Association of Hiccup and SARS-CoV-2 Infection with the Administration of Dexamethasone: A Case Report
Abstract
Introduction
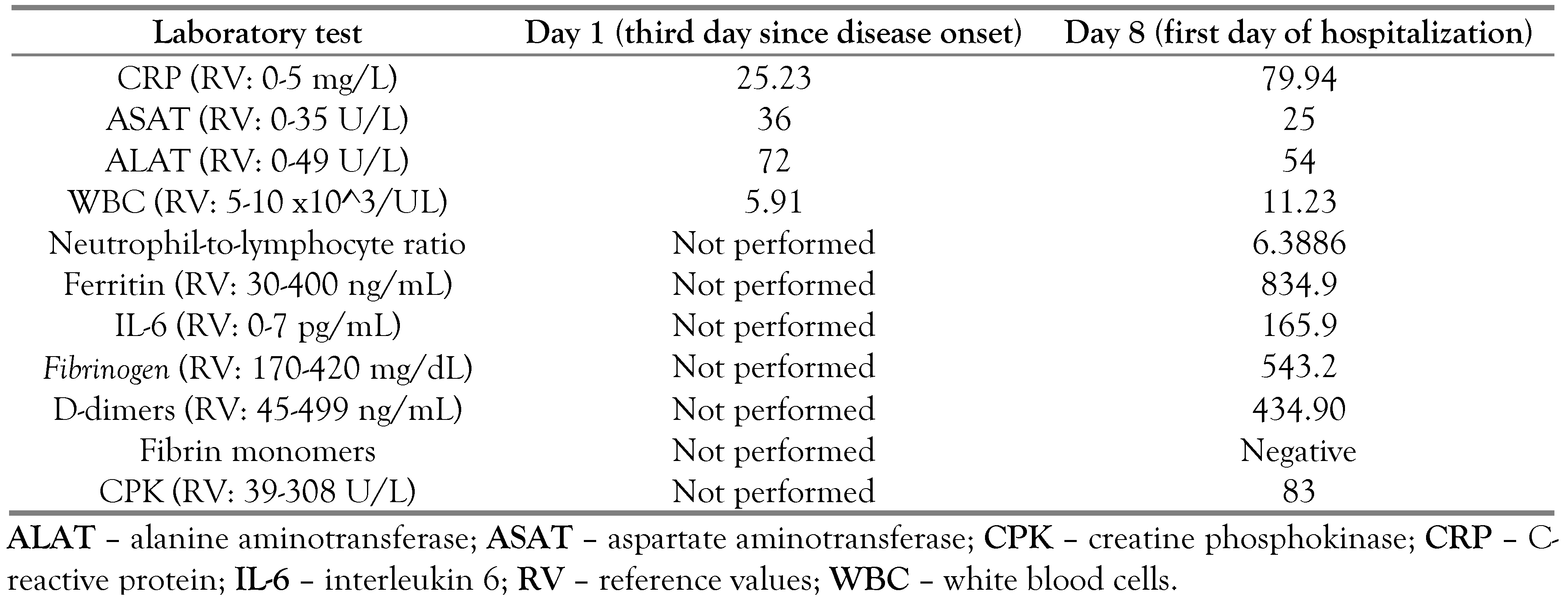
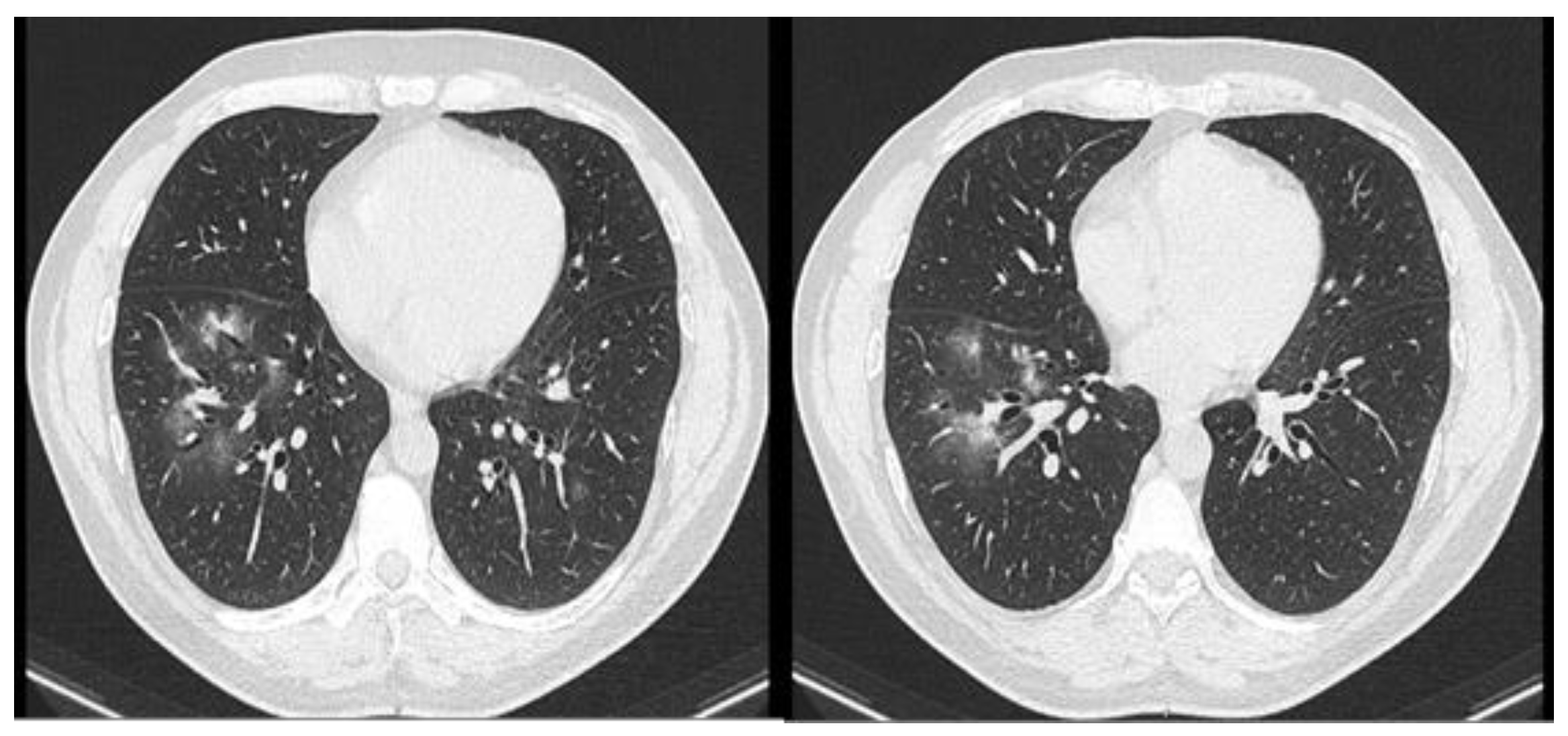
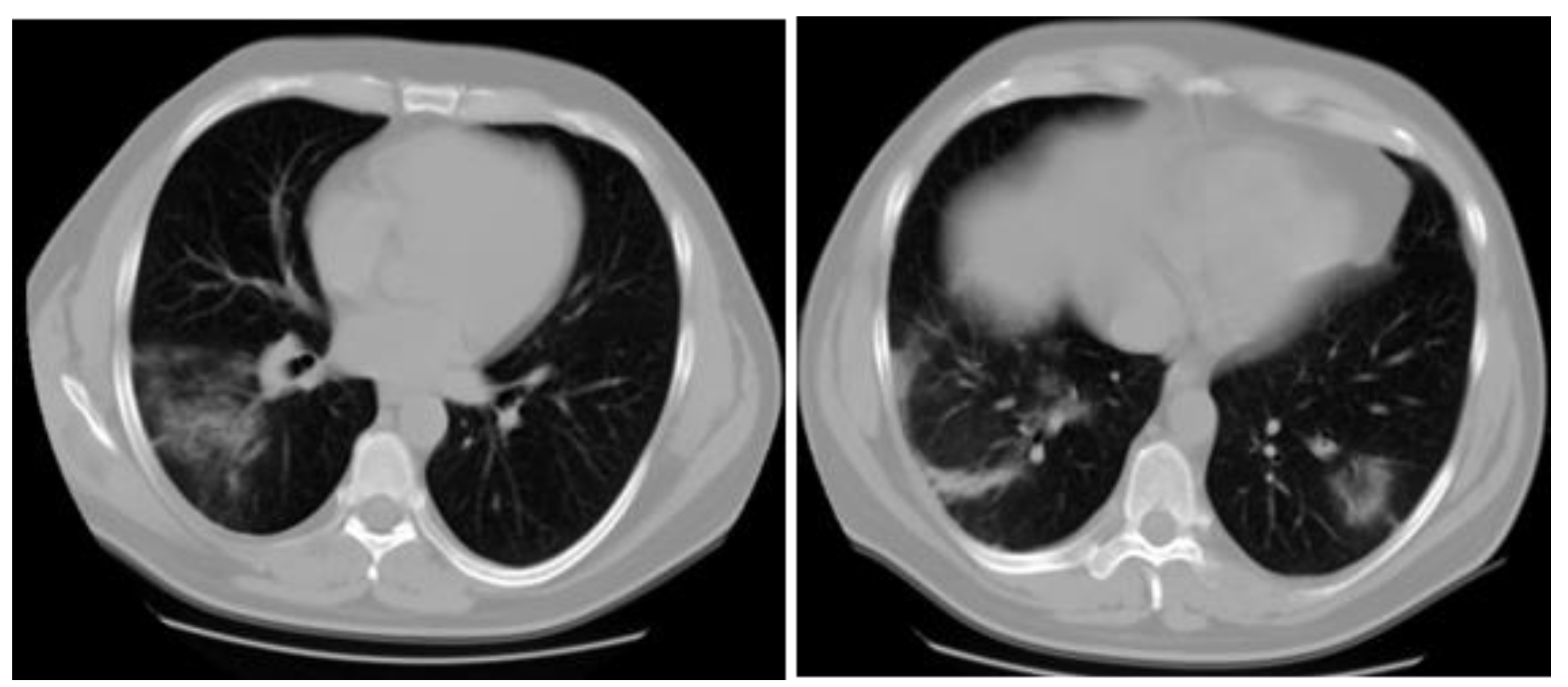
Case report
 |
Discussion
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of interest
References
- Birlutiu, V.; Birlutiu, R.M.; Feiereisz, A.I. SARS-CoV-2 infection associated with micturition syncope: Our experience with 4 case reports. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020, 99, e21512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Sánchez, F.J.; Del Toro, E.; Cardassay, E.; et al. Clinical presentation and outcome across age categories among patients with COVID-19 admitted to a Spanish Emergency Department. Eur Geriatr Med. 2020, 11, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Hanna, J.; Walsh, E.E.; Falsey, A.R.; Laguio-Vila, M.; Lesho, E. Syncope, near syncope, or nonmechanical falls as a presenting feature of COVID-19. Ann Emerg Med. 2020, 76, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iancu, G.M.; Solomon, A.; Birlutiu, V. Viral exanthema as manifestation of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020, 99, e21810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recalcati, S. Cutaneous manifestations in COVID-19: A first perspective. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020, 34, e212–e213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, G.; Moltrasio, C.; Berti, E.; Marzano, A.V. Skin manifestations associated with COVID-19: Current knowledge and future perspectives. Dermatology. 2021, 237, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birlutiu, V.; Feiereisz, A.I.; Oprinca, G.; et al. Cutaneous manifestations associated with anosmia, ageusia and enteritis in SARS-CoV-2 infection—A possible pattern? Observational study and review of the literature. Int J Infect Dis. 2021, 107, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, G.; Sergel, M. Persistent hiccups as an atypical presenting complaint of COVID-19. Am J Emerg Med. 2020, 38, 1546.e5-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budrewićz, S.; Góral, M.; Podemski, R. [Pathophysiology and treatment of hiccup]. Przegl Lek. 2002, 59, 924–926. [Google Scholar]
- Bryer, E.; Bryer, J. Persistent postoperative hiccups. Case Rep Anesthesiol. 2020, 2020, 8867431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsanious, D.; Khoury, S.; Martinez, E.; et al. Ultrasound-guided phrenic nerve block for intractable hiccups following placement of esophageal stent for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Pain Physician. 2016, 19, E653–E656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krysiak, W.; Szabowski, S.; Stepień, M.; Krzywkowska, K.; Krzywkowski, A.; Marciniak, P. Hiccups as a myocardial ischemia symptom. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2008, 118, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyukhatipoglu, H.; Sezen, Y.; Yildiz, A.; Kucukdurmaz, Z.; Faruk, O. Hiccups as a sign of chronic myocardial ischemia. South Med J. 2010, 103, 1184–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Zhang, B.; Song, L.; Yao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, M. Acute proximal left anterior descending thrombosis manifested by persistent hiccups: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019, 98, e18096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassen, G.W.; Singh, M.M.; Kalantari, H.; Yemane-Merriwether, S.; Ferrante, S.; Shaw, R. Persistent hiccups as a rare presenting symptom of pulmonary embolism. West J Emerg Med. 2012, 13, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launois, S.; Bizec, J.L.; Whitelaw, W.A.; Cabane, J.; Derenne, J.P. Hiccup in adults: An overview. Eur Respir J. 1993, 6, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakheet, N.; Fouad, R.; Kassem, A.M.; Hussin, W.; El-Shazly, M. Persistent hiccup: A rare presentation of COVID-19. Respir Investig. 2021, 59, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorgalaleh, A.; Dabbagh, A.; Tabibian, S.; Bahraini, M.; Rafieemehr, H. Persistent hiccups in a patient with mild congenital factor V deficiency and COVID-19; clinical and laboratory finding of a rare bleeding disorder. Int J Lab Hematol. 2021, 43, e87–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.W.; Oh, S.Y.; Kang, M.H.; et al. Treatment of dexamethasone-induced hiccup in chemotherapy patients by methylprednisolone rotation. Oncologist. 2013, 18, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.H.; Hui, D.; Kim, M.J.; et al. Corticosteroid rotation to alleviate dexamethasone-induced hiccup: A case series at a single institution. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2012, 43, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.C.; Yu, C.J.; Chang, S.C.; et al. Pulmonary sequelae in convalescent patients after severe acute respiratory syndrome: Evaluation with thin-section CT. Radiology. 2005, 236, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© GERMS 2022.
Share and Cite
Bîrluţiu, V.; Şofariu, C.R. Association of Hiccup and SARS-CoV-2 Infection with the Administration of Dexamethasone: A Case Report. Germs 2022, 12, 107-111. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1312
Bîrluţiu V, Şofariu CR. Association of Hiccup and SARS-CoV-2 Infection with the Administration of Dexamethasone: A Case Report. Germs. 2022; 12(1):107-111. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1312
Chicago/Turabian StyleBîrluţiu, Victoria, and Ciprian Radu Şofariu. 2022. "Association of Hiccup and SARS-CoV-2 Infection with the Administration of Dexamethasone: A Case Report" Germs 12, no. 1: 107-111. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1312
APA StyleBîrluţiu, V., & Şofariu, C. R. (2022). Association of Hiccup and SARS-CoV-2 Infection with the Administration of Dexamethasone: A Case Report. Germs, 12(1), 107-111. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2022.1312




