Abstract
Introduction: This study aimed to identify factors associated with self-medication in patients with COVID-19. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted using medical records of patients with COVID-19 who self-medicated before admission to a hospital in Piura, Peru. Prevalence ratios and 95% confidence intervals were estimated using generalized linear models with Poisson distribution family, log link function, and robust variance. Results: Out of 301 patients, 165 (54.8%) self-medicated before hospital admission, being more frequent self-medication with ivermectin (85.5%) and azithromycin (71.5%). The frequency of self-medication in those aged between 30–59 years was 2.53-fold higher than in those between 18–29 years. Male patients, dyslipidemia, smoking, and hepatic steatosis were associated with self-medication. Clinical characteristics associated with self-medication were fever, cough, headache, anosmia, dysgeusia, nausea/vomiting, and gastroesophageal reflux. Conclusions: A high frequency of self-medication before hospital admission was observed in Peruvian patients with COVID-19, mainly of drugs without proven efficacy.
Introduction
On 11 March 2020, COVID-19 was classified as a pandemic by the World Health Organization, after cases were confirmed in 114 countries [1]. The first wave of the pandemic reached Peru in mid-March, and it has become one of the most affected countries, showing unprecedented mortality rates [2,3]. In particular, Piura was the third most affected region in the country, with 13799 cases and up to 88 deaths per day in June 2020 [4].
Individuals with COVID-19 mostly develop mild symptoms (such as fever, cough, and shortness of breath) [5,6]. However, disease may be aggravated by complications, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), acute liver injury, acute kidney injury, and sepsis, which can lead to death [7]. By mid-2021, post-exposure prophylaxis or treatment with monoclonal antibodies has been recommended for mild-moderate outpatient cases with high risk of disease progression [8]. However, in the first wave of the pandemic, Peru opted to treat patients with COVID-19 with hydroxychloroquine, ivermectin, and azithromycin alone or in combination [9]. These drugs were subsequently discarded because they showed no benefits and even higher risk when combined [10].
Self-medication is a bad practice that represents a public health problem worldwide [11], which can lead to overdose, adverse reactions, masking symptoms/signs of disease and other health problems [11]. A study found that half of all consumers in pharmacies and drugstores in Peru self-medicate, mainly young uninsured males [12]. The most commonly used drugs were non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and antibiotics [12].
Due to the current COVID-19 pandemic, self-medication practices may increase, but this is more evident with healthcare collapse and fear of contagion [13]. This together with social restrictions may raise anxiety levels in the population and therefore make them more prone to self-medication [14,15].
Some studies have studied self-medication for prevention or treatment of COVID-19 [14,16,17,18] without taking into account factors associated with self-medication or inclusion of hospitalized patients. So far in Peru a study has evaluated practices of self-medication during the pandemic; however, adults not necessarily presenting infection were included [18]. Therefore, we aimed to determine the prevalence and factors associated with self-medication for COVID-19 treatment in hospitalized patients from a hospital in northern Peru.
Methods
Study design
A cross-sectional study was conducted to identify potential factors associated with self-medication in patients with COVID-19 treated at the Cayetano Heredia Hospital, Piura-Peru, during the period from May to June 2020.
Population and sample
The population were patients hospitalized in COVID-19 areas of the Cayetano Heredia Hospital (hospitalization service and adult intensive care unit) who self-medicated before admission. Patients over 18 years of age who had a confirmatory diagnosis of COVID-19 with at least one serological (immunochromatography, chemiluminescent immunoassay) or molecular (qRT-PCR) reactive test were included. Patients with incomplete clinical or laboratory information were excluded from the analysis of this investigation.
A sample size of 242 individuals was calculated to identify a self-medication prevalence of 33.4% [18] with a precision of 5% and confidence level of 95%. Assuming a 30% loss, we estimated a total sample size of 346 patients.
Procedure
Authorization was requested from the Cayetano Heredia Hospital. Then, a data collection form was designed and used from the beginning of hospitalization of the COVID-19 patient until discharge, death, or referral of the patient to another health institution. Epidemiological, clinical and self-medication history data were collected and entered into a database designed in Microsoft Excel 2016.
Instrument and variables
The data collection form consisted of general and clinical data. Epidemiological data such as sex, age (categorized in young: 18–29 years, middle aged: 30–59 years, and older: >60 years), and self-medication were evaluated in this form. In the clinical section, information was collected on body mass index, symptoms, and presence of comorbidities (diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, heart disease, smoking, hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), hepatic steatosis, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcer, cirrhosis, cancer, chronic kidney disease, and pulmonary tuberculosis).
The dependent variable was the self-report of having self-medicated for COVID-19, operationally defined as having received any medication without a physician’s indication. The independent variables were general and clinical characteristics detailed above.
Data analysis
Statistical analysis was performed in Stata version 15.0 (StataCorp, USA). In the descriptive analysis, absolute and relative frequencies were reported for categorical variables.
In bivariate analysis, factors associated with self-medication were investigated using the chi-square test. A significance level of 5% was used.
For simple and multiple regression analysis, prevalence ratios (PR) with 95% confidence intervals were estimated. Generalized linear models of the Poisson distribution family, log link function, and robust variances were used. For the inclusion of variables in the adjusted model, a forward stepwise selection was applied.
Ethical aspects
The study was authorized by the ethics committee of Cayetano Heredia Hospital, Piura, with code 0324-034-20CEI. Informed consent was waived since data were collected from medical records. Patient confidentiality was maintained, using anonymized codes in the database.
Results
A total of 311 medical records of patients hospitalized for COVID-19 were collected. Ten records (3.2%) were excluded due to missing clinical (n=8) or laboratory (n=2) information. The resulting sample for analysis was 301 patients.
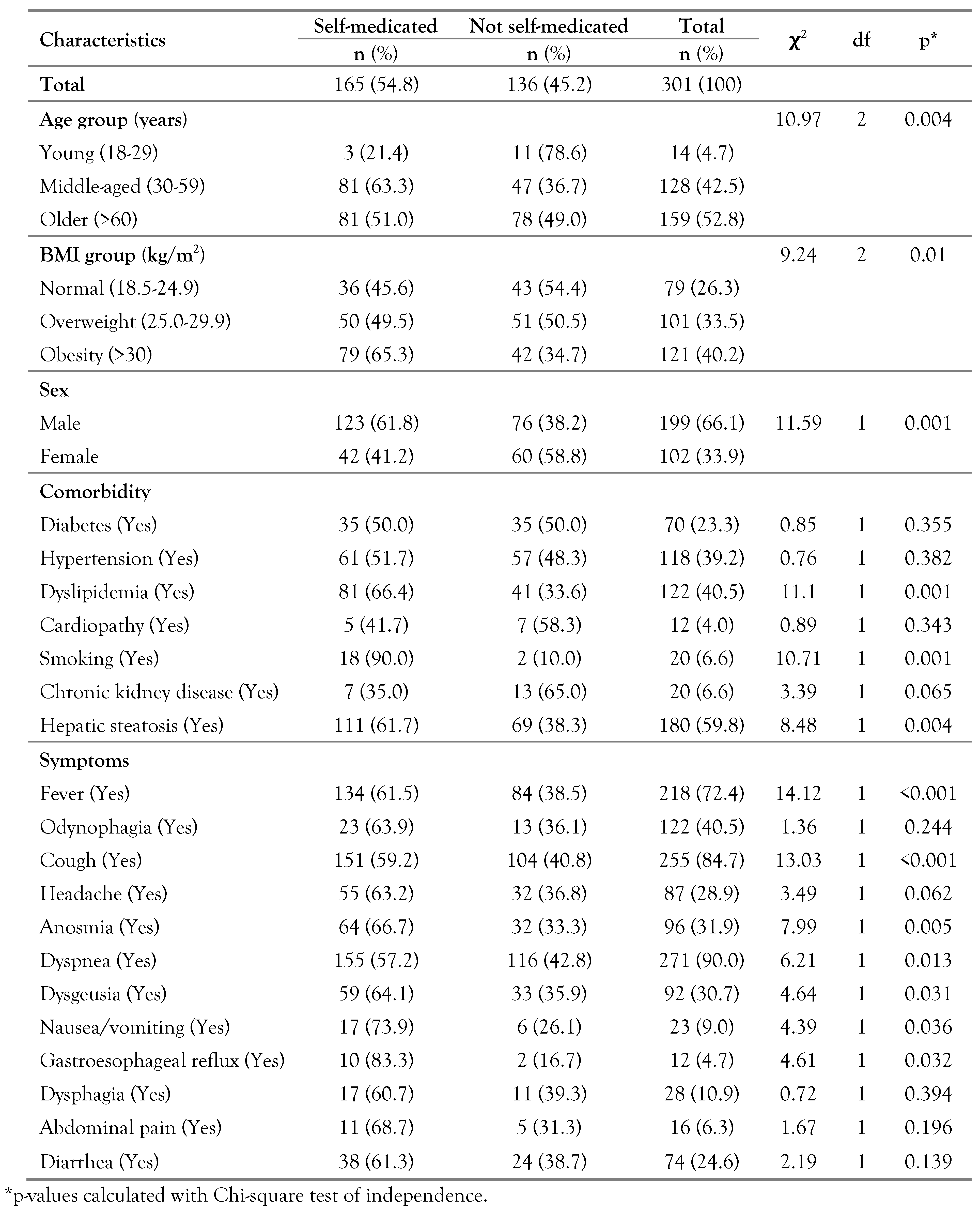
The mean age was 58.6±16.4 years and 66.1% were male. The median length of in-hospital stay was 9 days (IQR: 6–15). Of the total number of patients, 165 (54.8%) had self-medicated before admission, the most frequent self-medication being with ivermectin (85.5%), followed by azithromycin (71.5%), corticosteroids (46.7%), and NSAIDs (31.5%)—Table 1.

Table 1.
Clinical-epidemiological comparison of self-medication before admission in patients hospitalized for COVID-19 in a hospital in northern Peru.
In the bivariate analysis, it was found that middle-aged and older adults presented a higher frequency of self-medication than young adults (63.3% and 51%, respectively, vs. 21.4%; p=0.004). Males presented a higher frequency of self-medication than females (61.8% vs. 41.2%; p=0.001). With respect to comorbidities, it was found that patients with a diagnosis of dyslipidemia, smoking and hepatic steatosis presented a higher frequency of self-medication than those who did not present these comorbidities.
Among the patients who self-medicated, 61.5% presented symptoms of fever, 59.2% cough, 66.7% anosmia and 57.2% dyspnea—Table 1.
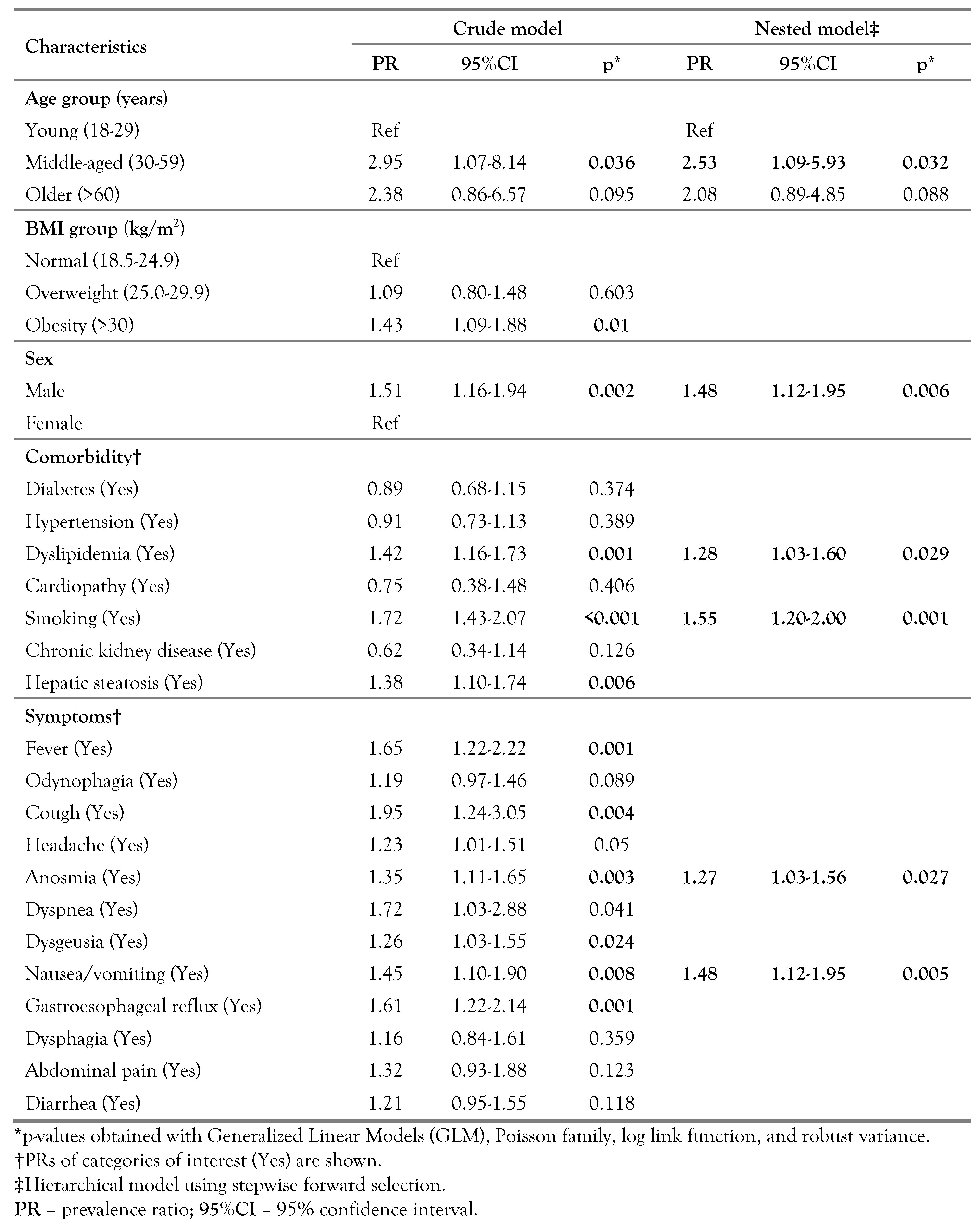
In the simple regression analysis, the frequency of self-medication in middle-aged adults was 2.95-fold higher than observed in young adults (PR: 2.95; p=0.036). Male sex (PR: 1.51; p=0.002), dyslipidemia (PR: 1.42; p=0.001), smoking (PR: 1.72; p<0.001), and hepatic steatosis (PR: 1.38; p=0.006) were associated with self-medication. Clinical features associated with self-medication were fever, cough, headache, anosmia, dysgeusia, nausea/vomiting, and gastroesophageal reflux.
In the multivariate model, it was observed that adult age (PR: 2.53; p=0.032), male sex (PR: 1.48; p=0.006), dyslipidemia (PR: 1.28; p=0.029), smoking (PR: 1.55; p=0.001), anosmia (PR: 1.27; p=0.027), and the presence of nausea/vomiting (PR: 1.48; p=0.005) were associated with self-medication—Table 2.

Table 2.
Association of clinical-epidemiological characteristics with self-medication before admission in patients hospitalized for COVID-19 in a hospital in northern Peru.
Discussion
Our research found that the frequency of self-medication for COVID-19 treatment was 54.8%. Additionally, factors associated with self-medication for COVID-19 treatment were: being an adult, being male, having dyslipidemia, smoking, having anosmia, and nausea/vomiting.
Self-medication for COVID-19 treatment in this study was 54.8%. Studies of similar designs have found higher and lower values of self-medication for COVID-19 treatment [12,17,18]. This research reported a higher prevalence than found in a cross-sectional study [18]. However, its main limitation was that the survey was conducted through social networks, excluding an important part of the study population that may or may not have been infected.
In addition, the frequency of self-medication was lower than reported in a study conducted through the National Health Services User Satisfaction Survey [12]. This difference may exist because participants from the latter were customers of pharmacies or drugstores surveyed after making a purchase for their own use and were therefore more likely to self-medicate. Furthermore, it is minimally lower than reported in a study conducted in Kenya; however, its sample only included health professionals, and the increase in the prevalence of self-medication after the COVID-19 pandemic was evident [17].
Our estimated high frequency of self-medication could be due to the diffusion of various allegedly curative drugs throughout the pandemic [19], as well as the fear of going to medical centers as a way to avoid contagion [20].
Studies on self-medication affirm that it is a very common practice, especially in economically disadvantaged communities, with a higher use by men, over 40 years of age, and with a moderate level of occupational activity [11,21]. In our study, the frequency of self-medication in middle-aged adults was found to be 2.53-fold higher than in young adults, and males were 48% more likely to self-medicate than females. This has been reported in a previous study in Peru, where older respondents were found to have a higher frequency of antiretroviral self-medication (aPR: 1.07; 95%CI: 1.00–1.14; p=0.043) [18]. It is also a common practice in Peru: a survey [22] showed a frequency of 56.5%, with higher values in males (51.3%), mostly suggested by the user himself (49.1%) and by family members (21.7%), with pain as the main symptom for self-medication (40.4%).
Having a history of dyslipidemia and smoking represented a 28% and 55% higher frequency of self-medication compared with those without such history. This finding is similar to a study of self-medication in chronic smokers, which found that all participants acquired nicotine preparations without prescription to quit smoking and 94% of them abandoned this practice after one month due to unsatisfactory results [23].
In the bivariate analysis, patients with fever, cough, anosmia, dysgeusia, nausea/vomiting, or GERD were more likely to report self-medication compared with those without these symptoms. Self-reported knowledge of the difference between viral and bacterial infections was found to be positively associated with taking antibiotics (OR: 1.16; p=0.028) [14]. Antibiotic takers believed they were more knowledgeable than non-antibiotic takers. People using antibiotics for COVID-19 also reported that antibiotics can treat influenza (50.7%), compared with those who did not take antibiotics (30.1%) [14]. On the other hand, symptoms such as cough, fever, anosmia, and dysgeusia are the most frequent symptoms reported in COVID-19 [24]. However, in our final model only anosmia and nausea/vomiting were associated with self-medication. This finding is similar to a study that found that 31% of patients with gastroenteritis resorted to self-medication at least once (antiemetics, antidiarrheals, or oral rehydration therapy); furthermore, cases with vomiting and diarrhea were 3.6-fold more likely to use at least one of the three over-the-counter medications than cases with vomiting or diarrhea only [25].
The findings of this research are relevant because self-medication is among the main risk factors for the aggravation of COVID-19 and the late arrival of patients at hospitals. In addition to these, some drugs without proven clinical efficacy generate a false sense of security in the population, which could lead to non-compliance with basic preventive health measures.
This study has important limitations. Data were collected from a single care center and the number of patients was limited. Therefore, it has a potential selection bias. In addition, there is a risk of measurement bias because it was not possible to measure other variables such as type of self-prescription and time that patients self-medicated with each type of drug.
However, our results represent an important basis for knowing how frequent self-medication is in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and what characteristics increase their behavior. In this manner, the information may be useful to promote the responsible use of medications, especially in population affected by the pandemic. Also, the study included a wide range of ages and comorbidities.
Conclusions
A high frequency of self-medication was observed in Peruvian patients hospitalized for COVID-19, mainly with drugs of unproven efficacy. Adult age, male sex, dyslipidemia, smoking, anosmia, and nausea/vomiting were factors associated with self-medication.
Author Contributions
LEVE: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Writing—original draft. VEFR: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Writing—original draft. RNMR: Visualization, Investigation, Supervision, Writing—review & editing. NMA: Visualization, Investigation, Supervision, Writing—review & editing. MSTR: Visualization, Investigation, Supervision, Writing—review & editing. MJVG: Methodology, Supervision, Software, Validation, Writing—review & editing. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
None to declare.
Conflicts of interest
All authors—none to declare.
References
- World Health Organization. 2020. Alocución de apertura del Director General de la OMS en la rueda de prensa sobre la COVID-19 celebrada el 11 de marzo de 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---11-march-2020 (accessed on 26 August 2020).
- Centro Nacional de Epidemiología, Prevención y Control de Enfermedades. 2020. Available online: https://www.dge.gob.pe/portal/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=678 (accessed on 26 August 2020).
- World Health Organization. 2020. WHO Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int (accessed on 28 August 2020).
- El Comercio Perú. 2020. ¿Cuánto han aumentado los casos de COVID-19 en Piura? Available online: https://elcomercio.pe/peru/cuanto-han-aumentado-los-casos-de-covid-19-en-piura-noticia/ (accessed on 22 December 2021).
- Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Dong, X.; et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet 2020, 395, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, M.; Hussein, M.H.; Attia, A.S.; et al. COVID-19 and liver dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis of retrospective studies. J Med Virol. 2020, 92, 1825–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institutes of Health. COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel. 2020 coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) treatment guidelines. Available online: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/ (accessed on 29 September 2021).
- Ministerio de Salud. 2020. Resolución Ministerial N° 270-2020-MINSA—Prevención, Diagnóstico y Tratamiento de personas afectadas por COVID-19. Available online: https://cdn.www.gob.pe/uploads/document/file/694719/RM_270-2020-MINSA.PDF (accessed on 14 April 2021).
- Soto-Becerra, P.; Culquichicón, C.; Hurtado-Roca, Y.; Araujo-Castillo, R.V. Real-world effectiveness of hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin, and ivermectin among hospitalized COVID-19 patients: Results of a target trial emulation using observational data from a nationwide healthcare system in Peru. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennadi, D. Self-medication: A current challenge. J Basic Clin Pharm. 2013, 5, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urrunaga-Pastor, D.; Benites-Zapata, V.A.; Mezones-Holguín, E. Factors associated with self-medication in users of drugstores and pharmacies in Peru: An analysis of the National Survey on User Satisfaction of Health Services, ENSUSALUD 2015. F1000Res 2019, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faqihi, A.H.M.A.; Sayed, S.F. Self-medication practice with analgesics (NSAIDs and acetaminophen), and antibiotics among nursing undergraduates in University College Farasan Campus, Jazan University, KSA. Ann Pharm Fr. 2021, 79, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Hobman, E.V.; De Barro, P.; Young, A.; Carter, D.J.; Byrne, M. Self-medication with antibiotics for protection against COVID-19: The role of psychological distress, knowledge of, and experiences with antibiotics. Antibiotics (Basel) 2021, 10, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, R.P. COVID-19 and mental health: A review of the existing literature. Asian J Psychiatr. 2020, 52, 102066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansuri, F.M.A.; Zalat, M.M.; Khan, A.A.; Alsaedi, E.Q.; Ibrahim, H.M. Estimating the public response to mitigation measures and self-perceived behaviours towards the COVID-19 pandemic. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2020, 15, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onchonga, D.; Omwoyo, J.; Nyamamba, D. Assessing the prevalence of self-medication among healthcare workers before and during the 2019 SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) pandemic in Kenya. Saudi Pharm J. 2020, 28, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quispe-Cañari, J.F.; Fidel-Rosales, E.; Manrique, D.; et al. Self-medication practices during the COVID-19 pandemic among the adult population in Peru: A cross-sectional survey. Saudi Pharm J. 2021, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huaroto, F.; Reyes, N.; Huamán, K.; et al. Intervenciones farmacológicas para el tratamiento de la Enfermedad por Coronavirus (COVID-19). An Fac Med. 2020, 81, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, E.; Savastano, S. Fear of contagion: One of the most devious enemies to fight during the COVID-19 pandemic. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2021, 15, e8–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaraj, K.; Kumar, S.G.; Ramalingam, A. Prevalence of self-medication practices and its associated factors in Urban Puducherry, India. Perspect Clin Res. 2014, 5, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermoza-Moquillaza, R.; Loza-Munarriz, C.; Rodríguez-Hurtado, D.; Arellano-Sacramento, C.; Hermoza-Moquillaza, V. Automedicación en un distrito de Lima Metropolitana, Perú. Revista Medica Herediana. 2016, 27, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kałucka, S. [Self-medication in smoking cessation among smokers]. Przegl Lek. 2015, 72, 522–525. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alimohamadi, Y.; Sepandi, M.; Taghdir, M.; Hosamirudsari, H. Determine the most common clinical symptoms in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Prev Med Hyg. 2020, 6, E304–E312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frosst, G.O.; Majowicz, S.E.; Edge, V.L. Factors associated with the use of over-the-counter medications in cases of acute gastroenteritis in Hamilton, Ontario. Can J Public Health 2006, 97, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© GERMS 2022.