Antibiotic Resistance Pattern of Pseudomonas spp. from Patients in a Tertiary Hospital in South-West Nigeria
Abstract
Introduction
Methods
Study Area, Sample Size and Ethical Approval
Isolates Collection and Characterization
Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing
DNA Extraction
Identification of Pseudomonas spp. and Pseudomonas aeruginosa by PCR
Data Analysis
Results
Discussion
Conclusions
Funding
Authors’ Contributions Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wisplinghoff, H. Pseudomonas spp., Acinetobacter spp. and miscellaneous Gram-negative bacilli. In Infectious Diseases, 4th ed.; Cohen, J., Powderly, W.G., Opal, S.M., et al., Eds.; Elsevier, 2017; pp. 1579–1599.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachori, P.; Gothalwal, R.; Gandhi, P. Emergence of antibiotic resistance Pseudomonas aeruginosa in intensive care unit; a critical review. Genes Dis. 2019, 6, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, G.; Kapil, A.; Kabra, S.K.; Das, B.K.; Dwivedi, S.N. Characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from chronically infected children with cystic fibrosis in India. BMC Microbiol. 2005, 5, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Hassan, A.A.I.; Jarir, S.; et al. Emergence of multidrug-and pandrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa from five hospitals in Qatar. Infect Prev Pract. 2019, 1, 100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, S.; Oberhettinger, P.; Schuele, L.; et al. Genomic characterisation of clinical and environmental Pseudomonas putida group strains and determination of their role in the transfer of antimicrobial resistance genes to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Genomics. 2017, 18, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, H.A.; Ahmad, A.; Mehboob, R. Nosocomial infections and their control strategies. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2015, 5, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dahmoshi, H.; Al-Obaidi, R.D.; Al-Khafaji, N. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Diseases, biofilm and antibiotic resistance. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biofilm Formation, Infections and Treatments; Das, T., Ed.; IntechOpen, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheesbrough, M. District Laboratory Practice in Tropical Countries. Part 2, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 2006; pp. 319–329. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 27th ed.; CLSI supplement M100; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Krumperman, P.H. Multiple antibiotic resistance indexing of Escherichia coli to identify high-risk sources of fecal contamination of foods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983, 46, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spilker, T.; Coenye, T.; Vandamme, P.; LiPuma, J.J. PCR-based assay for differentiation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from other Pseudomonas species recovered from cystic fibrosis patients. J Clin Microbiol. 2004, 42, 2074–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, N.; Goel, A.K.; Lukka, H.; Bhattacharya, P.; Kamboj, D.V. Prevalence of drug resistant and exotoxin A producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cutaneous infections in a tribal area in South India. Afr J Microbiol Res. 2011, 5, 5512–5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglewski, B.H. Pseudomonas. In Medical Microbiology, 4th ed.; University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Gad, G.F.; El-Domany, R.A.; Zaki, S.; Ashour, H.M. Characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from clinical and environmental samples in Minia, Egypt: Prevalence, antibiogram and resistance mechanisms. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007, 60, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, S.; Amatya, R.; Adhikari, R.P. Prevalence and antibiogram of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from clinical specimens in a Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu. Int J Infect Dis. 2016, 45, 115–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okon, K.; Agukwe, P.; Oladosu, W.; Balogun, S.; Uba, A. Antibiotic resistance pattern of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from clinical specimens in a tertiary hospital in northeastern Nigeria. Internet J Microbiol. 2009, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Appiah-Korang, L.; Asare-Gyasi, S.; Yawson, A.E.; Searyoh, K. Aetiological agents of ear discharge: A two year review in a teaching hospital in Ghana. Ghana Med J. 2014, 48, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Umar, A.I.; Garba, I.; Jidda, M.L.; et al. Multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from ear and wound swabs in some selected hospital laboratories in Sokoto Metropolis, Nigeria. Calabar J Health Sci. 2020, 3, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peshattiwar, P.D.; Peerapur, B.V. ESBL and MBL mediated resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: An emerging threat to clinical therapeutics. J Clin Diagn Res. 2011, 5, 1552–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, I.; Arzai, A.H.; Haruna, M.; Sharif, A.A.; Mi, G. Detection of multi drug resistant bacteria in major hospitals in Kano, North-West, Nigeria. Braz J Microbiol. 2014, 45, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adejuyigbe, E.A.; Adeodu, O.O.; Ako-Nai, K.A.; Taiwo, O.; Owa, J.A. Septiceamia in high risk neonates at a teaching hospital in Ile-Ife, Nigeria. East Afr Med J. 2001, 78, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oluranti, O.O.; Ubanagu, C.I.; Oluwasemowo, O.O.; Akinola, O.T.; Nejo, Y.T.; Motayo, B.O. Prevalence and antibiotic resistance profile of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from hospital sinks in South Western Nigeria. J Adv Med Med Res. 2019, 29, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Igbalajobi, O.A.; Oluyege, A.O.; Oladeji, A.C.; Babalola, J.A. Antibiotic resistance pattern of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from clinical samples in Ekiti State University Teaching Hospital, Ado-Ekiti, Ekiti State of Nigeria. Br Microbiol Res J. 2016, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iduh, U.M.; Chollom, C.S.; Nuhu, A.; et al. Nosocomial infections in post-operative wounds due to Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Benue State Nigeria. Afr J Microbiol Res. 2015, 9, 1989–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
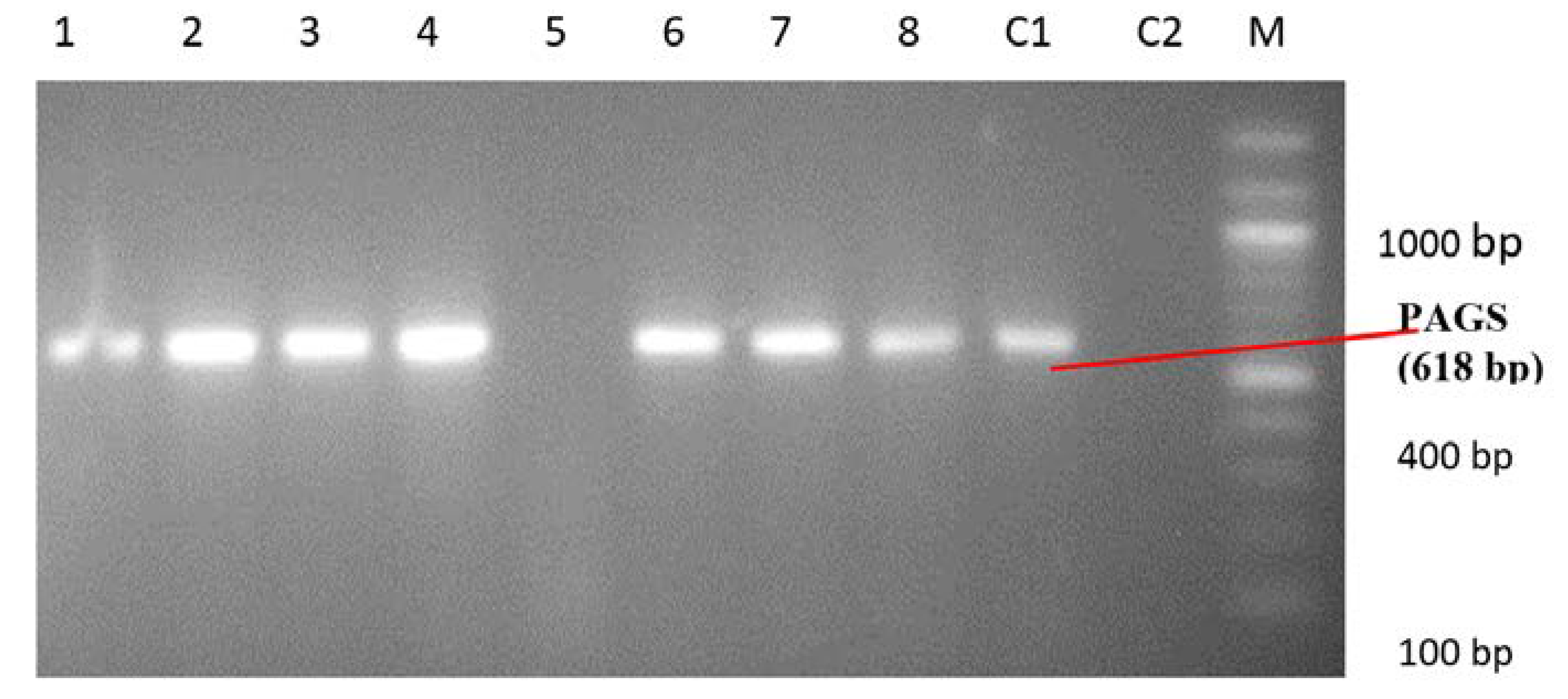
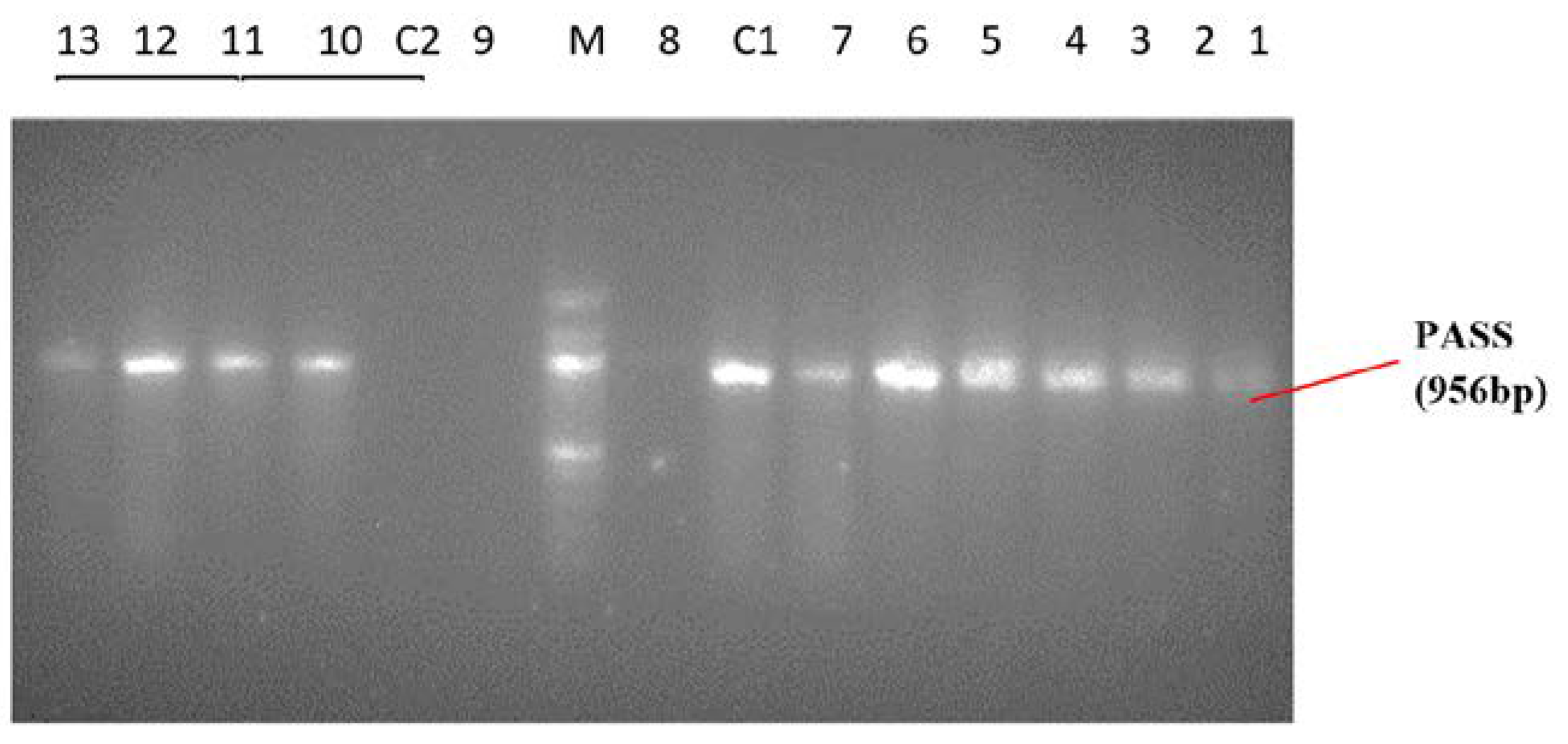
| Parameter | No of Pseudomonas spp. Isolated (n = 150), n (%) |
|---|---|
| Age groups | |
| <10 years | 11 (7.3) |
| 10–19 years | 13 (8.7) |
| 20–29 years | 24 (16) |
| 30–39 years | 43 (28.7) |
| 40–49 years | 18 (12) |
| 50–59 years | 11 (7.3) |
| ≥60 years | 30 (20) |
| Gender | |
| Male | 74 (49.3) |
| Female | 76 (50.7) |
| Hospital stay | |
| Recent admission (<4 weeks) | 60 (40) |
| No recent admission (>4 weeks) | 90 (60) |
| Invasive medical device | |
| IV/catheter use | 54 (36) |
| No IV/catheter use | 96 (64) |
| Drug use | |
| No antibiotic use | 123 (82) |
| Antibiotic use | 27 (18) |
| Comorbidity | |
| No comorbidity | 102 (68) |
| Comorbidity | 48 (32) |
| Type of clinical specimen | |
| Wound swab | 66 (44.0) |
| Urine | 45 (30.0) |
| Blood | 10 (6.7) |
| Ear swab | 12 (8.0) |
| Pus | 3 (2.0) |
| Eye swab | 2 (1.3) |
| Aspirate | 3 (2.0) |
| Urethral swab | 3 (2.0) |
| Pleural fluid | 2 (1.3) |
| Catheter tip | 2 (1.3) |
| Sputum | 1 (0.67) |
| HVS | 1 (0.67) |
| Antibiotic Class | Antibiotics | Susceptible isolates, n (%) | Resistant Isolates, n (%) | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Pseudomonas putida | Pseudomonas fluorescens | Burkholderia pseudomallei | ||||
| Aminoglycosides | Gentamicin Amikacin | 98 (65) 130 (87) | 47 (31.3) 17 (11.3) | 1 (0.7) 1 (0.7) | 3 (2) 1 (0.7) | 1 (0.7) 1 (0.7) | 52 (35) 20 (13) |
| Quinolone | Ciprofloxacin Levofloxacin | 106 (71) 108 (72) | 40 (26.7) 39 (26) | 1 (0.7) 1 (0.7) | 2 (1.3) 1 (0.7) | 1 (0.7) 1 (0.7) | 44 (29) 42 (28) |
| Beta-lactam | Piperacillin Piperacillin-tazobactam | 124 (83) 141 (94) | 25 (16.7) 8 (5.3) | 1 (0.7) 1 (0.7) | 1 (0.7) 0 (0) | 1 (0.7) 0 (0) | 28 (17) 9 (6) |
| Carbapenem | Imipenem Meropenem | 139 (93) 134 (89) | 11 (7.3) 13 (8.6) | 0 (0) 1 (0.7) | 0 (0) 1 (0.7) | 0 (0) 1 (0.7) | 11 (7) 16 (11) |
| Pseudomonas spp. | No (%) of Isolates | Multidrug Resistant Strains, n (%) | Multiple Antibiotic Resistance (MAR) Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 144 (96.0) | 16 (84.2) | 0.5–1.0 |
| Pseudomonas fluorescens | 4 (2.7) | 1 (5.6) | 0.75 |
| Pseudomonas putida | 1 (0.67) | 1 (5.6) | 0.875 |
| Burkholderia pseudomallei | 1 (0.67) | 1 (5.6) | 0.75 |
| Total | 150 (100) | 19 (12.7) | 0.5–1.0 |
© GERMS 2021.
Share and Cite
Adejobi, A.; Ojo, O.; Alaka, O.; Odetoyin, B.; Onipede, A. Antibiotic Resistance Pattern of Pseudomonas spp. from Patients in a Tertiary Hospital in South-West Nigeria. Germs 2021, 11, 238-245. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2021.1260
Adejobi A, Ojo O, Alaka O, Odetoyin B, Onipede A. Antibiotic Resistance Pattern of Pseudomonas spp. from Patients in a Tertiary Hospital in South-West Nigeria. Germs. 2021; 11(2):238-245. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2021.1260
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdejobi, Adesola, Olabisi Ojo, Olubunmi Alaka, Babatunde Odetoyin, and Anthony Onipede. 2021. "Antibiotic Resistance Pattern of Pseudomonas spp. from Patients in a Tertiary Hospital in South-West Nigeria" Germs 11, no. 2: 238-245. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2021.1260
APA StyleAdejobi, A., Ojo, O., Alaka, O., Odetoyin, B., & Onipede, A. (2021). Antibiotic Resistance Pattern of Pseudomonas spp. from Patients in a Tertiary Hospital in South-West Nigeria. Germs, 11(2), 238-245. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2021.1260




