Antibiotic Resistance Profile and Detection of Degradative Enzymes by Enterobacteriaceae Isolated from Raw Goat Milk
Abstract
Introduction
Methods
Milk samples and bacterial isolation
Identification of the Enterobacteriaceae isolates
Qualitative assessment of biofilm production
Screening for proteolytic, lipolytic, and hemolytic activity
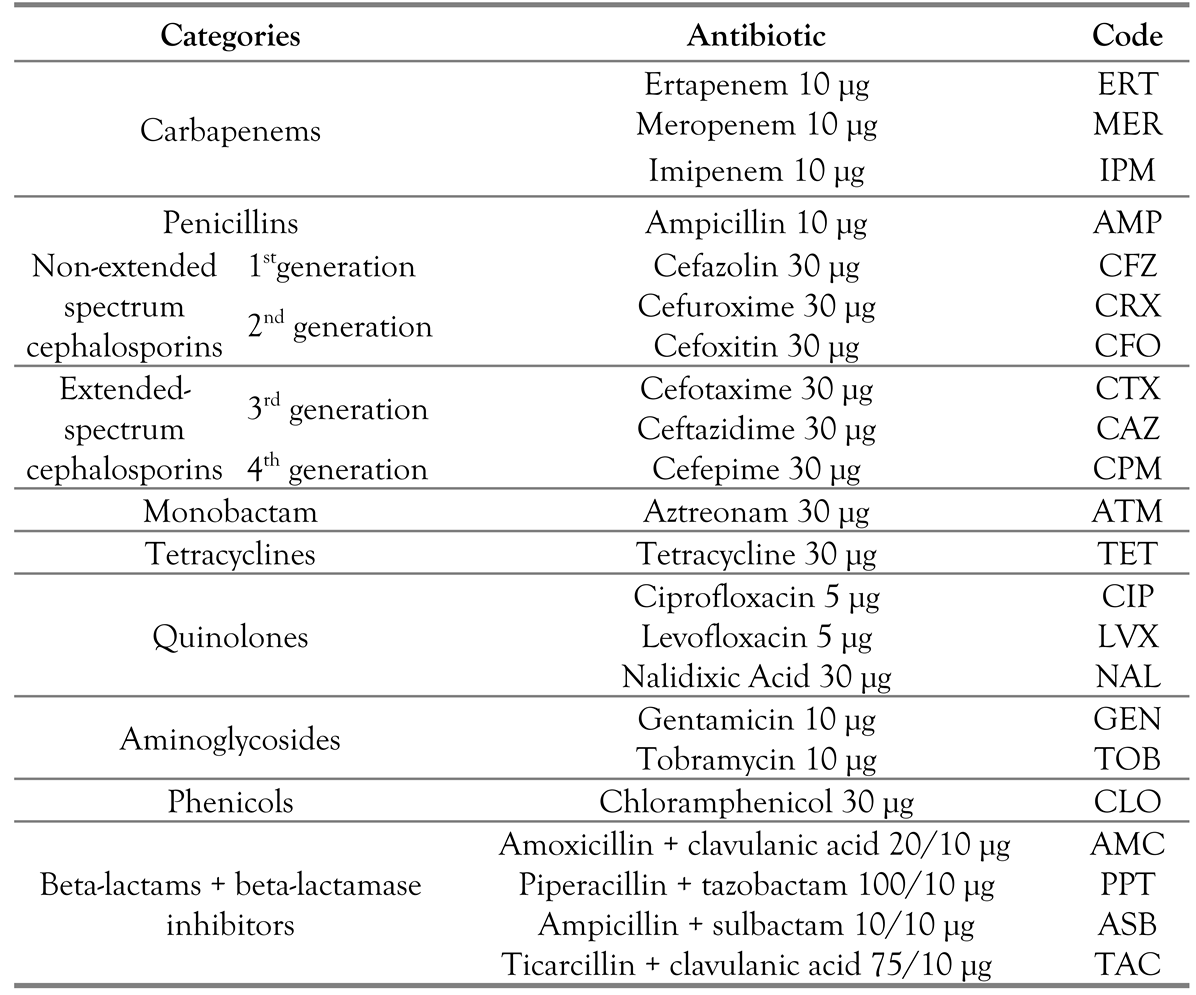
Antibiotic resistance profiles
Presumptive identification of ESBL-producing and KPC-producing phenotypes
Results
Discussion
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ntuli, V.; Njage, P.M.K.; Buys, E.M. Characterization of Escherichia coli and other Enterobacteriaceae in producer- distributor bulk milk. J Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 9534–9549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, N.H.; Trmčić, A.; Hsieh, T.; Boor, K.J.; Wiedmann, M. The evolving role of coliforms as indicators of unhygienic processing conditions in dairy foods. Front Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamilari, E.; Anagnostopoulos, D.A.; Papademas, P.; Efthymiou, M.; Tretiak, S.; Tsaltas, D. Snapshot of Cyprus raw goat milk bacterial diversity via 16S rDNA high-throughput sequencing; impact of cold storage conditions. Fermentation. 2020, 6, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, G.L.P.A.; Nascimento, J.S. Characterization of Acinetobacter spp. from raw goat milk. Ciência Rural. 2019, 49, e20190404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, G.J.; Mendonça, N. Association between antimicrobial resistance and virulence in Escherichia coli. Virulence. 2012, 3, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odenthal, S.; Akineden, Ö.; Usleber, E. Extended-spectrum β-lactamase producing Enterobacteriaceae in bulk tank milk from German dairy farms. Int J Food Microbiol. 2016, 238, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizzini, A.; Durussel, C.; Bille, J.; Greub, G.; Prod'Hom, G. Performance of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry for identification of bacterial strains routinely isolated in a clinical microbiology laboratory. J Clin Microbiol. 2010, 48, 1549–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, D.J.; Falkiner, F.R.; Keane, C.T. New method for detecting slime production by coagulase negative staphylococci. J Clin Pathol. 1989, 42, 872–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantsis-Zacharov, E.; Halpern, M. Culturable psychrotrophic bacterial communities in raw milk and their proteolytic and lipolytic traits. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007, 73, 7162–7168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, R.M. Handbook of Microbiological Media, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing: twenty-fifth informational supplement; CLSI Document M100-S25; CLSI: Wayne, PA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Usman, J.; Kaleem, F.; Omair, M.; Khalid, A.; Iqbal, M. Evaluation of different detection methods of biofilm formation in the clinical isolates. Braz J Infect Dis. 2011, 15, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheriff, R.; Sheena, A. Assessment of biofilm production in clinically significant isolates of Staphylococcus epidermidis and comparison of qualitative and quantitative methods of biofilm production in a tertiary care hospital. Int J Sci Stud. 2016, 4, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Sosnowski, M.; Rola, J.G.; Osek, J. Alkaline phosphatase activity and microbiological quality of heat-treated goat milk and cheeses. Small Ruminant Res. 2016, 136, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlangu, P.; Maina, N.; Kagira, J. Prevalence, risk factors, and antibiogram of bacteria isolated from milk of goats with subclinical mastitis in Thika East Subcounty, Kenya. J Vet Med. 2018, 2018, 3801479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Lei, F.; et al. Bacterial diversity in goat milk from the Guanzhong area of China. J Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 7812–7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabla, R.; Goméz, A.; Simancas, A.; Rebollo, J.E.; Molina, F.; Roa, I. Early blowing in raw goats' milk cheese: gas production capacity of Enterobacteriaceae species present during manufacturing and ripening. J Dairy Res. 2018, 85, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurrel, E.; Kucerova, E.; Loughlin, M.; Caubilla-Barron, J.; Forsythe, S.J. Biofilm formation on enteral feeding tubes by Cronobacter sakazakii, Salmonella serovars and other Enterobacteriaceae. Int J Food Microbiol. 2009, 136, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogha, K.V.; Shah, N.P.; Prajapati, J.B.; Chaudhari, A.R. Biofilm - a threat to dairy industry. Indian J Dairy Sci. 2014, 67, 459–466. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Qi, J.; Dong, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. Characterization of attachment and biofilm formation by meat-borne Enterobacteriaceae strains associated with spoilage. LWT. 2017, 86, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, S.; De Block, J.; De Jonghe, V.; Coorevits, A.; Heyndrickx, M.; Herman, L. Biofilm formation in milk production and processing environments; influence on milk quality and safety. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2012, 11, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, C.; Krewinkel, M.; Kranz, B.; et al. Quantification of the proteolytic and lipolytic activity of microorganisms isolated from raw milk. Int Dairy J. 2015, 49, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nörnberg, M.F.B.L.; Friedrich, R.S.C.; Weiss, R.D.N.; Tondo, E.C.; Brandelli, A. Proteolytic activity among psychrotrophic bacteria isolated from refrigerated raw milk. Int J Dairy Technol. 2010, 63, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, S.G.; Da Silva, F.L.; Bazzolli, D.M.; Heyndrickx, M.; Costa, P.M.D.A.; Vanetti, M.C.D. Pseudomonas spp. and Serratia liquefaciens as predominant spoilers in cold raw milk. J Food Sci. 2015, 80, M1842–M1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Samaranayake, L.P.; Yau, J.Y. Candida species exhibit differential in vitro hemolytic activities. J Clin Microbiol. 2001, 39, 2971–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.R. Microbiologia Médica, 4th ed.; Guanabara Koogan: Rio de Janeiro, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gundogan, N.; Yakar, U.A. Siderophore production, serum resistance, hemolytic activity and extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella species isolated from milk and milk products. J Food Saf. 2007, 27, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, A.G.; Csabai, I.; Krikó, E.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance genes in raw milk for human consumption. Sci Rep. 2020, 10, 7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.X.; Zhao, J.L.; Shen, J.Z.; et al. Prevalence and molecular characterization of fluoroquinolone resistance in Escherichia coli isolates from dairy cattle with endometritis in China. Microb Drug Resist. 2014, 20, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awosile, B.B.; McClure, J.T.; Sanchez, J.; et al. Short communication: Extended-spectrum cephalosporin- resistant Escherichia coli in colostrum from New Brunswick, Canada, dairy cows harbor blaCMY-2 and blaTEM resistance genes. J Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 7901–7905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decimo, M.; Silvetti, T.; Brasca, M. Antibiotic resistance patterns of Gram-negative psychrotrophic bacteria from bulk tank milk. J Food Sci. 2016, 81, M944–M951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podder, M.P.; Rogers, L.; Daley, P.K.; Keefe, G.P.; Whitney, H.G.; Tahlan, K. Klebsiella species associated with bovine mastitis in Newfoundland. PLoS One. 2014, 9, e106518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Medina, N.; Barrios-Camacho, H.; Duran- Bedolla, J.; Garza-Ramos, U. Klebsiella variicola: an emerging pathogen in humans. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 973–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miriagou, V.; Papagiannitsis, C.C.; Kotsakis, S.D.; et al. Sequence of pNL194, a 79.3-kilobase IncN plasmid carrying the blaVIM-1 metallo-beta-lactamase gene in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4497–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girlich, D.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Comparison of the SUPERCARBA, CHROMagar KPC, and Brilliance CRE screening media for detection of Enterobacteriaceae with reduced susceptibility to carbapenems. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013, 75, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codjoe, F.; Donkor, E. Carbapenem resistance: a review. Med Sci (Basel). 2017, 6, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezende, T.F.T.; Doi, A.M.; Quiles, M.G.; et al. Detection of colonization by carbapenem resistant organisms (CRO) by real time PCR (qPCR) from rectal swabs in a large population of patients with chronic renal disease. J Hosp Infect. 2017, 96, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Identification | Isolate code | Biofilm Production | Proteolytic activity | Lipolytic activity | Hemolytic activity |
| Enterobacter spp. (n=2) | 0409 | + | - | - | - |
| 1206 | + | - | - | - | |
| 0401 | + | - | - | - | |
| 0402 | + | - | - | - | |
| 0403 | + | - | - | - | |
| 0406 | + | - | - | - | |
| 0413 | + | - | - | - | |
| 1207 | + | - | - | - | |
| Enterobacter asburiae (n=13) | 1209 | + | - | - | - |
| 1211 | + | - | - | - | |
| 1213 | + | - | - | - | |
| 1215 | + | - | - | - | |
| 1406 | + | - | - | + | |
| 1429 | + | - | - | + | |
| 1430 | - | - | - | - | |
| 0408 | + | - | - | - | |
| 0412 | + | - | - | - | |
| 0414 | + | - | - | - | |
| 0415 | + | - | - | - | |
| Enterobacter cloacae (n=9) | 0416 | + | - | - | - |
| 0501 | + | - | - | - | |
| 1208 | + | - | - | - | |
| 1409 | + | - | - | + | |
| 1418 | + | - | - | + | |
| 0410 | + | - | - | - | |
| Enterobacter hormaechei (n=3) | 0411 | + | - | - | - |
| 2101 | + | + | + | + | |
| 1408 | + | - | - | + | |
| Enterobacter kobei (n=3) | 1411 | + | - | - | - |
| 1424 | - | - | - | + | |
| 0404 | + | - | - | - | |
| Escherichia coli (n=3) | 0405 | + | - | - | - |
| 1205 | - | - | - | - | |
| Hafnia alvei (n=2) | 0514 | - | - | - | + |
| 0515 | - | - | - | + | |
| Klebsiella oxytoca (n=1) | 1501 | + | - | - | + |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae (n=1) | 2015 | + | + | + | + |
| Klebsiella variicola (n=4) | 1402 | - | - | - | - |
| 1403 | - | - | - | + | |
| Identification | Isolate code | Biofilm Production | Proteolytic activity | Lipolytic activity | Hemolytic activity |
| 1404 | + | + | + | + | |
| 1909 | + | + | + | + | |
| Leclercia adecarboxylata (n=1) | 0701 | - | - | - | - |
| Moellerella wisconsensis (n=1) | 0604 | + | - | - | - |
| 0503 | + | - | - | - | |
| 0507 | + | - | - | - | |
| Pantoea agglomerans (n=5) | 0510 | + | - | - | + |
| 0512 | + | - | - | + | |
| 0519 | + | - | - | + | |
| 0502 | + | - | - | - | |
| Raoultella ornithinolytica (n=3) | 0517 | + | - | - | - |
| 1412 | + | + | - | - | |
| 0504 | + | + | + | - | |
| 0505 | + | + | + | - | |
| 0506 | + | + | - | - | |
| Serratia liquefaciens (n=8) | 0508 | + | + | + | - |
| 0509 | + | + | + | - | |
| 0511 | + | + | + | - | |
| 0513 | + | - | + | - | |
| 0520 | + | - | + | - | |
| Total (n=59) | 53 (90%) | 14 (24%) | 10 (17%) | 16 (27%) |
| Identification | Isolate code | Antimicrobial resistance determined by disk diffusion | MDR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enterobacter hormaechei | 2101 | IPM | No |
| Escherichia coli | 1205 | CFO | No |
| Klebsiella oxytoca | 1501 | CFZ, TET | No |
| 1909 | CFZ, TET | No | |
| Klebsiella variicola | 1403 | CFO, TET, CFZ, CRX | No |
| 1404 | AMC, CFZ, PPT, CRX, NAL | Yes | |
| Pantoea agglomerans | 0507 | CFO, AMC, CFZ | No |
| Raoultella ornithinolytica | 1412 | AMP, TET | No |
© GERMS 2021.
Share and Cite
Ramos, G.L.d.P.A.; Nascimento, J.d.S. Antibiotic Resistance Profile and Detection of Degradative Enzymes by Enterobacteriaceae Isolated from Raw Goat Milk. Germs 2021, 11, 211-220. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2021.1258
Ramos GLdPA, Nascimento JdS. Antibiotic Resistance Profile and Detection of Degradative Enzymes by Enterobacteriaceae Isolated from Raw Goat Milk. Germs. 2021; 11(2):211-220. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2021.1258
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamos, Gustavo Luis de Paiva Anciens, and Janaína dos Santos Nascimento. 2021. "Antibiotic Resistance Profile and Detection of Degradative Enzymes by Enterobacteriaceae Isolated from Raw Goat Milk" Germs 11, no. 2: 211-220. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2021.1258
APA StyleRamos, G. L. d. P. A., & Nascimento, J. d. S. (2021). Antibiotic Resistance Profile and Detection of Degradative Enzymes by Enterobacteriaceae Isolated from Raw Goat Milk. Germs, 11(2), 211-220. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2021.1258




