Abstract
Introduction: Tuberculosis is a multisystem disease that may affect any organ or tissue. Tuberculous meningitis (TBM) is the most severe form of tuberculosis and commonly affects the brain. We aimed to study the epidemiological, clinical, therapeutic and evolutionary features of TBM among adults and to compare them with other forms of extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Methods: We conducted a retrospective study including all patients hospitalized for extrapulmonary tuberculosis in the infectious disease department in Sfax, Tunisia between 1993 and 2018. We specified the particularities of TBM cases, and we compared them with other extrapulmonary tuberculosis cases. Results: We encountered 78 patients diagnosed with TBM, among 519 patients with extrapulmonary tuberculosis (15%). The median age was 36 years (23-50) years. There were 44 females (56.4%). In comparison with other forms of extrapulmonary tuberculosis, fever [odds ratio (OR)=4.4; p<0.001], asthenia (OR=3.4; p<0.001) and anorexia (OR=2.3; p=0.001) were significantly more frequent in TBM patients. Adverse effects of antitubercular therapy were more frequent among TBM patients (OR=3.1; p<0.001). The mean duration of antitubercular therapy was 15 (12-20) months. Recovery occurred in 66 cases (84.6%), complications in 44 cases (56.4%) and death in 7 cases (9%). Comparison of the disease evolution showed that complications (OR=7.4; p<0.001) and mortality rates (OR=10.7; p<0.001) were significantly more frequent in TBM patients, while recovery was significantly more frequent in other sites of extrapulmonary tuberculosis patients (OR=0.5; p=0.02). Conclusions: In our country, TBM remains a disabling disease. Despite antitubercular therapy, the prognosis was more severe with the occurrence of not only complications but also a high mortality rate in comparison with other forms of extrapulmonary tuberculosis. When clinical and laboratory features suggest the diagnosis of TBM, clinicians should look for tuberculosis elsewhere in the body.
Introduction
Tuberculosis (TB), a public health concern, was responsible for 10 million new cases in 2018, among which an estimated 1.4 million people died [1]. It is a multisystem disease that may affect any organ or tissue, such as the central nervous system (CNS), which represents 10% of all TB cases [2]. The most common manifestation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in the CNS is meningitis [3]. It may also manifest as radiculomyelitis or tuberculoma/tuberculous abscess [4]. Its indolent clinical presentation and the paucibacillary nature of M. tuberculosis infection in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) explain the diagnostic challenge [5]. The diagnosis of TB of other sites elsewhere in the body might help the clinicians. In fact, miliary disease increases the risk of hematogenous spread to the CNS, which is the main mechanism explaining the involvement of TB in the CNS [4]. After a prolonged duration, the rupture of the tuberculous lesion, formed during bacteremia of primary TB and deposit in the brain, marks the onset of tuberculous meningitis (TBM).3
Treatment of TBM is also challenging, since the ability of antitubercular therapy to cross the blood-CSF and blood-brain barriers varies [6]. The World Health Organization reported that TB is one of the top 10 causes of death worldwide.1 In fact, the mortality rate varies widely according to the clinical presentation. Tuberculous meningitis is the most severe form of TB [5]. Around one fifth of TBM cases die, even with prompt diagnosis and treatment, and over half of the survivors have neurological deficit [6].
In Tunisia, an intermediate endemicity country for TB, despite a national control program, an increase of this infection in recent years was noted [7]. Children have shown common presentation of TBM in terms of severity and outcome [8]. Recent and exhaustive data about TBM among adults in our country are lacking. In this perspective, we aimed to study the epidemiological, clinical, therapeutic and evolutionary features of TBM among adults and to compare them with other forms of extrapulmonary tuberculosis (EPT).
Methods
Study design
We conducted a retrospective study including all patients hospitalized for EPT in the infectious disease department in Sfax, Tunisia between 1993 and 2018. We specified the particularities of TBM cases, and we compared them with other extrapulmonary tuberculosis cases.
Data collection and case definition
Demographical data including gender, age and urbanity of residence were collected. We defined three age groups including patients aged between 15 and 39 years, between 40 and 59 years and patients aged 60 years and above. Rural area was defined as an area located more than 11 kilometers away from the city center. Otherwise, it was defined as urban area. Previous personal medical history and family history of TB were notified. The systemic symptoms represented by fever, night sweats, anorexia, weight loss and asthenia were reported. Data including the clinical presentation and laboratory investigations were reviewed.
A positive culture or a positive polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for M. tuberculosis from CSF confirmed the diagnosis of TBM. In default, clinical signs of meningitis in the presence of compatible CSF findings of TBM associated with other positive culture specimens for M. tuberculosis or positive TB histology (caseous necrosis) from another localization confirmed the diagnosis. Compatible CSF findings of TBM were represented by lymphocyte predominant pleocytosis, elevated protein and reduced glucose. In default, it was based on strong clinical evidence represented by compatible CSF findings of TBM associated with positive tuberculin skin test. Culture and PCR for M. tuberculosis were negative and no caseous necrosis was found in specimen from another localization taken for histological examination. These clinically diagnosed cases were at first considered as probable TBM until adequate response to antitubercular treatment was obtained, confirming, therefore, the diagnosis.
The specimens obtained were cultured in solid (Löwenstein-Jensen) and liquid (MGIT 960) media. For positive initial culture, drug susceptibility testing to isoniazid and rifampicin were performed. We used a CFX96TM real-time PCR cycler (Biorad, USA) to determine quantitative PCR.
Antitubercular therapy was initiated after microbiological or histological confirmation of the diagnosis. Otherwise, it was initiated based on strong clinical evidence associated with compatible CSF findings of TBM while waiting for confirmation of the diagnosis. The treatment regimen was based on a quadritherapy for 2 month-duration and followed by a bitherapy based on isoniazid (INH) and rifampicin (RIF) for the rest of the period. The quadritherapy included INH at a dose of 5 mg/kg daily, RIF at a dose of 10 mg/kg daily, pyrazinamide (PZA) at a dose of 25 mg/kg daily and ethambutol (EMB) at a dose of 15 mg/kg daily. Separate drug formulations were based on the following tablets: INH 100 mg, RIF 300 mg, PZA 500 mg and EMB 400 mg. Fixed-dose combinations were administrated in tablets of RHZE (RIF 150 mg/INH 75 mg/PZA400 mg/EMB 275 mg) and RH (RIF 150 mg/INH 75 mg). Based on the patient’s weight, we determined the dosages of each preparation required.
Patients who were lost to follow up were excluded from the study at enrollment. Only adult patients were included in the study.
Other EPT sites included cases of lymph node TB, abdominal TB, osteoarticular TB and urogenital TB.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS v 20 (IBM Corp., USA). Qualitative variables were presented as numbers and percentages. Quantitative variables were reported by means and standard deviation if they were normally distributed. Otherwise, medians and interquartile ranges were reported. Chi square test was used to compare two frequencies and student t-test to compare two means in independent samples, when they were normally distributed. Otherwise, we used Mann-Whitney test. The difference between the groups was considered significant when p<0.05.
Results
Characteristics of patients with tuberculous meningitis
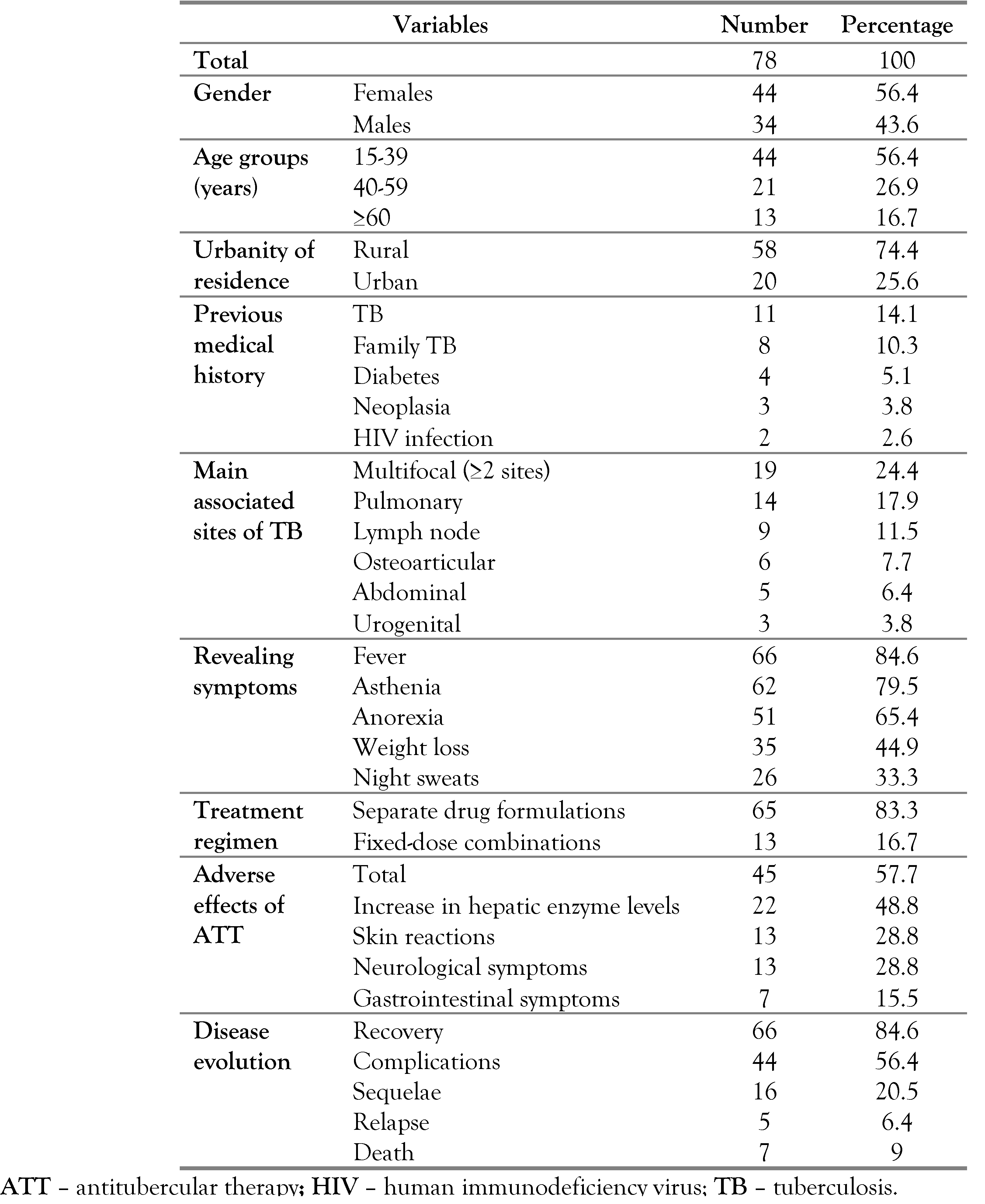
During the study period, we encountered 78 patients diagnosed with TBM, among 519 patients with EPT (15%). There were 44 females (56.4%). The median age was 36 years (23-50) years. Patients aged between 15 and 39 years were the most affected age group (56.4%). According to residency, 58 patients came from a rural area (74.4%). Eleven patients were previously treated for TB (14.1%) and two patients were living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) (2.6%). Eight patients had a family history of TB (10.3%). Sixty-six patients had fever (84.6%) associated with asthenia (62 cases; 79.5%), anorexia (51 cases; 65.4%) and weight loss (35 cases; 44.9%). Multifocal TB was noted in 19 cases (24.4%). Lymph node TB was associated with TBM in 9 cases (11.5%) and followed by osteoarticular TB in 6 cases (7.7%). There were 14 cases of pulmonary TB associated with TBM (17.9%) – Table 1.

Table 1.
Socio-demographic, clinical and evolutionary characteristics of patients with tuberculous meningitis.
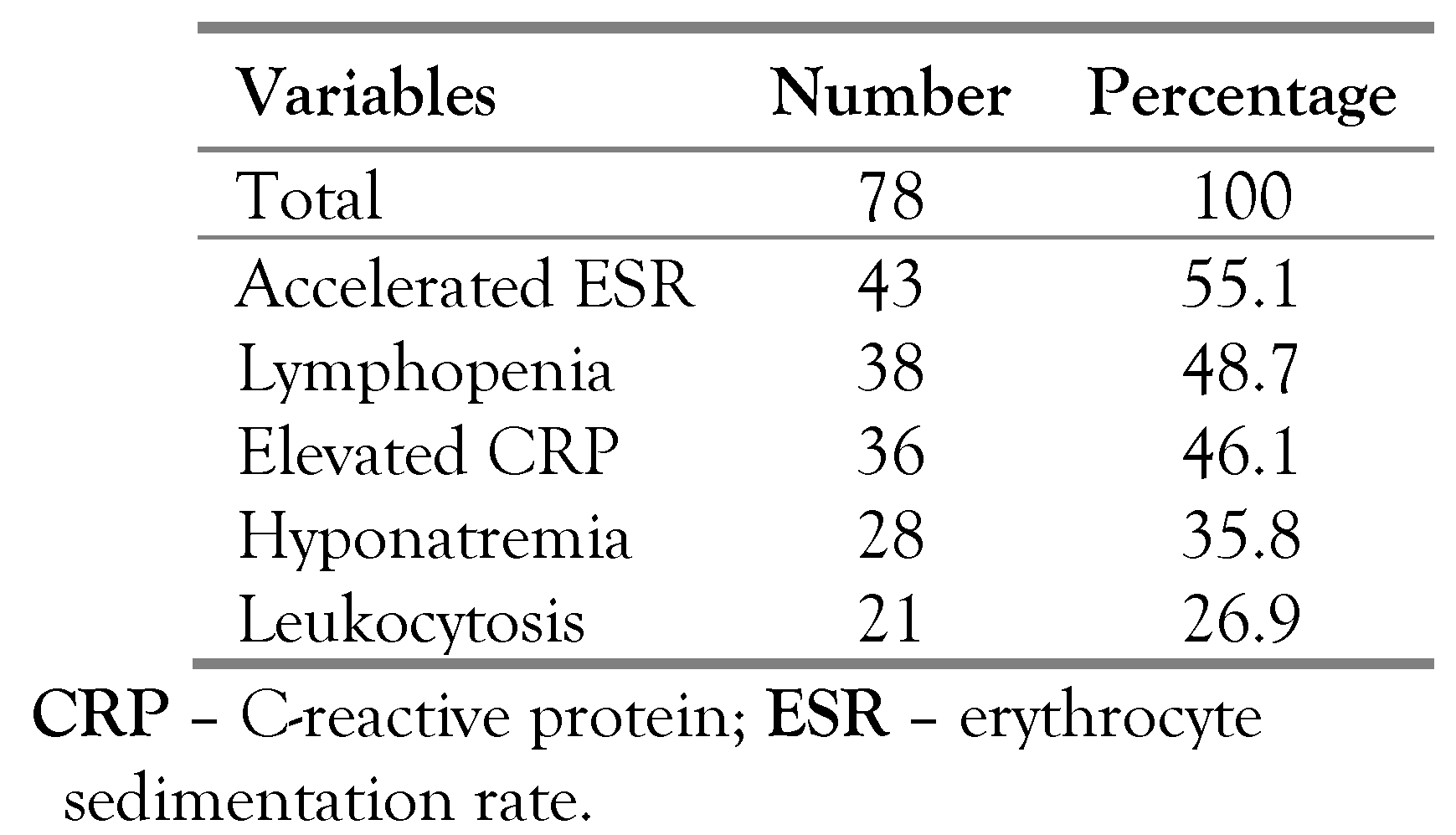
The diagnosis was bacteriologically confirmed in 32 cases (41%), mostly represented by the detection of M. tuberculosis in the CSF in 23 cases (71.8%) by culture (17 cases; 53.1%) or by PCR (6 cases; 18.7%). Sputum (2 cases; 6.3%), urine (3 cases; 9.4%) and lymph node (4 cases; 12.5%) cultures were positives for M. tuberculosis. Culture results revealed no resistance to rifampicin or isoniazid. The diagnosis was histologically confirmed in 5 cases (6.4%). There were 41 clinically diagnosed cases (52.6%). Tuberculin skin test was positive in 46 cases (59%). Laboratory investigations revealed an accelerated erythrocyte sedimentation rate in 43 cases (55.1%) and lymphopenia in 38 cases (48.7%)–Table 2.

Table 2.
Laboratory investigations of patients with tuberculous meningitis.
Treatment regimen was based on separate drug formulations in 65 cases (83.3%). The median duration of antitubercular therapy was 15 (12-20) months. All the patients received a long course regimen based on antitubercular treatment for more than 6 months duration. Adverse effects of antitubercular therapy were noted in 45 cases (57.7%), represented mostly by the increase in hepatic enzyme levels (alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase) in 22 cases (48.8%). Corticosteroids were prescribed in 46 cases (59%) for a median duration of 1 month, ranging from 15 days to 5 months. The median duration of hospitalization was 21 days (3-75 days). The disease evolution was marked by the occurrence of recovery in 66 cases (84.6%). There were 5 relapsing cases (6.4%). Seven patients died (9%) – Table 1. The administration of corticosteroids was significantly associated with the absence of sequelae (52.5% vs 47.5%; p=0.011). As for the occurrence of complications and death, no significant difference was noted.
Particularities of tuberculous meningitis in comparison with other forms of extrapulmonary tuberculosis
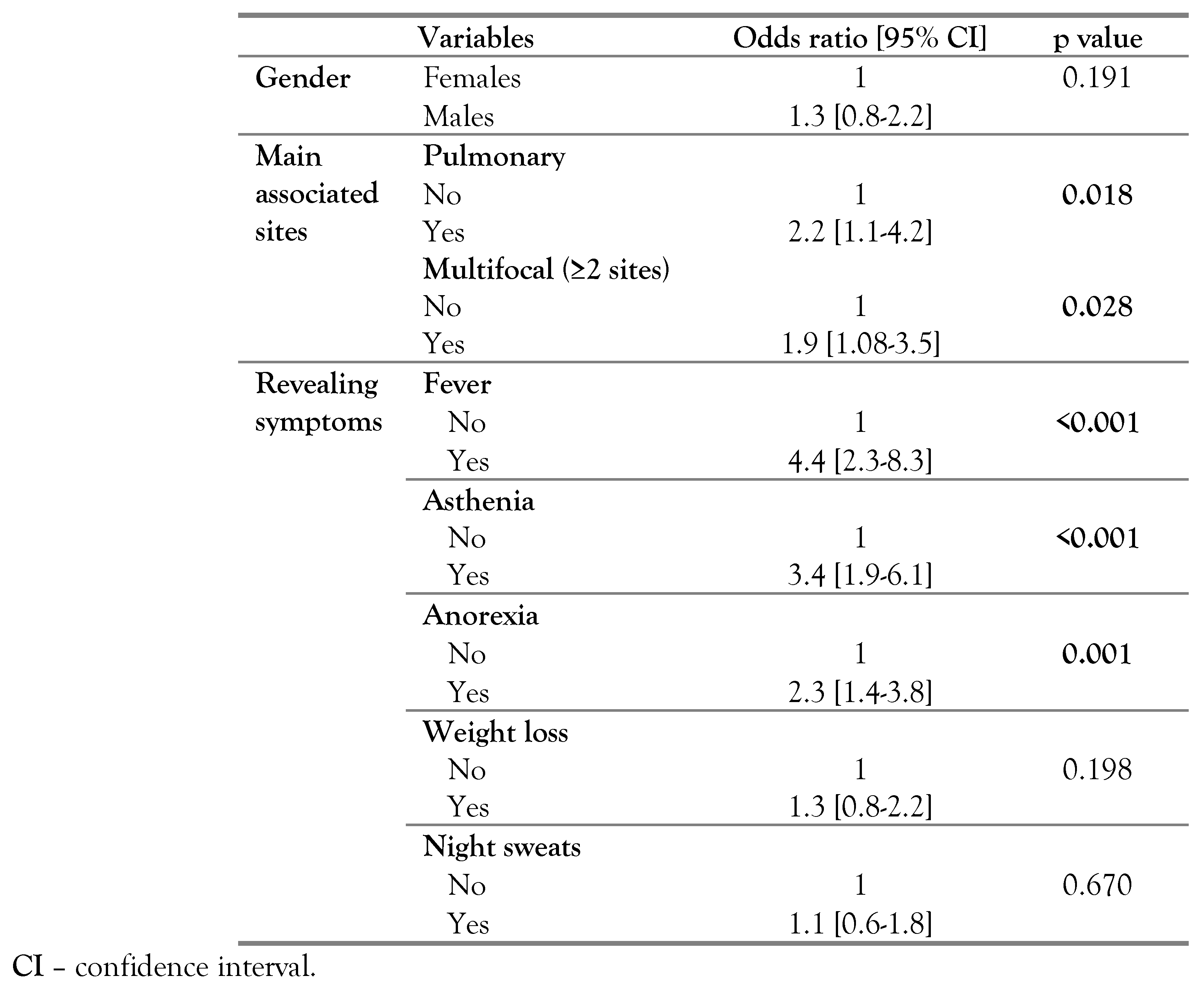
According to the revealing symptoms, fever [odds ratio (OR)=4.4; p<0.001], asthenia (OR=3.4; p<0.001) and anorexia (OR=2.3; p=0.001) were significantly more frequent in TBM patients. No significant difference was noted concerning weight loss (p=0.198) and night sweats (p=0.670) between patients with TBM and other forms of EPT (Table 3).

Table 3.
Epidemiological and clinical features associated with tuberculous meningitis in comparison with other extrapulmonary tuberculosis forms.
The median age at diagnosis was 36 years (23-50) years among TBM cases and 36 years (25- 57) years among other forms of EPT cases, with no significant difference (p=0.462). Multifocal TB was significantly more frequent in TBM cases (OR=1.9; p=0.028). Pulmonary TB was significantly associated with TBM cases (OR=2.2; p=0.018) – Table 3.
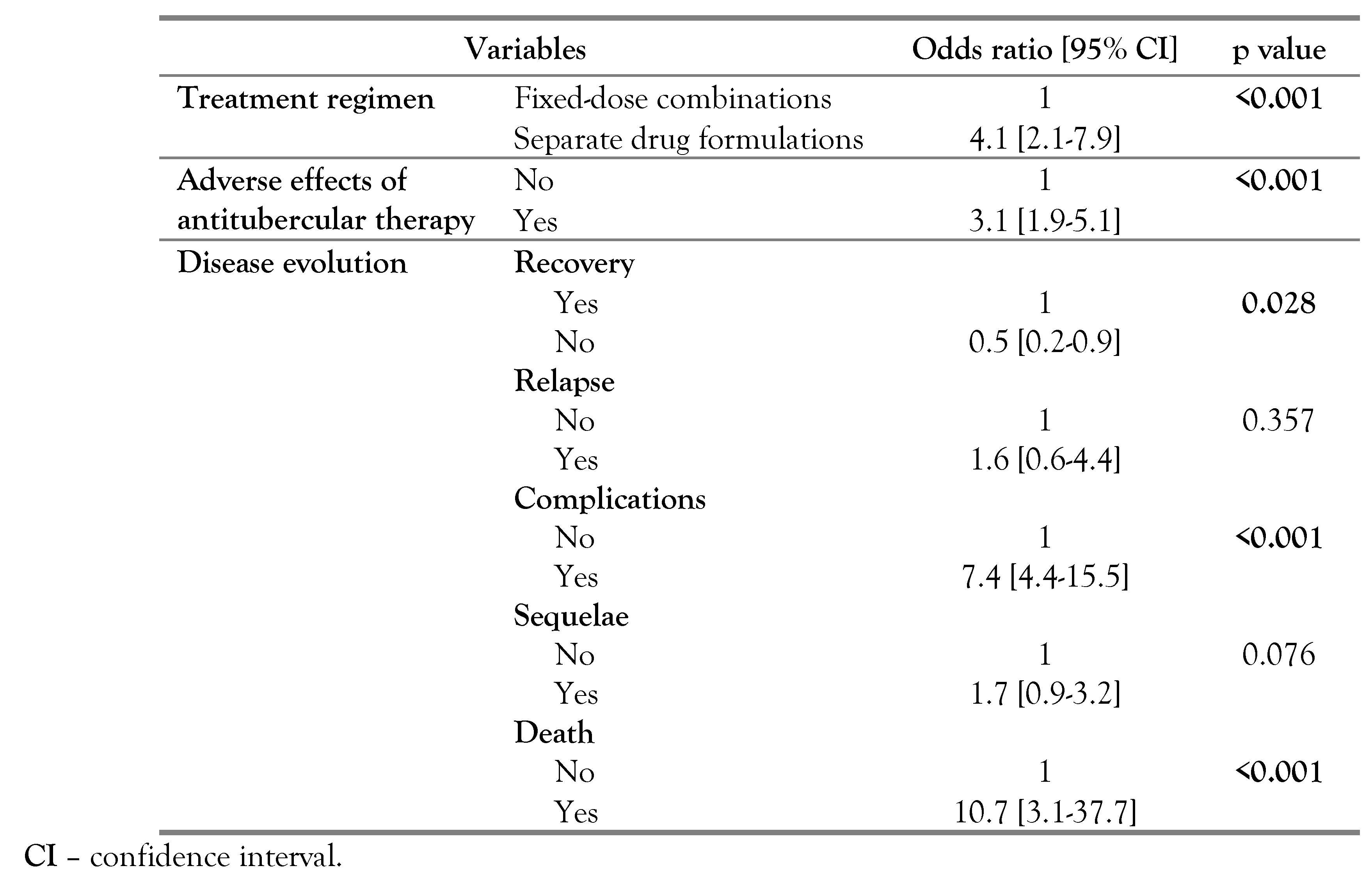
Treatment duration was significantly longer in TBM cases [15 (12-20) vs 10 (9-12) months; p<0.001]. Treatment regimen of separate drug formulations was significantly more frequently prescribed for patients with TBM (OR=4.1; p<0.001). Adverse effects of antitubercular therapy were more frequent among TBM cases (OR=3.1; p<0.001). Comparison of the disease evolution showed that complications (OR=7.4; p<0.001) and mortality rates (OR=10.7; p<0.001) were significantly more frequent in TBM patients, while recovery was significantly more frequent for patient with other sites of EPT (OR=0.5; p=0.028). As for sequelae, no significant difference was noted (p=0.076) – Table 4.

Table 4.
Therapeutic and evolutionary features associated with tuberculous meningitis in comparison with other extrapulmonary tuberculosis forms.
Discussion
Our study highlighted the burden of TBM among adults compared with others EPT sites. TBM is a life-threatening disease with a poor prognosis marked by the occurrence of not only complications, but also death, and requiring a long duration of antitubercular therapy. Its incidence is underestimated and varies in cohorts according to the local TB prevalence, age and HIV prevalence [9]. In Tunisia, a low HIV prevalence country, the impact of the HIV epidemic on TB is minor with a prevalence less than 0.1% [7]. Globally, an estimated 100,000 individuals develop TBM annually [9]. M. tuberculosis disseminates from the primary site of infection, migrates into the lymphatic system or blood stream and overcomes protective barriers to enter the CNS [10]. The dissemination of the infection from the lungs explains the association between TBM and pulmonary TB, and the frequency of multifocal TB cases in comparison with other EPT sites.
The major clinical features of TBM are fever, weight loss, headache and vomiting [11]. In fact, most sites of active TB manifest with at least one of following: cough, fever, weight loss or night sweats in over 80% of patients [12]. In our study, we found that fever, asthenia and anorexia were significantly more frequent in TBM patients in comparison with other sites of EPT patients. The non-specific clinical features might contribute to the delayed diagnosis. Clinicians must be vigilant against the disease and exercise good clinical judgment. Considering the previous medical history of patients is of great importance. Previous studies reported a positive contact history of TB between 33% to 69% of cases [13]. The rate noted in our study was 10.3% of cases, while 14.1% of patients had been previously treated for TB.
The cornerstones of TBM diagnosis remain the detection of acid-fast bacilli using Ziehl- Neelsen stain by microscopy in the CSF and bacterial culture [14]. In fact, the sensitivity of the Ziehl-Neelsen stain in cases of TBM is very low, about 10% to 20% [15]. Culture of M. tuberculosis from the CSF is more sensitive, reaching 60% to 70%, but it is too slow and the results are not available for weeks [16]. In order to overcome the limitations of conventional methods, nucleic acid amplification (NAAT) tests have emerged, among which the PCR is the most common methodology [15]. It has 56% sensitivity and 98% specificity in the diagnosis of TBM [17]. Despite its speed to diagnosis, ability to detect drug resistance and ability to reduce the time to effective treatment, [16] NAAT tests replace neither microscopy, nor culture and cannot be reliable to rule out the diagnosis of TBM.15 The PCR in the CSF should be performed in suspected cases, but a negative result does not exclude the disease [17]. In Tunisia, a recent study reported that the GeneXpert MTB/RIF was the most useful tool in the rapid diagnosis of lymph node TB with a sensitivity of 87.5% and a specificity of 73.3% [18]. The low rate of the detection of M. tuberculosis by PCR reported in our study might be improved with the use of this technology.
Before the onset of coma, the strongest survival predictor is antitubercular therapy [19]. It is based on the same regimen used against pulmonary TB with rifampicin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide and ethambutol, as first line agents, for 2 months and followed by rifampicin and isoniazid for an additional 7 to 10 months [19,20]. The treatment of TBM remains challenging since antitubercular therapy must cross the blood-brain barrier and blood-CSF barrier and remain in the brain or CSF at sufficient concentrations for a sufficient period of time [21]. Concentrations of rifampicin in the CSF, a key component of treatment, are less than 30% of the concentration in plasma [5]. Various strategies were proposed in order to optimize TBM treatment, such as prolonging the treatment [21]. Compared with other sites of EPT, treatment duration was significantly longer in TBM cases. However, comparing the effects of six months regimens versus prolonged- course regimens for TBM patients showed that regardless of the duration of treatment, relapse was an uncommon event, and there was no higher proportion of deaths among those treated for six months [22]. Since all patients included in our study received long course regimen, we couldn’t evaluate the outcome in patients receiving short course vs long course regimens. Another promising strategy is to increase drug exposures in the CNS, which may be achieved by increasing doses of poorly penetrating drugs, adding or replacing drugs with a better characteristic of penetration, such as glutathione, fluoroquinolones, thalidomide and bedaquilline [21]. Previous randomized controlled trials found that high-dose intravenous rifampicin during the first two weeks of treatment increased the CSF drug concentration and improved the survival of patients with TBM [23,24].
The World Health Organization recommend the use of fixed-dose combinations over separate drug formulations in drug-susceptible TB cases [25]. In fact, a recent systematic review concluded similar efficacy of fixed-dose combinations compared with separate drug formulations in terms of treatment failure, death and sputum smear or culture conversion [26]. However, patient satisfaction was higher among those treated with fixed-dose combinations [25]. Compared with other EPT sites, we found that treatment regimen of separate drug formulations was significantly more prescribed for patients with TBM. This might be explained by the occurrence of adverse effects, which was significantly more frequent among TBM patients, usually requiring the discontinuation of fixed-drug combinations followed by the reintroduction of antitubercular drugs one by one.
Besides antitubercular treatment, an initial corticosteroid therapy with dexamethasone or prednisolone prescribed for 6 to 8 weeks is recommended for patients with TBM [25]. Corticosteroids reduce mortality in TBM patients, but no effect on rates of disabling neurological deficit in patients who survive was noted, [27] which was discordant with our results. The retrospective nature of our study and the limited data might explain the discordance between the results. More studies are required to confirm the effects of corticosteroids in TBM cases.
The main determinants of outcome in TBM patients are early diagnosis, prompt antitubercular treatment and corticosteroids [28]. In fact, treatment outcome remains very poor, especially for patients with HIV co-infection [11]. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis showed that 24% of TBM patients died during the treatment and mortality increased with the severity of the disease.11 A large cohort in the United States reported a neurological complication or death in more than half of all patients and the majority of neurological complications occurred during the index hospitalization [29]. We found that complications and mortality rates were significantly more frequent in TBM patients.
Conclusions
In Tunisia, TBM remains a disabling disease. Despite antitubercular therapy, the prognosis was more severe with the occurrence of not only complications but also a high mortality rate in comparison with other forms of ETP. When clinical and laboratory features suggest the diagnosis of TBM, clinicians should look for TB elsewhere in the body. Antitubercular therapy, for the appropriate duration, along with corticosteroids are essential in order to reduce complications and to improve late prognosis.
Author Contributions
FH, MK, WF, CM and MBJ designed and supervised the study and drafted the manuscript. FH, MK, AC, KR and MBJ collected and analyzed the data and performed the background literature review for the manuscript. FH, MK and FS carried out the laboratory work, conducted the statistical analyses and drafted the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
None to declare.
Conflicts of interest
All authors – none to declare.
References
- World Health Organization. In Global Tuberculosis Report 2019; WHO: Geneva, 2019.
- Munakomi, S.; Grasso, G.; Chapagain, R. Multi-spectral pattern of clinical presentation and the resultant outcome in central nervous system tuberculosis: a single center study on the ubiquitous pathogen. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020, 1271, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, B.D.; Grace, G.A.; Natrajan, M. Tuberculous meningitis in children: clinical management & outcome. Indian J Med Res. 2019, 150, 117–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marais, S.; Van Toorn, R.; Chow, F.C.; et al. Management of intracranial tuberculous mass lesions: how long should we treat for? Wellcome Open Res 2019, 4, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méchaï, F.; Bouchaud, O. Tuberculous meningitis: challenges in diagnosis and management. Rev Neurol (Paris) 2019, 175, 451–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, J.A.; Thwaites, G.E.; Tuberculous Meningitis International Research Consortium. Tuberculous meningitis: new tools and new approaches required. Wellcome Open Res. 2019, 4, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Republique Tunisienne Ministère de la Santé. Direction des soins de santé de base. In Le guide national de prise en charge de la tuberculose.; 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Khemiri, M.; Bagais, A.; Becher SBen et, a.l. Tuberculous meningitis in Bacille Calmette-Guérin-vaccinated children: clinical spectrum and outcome. J Child Neurol. 2012, 27, 741–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, J.A.; Tugume, L.; Solomons, R.; Prasad, K.; Bahr, N.C.; Tuberculous Meningitis International Research Consortium. The current global situation for tuberculous meningitis: epidemiology, diagnostics, treatment and outcomes. Wellcome Open Res. 2019, 4, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.G.; Rohlwink, U.K.; Proust, A.; Figaji, A.A.; Wilkinson, R.J. The pathogenesis of tuberculous meningitis. J Leukoc Biol. 2019, 105, 267–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.; He, J. Treatment outcomes of tuberculous meningitis in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pulm Med. 2019, 19, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, B.; Liang, S.Y.; Koyfman, A.; Gottlieb, M. Tuberculosis: a focused review for the emergency medicine clinician. Am J Emerg Med. 2020, 38, 1014–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatema, K.; Rahman, M.; Akhter, S.; et al. Clinicoradiologic profile and outcome of children with tubercular meningitis in a tertiary care hospital in Bangladesh. J Child Neurol. 2020, 35, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, N.T.; Thwaites, G.E. Recent advances in the diagnosis and management of tuberculous meningitis. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2017, 30, 123–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Xie, B.D. Progress on diagnosis of tuberculous meningitis. Methods Mol Biol. 2018, 1754, 375–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pormohammad, A.; Nasiri, M.J.; McHugh, T.D.; Riahi, S.M.; Bahr, N.C. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of nucleic acid amplification tests for tuberculous meningitis. J Clin Microbiol. 2019, 57, e01113–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleiman-Meigooni, S. Central nervous system tuberculosis. In The microbiology of central nervous system infections; Kon, K., Rai, M., Eds.; Academic Press: London. [CrossRef]
- Ghariani, A.; Jaouadi, T.; Smaoui, S.; et al. Diagnosis of lymph node tuberculosis using the GeneXpert MTB/RIF in Tunisia. Int J Mycobacteriology. 2015, 4, 270–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, R.J.; Rohlwink, U.; Misra, U.K.; et al. Tuberculous meningitis. Nat Rev Neurol. 2017, 13, 581–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, J.; Figaji, A.; Imran, D.; Phu, N.H.; Rohlwink, U.; Thwaites, G.E. The neurocritical care of tuberculous meningitis. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 771–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cresswell, F.V.; Te Brake, L.; Atherton, R.; et al. Intensified antibiotic treatment of tuberculosis meningitis. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2019, 12, 267–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jullien, S.; Ryan, H.; Modi, M.; Bhatia, R. Six months therapy for tuberculous meningitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016, 9, CD012091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruslami, R.; Ganiem, A.R.; Dian, S.; et al. Intensified regimen containing rifampicin and moxifloxacin for tuberculous meningitis: an open-label, randomised controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013, 13, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Te Brake, L.; Dian, S.; Ganiem, AR.; et al. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic analysis of an intensified regimen containing rifampicin and moxifloxacin for tuberculous meningitis. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2015, 45, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for treatment of drug-susceptible tuberculosis and patient care, 2017 update, ECDC: Stockholm, 2017; 392–397.
- Gallardo, C.R.; Rigau Comas, D.; Valderrama Rodríguez, A.; et al. Fixed-dose combinations of drugs versus single-drug formulations for treating pulmonary tuberculosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016, 2016, CD009913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.; Singh, M.B.; Ryan, H. Corticosteroids for managing tuberculous meningitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016, 4, CD002244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thwaites, G.E.; van Toorn, R.; Schoeman, J. Tuberculous meningitis: more questions, still too few answers. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkler, A.E.; Reynolds, A.S.; Gialdini, G.; et al. Neurological complications after tuberculous meningitis in a multi-state cohort in the United States. J Neurol Sci. 2017, 375, 460–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© GERMS 2021.