Investigating the Antimicrobial Activity of Essential Oils Against Pathogens Isolated from Sewage Sludge of Southern Lebanese Villages
Abstract
Introduction
Methods
Collection of wastewater samples
Identification of microorganisms
Isolation of bacteria and yeast
Antibiogram assay
Essential oils collection and sample preparation
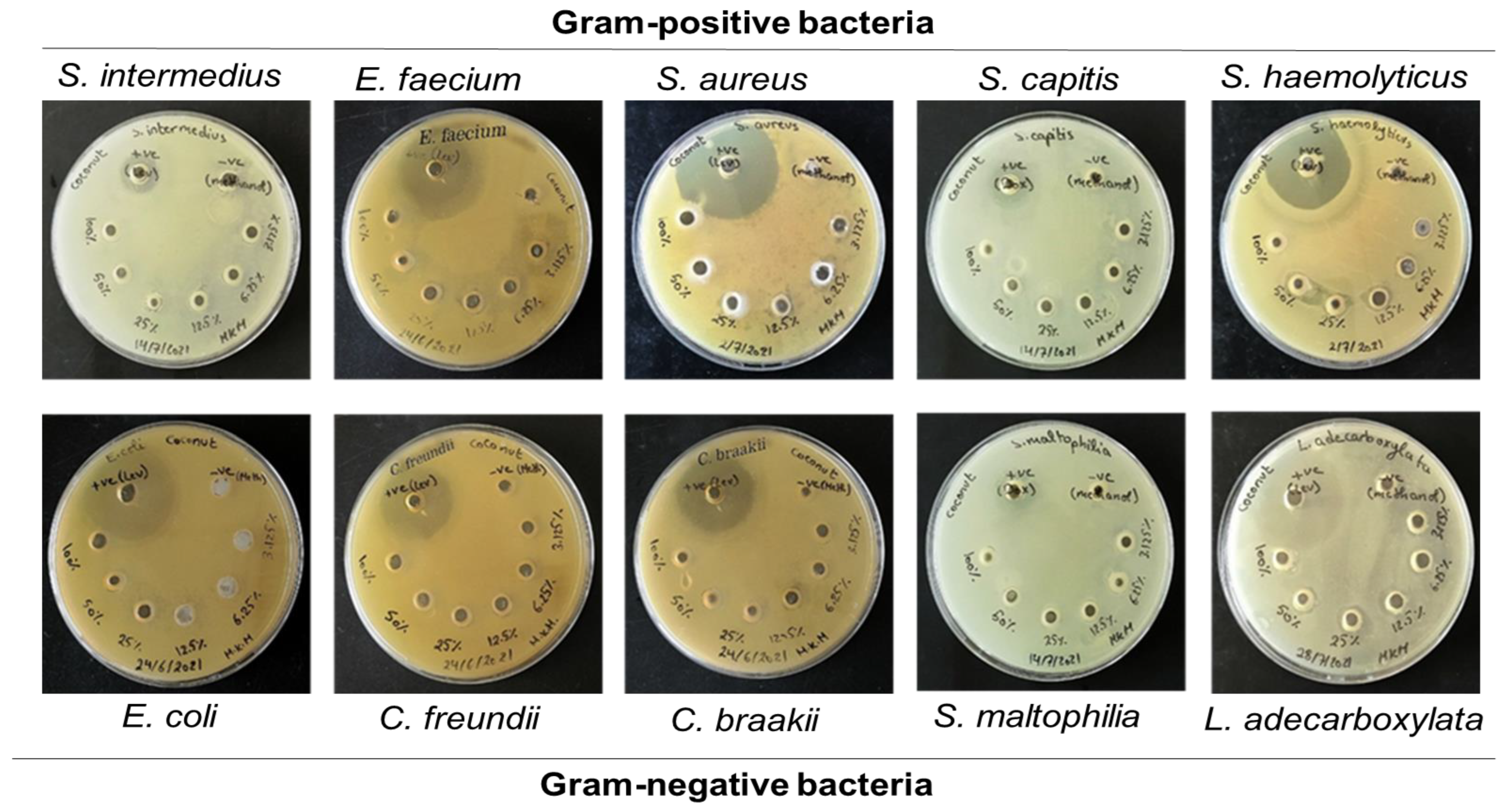
Agar well diffusion assay
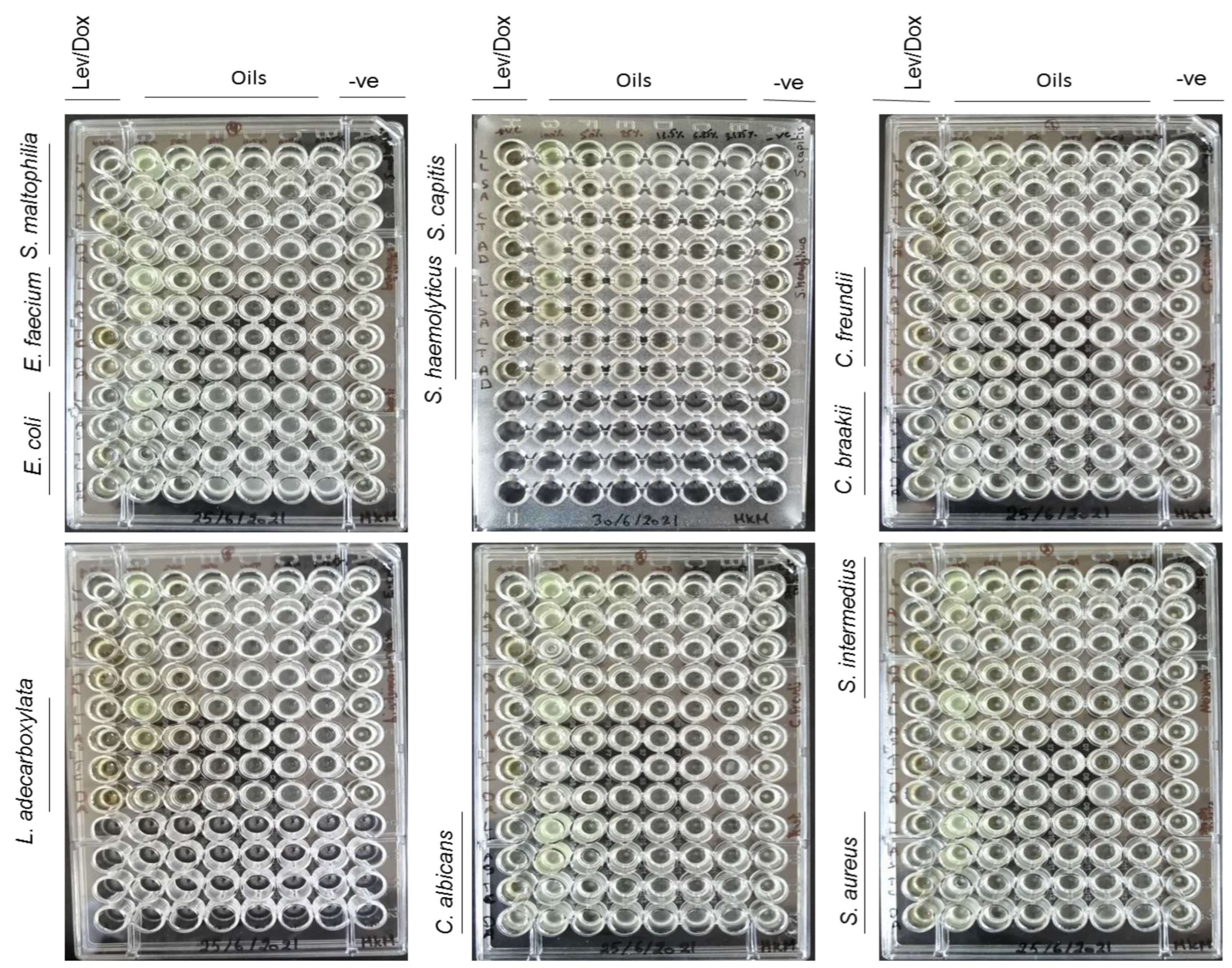
MIC and MBC broth microdilution assay
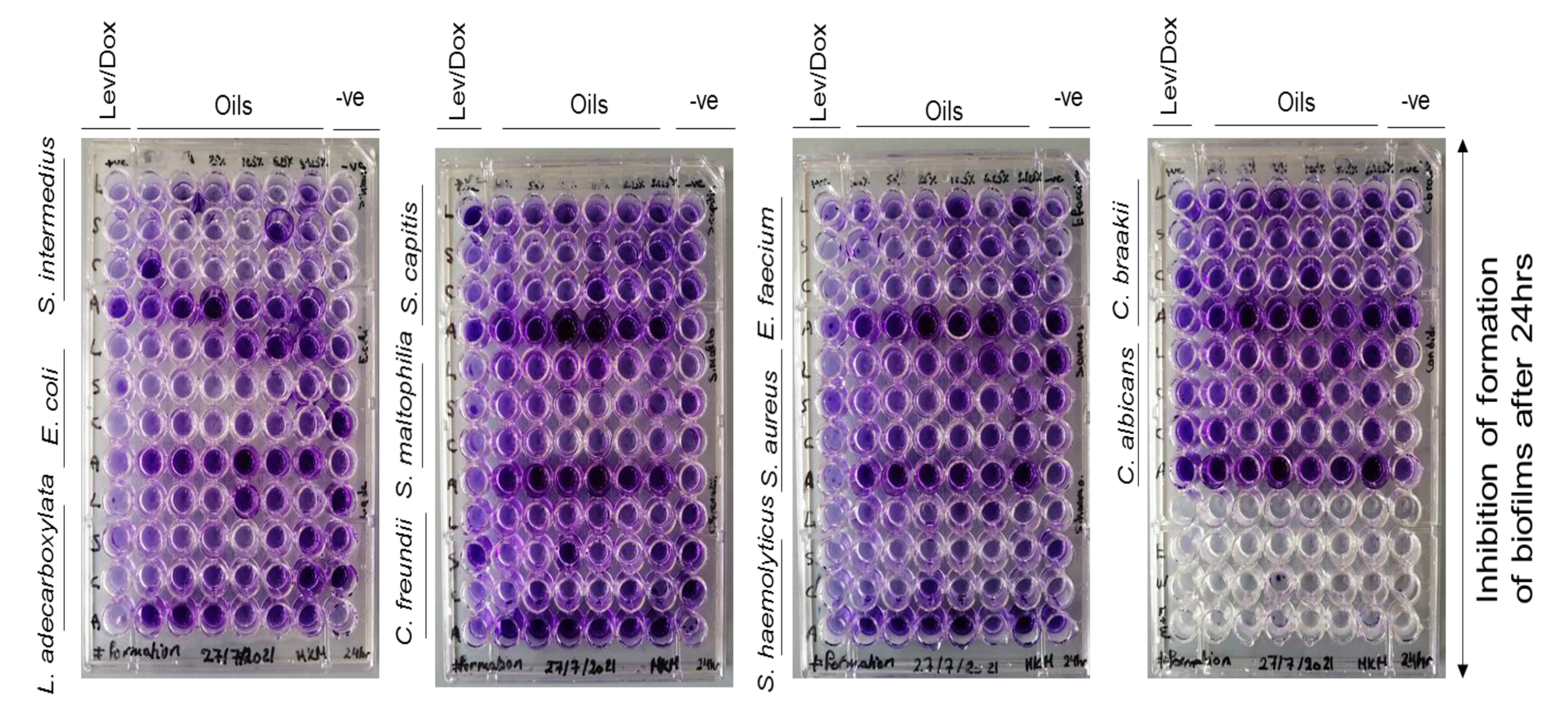
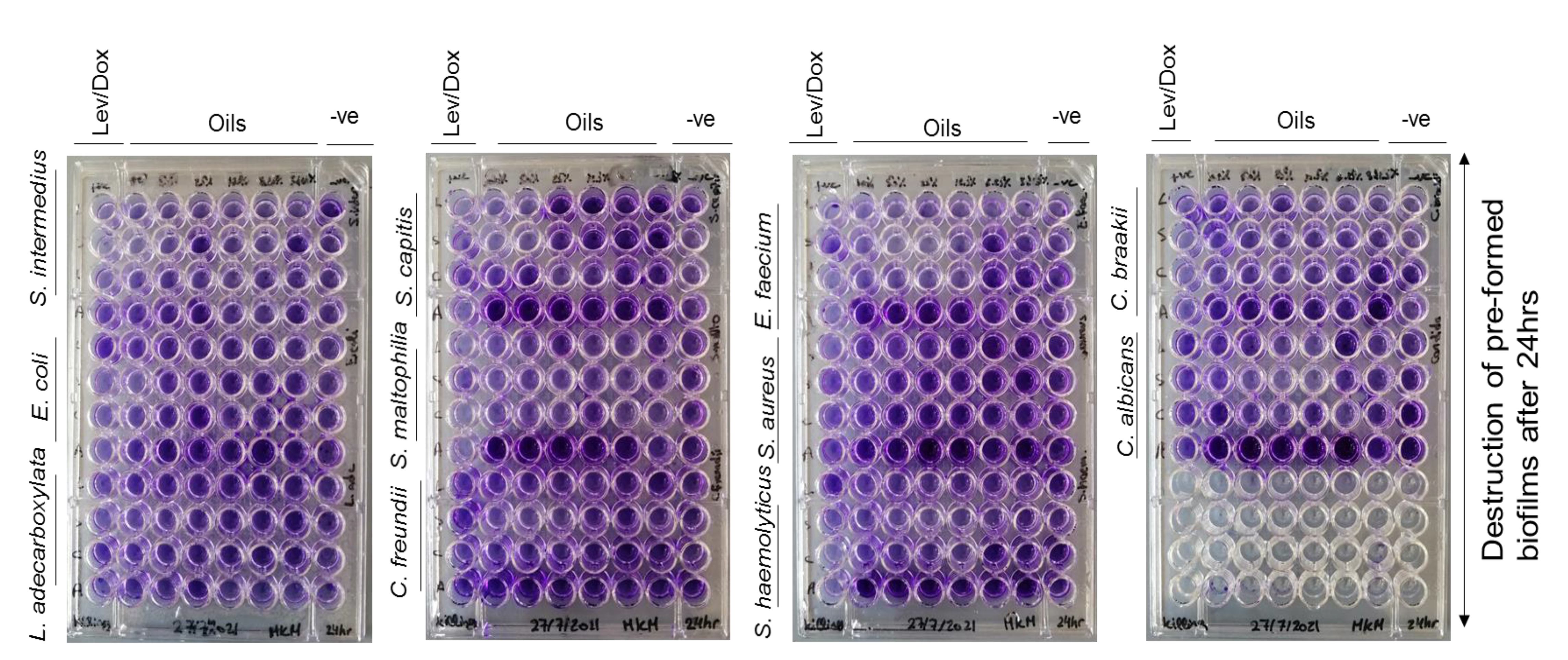
Antibiofilm screening
Statistical analysis
Results
Identification of bacterial isolates and yeast
Antibiotic susceptibility of the bacterial isolates
Oil susceptibility of the bacterial and fungal isolates
Determination of the MIC and MBC/MFC of the tested EOs against bacterial and fungal isolates
Antibiofilm screening results
GC-MS analysis showing the different major components of the tested EOs
Discussion
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of interest
References
- Al-Gheethi, A.A.; Efaq, A.N.; Bala, J.D.; Norli, I.; Abdel-Monem, M.O.; Ab. Kadir, M.O. Removal of pathogenic bacteria from sewage-treated effluent and biosolids for agricultural purposes. Appl Water Sci. 2018, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romdhana, M.H.; Lecomte, D.; Ladevie, B.; Sablayrolles, C. Monitoring of pathogenic microorganisms contamination during heat drying process of sewage sludge. HAL Id: hal-01651373. Process Saf Environ Prot. 2009, 87, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanos, D.; Nemer, N.; Khairallah, Y.; Abi Saab, M.T. Assessing the quality of sewage sludge as an agricultural soil amendment in Mediterranean habitats. Int J Recycl Org Waste Agric. 2019, 8, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, M.K.; Akhtar, M.S.; Sinniah, U.R. Antimicrobial properties of plant essential oils against human pathogens and their mode of action: an updated review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016, 2016, 3012462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzaro, F.; Fratianni, F.; De Martino, L.; Coppola, R.; De Feo, V. Effect of essential oils on pathogenic bacteria. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2013, 6, 1451–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavaniramya, S.; Vishnupriya, S.; Al-Aboody, M.S.; Vijayakumar, R.; Baskaran, D. Role of essential oils in food safety: antimicrobial and antioxidant applications. Grain Oil Sci Technol. 2019, 2, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasireddy, L.; Bingle, L.E.H.; Davies, M.S. Antimicrobial activity of essential oils against multidrug-resistant clinical isolates of the Burkholderia cepacia complex. PLoS One. 2018, 13, e0201835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. CLSI M100-ED29: 2019 Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 29th ed.CLSI, 2019; pp. 50–51. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Q.; Huang, Y.; Wang, H.; Fang, T. Diversity and abundance of bacterial pathogens in urban rivers impacted by domestic sewage. Environ Pollut. 2019, 249, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, R.P. Identification of essential oil components by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry, 4th ed.Carol stream: Allured publishing corporation, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Iseppi, R.; Tardugno, R.; Brighenti, V.; et al. Phytochemical composition and in vitro antimicrobial activity of essential oils from the Lamiaceae family against Streptococcus agalactiae and Candida albicans biofilms. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020, 9, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famuyide, I.M.; Aro, A.O.; Fasina, F.O.; Eloff, J.N.; McGaw, L.J. Antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of acetone leaf extracts of nine under-investigated south African Eugenia and Syzygium (Myrtaceae) species and their selectivity indices. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019, 19, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jisr, N.; Younes, G.; El Omari, K.; Hamze, M.; Sukhn, C.; El-Dakdouki, M.H. Levels of heavy metals, total petroleum hydrocarbons, and microbial load in commercially valuable fish from the marine area of Tripoli, Lebanon. Environ Monit Assess. 2020, 192, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, H.; Sugiyama, S. Sepsis and Leclercia adecarboxylata. QJM. 2018, 111, 733–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegoke, A.A.; Stenström, T.A.; Okoh, A.I. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia as an emerging ubiquitous pathogen: looking beyond contemporary antibiotic therapy. Front Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halawi, M.H.; Nasser, R. First case of identification of Candida kefyr and Pichia kluyveri in Lebanese Water. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, V.R.; Perry, C.M. Levofloxacin: a review of its use as a high-dose, short-course treatment for bacterial infection. Drugs. 2008, 68, 535–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, B.J.; Khanna, N.R.; Vijhani, P. Amoxicillin. StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island (FL), 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yılmaz, Ç.; Özcengiz, G. Antibiotics: pharmacokinetics, toxicity, resistance and multidrug efflux pumps. Biochem Pharmacol. 2017, 133, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiou, T.I.; Mandalakis, M.; Krigas, N.; et al. Comparative evaluation of essential oils from medicinal-aromatic plants of Greece: chemical composition, antioxidant capacity and antimicrobial activity against bacterial fish pathogens. Molecules. 2019, 25, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, J.F.; do Socorro Costa, M.; Tintino, S.R.; et al. Antibiotic activity potentiation and physicochemical characterization of the fixed Orbignya speciosa almond oil against MDR Staphylococcus aureus and other bacteria. Antibiotics (Basel). 2019, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, A.; Barreto, A.S.; Semedo-Lemsaddek, T. Antimicrobial effects of essential oils on oral microbiota biofilms: the toothbrush in vitro model. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, B.K.; Jackman, J.A.; Valle-González, E.R.; Cho, N.J. Antibacterial free fatty acids and monoglycerides: biological activities, experimental testing, and therapeutic applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2018, 19, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğan, A.; Otlu, S.; ÇelebiO. An investigation of antibacterial effects of steroids. Turkish J Vet Anim Sci. 2017, 41, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fozzard, H.A.; Sheets, M.F. Cellular mechanism of action of cardiac glycosides. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1985, 5, 10A–15A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Bacterial isolates | Levofloxacin | Amoxicillin | Tetracycline | Doxycycline |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram-positive bacteria | ||||
| S. intermedius | 25.6 ± 0.3 (S) | 0 (R) | 20.3 ± 0.3 (I) | 21.6 ± 0.3 (I) |
| E. faecium | 32.3 ± 0.3 (S) | 0 (R) | 20.6 ± 0.6 (S) | 29.6 ± 0.6 (S) |
| S. aureus | 16.6 ± 0.3 (I) | 0 (R) | 0 (R) | 20 (S) |
| S. capitis | 15.3 ± 0.3 (I) | 0 (R) | 25.6 ± 0.3 (S) | 27.6 ± 0.3 (S) |
| S. haemolyticus | 27.6 ± 0.3 (S) | 0 (R) | 14.3 ± 0.3 (I) | 21 ± 0.5 (S) |
| Gram-negative bacteria | ||||
| E. coli | 37.6 ± 0.3 (S) | 19.6 ± 0.6 (S) | 26.6 ± 0.3 (S) | 20.3 ± 0.3 (S) |
| C. freundii | 17.3 ± 0.3 (I) | 0 (R) | 0 (R) | 20.3 ± 0.3 (S) |
| C. braakii | 34.6 ± 0.3 (S) | 0 (R) | 14 (I) | 24.3 ± 0.3 (S) |
| S. maltophilia | 32.6 ± 0.3 (S) | 0 (R) | 31.6 ± 0.6 (S) | 41.3 ± 0.6 (S) |
| L. adecarboxylata | 30.3 ± 0.3 (S) | 20.3 ± 0.3 (S) | 23.3 ± 0.6 (S) | 21 (S) |
| Total S | 7 | 2 | 5 | 9 |
| % Sensitive | 70 | 20 | 50 | 90 |
| Total I | 3 | 0 | 3 | 1 |
| % Intermediate | 30 | 0 | 30 | 10 |
| Total R | 0 | 8 | 2 | 0 |
| % Resistant | 0 | 80 | 20 | 0 |
| Bacterial/fungal isolates | Concentrations of oils (%) and antimicrobial diameters (mm) of inhibition | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.125% | 6.25% | 12.5% | 25% | 50% | |
| Lettuce oil | |||||
| S. aureus | 8.1±0.48 (p=0.050) | 8.2±0.24 (p=0.050) | 8.2±0.24 (p=0.050) | 8.3±0.24 (p=0.003) | 8.3±0.2 (p=0.002) |
| S. capitis | 0±0.0 (p=0.002) | 0±0.0 (p=0.002) | 6.6±0.3 (p=0.002) | 7±0.0 (p=0.03) | 8.6±0.3 (p=0.002) |
| E. coli | 8±0.0 (p=0.006) | 8±0.0 (p=0.037) | 8±0.0 (p=0.03) | 8.2±0.3 (p=0.002) | 8±0.0 (p=0.050) |
| C. freundii | 0±0.0 (p=0.015) | 6.75±0.25 (p˂0.001) | 7.8±0.24 (p˂0.001) | 7.8±0.24 (p=0.015) | 8±0.0 (p=0.015) |
| C. braakii | 0±0.0 (p=0.015) | 6.85±0.3 (p˂0.001) | 6.75±0.25 (p˂0.001) | 8±0.0 (p˂0.001) | 8±0.0 (p=0.015) |
| S. maltophilia | 0±0.0 (p=0.002) | 6.26±0.25 (p=0.009) | 9.5±0.5 (p=0.013) | 9.5±0.5 (p=0.005) | 9.75±0.25 (p=0.002) |
| L. adecarboxylata | 7.6±0.24 (p=0.005) | 7.4±0.24 (p=0.005) | 7.6±0.24 (p=0.004) | 8±0.0 (p=0.005) | 8±0.0 (p=0.001) |
| C. albicans | 0±0.0 (p˂0.001) | 0±0.0 (p˂0.001) | 6.75±0.25 (p˂0.001) | 6.7±0.25 (p˂0.001) | 8±0.0 (p=0.015) |
| Coconut oil | |||||
| S. intermedius | 8±0.0 (p=0.002) | 7.75±0.25 (p=0.003) | 8±0.0 (p=0.002) | 8.2±0.25 (p=0.002) | 8±0.0 (p=0.050) |
| S. aureus | 8±0.0 (p=0.002) | 8±0.0 (p=0.002) | 8±0.0 (p=0.002) | 8±0.0 (p=0.003) | 8±0.0 (p=0.050) |
| S. capitis | 0±0.0 (p=0.002) | 6±0.0 (p=0.037) | 6±0.0 (p=0.037) | 7.2±0.25 (p=0.057) | 7.3±0.3 (p=0.002) |
| S. haemolyticus | 6±0.0 (p=0.015) | 6.6±0.3 (p=0.002) | 11±0.0 (p˂0.001) | 10±0.0 (p=0.001) | 11±0.0 (p˂0.001) |
| E. coli | 0±0.0 (p=0.050) | 0±0.0 (p=0.050) | 8±0.3 (p=0.006) | 8.3±0.3 (p=0.006) | 8±0.0 (p=0.002) |
| S. maltophilia | 0±0.0 (p=0.050) | 6.75±0.25 (p=0.003) | 7.5±0.25 (p=0.002) | 7.5±0.25 (p=0.003) | 7.8±0.28 (p=0.050) |
| L. adecarboxylata | 6.6±0.24 (p=0.003) | 9.2±0.48 (p=0.015) | 10.4±0.97 (p=0.016) | 10.5±0.95 (p=0.030) | 10±0.0 (p=0.002) |
| C. albicans | 7±0.0 (p˂0.001) | 7.75±0.25 (p=0.015) | 7.45±0.35 (p˂0.001) | 7.25±0.25 (p=0.050) | 7.3±0.3 (p˂0.001) |
| Almond oil | |||||
| S. intermedius | 8±0.0 (p=0.002) | 8±0.0 (p=0.002) | 8±0.0 (p=0.003) | 8±0.0 (p=0.015) | 7.3±0.3 (p˂0.001) |
| S. aureus | 8±0.0 (p=0.003) | 8±0.0 (p=0.001) | 8±0.0 (p=0.002) | 7.4±0.24 (p=0.001) | 7.5±0.25 (p=0.050) |
| S. capitis | 0±0.0 (p=0.001) | 6±0.0 (p=0.001) | 6±0.0 (p=0.001) | 7.5±0.3 (p=0.050) | 7.5±0.3 (p=0.050) |
| S. haemolyticus | 6±0.0 (p=0.002) | 6.6±0.3 (p=0.002) | 11±0.0 (p=0.015) | 10±0.0 (p=0.019) | 11.6±0.3 (p=0.002) |
| E. coli | 0±0.0 (p=0.050) | 0±0.0 (p=0.050) | 8±0.3 (p=0.050) | 8±0.0 (p=0.013) | 8±0.0 (p=0.050) |
| S. maltophilia | 0±0.0 (p=0.003) | 6.75±0.25 (p=0.003) | 7.75±0.25 (p=0.003) | 7.75±0.25 (p=0.003) | 8±0.0 (p=0.003) |
| L. adecarboxylata | 6.6±0.24 (p=0.002) | 9.2±0.48 (p=0.002) | 10±0.0 (p=0.003) | 10.4±0.97 (p=0.001) | 9.5±0.75 (p=0.002) |
| C. albicans | 0±0.0 (p˂0.001) | 0±0.0 (p˂0.001) | 7±0.0 (p=0.015) | 7.5±0.25 (p=0.050) | 7.5±0.25 (p˂0.001) |
| MICs and MBCs (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial/fungal isolates | Lettuce oil | Coconut oil | Almond oil | |||
| MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | |
| Gram-positive bacteria | ||||||
| S. intermedius | - | - | 25% | - | 6.25% | 12.5% |
| E. faecium | - | - | - | - | 3.125% | - |
| S. aureus | 12.5% | - | 12.5% | - | 25% | - |
| S. capitis | 50% | - | 25% | - | 6.25% | 12.5% |
| S. haemolyticus | - | - | 12.5% | - | 12.5% | - |
| Gram-negative bacteria | ||||||
| E. coli | 25% | - | 25% | - | - | - |
| C. freundii | 12.5% | - | - | - | 3.125% | 12.5% |
| C. braakii | 25% | - | - | - | 6.25% | 25% |
| S. maltophilia | 12.5% | - | 12.5% | - | - | - |
| L. adecarboxylata | 25% | 50% | 12.5% | - | 25% | - |
| Yeast | ||||||
| C. albicans | 50% | - | 6.25% | - | 25% | - |
| Concentrations of oils (%) and % of inhibition of biofilms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial/fungal biofilms | Inhibition of formation of the biofilms | Destruction of pre-formed biofilms | ||
| Inhibitory concentration of oil (%) | % of formation inhibition (%) | Destruction concentration of oil (%) | % of destruction (%) | |
| Lettuce oil | ||||
| E. faecium | - | - | 50 | 65±0.03 (p=0.001) |
| S. haemolyticus | - | - | 3.125 | 54±0.01 (p=0.003) |
| C. freundii | - | - | 12.5 | 56±0.003 (p=0.041) |
| C. braakii | - | - | 50 | 58±0.001 (p=0.004) |
| S. maltophilia | 3.125 | 31±0.02 (p=0.001) | 25 | 27±0.03 (p=0.001) |
| C. albicans | - | - | 50 | 65±0.03 (p=0.050) |
| Coconut oil | ||||
| S. intermedius | - | - | 12.5 | 51±0.01 (p=0.050) |
| E. faecium | - | - | 12.5 | 56±0.02 (p=0.038) |
| S. aureus | - | - | 25 | 21±0.02 (p=0.009) |
| S. capitis | - | - | 12.5 | 51±0.01 (p=0.001) |
| S. haemolyticus | 50 | 31±0.03 (p=0.032) | 6.25 | 64±0.02 (p˂0.001) |
| E. coli | 6.25 | 33±0.0006 (p=0.004) | - | - |
| C. freundii | - | - | 50 | 42±0.001 (p=0.011) |
| C. braakii | - | - | 3.125 | 58±0.02 (p=0.008) |
| S. maltophilia | 6.25 | 67±0.01 (p˂0.001) | 25 | 53±0.003 (p=0.003) |
| L. adecarboxylata | - | - | 3.125 | 42±0.03 (p=0.015) |
| C. albicans | 3.125 | 59±0.02 (p˂0.001) | 12.5 | 51±0.01 (p=0.013) |
| Compound name | Molecular formula | Molecular weight | Relative abundance (%) | Retention time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lettuce oil [index value: HG-30/390] | ||||
| (E)-9-Tetradecen-1-ol | C12H28O | 212 | 32.99 | 7.10 |
| 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, dibutyl ester | C16H22O4 | 278 | 33.06 | 13.28 |
| Hexadecanoic acid | C16H32O2 | 256 | 78.85 | 14.19 |
| Oleic acid, methyl ester | C19H36O2 | 296 | 78.12 | 15.93 |
| Rescinnamine | C35H42N12O9 | 634 | 19.04 | 24.35 |
| Palmitic acid, butyl ester | C20H40O2 | 312 | 7.14 | 24.71 |
| Cholest-5-en-3-ol | C27H46O | 386 | 38.14 | 25.91 |
| Coconut oil [index value: HG-30/306] | ||||
| Myristic acid | C14H28O | 228 | 86.22 | 12.5 |
| Hexadecanoic acid | C16H32O2 | 256 | 79.91 | 14.18 |
| Ricinoleic acid | C18H34O3 | 298 | 20.74 | 15 |
| Hexadecanoic acid, butyl ester | C20H40O2 | 312 | 57.24 | 15.41 |
| Oleic acid, methyl ester | C19H36O2 | 296 | 86.17 | 15.87 |
| Palmitic acid, butyl ester | C18H36O2 | 284 | 86.59 | 20.94 |
| Rescinnamine | C35H42N2O9 | 634 | 8.94 | 25.71 |
| Hydrocortisone 21-acetate | C23H32O6 | 404 | 44.20 | 26.14 |
| Myristic acid, tetradecyl ester | C28H56O2 | 424 | 25.01 | 28.56 |
| Almond oil [index value: HG-30/308] | ||||
| Hexadecanoic acid | C16H32O2 | 256 | 72.13 | 14.27 |
| Oleic acid, methyl ester | C19H36O2 | 296 | 95.36 | 18.55 |
| Stearic acid | C18H36O2 | 284 | 86.38 | 16.24 |
| Palmitin, 1-mono- | C19H38O4 | 330 | 82.78 | 17 |
| Digitoxin | C41H64O13 | 764 | 82.53 | 20.21 |
© GERMS 2022.
Share and Cite
Mezher, M.; El Hajj, R.; Khalil, M. Investigating the Antimicrobial Activity of Essential Oils Against Pathogens Isolated from Sewage Sludge of Southern Lebanese Villages. Germs 2022, 12, 488-506. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1355
Mezher M, El Hajj R, Khalil M. Investigating the Antimicrobial Activity of Essential Oils Against Pathogens Isolated from Sewage Sludge of Southern Lebanese Villages. Germs. 2022; 12(4):488-506. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1355
Chicago/Turabian StyleMezher, Malak, Rana El Hajj, and Mahmoud Khalil. 2022. "Investigating the Antimicrobial Activity of Essential Oils Against Pathogens Isolated from Sewage Sludge of Southern Lebanese Villages" Germs 12, no. 4: 488-506. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1355
APA StyleMezher, M., El Hajj, R., & Khalil, M. (2022). Investigating the Antimicrobial Activity of Essential Oils Against Pathogens Isolated from Sewage Sludge of Southern Lebanese Villages. Germs, 12(4), 488-506. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1355




