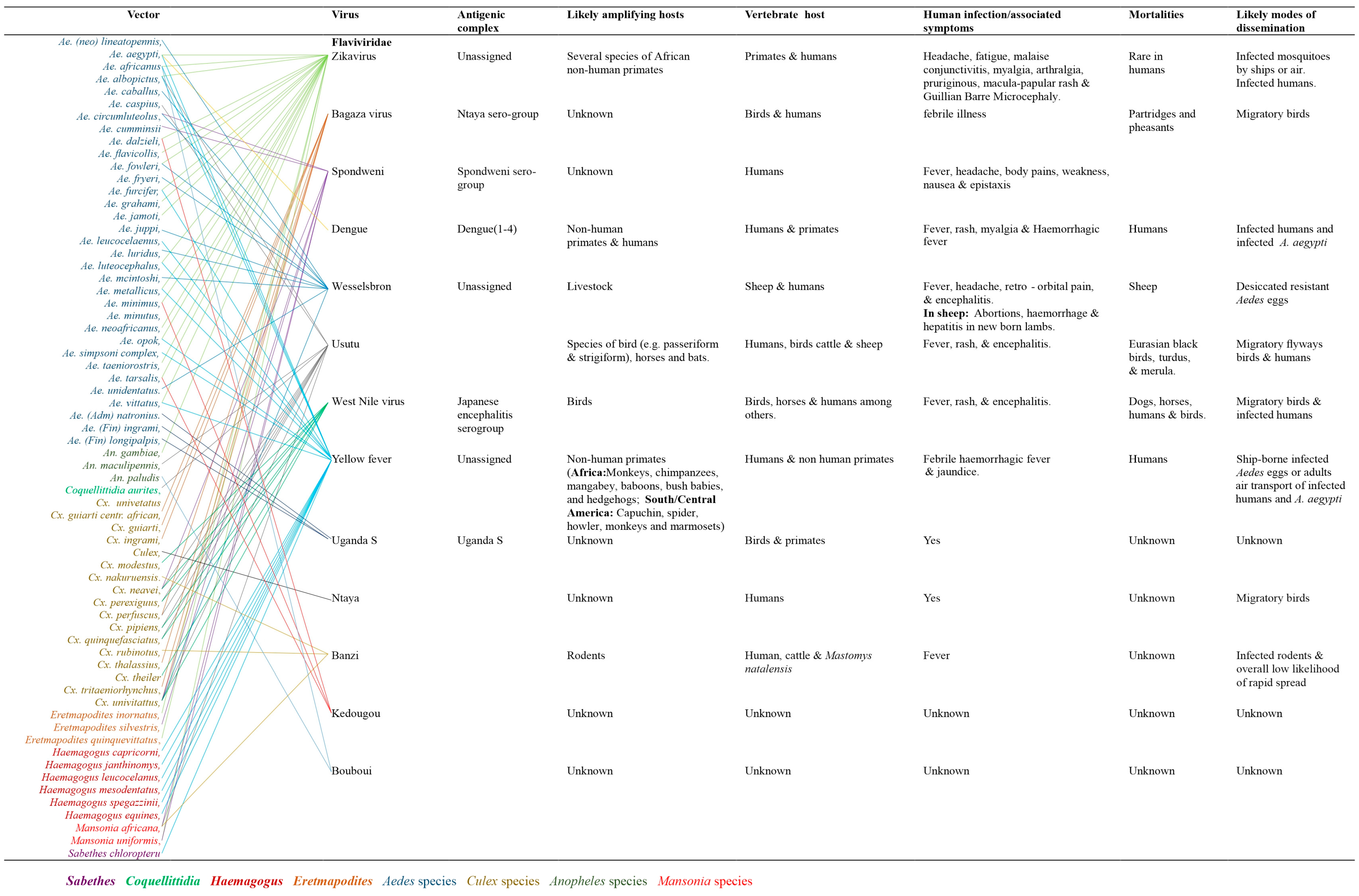
Family Flaviviridae
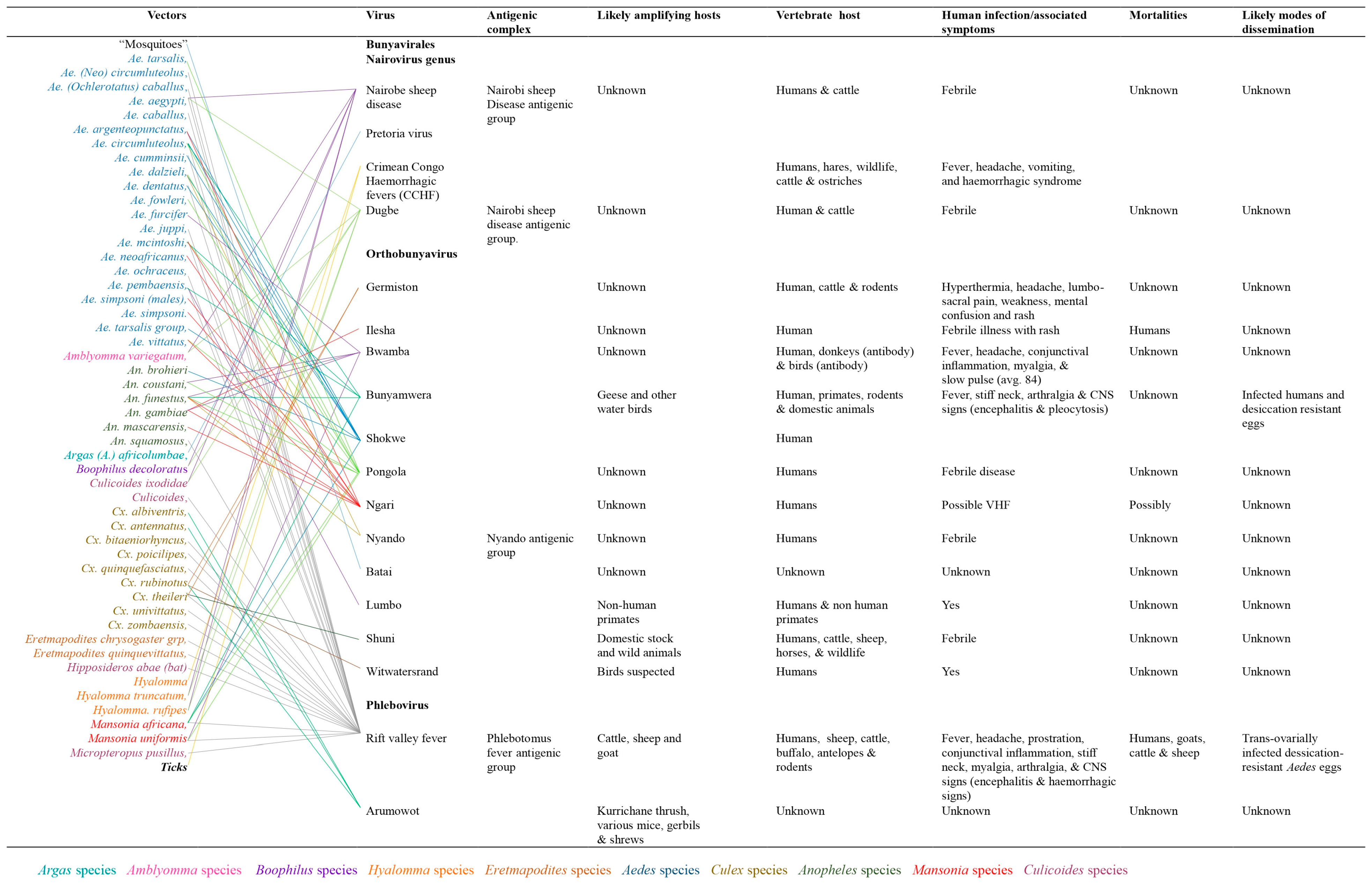
Arthropod vectors associated with arboviruses mobility and distribution
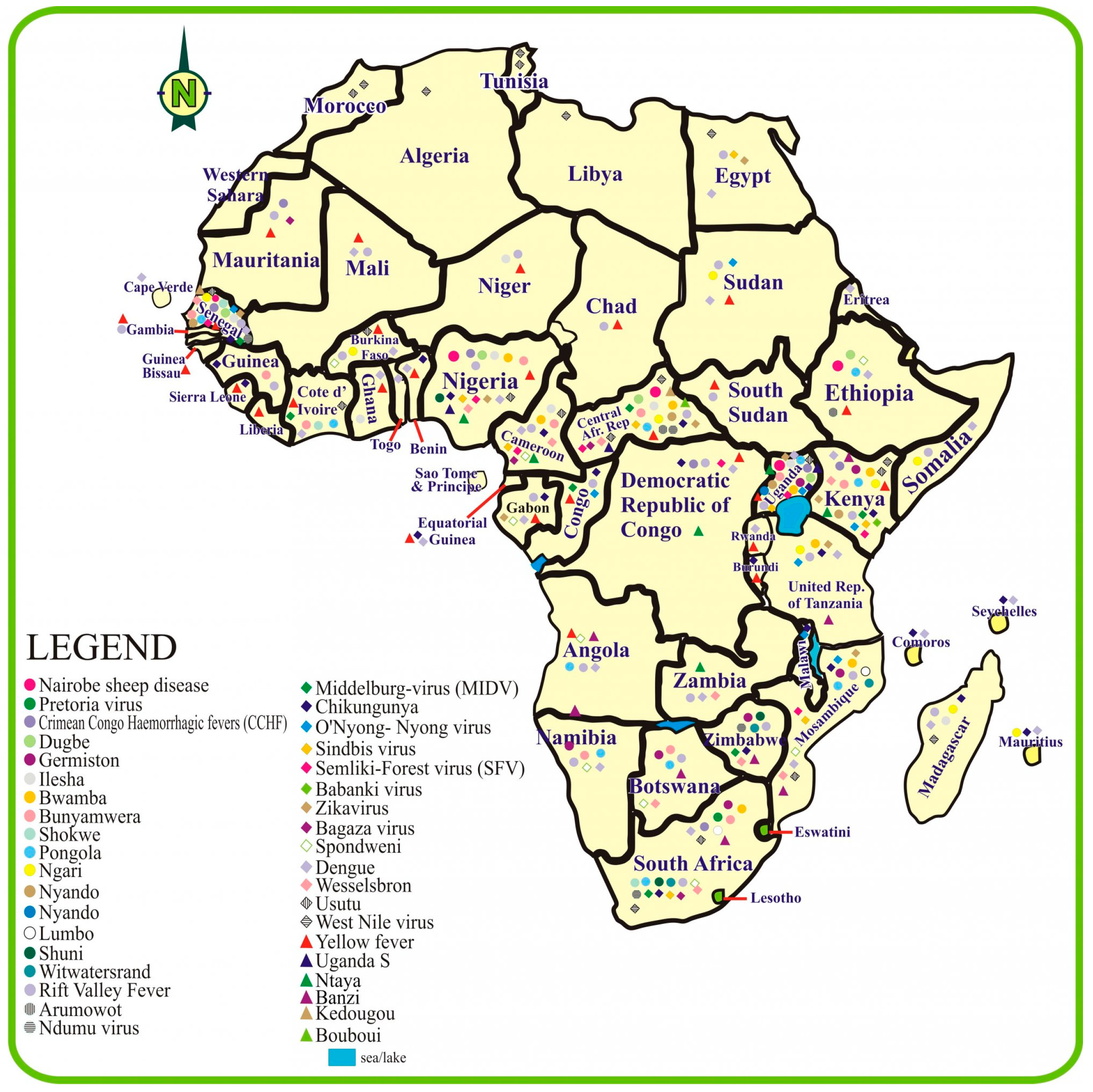
The distribution of arboviruses in sub-Saharan Africa
Survival potentials of arboviruses
Determinants of arbovirus emergence and transmission
Co-infection with SARS-CoV-2
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- García-Sastre, A.; Endy, T.P. Arboviruses. In Encyclopedia of microbiology; Schaechter, M., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, 2009; pp. 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing in human tripronuclear zygotes. Protein Cell 2015, 5, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, Y.Y.; Balasuriya, U.B.; Lee, C.K. Zoonotic encephalitides caused by arboviruses: Transmission and epidemiology of alphaviruses and flaviviruses. Clin Exp Vaccine Res 2014, 3, 58–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venter, M. Assessing the zoonotic potential of arboviruses of African origin. Curr Opin Virol 2018, 28, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braack, L.; Gouveia de Almeida, A.P.; Cornel, A.J.; Swanepoel, R.; de Jager, C. Mosquito-borne arboviruses of African origin: Review of key viruses and vectors. Parasit Vectors 2018, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajollahi, A.; Fonseca, D.M.; Kramer, L.D.; Kilpatrick, A.M. “Bird biting” mosquitoes and human disease: A review of the role of Culex pipiens complex mosquitoes in epidemiology. Infect Genet Evol 2011, 11, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edet, U.O.; Ebana, R.U.B.; Etok, C.A.; Nwamuo, L.C. Prevalence of human immunodeficiency virus and Plasmodium falciparum dual infection amongst residents of Kaduna South in North Western Nigeria. Int J Trop Dis Health 2016, 17, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.S. Understanding the implications of pandemic outbreaks on supply chains: An exploratory study of the effects caused by the COVID-19 across four South Asian countries and steps taken by firms to address the disruption. Int J Phys Distrib Logist Manage 2022, 52, 370–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, L.E.; Martin, S.W.; Lindsey, N.P.; et al. Epidemiology of dengue, chikungunya, and Zika virus disease in US States and Territories, 2017. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2019, 101, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contigiani, M.S.; Diaz, L.A. Togaviridae. In Arthropod borne diseases; Marcondes, C., Ed.; Springer: Cham, 2017; pp. 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marklewitz, M.; Junglen, S. Evolutionary and ecological insights into the emergence of arthropod-borne viruses. Acta Trop 2019, 190, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, P.; Becher, P.; Bukh, J.; et al. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Flaviviridae. J Gen Virol 2017, 98, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, K.M.; Vanlandingham, D.L. Bunyavirus-vector interactions. Viruses 2014, 6, 4373–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, S.C.; Reisen, W.K. Present and future arboviral threats. Antiviral Res 2010, 85, 328–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelman, Z.N.; Miller, D.M.; Myles, K.M. Bed bugs and infectious disease: A case for the arboviruses. PLoS Path 2013, 9, e1003462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briese, T.; Calisher, C.H.; Higgs, S. Viruses of the family Bunyaviridae: Are all available isolates reassortants? Virol 2013, 446, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayan, S.; Bokaean, M.; Shahrivar, M.R.; Chinikar, S. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever. Lab Med 2015, 46, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeller, H.; Bouloy, M. Bunyaviridae and Filoviridae. Rev Sci Tech 2000, 19, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostfeld, R.S.; Keesing, F. Effects of host diversity on infectious disease. Ann Rev Ecol Evol Syst 2012, 43, 157–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, T.A.; VerCauteren, K.C. Diseases and parasites [of white-tailed deer]. In Biology and management of white-tailed deer; Hewitt, D.G., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, 2011; pp. 232–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slovák, M.; Kazimírová, M.; Siebenstichová, M.; et al. Survival dynamics of tick-borne encephalitis virus in Ixodes ricinus ticks. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2014, 5, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villinger, J.; Mbaya, M.K.; Ouso, D.; Kipanga, P.N.; Lutomiah, J.; Masiga, D.K. Arbovirus and insect-specific virus discovery in Kenya by novel six genera multiplex high-resolution melting analysis. Mol Ecol Resour 2017, 17, 466–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farfan-Ale, J.A.; Loroño-Pino, M.A.; Garcia-Rejon, J.E.; et al. Detection of RNA from a novel West Nile-like virus and high prevalence of an insect-specific flavivirus in mosquitoes in the Yucatan Peninsula of Mexico. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2009, 80, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, C.; Sánchez-Seco, M.P.; Cáceres, F.; et al. Detection and monitoring of mosquito flaviviruses in Spain between 2001 and 2005. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2009, 9, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Seco, M.P.; Vázquez, A.; Collao, X.; et al. Surveillance of arboviruses in Spanish wetlands: Detection of new flavi-and phleboviruses. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2010, 10, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, R.C. Ross River virus: Ecology and distribution. Annu Rev Entomol 2002, 47, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.M. Bunyaviruses and climate change. Clin Microbiol Infect 2009, 15, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, J.; deShazo, R. Bed bugs (Cimex lectularius) and clinical consequences of their bites. JAMA 2009, 301, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brustolin, M.; Talavera, S.; Santamaría, C.; et al. Culex pipiens and S tegomyia albopicta (= Aedes albopictus) populations as vectors for lineage 1 and 2 West Nile virus in Europe. Med Vet Entomol 2016, 30, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, V.E.; Alencar, C.H.; Kamimura, M.T.; et al. Occurrence of natural vertical transmission of dengue-2 and dengue-3 viruses in Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus in Fortaleza, Ceará, Brazil. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunnill, M.; Boots, M. How important is vertical transmission of dengue viruses by mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae)? J Med Entomol 2016, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chompoosri, J.; Thavara, U.; Tawatsin, A.; et al. Vertical transmission of Indian Ocean Lineage of chikungunya virus in Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes. Parasit Vectors 2016, 9, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Dhama, K.; Malik, Y.S.; et al. Zika virus-emergence, evolution, pathology, diagnosis, and control: Current global scenario and future perspectives-a comprehensive review. Vet Q 2016, 36, 150–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliano, S.A.; Lounibos, L.P. Ecology of invasive mosquitoes: Effects on resident species and on human health. Ecol Lett 2005, 8, 558–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepin, M.; Bouloy, M.; Bird, B.H.; Kemp, A.; Paweska, J. Rift Valley fever virus (Bunyaviridae: Phlebovirus): An update on pathogenesis, molecular epidemiology, vectors, diagnostics and prevention. Vet Res 2010, 41, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, E.; van Hoek, A.H.; Wuite, M.; et al. Molecular hazard identification of non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labeaud, A.D.; Bashir, F.; King, C.H. Measuring the burden of arboviral diseases: The spectrum of morbidity and mortality from four prevalent infections. Popul Health Metr 2011, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marimoutou, C.; Vivier, E.; Oliver, M.; Boutin, J.P.; Simon, F. Morbidity and impaired quality of life 30 months after chikungunya infection: Comparative cohort of infected and uninfected French military policemen in Reunion Island. Medicine (Baltimore) 2012, 91, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, P.M.; Hahn, B.H. Origins of HIV and the AIDS pandemic. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2011, 1, a006841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aborode, A.T.; David, K.B.; Uwishema, O.; et al. Fighting COVID-19 at the expense of malaria in Africa: The consequences and policy options. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2021, 104, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© GERMS 2022.
Share and Cite
Mbim, E.N.; Edet, U.O.; Okoroiwu, H.U.; Nwaokorie, F.O.; Edet, A.E.; Owolabi, A.; Clement I, M. Arbovirus and Its Potential to Lead the Next Global Pandemic from Sub-Saharan Africa: What Lessons Have We Learned from COVID-19? GERMS 2022, 12, 538-547. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1358
Mbim EN, Edet UO, Okoroiwu HU, Nwaokorie FO, Edet AE, Owolabi A, Clement I M. Arbovirus and Its Potential to Lead the Next Global Pandemic from Sub-Saharan Africa: What Lessons Have We Learned from COVID-19? GERMS. 2022; 12(4):538-547. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1358
Chicago/Turabian StyleMbim, Elizabeth N., Uwem Okon Edet, Henshaw Uchechi Okoroiwu, Francisca O. Nwaokorie, Asanga Effiong Edet, Ayo Owolabi, and Mboto Clement I. 2022. "Arbovirus and Its Potential to Lead the Next Global Pandemic from Sub-Saharan Africa: What Lessons Have We Learned from COVID-19?" GERMS 12, no. 4: 538-547. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1358
APA StyleMbim, E. N., Edet, U. O., Okoroiwu, H. U., Nwaokorie, F. O., Edet, A. E., Owolabi, A., & Clement I, M. (2022). Arbovirus and Its Potential to Lead the Next Global Pandemic from Sub-Saharan Africa: What Lessons Have We Learned from COVID-19? GERMS, 12(4), 538-547. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1358



